From Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition to Antiproliferative Activity: New Biological Perspectives for Polyamine Analogs
Abstract
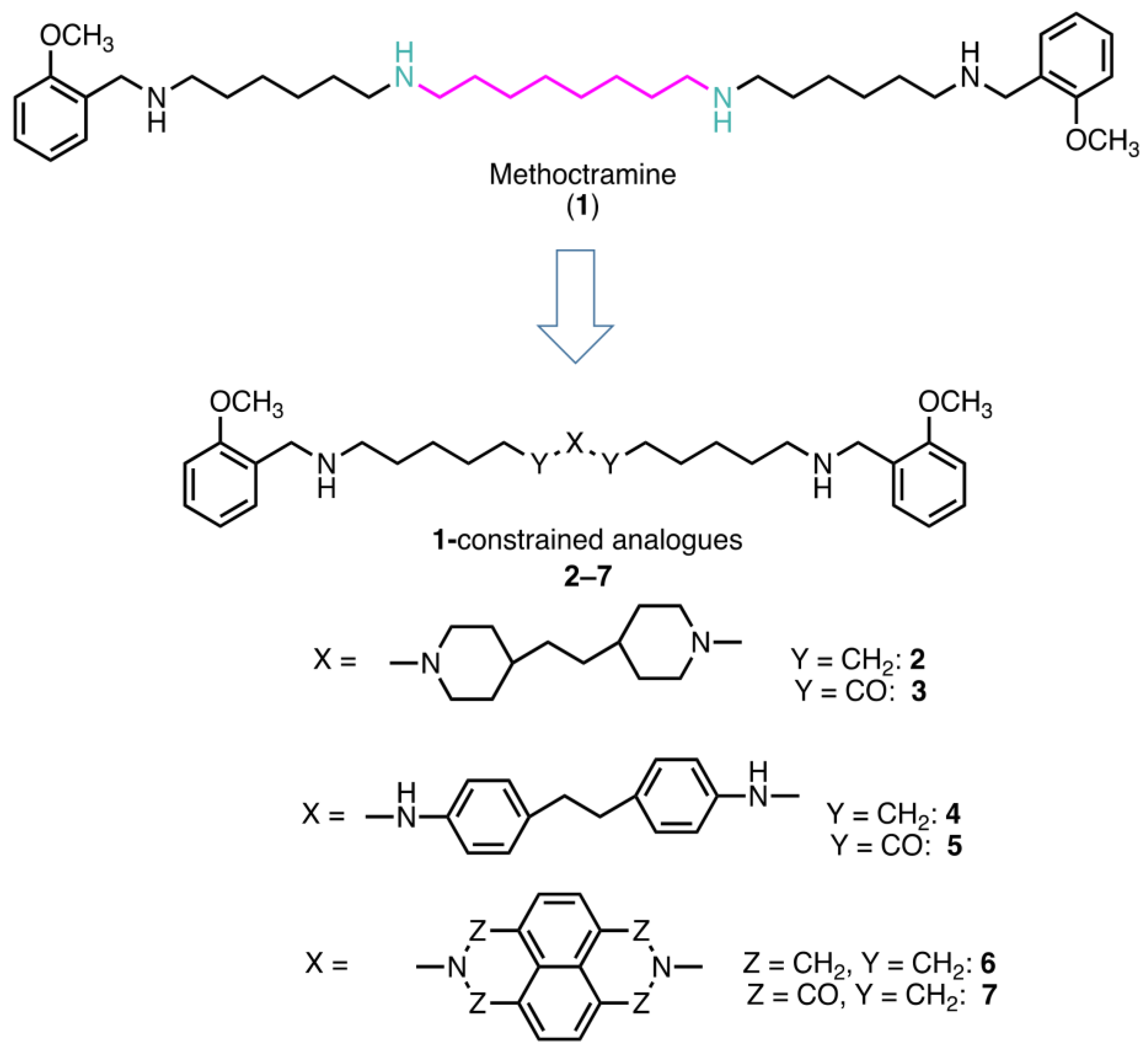
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Rational of Compound Selection
2.2. Effects of the Polyamine Derivatives 2–7 on the Activity of Amine Oxidases
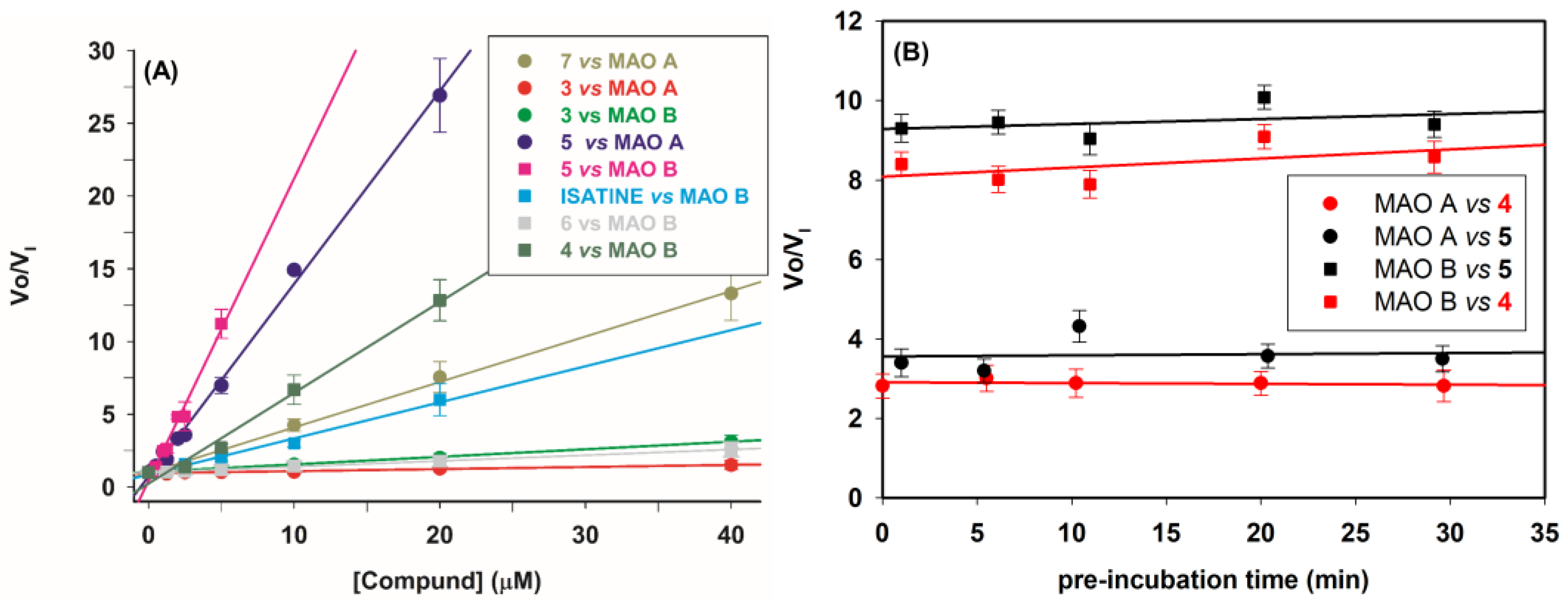
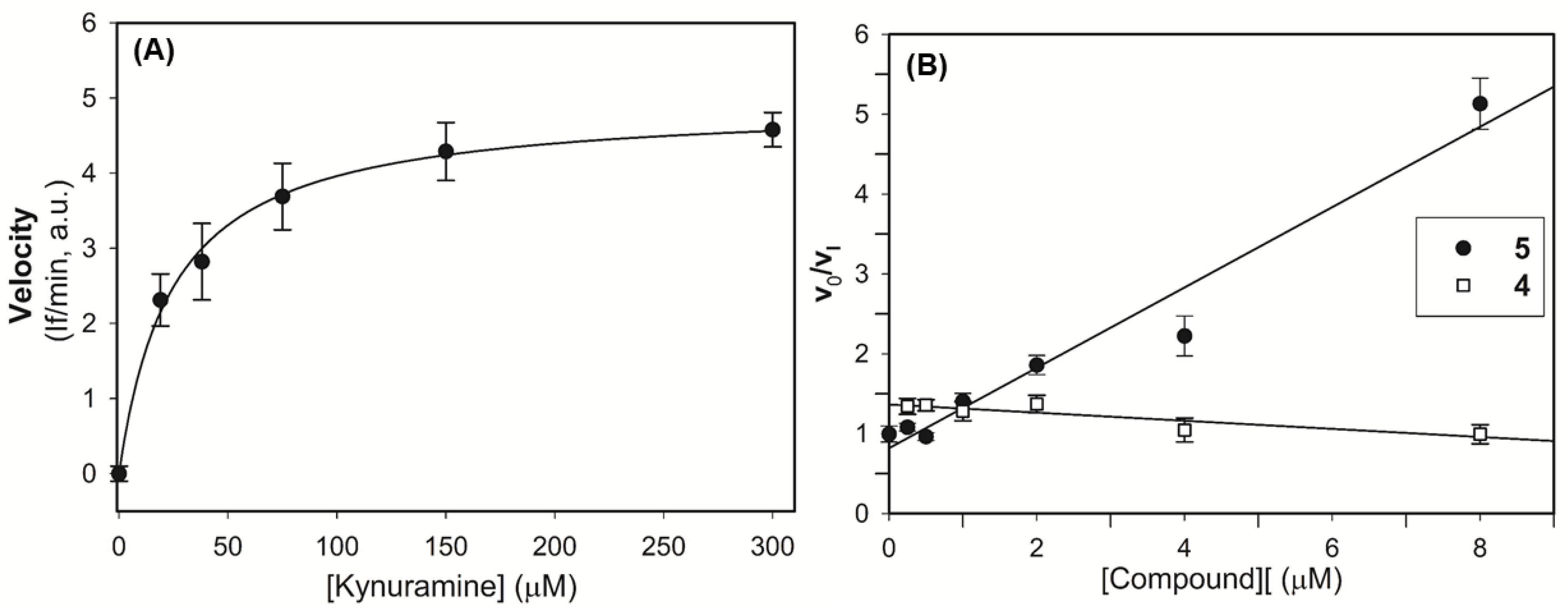
2.2.1. Inhibitory Activity of the Compounds on Human Recombinant MAOs
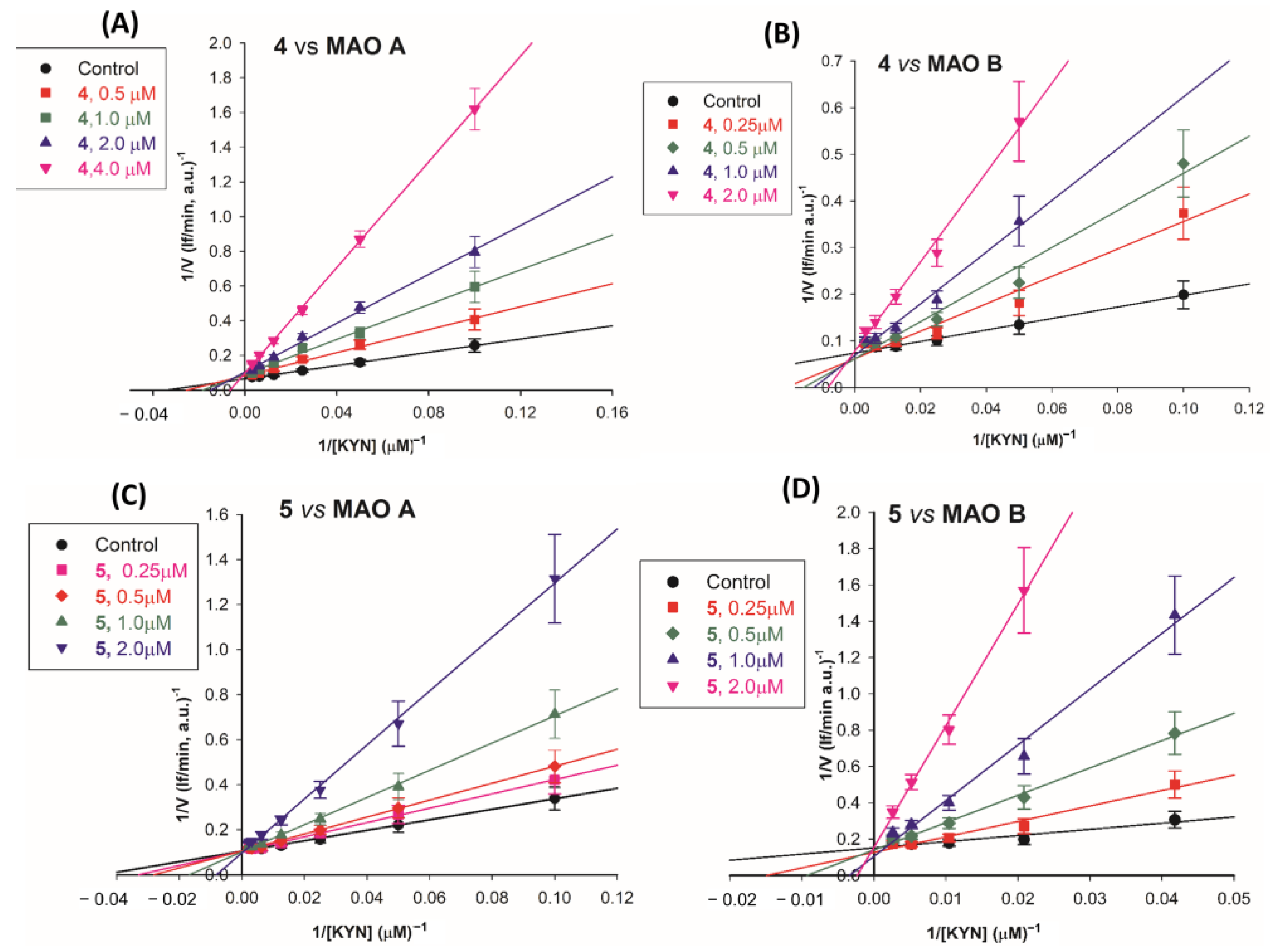
2.2.2. Mechanism of Inhibition
2.2.3. Selectivity of Compounds 1–3 and 5–7 versus Other Amine Oxidases
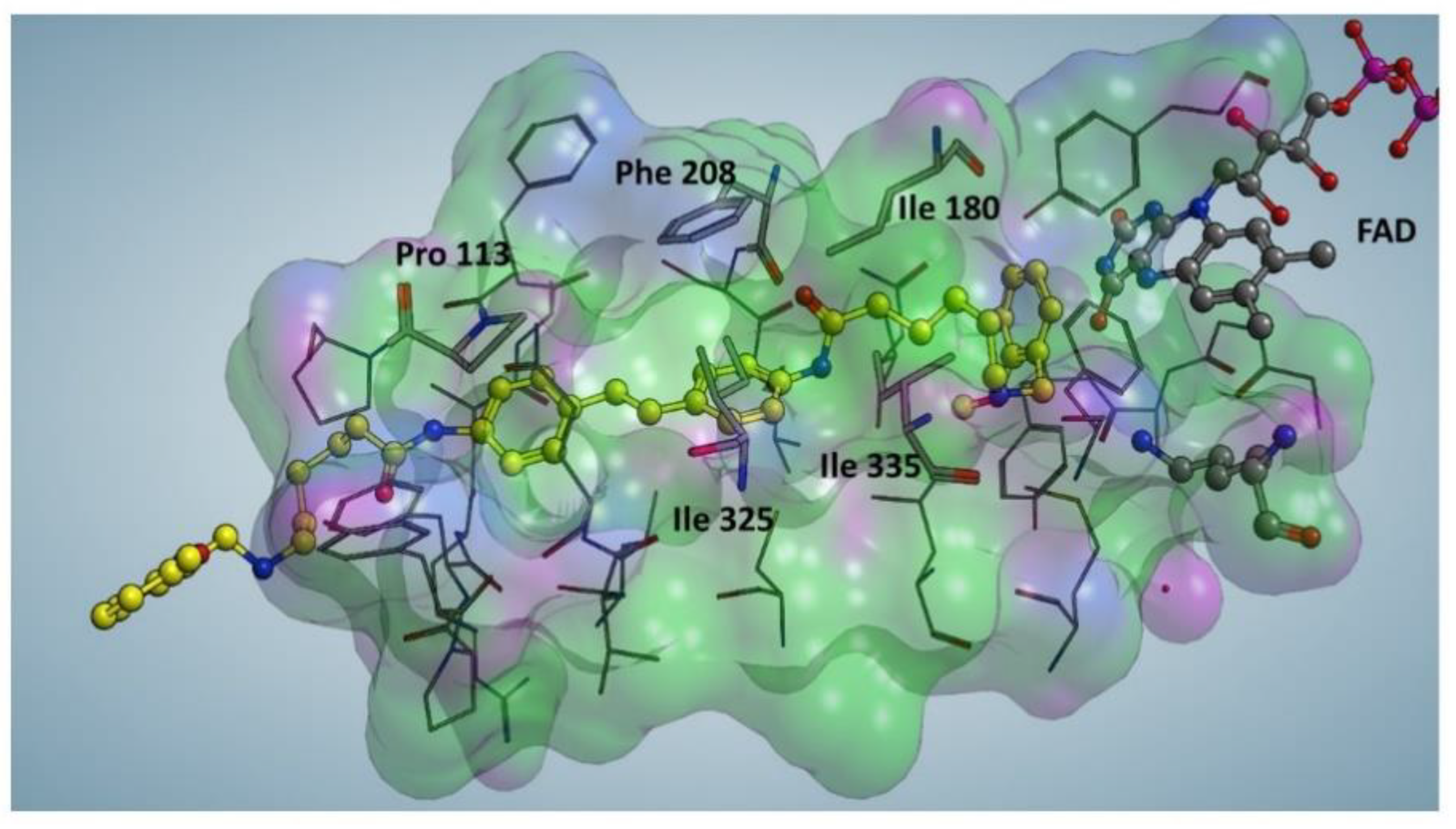
2.3. Docking Studies
2.4. Biological Evaluation
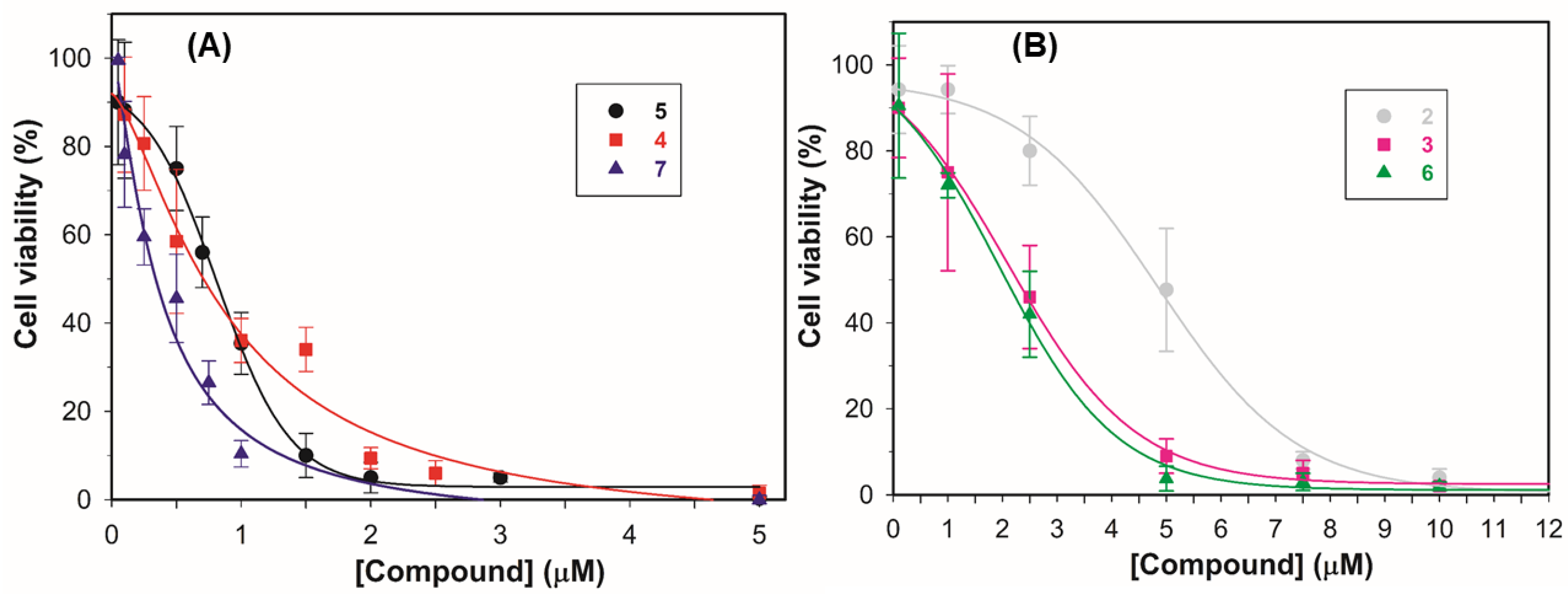
2.4.1. Antiproliferative Activity
2.4.2. Compounds 4 and 5 on MAO Activity in LN-229 Lysates
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
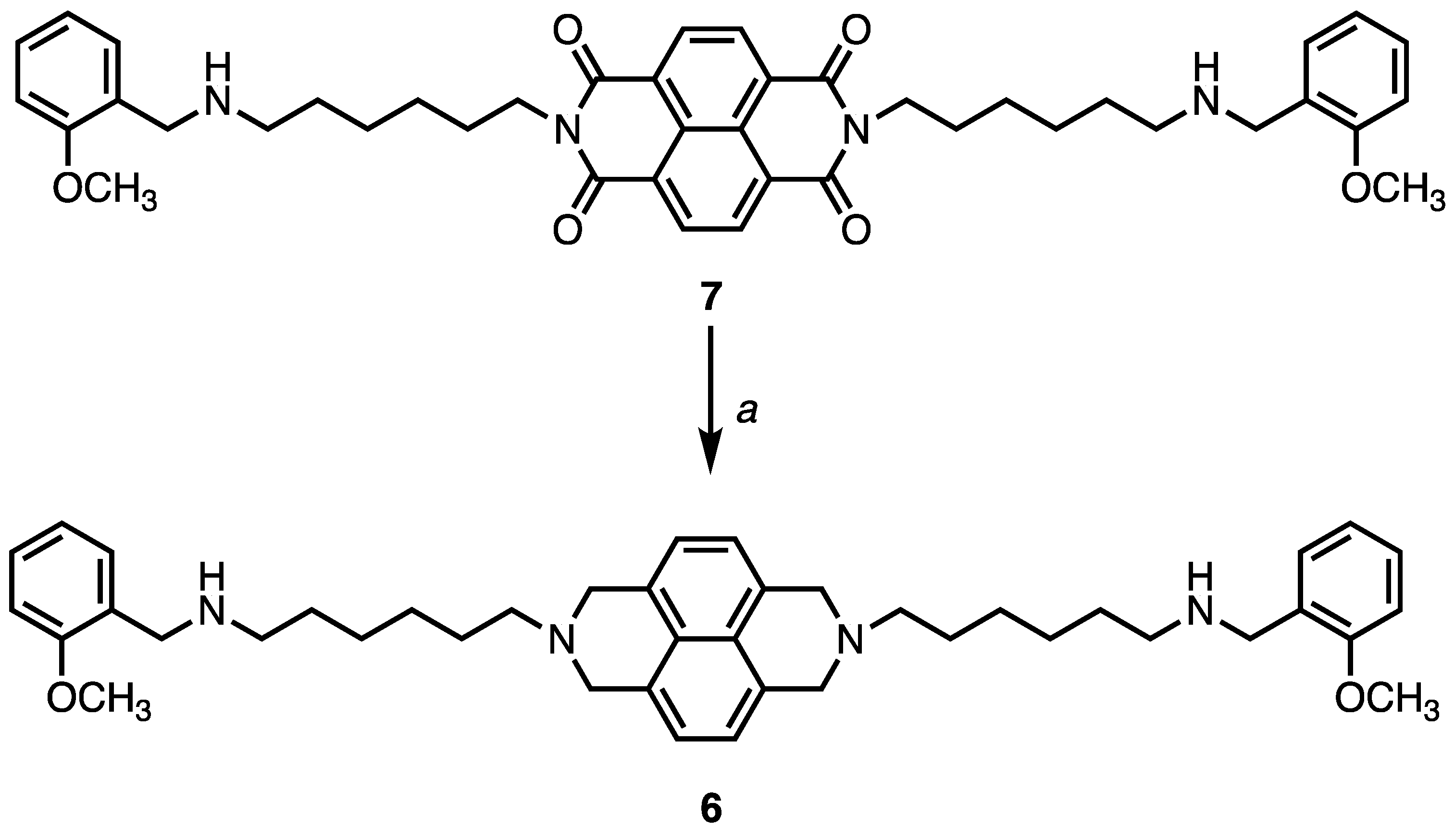
4.1. Chemistry
4.2. Amine Oxidase Assay Methods
Kinetic Analysis
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Cell Lysate
4.5. Inhibition Growth Assay
4.6. In Silico Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tipton, K.F. 90 years of monoamine oxidase: Some progress and some confusion. J. Neural. Transm. 2018, 125, 1519–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youdim, M.B.; Edmondson, D.; Tipton, K.F. The therapeutic potential of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.C.; Upadhyay, S.; Paliwal, S.; Saraf, S.K. Privileged scaffolds as MAO inhibitors: Retrospect and prospects. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 145, 445–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carradori, S.; Fantacuzzi, M.; Ammazzalorso, A.; Angeli, A.; De Filippis, B.; Galati, S.; Petzer, A.; Petzer, J.P.; Poli, G.; Tuccinardi, T.; et al. Resveratrol Analogues as Dual Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase B and Carbonic Anhydrase VII: A New Multi-Target Combination for Neurodegenerative Diseases? Molecules 2022, 27, 7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santin, Y.; Resta, J.; Parini, A.; Mialet-Perez, J. Monoamine oxidases in age-associated diseases: New perspectives for old enzymes. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 66, 101256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Wu, B.J. Monoamine oxidase A: An emerging therapeutic target in prostate cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1137050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenu, M.; Verma, V.K.; Seth, A.; Sahoo, R.K.; Gupta, P.; Arya, D.S. Association of Monoamine Oxidase A with Tumor Burden and Castration Resistance in Prostate Cancer. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp. 2020, 93, 100610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, J.C. Monoamine oxidase isoenzymes: Genes, functions and targets for behavior and cancer therapy. J. Neural. Transm. 2018, 125, 1553–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Ma, F.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, S.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.R.; Neal, A.; et al. Targeting monoamine oxidase A-regulated tumor-associated macrophage polarization for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hu, L.; Ma, Y.; Huang, B.; Xiu, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, K.; Tang, X. Increased expression of monoamine oxidase A is associated with epithelial to mesenchymal transition and clinicopathological features in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3245–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamand, V.; Zhao, H.; Peehl, D.M. Targeting monoamine oxidase A in advanced prostate cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 136, 1761–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabilondo, A.M.; Hostalot, C.; Garibi, J.M.; Meana, J.J.; Callado, L.F. Monoamine oxidase B activity is increased in human gliomas. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhabal, S.; Das, P.; Biswas, P.; Kumari, P.; Yakubenko, V.P.; Kundu, S.; Cathcart, M.K.; Kundu, M.; Biswas, K.; Bhattacharjee, A. Regulation of monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) expression, activity, and function in IL-13-stimulated monocytes and A549 lung carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 14040–14064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.B.; Shao, C.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Hu, P.; Shi, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Yin, F.; Liao, C.P.; et al. Monoamine oxidase A mediates prostate tumorigenesis and cancer metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2891–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peehl, D.M.; Coram, M.; Khine, H.; Reese, S.; Nolley, R.; Zhao, H. The significance of monoamine oxidase-A expression in high grade prostate cancer. J. Urol. 2008, 180, 2206–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, M.E.; Agus, D.B.; Dorff, T.B.; Pinski, J.K.; Quinn, D.I.; Castellanos, O.; Gilmore, P.; Shih, J.C. Phase 2 trial of monoamine oxidase inhibitor phenelzine in biochemical recurrent prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2021, 24, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushal, S.; Wang, W.; Vaikari, V.P.; Kota, R.; Chen, K.; Yeh, T.S.; Jhaveri, N.; Groshen, S.L.; Olenyuk, B.Z.; Chen, T.C.; et al. Monoamine oxidase A (MAO A) inhibitors decrease glioma progression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13842–13853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; He, Q.; Zhang, P.; Tang, X. The role of monoamine oxidase A in HPV-16 E7-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and HIF-1α protein accumulation in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2692–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, M.A.; Baskin, D.S. Monoamine oxidase B levels are highly expressed in human gliomas and are correlated with the expression of HiF-1α and with transcription factors Sp1 and Sp3. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3379–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Chien, M.H.; Lai, T.C.; Su, C.Y.; Jan, Y.H.; Hsiao, M.; Chen, C.L. Monoamine Oxidase B Expression Correlates with a Poor Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer Patients and Is Significantly Associated with Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition-Related Gene Signatures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljanabi, R.; Alsous, L.; Sabbah, D.A.; Gul, H.I.; Gul, M.; Bardaweel, S.K. Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) as a Potential Target for Anticancer Drug Design and Development. Molecules 2021, 26, 6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, B.; Kim, Y.J.; Wang, Y.C.; Li, Z.; Yu, J.; Zeng, S.; Ma, X.; Choi, I.Y.; Di Biase, S.; et al. Targeting monoamine oxidase A for T cell-based cancer immunotherapy. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabh2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehndiratta, S.; Qian, B.; Chuang, J.Y.; Liou, J.P.; Shih, J.C. N-Methylpropargylamine-Conjugated Hydroxamic Acids as Dual Inhibitors of Monoamine Oxidase A and Histone Deacetylase for Glioma Treatment. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 2208–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.T.; Choi, M.R.; Doh, M.S.; Jung, K.H.; Chai, Y.G. Effects of the monoamine oxidase inhibitors pargyline and tranylcypromine on cellular proliferation in human prostate cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 1587–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minarini, A.; Milelli, A.; Tumiatti, V.; Rosini, M.; Bolognesi, M.L.; Melchiorre, C. Synthetic polyamines: An overview of their multiple biological activities. Amino Acids 2010, 38, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karigiannis, G.; Papaioannou, D. Structure, biological activity and synthesis of polyamine analogues and conjugates. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 10, 1841–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casero, R.; Marton, L. Targeting polyamine metabolism and function in cancer and other hyperproliferative diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2007, 6, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casero, R.A., Jr.; Woster, P.M. Recent advances in the development of polyamine analogues as antitumor agents. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 4551–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casero, R.A., Jr.; Murray Stewart, T.; Pegg, A.E. Polyamine metabolism and cancer: Treatments, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolskaite, A.; Gardner, R.A.; Delcros, J.G.; Phanstiel, O., IV. Development of Polyamine Lassos as Polyamine Transport Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kaiser, M.; Copp, B.R. Investigation of Indolglyoxamide and Indolacetamide Analogues of Polyamines as Antimalarial and Antitrypanosomal Agents. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3138–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.K.; Hazeldine, S.; Crowley, M.L.; Hanson, A.; Beattie, R.; Varghese, S.; Senanayake, T.M.D.; Hirata, A.; Hirata, F.; Huang, Y.; et al. Polyamine-based small molecule epigenetic modulators. Med. Chem. Commun. 2012, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houdou, M.; Jacobs, N.; Coene, J.; Azfar, M.; Vanhoutte, R.; Van den Haute, C.; Eggermont, J.; Daniëls, V.; Verhelst, S.H.L.; Vangheluwe, P. Novel Green Fluorescent Polyamines to Analyze ATP13A2 and ATP13A3 Activity in the Mammalian Polyamine Transport System. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumiatti, V.; Minarini, A.; Milelli, A.; Rosini, M.; Buccioni, M.; Marucci, G.; Ghelardini, C.; Bellucci, C.; Melchiorre, C. Structure-activity relationships of methoctramine-related polyamines as muscarinic antagonist: Effect of replacing the inner polymethylene chain with cyclic moieties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 2312–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaiuto, E.; Minarini, A.; Tumiatti, V.; Milelli, A.; Lunelli, M.; Pegoraro, M.; Rizzoli, V.; Di Paolo, M.L. Synthetic polyamines as potential amine oxidase inhibitors: A preliminary study. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 913–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumiatti, V.; Milelli, A.; Minarini, A.; Micco, M.; Gasperi Campani, A.; Roncuzzi, L.; Baiocchi, D.; Marinello, J.; Capranico, G.; Zini, M.; et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of substituted naphthalene imides and diimides as anticancer agent. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7873–7877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, C.; Wang, J.; Pisani, L.; Caccia, C.; Carotti, A.; Salvati, P.; Edmondson, D.E.; Mattevi, A. Structures of human monoamine oxidase B complexes with selective noncovalent inhibitors: Safinamide and coumarin analogs. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5848–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubálek, F.; Binda, C.; Khalil, A.; Li, M.; Mattevi, A.; Castagnoli, N.; Edmondson, D.E. Demonstration of isoleucine 199 as a structural determinant for the selective inhibition of human monoamine oxidase B by specific reversible inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 15761–15766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Sablin, S.O.; Ramsay, R.R. Inhibition of monoamine oxidase A by beta-carboline derivatives. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1997, 337, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paolo, M.L.; Cervelli, M.; Mariottini, P.; Leonetti, A.; Polticelli, F.; Rosini, M.; Milelli, A.; Basagni, F.; Venerando, R.; Agostinelli, E.; et al. Exploring the activity of polyamine analogues on polyamine and spermine oxidase: Methoctramine, a potent and selective inhibitor of polyamine oxidase. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 740–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannecoeck, R.; Serruys, D.; Benmeridja, L.; Delanghe, J.R.; van Geel, N.; Speeckaert, R.; Speeckaert, M.M. Vascular adhesion protein-1: Role in human pathology and application as a biomarker. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 52, 284–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, M.; Jalkanen, S. Vascular Adhesion Protein-1: A Cell Surface Amine Oxidase in Translation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019, 30, 314–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Sun, D.; Zhang, J.; Xue, R.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Tang, W.; Dong, L. Spermine oxidase is upregulated and promotes tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, D.; Roh, S.; Hong, I.; Kim, H.; Ahn, T.S.; Kang, D.H.; Lee, M.S.; Baek, M.-J.; Kwak, H.J.; et al. Expression of Spermine Oxidase Is Associated with Colorectal Carcinogenesis and Prognosis of Patients. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöberg, R.L.; Wu, W.Y.; Dahlin, A.M.; Tsavachidis, S.; Bondy, M.L.; Melin, B.; Gliogene Group. Role of monoamine-oxidase-A-gene variation in the development of glioblastoma in males: A case control study. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 45, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconi, G.D.; Gallorini, M.; Carradori, S.; Guglielmi, P.; Cataldi, A.; Zara, S. The Up-Regulation of Oxidative Stress as a Potential Mechanism of Novel MAO-B Inhibitors for Glioblastoma Treatment. Molecules 2019, 24, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, C.J.; Mantle, T.-J.; Tipton, K.F. The nature of the inhibition of rat liver monoamine oxidase types A and B by the acetylenic inhibitors clorgyline, l-deprenyl and pargyline. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1982, 31, 3555–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarmouh, N.O.; Messeha, S.S.; Mateeva, N.; Gangapuram, M.; Flowers, K.; Eyunni, S.V.K.; Zhang, W.; Redda, K.K.; Soliman, K.F.A. The Antiproliferative Effects of Flavonoid MAO Inhibitors on Prostate Cancer Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resta, J.; Santin, Y.; Roumiguié, M.; Riant, E.; Lucas, A.; Couderc, B.; Binda, C.; Lluel, P.; Parini, A.; Mialet-Perez, J. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Prevent Glucose-Dependent Energy Production, Proliferation and Migration of Bladder Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.; Luo, J.; Yeh, S.; You, B.; Meng, J.; Chang, P.; Niu, Y.; Li, G.; Lu, C.; Zhu, Y.; et al. The MAO inhibitors phenelzine and clorgyline revert enzalutamide resistance in castration resistant prostate cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.; Olivero, J.; Choi, H.O.; Liao, C.P.; Kashemirov, B.A.; Katz, J.; Gross, M.E.; McKenna, C.E. Synthesis and anti-cancer potential of potent peripheral MAOA inhibitors designed to limit blood: Brain penetration. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2023, 92, 117425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benny, F.; Kumar, S.; Jayan, J.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Kumar, A.; Manoharan, A.; Susan, R.; Sudevan, S.T.; Mathew, B. Review of β-carboline and its derivatives as selective MAO-A inhibitors. Arch. Pharm. 2023, 356, e2300091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Panchuk-Voloshina, N. A one-step fluorometric method for the continuous measurement of monoamine oxidase activity. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 253, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santillo, M.F.; Liu, Y.; Ferguson, M.; Vohra, S.N.; Wiesenfeld, P.L. Inhibition of monoamine oxidase (MAO) by beta-carbolines and their interactions in live neuronal (PC12) and liver (HuH-7 and MH1C1) cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molecular Operating Environment (MOE), 2020.09 Chemical Computing Group ULC, 1010 Sherbooke St. West, Suite #910, Montreal, QC, Canada, H3A 2R7. 2020. Available online: https://www.chemcomp.com/Products.htm (accessed on 30 July 2023).
- Harvey, M.J.; Giupponi, G.V.; Fabritiis, G.D. ACEMD: Accelerating biomolecular dynamics in the microsecond time scale. J. Chem. Theor. Comput. 2009, 5, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | Structure | MAO A Ki (μM) | MAO B Ki (μM) | SI a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 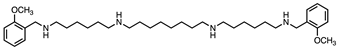 | 290 ± 60 | 470 ± 50 | 1:1.6 |
| 2 |  | 247 ± 42 | 330 ± 30 | 1:1.3 |
| 3 | 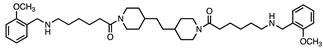 | 70 ± 7 | 19 ± 2 | 3.7:1 |
| 4 | 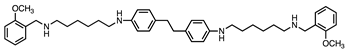 | 0.9 ± 0.2 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 3:1 |
| 5 |  | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 3:1 |
| 6 | 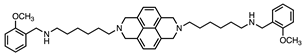 | 37 ± 4 | 27 ± 4 | 1.6:1 |
| 7 | 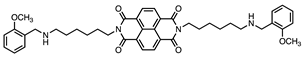 | 3.2 ± 0.2 | 4.2 ± 0.3 | 1:1.3 |
| Safinamide | 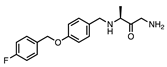 | >10 | (23 ± 4) × 10−3 | - |
| Isatine | 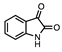 | 16 ± 3 | 4 ± 1 | 4:1 |
| Harmine |  | (2 ± 4) × 10−3 | >10 | - |
| Vmax/KM Relative to Control | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAP-1 | SMOX | MAO A | MAO B | |
| Compound 1 | 50 μM 1 | 10 μM | 10 μM | 10 μM |
| 1 | 1 | 0.21 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 2 | 0.60 | 0.61 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 3 | 0.37 | 0.47 | 0.95 | 0.64 |
| 5 | 0.48 | 0.46 | 0.06 | 0.02 |
| 6 | 0.50 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.30 |
| 7 | 0.55 | 0.16 | 0.71 | 0.75 |
| LN-229 | |
|---|---|
| Compounds | GI50 (μM) 1 |
| 1 | >20 |
| 2 | 4.6 ± 1.1 |
| 3 | 2.2 ± 0.9 |
| 4 | 0.9 ± 0.2 |
| 5 | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
| 6 | 2.0 ± 0.9 |
| 7 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| DOXO | 0.012 ± 0.004 |
| Inhibitor | Residual MAO Activity in Lysates |
|---|---|
| Deprenyl 1 (5 nM) | 0.74 ± 0.04 |
| Clorgyline 1 (5 nM) | 0.34 ± 0.10 |
| Pargyline 1 (0.5 mM) | 0.03 ± 0.02 |
| Safinamide 1 (0.2 μM) | 0.66 ± 0.04 |
| Harmine 1 (0.2 μM) | 0.37 ± 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nordio, G.; Piazzola, F.; Cozza, G.; Rossetto, M.; Cervelli, M.; Minarini, A.; Basagni, F.; Tassinari, E.; Dalla Via, L.; Milelli, A.; et al. From Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition to Antiproliferative Activity: New Biological Perspectives for Polyamine Analogs. Molecules 2023, 28, 6329. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176329
Nordio G, Piazzola F, Cozza G, Rossetto M, Cervelli M, Minarini A, Basagni F, Tassinari E, Dalla Via L, Milelli A, et al. From Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition to Antiproliferative Activity: New Biological Perspectives for Polyamine Analogs. Molecules. 2023; 28(17):6329. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176329
Chicago/Turabian StyleNordio, Giulia, Francesco Piazzola, Giorgio Cozza, Monica Rossetto, Manuela Cervelli, Anna Minarini, Filippo Basagni, Elisa Tassinari, Lisa Dalla Via, Andrea Milelli, and et al. 2023. "From Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition to Antiproliferative Activity: New Biological Perspectives for Polyamine Analogs" Molecules 28, no. 17: 6329. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176329
APA StyleNordio, G., Piazzola, F., Cozza, G., Rossetto, M., Cervelli, M., Minarini, A., Basagni, F., Tassinari, E., Dalla Via, L., Milelli, A., & Di Paolo, M. L. (2023). From Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition to Antiproliferative Activity: New Biological Perspectives for Polyamine Analogs. Molecules, 28(17), 6329. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176329









