Antibodies-Abzymes with Antioxidant Activities in Two Th and 2D2 Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice during the Development of EAE Pathology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Experimental Groups of Mice
2.2. Criteria Analysis of Catalytic Activities of Antibodies
2.3. Substrates of IgGs
2.4. In Time Changes in the Peroxidase Activity during the Development of EAE
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Experimental Animals
4.3. Immunization of Mice
4.4. IgG Purification
4.5. Assay of Redox Activities
4.6. In Situ Analysis of Peroxidase Activity
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- O’Connor, K.C.; Bar-Or, A.; Hafler, D.A. The neuroimmunology of multiple sclerosis: Possible roles of T and B lymphocytes in immunopathogenesis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2001, 21, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikehara, S.; Kawamura, M.; Takao, F. Organ-specific and systemic autoimmune diseases originate from defects in hematopoietic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8341–8344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andryushkova, A.A.; Kuznetsova, I.A.; Orlovskaya, I.A.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. Antibodies with amylase activity from the sera of autoimmune-prone MRL/MpJ-lpr mice. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 5089–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andryushkova, A.S.; Kuznetsova, I.A.; Orlovskaya, I.A.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. Nucleotide- hydrolyzing antibodies from the sera of autoimmune-prone MRL-lpr/lpr mice. Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Andryushkova, A.S.; Kuznetsova, I.A.; Buneva, V.N.; Toporkova, L.B.; Sakhno, L.V.; Tikhonova, M.A.; Chernykh, E.R.; Orlovskaya, I.A.; Nevinsky, G.A. Formation of different abzymes in autoimmune-prone MRL-lpr/lpr mice is associated with changes in colony formation of haematopoetic progenitors. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2007, 11, 531–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doronin, V.B.; Parkhomenko, T.A.; Korablev, A.; Toporkova, L.B.; Lopatnikova, J.A.; Alshevskaja, A.A.; Sennikov, S.V.; Buneva, V.N.; Budde, T.; Meuth, S.G.; et al. Changes in different parameters, lymphocyte proliferation and hematopoietic progenitor colony formation in EAE mice treated with myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulova, K.S.; Toporkova, L.B.; Lopatnikova, J.A.; Alshevskaya, A.A.; Sennikov, S.V.; Buneva, V.N.; Budde, T.; Meuth, S.G.; Popova, N.A.; Orlovskaya, I.A.; et al. Changes in haematopoietic progenitor colony differentiation and proliferation and the production of different abzymes in EAE mice treated with DNA. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3795–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulova, K.S.; Toporkova, L.B.; Lopatnikova, J.A.; Alshevskaya, A.A.; Sedykh, S.E.; Buneva, V.N.; Budde, T.; Meuth, S.G.; Popova, N.A.; Orlovskaya, I.A.; et al. Changes in cell differentiation and proliferation lead to production of abzymes in EAE mice treated with DNA-Histone complexes. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5816–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aulova, K.S.; Urusov, A.E.; Toporkova, L.B.; Sedykh, S.E.; Shevchenko, Y.A.; Tereshchenko, V.P.; Sennikov, S.V.; Budde, T.; Meuth, S.G.; Orlovskaya, I.A.; et al. Catalytic antibodies in the bone marrow and other organs of Th mice during spontaneous development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis associated with cell differentiation. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 1055–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulova, K.S.; Urusov, A.E.; Toporkova, L.B.; Sedykh, S.E.; Shevchenko, Y.A.; Tereshchenko, V.P.; Sennikov, S.V.; Budde, T.; Meuth, S.G.; Popova, N.A.; et al. Production of Abzymes in Th, CBA, and C57BL/6 Mice before and after MOG Treatment: Comparing Changes in Cell Differentiation and Proliferation. Biomolecules 2019, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulova, K.S.; Urusov, A.E.; Toporkova, L.B.; Sedykh, S.E.; Shevchenko, Y.A.; Tereshchenko, V.P.; Sennikov, S.V.; Orlovskaya, I.A.; Nevinsky, G.A. Cell Differentiation and Proliferation in the Bone Marrow and Other Organs of 2D2 Mice during Spontaneous Development of EAE Leading to the Production of Abzymes. Molecules 2022, 27, 2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keinan, E.E. (Ed.) Catalytic Antibodies; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Nevinsky, G.A. Autoimmune processes in multiple sclerosis: Production of harmful catalytic antibodies associated with significant changes in the hematopoietic stem cell differentiation and proliferation. In Multiple Sclerosis; Conzalez-Quevedo, A., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 100–147. [Google Scholar]
- Nevinsky, G.A.; Buneva, V.N. Natural catalytic antibodies–abzymes. In Catalytic Antibodies; Keinan, E., Ed.; VCH-Wiley Press: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; pp. 505–569. [Google Scholar]
- Nevinsky, G.A. Natural catalytic antibodies in norm and in autoimmune diseases. In Autoimmune Diseases: Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment; Brenner, K.J., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1–107. [Google Scholar]
- Nevinsky, G.A. Natural catalytic antibodies in norm and in HIV-infected patients. In Understanding HIV/AIDS Management and Care—Pandemic Approaches the 21st Century; Kasenga, F.H., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 151–192. [Google Scholar]
- Nevinsky, G.A. Catalytic antibodies in norm and systemic lupus erythematosus. In Lupus; Khan, W.A., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; pp. 41–101. [Google Scholar]
- Lerner, R.A.; Tramontano, A. Antibodies as enzymes. Trends Bioch. Sci. 1987, 12, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.D.; Benkovic, S.J. Recent developments in catalytic antibodies. Int. Rev. Immunol. 1993, 10, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.B.; Schultz, P.G. Opportunities at the interface of chemistry and biology. Trends Cell Biol. 1999, 9, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozyr, A.V.; Kolesnikov, A.V.; Aleksandrova, E.S.; Sashchenko, L.P.; Gnuchev, N.V.; Favorov, P.V.; Kotelnikov, M.A.; Iakhnina, E.I.; Astsaturov, I.A.; Prokaeva, T.B.; et al. Novel functional activities of anti-DNA autoantibodies from sera of patients with lymphoproliferative and autoimmune diseases. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1998, 75, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevinsky, G.A.; Buneva, V.N. Catalytic antibodies in healthy humans and patients with autoimmune and viral pathologies. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2003, 7, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, B.N. Dietary carcinogens and anticarcinogens. Oxygen radicals and degenerative diseases. Science 1983, 221, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, R.G. Antioxidants and aging. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 53, 373S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckman, K.B.; Ames, B.N. The free radical theory of aging matures. Physiol. Rev. 1998, 78, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuers, R.J.; Weindruch, R.; Hart, R.W. Caloric restriction, aging, and antioxidant enzymes. Mutat. Res. 1993, 295, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G. Free Radicals in Aging; CPC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; pp. 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zenkov, N.K.; Lankin, V.Z.; Men’shikova, E.B. Oxidative Stress. Biochemical and Pathophysiological Aspects; MAIK, Nauka/Interperiodica: Moscow, Russia, 2001; pp. 3–343. [Google Scholar]
- Frei, B.; Stoker, R.; Ames, B.N. Antioxidant defenses and lipid peroxidation in human blood plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 9748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, I.R. Stability of IgG isotypes in serum. MAbs 2010, 2, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikhmyangan, E.N.; Vasilenko, N.L.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. IgG antibodies with peroxidase-like activity from the sera of healthy Wistar rats. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikhmyangan, E.N.; Vasilenko, N.L.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G. Metal ions-dependent peroxidase and oxidoreductase activities of polyclonal IgGs from the sera of Wistar rats. J. Mol. Recognit. 2006, 19, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikhmyangan, E.N.; Vasilenko, N.L.; Sinitsina, O.I.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. Substrate specificity of rat sera IgG antibodies with peroxidase and oxidoreductase activities. J. Mol. Recognit. 2006, 19, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolmacheva, A.S.; Zaksas, N.P.; Buneva, V.N.; Vasilenko, N.L.; Nevinsky, G.A. Oxidoreductase activities of polyclonal IgG from the sera of Wistar rats are better activated by combinations of different metal ions. J. Mol. Recognit. 2009, 22, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolmacheva, A.S.; Vasilenko, N.L.; Zaksas, N.P.; Sinitsina, O.I.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. Immunoglobulins a from the blood of healthy Wistar rats oxidize amines. Russ. J. Immunol. 2009, 3, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Shcheglova, T.V.; Tolmacheva, A.S.; Ovchinnikova, L.P.; Sinitsina, O.I.; Vasilenko, N.L.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. Superoxide dismutase, catalase, peroxidase and H2O2-independent oxidoreductase IgG antibody activity from the blood of healthy Wistar rats. Russ. J. Immunol. 2011, 5, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Tolmacheva, A.S.; Blinova, E.A.; Ermakov, E.A.; Buneva, V.N.; Vasilenko, N.L.; Nevinsky, G.A. IgG abzymes with peroxidase and oxidoreductase activities from the sera of healthy humans. J. Mol. Recognit. 2015, 28, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolmacheva, A.S.; Ermakov, E.A.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. Substrate specificity of healthy human sera IgG antibodies with peroxidase and oxydoreductase activities. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolmacheva, A.S.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. Substrate specificity of IgGs with peroxidase and oxidoreductase activities from sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and multiple sclerosis. J. Mol. Recognit. 2019, 32, e2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolmacheva, A.S.; Nevinsky, G.A. Essential Protective Role of Catalytically Active Antibodies (Abzymes) with Redox Antioxidant Functions in Animals and Humans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxford, A.L.; Kurschus, F.C.; Waisman, A. Mouse models for multiple sclerosis: Historical facts and future implications. Bochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.D.; Karpus, W.J.; Davidson, T.S. Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in the Mouse. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2010, 88, 15-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overview and Model Selection Hooke Laboratories, Inc. Mouse EAE Models 2011–2013. Available online: https://hookelabs.com/services/cro/eae/ (accessed on 14 October 2022).
- Klotz, L.; Kuzmanov, I.; Hucke, S.; Gross, C.C.; Posevitz, V.; Dreykluft, A.; Schulte-Mecklenbeck, A.; Janoschka, C.; Lindner, M.; Herold, M.; et al. B7-H1 shapes T-cell-mediated brain endothelial cell dysfunction and regional encephalitogenicity in spontaneous CNS autoimmunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6182–E6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettelli, E. Building different mouse models for human MS. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1103, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettelli, E.; Pagany, M.; Weiner, H.L.; Linington, C.; Sobel, R.A.; Kuchroo, V.K. Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-specific T cell receptor transgenic mice develop spontaneous autoimmune optic neuritis. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinzel, S.; Lehmann-Horn, K.; Torke, S.; Häusler, D.; Winkler, A.; Stadelmann, C.; Payne, N.; Feldmann, L.; Saiz, A.; Reindl, M.; et al. Myelin-reactive antibodies initiate T cell-mediated CNS autoimmune disease by opsonization of endogenous antigen. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolmacheva, A.S.; Aulova, K.S.; Urusov, A.E.; Orlovskaya, I.A.; Nevinsky, G.A. Increase in Autoantibodies-Abzymes with Peroxidase and Oxidoreductase Activities in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice during the Development of EAE Pathology. Molecules 2021, 26, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souliotis, V.L.; Vlachogiannis, N.I.; Pappa, M.; Argyriou, A.; Ntouros, P.A.; Sfikakis, P.P. DNA Damage response and oxidative stress in systemic autoimmunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohl, K.; Tenbrock, K.; Kipp, M. Oxidative stress in multiple sclerosis: Central and peripheral mode of action. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 277, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibitoye, R.; Kemp, K.; Rice, C.; Hares, K.; Scolding, N.; Wilkins, A. Oxidative stress-related biomarkers in multiple sclerosis: A review. Biomark. Med. 2016, 10, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Fonseca, L.J.S.; Nunes-Souza, V.; Goulart, M.O.F.; Rabelo, L.A. Oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis: What the future might hold regarding novel biomarkers and add-on therapies. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7536805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smallwood, M.J.; Nissim, A.; Knight, A.R.; Whiteman, M.; Haigh, R.; Winyard, P.G. Oxidative stress in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 125, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, C. Perspectives of New Advances in the Pathogenesis of Vitiligo: From Oxidative Stress to Autoimmunity. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menshchikova, E.B.; Lankin, V.Z.; Zenkov, N.K.; Bondar, I.A.; Krugovykh, N.F.; Trufakin, V.A. Oxidative Stress. Prooxidants and Antioxidants; Slovo: Moscow, Russia, 2006; p. 556. [Google Scholar]
- Van Horssen, J.; Schreibelt, G.; Drexhage, J.; Hazes, T.; Dijkstra, C.D.; van der Valk, P.; de Vries, H.E. Severe oxidative damage in multiple sclerosis lesions coincides with enhanced antioxidant enzyme expression. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 1729–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Planque, S.A.; Nishiyama, Y.; Hanson, C.V.; Massey, R.J. Nature and nurture of catalytic antibodies. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 750, 56–75. [Google Scholar]
- Planque, S.A.; Nishiyama, Y.; Hara, M.; Sonoda, S.; Murphy, S.K.; Watanabe, K.; Mitsuda, Y.; Brown, E.L.; Massey, R.J.; Pimmeer, S.R.; et al. Physiological IgM class catalytic antibodies selective for transthyretin amyloid. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 13243–13258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agar, N.S.; Sadrzadeh, S.M.; Hallaway, P.E.; Eaton, J.W. Erythrocyte catalase. A somatic oxidant defense? J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 77, 319–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, A.D.; Jones, L.H.; Wentworth, P., Jr.; Janda, K.D.; Lerner, R.A. Antibodies have the intrinsic capacity to destroy antigens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10930–10935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wentworth, P., Jr.; Jones, L.H.; Wentworth, A.D.; Zhu, X.; Larsen, N.A.; Wilson, I.A.; Xu, X.; Goddard, W.A., 3rd; Janda, K.D.; Eschenmoser, A.; et al. Antibody catalysis of the oxidation of water. Science 2001, 293, 1806–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
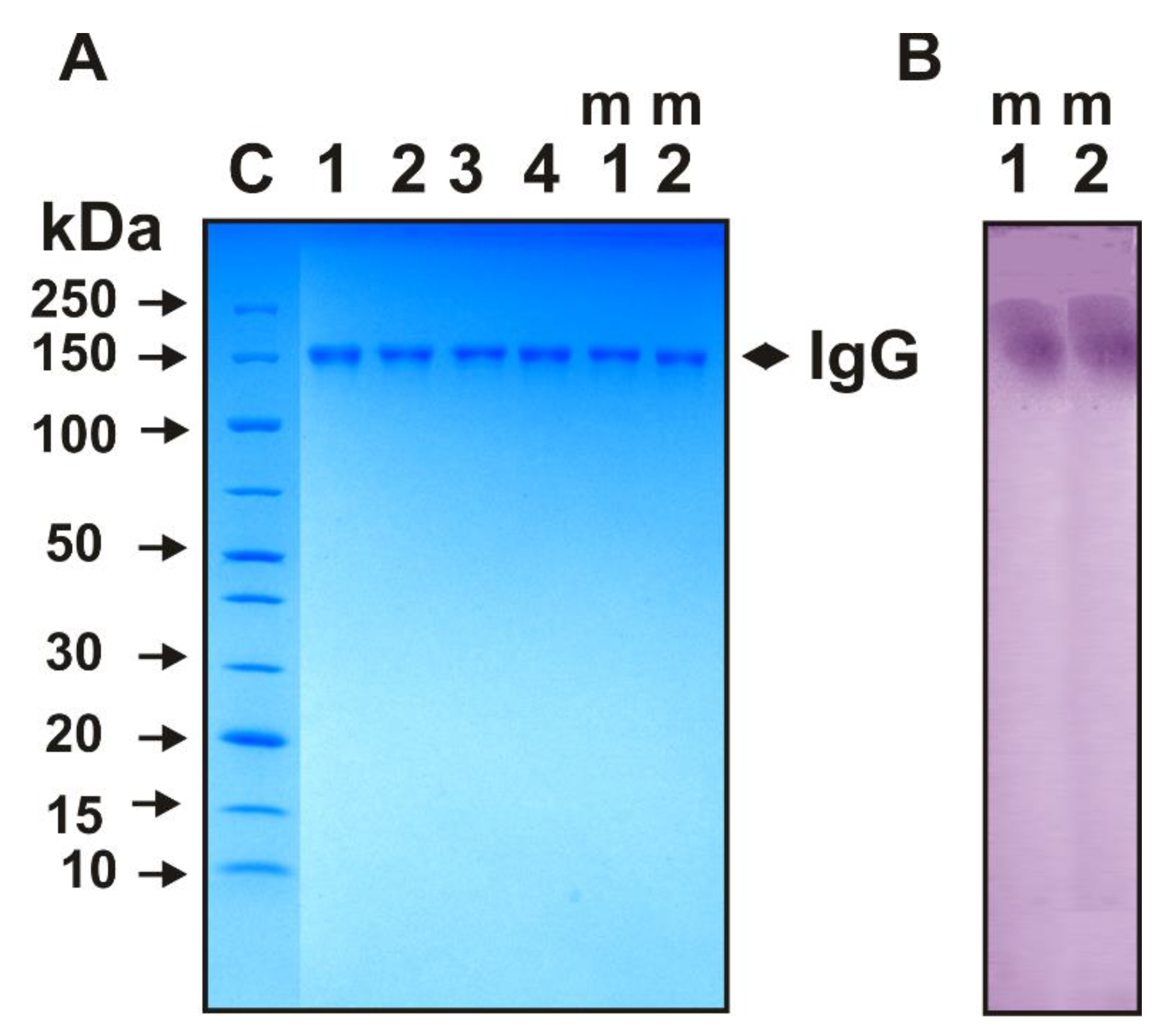

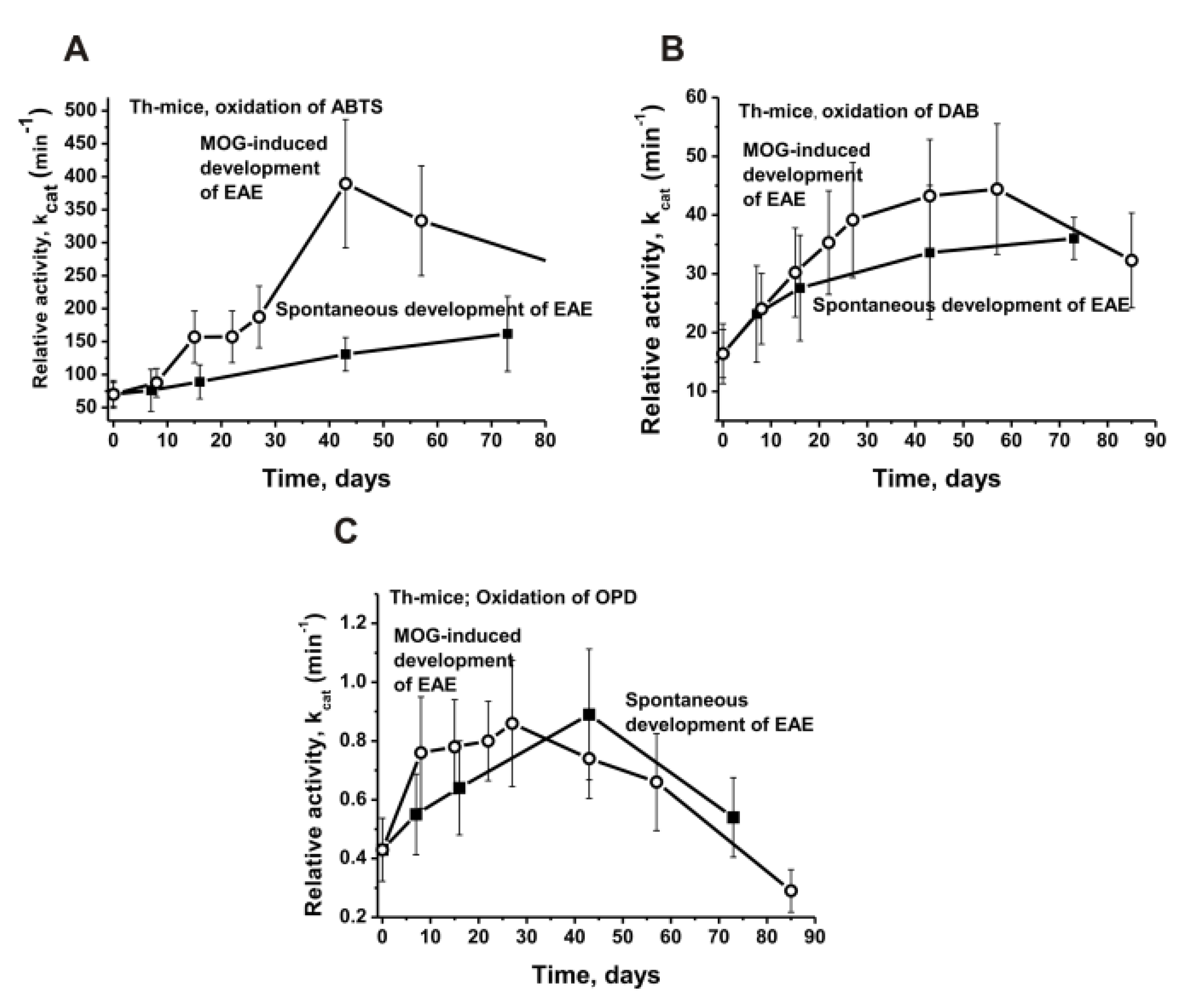
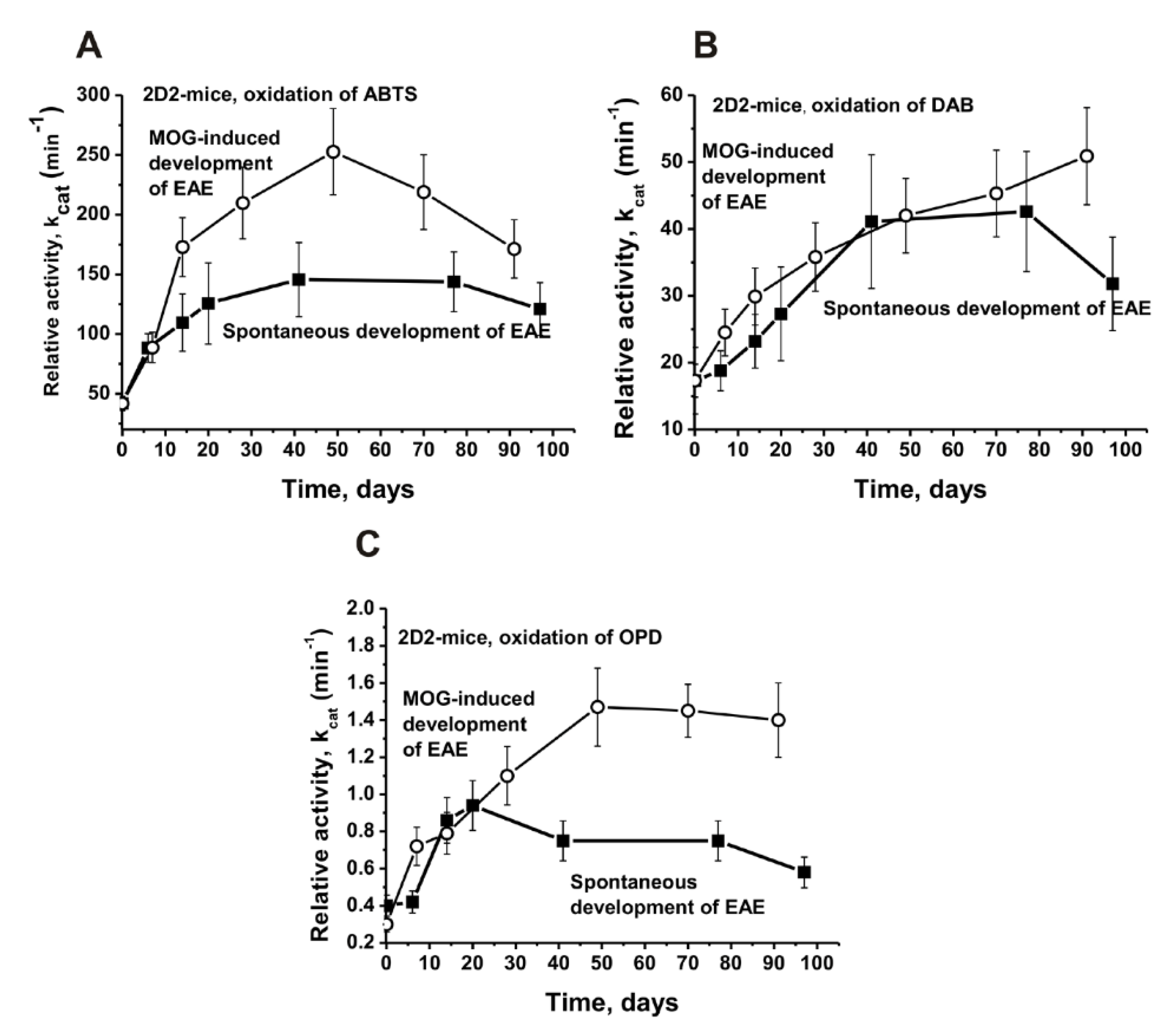

| Substrate | Values of kcat, min−1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero Time (3 Months of Age) | 40 Days after Spontaneous EAE Development | 40 Days after Treatment with MOG | Ratio of 2 to 1 | Ratio of 3 to 1 | Ratio of 3 to 2 | |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| H2O2-dependent peroxidase activity * | ||||||
| Th mice | ||||||
| ABTS | 70.0 ± 21.0 | 130.8 ± 25.4 | 389.5 ± 97.3 | 1.9 | 5.6 | 3.0 |
| DAB | 16.4 ± 5.1 | 33.6 ± 11.4 | 43.3 ± 9.6 | 2.0 | 2.6 | 1.3 |
| OPD | 0.43 ± 0.1 | 0.89 ± 0.2 | 0.89 ± 0.1 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 1.0 |
| 2D2 mice | ||||||
| ABTS | 41.8 ± 2.5 | 145.6 ± 2.5 | 252.7 ± 36.1 | 3.5 | 6.0 | 1.7 |
| DAB | 17.3 ± 5.0 | 41.1 ± 10.0 | 42.0 ± 5.6 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 1.0 |
| OPD | 0.30 ± 0.06 | 0.75 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 2.0 |
| C57BL/6 mice [48] | ||||||
| ABTS | 69.8 ± 23.1 | 100.4 ± 12.0 | 372.0 ± 40.0 | 1.4 | 5.3 | 3.7 |
| DAB | 5.2 ± 1.0 | 12.3 ± 1.2. | 26.7 ± 7.0 | 2.4 | 5.1 | 2.2 |
| H2O2-independent oxidoreductase activity ** | ||||||
| Th mice | ||||||
| ABTS | 17.5 ± 1.0 | 31.6 ± 1.8 | 71.0 ± 1.9 | 1.8 | 4.1 | 2.2 |
| 2D2 mice | ||||||
| ABTS | 20.6 ± 1.5 | 50.6 ± 2.8 | 92.5 ± 5.1 | 2.5 | 4.5 | 1.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tolmacheva, A.S.; Aulova, K.S.; Urusov, A.E.; Doronin, V.B.; Nevinsky, G.A. Antibodies-Abzymes with Antioxidant Activities in Two Th and 2D2 Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice during the Development of EAE Pathology. Molecules 2022, 27, 7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217527
Tolmacheva AS, Aulova KS, Urusov AE, Doronin VB, Nevinsky GA. Antibodies-Abzymes with Antioxidant Activities in Two Th and 2D2 Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice during the Development of EAE Pathology. Molecules. 2022; 27(21):7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217527
Chicago/Turabian StyleTolmacheva, Anna S., Kseniya S. Aulova, Andrey E. Urusov, Vasiliy B. Doronin, and Georgy A. Nevinsky. 2022. "Antibodies-Abzymes with Antioxidant Activities in Two Th and 2D2 Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice during the Development of EAE Pathology" Molecules 27, no. 21: 7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217527
APA StyleTolmacheva, A. S., Aulova, K. S., Urusov, A. E., Doronin, V. B., & Nevinsky, G. A. (2022). Antibodies-Abzymes with Antioxidant Activities in Two Th and 2D2 Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice during the Development of EAE Pathology. Molecules, 27(21), 7527. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217527








