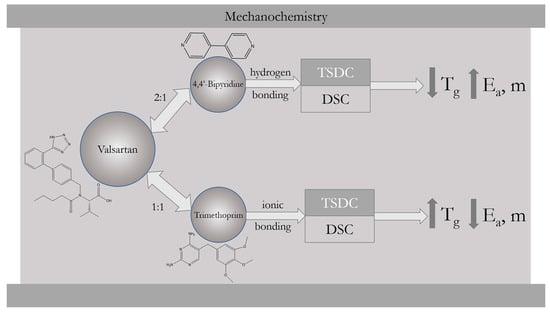
Coamorphous Systems of Valsartan: Thermal Analysis Contribution to Evaluate Intermolecular Interactions Effects on the Structural Relaxation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
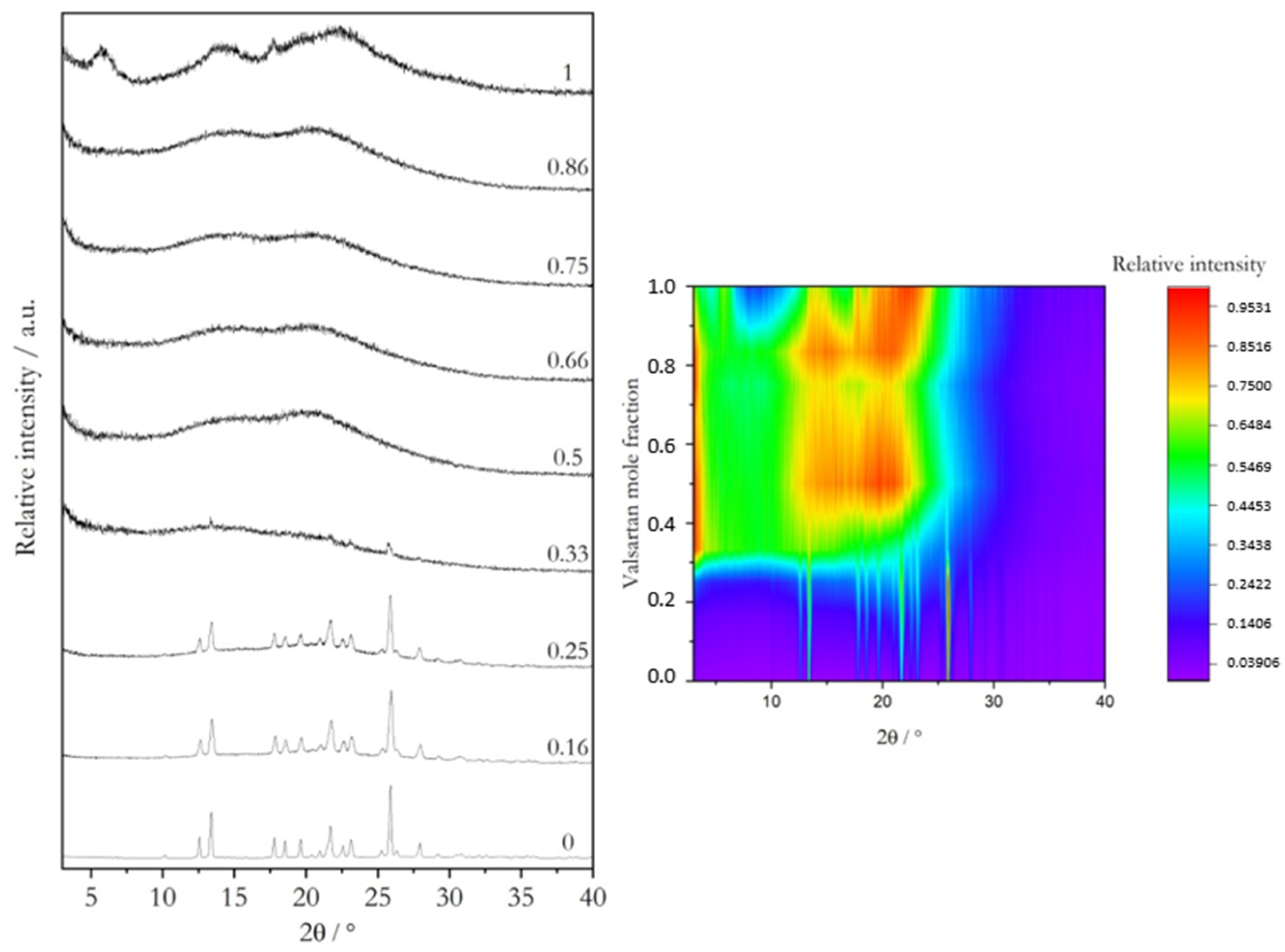
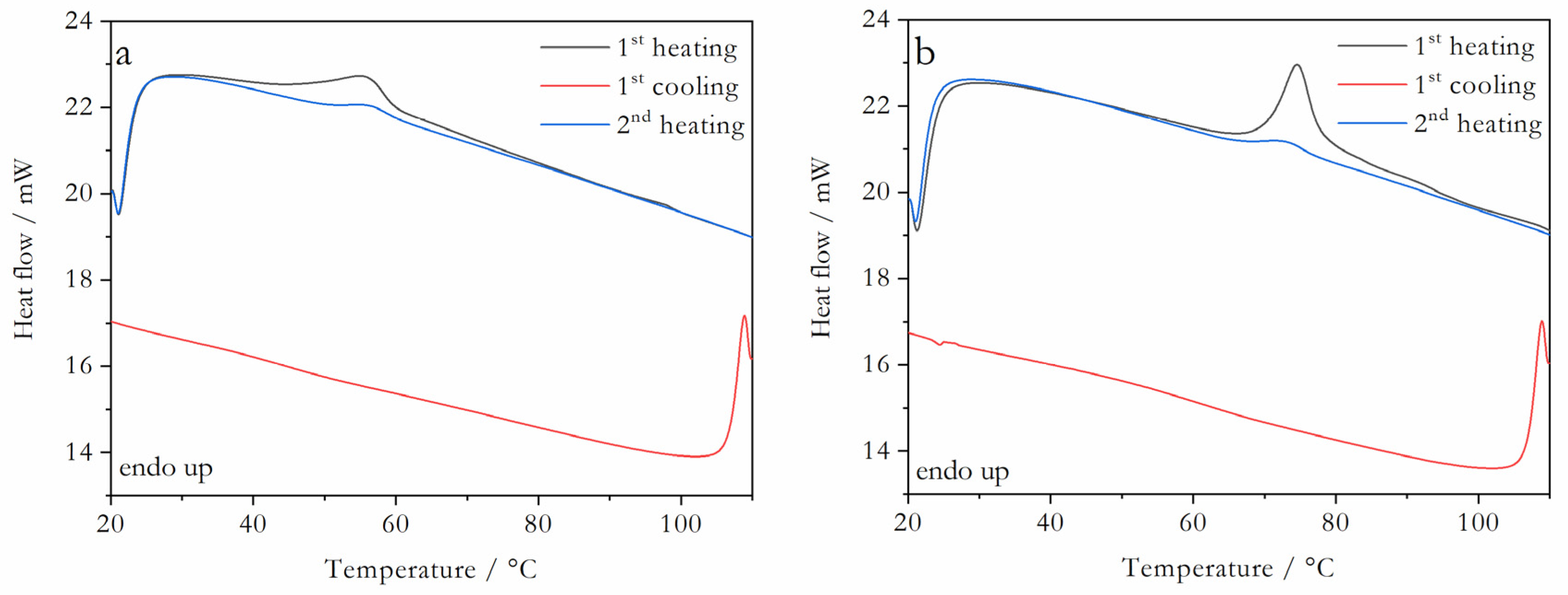
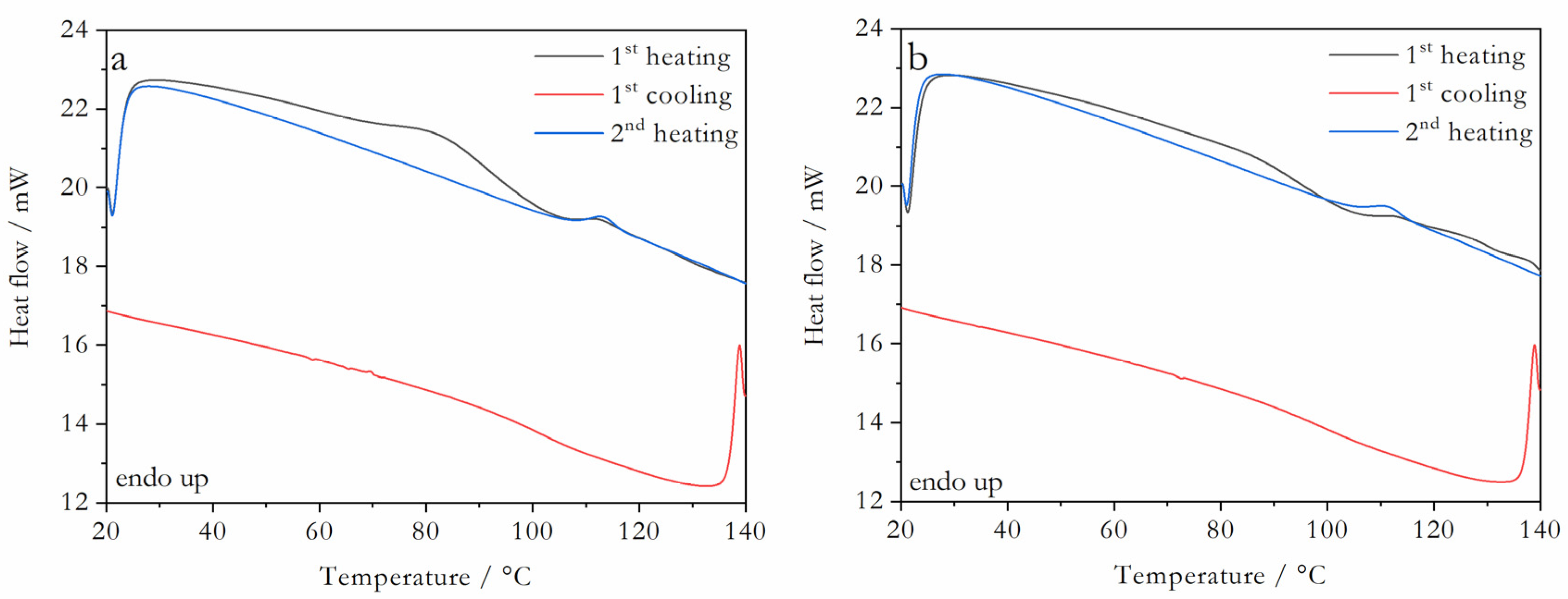
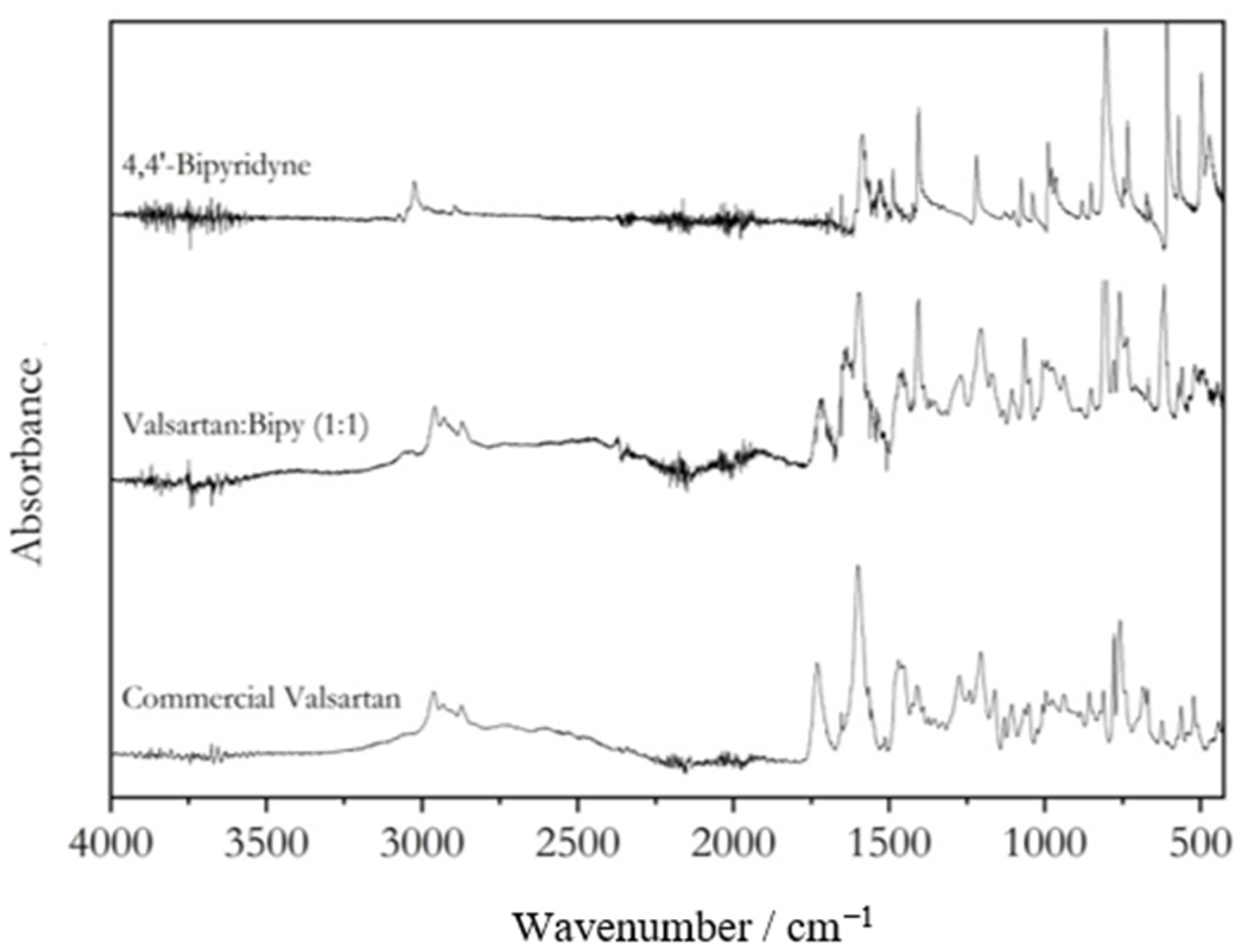
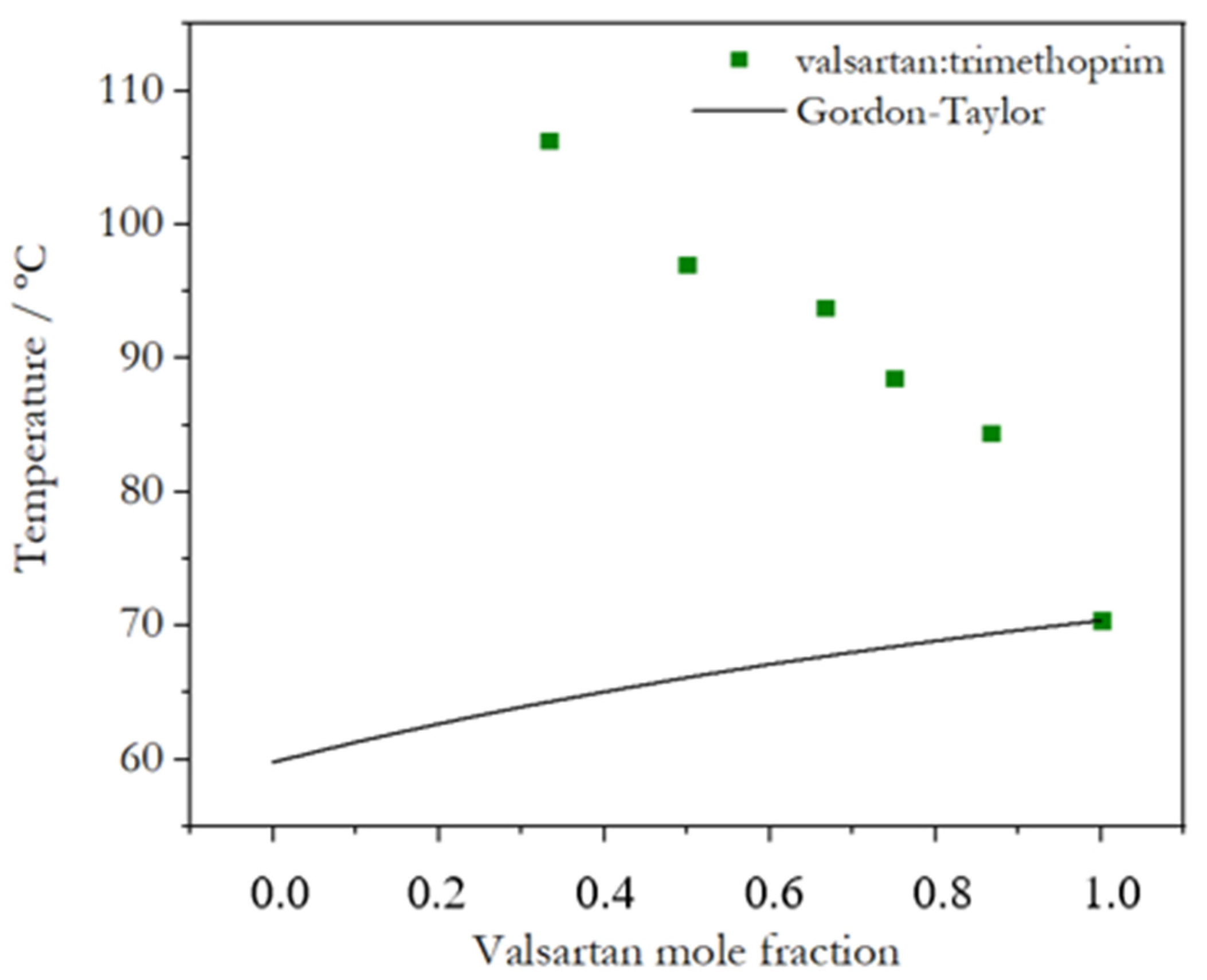
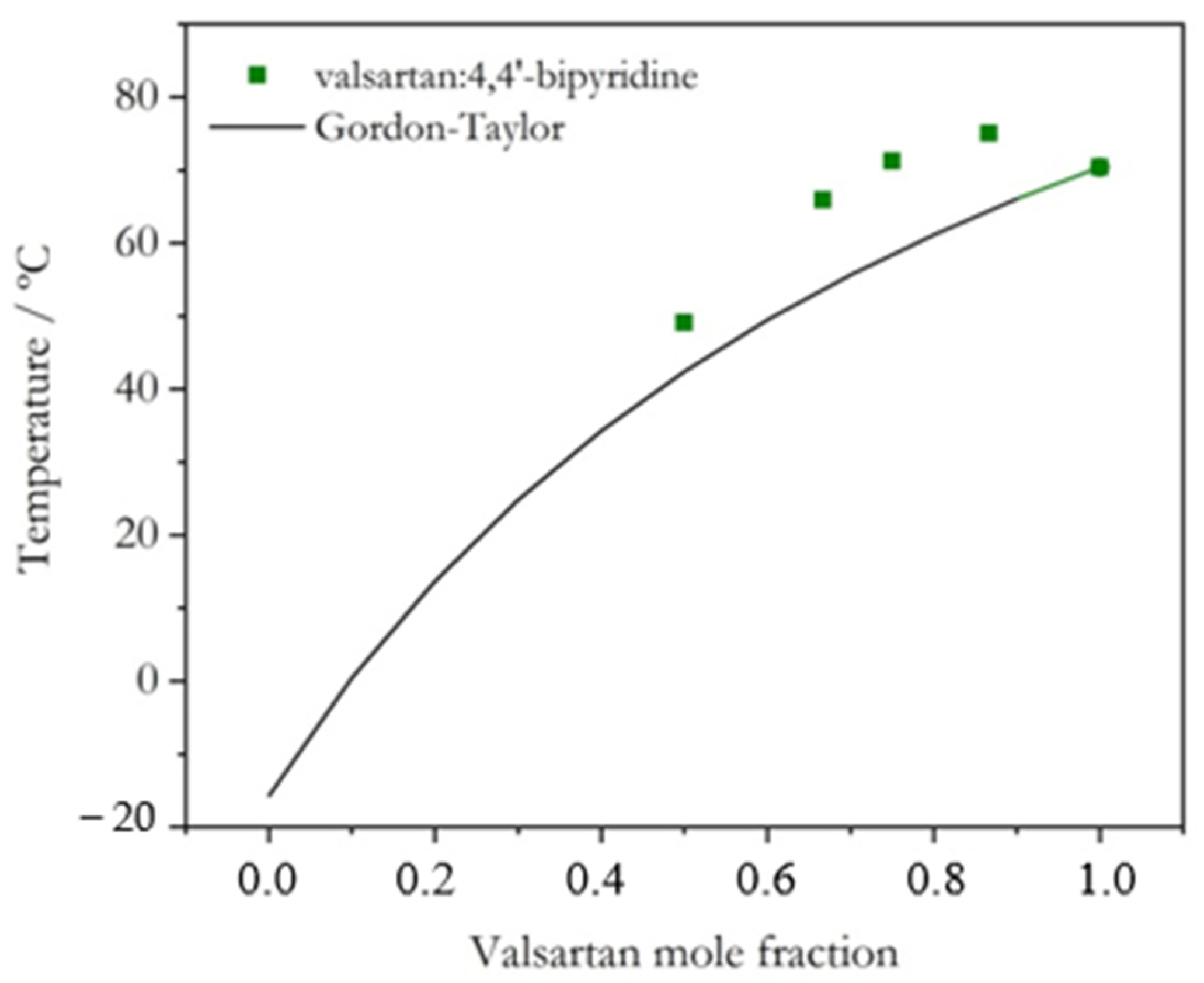
2.1. Coamorphous Systems Characterization
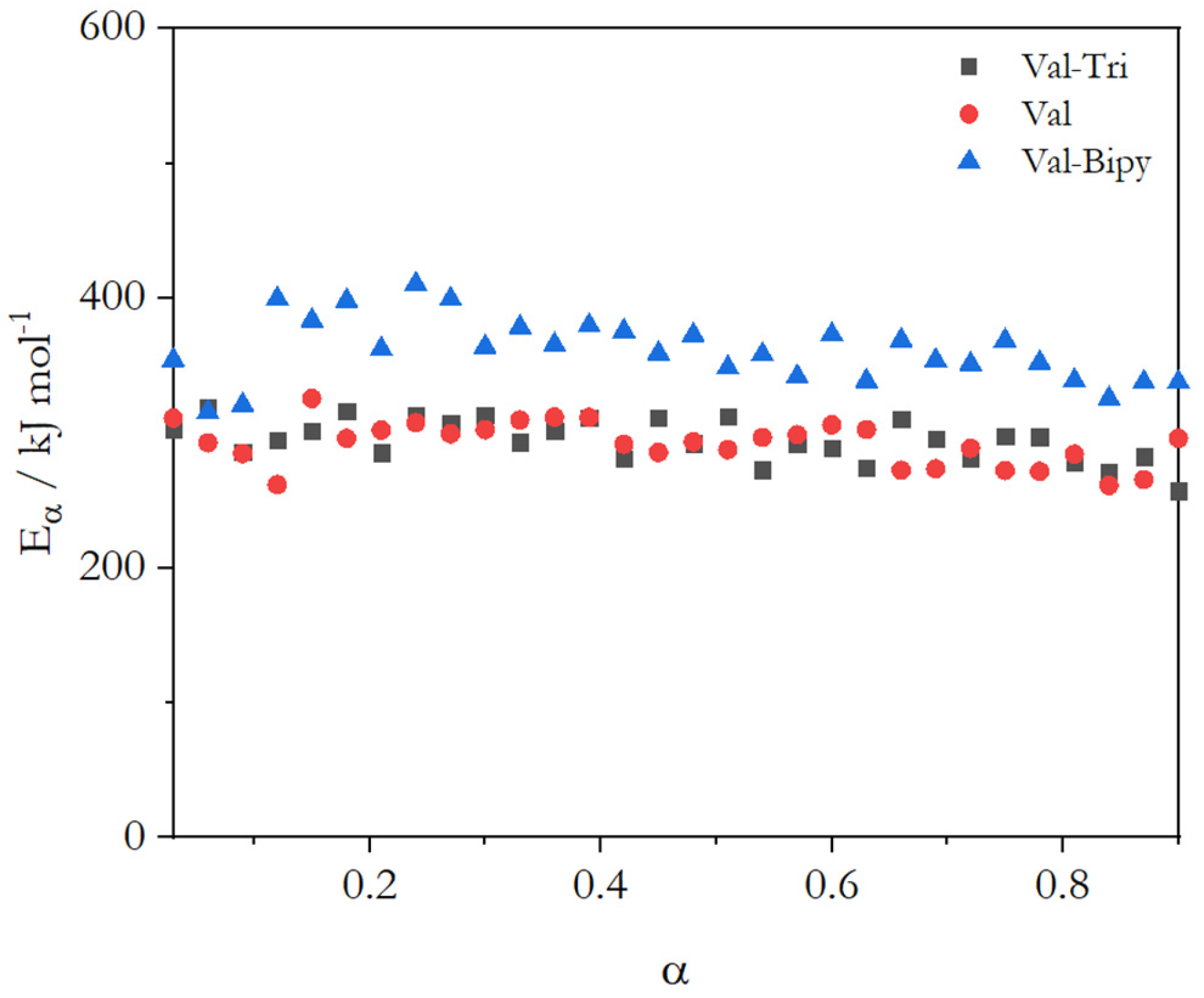
2.2. Activation Energy of Glass Transition for Selected Coamorphous Mixtures
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.3. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
3.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.5. Thermally Stimulated Depolarization Current (TSDS)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Wang, L.; Yan, F. Trans and Cis Conformations of the Antihypertensive Drug Valsartan Respectively Lock the Inactive and Ac-tive-like States of Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor: A Molecular Dynamics Study. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2018, 58, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.Z. Study on Co-Crystallization of LCZ696 Using In Situ ATR-FTIR and Imaging. Crystals 2020, 10, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodagekar, A.; Chavan, R.B.; Chella, N.; Shastri, N.R. Role of Valsartan as an Antiplasticizer in Development of Therapeutically Viable Drug–Drug Coamorphous System. Cryst. Growth Des. 2018, 18, 1944–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodagekar, A.; Chavan, R.B.; Mannava, M.C.; Yadav, B.; Chella, N.; Nangia, A.K.; Shastri, N.R. Co amorphous valsartan nifedipine system: Preparation, characterization, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 139, 105048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turek, M.; Różycka-Sokołowska, E.; Koprowski, M.; Marciniak, B.; Bałczewski, P. Role of Hydrogen Bonds in Formation of Co-amorphous Valsartan/Nicotinamide Compositions of High Solubility and Durability with Anti-hypertension and An-ti-COVID-19 Potential. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 1970–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Moinuddin, S.M.; Cai, T. Advances in coamorphous drug delivery systems. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, D.J.; Steed, J.W. Pharmaceutical cocrystals, salts and multicomponent systems; intermolecular interactions and property based design. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 117, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoguchi, R.; Waraya, H.; Hirakura, Y. Application of Co-Amorphous Technology for Improving the Physicochemical Properties of Amorphous Formulations. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2142–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, L.I.; Grohganz, H.; Palmelund, H.; Löbmann, K.; Rades, T.; Musa, O.M.; Steed, J.W. Predictive identification of co-formers in co-amorphous systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 157, 105636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomposo, J.A.; Eguiazabal, I.; Calahorra, E.; Cortázar, M. Glass transition behaviour and interactions in poly(p-vinyl phe-nol)polymethacrylate blends. Polymer 1993, 34, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, H.A. The Gordon-Taylor equation. Additivity and interaction in compatible polymer blends. Die Makromol. Chem. 1988, 189, 1941–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.T.; Larsen, F.H.; Löbmann, K.; Rades, T.; Grohganz, H. Influence of variation in molar ratio on co-amorphous drug-amino acid systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 107, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, A.D.; Knapik-Kowalczuk, J.; Paluch, M.; Hoang, T.X.; Wakabayashi, K. Theoretical Model for the Structural Relaxation Time in Coamorphous Drugs. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2992–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissi, E.O.; Grohganz, H.; Löbmann, K.; Ruggiero, M.T.; Zeitler, J.A.; Rades, T. Glass-Transition Temperature of the β-Relaxation as the Major Predictive Parameter for Recrystallization of Neat Amorphous Drugs. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 2803–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyazovkin, S. Isoconversional Kinetics of Polymers: The Decade Past. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2017, 38, 1600615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dranca, I.; Bhattacharya, S.; Vyazovkin, S.; Suryanarayanan, R. Implications of Global and Local Mobility in Amorphous Sucrose and Trehalose as Determined by Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyazovkin, S.; Dranca, I. Physical Stability and Relaxation of Amorphous Indomethacin. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 18637–18644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyazovkin, S.; Burnham, A.K.; Criado, J.M.; Pérez-Maqueda, L.A.; Popescud, C.; Sbirrazzuoli, N. ICTAC Kinetics Committee recom-mendations for performing kinetic computations on thermal analysis data. Thermochim. Acta 2011, 520, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercicek, F.; Harscoat-Schiavo, C.; Layrisse, P.; Marchivie, M.; Cartigny, Y.; Brandel, C.; Tassaing, T.; Conrad, M.; Marre, S.; Subra-Paternault, P. Naproxen-bipyridine cocrystallization assisted by pressurized carbon dioxide. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2023, 200, 105976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, G.; Maggi, L.; Monteforte, F.; Ferrara, C.; Capsoni, D.; Berbenni, V.; Milanese, C.; Girella, A.; Friuli, V.; Mustarelli, P.; et al. Zaltoprofen/4,4′-Bipyridine: A Case Study to Demonstrate the Potential of Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) in the Pharmaceutical Field. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 3690–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardiana, F.; Suciati; Indrayanto, G. Valsartan. In Profiles Drug Subst Excip Relat Methodol; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 431–493. [Google Scholar]
- Cagigal, E.; González, L.; Alonso, R.M.; Jiménez, R.M. pK a determination of angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARA II) by spec-trofluorimetry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001, 26, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flesch, G.; Müller, P.; Lloyd, P. Absolute bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of valsartan, an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, in man. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1997, 52, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neth, N.L.K.; Carlin, C.M.; Keen, O.S. Emerging investigator series: Transformation of common antibiotics during water disinfection with chlorine and formation of antibacterially active products. Environ. Sci. 2019, 5, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Thakuria, R.; Delori, A.; Jones, W.; Lipert, M.P.; Roy, L.; Rodríguez-Hornedo, N. Pharmaceutical cocrystals and poorly soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 101–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Cabeza, A.J. Acid–base crystalline complexes and the pKa rule. Crystengcomm 2012, 14, 6362–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aakeroy, C.B.; Salmon, D.J.; Smith, M.M.; Desper, J. Cyanophenyloximes: Reliable and Versatile Tools for Hydrogen-Bond Directed Supramolecular Synthesis of Cocrystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2006, 6, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Tothadi, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Ganguly, S.; Desiraju, G.R. Synthon identification in co-crystals and polymorphs with IR spectroscopy. Primary amides as a case study. Crystengcomm 2013, 15, 4640–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, J.A.; Van Eerdenbrugh, B.; Taylor, L.S. A Classification System to Assess the Crystallization Tendency of Organic Molecules from Undercooled Melts. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 3787–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djellouli, F.; Dahmani, A.; Hassani, A. Characterization of the polymorph changes in Trimethoprim. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.J.M.; Diogo, H.P. Thermal behavior and molecular mobility in the glassy state of three anti-hypertensive pharma-ceutical ingredients. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 10831–10840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skotnicki, M.; Gaweł, A.; Cebe, P.; Pyda, M. Thermal behavior and phase identification of Valsartan by standard and tempera-ture-modulated differential scanning calorimetry. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xivillé, N.R.; Lorente, L.T.; Kordikowski, A. MDSC parameter optimization for the determination of glass transitions using a Design of Experiments approach. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 422, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsac, P.J.; Li, T.; Taylor, L.S. Estimation of drug-polymer miscibility and solubility in amorphous solid dispersions using exper-imentally determined interaction parameters. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koetzle, T.F.; Williams, G.J.B. The crystal and molecular structure of the antifolate drug trimethoprim (2,4-diamino-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzyl)pyrimidine). A neutron diffraction study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 2074–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boag, N.M.; Coward, K.M.; Jones, A.C.; Pemble, M.E.; Thompson, J.R. 4,4′-Bipyridyl at 203K. Acta Crystallogr. C 1999, 55, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbmann, K.; Laitinen, R.; Strachan, C.; Rades, T.; Grohganz, H. Amino acids as co-amorphous stabilizers for poorly water-soluble drugs—Part 2: Molecular interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angell, C.A. Formation of Glasses from Liquids and Biopolymers. Science 1995, 267, 1924–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.J.M.; Diogo, H.P. The determination of the glass transition temperature by thermally stimulated depolarization currents. Comparison with the performance of other techniques. Phase Transit. 2017, 90, 1061–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diogo, H.P.; Viciosa, M.T.; Ramos, J.J.M. Differential scanning calorimetry and thermally stimulated depolarization currents study on the molecular dynamics in amorphous fenofibrate. Thermochim. Acta 2016, 623, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, K. Interpretation of the apparent activation energy of glass transition. J. Phys. Commun. 2021, 5, 095013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angell, C.A.; Ngai, K.L.; McKenna, G.B.; McMillan, P.F.; Martin, S.W. Relaxation in glass forming liquids and amorphous solids. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 3113–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.J.M.; Viciosa, M.T.; Diogo, H.P. Thermal behaviour of two anti-inflammatory drugs (celecoxib and rofecoxib) and slow relaxation dynamics in their amorphous solid state. Comparison between the dynamic fragility obtained by dielectric spectroscopy and by thermostimulated currents. Mol. Phys. 2019, 117, 644–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample (Stoichiometry) | Glass Transition Temperature (Tg/°C) | Effective Activation Energy at Tg (kJ mol−1) | Fragility (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valsartan | 70 a, 67(DSC) b, 65(TSDC) b | 300 a, 328(DSC) b, 304(TSDC) b | 46 a, 50(DSC) b, 47(TSDC) b |
| Val-Bipy (2:1) | 62 a, 67 c | 363a, 376 c | 57 a, 58 c |
| Val-Tri (1:1) | 97 a, 96 c | 308 a, 369 c | 44 a, 49 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ekawa, B.; Diogo, H.P.; Castro, R.A.E.; Caires, F.J.; Eusébio, M.E.S. Coamorphous Systems of Valsartan: Thermal Analysis Contribution to Evaluate Intermolecular Interactions Effects on the Structural Relaxation. Molecules 2023, 28, 6240. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176240
Ekawa B, Diogo HP, Castro RAE, Caires FJ, Eusébio MES. Coamorphous Systems of Valsartan: Thermal Analysis Contribution to Evaluate Intermolecular Interactions Effects on the Structural Relaxation. Molecules. 2023; 28(17):6240. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176240
Chicago/Turabian StyleEkawa, Bruno, Hermínio P. Diogo, Ricardo A. E. Castro, Flávio J. Caires, and M. Ermelinda S. Eusébio. 2023. "Coamorphous Systems of Valsartan: Thermal Analysis Contribution to Evaluate Intermolecular Interactions Effects on the Structural Relaxation" Molecules 28, no. 17: 6240. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176240
APA StyleEkawa, B., Diogo, H. P., Castro, R. A. E., Caires, F. J., & Eusébio, M. E. S. (2023). Coamorphous Systems of Valsartan: Thermal Analysis Contribution to Evaluate Intermolecular Interactions Effects on the Structural Relaxation. Molecules, 28(17), 6240. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176240