Assembling a Cinnamyl Pharmacophore in the C3-Position of Substituted Isatins via Microwave-Assisted Synthesis: Development of a New Class of Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
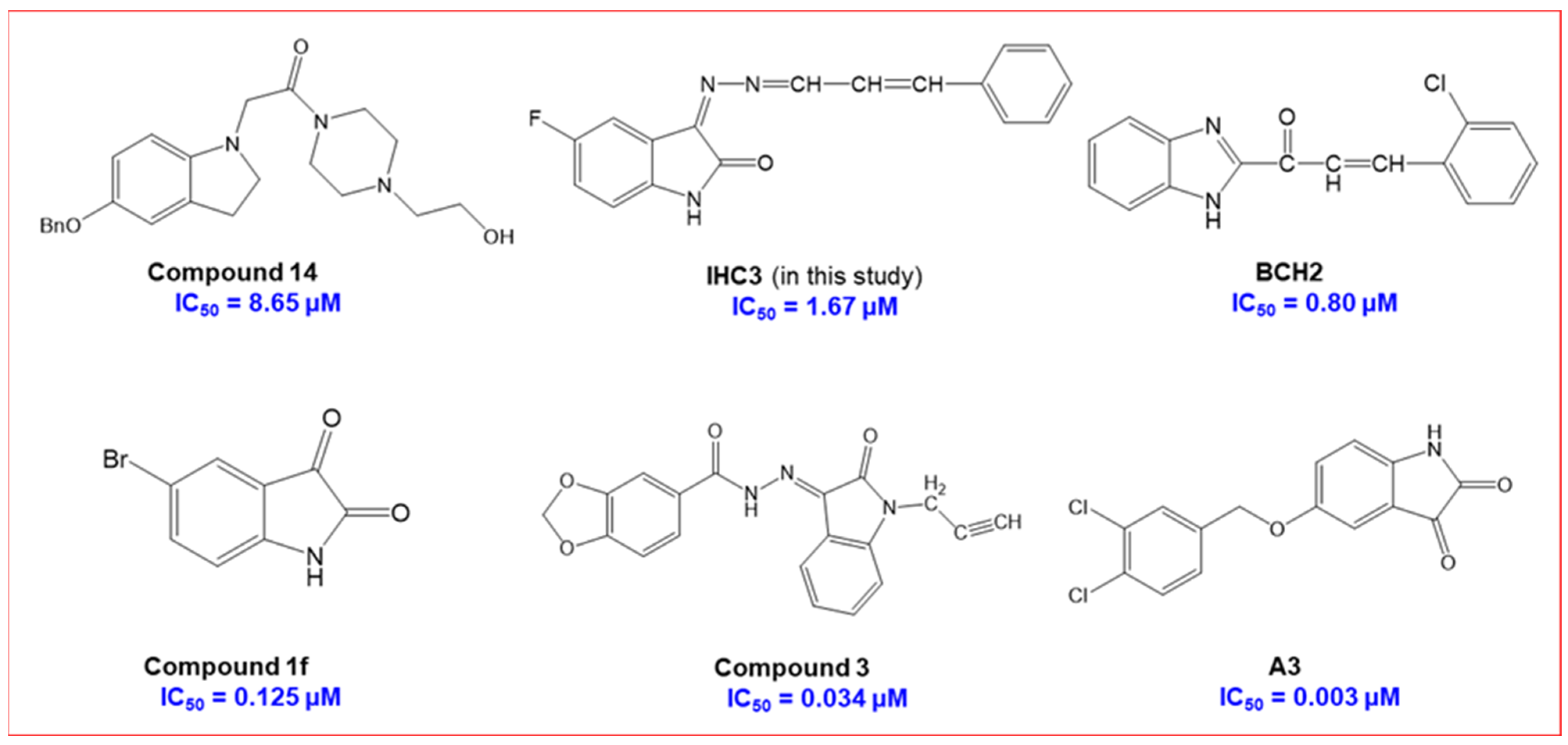
2. Results and Discussion
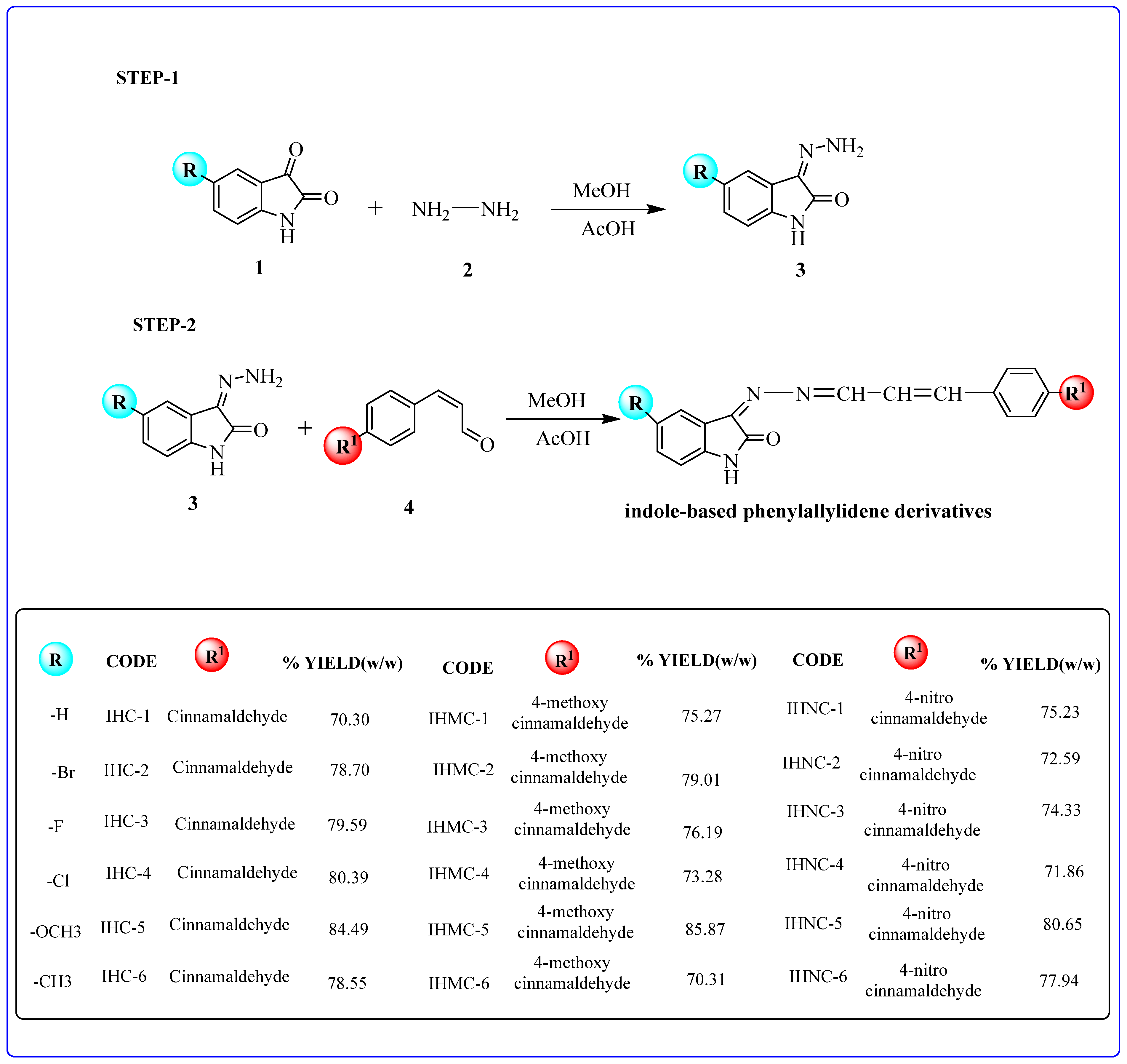
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biochemistry
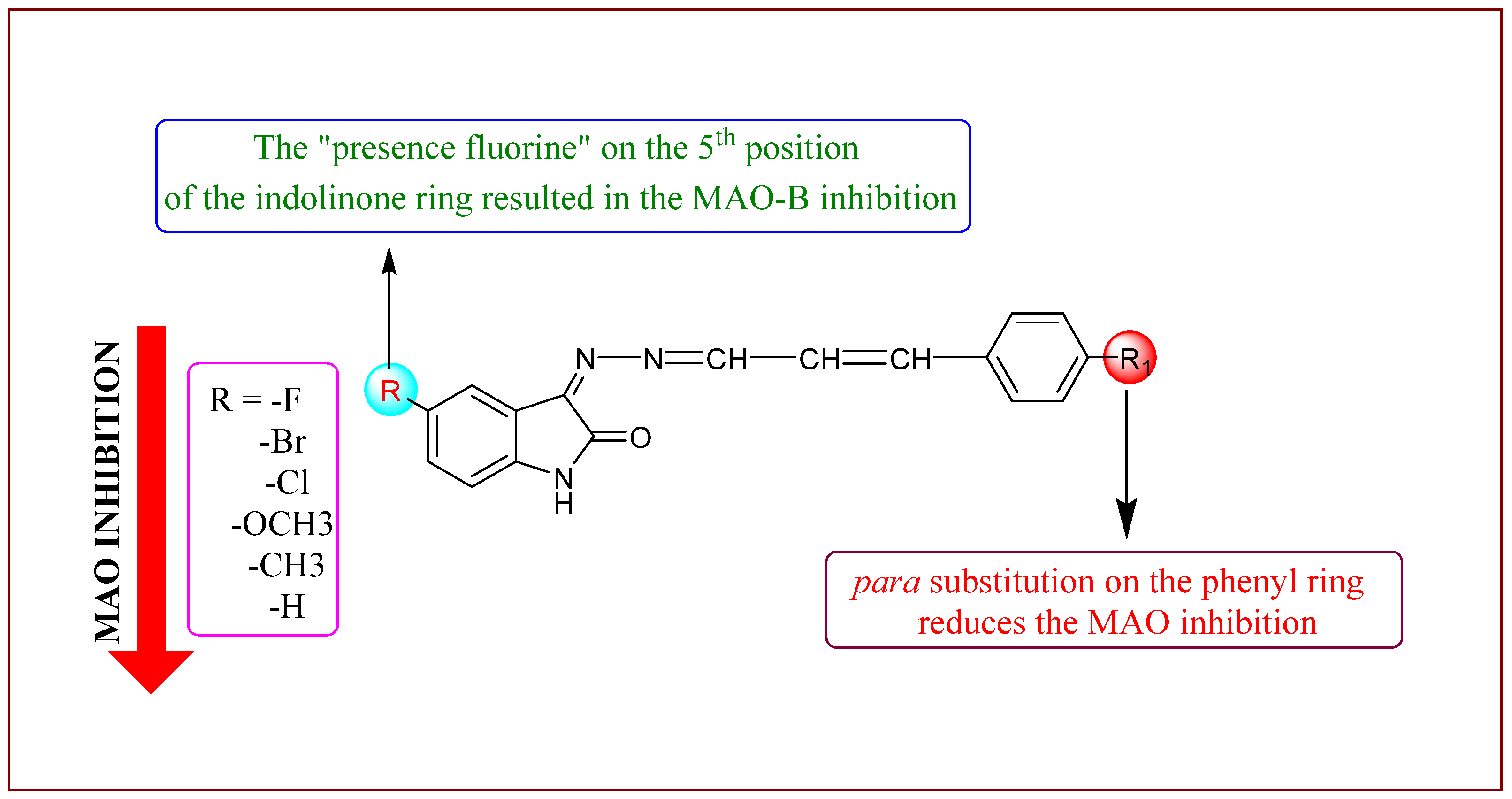
2.2.1. Inhibition Studies of MAO-A and MAO-B
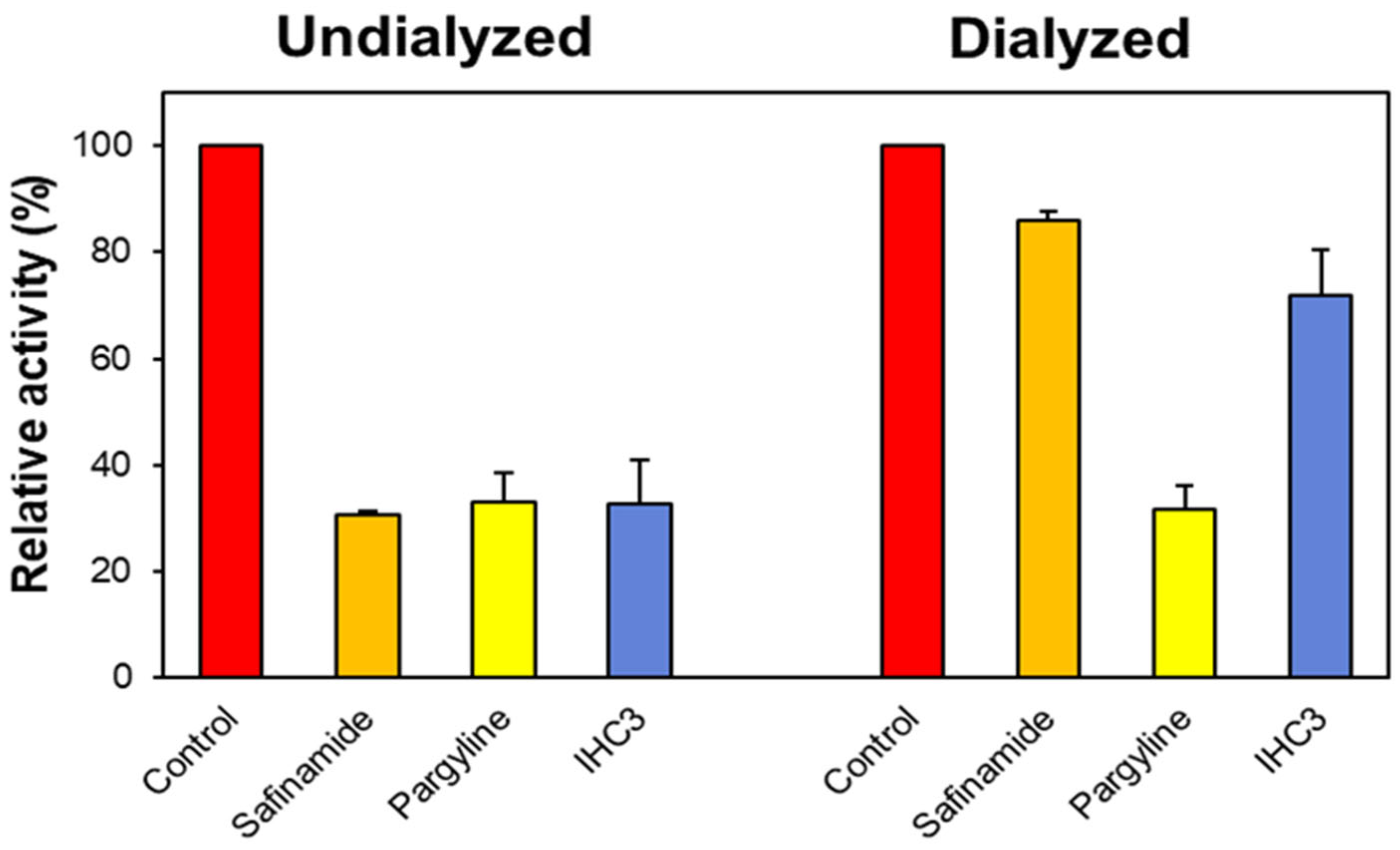
2.2.2. Reversibility Studies
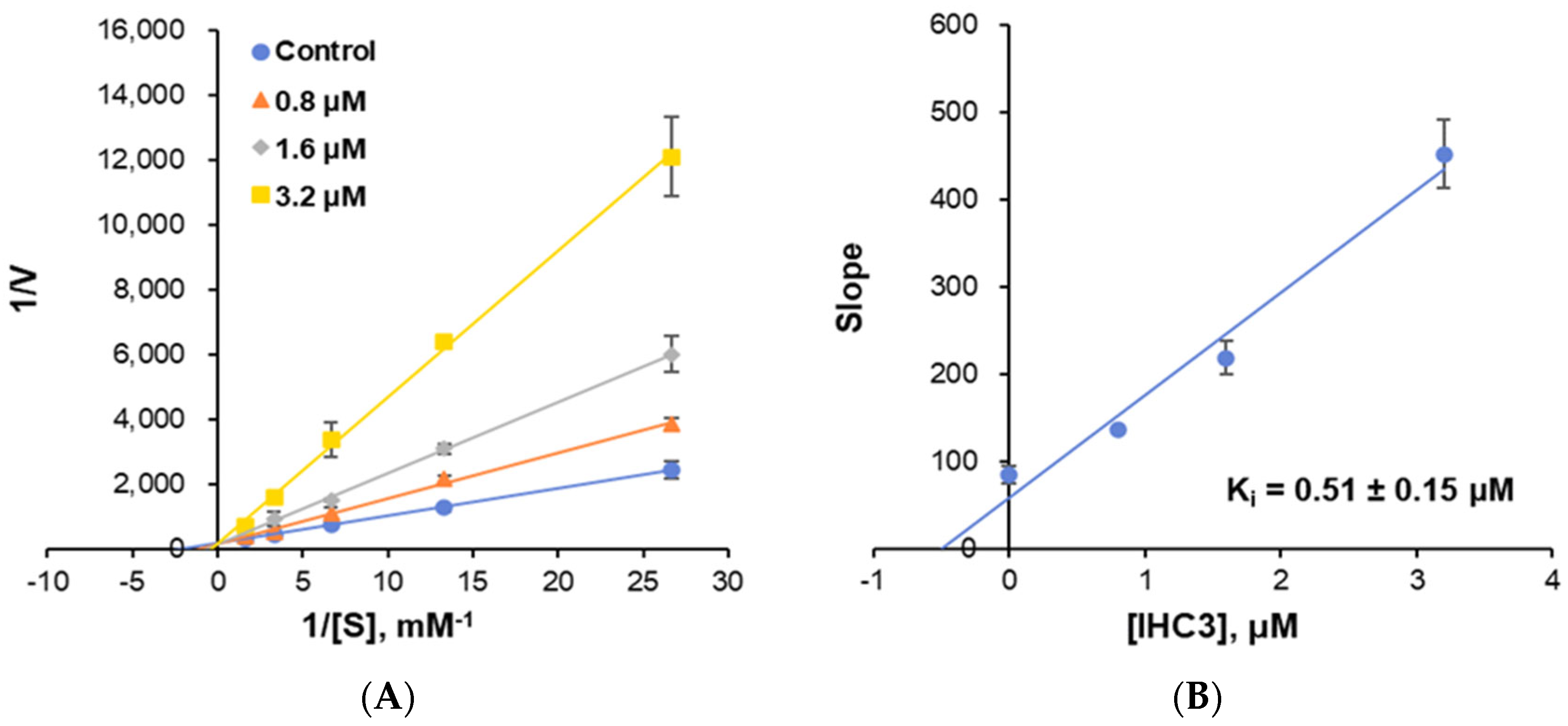
2.2.3. Enzyme Kinetics
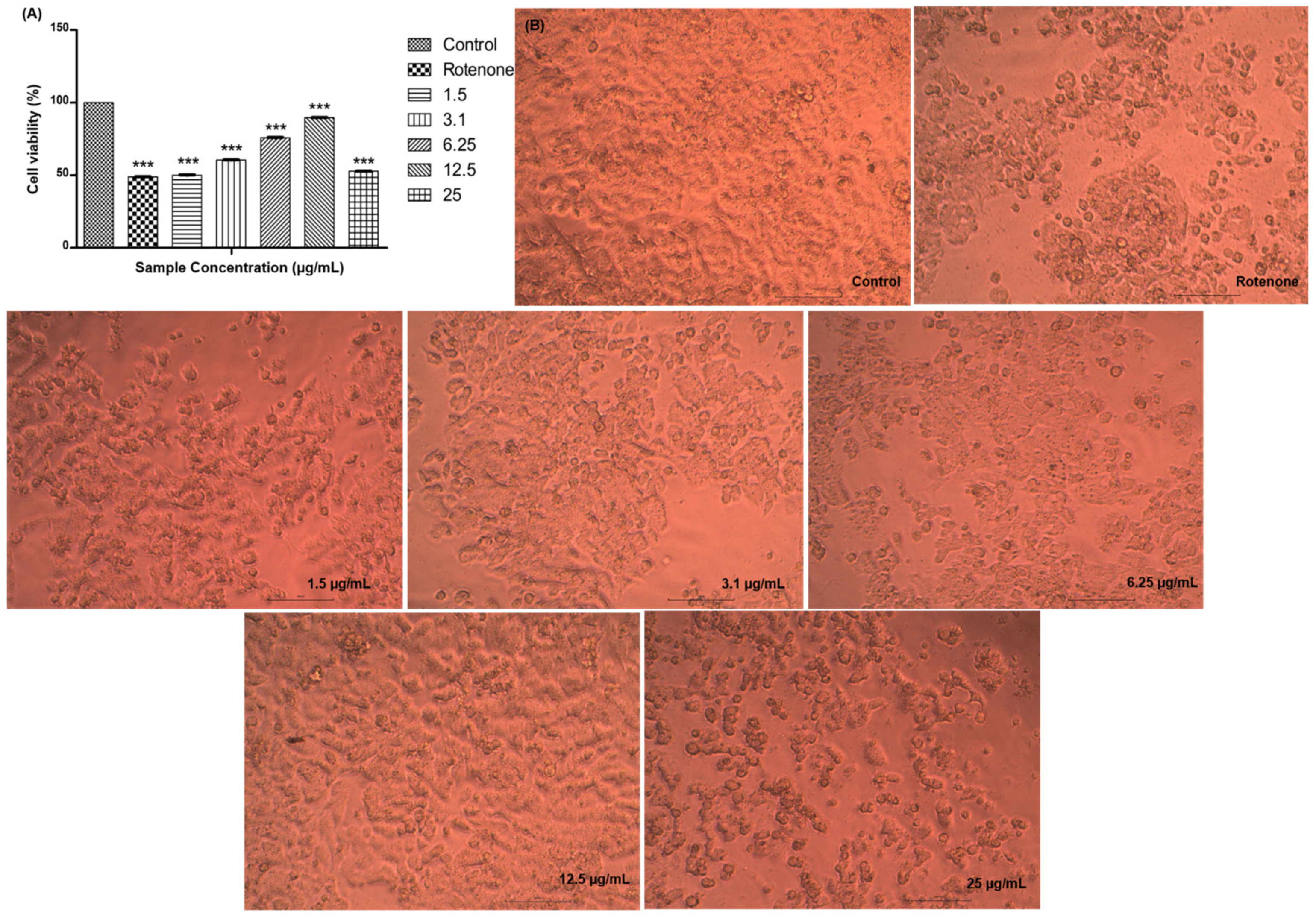
2.2.4. Neuroprotection Studies
2.3. Molecular Docking
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthetic Strategy
3.2. Biochemistry
3.2.1. Inhibition Studies of MAO-A and MAO-B
3.2.2. Reversibility Studies
3.2.3. Enzyme Kinetics
3.2.4. Neuroprotection Studies
3.3. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sonawane, R.P.; Tripathi, R.R. The chemistry and synthesis of 1H-indole-2,3-dione (isatin) and its derivatives. Int. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astron. 2013, 7, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, A.; Igosheva, N.; Crumeyrolle-Arias, M.; Glover, V. Isatin: Role in stress and anxiety. Stress 2005, 8, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.A.; Maalik, A. Advances in pharmacology of isatin and its derivatives: A review. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 14, 1937–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, A.S. Isatin derivatives with several biological activities. J. Int. Pharm. Res. 2014, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, J.F.; Garden, S.J.; Pinto, A.C. The chemistry of isatins: A review from 1975 to 1999. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2001, 12, 273–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varun; Sonam; Kakkar, R. Isatin and its derivatives: A survey of recent syntheses, reactions, and applications. Med. Chem. Comm. 2019, 10, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, G.; Nain, S. Recent advancement in synthesis of isatin as anticonvulsant agents: A review. Med. Chem. 2014, 4, 417–427. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, R.; Pathania, S.; Grover, G.; Akhtar, M.J. Isatin containing heterocycles for different biological activities: Analysis of structure activity relationship. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1222, 128900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Nair, A.S.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Mathew, B. Exploration of the detailed structure–activity relationships of isatin and their isomers as monoamine oxidase inhibitors. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 16244–16259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žari, S.; Kudrjashova, M.; Pehk, T.; Lopp, M.; Kanger, T. Remote activation of the nucleophilicity of isatin. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 1740–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popp, P.D. The chemistry of isatin. Chem. Isatin 1975, 18, 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G.S.; Desta, Z.Y. Isatins as privileged molecules in design and synthesis of spiro-fused cyclic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 6104–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, S.; Ding, P.; Jiang, H.; Wang, W.; Li, J. Facile creation of 3-indolyl-3-hydroxy-2-oxindoles by an organocatalytic enantioselective friedel-crafts reaction of indoles with isatins. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2010, 352, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-R.; Liu, X.-P.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Li, L.; Qiao, Y.-F.; Zhang, J.-M.; Xiao, W.-J. Organocatalytic asymmetric aldol reaction of ketones with isatins: Straightforward stereoselective synthesis of 3-alkyl-3-hydroxyindolin-2-ones. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 10437–10444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H. Isatin derivatives and their anti-bacterial activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 164, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakravan, P.; Kashanian, S.; Khodaei, M.M.; Harding, F.J. Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of isatin and its derivatives: From structure to activity. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandeya, S.N.; Smitha, S.; Jyoti, M.; Sridhar, S.K. Biological activities of isatin and its derivatives. Acta Pharm. 2005, 55, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raza, C.; Anjum, R.; Shakeel, N.U.A. Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms, translational models and management strategies. Life Sci. 2019, 226, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopade, P.; Chopade, N.; Zhao, Z.; Mitragotri, S.; Liao, R.; Chandran Suja, V. Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease therapies in the clinic. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2023, 8, e10367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Vélez, G.E.; Zoghbi, H.Y. Parkinson’s disease genetics and pathophysiology. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 44, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Yasuhara, H. Clinical pharmacology of MAO inhibitors: Safety and future. Neurotoxicology 2004, 25, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riederer, P.; Laux, G. MAO-inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurobiol. 2011, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justo, L.A.; Durán, R.; Alfonso, M.; Fajardo, D.; Faro, L.R.F. Effects and mechanism of action of isatin, a MAO inhibitor, on in vivo striatal dopamine release. Neurochem. Int. 2016, 99, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavari, M.; Malan, S.F.; Joubert, J. Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and docking studies of sulfonyl isatin derivatives as monoamine oxidase and caspase-3 inhibitors. Med. Chem. Comm. 2016, 7, 1628–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.K.P.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Ayyannan, S.R. Discovery of 3-hydroxy-3-phenacyloxindole analogues of isatin as potential monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Chem. Med. Chem. 2016, 11, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manley-King, C.I.; Bergh, J.J.; Petzer, J.P. Inhibition of monoamine oxidase by selected C5- and C6-substituted isatin analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, R.K.P.; Rai, G.K.; Ayyannan, S.R. Exploration of a library of 3,4-(methylenedioxy)aniline-derived semicarbazones as dual inhibitors of monoamine oxidase and acetylcholinesterase: Design, synthesis, and evaluation. Chem. Med. Chem. 2016, 11, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.K.P.; Ayyannan, S.R. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of 2-amino-6-nitrobenzothiazole-derived hydrazones as mao inhibitors: Role of the methylene spacer group. Chem. Med. Chem. 2016, 11, 1551–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnu, M.S.; Pavankumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Raja, A.S. Experimental and computational evaluation of piperonylic acid derived hydrazones bearing isatin moieties as dual inhibitors of cholinesterases and monoamine oxidases. Chem. Med. Chem. 2019, 14, 1359–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorri, M.; Hashemitabar, S.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Cinnamon (cinnamomum zeylanicum) as an antidote or a protective agent against natural or chemical toxicities: A review. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 41, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hou, Y.; Yi, D.; Ding, B.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y.; Gong, J.; Assaad, H.; et al. Beneficial roles of dietary oleum cinnamomi in alleviating intestinal injury. Front. Biosci. Landmark 2015, 20, 814–828. [Google Scholar]
- Angelopoulou, E.; Paudel, Y.N.; Piperi, C.; Mishra, A. Neuroprotective potential of cinnamon and its metabolites in parkinson’s disease: Mechanistic insights, limitations, and novel therapeutic opportunities. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajinejad, M.; Ghaddaripouri, M.; Dabzadeh, M.; Forouzanfar, F.; Sahab-Negah, S. Natural cinnamaldehyde and its derivatives ameliorate neuroinflammatory pathways in neurodegenerative diseases. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1034325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, W.-Y.; Choi, J.-S.; Jeong, J.-W. The Neuroprotective effects of cinnamic aldehyde in an mptp mouse model of parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Oh, J.M.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Khames, A.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Kumar, S.; Nath, L.R.; Sudevan, S.T.; Parambi, D.G.T.; Agoni, C.; et al. Conjugated dienones from differently substituted cinnamaldehyde as highly potent monoamine oxidase-b inhibitors: Synthesis, biochemistry, and computational chemistry. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 8184–8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viegas-Junior, C.; Danuello, A.; Bolzani, V.D.S.; Barreiro, E.J.; Fraga, C.A.M. Molecular hybridization: A useful tool in the design of new drug prototypes. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 1829–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyniewicz, J.; Lipiński, P.F.J.; Kosson, P.; Leśniak, A.; Bochyńska-Czyż, M.; Muchowska, A.; Tourwé, D.; Ballet, S.; Misicka, A.; Lipkowski, A.W. Hydrazone linker as a useful tool for preparing chimeric peptide/nonpeptide bifunctional compounds. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrhman, E.M.; El-Shetary, B.A.; Shebl, M.; Adly, O.M.I. Coordinating behavior of hydrazone ligand bearing chromone moiety towards Cu(II) ions: Synthesis, spectral, density functional theory (DFT) calculations, antitumor, and docking studies. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 35, e6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebretsadik, T.; Yang, Q.; Wu, J.; Tang, J. Hydrazone based spin crossover complexes: Behind the extra flexibility of the hydrazone moiety to switch the spin state. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 431, 213666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Jayan, J.; Manoharan, A.; Benny, F.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Ghoneim, M.M.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Thazhathuveedu Sudevan, S.; Aneesh, T.P.; Mathew, B. Discerning of isatin-based monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors for neurodegenerative disorders by exploiting 2D, 3D-QSAR modelling and molecular dynamics simulation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez, D.; Hrast, M.; Frlan, R.; Pišlar, A.; Žakelj, S.; Kos, J.; Gobec, S. Indoles and 1-(3-(benzyloxy)benzyl)piperazines: Reversible and selective monoamine oxidase B inhibitors identified by screening an in-house compound library. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 119, 105581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, A.; Lee, J.; Kumar, S.; Sudevan, S.T.; Uniyal, P.; Pappachen, L.K.; Kim, H.; Mathew, B. Inhibition of monoamine oxidases by benzimidazole chalcone derivatives. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2023, 66, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prinsloo, I.F.; Petzer, J.P.; Cloete, T.T.; Petzer, A. The evaluation of isatin analogues as inhibitors of monoamine oxidase. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2023, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Li, S.; Lv, X.; Tian, Y.; Kong, H.; Huang, X.; Duan, Y.; Han, J.; Xie, Z.; Liao, C. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel human monoamine oxidase B inhibitors based on a fragment in an X-ray crystal structure. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, S.; Maini, P.K. A century of enzyme kinetics: Reliability of the Km and Vmax estimates? Theor. Popul. Biol. 2003, 8, 169–187. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.W.; Ryu, H.W.; Kang, M.-G.; Park, D.; Oh, S.-R.; Kim, H. Potent selective monoamine oxidase B inhibition by maackiain, a pterocarpan from the roots of Sophora flavescens. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 4714–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.M.; Jang, H.-J.; Kim, W.J.; Kang, M.-G.; Baek, S.C.; Lee, J.P.; Park, D.; Oh, S.-R.; Kim, H. Calycosin and 8-O-methylretusin isolated from Maackia amurensis as potent and selective reversible inhibitors of human monoamine oxidase-B. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Ryu, H.W.; Kang, M.-G.; Park, D.; Lee, H.; Shin, H.M.; Oh, S.-R.; Kim, H. Potent inhibition of monoamine oxidase A by decursin from Angelica gigas Nakai and by wogonin from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compounds | Residual Activity at 10 µM (%) | IC50 (µM) | SI b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAO-A | MAO-B | MAO-A | MAO-B | ||
| IHC1 | 94.48 ± 2.10 | 89.30 ± 3.00 | >40 | >40 | |
| IHC2 | 92.37 ± 0.52 | 61.39 ± 3.42 | >40 | 16.934 ± 0.397 | >2.36 |
| IHC3 | 76.90 ± 1.55 | 11.39 ± 5.22 | >40 | 1.672 ± 0.022 | >23.92 |
| IHC4 | 86.74 ± 1.78 | 73.89 ± 8.87 | >40 | 27.485 ± 1.152 | >1.46 |
| IHC5 | 82.27 ± 1.80 | 75.79 ± 6.17 | >40 | >40 | |
| IHC6 | 98.10 ± 1.55 | 79.44 ± 3.25 | >40 | >40 | |
| IHMC1 | 89.92 ± 1.30 | 96.89 ± 0.95 | >40 | >40 | |
| IHMC2 | 86.63 ± 0.52 | 78.07 ± 1.12 | >40 | 25.192 ± 0.147 | >1.59 |
| IHMC3 | 85.54 ± 6.42 | 81.29 ± 4.61 | >40 | >40 | |
| IHMC4 | 81.46 ± 0.77 | 76.55 ± 3.27 | >40 | >40 | |
| IHMC5 | 84.48 ± 0.73 | 85.60 ± 4.27 | >40 | >40 | |
| IHMC6 | 89.80 ± 2.55 | 91.85 ± 3.48 | >40 | >40 | |
| IHNC1 | 88.70 ± 2.40 | 96.91 ± 3.36 | > 40 | >40 | |
| IHNC2 | 88.50 ± 0.71 | 71.25 ± 1.99 | >40 | 21.995 ± 0.354 | >1.82 |
| IHNC3 | 80.40 ± 0.57 | 78.93 ± 3.35 | >40 | >40 | |
| IHNC4 | 82.30 ± 0.99 | 74.50 ± 4.63 | >40 | 26.486 ± 0.600 | >1.51 |
| IHNC5 | 88.60 ± 1.98 | 81.99 ± 1.05 | >40 | >40 | |
| IHNC6 | 87.20 ± 1.13 | 81.09 ± 6.40 | >40 | >40 | |
| Toloxatone | 1.08 ± 0.03 | >40 | <0.027 | ||
| Safinamide | >40 | 0.021 ± 0.001 | >1904 | ||
| Clorgyline | 0.007 ± 0.001 | 1.853 ± 0.112 | 0.004 | ||
| Pargyline | 2.403 ± 0.358 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 17.16 | ||
| Compound | Docking Score (kcal) |
|---|---|
| IHC3 | −11.061 |
| Safinamide | −11.136 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manoharan, A.; Oh, J.M.; Benny, F.; Kumar, S.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Shaker, M.E.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Almohaimeed, H.M.; Gahtori, P.; et al. Assembling a Cinnamyl Pharmacophore in the C3-Position of Substituted Isatins via Microwave-Assisted Synthesis: Development of a New Class of Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Molecules 2023, 28, 6167. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166167
Manoharan A, Oh JM, Benny F, Kumar S, Abdelgawad MA, Ghoneim MM, Shaker ME, El-Sherbiny M, Almohaimeed HM, Gahtori P, et al. Assembling a Cinnamyl Pharmacophore in the C3-Position of Substituted Isatins via Microwave-Assisted Synthesis: Development of a New Class of Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Molecules. 2023; 28(16):6167. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166167
Chicago/Turabian StyleManoharan, Amritha, Jong Min Oh, Feba Benny, Sunil Kumar, Mohamed A. Abdelgawad, Mohammed M. Ghoneim, Mohamed E. Shaker, Mohamed El-Sherbiny, Hailah M. Almohaimeed, Prashant Gahtori, and et al. 2023. "Assembling a Cinnamyl Pharmacophore in the C3-Position of Substituted Isatins via Microwave-Assisted Synthesis: Development of a New Class of Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease" Molecules 28, no. 16: 6167. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166167
APA StyleManoharan, A., Oh, J. M., Benny, F., Kumar, S., Abdelgawad, M. A., Ghoneim, M. M., Shaker, M. E., El-Sherbiny, M., Almohaimeed, H. M., Gahtori, P., Kim, H., & Mathew, B. (2023). Assembling a Cinnamyl Pharmacophore in the C3-Position of Substituted Isatins via Microwave-Assisted Synthesis: Development of a New Class of Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Molecules, 28(16), 6167. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166167








