Enhanced Reactive Brilliant Blue Removal Using Chitosan–Biochar Hydrogel Beads
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
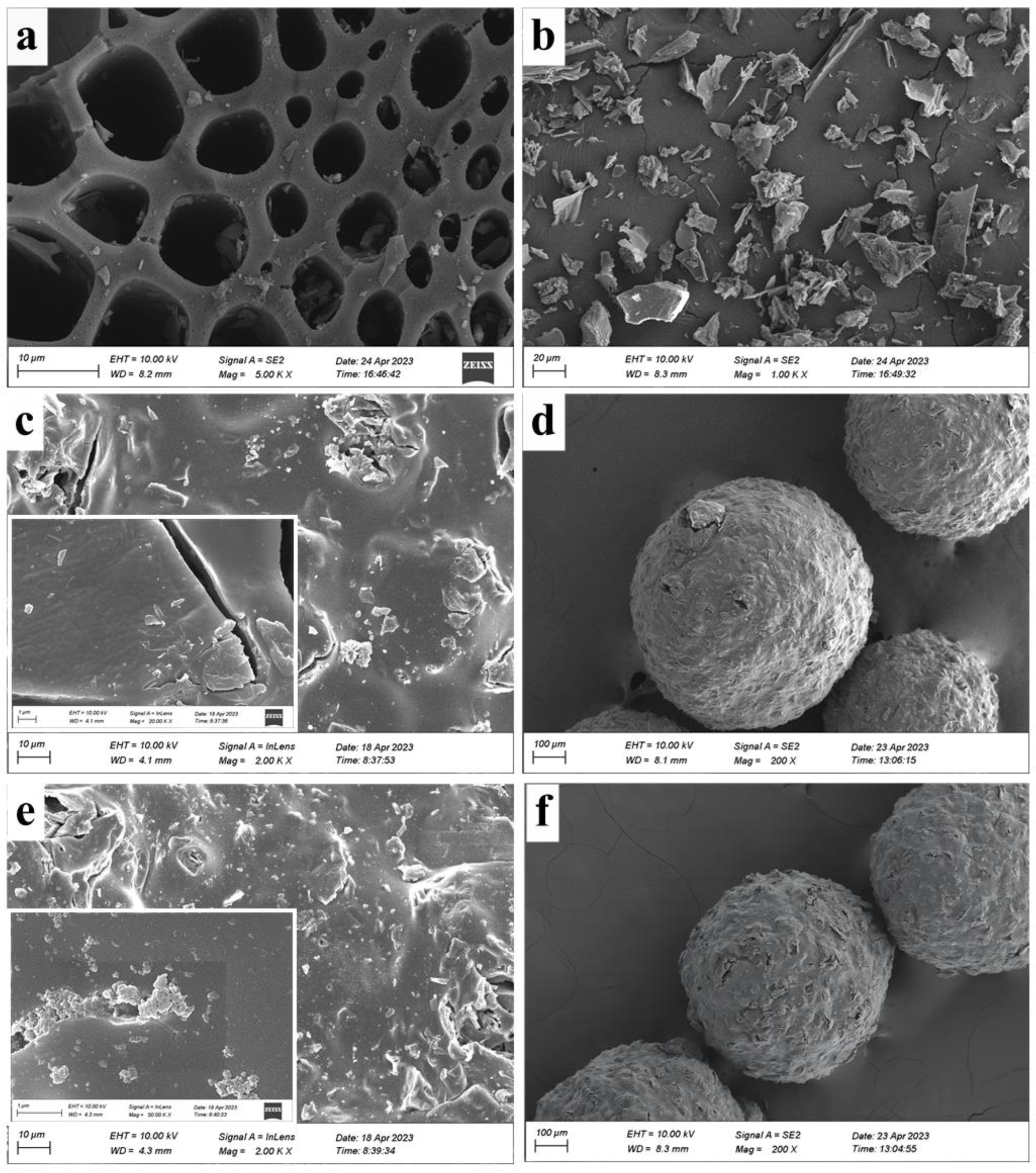
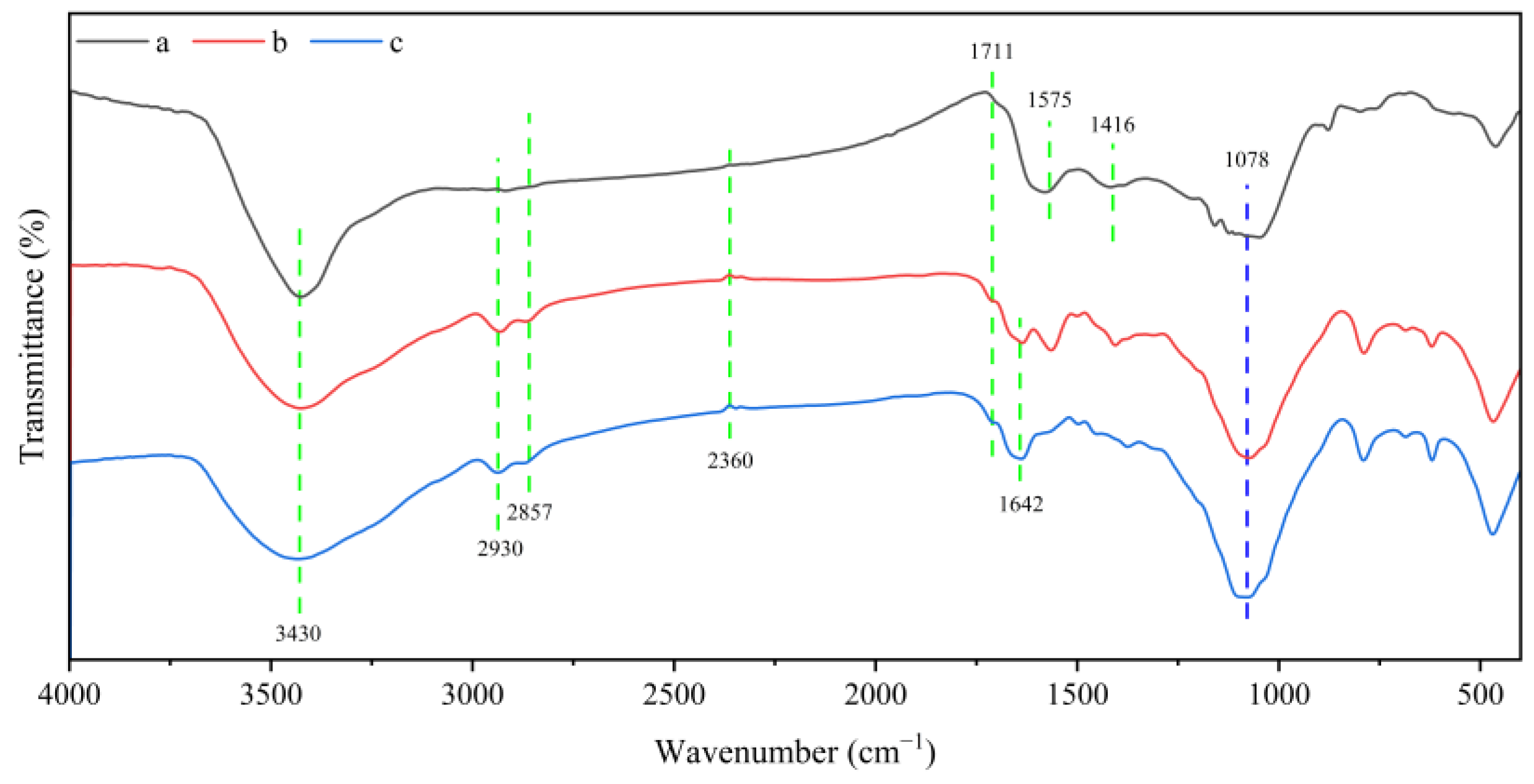
2.1. Characterization Results
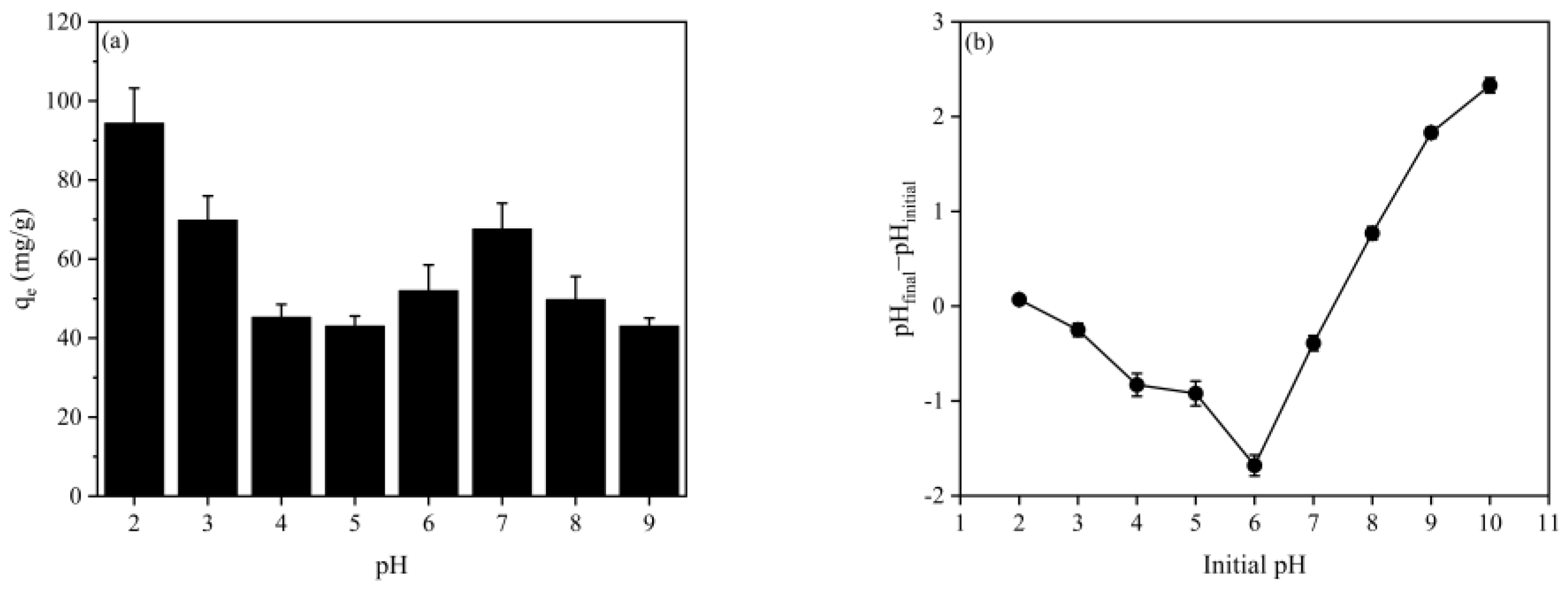
2.2. Effect of Solution pH
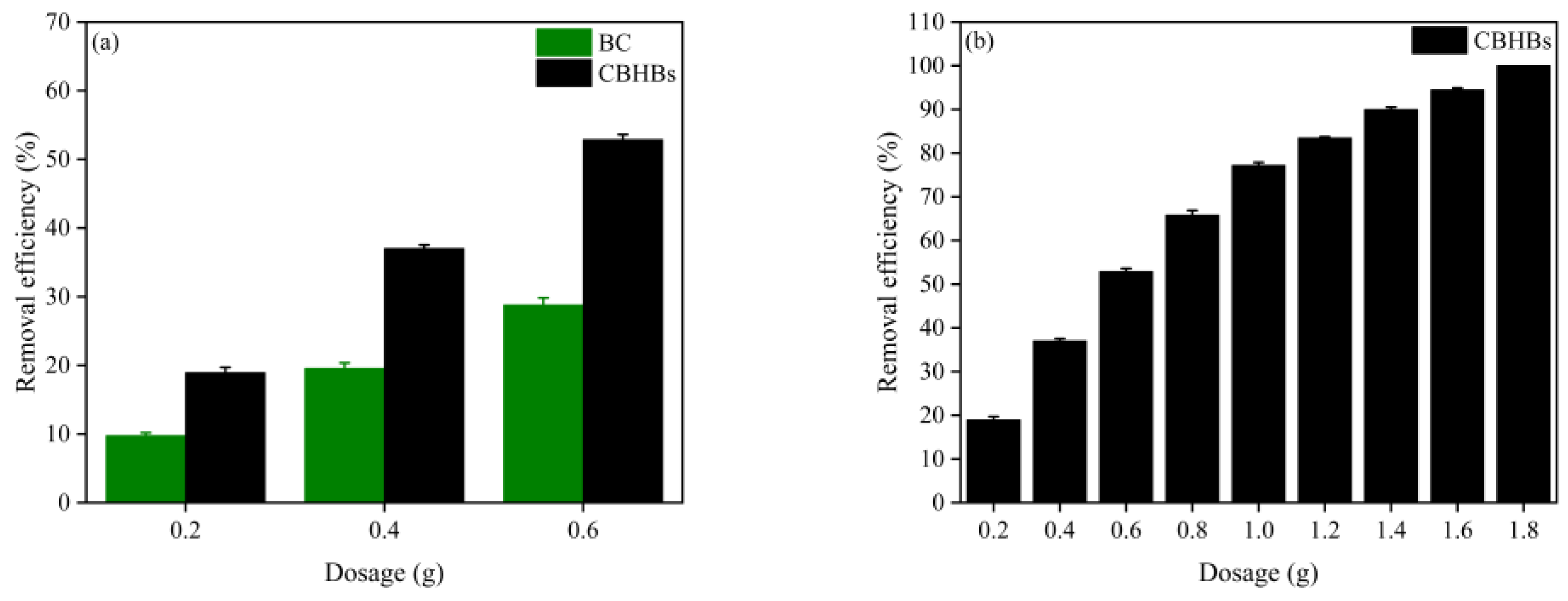
2.3. Comparison of BC and CBHBs
2.4. Effect of CBHBs Dosage
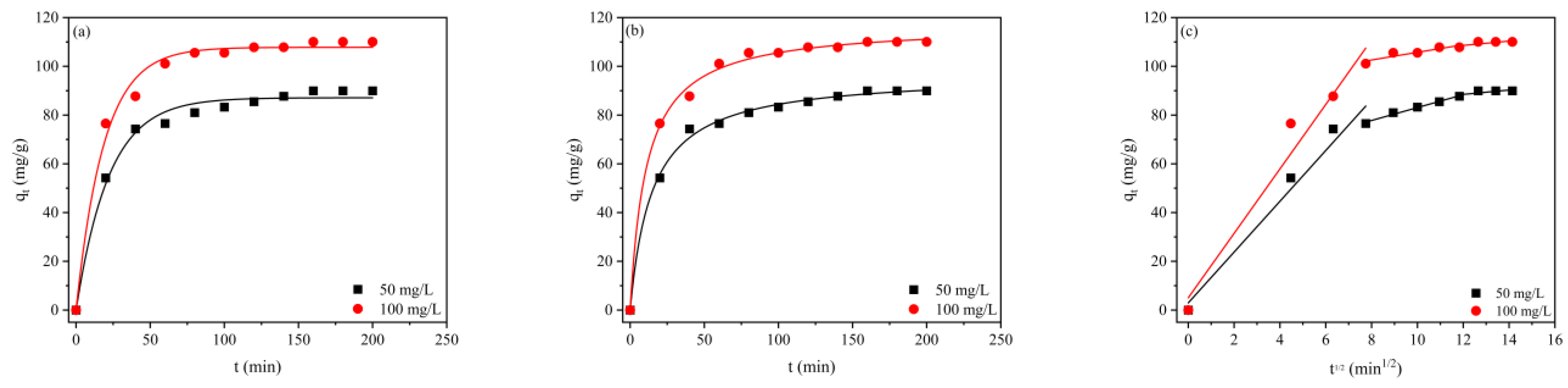
2.5. Adsorption Kinetics
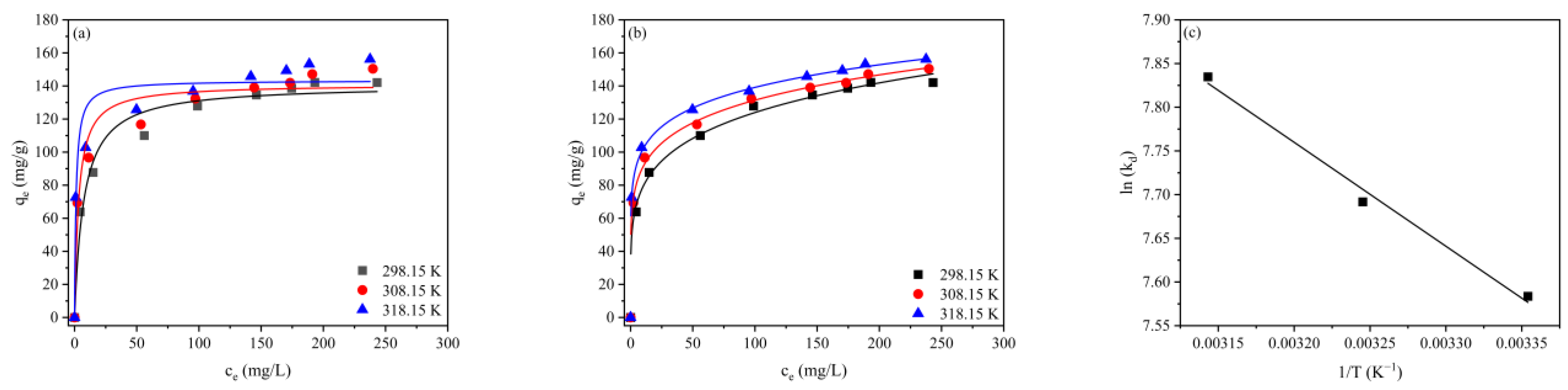
2.6. Adsorption Isotherms and Thermodynamics
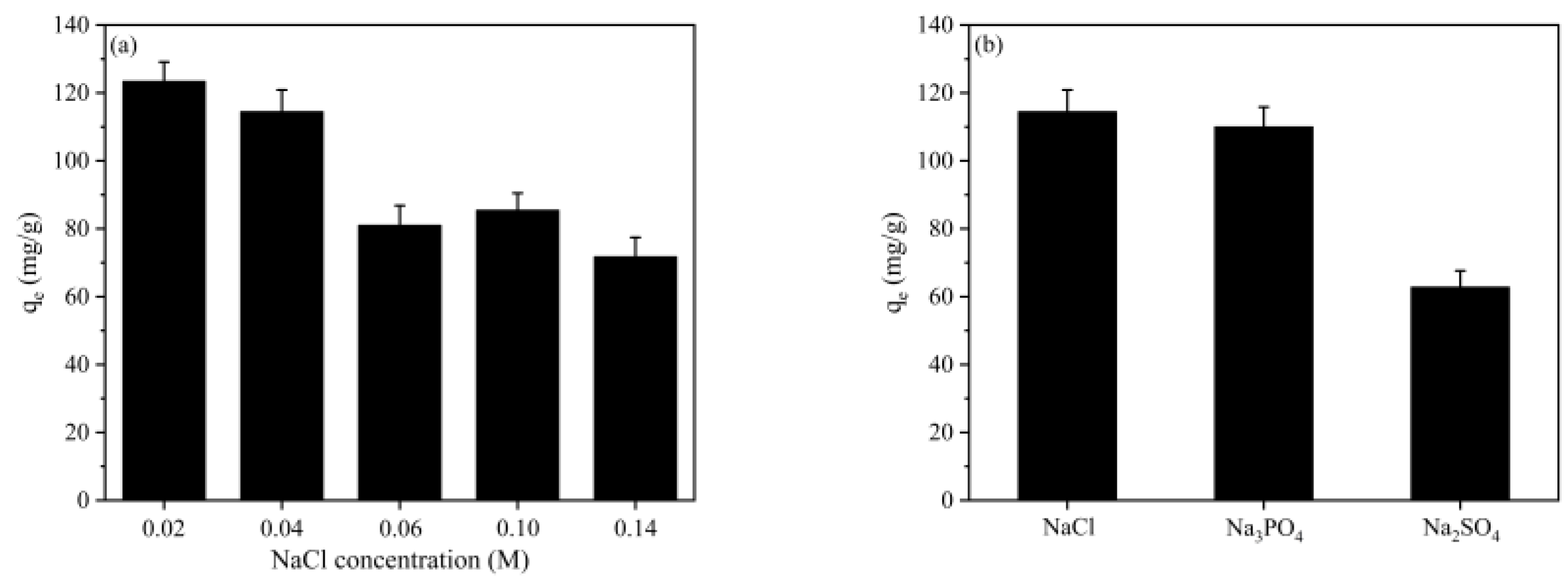
2.7. Effect of Ionic Strength and Coexisting Substances
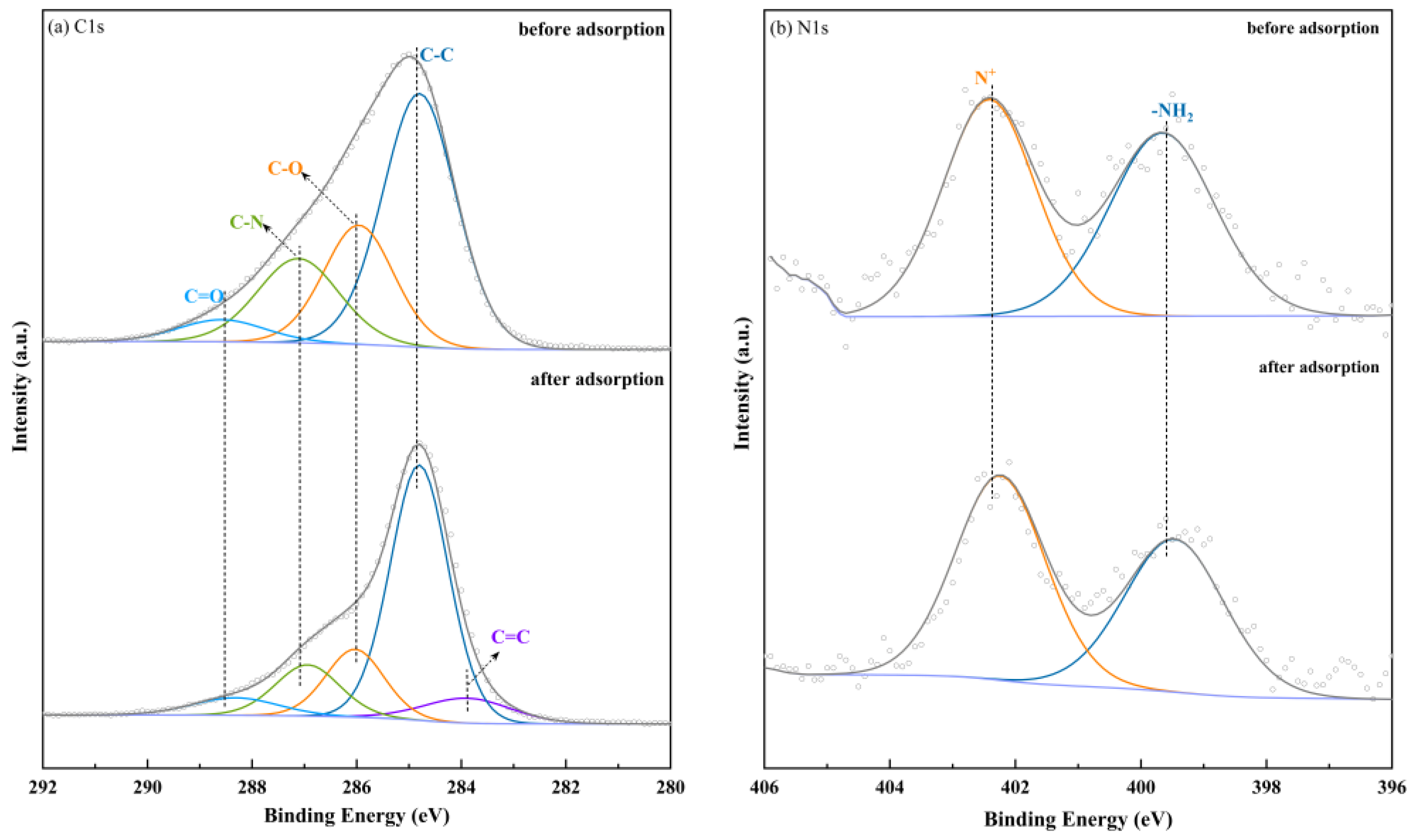
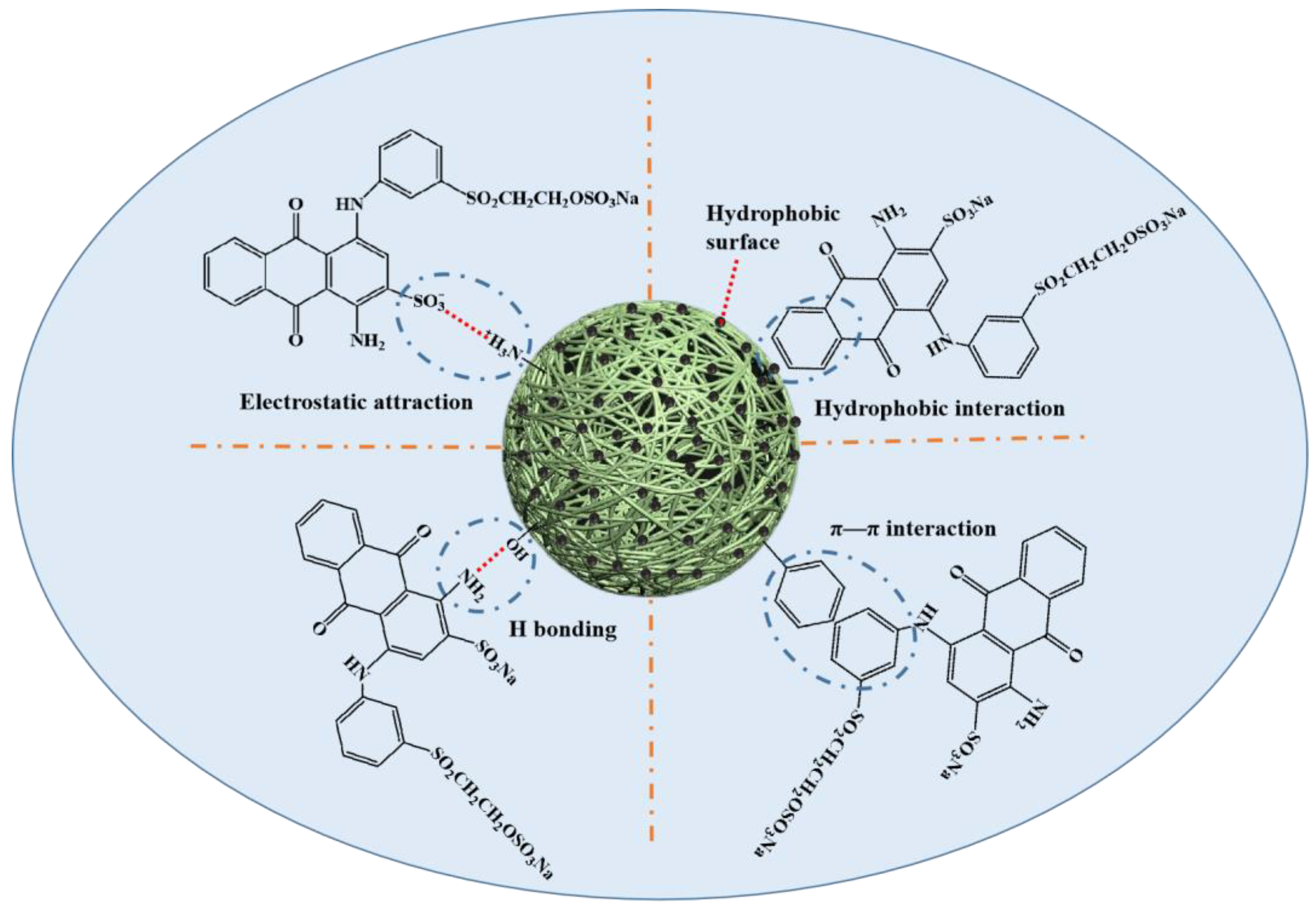
2.8. Adsorption Mechanism
2.9. Desorption and Reusability
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
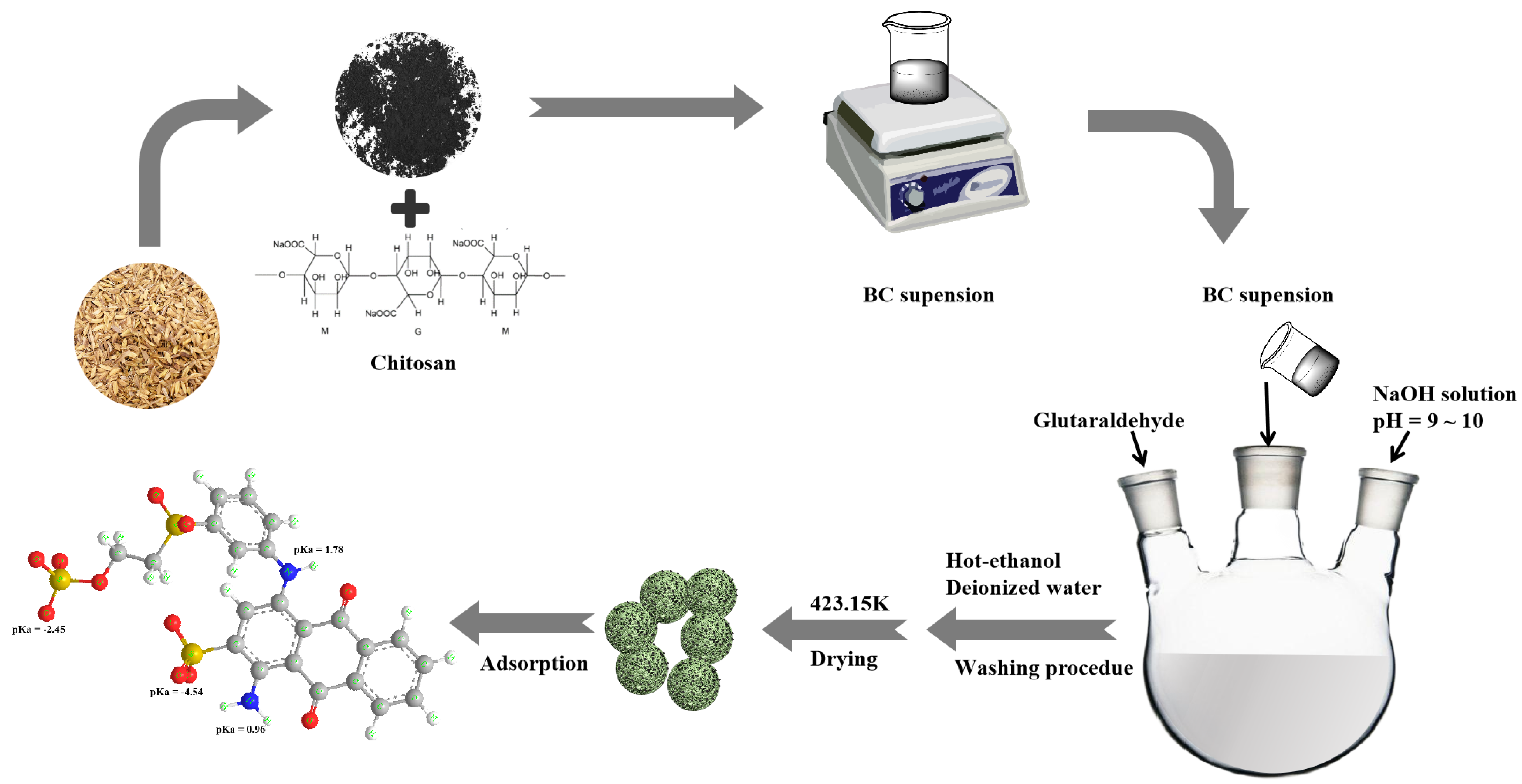
3.2. Preparation of CBHBs
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Adsorption Experiments
3.5. Desorption and Regeneration Studies
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Tkaczyk, A.; Mitrowska, K.; Posyniak, A. Synthetic organic dyes as contaminants of the aquatic environment and their implications for ecosystems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkhaya, S.; M’rabet, S.; El Harfi, A. A review on classifications, recent synthesis and applications of textile dyes. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 115, 107891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Gupta, B.; Srivastava, S.K.; Gupta, A.K. Recent advances on the removal of dyes from wastewater using various adsorbents: A critical review. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 4497–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slama, H.B.; Chenari Bouket, A.; Pourhassan, Z.; Alenezi, F.N.; Silini, A.; Cherif-Silini, H.; Oszako, T.; Luptakova, L.; Golińska, P.; Belbahri, L. Diversity of Synthetic Dyes from Textile Industries, Discharge Impacts and Treatment Methods. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.; Rakholiya, P.; Ng, H.Y.; You, S.; Teixeira, J.A. Microbial degradation of dyes: An overview. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhao, F.; Li, M.; Wang, P.; Fu, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, X. Construction of hollow binary oxide heterostructures by Ostwald ripening for superior photoelectrochemical removal of reactive brilliant blue KNR dye. Adv. Powder Mater. 2023, 2, 100117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, V.; Karthika, T.S.; Mansiya, C.; Alagar, M. An over review on recently developed techniques, mechanisms and intermediate involved in the advanced azo dye degradation for industrial applications. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1224, 129195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindhal, T.; Rakholiya, P.; Varjani, S.; Pandey, A.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Ng, H.Y.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A critical review on advances in the practices and perspectives for the treatment of dye industry wastewater. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rápó, E.; Tonk, S. Factors affecting synthetic dye adsorption; desorption studies: A review of results from the last five years (2017–2021). Molecules 2021, 26, 5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Xi, F.; Tan, W.; Meng, X.; Hu, B.; Wang, X. Review of organic and inorganic pollutants removal by biochar and biochar-based composites. Biochar 2021, 3, 255–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Gayathri, R.; Rathi, B.S. A review on adsorptive separation of toxic metals from aquatic system using biochar produced from agro-waste. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Li, X.; Xing, J.; Xu, G. Adsorption of potentially toxic elements in water by modified biochar: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Xu, Z.; Hou, D.; Gao, B.; Cao, X.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Bolan, N.S.; Tsang, D.C. Waste-derived biochar for water pollution control and sustainable development. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambaye, T.; Vaccari, M.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Amrane, A.; Rtimi, S. Mechanisms and adsorption capacities of biochar for the removal of organic and inorganic pollutants from industrial wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 3273–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ye, J.; Lin, Y.; Wu, J.; Price, G.; Burton, D.; Wang, Y. Removal of Cadmium (II) using water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) biochar alginate beads in aqueous solutions. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palansooriya, K.N.; Kim, S.; Igalavithana, A.D.; Hashimoto, Y.; Choi, Y.-E.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Sarkar, B.; Ok, Y.S. Fe (III) loaded chitosan-biochar composite fibers for the removal of phosphate from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Du, W.; Zhang, M.; Ling, G.; Zhang, P. Chitosan-modified biochar: Preparation, modifications, mechanisms and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 209, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, J.F.; Heng, Z.W.; Teoh, H.C.; Chong, W.C.; Pang, Y.L. Recent development of magnetic biochar crosslinked chitosan on heavy metal removal from wastewater–modification, application and mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 133035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Zou, W.; He, F.; Hu, X.; Tsang, D.C.; Ok, Y.S.; Gao, B. Biochar technology in wastewater treatment: A critical review. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.Z.; Sun, X.-F.; Liu, J.; Song, C.; Wang, S.-G.; Javed, A. Enhancement of ciprofloxacin sorption on chitosan/biochar hydrogel beads. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xiao, R.; Li, R.; Ali, A.; Chen, A.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced aqueous Cr (VI) removal using chitosan-modified magnetic biochars derived from bamboo residues. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micháleková-Richveisová, B.; Frišták, V.; Pipíška, M.; Ďuriška, L.; Moreno-Jimenez, E.; Soja, G. Iron-impregnated biochars as effective phosphate sorption materials. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Wang, L.; Ma, F.; Zhu, S.; Xiao, T.; Yu, T.; Wang, Y. Self-assembly biochar colloids mycelial pellet for heavy metal removal from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. A versatile EDTA and chitosan bi-functionalized magnetic bamboo biochar for simultaneous removal of methyl orange and heavy metals from complex wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, X. Treatment of wastewater containing Reactive Brilliant Blue KN-R using TiO2/BC composite as heterogeneous photocatalyst and adsorbent. Chemosphere 2018, 206, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, T.L.; Ronix, A.; Pezoti, O.; Souza, L.S.; Leandro, P.K.T.; Bedin, K.C.; Beltrame, K.K.; Cazetta, A.L.; Almeida, V.C. Mesoporous activated carbon from industrial laundry sewage sludge: Adsorption studies of reactive dye Remazol Brilliant Blue R. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Nag, S.; Dahiya, A.; Pandey, P.; Arora, M.; Babu, J.N. Effect of pyrolysis temperature on mechanistic transformation for adsorption of methylene blue on leached rice-straw biochar. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2022, 50, 2100108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, H.; Peng, Y. Adsorption and co-adsorption of tetracycline and doxycycline by one-step synthesized iron loaded sludge biochar. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Li, L.; Iqbal, J.; Yang, Z.; Du, Y. Preparation of magnetic chitosan corn straw biochar and its application in adsorption of amaranth dye in aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 199, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son Tran, V.; Hao Ngo, H.; Guo, W.; Ha Nguyen, T.; Mai Ly Luong, T.; Huan Nguyen, X.; Lan Anh Phan, T.; Trong Le, V.; Phuong Nguyen, M.; Khai Nguyen, M. New chitosan-biochar composite derived from agricultural waste for removing sulfamethoxazole antibiotics in water. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 385, 129384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, J.; Feng, P.; Huang, G.; Xu, C.; Lin, B. High-efficiency removal of dyes from wastewater by fully recycling litchi peel biochar. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, K.L.; Lee, X.J.; Ong, H.C.; Chen, W.-H.; Chang, J.-S.; Lin, C.-S.; Show, P.L.; Ling, T.C. Adsorptive removal of cationic methylene blue and anionic Congo red dyes using wet-torrefied microalgal biochar: Equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism modeling. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 115986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, S.; Pahi, S.; Tripathy, S.; Singh, S.K.; Behera, A.; Sahu, U.K.; Patel, R.K. Adsorption of methylene blue on chemically modified lychee seed biochar: Dynamic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic study. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 315, 113743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Islam, K.; Hasan, M.A.; Khan, H.M.J.; Khan, M.A.R.; Deb, A.; Al Raihan, M.; Rahman, M.W. Adsorption of crystal violet dye by coconut husk powder: Isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics perspectives. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Ashokkumar, T. Characterization and evaluation of reactive dye adsorption onto Biochar Derived from Turbinaria conoides Biomass. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2019, 38, 13143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergene, A.; Ada, K.; Tan, S.; Katırcıoğlu, H. Removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue R dye from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto immobilized Scenedesmus quadricauda: Equilibrium and kinetic modeling studies. Desalination 2009, 249, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinoune, K.; Bentaleb, K.; Bouberka, Z.; Nadim, A.; Maschke, U. Adsorption of reactive dyes from aqueous solution by dirty bentonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 123, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reghioua, A.; Barkat, D.; Jawad, A.H.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Rangabhashiyam, S.; Khan, M.R.; Alothman, Z.A. Magnetic Chitosan-Glutaraldehyde/Zinc Oxide/Fe3O4 Nanocomposite: Optimization and Adsorptive Mechanism of Remazol Brilliant Blue R Dye Removal. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 3932–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Panigrahy, A.; Vinu, R. Development of novel chitosan–lignin composites for adsorption of dyes and metal ions from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.H.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Surip, S.N.; Alothman, Z.A. Hybrid multifunctional biocomposite of chitosan grafted benzaldehyde/montmorillonite/algae for effective removal of brilliant green and reactive blue 19 dyes: Optimization and adsorption mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 393, 136334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhen, D.; Liu, F.; Chen, R.; Peng, Q.; Wang, Z. An achieved strategy for magnetic biochar for removal of tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones: Adsorption and mechanism studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 369, 128440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, M.; Li, P.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; Gao, F.; Qi, X.; Zhang, Z. Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic sludge biochar for tetracycline and ciprofloxacin adsorptive removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-J.; Li, M.-F.; Ma, J.-F.; Bian, J.; Peng, F. Chitosan crosslinked composite based on corncob lignin biochar to adsorb methylene blue: Kinetics, isotherm, and thermodynamics. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 642, 128621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, B.; Chai, L.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Wang, X.; Zeng, W.; Shang, M.; Deng, J.; Zhou, Z. Enhancement of As (V) adsorption from aqueous solution by a magnetic chitosan/biochar composite. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 10891–10900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janaki, V.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Ramasamy, A.K.; Lee, K.-J.; Oh, B.-T.; Kamala-Kannan, S. Competitive adsorption of Reactive Orange 16 and Reactive Brilliant Blue R on polyaniline/bacterial extracellular polysaccharides composite—A novel eco-friendly polymer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 241–242, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zou, Z.; Chen, Y.; Long, X.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tan, J.; Chen, R. Synergistic effect of hydrogen bonding and π-π interaction for enhanced adsorption of rhodamine B from water using corn straw biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 320, 121060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, Z.; Gao, C.; Sun, Q.; Liu, J.; She, D. Synthesis of honeycomb lignin-based biochar and its high-efficiency adsorption of norfloxacin. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 369, 128402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Shang, H.; Cao, Y.; Yang, C.; Hu, W.; Feng, Y.; Yu, Y. Influence of adsorption sites of biochar on its adsorption performance for sulfamethoxazole. Chemosphere 2023, 326, 138408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidado, S.M.; Akanyeti, İ. Comparison of Remazol Brilliant Blue Reactive Adsorption on Pristine and Calcined ZnAl, MgAl, ZnMgAl Layered Double Hydroxides. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, R.A.; Lima, E.C.; Benetti, A.D.; Naushad, M.; Thue, P.S.; Mello, B.L.; Dos Reis, G.S.; Rabiee, N.; Franco, D.; Seliem, M.K. Employ a Clay@ TMSPDETA hybrid material as an adsorbent to remove textile dyes from wastewater effluents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 86010–86024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lv, L.; Qin, Y.; Xu, M.; Jia, X.; Chen, Z. Removal of aqueous Cr (VI) by a magnetic biochar derived from Melia azedarach wood. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajahmundry, G.K.; Garlapati, C.; Kumar, P.S.; Alwi, R.S.; Vo, D.-V.N. Statistical analysis of adsorption isotherm models and its appropriate selection. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Cao, C.; Li, Y.; Yin, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Zhu, Y. β-CD-Induced Precipitation of Eriochrome Black T Recovered via CTAB-Assisted Foam Fractionation for Adsorption of Trace Cu (II). Molecules 2023, 28, 4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| c0 (mg/L) | qe,exp (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic | Intraparticle Diffusion Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe,cal (mg/g) | k1 (min−1) | R2 | qe,cal (mg/g) | k2 (g/(mg·min)) | R2 | kf (mg/(g·min−1/2)) | θ (mg/g) | R2 | ||
| 50 | 89.95 | 87.11 | 0.0451 | 0.9875 | 96.90 | 6.970 × 10−4 | 0.9968 | 2.645 | 56.64 | 0.9830 |
| 100 | 110.04 | 107.82 | 0.0531 | 0.9883 | 117.23 | 7.731 × 10−4 | 0.9967 | 1.564 | 90.10 | 0.8028 |
| T (K) | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL (L/g) | qm (mg/g) | RL | R2 | KF (mg(1−n) Ln/g) | 1/n | R2 | |
| 298.15 | 0.136 | 140.74 | 0.8803 | 0.9714 | 50.57 | 0.1947 | 0.9864 |
| 308.15 | 0.307 | 140.98 | 0.7651 | 0.9532 | 63.18 | 0.1590 | 0.9932 |
| 318.15 | 0.825 | 143.38 | 0.5479 | 0.9318 | 74.65 | 0.1352 | 0.9975 |
| Adsorbent | qm (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Mesoporous activated carbon from industrial laundry sewage sludge | 33.47 | [26] |
| T. conoides-derived biochar | 92.5 | [35] |
| Active S. quadricauda/alginate (IASq) | 68 | [36] |
| Heat inactivated S. quadricauda/alginate (IHISq) | 95.2 | [36] |
| Mg(OH)2-bentonite | 66.90 | [37] |
| CHT-GLA/ZnO/Fe3O4 | 176.6 | [38] |
| Chitosan–alkali lignin composite | 111.11 | [39] |
| Chitosan grafted-benzaldehyde/montmorillonite/algae | 213.6 | [40] |
| T (k) | ΔG (KJ/mol) | ΔH (KJ/mol) | ΔS (KJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 298.15 | −18.77 | 9.883 | 0.0961 |
| 308.15 | −19.73 | ||
| 318.15 | −20.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, R.; Lu, F.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Deng, D.; Wu, M.; Li, Y. Enhanced Reactive Brilliant Blue Removal Using Chitosan–Biochar Hydrogel Beads. Molecules 2023, 28, 6137. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166137
Zhao Y, Song Y, Li R, Lu F, Yang Y, Huang Q, Deng D, Wu M, Li Y. Enhanced Reactive Brilliant Blue Removal Using Chitosan–Biochar Hydrogel Beads. Molecules. 2023; 28(16):6137. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166137
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yangyang, Yang Song, Rui Li, Fengfan Lu, Yibin Yang, Qiongjian Huang, Dongli Deng, Mingzhu Wu, and Ying Li. 2023. "Enhanced Reactive Brilliant Blue Removal Using Chitosan–Biochar Hydrogel Beads" Molecules 28, no. 16: 6137. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166137
APA StyleZhao, Y., Song, Y., Li, R., Lu, F., Yang, Y., Huang, Q., Deng, D., Wu, M., & Li, Y. (2023). Enhanced Reactive Brilliant Blue Removal Using Chitosan–Biochar Hydrogel Beads. Molecules, 28(16), 6137. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166137







