High-Throughput Phytochemical Unscrambling of Flowers Originating from Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.) P. K. Hsiao and Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bug. by Applying the Intagretive Plant Metabolomics Method Using UHPLC−Q−TOF−MS/MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
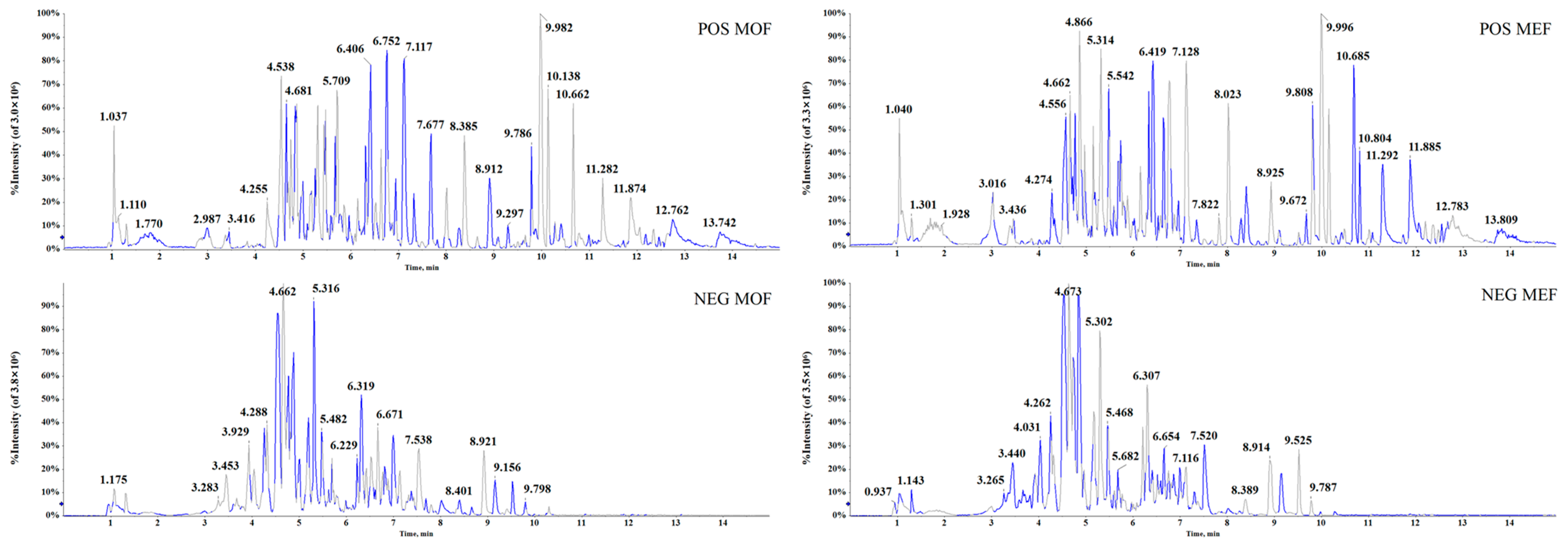
2.1. Conditions for UHPLC−Q−TOF−MS/MS Platform
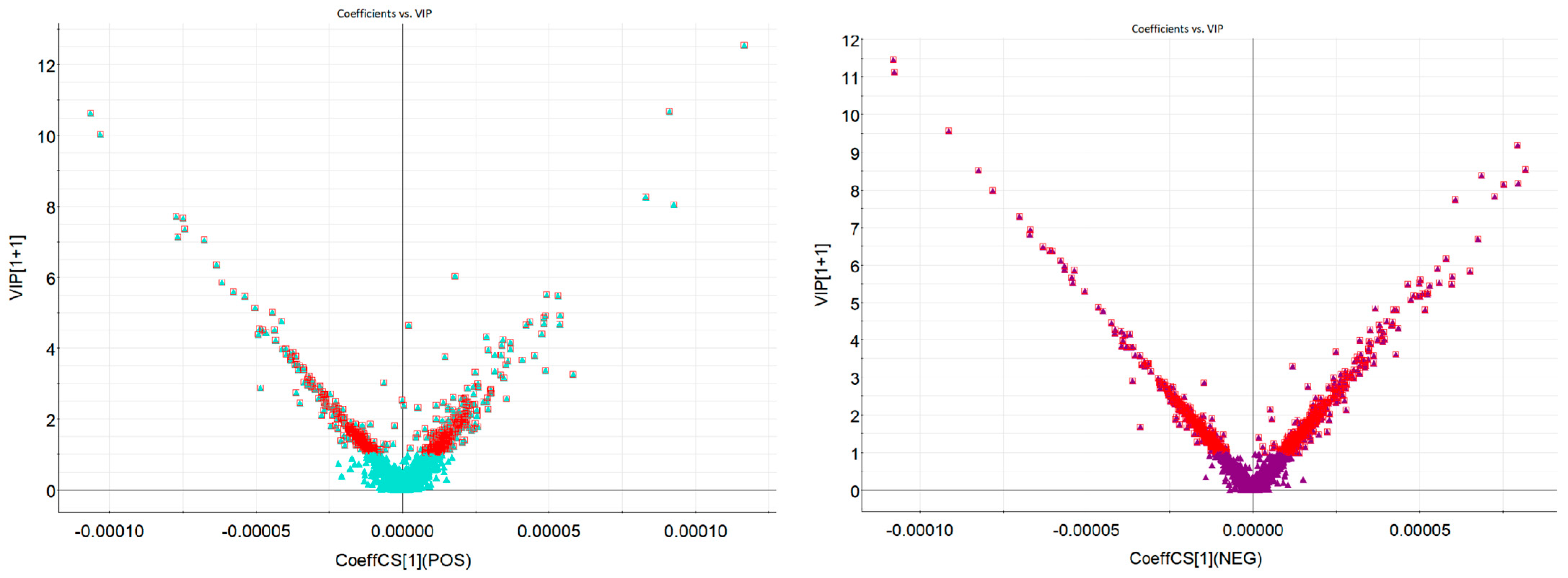
2.2. Multivariate Process and Statistical Data Analysis for Metabolomics Profiling
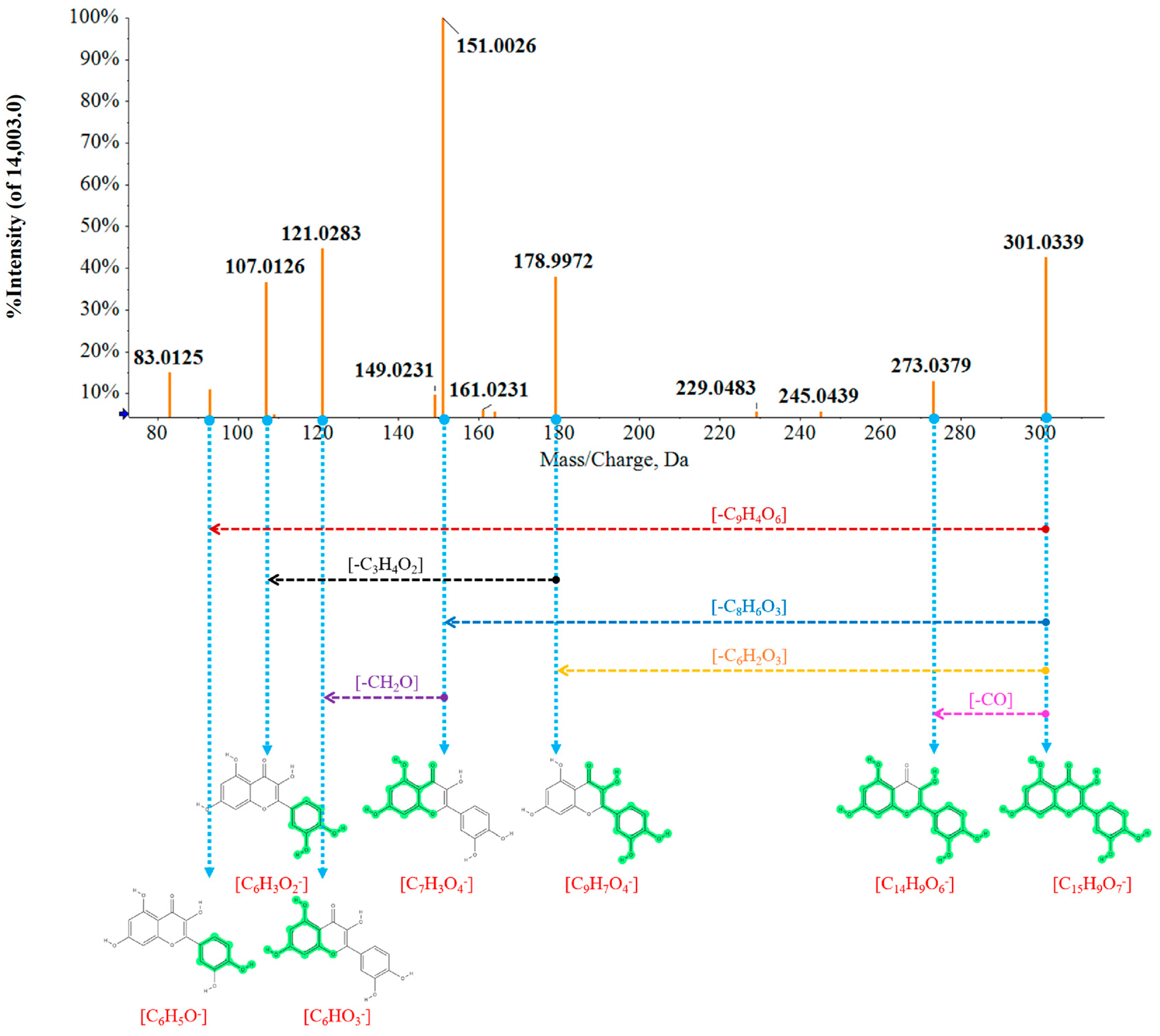
2.3. Rapid Identification of Chemical Metabolites between MOF Group and MEF Group
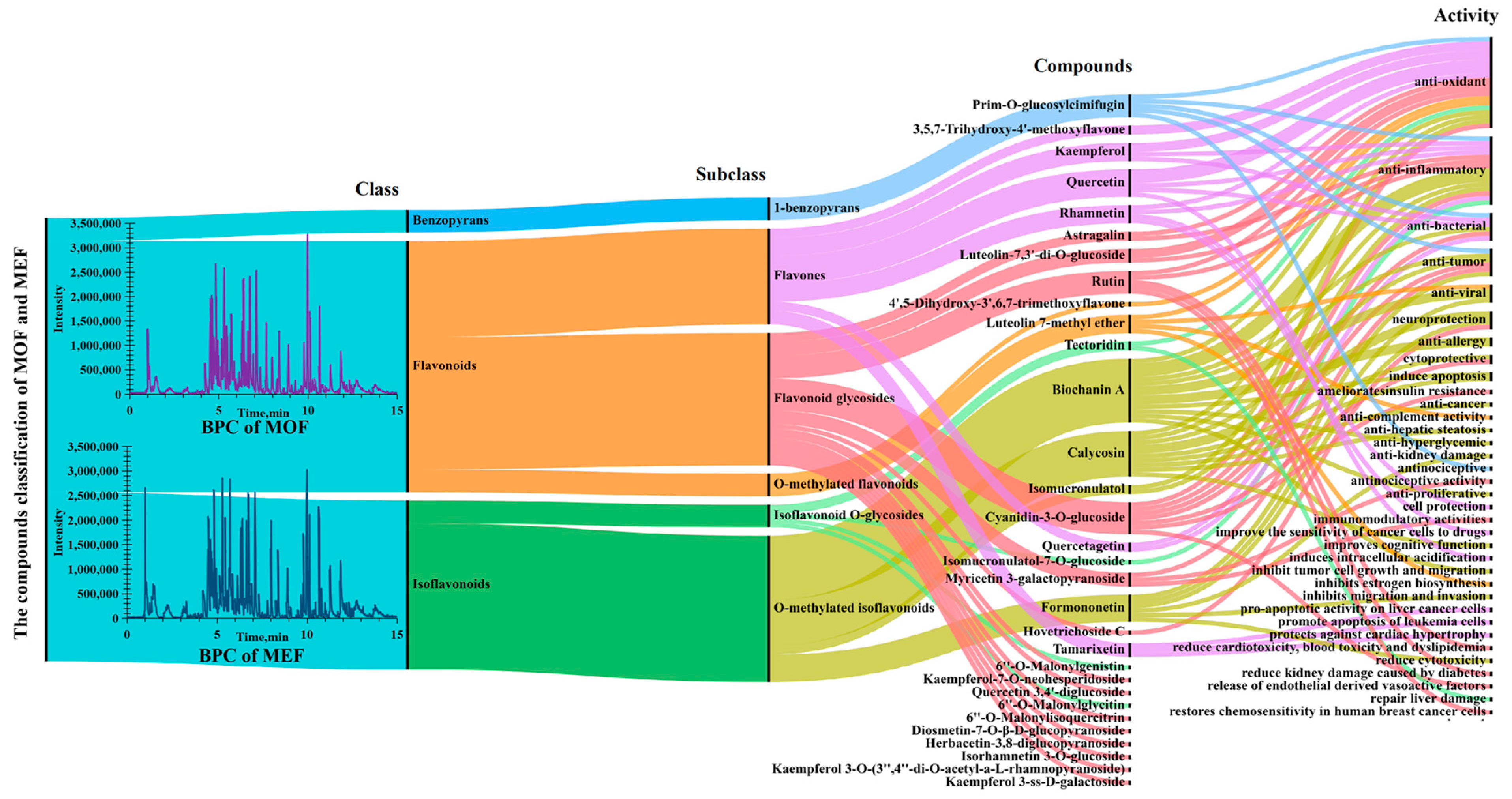
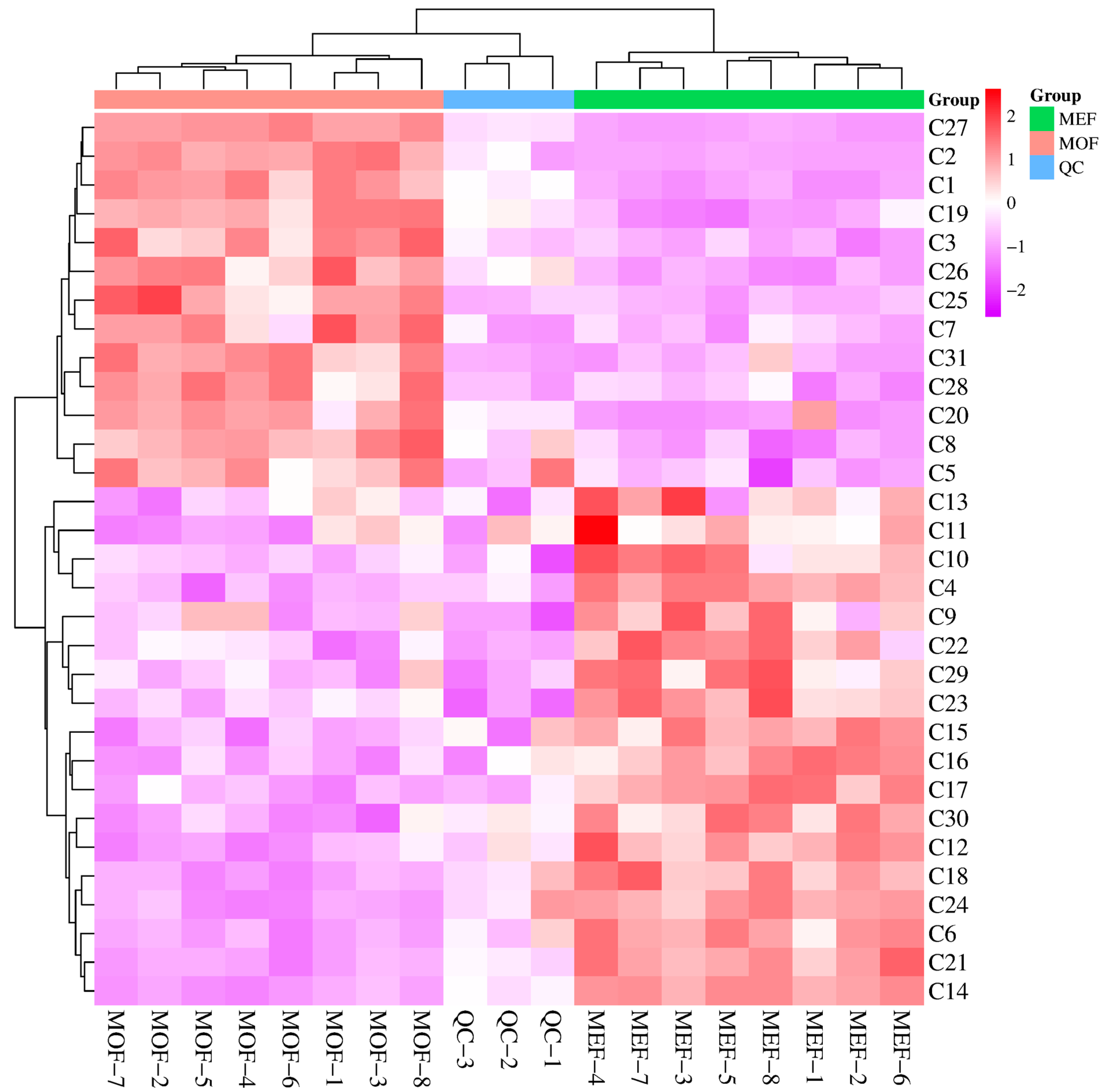
2.4. Comparison of Intensity of Flavonoid Metabolites between MOF and MEF
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Extraction of Samples for UHPLC−Q−TOF−MS/MS Analysis
3.3. Conditions of UHPLC−Q−TOF−MS/MS Platform
3.4. Matrix Establishment and PCA Analysis
3.5. Screening and Identification of Chemical Markers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Gao, C.; Chen, W.; Vong, C.T.; Yao, P.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Tang, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Astragali Radix (Huangqi): A promising edible immunomodulatory herbal medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 258, 112895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qu, H.; Yang, T.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, H. Astragaloside IV attenuate MI-induced myocardial fibrosis and cardiac remodeling by inhibiting ROS/caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway. Cell Cycle 2022, 21, 2309–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Jiao, Y.; Guo, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, R.; Li, X.; Shen, L.; Zhou, Z.; Kim, S.C.; Liu, J. Astragaloside IV blocks monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension by improving inflammation and pulmonary artery remodeling. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Hu, X.; Wang, S.; Jiao, Z.; Sun, T.; Liu, T.; Song, K. Characterization and anti-tumor bioactivity of astragalus polysaccharides by immunomodulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 985–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.C.; Doan, L.H.; Huang, Z.Y.; Chu, L.W.; Shi, T.H.; Lee, Y.R.; Wu, C.T.; Lin, C.H.; Chiang, S.T.; Liu, H.K.; et al. Honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica) and Huangqi (Astragalus membranaceus) Suppress SARS-CoV-2 Entry and COVID-19 Related Cytokine Storm in Vitro. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 765553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, R.; Jian, G.; Chen, T.; Xie, L.; Xue, R.; Gao, C.; Wang, N.; Xu, Y.; Gui, D. Astragalus membranaceus and Panax notoginseng, the Novel Renoprotective Compound, Synergistically Protect against Podocyte Injury in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 1602892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.F.; Dai, Y.J.; Gao, J.R.; Chen, P.J. Uncovering the Mechanism of Astragalus membranaceus in the Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy Based on Network Pharmacology. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 5947304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, T.; Gu, J.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J.; Wang, R.; Duan, T.; Li, Z.; Dong, R.; Wang, W.; et al. Intake of flavonoids from Astragalus membranaceus ameliorated brain impairment in diabetic mice via modulating brain-gut axis. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Ma, Y.; Guo, L.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J. Chemical Discrimination of Astragalus mongholicus and Astragalus membranaceus Based on Metabolomics Using UHPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS Approach. Molecules 2019, 24, 4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, E.A.E.H.; Essawy, A.E.; Al-Shami, A.S. Astragalus species: Phytochemistry, biological actions and molecular mechanisms underlying their potential neuroprotective effects on neurological diseases. Phytochemistry 2022, 202, 113293. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.B.; Thwe, A.A.; Li, X.; Tuan, P.A.; Zhao, S.; Park, C.G.; Lee, J.W.; Park, S.U. Accumulation of flavonoids and related gene expressions in different organs of Astragalus membranaceus Bge. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 173, 2076–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Jia, X.; Sun, S.; Su, Y.; Chen, G. Differential Expression of Calycosin-7-O-beta-D-glucoside Biosynthesis Genes and Accumulation of Related Metabolites in Different Organs of Astragalus membranaceus Bge. Var. Mongholicus (Bge.) Hsiao Under Drought Stress. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 3182–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.H.; Zeng, J.; Yu, H.Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Bao, X.F.; Qin, S.Y.; Chen, G.D.; Zhou, Z.J.; Zhi, H.; Yao, X.S.; et al. Astramalabaricosides A-T, Highly Oxygenated Malabaricane Triterpenoids with Migratory Inhibitory Activity from Astragalus membranaceus var. Mongholicus. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 2312–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.F.; Cao, P.H.; Zeng, J.; Xiao, L.M.; Luo, Z.H.; Zou, J.; Wang, C.X.; Zhao, Z.X.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Zhi, H.; et al. Bioactive pterocarpans from the root of Astragalus membranaceus var. Mongholicus. Phytochemistry 2022, 200, 113249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, H.; Qian, D.W.; Wang, H.Q.; Yu, J.Q.; Duan, J.A. Comparative analysis of twenty-five compounds in different parts of Astragalus membranaceus var. Mongholicus and Astragalus membranaceus by UPLC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Anal. 2019, 9, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhafez, O.H.; Othman, E.M.; Fahim, J.R.; Desoukey, S.Y.; Pimentel-Elardo, S.M.; Nodwell, J.R.; Schirmeister, T.; Tawfike, A.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Metabolomics analysis and biological investigation of three Malvaceae plants. Phytochem. Anal. 2020, 31, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Moore, R.; Gao, Y.; Chen, P.; Yu, L.; Zhang, M.; Sun, J. Comparison of phytochemical profiles of wild and cultivated american ginseng using metabolomics by Ultra-High performance liquid Chromatography-High-Resolution mass spectrometry. Molecules 2022, 28, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.P.; Joshi, R.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, U. Comparative phytochemical analysis of Ferula assa-foetida with Ferula jaeschkeana and commercial oleo-gum resins using GC-MS and UHPLC-PDA-QTOF-IMS. Food Res. Int. 2023, 164, 112434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Qi, W.; Xiong, D.; Long, M. Quercetin: Its antioxidant mechanism, antibacterial properties and potential application in prevention and control of toxipathy. Molecules 2022, 27, 6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Hu, M.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Cui, Y.L. Antioxidant activities of quercetin and its complexes for medicinal application. Molecules 2019, 24, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, L.; Ji, Y.; Yan, C.; Zhang, X. Protective effects of quercetin against inflammation and oxidative stress in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis. Drug Dev. Res. 2019, 80, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saivish, M.V.; Menezes, G.L.; Da, S.R.; Fontoura, M.A.; Shimizu, J.F.; Da, S.G.; Teixeira, I.; Mistrao, N.; Hernandes, V.M.; Rahal, P.; et al. Antiviral Activity of Quercetin Hydrate against Zika Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Xiang, L.; Xiao, L. Quercetin alleviates atherosclerosis by suppressing oxidized LDL-induced senescence in plaque macrophage via inhibiting the p38MAPK/p16 pathway. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 116, 109314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhai, X.; Cui, T.; Wang, G.; Pang, Q. The effect of biochanin a on cell growth, apoptosis, and migration in osteosarcoma cells. Pharmazie 2018, 73, 335–341. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Yang, X.; Pan, J.; Fan, H.; Mei, J.; Hua, D. Biochanin a suppresses tumor progression and PD-L1 expression via inhibiting ZEB1 expression in colorectal cancer. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 3224373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Ye, L.; Ren, Z.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Pan, L.L.; Sun, J. Biochanin a ameliorates caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis and associated intestinal injury in mice by inhibiting TLR4 signaling. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2023, 113, 109229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlow, B.E.; Flythe, M.D.; Klotz, J.L.; Harmon, D.L.; Aiken, G.E. Effect of biochanin a on the rumen microbial community of Holstein steers consuming a high fiber diet and subjected to a subacute acidosis challenge. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e253754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, V.; Tiwari, R.; Tiwari, G. Biochanin-A: A bioactive natural product with versatile therapeutic perspectives. Curr. Drug Res. Rev. 2022, 14, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Qin, X.; Liu, B.; Mo, H.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, Z. Integrative findings indicate anti-tumor biotargets and molecular mechanisms of calycosin against osteosarcoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 126, 110096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.Y.; Day, C.H.; Kuo, C.H.; Wang, T.F.; Ho, T.J.; Lai, P.F.; Chen, R.J.; Yao, C.H.; Viswanadha, V.P.; Kuo, W.W.; et al. Calycosin alleviates H(2) O(2) -induced astrocyte injury by restricting oxidative stress through the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Environ. Toxicol. 2022, 37, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Ban, Y.; Khan, S. Antioxidant activity of calycosin against alpha-synuclein amyloid fibrils-induced oxidative stress in neural-like cells as a model of preventive care studies in Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, J.; Tao, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Song, Y.; Qu, X. Calycosin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation via the sirtuin 1-NOD-like receptor protein 3 pathway. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, X.F.; Wei, W.S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.Z. The cardiovascular protective effect and mechanism of calycosin and its derivatives. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 18, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Cao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Hong, X.; Tang, Y.; Yu, J.; Hu, H.; Ma, W.; Qin, K.; Bao, R. Calycosin alleviates Sepsis-Induced acute lung injury via the inhibition of mitochondrial ROS-Mediated inflammasome activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 690549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhenxia, Z.; Min, L.; Peikui, Y.; Zikai, C.; Yaqun, L.; Junli, W.; Fenlian, Y.; Yuzhong, Z. Inhibition of tau aggregation and associated cytotoxicity on neuron-like cells by calycosin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 171, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Ma, Y.; Ma, S.; Mu, F.; Deng, J.; Duan, J.; Xiong, L.; Yin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xi, M.; et al. The role of TRPC6 in the neuroprotection of calycosin against cerebral ischemic injury. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Liu, Z.L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, Z.M.; Liu, C.H. A combination of astragaloside I, levistilide a and calycosin exerts anti-liver fibrosis effects in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Liu, N.; Liu, H.; Huang, N.; Sun, X.; Zhang, G. Bioinformatic and biochemical findings disclosed anti-hepatic steatosis mechanism of calycosin. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 100, 103914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.Y.; Chen, K.M.; Kuo, W.W.; Lai, S.C.; Ho, T.J.; Lai, P.T.; Huang, C.Y.; Wang, T.F. Calycosin attenuates Angiostrongylus cantonensis-induced parasitic meningitis through modulation of HO-1 and NF-kappaB activation. Parasitology 2022, 150, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cui, J.; Ji, X.; Yao, L. Neuroprotective functions of calycosin against intracerebral hemorrhage-induced oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. Future Med. Chem. 2020, 12, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Shen, P.; Wang, C.; Gao, J.; Ye, C.; Wu, F. Calycosin plays a protective role in diabetic kidney disease through the regulation of ferroptosis. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.C.; Hseu, Y.C.; Shih, Y.C.; Sivakumar, G.; Syu, J.T.; Chen, G.L.; Lu, M.T.; Chu, P.C. Calycosin, a common dietary isoflavonoid, suppresses melanogenesis through the downregulation of PKA/CREB and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, W.; Dou, D.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Zhong, W.; Meng, J.; Bai, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin enhances the antitumour effect of PD-1 inhibition by targeting myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J. Immunother Cancer 2019, 7, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, O.; Ruixue, Y.; Jiaqiang, D.; Kaiyu, W.; Jing, F.; Yi, G.; Xiaoli, H.; Defang, C.; Weimin, L.; Li, T.; et al. Subinhibitory concentrations of Prim-O-Glucosylcimifugin decrease the expression of Alpha-Hemolysin in staphylococcus aureus (USA300). Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2018, 2018, 7579808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, G. Protective Effect of Prim-O-Glucosylcimifugin on Ulcerative Colitis and its Mechanism. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 882924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.Q.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Xu, S.H.; Yang, Z.Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, J. Antinociceptive effects of Prim-O-Glucosylcimifugin in inflammatory nociception via reducing spinal COX-2. Biomol. Ther. 2016, 24, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, X.; Xu, F.; Lv, P.; Yang, H.; Bao, H.; Xu, Y. Analysis of antioxidant capacity of chromones in saposhnikoviae radix obtained by Ultrasonic-Assisted deep eutectic solvents extraction. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2020, 2020, 8875788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| No. | Retention Time (min.) | m/z | CAS Numbers | Identified Results | Adducts | Formulas | Mass Error (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 2.76 | 417.1210 | 551-15-5 | Liquiritin | M − H | C21H22O9 | 4.64 |
| C2 | 2.94 | 445.1503 | 94367-43-8 | Isomucronulatol-7-O-glucoside | M − H2O − H, M + FA − H | C23H28O10 | −0.29 |
| C3 | 3.55 | 625.1463 | 99224-12-1 | Herbacetin-3,8-diglucopyranoside | M − H, M + FA − H | C27H30O17 | 8.36 |
| C4 | 3.64 | 343.0848 | 41365-32-6 | 4′,5-Dihydroxy-3′,6,7-trimethoxyflavone | M − H, M + FA − H | C18H16O7 | 7.20 |
| C5 | 3.73 | 609.1512 | 52187-80-1 | Luteolin-7,3′-di-O-glucoside | M − H | C27H30O16 | 8.30 |
| C6 | 4.04 | 449.1116 | 210050-28-5 | Hovetrichoside C | M − H | C21H22O11 | 5.86 |
| C7 | 4.08 | 625.1459 | 29125-80-2 | Quercetin 3,4′-diglucoside | M − H, M + FA − H | C27H30O17 | 7.86 |
| C8 | 4.21 | 479.0868 | 15648-86-9 | Myricetin 3-galactopyranoside | M − H | C21H20O13 | 7.63 |
| C9 | 4.30 | 609.1515 | 153-18-4 | Rutin | M − H | C27H30O16 | 8.87 |
| C10 | 4.46 | 593.1558 | 17353-03-6 | Kaempferol-7-O-neohesperidoside | M − H | C27H30O15 | 7.68 |
| C11 | 4.48 | 287.0541 | 520-18-3 | Kaempferol | M + H | C15H10O6 | −3.17 |
| C12 | 4.50 | 449.1067 | 23627-87-4 | Kaempferol 3-ss-D-galactoside | M + H | C21H20O11 | −2.57 |
| C13 | 4.63 | 551.1016 | 96862-01-0 | 6″-O-Malonylisoquercitrin | M + H, M + Na | C24H22O15 | −2.82 |
| C14 | 4.68 | 519.1125 | 51011-05-3 | 6″-O-Malonylgenistin | M + H | C24H22O13 | −1.51 |
| C15 | 4.74 | 449.1065 | 7084-24-4 | Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside | M + H | C21H20O11 | −2.95 |
| C16 | 4.77 | 479.1169 | 5041-82-7 | Isorhamnetin 3-O-glucoside | M + H | C22H22O12 | −3.19 |
| C17 | 4.77 | 317.0645 | 603-61-2 | Tamarixetin | M + H | C16H12O7 | −3.30 |
| C18 | 5.12 | 513.1653 | 80681-45-4 | Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin | M + FA − H | C22H28O11 | 8.38 |
| C19 | 5.14 | 317.0646 | 90-19-7 | Rhamnetin | M + H | C16H12O7 | −3.03 |
| C20 | 5.15 | 515.1234 | 77307-50-7 | Kaempferol 3-O-(3″,4″-di-O-acetyl-α-L-rhamnopyranoside) | M − H | C25H24O12 | 7.55 |
| C21 | 5.15 | 533.1278 | 137705-39-6 | 6″-O-Malonylglycitin | M + H | C25H24O13 | −2.24 |
| C22 | 5.21 | 301.0364 | 117-39-5 | Quercetin | M − H | C15H10O7 | 3.55 |
| C23 | 5.21 | 299.0210 | 90-18-6 | Quercetagetin | M − H2O − H, M − H | C15H10O8 | 3.89 |
| C24 | 5.24 | 285.0747 | 20575-57-9 | Calycosin | M + H | C16H12O5 | −3.55 |
| C25 | 5.24 | 301.0697 | 491-54-3 | 3,5,7-Trihydroxy-4′-methoxyflavone | M + H | C16H12O6 | −3.08 |
| C26 | 5.24 | 463.1224 | 20126-59-4 | Diosmetin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside | M + H, M + Na | C22H22O11 | −2.27 |
| C27 | 5.25 | 461.1120 | 611-40-5 | Tectoridin | M − H | C22H22O11 | 6.63 |
| C28 | 5.50 | 299.0572 | 20243-59-8 | Luteolin 7-methyl ether | M − H | C16H12O6 | 3.70 |
| C29 | 5.66 | 267.0674 | 485-72-3 | Formononetin | M − H | C16H12O4 | 4.34 |
| C30 | 5.76 | 301.1095 | 64474-51-7 | Isomucronulatol | M − H | C17H18O5 | 4.35 |
| C31 | 5.97 | 283.0626 | 491-80-5 | Biochanin A | M − H | C16H12O5 | 4.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Gu, M.; Kong, W.; Lin, Z.; Mao, J.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. High-Throughput Phytochemical Unscrambling of Flowers Originating from Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.) P. K. Hsiao and Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bug. by Applying the Intagretive Plant Metabolomics Method Using UHPLC−Q−TOF−MS/MS. Molecules 2023, 28, 6115. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166115
Liu Q, Li J, Gu M, Kong W, Lin Z, Mao J, Zhang M, Jiang L, Liu C, Wang Y, et al. High-Throughput Phytochemical Unscrambling of Flowers Originating from Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.) P. K. Hsiao and Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bug. by Applying the Intagretive Plant Metabolomics Method Using UHPLC−Q−TOF−MS/MS. Molecules. 2023; 28(16):6115. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166115
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qi, Jinghui Li, Meiling Gu, Wanying Kong, Zhao Lin, Jialin Mao, Meng Zhang, Liyan Jiang, Can Liu, Yumei Wang, and et al. 2023. "High-Throughput Phytochemical Unscrambling of Flowers Originating from Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.) P. K. Hsiao and Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bug. by Applying the Intagretive Plant Metabolomics Method Using UHPLC−Q−TOF−MS/MS" Molecules 28, no. 16: 6115. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166115
APA StyleLiu, Q., Li, J., Gu, M., Kong, W., Lin, Z., Mao, J., Zhang, M., Jiang, L., Liu, C., Wang, Y., & Liu, J. (2023). High-Throughput Phytochemical Unscrambling of Flowers Originating from Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge.) P. K. Hsiao and Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bug. by Applying the Intagretive Plant Metabolomics Method Using UHPLC−Q−TOF−MS/MS. Molecules, 28(16), 6115. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28166115







