Preparation and Application of Magnetic Composites Using Controllable Assembly for Use in Water Treatment: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Nano-Fe3O4 Particle Preparation
3. Controlled Assembly of Magnetic Composites
3.1. In Situ Assembly
| In Situ Assembly | Ectopic Assembly | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ectopic Assembly with Inorganic Polymers | Ectopic Assembly with Organic Polymers | Ectopic Assembly with Biopolymers | ||
| Composition | Iron precursors + polymers | Nano-Fe3O4+ inorganic polymers | Nano-Fe3O4+ organic polymers | Nano-Fe3O4+ biopolymer |
| Synthesis method | One-step method | Electrostatic adherence | Coating, “grafting-to” reaction | coating, “grafting-to” reaction |
| Performance | Low or even negative surface charges | Strong poly-aggregation characteristics | Strong flocculation performance | Strong flocculation and adsorption performance |
| Samples | Fe3O4@PP [51] | PAC/Fe3O4 [68], MFPAC [69] | Fe3O4@PEI [70], Fe3O4@SiO2@PAMAM [71] | Fe3O4@APFS-G-CS MNPs [72] |
| Application | Microalgae harvesting | Microalgae harvesting, pre-concentrating waste leachate | Microalgae harvesting, graphene oxide wastewater | Oily wastewater |
3.2. Ectopic Assembly
3.2.1. Ectopic Assembly with Inorganic Polymers
3.2.2. Ectopic Assembly with Organic Polymers
3.2.3. Ectopic Assembly with Biopolymers
4. Application of Magnetic Composites in Water Treatment
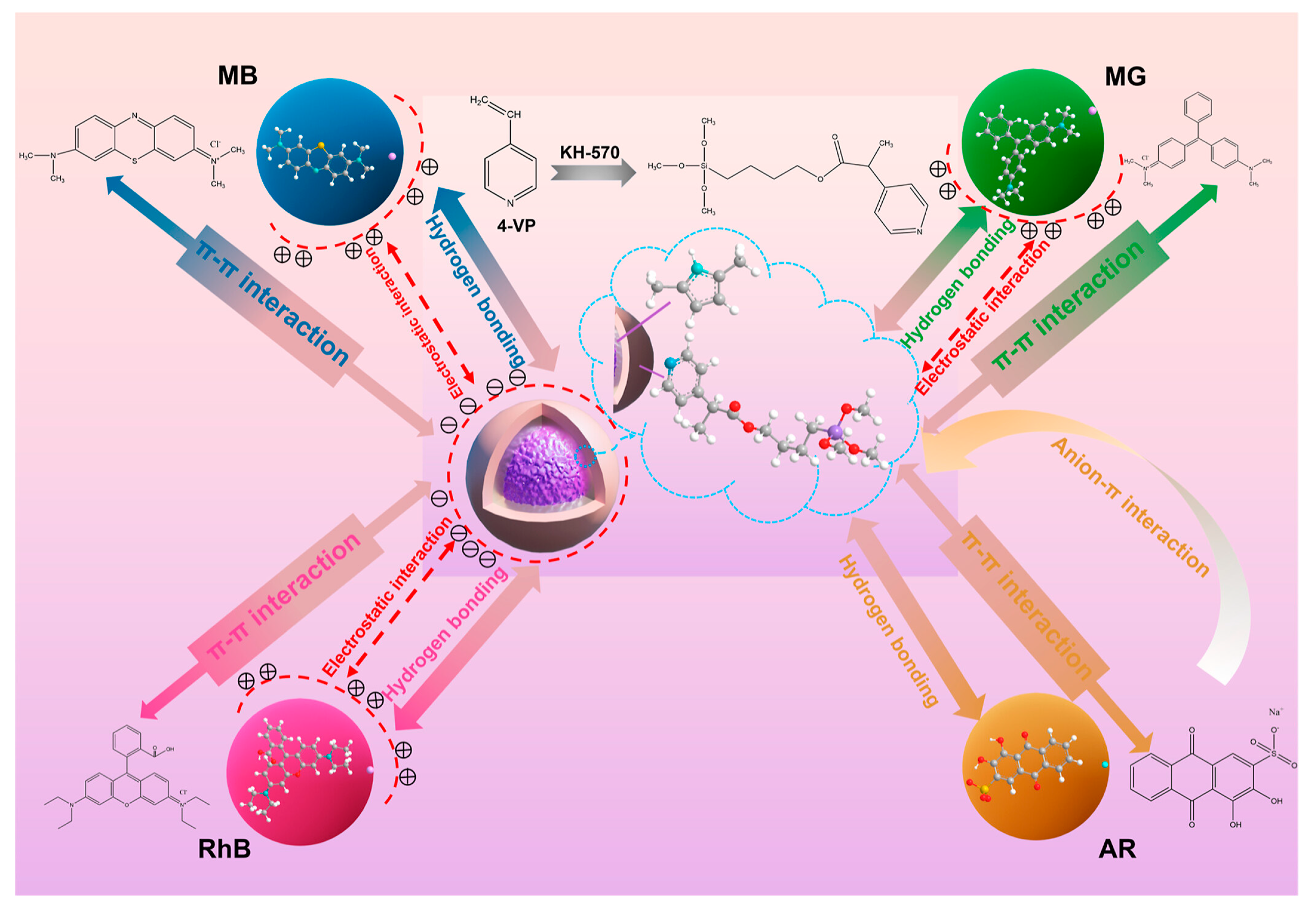
4.1. Decolorization of Dye Wastewater
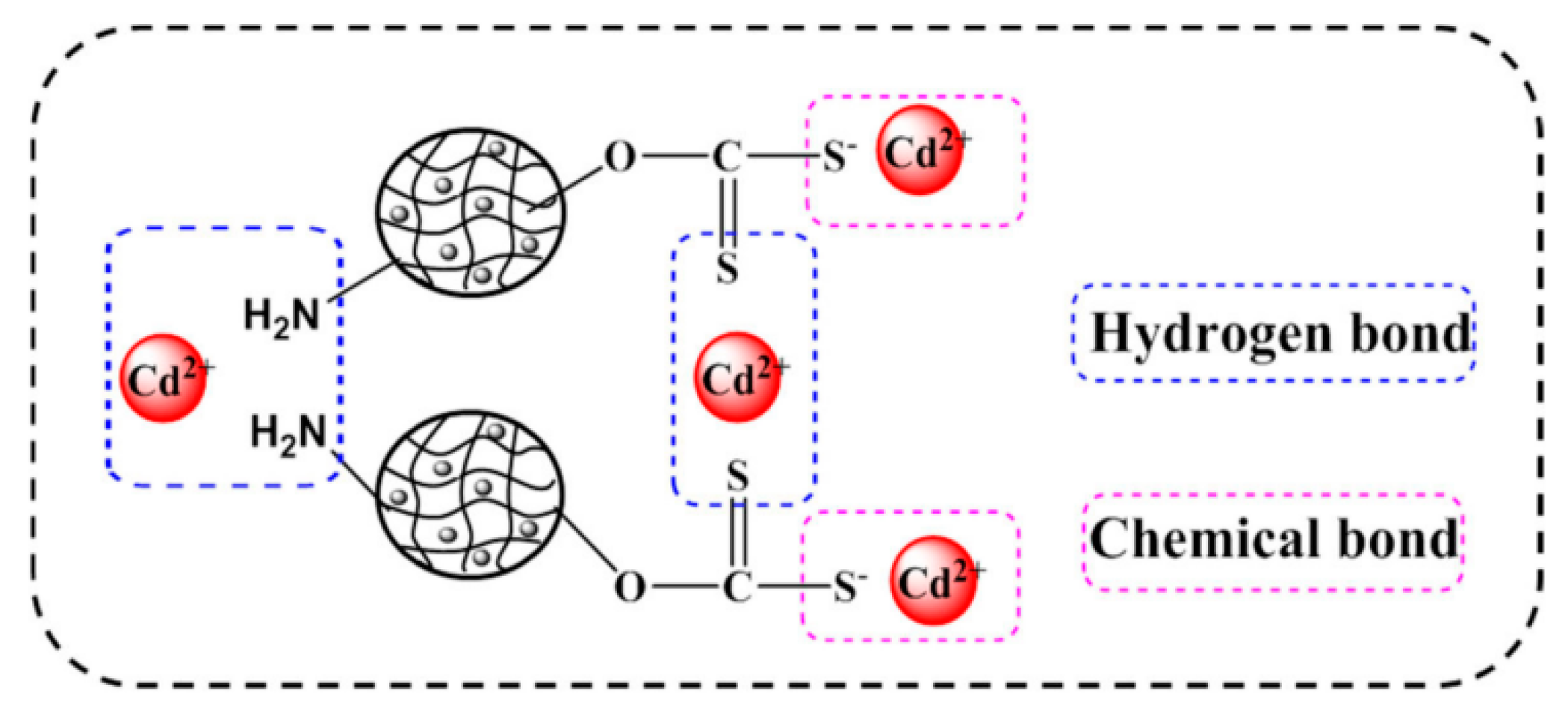
4.2. Heavy Metal Removal
4.3. Removal and Separation of Microalgae
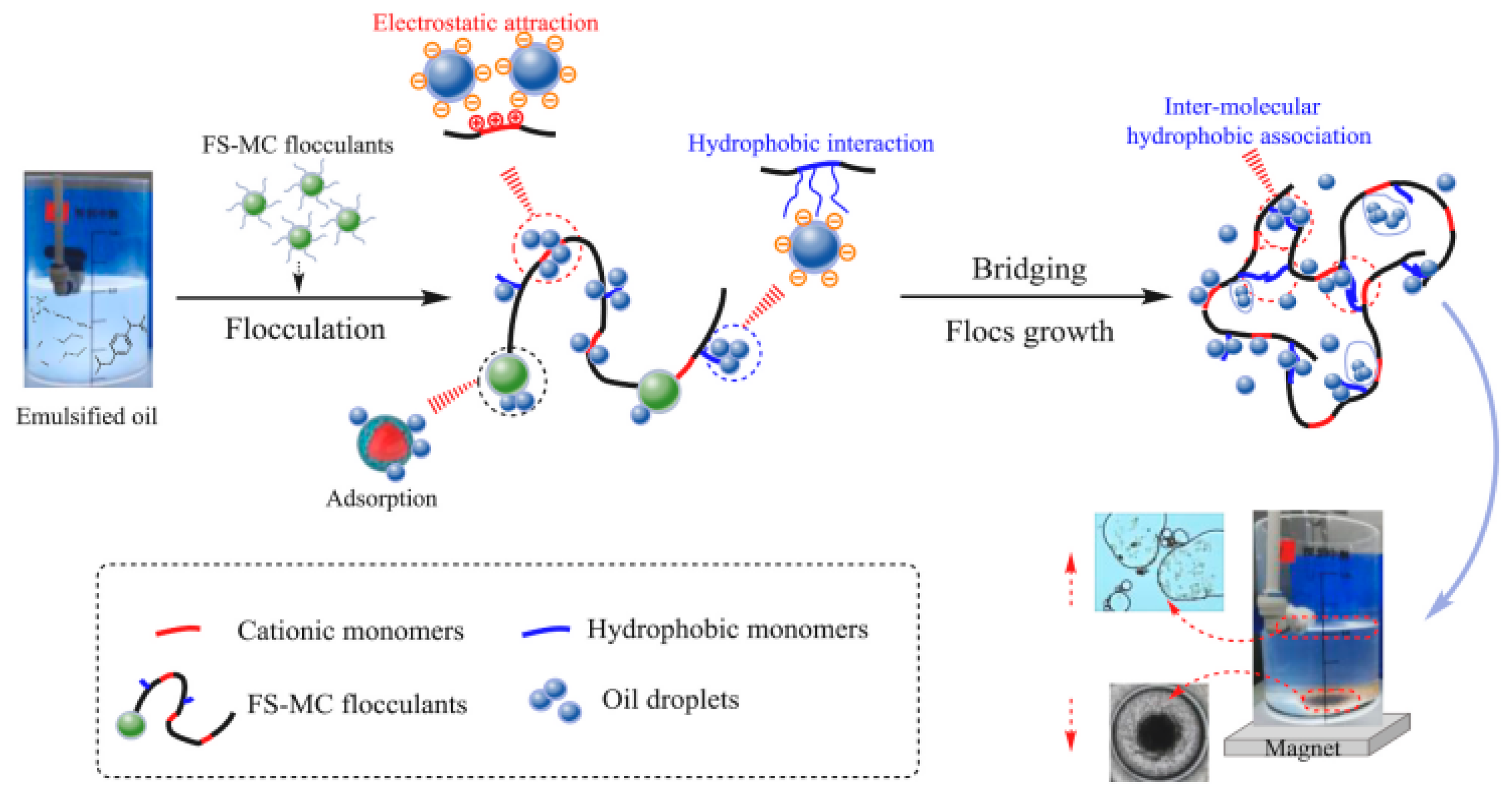
4.4. Emulsification and Separation of Oily Wastewater
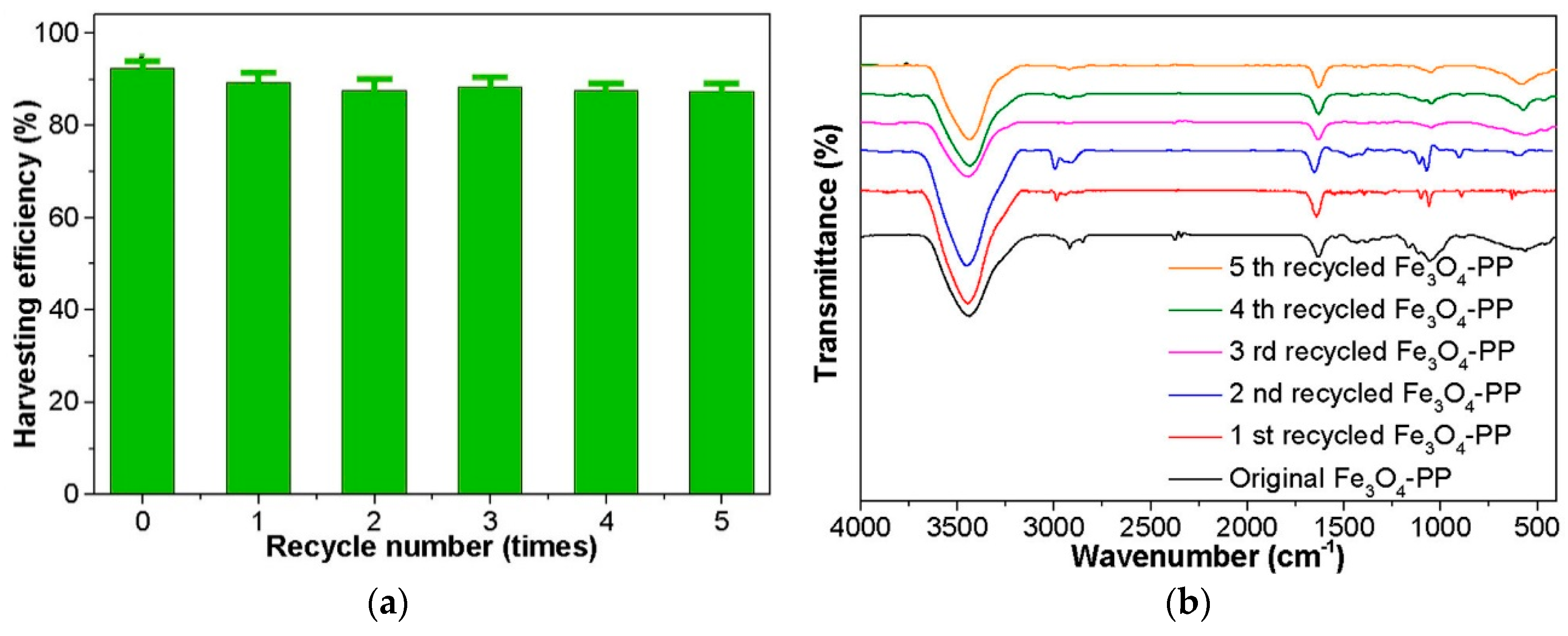
5. Recycling of Magnetic Composites
6. Conclusions
7. Prospects
- (i)
- Taking assembly polymers as the starting point, to further improve the assembly stability of magnetic composites, and the regeneration and reusing properties can be promoted accordingly, thus consistent separation efficiency will be ensured.
- (ii)
- To develop more efficient, biocompatible, degradable, highly assessable and reusable magnetic composites, which have a minimum environmental impact.
- (iii)
- More thorough understanding of the composites–targets interactions in the magnetic separation process is essential, which could refer to the classical DLVO model and the magnetism modified M-DLVO, thus assisting in the design of magnetic composites and optimization of the magnetic separation process.
- (iv)
- The downstream processes following magnetic separation still need to be investigated, including the re-separation of magnetic composites from the culture medium/suspensions, the extraction of desired products, etc. In addition, the design process should take the characteristic of the desired end products into account.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, D.; Xu, M.; Shen, Q.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Ding, S. A critical review of the appearance of black-odorous waterbodies in China and treatment methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazvini, M.; Kavosi, M.; Sharma, R.; Kim, M. A review on mechanical-based microalgae harvesting methods for biofuel production. Biomass Bioenergy 2022, 158, 106348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Qin, L.; Li, H.; Liang, W. Magnetic coagulation and flocculation of a kaolin suspension using Fe3O4 coated with SiO2. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, E.A.; Guzman, M.T.; Baizaval, J.L.; Teran, A.O. Coagulation-flocculation mechanisms in wastewater treatment plants through zeta potential measurements. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 279, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugazhendhi, A.; Shobana, S.; Bakonyi, P.; Nemestothy, N.; Xia, A.; Banu, J.R.; Kumar, G. A review on chemical mechanism of microalgae flocculation via polymers. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 21, e00302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hu, T.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Chu, R.; Yin, Z.; Mo, F.; Zhu, L. A review on flocculation as an efficient method to harvest energy microalgae: Mechanisms, performances, influencing factors and perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 131, 110005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Han, Y.; Li, W.; Zhu, Y. Study on polymer-bridging flocculation performance of ultrafine specular hematite ore and its high gradient magnetic separation behavior: Description of floc microstructure and flocculation mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Lu, D.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Z.; Xu, S. Development of a high-gradient magnetic separator for enhancing selective separation: A review. Powder Technol. 2023, 421, 118435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Du, S.; Liang, W. Synthesis of chitosan-based grafting magnetic flocculants for flocculation of kaolin suspensions. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 139, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cheng, S.; Zhou, L.; Han, Y. Enhanced iron recovery from magnetic separation of ultrafine specularite through polymer-bridging flocculation: A study of flocculation performance and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 308, 122882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wu, G.; Zhang, R.; Xia, W.; Nie, Y.; Kong, Y.; Jia, B.; Li, S. Emulsified oil removal from steel rolling oily wastewater by using magnetic chitosan-based flocculants: Flocculation performance, mechanism, and the effect of hydrophobic monomer ratio. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 304, 122329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, Q.; Wang, K.; Li, S.; Luo, W.; Liang, Q.; Zhong, J.; Ding, M. Recent advances in development of functional magnetic adsorbents for selective separation of proteins/peptides. Talanta 2023, 253, 123919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lin, J. Recent advances on magnetic nanobead based biosensors: From separation to detection. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 128, 115915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlani, I.L.; Oliveira, R.V.; Cass, Q.B. Immobilization of cytochrome P450 enzymes onto magnetic beads: An approach to drug metabolism and biocatalysis. Talanta Open 2023, 7, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yu, B.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Cong, H. Preparation, surface functionalization and application of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interfac. 2020, 281, 102165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Tukhani, M.; Hussain, C.M. Sustainable plant and microbes-mediated preparation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and industrial application of its chitosan, starch, cellulose, and dextrin-based nanocomposites as catalysts. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 179, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, T.; Sridhar, D.; Algadi, H.; Xu, B.B.; El-Bahy, Z.M.; Li, H.; Ma, Y.; Li, T.; et al. An overview of metal-organic frameworks and their magnetic composites for the removal of pollutants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 320, 124144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, F.; Genc, O.; Gökcek, M.; Çolak, A.B. An experimental and new study on thermal conductivity and zeta potential of Fe3O4/water nanofluid: Machine learning modeling and proposing a new correlation. Powder Technol. 2023, 420, 118388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochazkova, G.; Podolova, N.; Safarik, I.; Zachleder, V.; Branyik, T. Physicochemical approach to freshwater microalgae harvesting with magnetic particles. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 112, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Shen, J.; Hu, Z.; Bai, G.; Wang, M.; Peng, B.; Shen, R.; Linghu, W. High-efficient scavenging of U(VI) by magnetic Fe3O4@gelatin composite. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 221, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Fan, Q.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Jiao, L.; Liang, W. Application of Fe3O4 coated with modified plant polyphenol to harvest oleaginous microalgae. Algal Res. 2019, 38, 101417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Jiang, R.; Zhu, F.; Liu, H.; Ouyang, G. Application of functionalized magnetic nanoparticles in sample preparation. Anal Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 377–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, G.; Bala, N. Corrosion behavior and characterization of HA/Fe3O4/CS composite coatings on AZ91 Mg alloy by electrophoretic deposition. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 237, 121884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Huang, Z.; Yin, Y.; Liang, X.; Qin, Y.; Liang, J. Valorization of manganese residue to prepare a highly stable and active Fe3O4@SiO2/starch-derived carbon composite for catalytic degradation of dye waste water. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Cai, Y.; Su, Z.; Ma, X.; Wu, W. High positively charged Fe3O4 nanocomposites for efficient and recyclable demulsification of hexadecane-water micro-emulsion. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 133050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, P.Y.; Ng, B.W.; Chong, C.; Ahmad, A.L.; Yang, J.W.; Derek, C.J.C.; Lim, J.K. Magnetophoretic separation of microalgae: The role of nanoparticles and polymer binder in harvesting biofuel. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 4114–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.K.; Chieh, D.C.J.; Jalak, S.A.; Toh, P.Y.; Yasin, N.H.M.; Ng, B.W.; Ahmad, A.L. Rapid magnetophoretic separation of microalgae. Small 2012, 8, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Stiles, A.R.; Guo, C.; Liu, C. Harvesting microalgae by magnetic separation: A review. Algal Res. 2015, 9, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R.; Bahreinizad, H.; Amiri, Z.; Aliabadi, H.A.M.; Salimi-Bani, M.; Nakisa, A.; Davoodi, F.; Tahmasebi, B.; Ahmadpour, F.; Radinekiyan, F.; et al. Functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for the separation and purification of proteins and peptides. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 141, 116291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Liang, W. In-situ self-assembly of plant polyphenol-coated Fe3O4 particles for oleaginous microalgae harvesting. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 214, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Teoh, W.Y.; Gooding, J.J.; Selomulya, C.; Amal, R. Functionalization Strategies for Protease Immobilization on Magnetic Nanoparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobyliukh, A.; Olszowska, K.; Szeluga, U.; Pusz, S. Iron oxides/graphene hybrid structures—Preparation, modification, and application as fillers of polymer composites. Adv. Colloid Interfac. 2020, 285, 102285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, C.; Tian, X.; Chang, X.; Ren, Y.; Yu, S. Applications of surface functionalized Fe3O4 NPs-based detection methods in food safety. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.; Kumar, P.; Sillanpaa, M.; Kumar, D.; Nemiwal, M. Immobilized ionic liquids on Fe3O4 nanoparticles: A potential catalyst for organic synthesis. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 145, 110055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, R.; Dhanyaprabha, K.C.; Thomas, H.; Sini, R. Optical characterisation of cadmium doped Fe3O4 ferrofluids by co-precipitation method. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 25, A1–A5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatamian, M.; Divband, B.; Shahi, R. Ultrasound assisted co-precipitation synthesis of Fe3O4/bentonite nanocomposite: Performance for nitrate, BOD and COD water treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 31, 100870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga-Garcia, P.; Kubbutat, P.; Brammen, M.; Schwaminger, S.; Berensmeier, S. Bare iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic harvesting of microalgae: From interaction behavior to process realization. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, R.; Permana, M.G.; Harison, B.; Nugraha; Yuliarto, B.; Suyatman; Kurniadi, D. Optimization of frequency and stirring rate for synthesis of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles by using coprecipitation-ultrasonic irradiation methods. Procedia Eng. 2017, 170, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, L.; Tao, J.; Bai, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; Meng, S.; Wu, J. Facile hydrothermal synthesis of polyimide/Fe3O4 aerogel microspheres as magnetically controllable oil sorbents. Fuel 2023, 333, 126288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoobi, M.; Asjadi, F.; Sanikhani, M. A facile one-step green hydrothermal synthesis of paramagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles with highly efficient dye removal. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 144, 104774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.; Wang, R.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, J.; Sun, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, G. In-situ growth of small-size Fe3O4 nanoparticles on N-doped hollow carbon spheres for electrochemical high-efficiency determination of ofloxacin-contaminated water. Microchem. J. 2023, 191, 108927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, L. Synthesis of Fe3O4/C composites derived from cornstalk by one-step hydrothermal method as a reusable adsorbent for dyes. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 143, 109762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, N.; Dehiya, B.S. Influence of anionic and non-ionic surfactants on the synthesis of core-shell Fe3O4@TiO2 nanocomposite synthesized by hydrothermal method. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 23516–23525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, S.T.; Babamoradi, M.; Rouhi, M.; Maleki, A.; Hajizadeh, Z. Facile hydrothermal synthesis and microwave absorption of halloysite/polypyrrole/Fe3O4. Synth. Met. 2022, 290, 117142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesu, A.C.B.; Jesus, J.R.; Limac, R.J.S.; Mourad, K.O.; Almeidae, J.M.A.; Duquea, J.G.S.; Meneses, C.T. Synthesis and magnetic interaction on concentrated Fe3O4 nanoparticles obtained by the co-precipitation and hydrothermal chemical methods. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 11149–11153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banic, N.; Merkulov, D.S.; Despotovic, V.; Fincur, N.; Ivetic, T.; Bognar, S.; Jovanovic, D.; Abramovic, B. Rapid removal of organic pollutants from aqueous systems under solar irradiation using ZrO2/Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Molecules 2022, 27, 8060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Huang, M.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G. Magnetic separation techniques in sample preparation for biological analysis: A review. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2014, 101, 84–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markeb, A.A.; Llimos-Turet, J.; Ferrer, I.; Blanquez, P.; Alonso, A.; Sanchez, A.; Moral-Vico, J.; Font, X. The use of magnetic iron oxide based nanoparticles to improve microalgae harvesting in real wastewater. Water Res. 2019, 159, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lei, M.; Zeng, W.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, D.; Liu, C. Synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2-(-NH2/-COOH) nanoparticles and their application for the removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 20470–20479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Qin, L.; Liang, W. Self-assembly of Fe3O4 with natural tannin as composites for microalgal harvesting. Fuel 2022, 321, 124038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Shen, T.; Wang, X. Preparation and characterization of polymer-coated Fe3O4 magnetic flocculant. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, W.; Hong, Y.; Hou, Y. Magnetic nanoparticles grafted with amino-riched dendrimer as magnetic flocculant for efficient harvesting of oleaginous microalgae. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 297, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Guo, C.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Pan, F.; Liu, C. Improvement of microalgae harvesting by magnetic nanocomposites coated with polyethylenimine. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 242, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, F.; Hu, Y.; Stiles, A.R.; Guo, C.; Liu, C. Magnetic flocculant for high efficiency harvesting of microalgal cells. ACS Appl. Mat. Interfaces 2014, 6, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Fan, Q.; Li, X.; Jiao, L.; Liang, W. Harvesting of Chlorella vulgaris using Fe3O4 coated with modified plant polyphenol. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 26246–26258. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Xia, W.; Fu, X.; Ding, L.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fu, K. Magnetic flocculation of algae-laden raw water and removal of extracellular organic matter by using composite flocculant of Fe3O4/cationic polyacrylamide. J. Cleaner Prod. 2020, 248, 119276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Yoon, I.H.; Kim, I. Application of polyethylenimine-coated magnetic nanocomposites for the selective separation of Cs-enriched clay particles from radioactive soil. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 21822–21829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Tu, H.; Niu, F.; Lu, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, K.; Chen, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, Z. Synthesis of polymer-functionalized β-cyclodextrin, Mg2+ doped, coating magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticle carriers for penicillin G acylase immobilization. Colloids Surf. A 2023, 657, 130609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingrajiya, R.D.; Patel, M.P. Fe3O4 modified chitosan based co-polymeric magnetic composite hydrogel: Synthesis, characterization and evaluation for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125251. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yue, D.; Wang, H. In situ Fe3O4 nanoparticles coating of polymers for separating hazardous PVC from microplastic mixtures. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 127170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabzendedar, S.; Modarresi-Alam, A.R.; Noroozifar, M.; Kerman, K. Core-shell nanocomposite of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles with poly(m-aminobenzenesulfonic acid) for polymer solar cells. Org. Electron. 2020, 77, 105462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, W.; Zhao, X.; Gan, T.; Lu, Y.; Li, P.; Xu, W. In situ construction of Fe3O4@PDA@Au multi hotspot SERS probe for trace detection of benzodiazepines in serum. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2023, 300, 122897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Liang, W. Magnetic polyphenol nanocomposite of Fe3O4/SiO2/PP for Cd(II) adsorption from aqueous solution. Environ. Technol. 2020, 43, 935–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Shen, W. Preparation and characterization of the magnetic Fe3O4@TiO2 nanocomposite with the in-situ synthesis coating method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 216, 496–501. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Ur Rehman, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Long, F.; Shen, S.; Chen, C.; Liang, T. In situ synthesis of Fe3O4 coated on iron-based magnetic microwave absorbing materials and the influence of oxide magnetic materials on microwave absorption mechanism. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 12972–12979. [Google Scholar]
- An, G.S.; Han, J.S.; Shin, J.R.; Chae, D.H.; Hur, J.U.; Park, H.Y.; Jung, Y.G.; Choi, S.C. In situ synthesis of Fe3O4@SiO2 core–shell nanoparticles via surface treatment. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 12233–12237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liang, W.; Liu, L.; Li, F.; Fan, Q.; Sun, X. Harvesting Chlorella vulgaris by magnetic flocculation using Fe3O4 coating with polyaluminium chloride and polyacrylamide. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 198, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Duan, X.; Zhan, P.; Liu, R.; Nie, F. Coagulation performance and microstructural morphology of a novel magnetic composite coagulant for pre-treating landfill leachate. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 14, 2507–2518. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, W.; Zhou, X.; Han, S.; Tu, R.; Feng, X.; Jensen, P.D.; Wang, Q. Efficient harvesting of Chlorella pyrenoidosa and Scenedesmus obliquus cultivated in urban sewage by magnetic flocculation using nano-Fe3O4 coated with polyethyleneimine. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 290, 121771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Dendrimer modified composite magnetic nano-flocculant for efficient removal of graphene oxide. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 307, 122851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, T.; Chen, Y.; Qi, D.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, H. Treatment of emulsified oil wastewaters by using chitosan grafted magnetic nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 696, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Yoon, I.H.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, I. Selective separation of Cs-contaminated clay from soil using polyethylenimine-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 136020. [Google Scholar]
- Gerulová, K.; Bartošová, A.; Blinová, L.; Bártová, K.; Dománková, M.; Garaiová, Z.; Palcut, M. Magnetic Fe3O4-polyethyleneimine nanocomposites for efficient harvesting of Chlorella zofingiensis, Chlorella vulgaris, Chlorella sorokiniana, Chlorella ellipsoidea and Botryococcus braunii. Algal Res. 2018, 33, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hu, D.; Li, S.; Chu, R.; Liu, C.; Lv, Y.; Bao, J.; Xiang, M.; Zhu, L. Biocompatible magnetic flocculant for efficient harvesting of microalgal cells: Isotherms, mechanisms and water recycling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119679. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Gao, B.; Wang, J.; Yue, Q. Synchronous removal of CuO nanoparticles and Cu2+ by polyaluminum chloride-Enteromorpha polysaccharides: Effect of Al species and pH. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 88, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zheng, H.; Xiang, W.; An, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, S. Magnetic flocculation of anion dyes by a novel composite coagulant. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 143, 282–294. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Jiang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Tan, M.; Feng, L.; Liu, L.; Chen, W. Study on structural characterization and algae-removing efficiency of polymeric aluminum ferric sulfate (PAFS). Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 5674–5681. [Google Scholar]
- Ajao, V.; Fokkink, R.; Leermakers, F.; Bruning, H.; Rijnaarts, H.; Temmink, H. Bioflocculants from wastewater: Insights into adsorption affinity, flocculation mechanisms and mixed particle flocculation based on biopolymer size-fractionation. J. Colloid Interf. Sci 2021, 581, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liimatainen, H.; Sirvio, J.; Sundman, O.; Visanko, M.; Hormi, O.; Niinimaki, J. Flocculation performance of a cationic biopolymer derived from a cellulosic source in mild aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9626–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, G.; Wu, W.; Ali, A.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Qi, W.; Li, R.; Zhang, Z. Magnetic biochar composite decorated with amino-containing biopolymer for phosphorus recovery from swine wastewater. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 634, 127980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, M.; Akbari, A. Facile fabrication of magnetic chitosan hydrogel beads and modified by interfacial polymerization method and study of adsorption of cationic/anionic dyes from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, F.; He, B.; Wang, G.; Xie, W.; Liang, E. Efficient Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions by A Novel AO-PAN-g-Chitosan/Fe3O4 Composite. ChemistrySelect 2020, 5, 8033–8039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Geng, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chu, L.; Luo, X.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Y. Preparation of the chitosan grafted poly (quaternary ammonium)/Fe3O4 nanoparticles and its adsorption performance for food yellow 3. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 152, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Nan, J.; Chen, M.; Song, L.; Wu, F. Superior performance of novel chitosan-based flocculants in decolorization of anionic dyes: Responses of flocculation performance to flocculant molecular structures and hydrophobicity and flocculation mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131273. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Hu, P. Environmentally benign magnetic chitosan/Fe3O4 composites as reductant and stabilizer for anchoring Au NPs and their catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 2, 13471–13478. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, D.; Qv, M.; Liu, D.; Tang, C.; Wang, W.; Wu, Q.; Yin, Z.; Zhu, L. Structural insights into mechanisms of rapid harvesting of microalgae with pH regulation by magnetic chitosan composites: A study based on E-DLVO model and component fluorescence analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 456, 141071. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Chu, R.; Zhu, L.; Li, S.; Mo, F.; Hu, D.; Liu, C. Application of chitosan-based flocculants to harvest microalgal biomass for biofuel production: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 145, 111159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, B.; Esmaeili, H. Application of Fe3O4/SiO2@ZnO magnetic composites as a recyclable heterogeneous nanocatalyst for biodiesel production from waste cooking oil: Response surface methodology. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 11452–11463. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Kurniawan, T.A.; You, Y.; Dzarfan Othman, M.H.; Avtar, R.; Fu, D.; Hwang, G.H. Fabrication, characterization, and application of ternary magnetic recyclable Bi2WO6/BiOI@Fe3O4 composite for photodegradation of tetracycline in aqueous solutions. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110839. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; Qin, P.; Lei, M.; Zeng, Q.; Song, H.; Yang, J.; Shao, J.; Liao, B.; Gu, J. Modifying Fe3O4 nanoparticles with humic acid for removal of Rhodamine B in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209–210, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wang, C.; Ding, J.; Li, T.; Ma, Y. Magnetic core–shell Fe3O4@polypyrrole@4-vinylpyridine composites for the removal of multiple dyes. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 9449–9462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Wang, S. Magnetic natural composite Fe3O4-chitosan@bentonite for removal of heavy metals from acid mine drainage. J. Colloid Interf. Sci 2019, 538, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, A.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, H.; Sun, P.; Yao, B.; Zang, Y.; Du, X.; Dong, L. Xanthate-modified magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2-based polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan composite material for efficient removal of heavy metal ions from water. Polymers 2022, 14, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jia, W.; Ren, S.; Wang, J. Novel and recyclable demulsifier of expanded perlite grafted by magnetic nanoparticles for oil separation from emulsified oil wastewaters. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Fu, X.; Xia, W.; Zhang, R.; Fu, K.; Wu, G.; Jia, B.; Li, S.; Li, J. Removal of emulsified oil from water by using recyclable chitosan based covalently bonded composite magnetic flocculant: Performance and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126529. [Google Scholar]
- Neves, T.D.F.; Dalarme, N.B.; Silva, P.M.M.d.; Landers, R.; Picone, C.S.F.; Prediger, P. Novel magnetic chitosan/quaternary ammonium salt graphene oxide composite applied to dye removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103820. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.; Sun, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y. Supramolecular gel composites reinforced by using halloysite nanotubes loading with in-situ formed Fe3O4 nanoparticles and used for dye adsorption. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 122, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, X.; Chen, A. Heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions by chitosan-based magnetic composite flocculants. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 108, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Wang, T.; Yang, Z.; Hong, Y.; Hou, Y. Long-chain poly-arginine functionalized porous Fe3O4 microspheres as magnetic flocculant for efficient harvesting of oleaginous microalgae. Algal Res. 2017, 27, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Han, D.; Hua, Z.; Yang, S. Porous Fe3O4 and gamma-Fe2O3 foams synthesized in air by sol-gel autocombustion. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 684, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, T.; Yang, Z.; Hong, Y.; Xie, X.; Hou, Y. Effects of Fe3O4 nanoparticle fabrication and surface modification on Chlorella sp. harvesting efficiency. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesas, R.H.; Baei, M.S.; Rostami, H.; Gardy, J.; Hassanpour, A. An investigation on the capability of magnetically separable Fe3O4/mordenite zeolite for refinery oily wastewater purification. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 241, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, S.; Liu, Q.; Fan, Z.; Tong, Q.; Cai, L.; Fu, Y. Magnetic hyperbranched molecular materials for treatment of oily sewage containing polymer in oilfield compound flooding. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 865832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, R.; Yan, L.; Yang, K.; Yu, S.; Hao, Y.; Yu, H.; Du, B. Magnetic Fe3O4/MgAl-LDH composite for effective removal of three red dyes from aqueous solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 252, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, B.; Ye, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Feng, Y.; Han, W.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Magnetic, superelastic and superhydrophobic porous thermoplastic polyurethane monolith with nano-Fe3O4 coating for highly selective and easy-recycling oil/water separation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 535, 147690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zuo, X.; Gao, W.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Cong, T.; Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Pan, L. Recyclable ZnO/Fe3O4 nanocomposite with piezotronic effect for high performance photocatalysis. Mater. Res. Bull. 2022, 148, 111677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhong, D.; Zhang, D.; Pu, X.; Shao, X.; Su, C.; Yao, X.; Li, S. Thermal regeneration of recyclable reduced graphene oxide/Fe3O4 composites with improved adsorption properties. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Badruddoza, A.Z.M.; Hidajat, K.; Uddin, M.S. Adsorptive removal of emerging contaminants from water using superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles bearing aminated β-cyclodextrin. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, S.; Li, R.; Peng, Y.; Sun, C.; Vakili, M.; Yu, G.; Deng, S. Preparation of magnetic powdered carbon/nano-Fe3O4 composite for efficient adsorption and degradation of trichloropropyl phosphate from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Physical Methods | Chemical Methods | |
|---|---|---|
| Methods | Ball milling, ultrasonic treatment | Liquid-phase reactions, hydrothermal synthesis |
| Advantages | Simple operation process | Mild reaction conditions, single reaction mechanism |
| Disadvantages | Uneven particle size distribution, different morphologies, prone to oxidation | Easy agglomeration, irregular particle size distribution |
| Processing Object | Dye Wastewater | Heavy Metal | Microalgae | Oily Wastewater |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Fe3O4/HA [91] Fe3O4@PPy@4-VP [92] | Fe3O4-CS@BT [93] XMPC [94] | Fe3O4/CPAM [57] | EP@APTES-Fe3O4 [95] FS-MC [96] |
| Targets | Rhodamine B multiple dyes | Cr(VI) Pd(II), Cu(II), Cd(II) | Algae-laden raw water Chlorella sp. | Emulsified oil |
| Mechanism | Adsorption | Adsorption, chelating | Flocculation | Flocculation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Fan, Q.; Zhu, C.; Liu, J.; Zhu, M.; Wang, X.; Niu, A. Preparation and Application of Magnetic Composites Using Controllable Assembly for Use in Water Treatment: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 5799. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155799
Zhao Y, Liu Y, Xu H, Fan Q, Zhu C, Liu J, Zhu M, Wang X, Niu A. Preparation and Application of Magnetic Composites Using Controllable Assembly for Use in Water Treatment: A Review. Molecules. 2023; 28(15):5799. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155799
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yuan, Yinhua Liu, Hang Xu, Qianlong Fan, Chunyou Zhu, Junhui Liu, Mengcheng Zhu, Xuan Wang, and Anqi Niu. 2023. "Preparation and Application of Magnetic Composites Using Controllable Assembly for Use in Water Treatment: A Review" Molecules 28, no. 15: 5799. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155799
APA StyleZhao, Y., Liu, Y., Xu, H., Fan, Q., Zhu, C., Liu, J., Zhu, M., Wang, X., & Niu, A. (2023). Preparation and Application of Magnetic Composites Using Controllable Assembly for Use in Water Treatment: A Review. Molecules, 28(15), 5799. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28155799






