CO2 Capture Mechanism by Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed by Choline Prolinate and Ethylene Glycol
Abstract
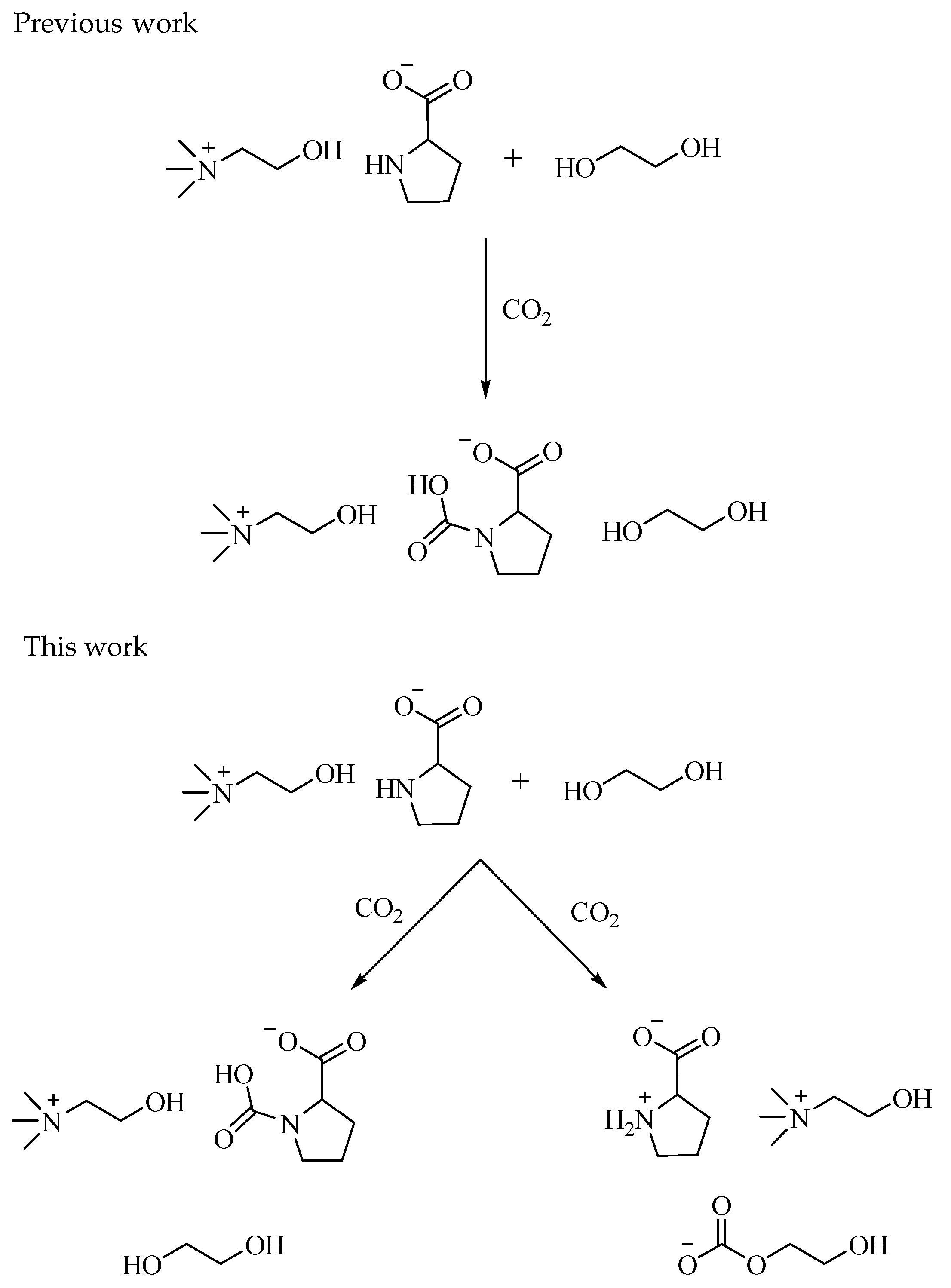
1. Introduction
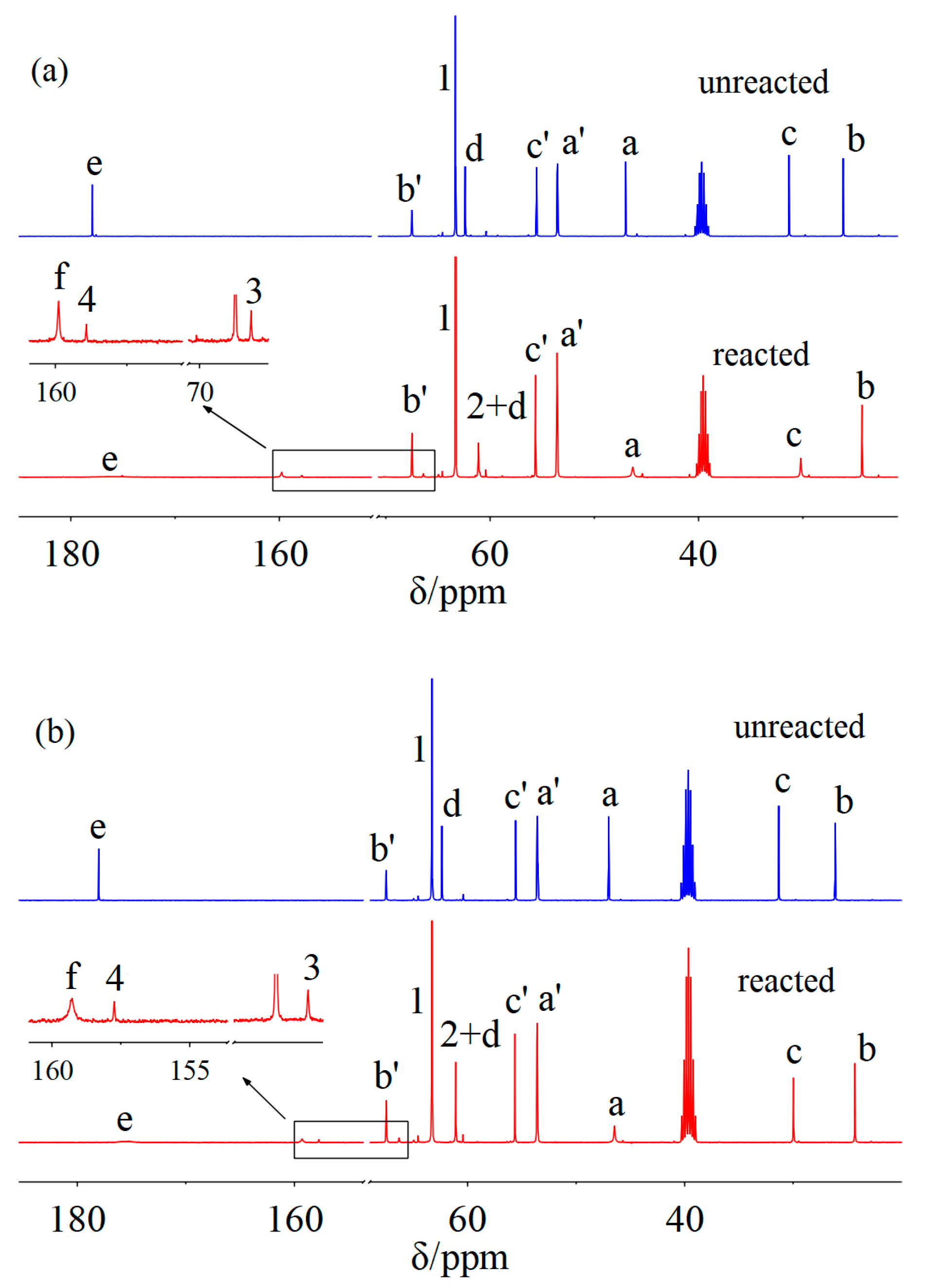
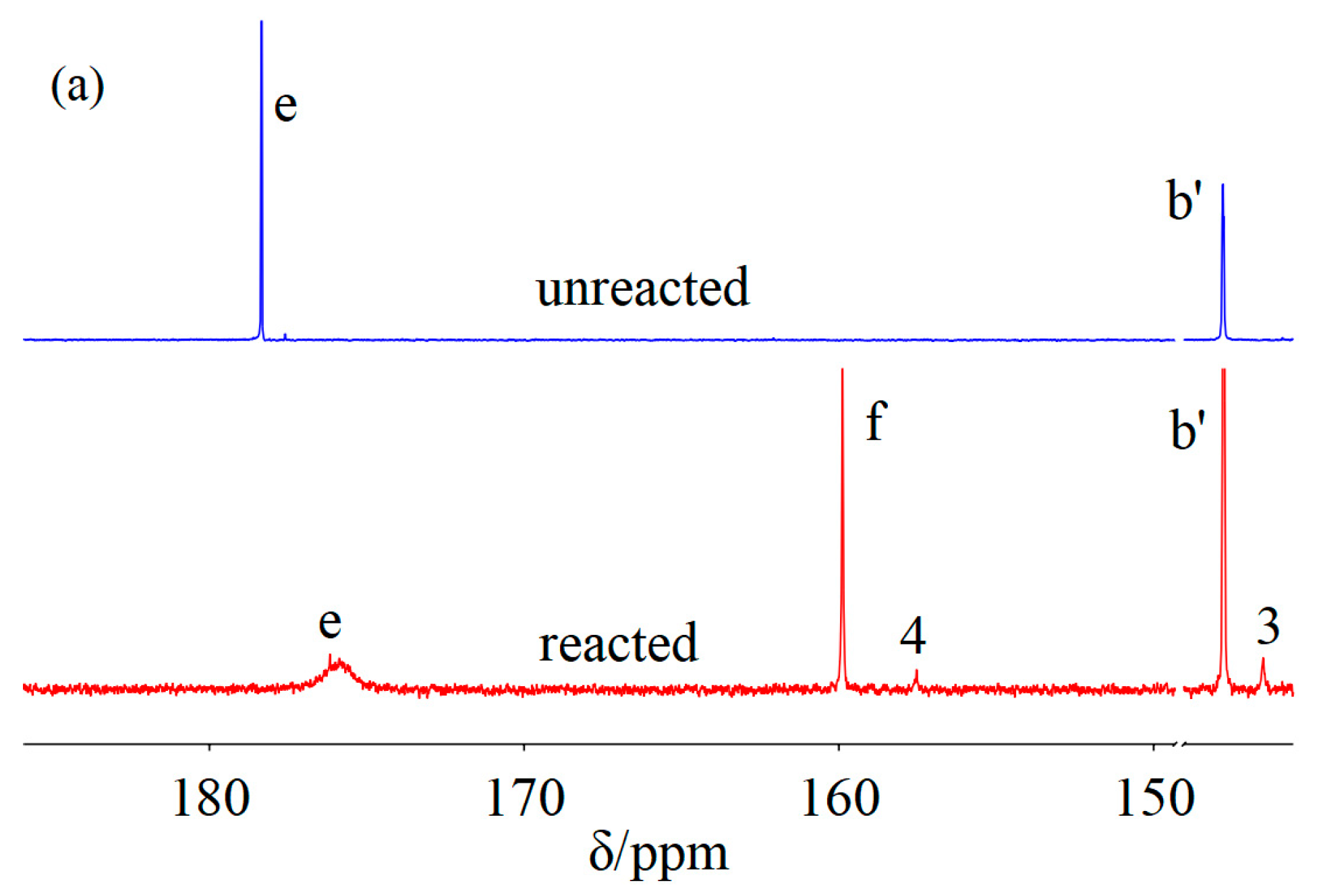
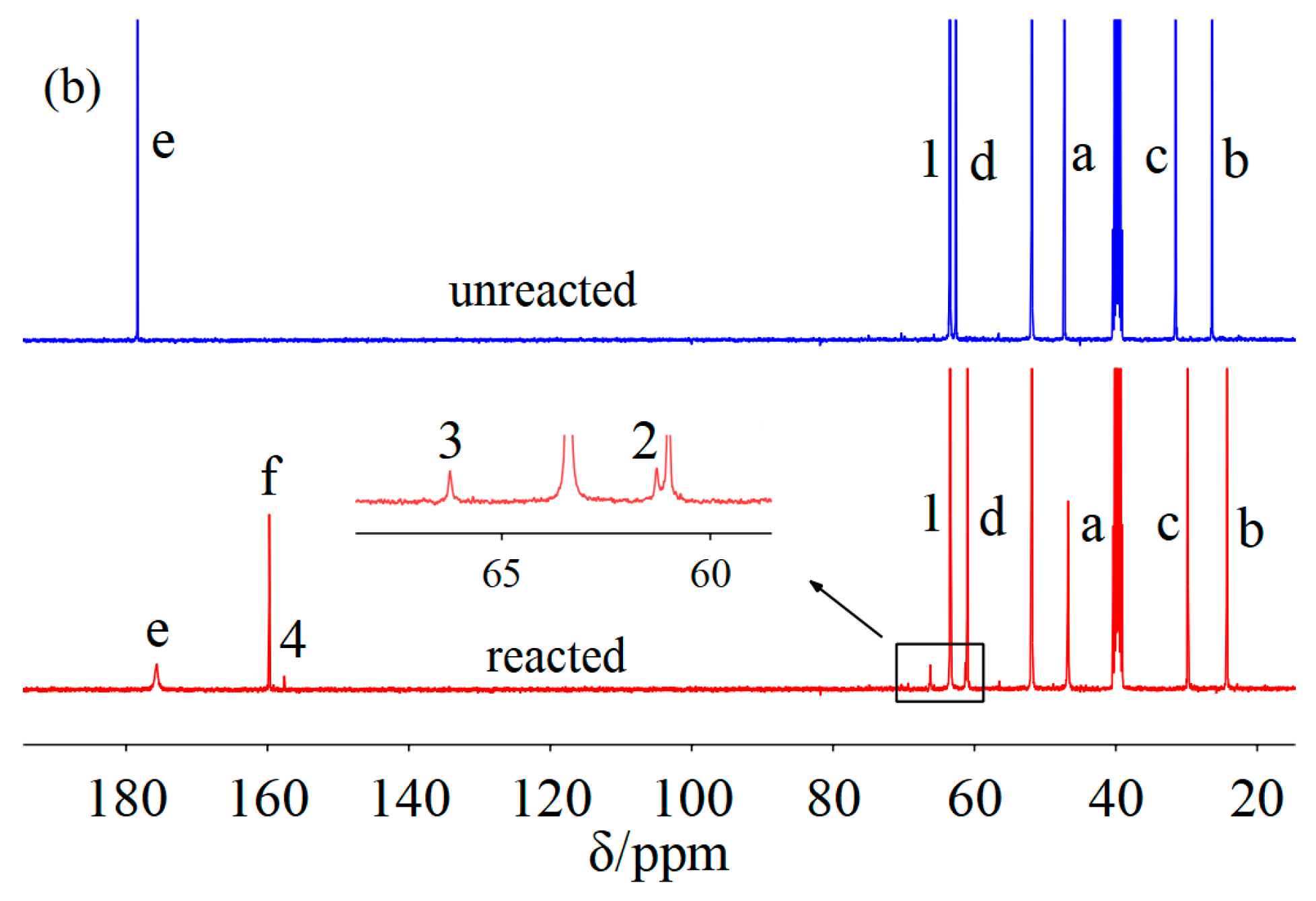
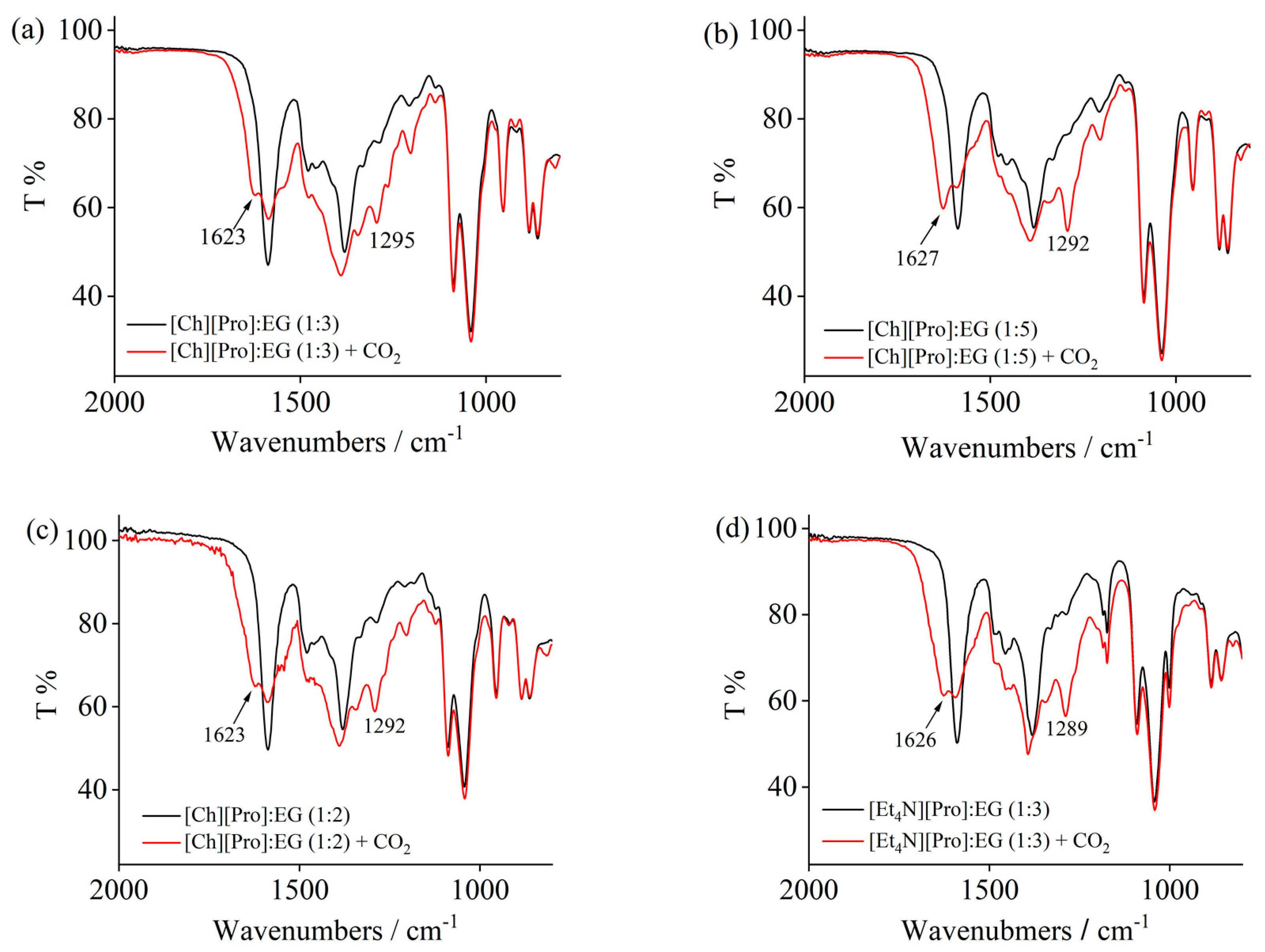
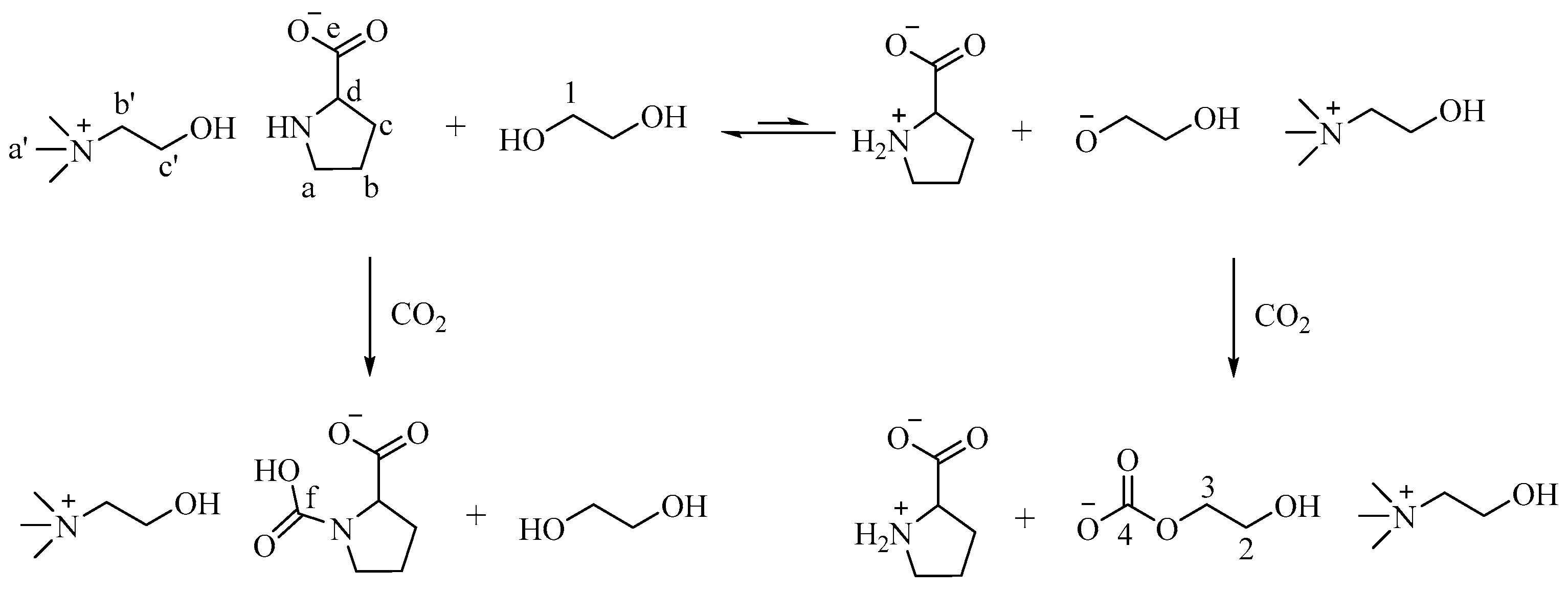
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Characterizations
3.2. Synthesis of Proline-Based ILs
3.3. Synthesis of DESs
- [Ch][Pro]:EG (1:2): 13C NMR (151 MHz, d6-DMSO) δ = 178.2, 67.4, 63.2, 62.4, 55.4, 53.4, 47.0, 31.3, 26.1 ppm. FTIR: ν = 3282, 2920, 2866, 1587, 1480, 1378, 1089, 1037, 958, 885, 863, 635 cm−1.
- [Ch][Pro]:EG (1:3): 13C NMR (151 MHz, d6-DMSO) δ = 177.8, 67.3, 63.2, 62.2, 55.4, 53.4, 46.8, 31.1, 26.0 ppm. FTIR: ν = 3283, 2924, 2872, 1587, 1480, 1381, 1086, 1039, 954, 884, 861, 627 cm−1.
- [Ch][Pro]:EG (1:4): 13C NMR (151 MHz, d6-DMSO) δ = 178.4, 67.5, 63.2, 62.4, 55.5, 53.5, 46.9, 31.3, 26.1 ppm. FTIR: ν = 3285, 2928, 2870, 1587, 1480, 1382, 1087, 1039, 953, 883, 861, 624 cm−1.
- [Ch][Pro]:EG (1:5): 13C NMR (151 MHz, d6-DMSO) δ = 177.9, 67.3, 63.1, 62.2, 55.4, 53.4, 46.8, 31.3, 26.0 ppm. FTIR: ν = 3290, 2932, 2864, 1587, 1480, 1382, 1087, 1038, 954, 884, 861, 623 cm−1.
- [Et4N][Pro]:EG (1:3): 13C NMR (151 MHz, d6-DMSO) δ = 178.1, 63.2, 62.4, 51.6, 47.1, 31.3, 26.1, 7.1 ppm. FTIR: ν = 3285, 2922, 2869, 1588, 1457, 1382, 1175, 1092, 1043, 1002, 884, 855, 784, 636 cm−1.
3.4. Absorption of CO2
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Raganati, F.; Miccio, F.; Ammendola, P. Adsorption of Carbon Dioxide for Post-combustion Capture: A Review. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 12845–12868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omodolor, I.S.; Otor, H.O.; Andonegui, J.A.; Allen, B.J.; Alba-Rubio, A.C. Dual-Function Materials for CO2 Capture and Conversion: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 17612–17631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Liang, S.; Wang, R.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Xie, B.; Toe, C.Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Industrial carbon dioxide capture and utilization: State of the art and future challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8584–8686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langie, K.M.G.; Tak, K.; Kim, C.; Lee, H.W.; Park, K.; Kim, D.; Jung, W.; Lee, C.W.; Oh, H.-S.; Lee, D.K.; et al. Toward economical application of carbon capture and utilization technology with near-zero carbon emission. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghel, B.; Janati, S.; Wongwises, S.; Shadloo, M.S. Review on CO2 capture by blended amine solutions. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2022, 119, 103715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyanaya, M.I.; Yushkin, A.A.; Bakhtin, D.S.; Legkov, S.A.; Bazhenov, S.D. Perstraction of Heat-Stable Salts from Aqueous Alkanolamine Solutions. Pet. Chem. 2022, 62, 1254–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Cui, C.; Dong, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, H. An overview on the corrosion mechanisms and inhibition techniques for amine-based post-combustion carbon capture process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 304, 122091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.E.; Pattanayak, S.; Berben, L.A. Reactive Capture of CO2: Opportunities and Challenges. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 766–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Zhang, X.; Bai, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Bao, D.; Li, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S. Ionic-Liquid-Based CO2 Capture Systems: Structure, Interaction and Process. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9625–9673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, Q.R.; Schneider, W.F.; Maginn, E.J. Role of Molecular Modeling in the Development of CO2–Reactive Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 5242–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaie, M.; Rezaei, N.; Zendehboudi, S. A systematic review on CO2 capture with ionic liquids: Current status and future prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 96, 502–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.-F.; Huang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Zhu, X.; Tao, D.-J.; Jiang, D.-E.; Dai, S. Multi-Molar Absorption of CO2 by the Activation of Carboxylate Groups in Amino Acid Ionic Liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7166–7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shama, V.M.; Swami, A.R.; Aniruddha, R.; Sreedhar, I.; Reddy, B.M. Process and engineering aspects of carbon capture by ionic liquids. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 48, 101507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Xue, Z.; Mu, T. Deep eutectic solvents as a green toolbox for synthesis. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2022, 3, 100809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Achkar, T.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fourmentin, S. Basics and properties of deep eutectic solvents: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liang, Q.; Yu, X.; Lü, Q.-F.; Ma, L.; Qin, X.; Chen, G.; Li, B. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Boosting Electrochemical Energy Storage and Conversion: A Review and Perspective. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2011102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.A.; Sadeghi, R. Physicochemical properties of deep eutectic solvents: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 360, 119524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.B.; Spittle, S.; Chen, B.; Poe, D.; Zhang, Y.; Klein, J.M.; Horton, A.; Adhikari, L.; Zelovich, T.; Doherty, B.W.; et al. Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review of Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 1232–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Xue, Z.; Mu, T. Eutectics: Formation, properties, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8596–8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Vicent-Luna, J.M.; Tao, S.; Calero, S.; Jiménez Riobóo, R.J.; Ferrer, M.L.; del Monte, F.; Gutiérrez, M.C. Transitioning from Ionic Liquids to Deep Eutectic Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 1232–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skowrońska, D.; Wilpiszewska, K. Deep Eutectic Solvents for Starch Treatment. Polymers 2022, 14, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, D.-J.; Qu, F.; Li, Z.-M.; Zhou, Y. Promoted absorption of CO at high temperature by cuprous-based ternary deep eutectic solvents. AIChE J. 2021, 67, e17106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shi, M.; Zhang, P.; Tu, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y. Tuning the composition of deep eutectic solvents consisting of tetrabutylammonium chloride and n-decanoic acid for adjustable separation of ethylene and ethane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Ji, X. Ionic liquids/deep eutectic solvents for CO2 capture: Reviewing and evaluating. Green Energy Environ. 2021, 6, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, D.; Ge, C.; Fan, W.; Chen, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; et al. Tuning ionic liquid-based functional deep eutectic solvents and other functional mixtures for CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 463, 142298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, M.; van den Bruinhorst, A.; Zubeir, L.F.; Peters, C.J.; Kroon, M.C. A new low transition temperature mixture (LTTM) formed by choline chloride + lactic acid: Characterization as solvent for CO2 capture. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2013, 340, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leron, R.B.; Caparanga, A.; Li, M.-H. Carbon dioxide solubility in a deep eutectic solvent based on choline chloride and urea at T = 303.15–343.15K and moderate pressures. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 44, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, X.; Lu, X. Choline-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 separation: Review and thermodynamic analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 97, 436–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmad, S.; Xie, Y.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Ji, X. Screening of deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as green CO2 sorbents: From solubility to viscosity. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Keshri, S.; Bharti, A.; Kumar, S.; Mogurampelly, S. Solubility of Gases in Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents from Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 4659–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, E.; Hadj-Kali, M.K.; Mulyono, S.; Alnashef, I. Analysis of operating conditions for CO2 capturing process using deep eutectic solvents. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2016, 47, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Huang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Gao, J.; Zeng, S. Imidazole tailored deep eutectic solvents for CO2 capture enhanced by hydrogen bonds. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 27306–27316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, T.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Jeong, Y.K.; Choi, J.W. Deep eutectic solvents as attractive media for CO2 capture. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 2834–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Nikjoo, D.; Mikkola, J.-P. Is basicity the sole criterion for attaining high carbon dioxide capture in deep-eutectic solvents? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 966–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Ren, S.; Wu, W. Efficient and Reversible Absorption of CO2 by Functional Deep Eutectic Solvents. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 7727–7733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Ren, S.; Sun, Y.; Wu, W. Hydrophobic Functional Deep Eutectic Solvents Used for Efficient and Reversible Capture of CO2. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 6809–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Hao, J.; Zhu, M.; Sun, P.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Xu, X. Development of green solvents for efficient post-combustion CO2 capture with good regeneration performance. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 59, 101955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Lv, M.; Yang, D. Efficient CO2 absorption by azolide-based deep eutectic solvents. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 1426–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Yang, D. CO2 capture by 1,2,3-triazole-based deep eutectic solvents: The unexpected role of hydrogen bonds. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 7376–7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-Y.; Penley, D.; Klemm, A.; Dean, W.; Gurkan, B. Deep Eutectic Solvent Formed by Imidazolium Cyanopyrrolide and Ethylene Glycol for Reactive CO2 Separations. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wu, C.; Yang, D. The Influence of Hydrogen Bond Donors on the CO2 Absorption Mechanism by the Bio-Phenol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Molecules 2021, 26, 7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Zhao, L.; Bai, Y.; Li, F.; Dong, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, S. Superbase Ionic Liquid-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents for Improving CO2 Absorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 2523–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Wang, X.; Sang, H.; Liu, J.; Lin, X.; Zhang, L. Highly efficient absorption of carbon dioxide by EG-assisted DBU-based deep eutectic solvents. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 43, 101372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, H.; Su, L.; Han, W.; Si, F.; Yue, W.; Zhou, X.; Peng, Z.; Fu, H. Basicity-controlled DBN-based deep eutectic solvents for efficient carbon dioxide capture. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 65, 102201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Yang, D.; Wu, C.; Chen, J. Deep eutectic solvents composed of bio-phenol-derived superbase ionic liquids and ethylene glycol for CO2 capture. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 2160–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Ma, J.; Yang, N.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Tantai, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L. Superbase/Acylamido-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents for Multiple-Site Efficient CO2 Absorption. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 7569–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, M.; Lu, B.; Zhang, S.; Yang, D. Effect of Hydrogen Bonds on CO2 Capture by Functionalized Deep Eutectic Solvents Derived from 4-Fluorophenol. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 6272–6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, L. Highly Efficient and Reversible CO2 Capture by Task-Specific Deep Eutectic Solvents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 13321–13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Mikkola, J.-P. Intermolecular interactions upon carbon dioxide capture in deep-eutectic solvents. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 24591–24601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, A.; Vicchio, S.P.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Cagli, E.; Park, Y.; Zeeshan, M.; Dikki, R.; Liu, H.; Kidder, M.K.; Getman, R.B.; et al. Impact of Hydrogen Bonds on CO2 Binding in Eutectic Solvents: An Experimental and Computational Study toward Sorbent Design for CO2 Capture. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 3740–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, R.; Tang, F.; You, K.; Luo, H.A.; Zhang, X. SnO2/ATP catalyst enabling energy-efficient and green amine-based CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 453, 139801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Tan, Z.; Zhao, S.; Peng, Y.; Xiang, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, R. One-step synthesis of efficient manganese-based oxide catalyst for ultra-rapid CO2 absorption in MDEA solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Tang, F.; Tan, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, S.; Xiang, C.; Sun, H.; Zhao, F.; You, K.; et al. Solid base LDH-catalyzed ultrafast and efficient CO2 absorption into a tertiary amine solution. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 278, 118889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, M.; Xu, J. CO2 Capture Mechanism by Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed by Choline Prolinate and Ethylene Glycol. Molecules 2023, 28, 5461. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145461
Chen M, Xu J. CO2 Capture Mechanism by Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed by Choline Prolinate and Ethylene Glycol. Molecules. 2023; 28(14):5461. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145461
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Mingzhe, and Jinming Xu. 2023. "CO2 Capture Mechanism by Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed by Choline Prolinate and Ethylene Glycol" Molecules 28, no. 14: 5461. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145461
APA StyleChen, M., & Xu, J. (2023). CO2 Capture Mechanism by Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed by Choline Prolinate and Ethylene Glycol. Molecules, 28(14), 5461. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145461





