Degradation and Extraction of Organochlorine Pollutants from Environmental Solids under Subcritical Water Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Chlorinated Pollutants
1.2. Traditional Remediation Methods
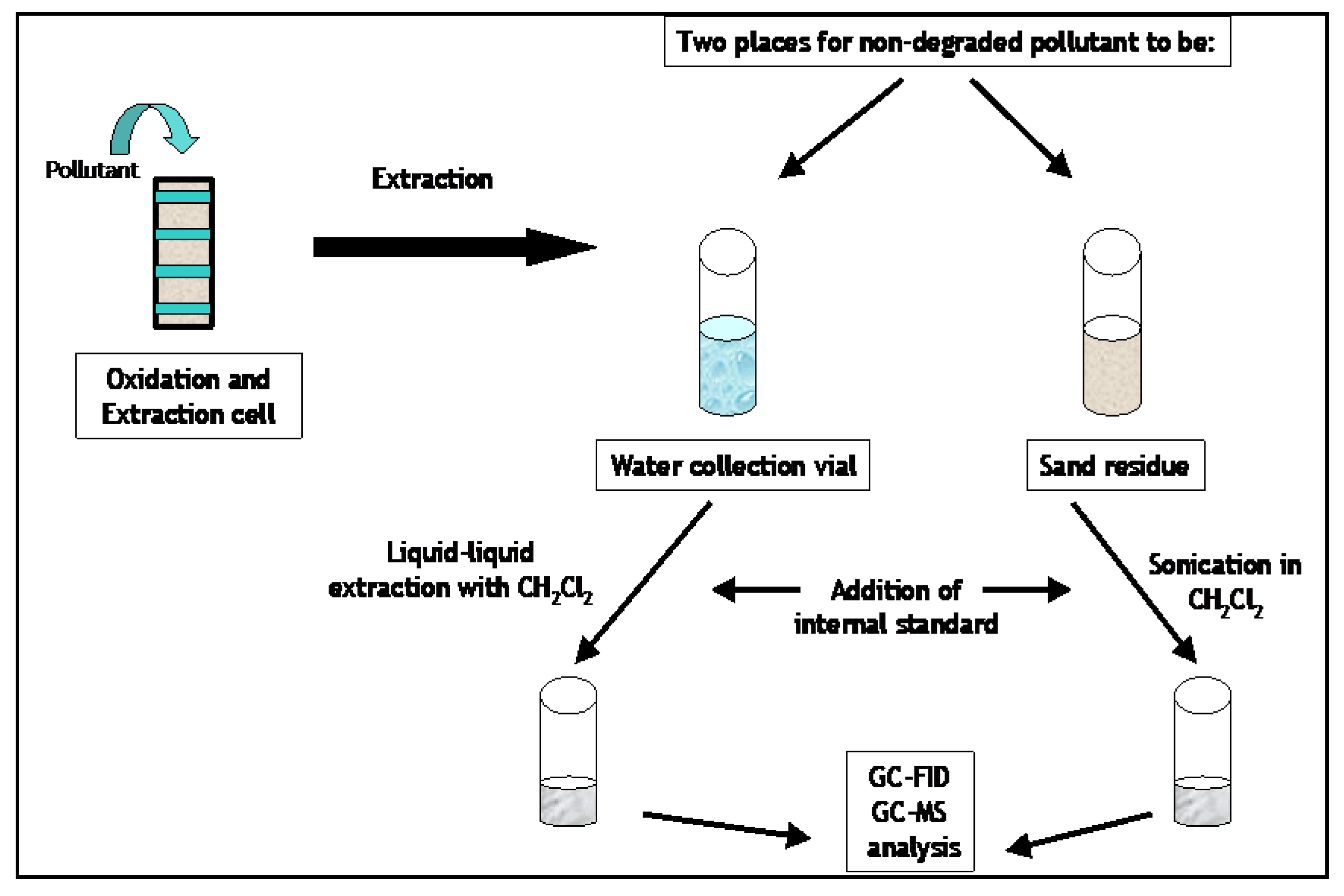
1.3. Extractions of Contaminated Environmental Solids
1.4. Chemical Conversion and Destruction Methods
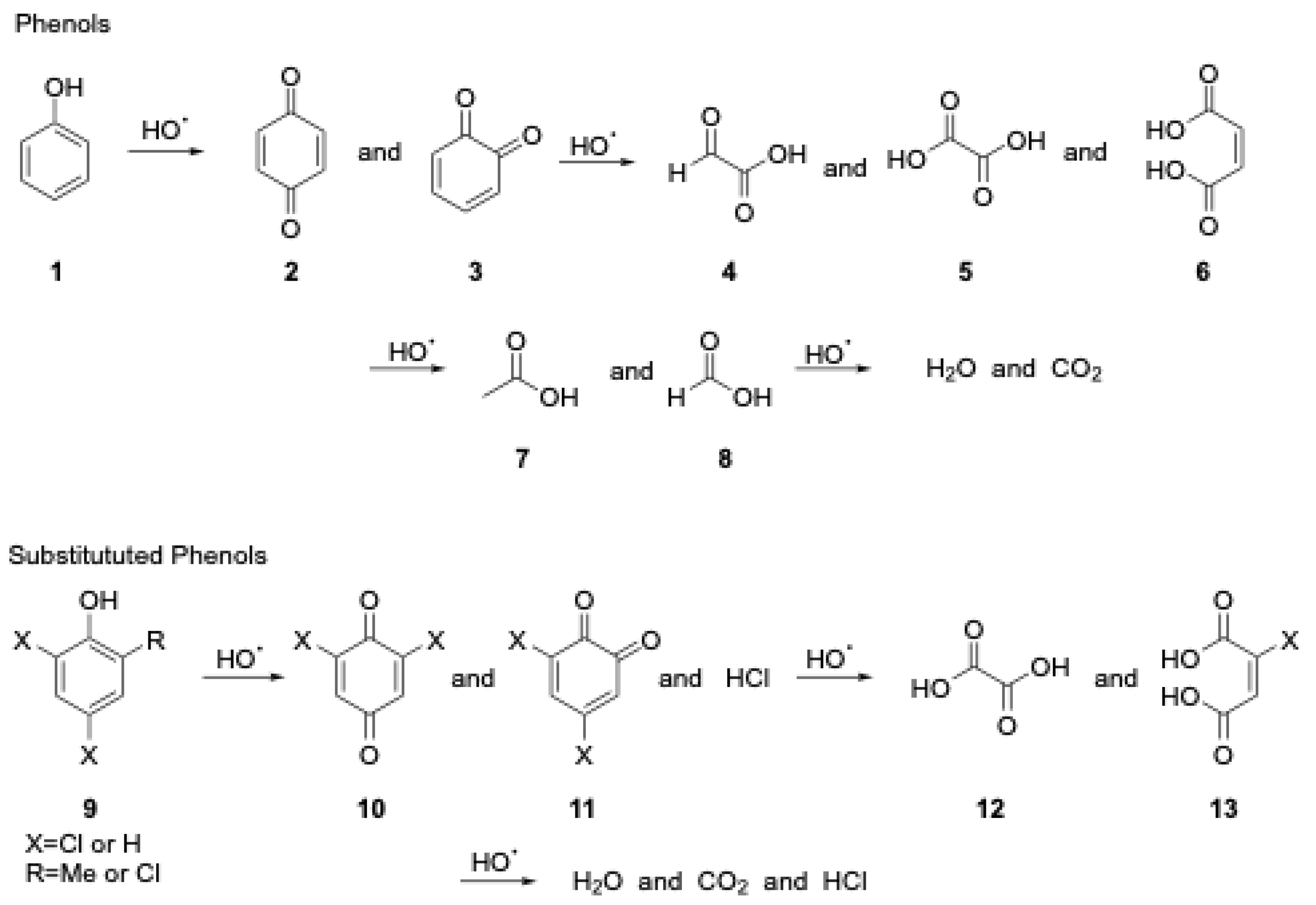
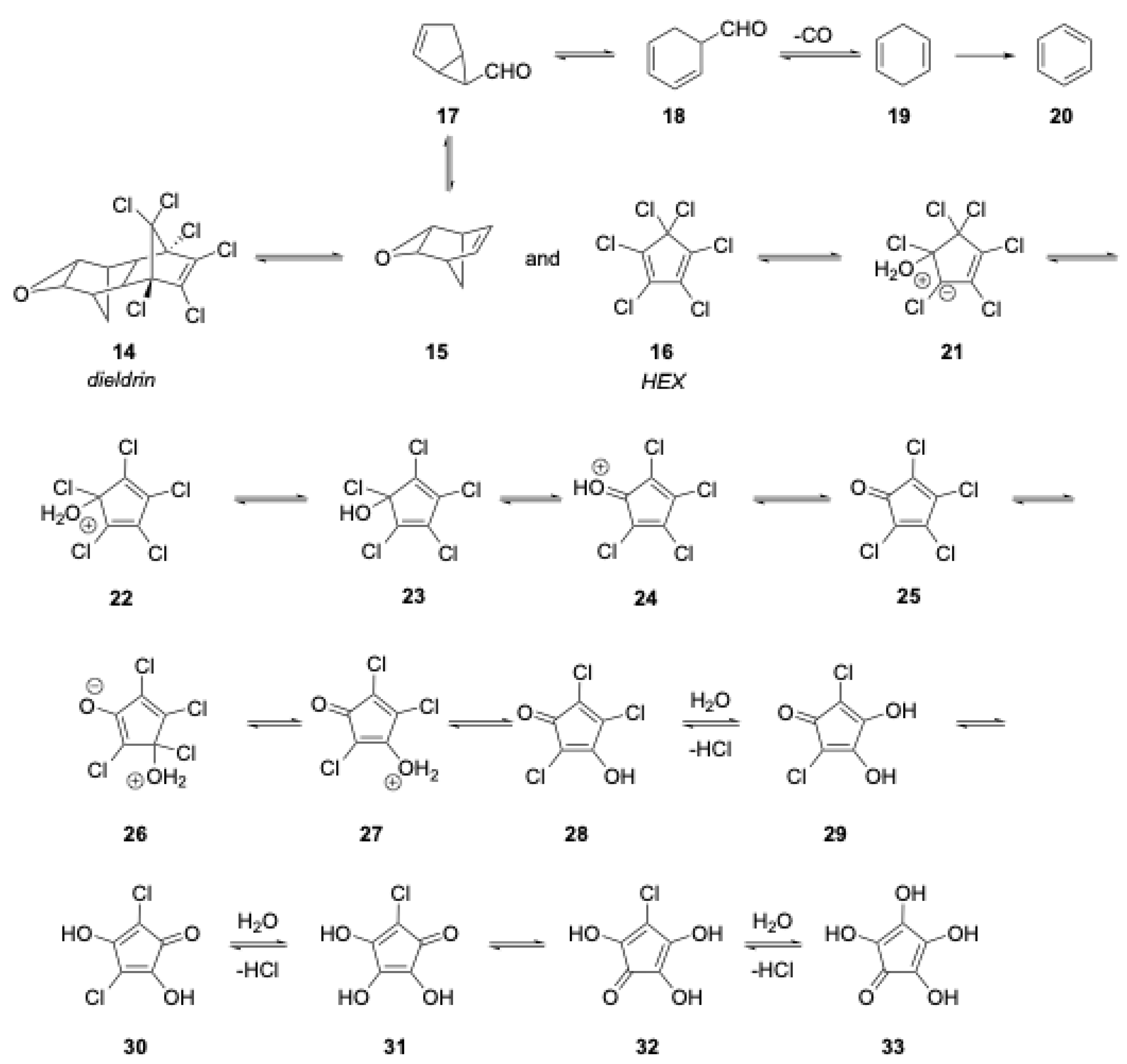
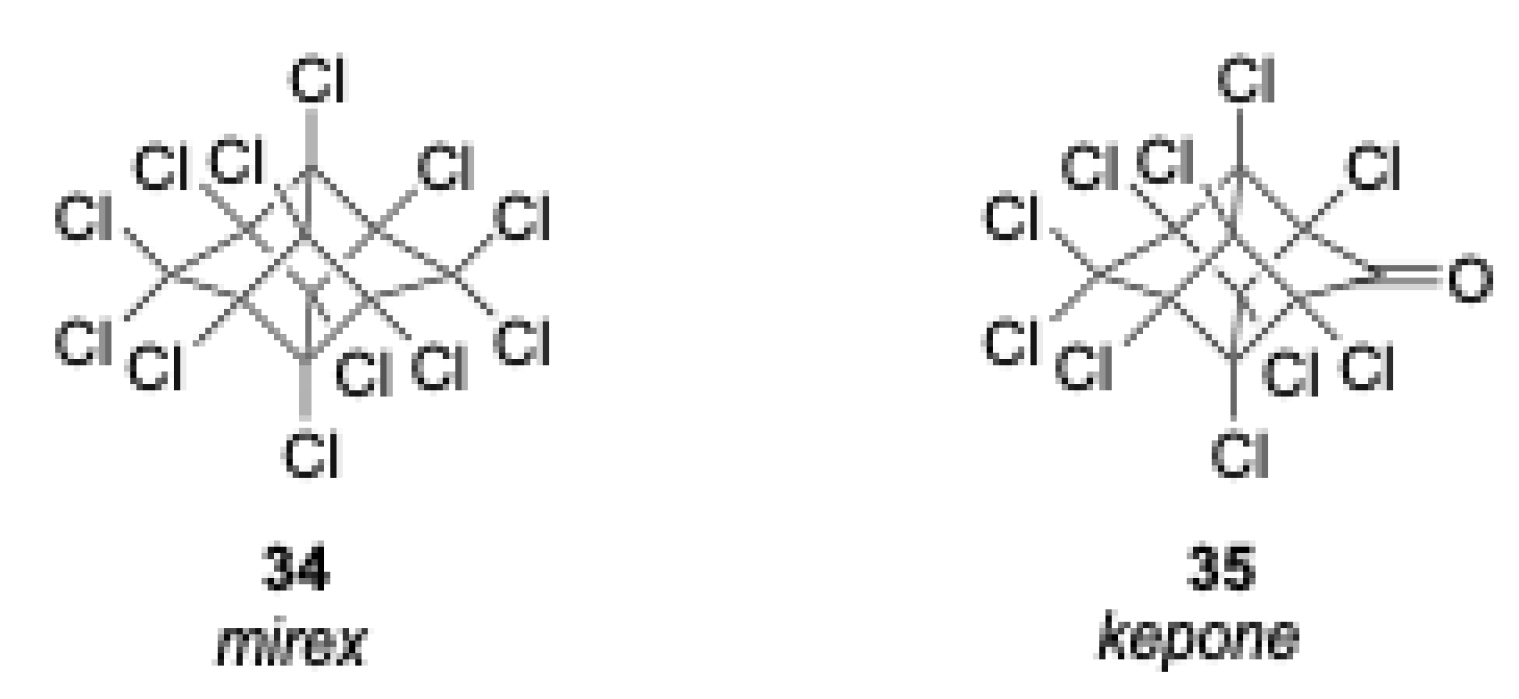
1.5. Organic Degradation Mechanisms
1.6. Purpose of This Study
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Wet Oxidation
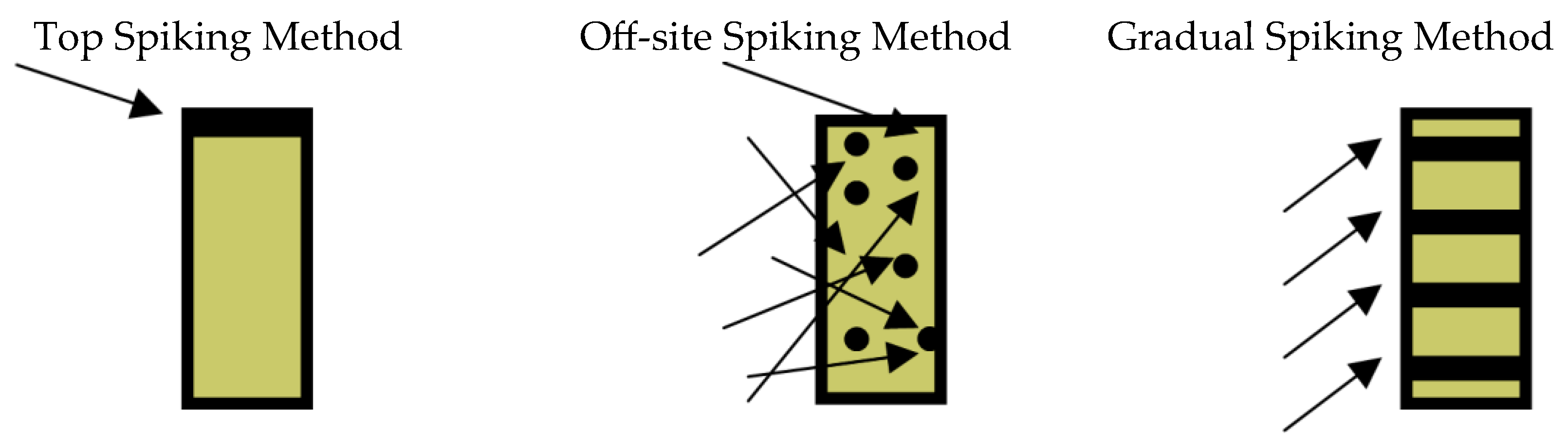
2.2. Spiking Studies
2.3. Oxidation and Extraction of Chlorophenols from Sand
2.4. Degradation and Extraction of PBT Compounds from Sand
2.4.1. Dieldrin
2.4.2. Mirex
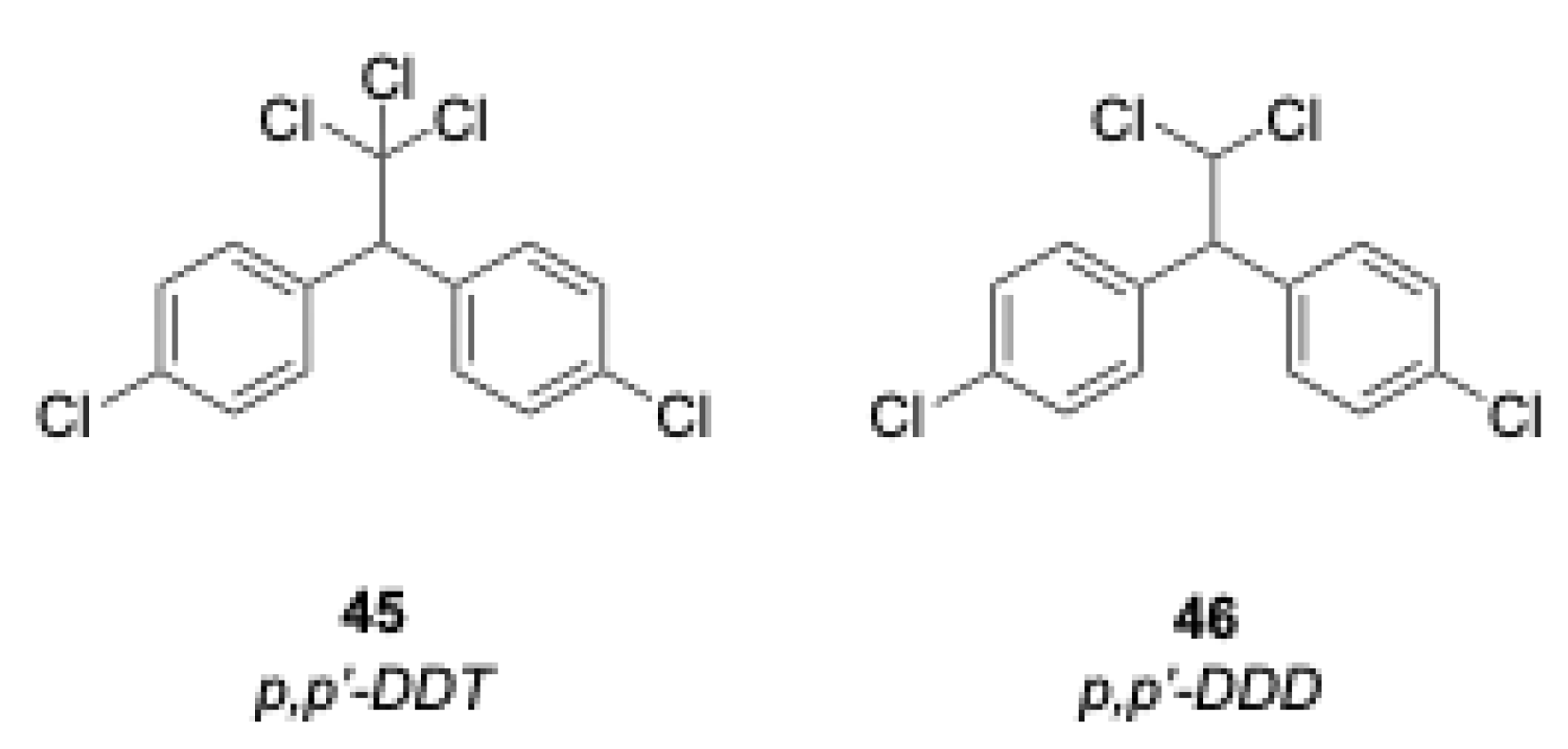
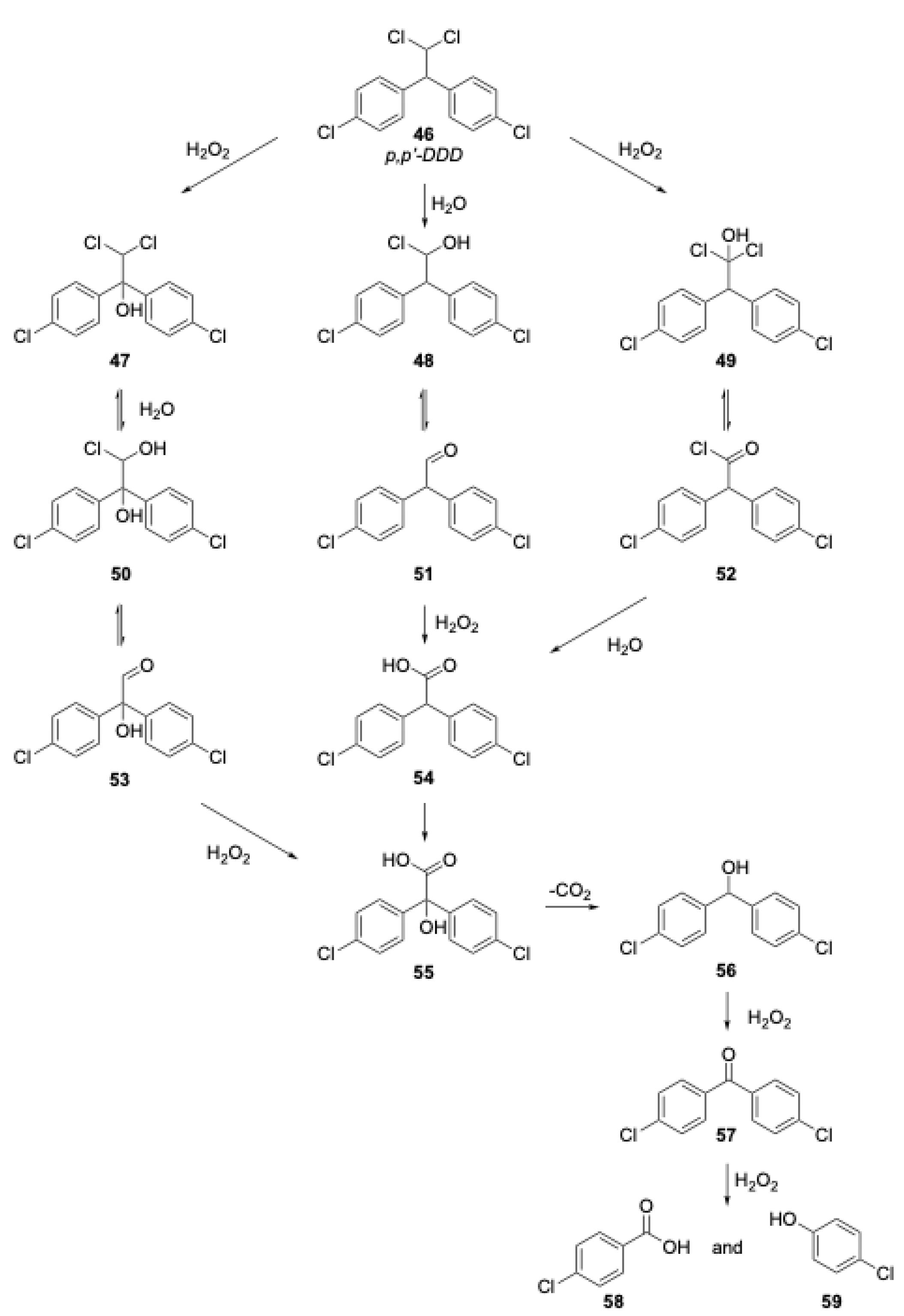
2.4.3. p,p′-DDD
2.5. Degradation and Extraction of DDT from Environmental Solid Samples
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Reagents and Materials
3.2. Standard and Sample Preparations
3.3. Procedures
3.3.1. Wet Oxidation
3.3.2. Spiking Methods
3.3.3. Oxidation and Extraction of Chlorophenols from Sand
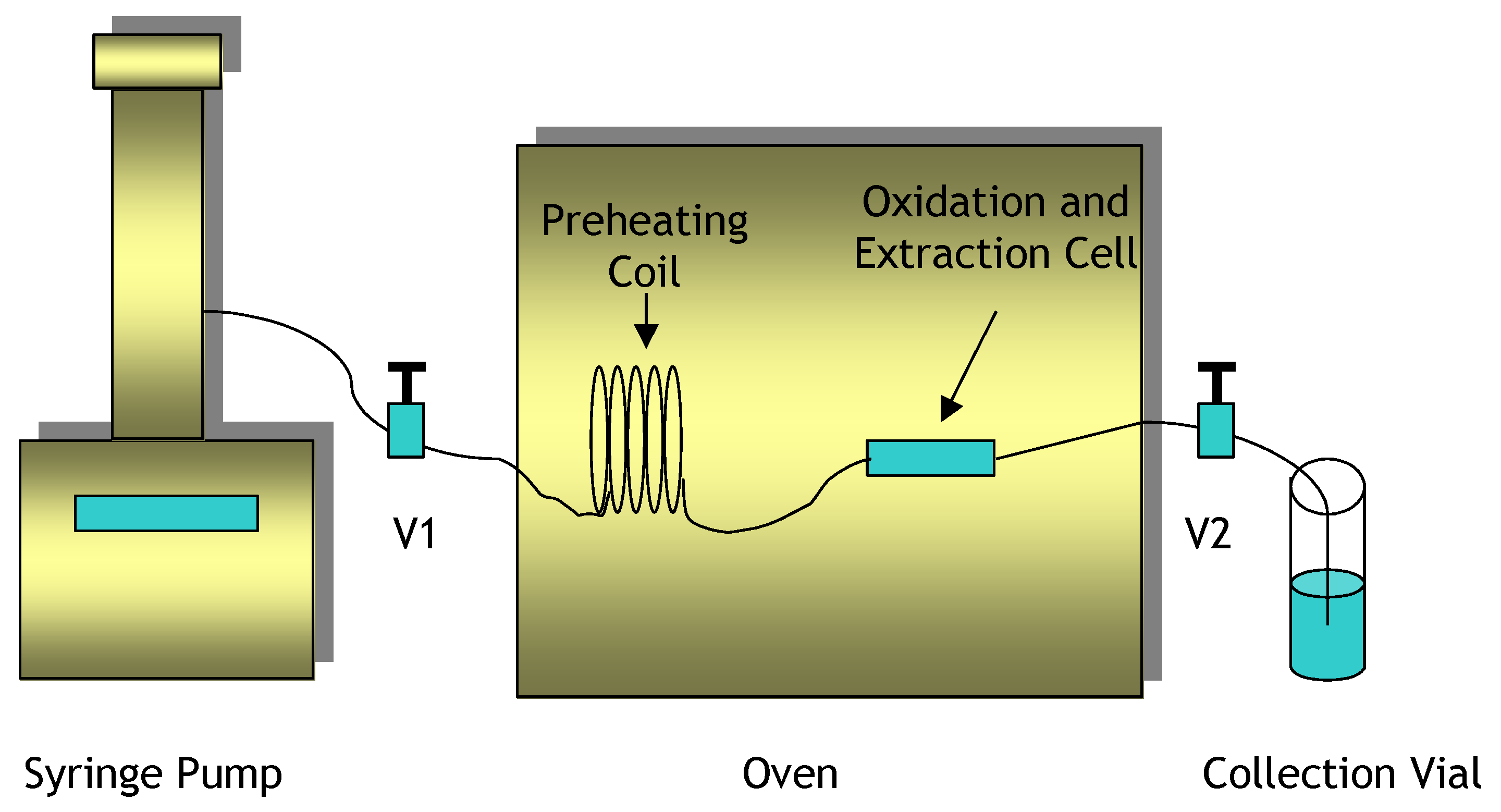
3.3.3.1. Hydrogen Peroxide Oxidation and Subcritical Water Extraction System
3.3.3.2. Preparation for Analysis
3.3.3.3. Water Extract
3.3.3.4. Sand Residues
3.4. Degradation and Extraction of PBT Pollutants from Sand
3.5. Degradation and Extraction of DDT from an Environmental Soil Sample
3.6. Gas Chromatographic Analysis
3.7. UV–Vis Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Persistent, Bioaccumulative, and Toxic (PBT) Chemicals under TSCA Section 6(h). PBT Program Accomplishments. 2000. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/assessing-and-managing-chemicals-under-tsca/persistent-bioaccumulative-and-toxic-pbt-chemicals (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- Forstner, U. Lecture Notes in Earth Sciences: Contaminated Sediments; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, J.R. Extraction Methods for Environmental Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lagadec, A.J.M.; Miller, D.J.; Lille, A.V.; Hawthorne, S.B. Pilot-Scale Subcritical Water Remediation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon- and Pesticide-Contaminated Soil. ACS Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne, S.B.; Lagadec, A.J.M.; Kalderis, D.; Lilke, A.V.; Miller, D.J. Pilot-Scale Destruction of TNT, RDX, and HMX on Contaminated Soils Using Subcritical Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3224–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Park, J.; Shin, M.; Park, H. Decontamination of PCBs-containing soil using subcritical water extraction process. Chemosphere 2014, 109, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doctor, N.; Yang, Y. Destruction of Polychlorinated Biphenyls under Subcritical Water Conditions in the Presence of Hydrogen Peroxide or Sodium Hydroxide. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 2018, 9, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.E.; Anderson, M.A.; Hill, C.G.; Zeltner, W.A. Wet Peroxide Oxidation of Sediments Contaminated with PCBs. ACS Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3199–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronholm, J.; Kalpala, J.; Hartonen, K.; Reikkola, M. Pressurized hot water extraction coupled with supercritical water oxidation in remediation of sand and soil containing PAHs. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2002, 23, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabalak, E.; Murat Gizir, A. Treatment of agrochemical wastewater by subcritical water oxidation method: Chemical composition and ion analysis of treated and untreated samples. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 55, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Miao, Z.; Shao, X.; Chen, J.; Lu, X. Comparison of subcritical water extraction and microwave-assisted water extraction for the determination of chlorophenols in polluted lake sediments. Anal. Methods 2012, 4, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Taniguchi, S.; Giri, R.R.; Ozaki, H. Oxidative degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) in subcritical and supercritical waters. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachance, R.; Paschkewitz, J.; DiNaro, J.; Tester, J.W. Thiodiglycol hydrolysis and oxidation in sub- and supercritical water. J. Supercrit. Fluids 1999, 16, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubatova, A.; Lagadec, A.J.M.; Hawthorne, S.B. Dechlorination of Lindane, Dieldrin, Tetrachloroethane, Trichloroethene, and PVC in Subcritical Water. ACS Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, A.; Abouseoud, M.; Amrane, A. Phenol Removal by a Sequential Combined Fenton-Enzymatic Process. Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2017, 16, 321–330. [Google Scholar]
- Bautista, P.; Mohendano, A.; Amrane, A. An overview of the application of Fenton oxidation to industrial wastewaters treatments. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 83, 1323–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemperline, P.J.; Yang, Y.; Bian, Z. Characterization of subcritical water oxidation with in situ monitoring and self-modeling curve resolution. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 485, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluyev, N.; Cheleptchikov, A.; Brodsky, E.; Soyfer, V.; Zhilnikov, V. Reductive dechlorination of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins by zerovalent iron in subcritical water. Chemosphere 2002, 46, 1293–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, P.A.; Gschwend, P.M.; Swallow, K.C.; Peters, W.A.; Tester, J.W. Product distribution and reaction pathways for methylene chloride hydrolysis and oxidation under hydrothermal conditions. J. Supercrit. Fluids 1998, 12, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmarathane, W.N.K.; Mackie, J.C.; Kennedy, E.M.; Stockenhuber, M. Pyrolysis of Dieldrin and Formation of Toxic Products; The University of Newcastle: Newcastle, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Newcomer, J.S.; McBee, E.T. The Chemical Behavior of Hexachlorocyclopentadiene. I. Transformation to Octachloro-3a,4,7,7a-Tetrahydro-4,7-methanoindene-1,8-dione. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1949, 71, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, M. Carpentier “Cyclic polycarbonyl compounds. VI. Products resulting from the degradation of 1,2,4-trihydroxycyclopent-1-ene-3,5-dione in sulfuric acid medium. Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 1973, 7–8, 2214–2216. [Google Scholar]
- Beattie, J.K.; Fleming, D.S. Destructive Oxidation of Mirex. Aust. J. Chem. 1998, 51, 973–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, D.A.; Konyha, K.D.; Wheeler, W.B.; Marshall, G.P.; Zaylskie, R.G. Mirex in the Environment: Its Degradation to Kepone and Related Compounds. Science 1976, 194, 939–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoro, J.A.; Hunter, J.M.; Eglington, G. Degradation of p,p’-DDT in Reducing Environments. Nature 1974, 247, 235–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
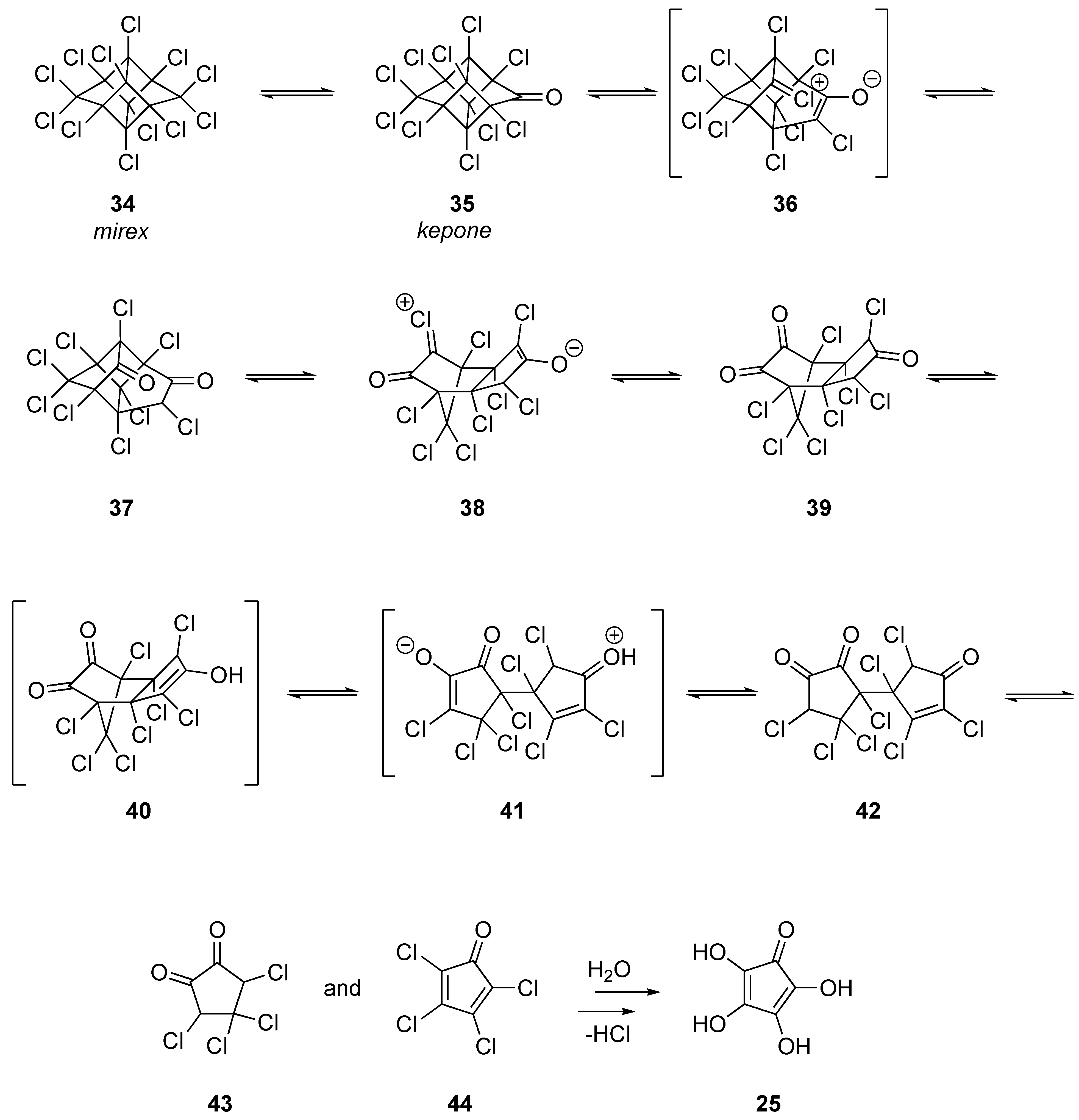
| 150 °C | 200 °C | 250 °C | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % Removed (%RSD) | % Degraded (%RSD) | % Removed (%RSD) | % Degraded (%RSD) | % Removed (%RSD) | % Degraded (%RSD) | |
| 100% H2O | 80.3(178) | 46.9(29) | 97.8(0) | 64.9(24) | 99.9(0) | 97.5(4) |
| 3% H2O2 | 68.5(21) | 41.6(23) | 97.9(0) | 86.8(5) | 100(0) | 99.4(1) |
| 200 °C | 250 °C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % Removed (%RSD) | % Degraded (%RSD) | % Removed (%RSD) | % Degraded (%RSD) | |
| 100% H2O | 99.0(0) | 33.3(10) | 99.9(0) | 58.3(3) |
| 3% H2O2 | 90.8(18) | 50.0(40) | 100(0) | 58.2(17) |
| 200 °C | 250 °C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % Removed (%RSD) | % Degraded (%RSD) | % Removed (%RSD) | % Degraded (%RSD) | |
| 100% H2O | 99.6(1) | 51.2(7) | 99.8(1) | 92.6(8) |
| 3% H2O2 | 84.6(16) | 72.4(16) | 99.8(1) | 92.8(12) |
| 200 °C | 250 °C | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| % Removed (%RSD) | % Degraded (%RSD) | % Removed (%RSD) | % Degraded (%RSD) |
| 97.8(0.7) | 94.0(0.7) | 99.9(0.1) | 99.8(0.1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jones, A.D.; Morehead, A.T., Jr.; Yang, Y. Degradation and Extraction of Organochlorine Pollutants from Environmental Solids under Subcritical Water Conditions. Molecules 2023, 28, 5445. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145445
Jones AD, Morehead AT Jr., Yang Y. Degradation and Extraction of Organochlorine Pollutants from Environmental Solids under Subcritical Water Conditions. Molecules. 2023; 28(14):5445. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145445
Chicago/Turabian StyleJones, Aaryn D., Andrew T. Morehead, Jr., and Yu Yang. 2023. "Degradation and Extraction of Organochlorine Pollutants from Environmental Solids under Subcritical Water Conditions" Molecules 28, no. 14: 5445. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145445
APA StyleJones, A. D., Morehead, A. T., Jr., & Yang, Y. (2023). Degradation and Extraction of Organochlorine Pollutants from Environmental Solids under Subcritical Water Conditions. Molecules, 28(14), 5445. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145445







