The Enhancement of CO2 and CH4 Capture on Activated Carbon with Different Degrees of Burn-Off and Surface Chemistry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Adsorption of Carbon Dioxide and Methane on Activated Carbon
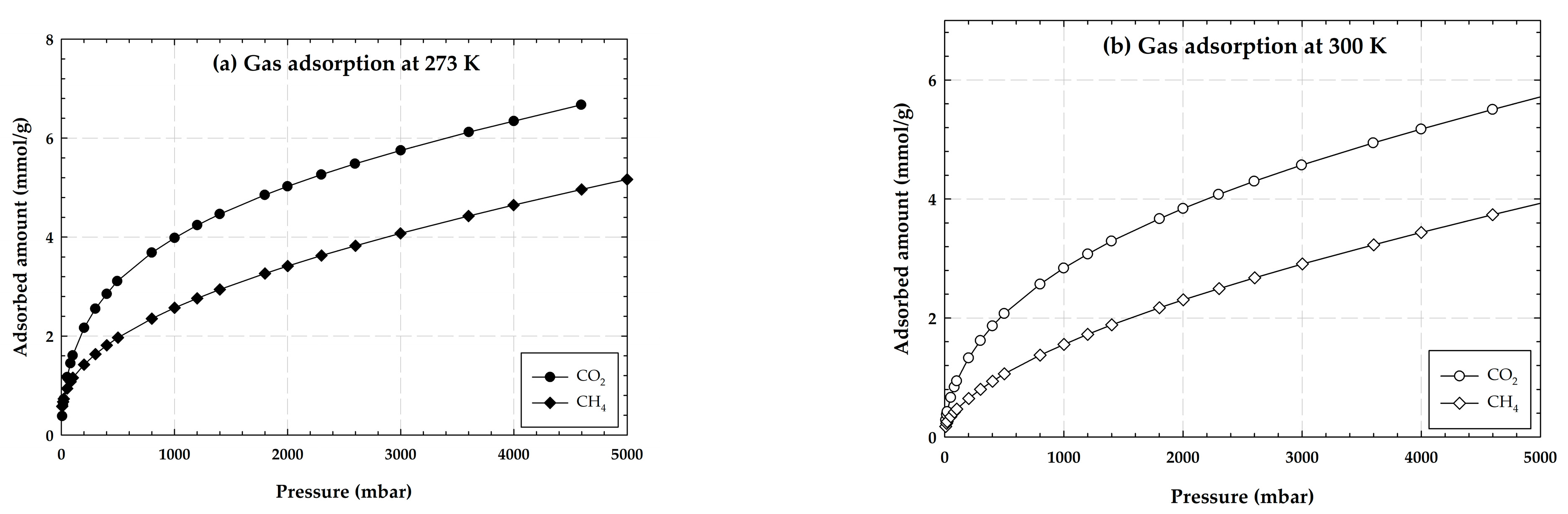
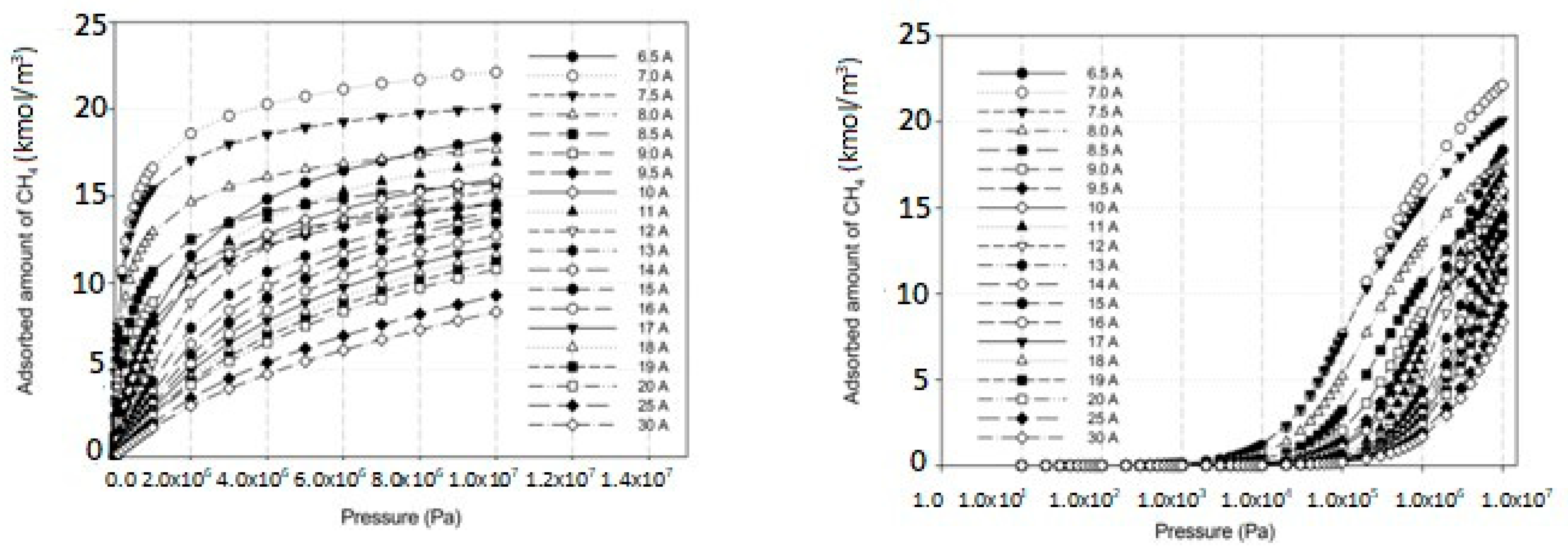
2.1.1. Adsorption Isotherms of CO2 and CH4 on Activated Carbon
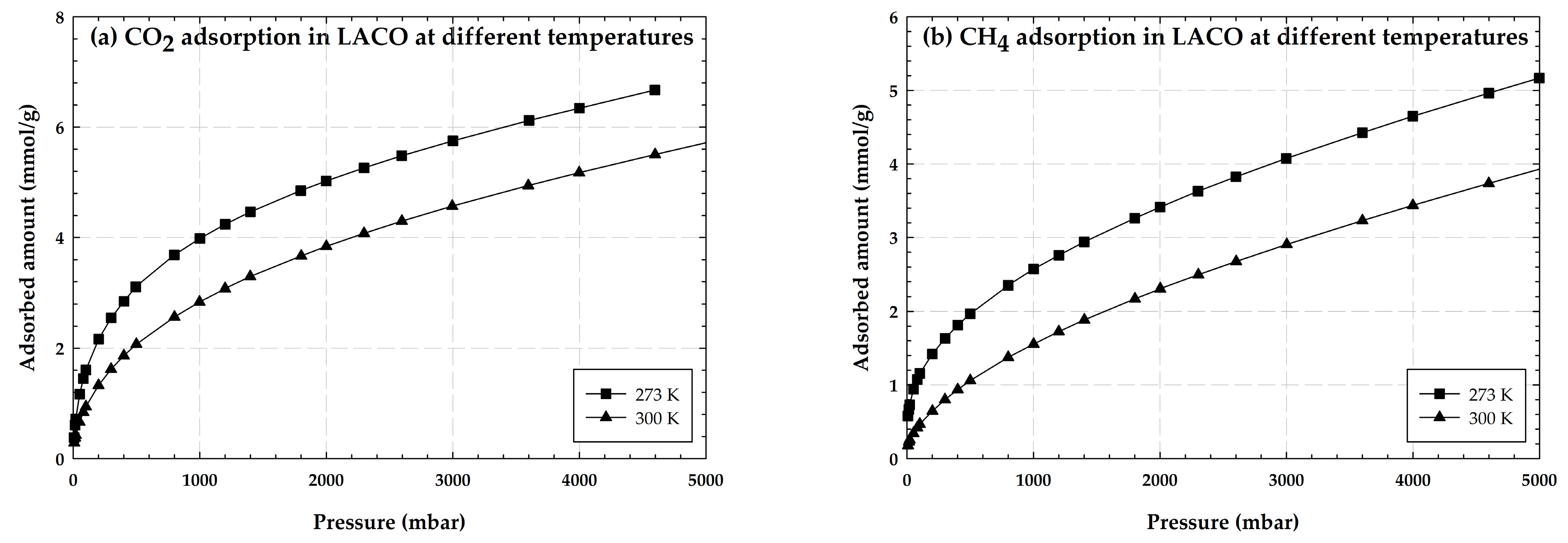
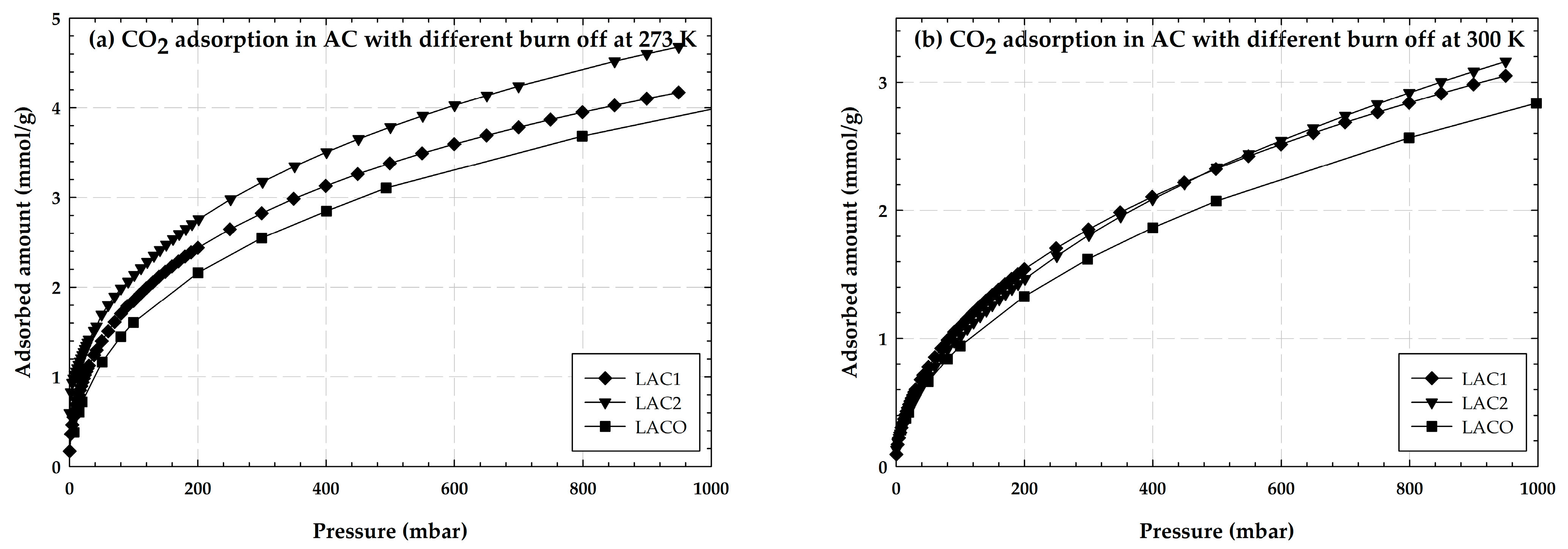
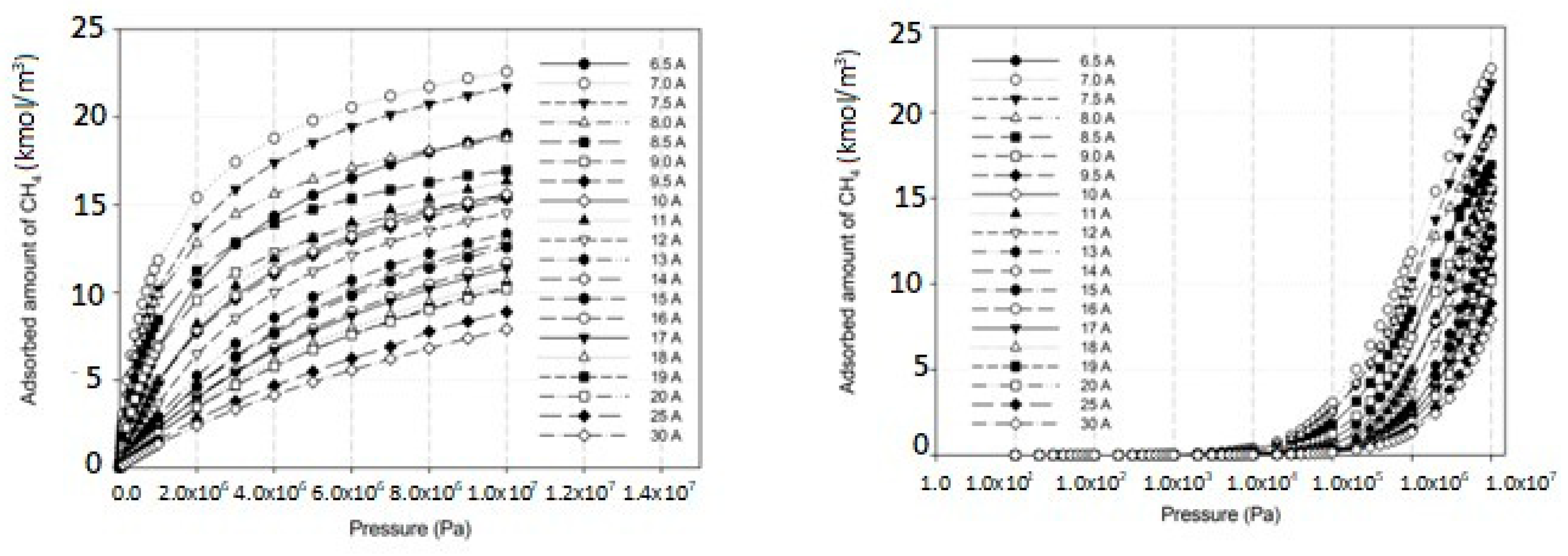
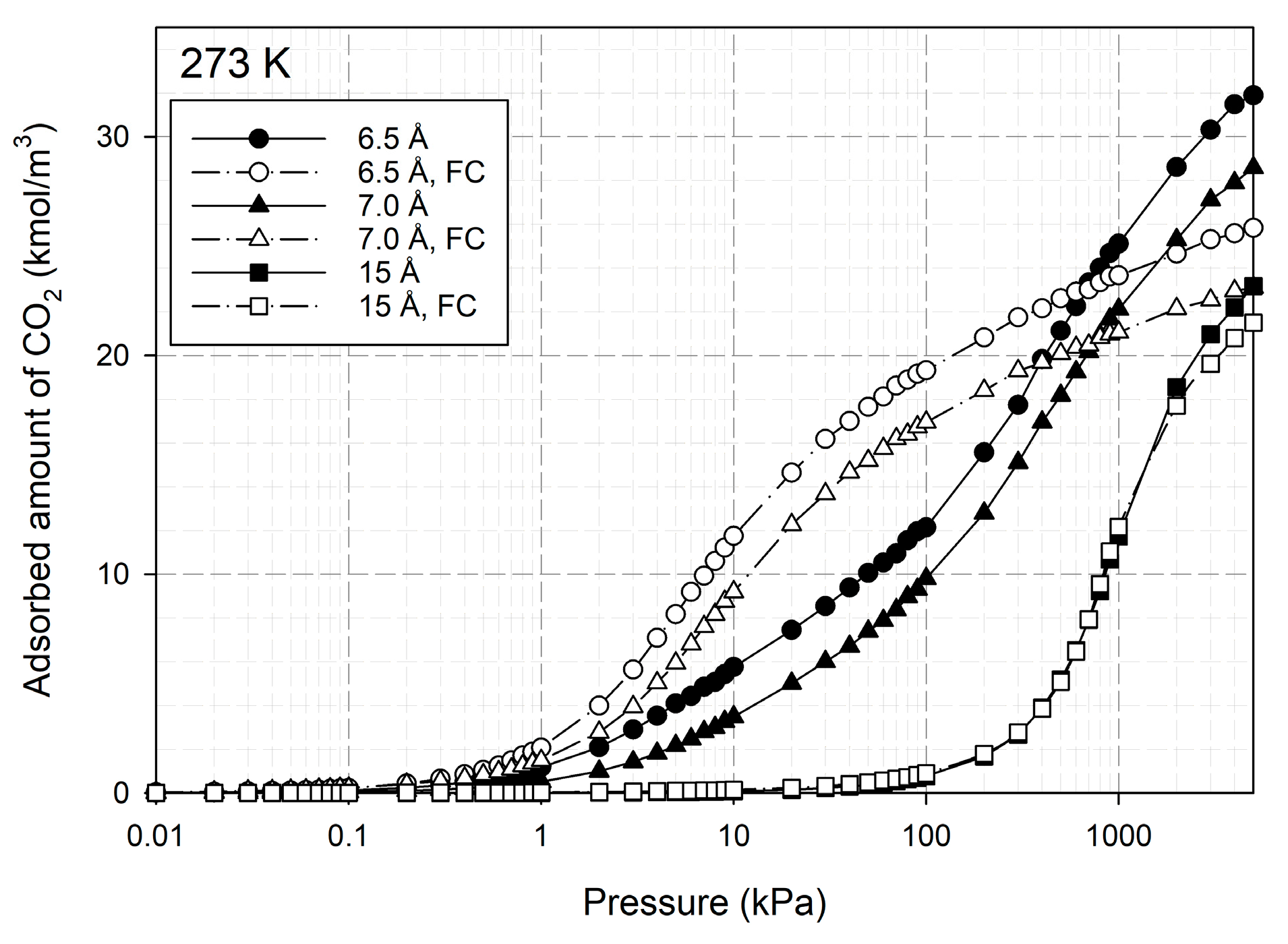
2.1.2. Adsorption of CO2 on Activated Carbon with Different Burn-Off
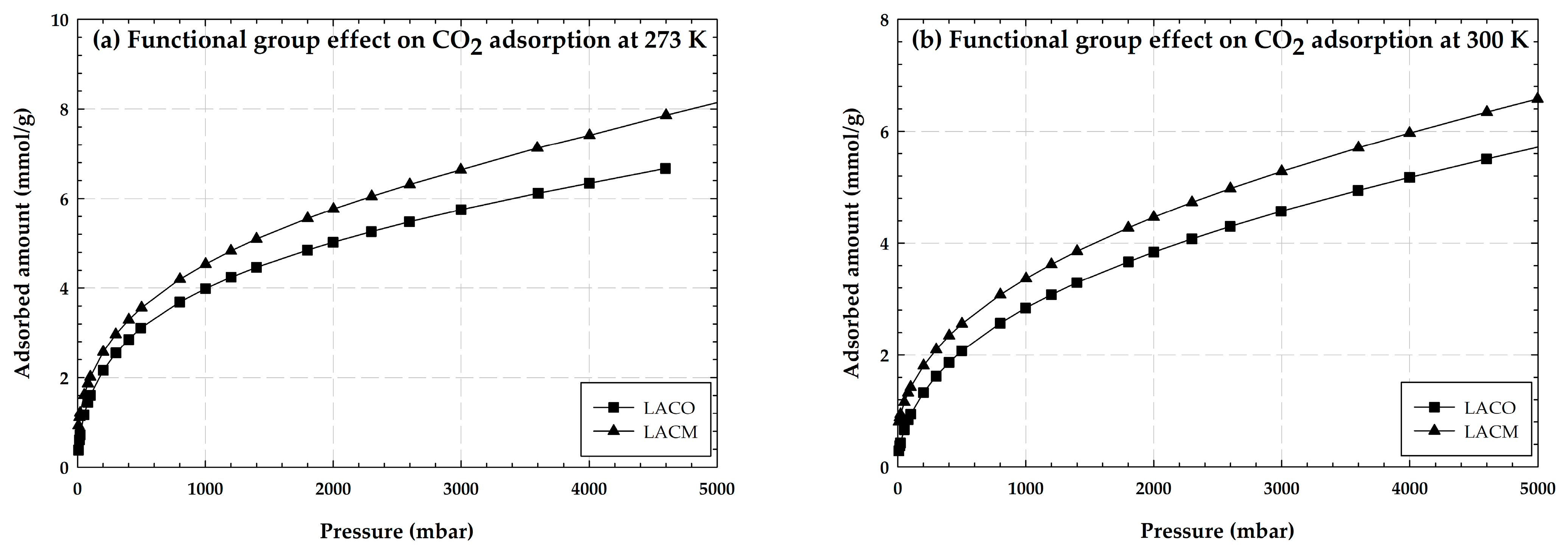
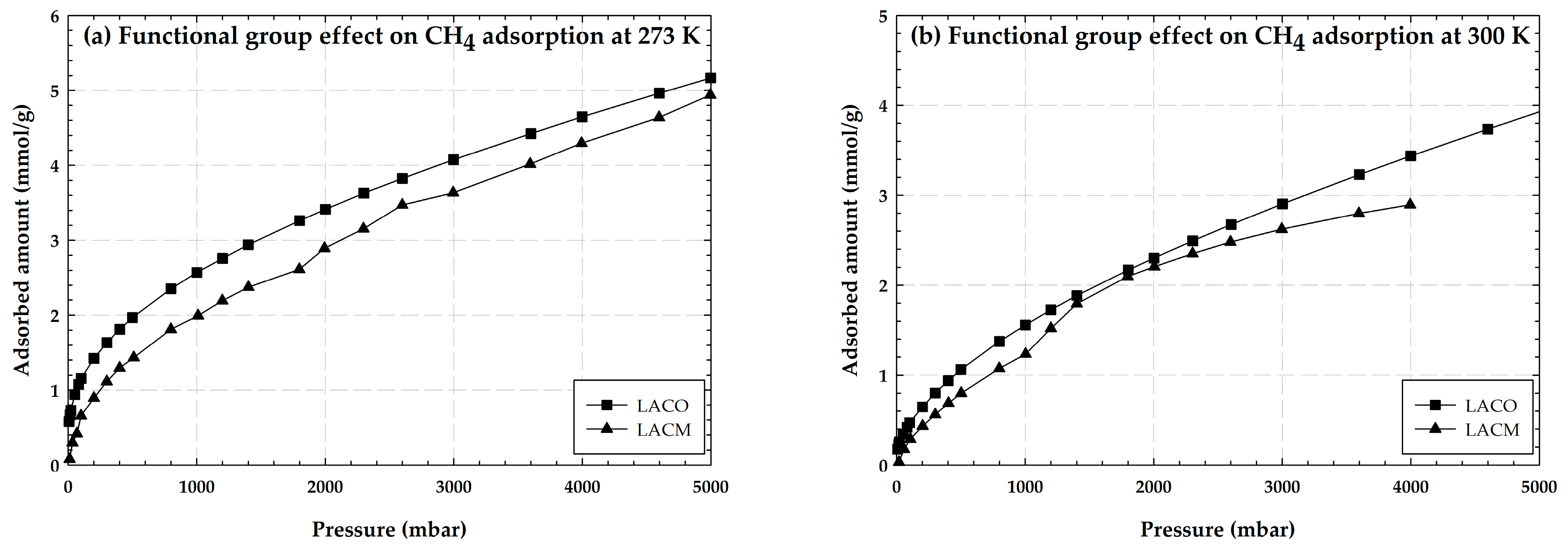
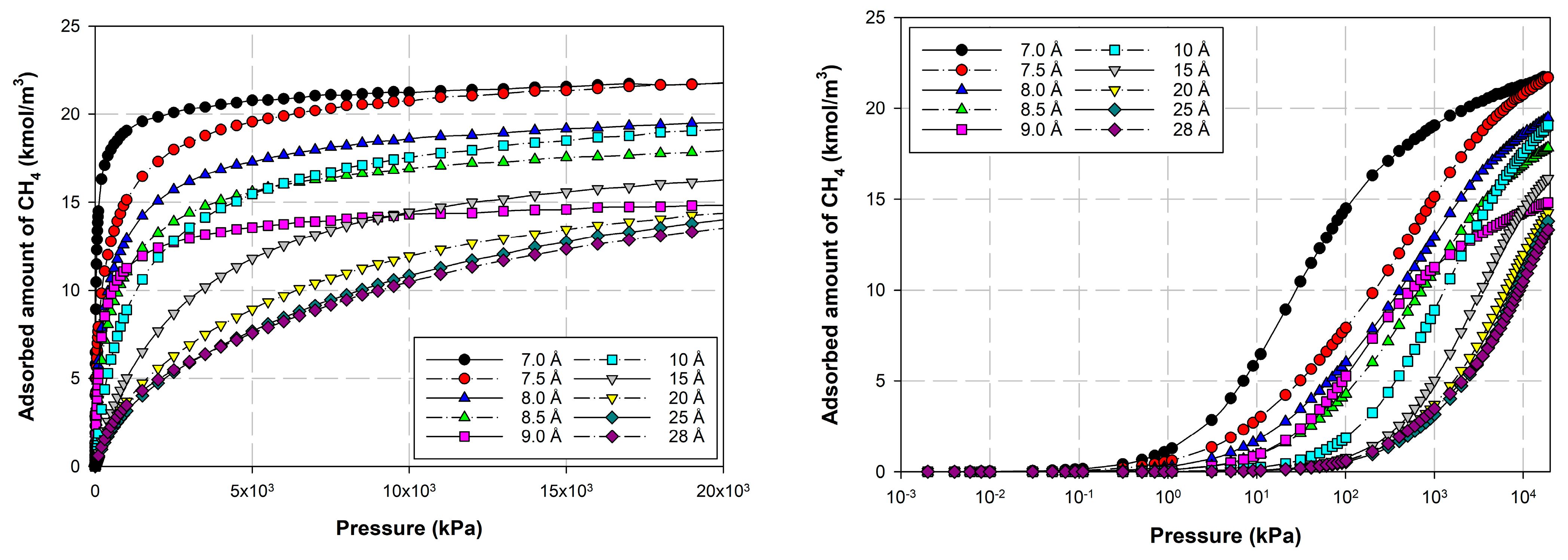
2.1.3. Adsorption of CO2 and CH4 on Activated Carbon Containing Hydroxyl Groups
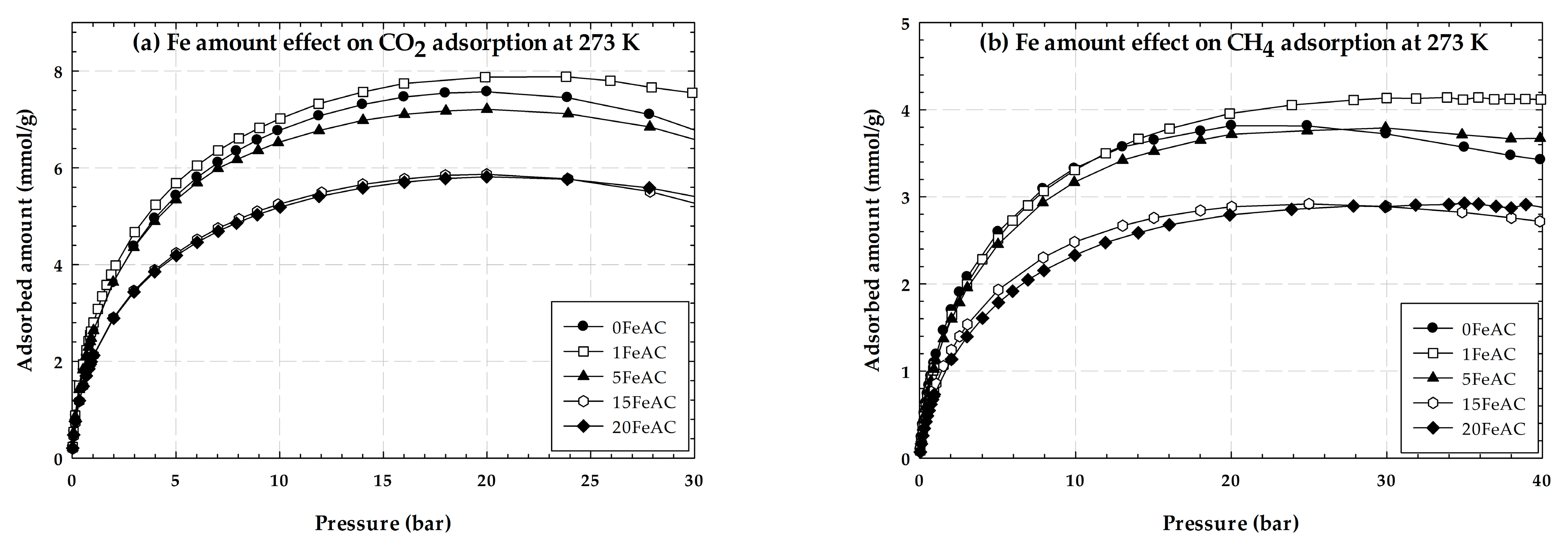
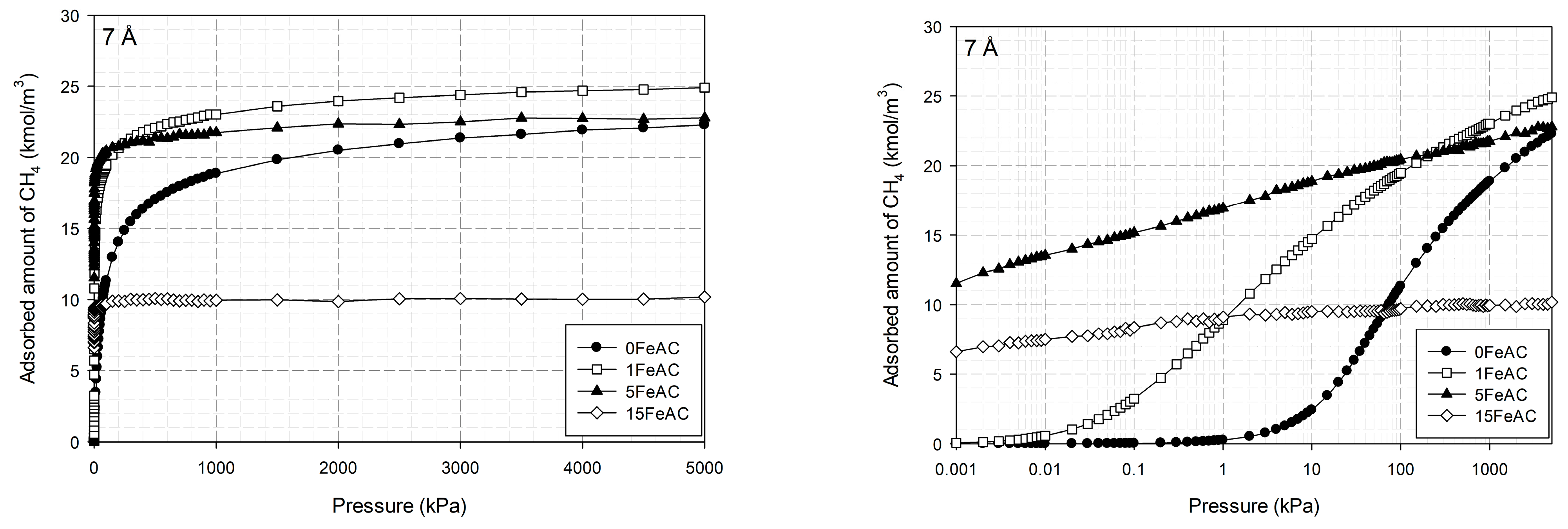
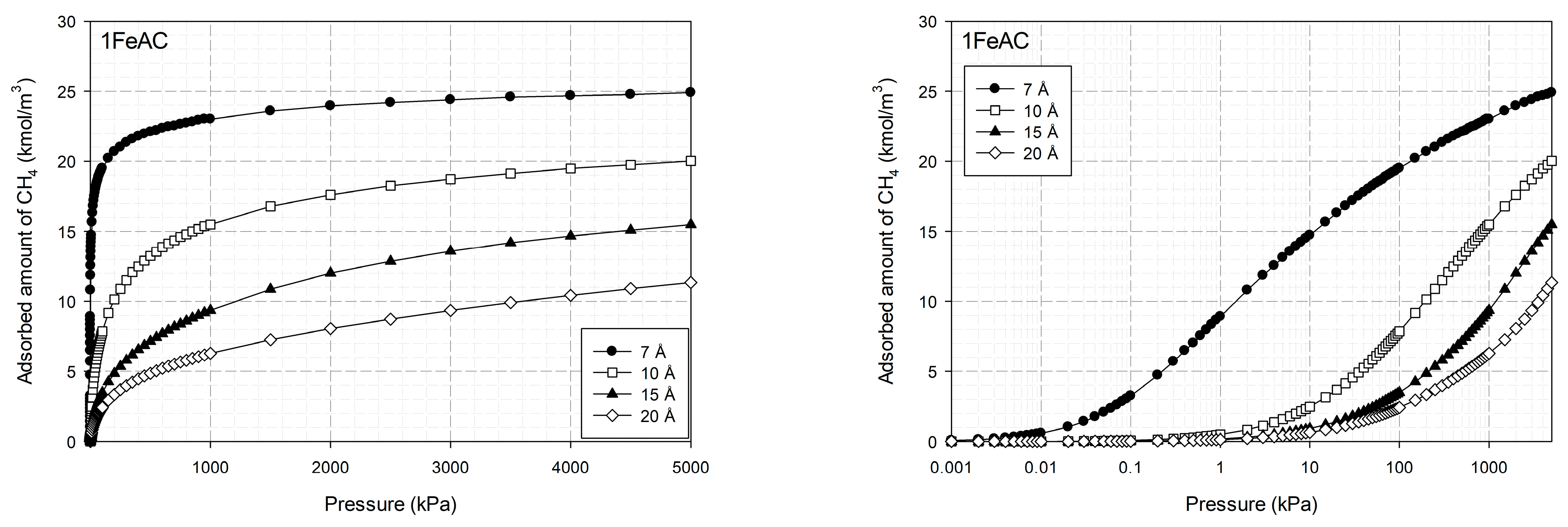
2.1.4. Properties of Activated Carbon with Different Iron Concentrations on Its Surface and Adsorption Isotherms of CO2 and CH4
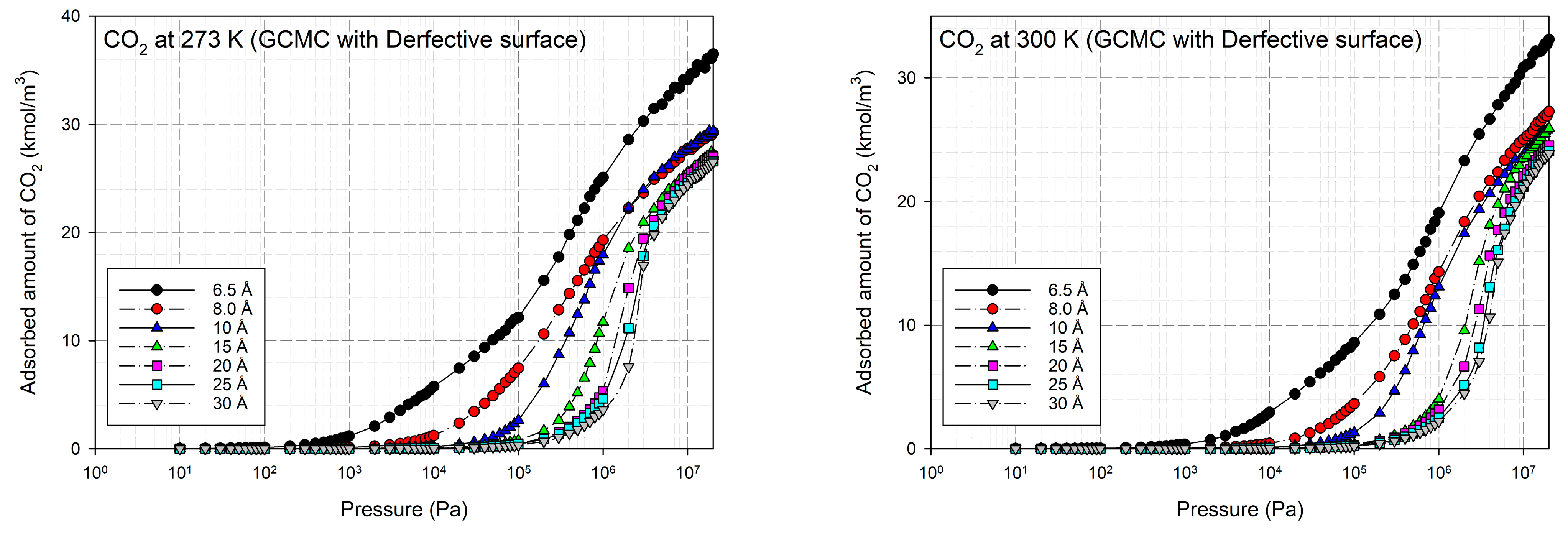
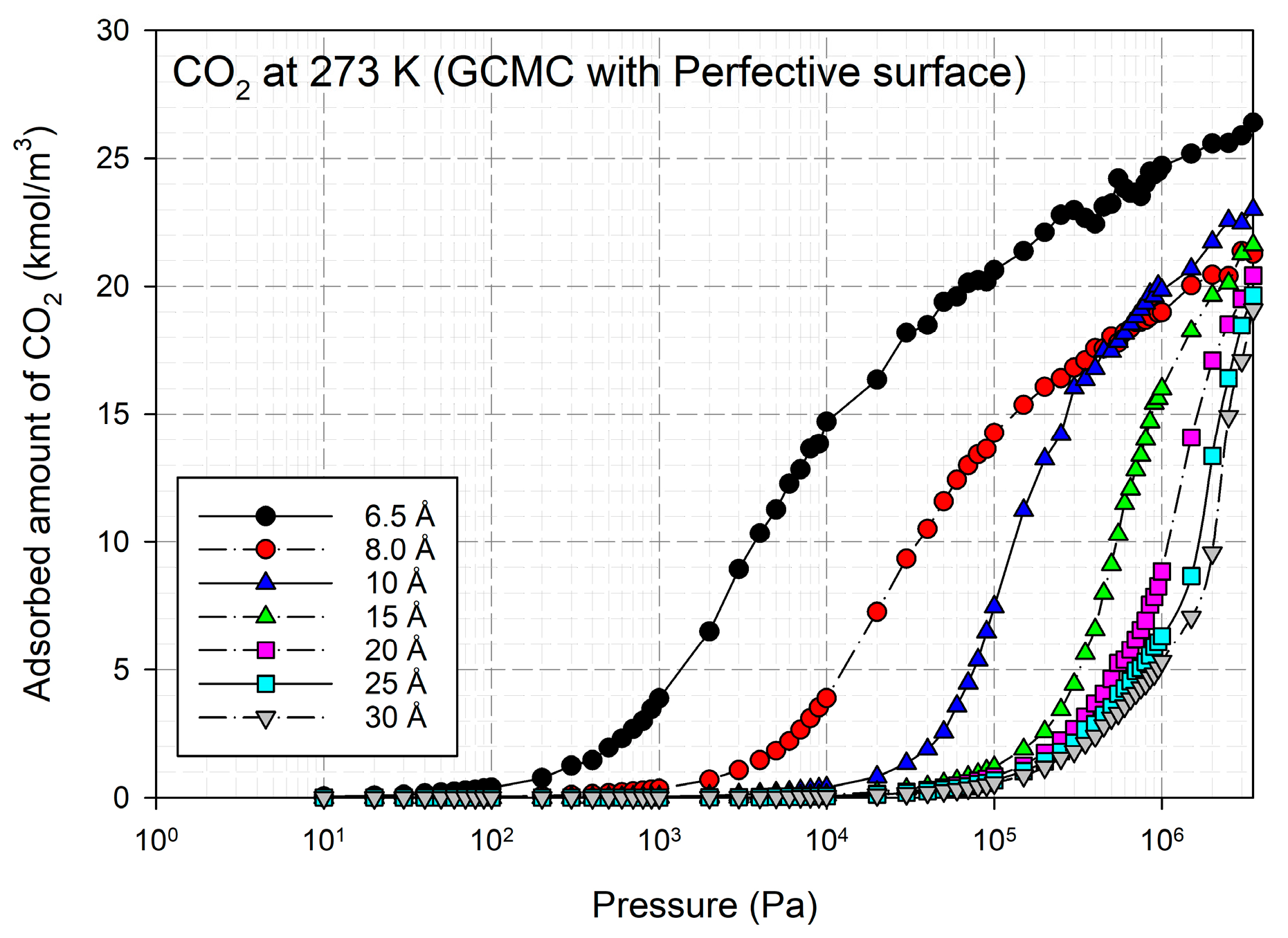
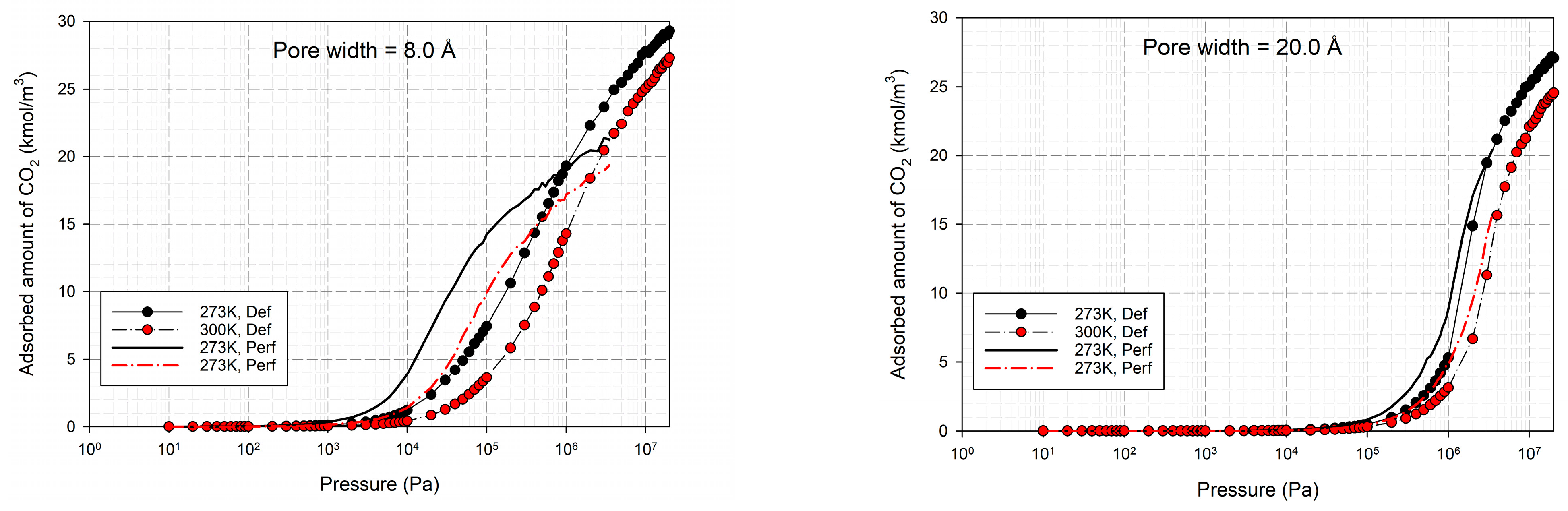
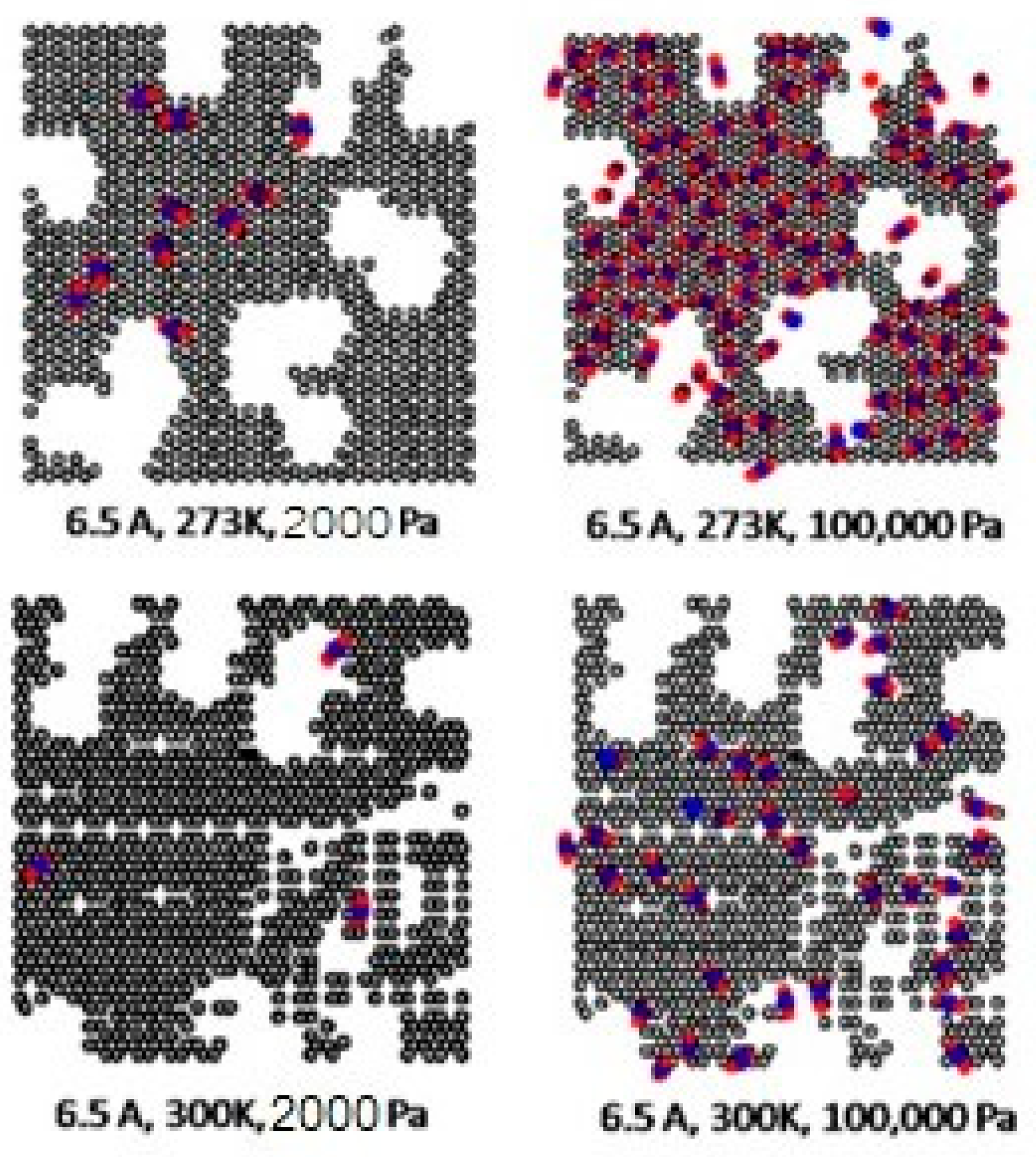
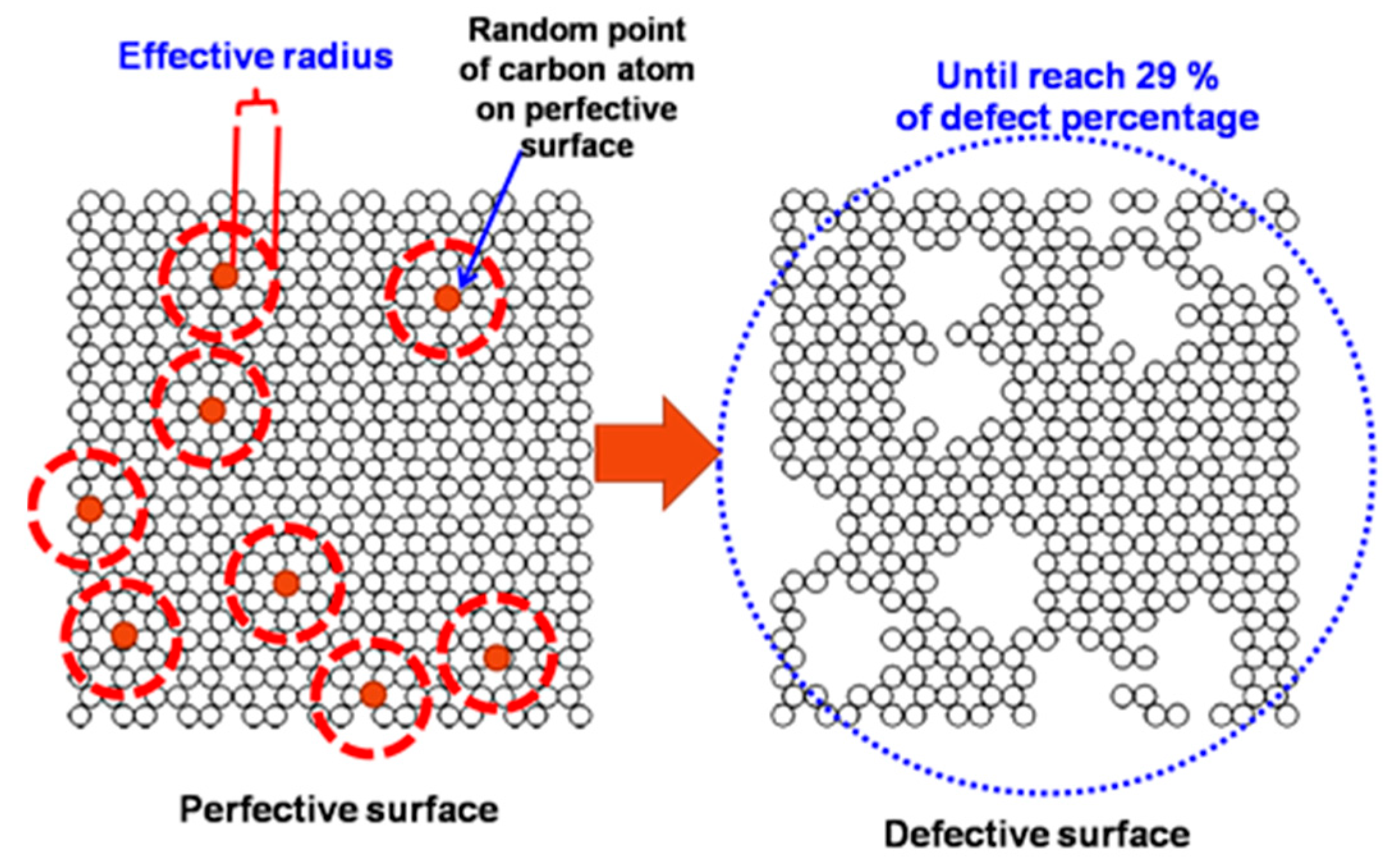
2.2. Simulation Study for CO2 on Perfect and Defective Surfaces
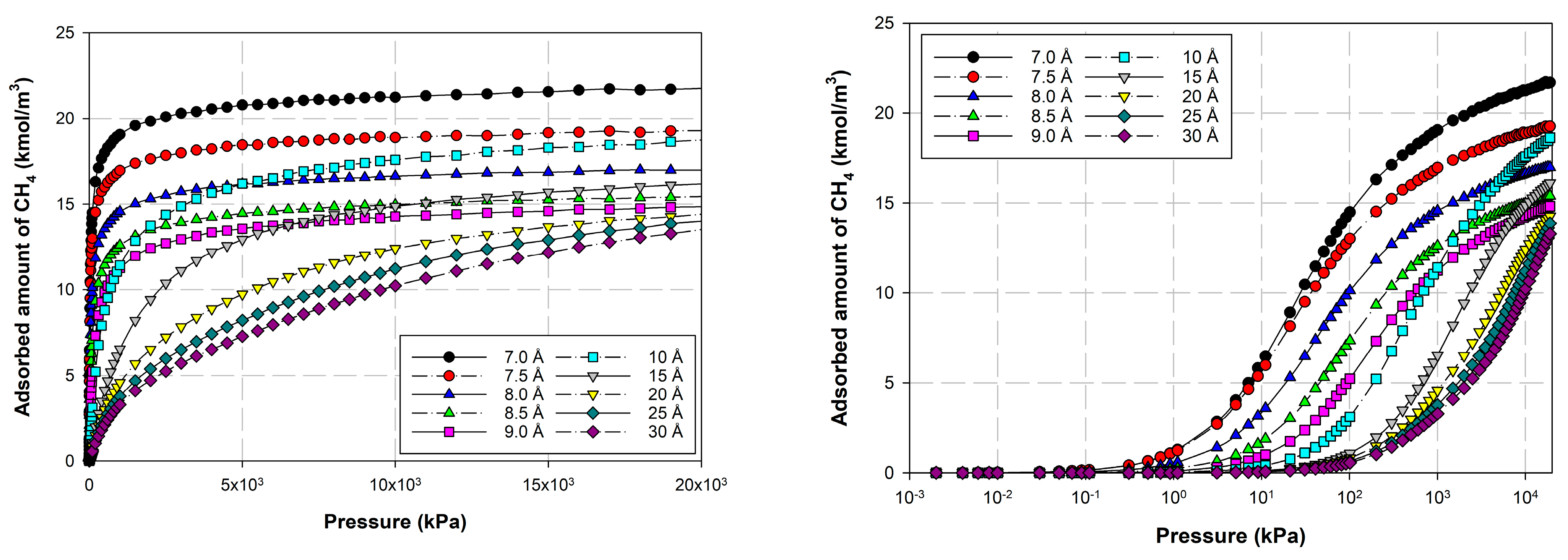
2.3. Simulation Study for CH4 on Perfect and Defective Surfaces
2.4. Effects of Iron Loading on Adsorption Isotherms
2.5. Effect of Hydroxyl Groups (OH) on CO2 Adsorption
3. Methodology
3.1. Computer Simulation
3.1.1. Fluid Model
3.1.2. Perfect Surface Model
3.1.3. Defective Surface Model
3.1.4. Functional Group Model
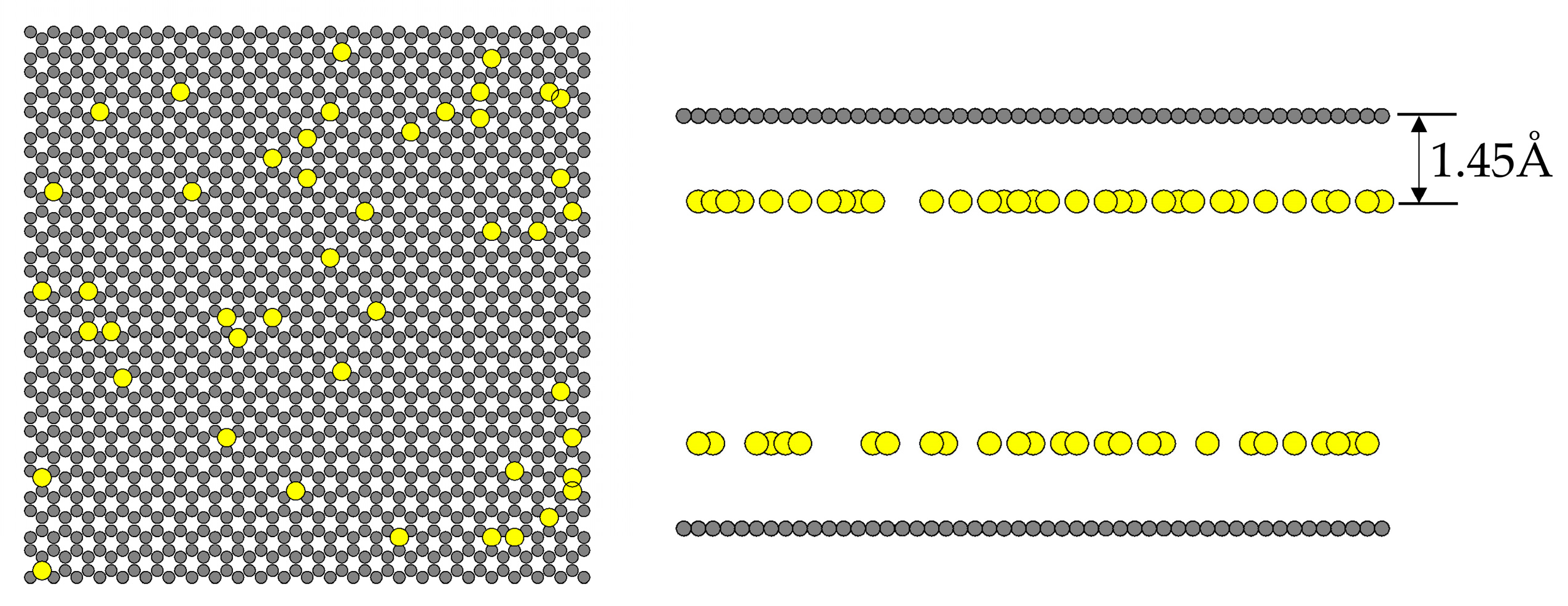
3.1.5. Iron Oxide Model
3.1.6. Grand Canonical Monte Carlo (GCMC) Simulation
3.2. Experimental Work
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Sircar, S. Applications of Gas Separation by Adsorption for the Future. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2001, 19, 347–366. [Google Scholar]
- Yon, C.M.; Sherman, J.D. Adsorption, Gas Separation. In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 617–663. [Google Scholar]
- Pullumbi, P.; Brandani, F.; Brandani, S. Gas Separation by Adsorption: Technological Drivers and Opportunities for Improvement. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2019, 24, 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, A.; Loh, W.S.; Rahman, K.A.; Thu, K.; Surayawan, B.; Alhamid, M.I.; Nasruddin; Ng, K.C. Adsorption Isotherms of CH4 on Activated Carbon from Indonesian Low Grade Coal. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunter, G.W.; Finneran, J.M.; Hartmann, D.J.; Miller, J.D. Early Determination of Reservoir Flow Units Using an Integrated Petrophysical Method. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, San Antonio, TX, USA, 5–8 October 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Flessa, H.; Ruser, R.; Dörsch, P.; Kamp, T.; Jimenez, M.A.; Munch, J.C.; Beese, F. Integrated Evaluation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions (CO2, CH4, N2O) from Two Farming Systems in Southern Germany. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 91, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottiger, S.; Pini, R.; Storti, G.; Mazzotti, M. Competitive Adsorption Equilibria of CO2 and CH4 on a Dry Coal. Adsorption 2008, 14, 539–556. [Google Scholar]
- Pini, R.; Ottiger, S.; Burlini, L.; Storti, G.; Mazzotti, M. Role of Adsorption and Swelling on the Dynamics of Gas Injection in Coal. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matranga, K.R.; Myers, A.L.; Glandt, E.D. Storage of Natural Gas by Adsorption on Activated Carbon. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1992, 47, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar]
- Rasoolzadeh, M.; Fatemi, S.; Gholamhosseini, M.; Moosaviyan, M.A. Study of Methane Storage and Adsorption Equilibria in Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2008, 27, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Kongnoo, A.; Intharapat, P.; Worathanakul, P.; Phalakornkule, C. Diethanolamine Impregnated Palm Shell Activated Carbon for CO2 Adsorption at Elevated Temperatures. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Atta-Obeng, E.; Dawson-Andoh, B.; Felton, E.; Dahle, G. Carbon Dioxide Capture Using Amine Functionalized Hydrothermal Carbons from Technical Lignin. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 10, 2725–2731. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, L.; Ju, S.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, Q.; Zhan, G.; Yu, X. Highly Selective CO2 Uptake in Novel Fishnet-like Polybenzoxazine-Based Porous Carbon. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 11454–11464. [Google Scholar]
- Younas, M.; Leong, L.K.; Mohamed, A.R. Sumathi Sethupathi CO2 Adsorption by Modified Palm Shell Activated Carbon (PSAC) via Chemical and Physical Activation and Metal Impregnation. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2016, 203, 1455–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, A.; Abu Tahari, M.N.; Marliza, T.S.; Wan Isahak, W.N.R.; Yusop, M.R.; Mohamed Hisham, M.W.; Yarmoa, M.A. Study of CO2 adsorption and desorption on activated carbon supported iron oxide by temperature programmed desorption. J. Teknol. 2015, 77, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirbiyik, Ç. Modification of Biomass-Derived Activated Carbon with Magnetic-Fe2O3 nanoparticles for CO2 and CH4 adsorption. Turk. J. Chem. 2019, 43, 687–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, D.D.; Do, H.D. Pore Characterization of Carbonaceous Materials by DFT and GCMC Simulations: A Review. Adsorp. Sci. Technol. 2003, 21, 389–423. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, E.A.; Rull, L.F.; Vega, L.F.; Gubbins, K.E. Adsorption of Water on Activated Carbons: A Molecular Simulation Study. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Maddox, M.; Ulberg, D.; Gubbins, K.E. Molecular Simulation of Simple Fluids and Water in Porous Carbons. Fluid Phase Equilibria 1995, 104, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.E. Crystallite Growth in Graphitizing and Non-Graphitizing Carbons. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. 1951, 209, 196–218. [Google Scholar]
- Do, D.D. Adsorption Analysis: Equilibria and Kinetics (with Cd Containing Computer Matlab Programs); World Scientific: Singapore, 1998; ISBN 9781783262243. [Google Scholar]
- Wongkoblap, A.; Junpirom, S.; Do, D.D. Adsorption of Lennard-Jones Fluids in Carbon Slit Pores of a Finite Length. A Computer Simulation Study. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2005, 23, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Rios, R.B.; Stragliotto, F.M.; Peixoto, H.R.; Torres, A.E.B.; Bastos-Neto, M.; Azevedo, D.C.S.; Cavalcante, C.L., Jr. Studies on the Adsorption Behavior of CO2-CH4 Mixtures Using Activated Carbon. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 939–951. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas, D.P.; Giraldo, L.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C. Carbon Dioxide and Methane Adsorption at High Pressure on Activated Carbon Materials. Adsorption 2013, 19, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, H.B.W. Adsorption. In Bleaching and Purifying Fats and Oils: Theory and Practice, 2nd ed.; List, G., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Artioli, Y. Adsorption. In Encyclopedia of Ecology; Jørgensen, S.E., Fath, B.D., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 60–65. ISBN 9780080454054. [Google Scholar]
- Wongkoblap, A.; Intomya, W.; Somrup, W.; Charoensuk, S.; Junpirom, S.; Tangsathitkulchai, C. Pore Size Distribution of Carbon with Different Probe Molecules. Eng. J. 2010, 14, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W. Reporting Physisorption Data for Gas/Solid Systems with Special Reference to the Determination of Surface Area and Porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Tangsathitkulchai, C.; Naksusuk, S.; Wongkoblap, A.; Phadungbut, P.; Borisut, P. Equilibrium and Kinetics of CO2 Adsorption by Coconut Shell Activated Carbon Impregnated with Sodium Hydroxide. Processes 2021, 9, 201. [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel, D.; Smit, B. Understanding Molecular Simulation: From Algorithms to Applications; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2002; ISBN 9780080519982. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J.G.; Yung, K.H. Carbon Dioxide’s Liquid-Vapor Coexistence Curve and Critical Properties as Predicted by a Simple Molecular Model. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 12021–12024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Madura, J.D.; Swenson, C.J. Optimized Intermolecular Potential Functions for Liquid Hydrocarbons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 6638–6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teerachawanwong, P.; Makkaroon, B.; Boonfung, C.; Tangsathitkulchai, C.; Wongkoblap, A. Computer Simulation Study for Functional Group Effect on Methane Adsorption in Porous Silica Glass. Eng. J. 2019, 23, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Wongkoblap, A.; Do, D.D. Characterization of Cabot Non-Graphitized Carbon Blacks with a Defective Surface Model: Adsorption of Argon and Nitrogen. Carbon 2007, 45, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, M.; Schumacher, C.; Seaton, N.A. Simulation Study of the Effect of the Chemical Heterogeneity of Activated Carbon on Water Adsorption. Langmuir 2002, 18, 9296–9306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markevich, A.; Baldoni, M.; Warner, J.H.; Kirkland, A.I.; Besley, E. Dynamic Behavior of Single Fe Atoms Embedded in Graphene. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 21998–22003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, G.J.; Zhen, S. Metallic Foams: Their Production, Properties and Applications. J. Mater. Sci. 1983, 18, 1899–1911. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.K.; Zollweg, J.A.; Gubbins, K.E. The Lennard-Jones Equation of State Revisited. Mol. Phys. 1993, 78, 591–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawtae, P.; Tangsathitkulchai, C. A New Approach for Controlling Mesoporosity in Activated Carbon by the Consecutive Process of Air Oxidation, Thermal Destruction of Surface Functional Groups, and Carbon Activation (the OTA Method). Molecules 2021, 26, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawtae, P.; Phothong, K.; Wongkoblap, A.; Tangsathitkulchai, C. Pore Size Distributions of Micro-Mesoporous Activated Carbons Determined from Isotherms of Gas Adsorption on Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Surfaces: Experiment and Computer Simulations. Molecules 2021, 26, 842–848. [Google Scholar]
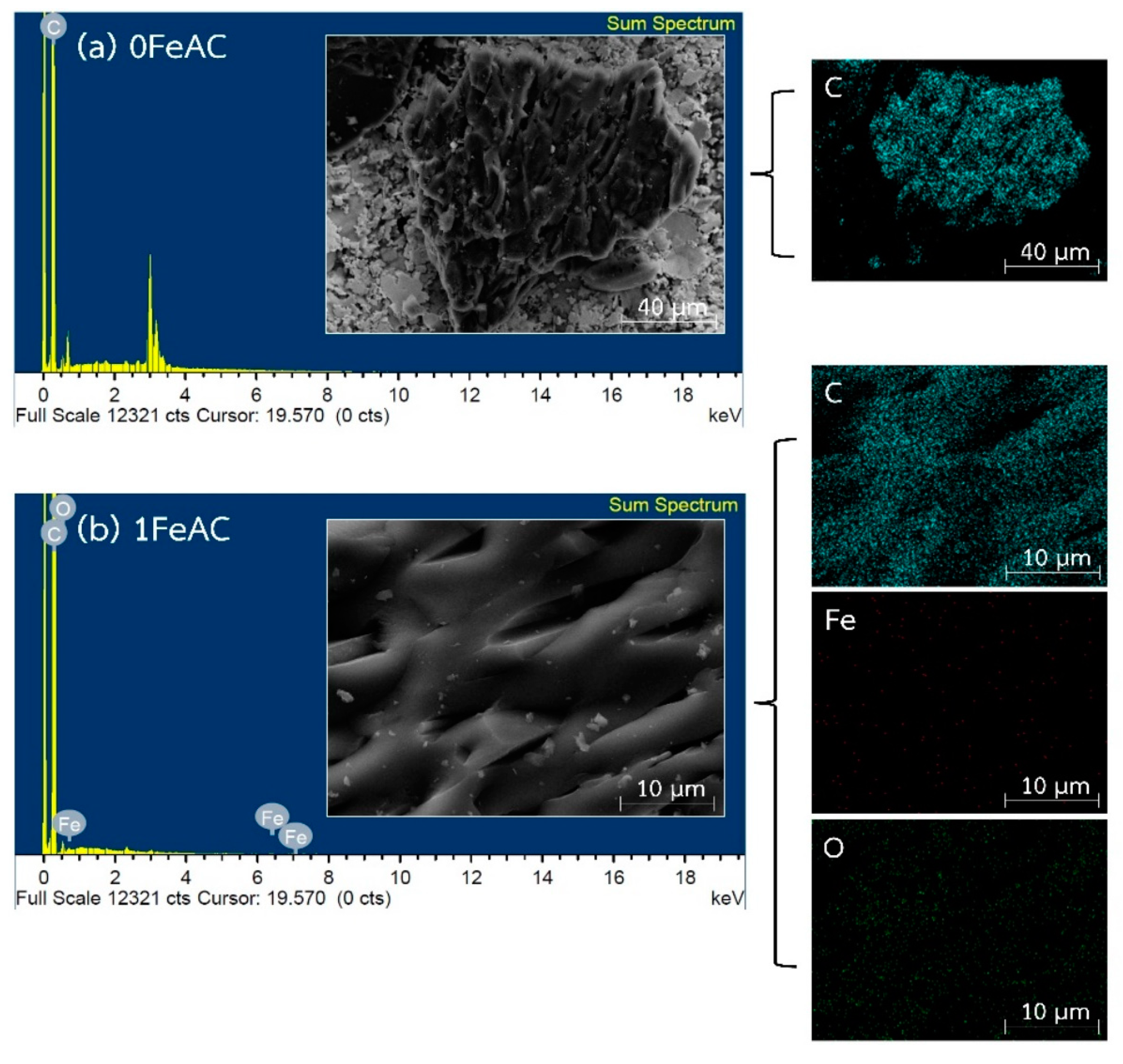
| Sample | Composition (wt.%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | O | C | |
| 0 FeAC | - | - | 100 |
| 1 FeAC | 0.65 | 2.63 | 96.72 |
| 5 FeAC | 3.12 | 8.85 | 88.03 |
| 15 FeAC | 14.59 | 13.89 | 71.51 |
| 20 FeAC | 20.48 | 16.83 | 62.69 |
| Pore Width 6.3 Å | Pore Width 15 Å | Pore Width 30 Å |
|---|---|---|
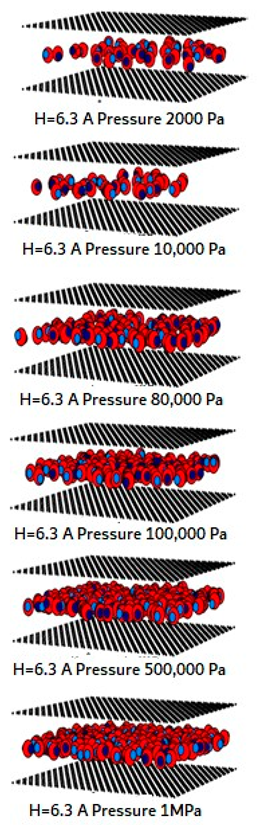 |  | 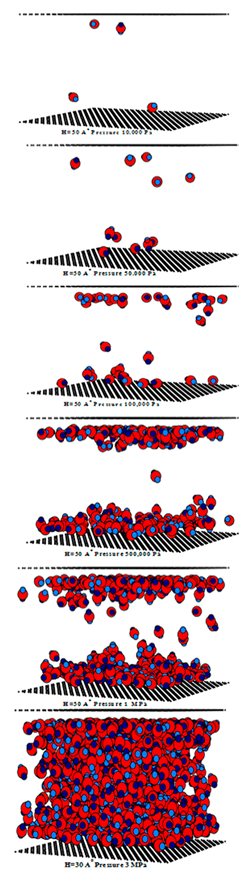 |
| Pore Width 6.5 Å | Pore Width 15 Å | Pore Width 30 Å |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
| Pore Width 6.5 Å | Pore Width 15 Å | Pore Width 30 Å |
|---|---|---|
 | 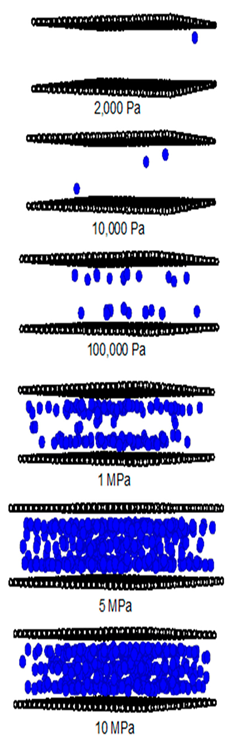 |  |
| Pore Width 6.5 Å | Pore Width 15 Å | Pore Width 30 Å |
|---|---|---|
 |  | 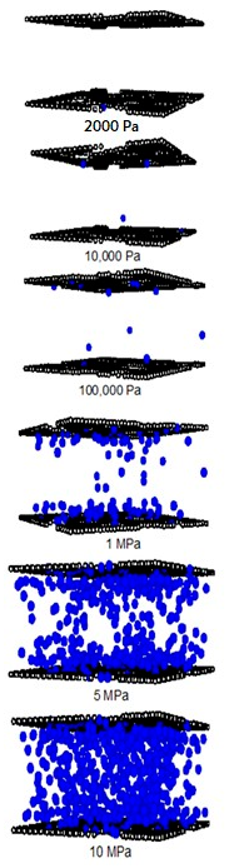 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Inthawong, S.; Wongkoblap, A.; Intomya, W.; Tangsathitkulchai, C. The Enhancement of CO2 and CH4 Capture on Activated Carbon with Different Degrees of Burn-Off and Surface Chemistry. Molecules 2023, 28, 5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145433
Inthawong S, Wongkoblap A, Intomya W, Tangsathitkulchai C. The Enhancement of CO2 and CH4 Capture on Activated Carbon with Different Degrees of Burn-Off and Surface Chemistry. Molecules. 2023; 28(14):5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145433
Chicago/Turabian StyleInthawong, Supawan, Atichat Wongkoblap, Worapot Intomya, and Chaiyot Tangsathitkulchai. 2023. "The Enhancement of CO2 and CH4 Capture on Activated Carbon with Different Degrees of Burn-Off and Surface Chemistry" Molecules 28, no. 14: 5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145433
APA StyleInthawong, S., Wongkoblap, A., Intomya, W., & Tangsathitkulchai, C. (2023). The Enhancement of CO2 and CH4 Capture on Activated Carbon with Different Degrees of Burn-Off and Surface Chemistry. Molecules, 28(14), 5433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145433







