The Composition, Structure, and Functionalities of Prolamins from Highland Barley
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Amino Acid Composition
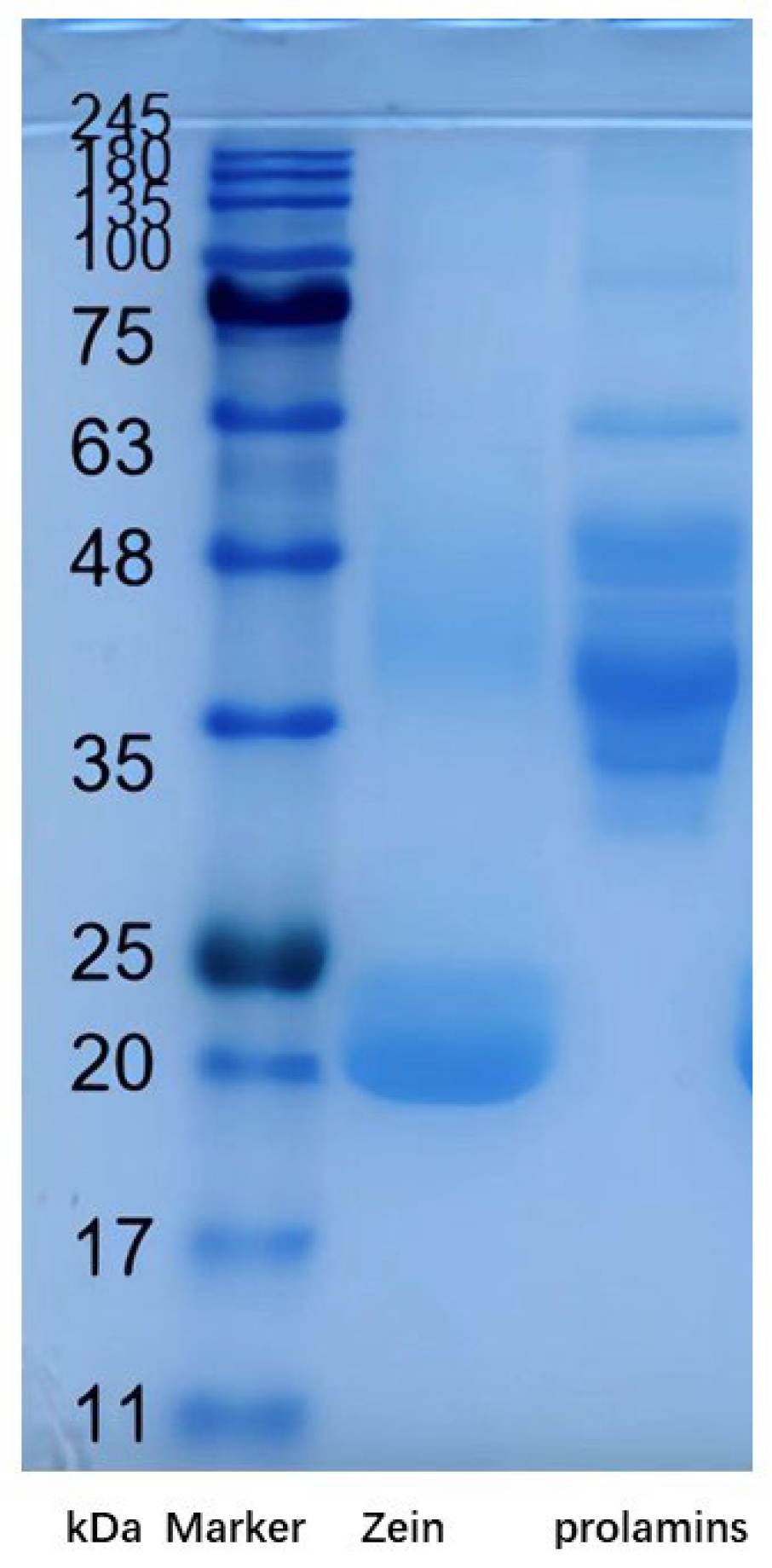
2.2. SDS-PAGE Analysis
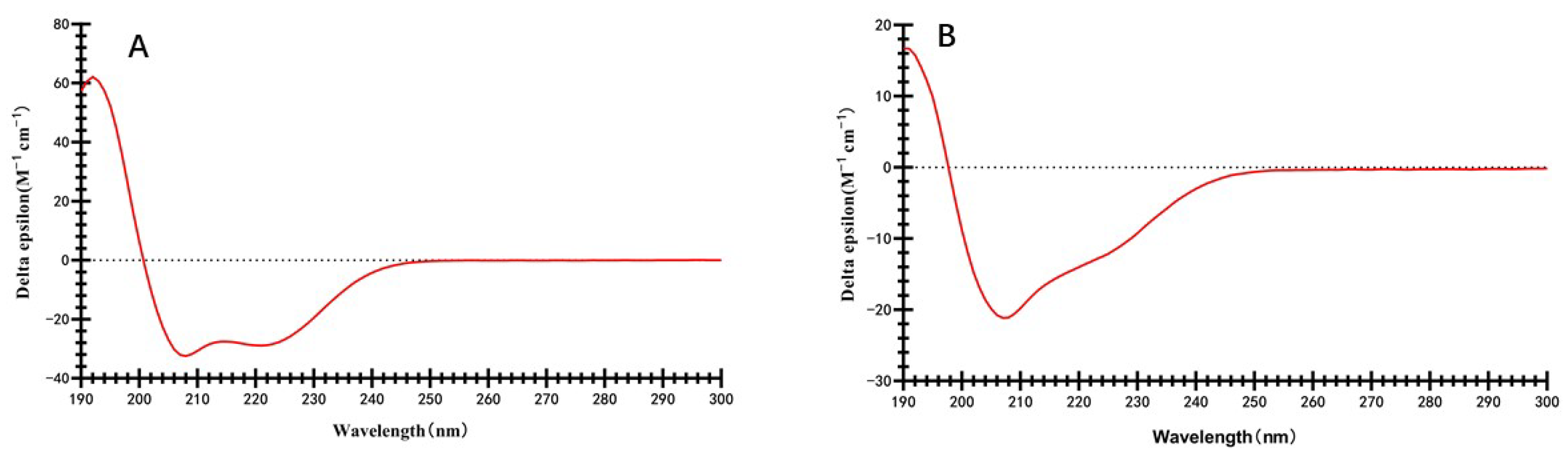
2.3. Secondary Structures
2.4. Physico-Chemical Properties
2.4.1. Thermal Properties
2.4.2. Surface Hydrophobicity
2.4.3. Emulsifying Properties
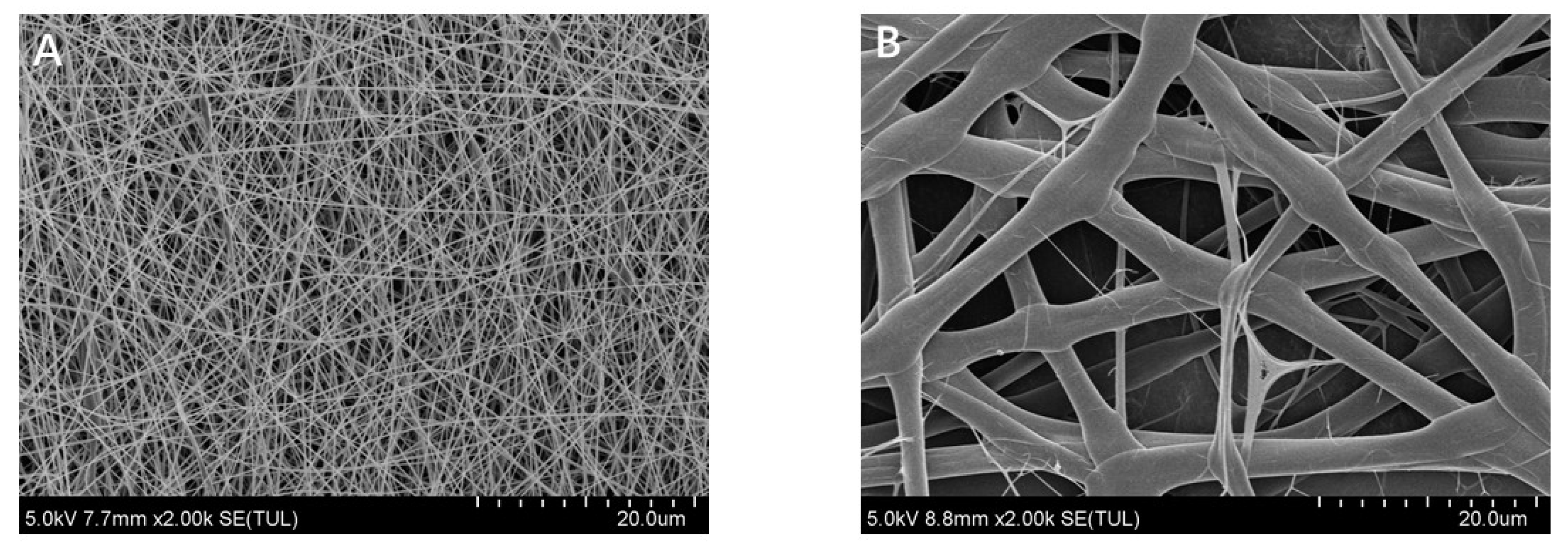
2.5. Morphology of Electrospun Fibers
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Prolamins from Highland Barley
3.3. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
3.4. Amino Acid Composition Analyses
3.5. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
3.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
3.7. Surface Hydrophobicity Index
3.8. Emulsifying Properties
3.9. Preparation and Characterization of the Electrospun Fibers
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Lyu, Y.; Ma, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. A systematic review of highland barley: Ingredients, health functions and applications. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2022, 5, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, R.H. Bioactive compounds of highland barley and their health benefits. J. Cereal Sci. 2022, 103, 103366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.J.; Dong, S.K.; Wei, X.H.; Pu, X.P. The effect of supplementary feeds on the bodyweight of yaks in cold season. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2005, 93, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Hernández, J.A.; Del-Toro-Sánchez, C.L.; Cinco-Moroyoqui, F.J.; Juárez-Onofre, J.E.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; López-Ahumada, G.A.; Castro-Enriquez, D.D.; Barreras-Urbina, C.G.; Rodríguez-Felix, F. Prolamins from cereal by-products: Classification, extraction, characterization and its applications in micro- and nanofabrication. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 90, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hu, Q.; Liang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, J. Physicochemical properties and application in film preparation of prolamin from distiller’s grains. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 5206–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Zhou, H.; Guo, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L. Zein structure and its hidden zearalenone: Effect of zein extraction methods. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah; Fang, J.P.; Liu, X.D.; Javed, H.U.; Cai, J.Y.; Zhou, Q.Z.; Huang, Q.R.; Xiao, J. Recent advances in self-assembly behaviors of prolamins and their applications as functional delivery vehicles. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Cao, X.; Ye, Y.; Sun, H. Comparison of crude prolamins from seven kidney beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) based on composition, structure and functionality. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Electrospinning of Prolamin Proteins in Acetic Acid: The Effects of Protein Conformation and Aggregation in Solution. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2012, 297, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazanfarzadeh, Z.; Kadivar, M.; Shekarchizadeh, H.; Porta, R. Functional Properties of Rye Prolamin (Secalin) and Their Improvement by Protein Lipophilization through Capric Acid Covalent Binding. Foods 2021, 10, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jing, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X. Effects of moderate-intensity pulsed electric field on the structure and physicochemical properties of foxtail millet (Setaria italica) prolamin. Cereal Chem. 2023, 100, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.-J.; Wang, Z.-W. Structure characteristics of Coix seeds prolamins and physicochemical and mechanical properties of their films. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Shen, Q. Comparison of the characteristics of prolamins among foxtail millet varieties with different palatability: Structural, morphological, and physicochemical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, A.; Wu, L.; Yan, W.; Tong, Y.; Wang, P. Circular Extraction: Innovative Use of a Switchable Composite Extractant for Prolamin Extraction from Grain Byproducts. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Kan, J. Comparison of Structure Characteristics of Gliadin and Glutenin in Highland Barley and Wheat. Food Sci. 2016, 3, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; He, J.; Mo, H. Antioxidant Activity, Functional Properties, and Cytoprotective Effects on HepG2 Cells of Tree Peony (Paeonia suffruticosa Andr.) Seed Protein Hydrolysate as Influenced by Molecular Weights Fractionation. Foods 2022, 11, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C. Circular dichroism of biopharmaceutical proteins in a quality-regulated environment. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 219, 114945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micsonai, A.; Moussong, É.; Murvai, N.; Tantos, Á.; Toke, O.; Réfrégiers, M.; Wien, F.; Kardos, J. Disordered-ordered protein binary classification by circular dichroism spectroscopy. Biophys. J. 2023, 122, 344a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turasan, H.; Kokini, J.L. Advances in Understanding the Molecular Structures and Functionalities of Biodegradable Zein-Based Materials Using Spectroscopic Techniques: A Review. Biomacromolecules 2016, 18, 331–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selling, G.W.; Hamaker, S.A.H.; Sessa, D.J. Effect of Solvent and Temperature on Secondary and Tertiary Structure of Zein by Circular Dichroism. Cereal Chem. 2007, 84, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, N.; Arora, P.S. Hydrogen Bond Surrogate Stabilization of β-Hairpins. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 2027–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahiri, P.; Verma, H.; Ravikumar, A.; Chatterjee, J. Protein stabilization by tuning the steric restraint at the reverse turn. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 4600–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, B.E.; Cole, K.D. Differential scanning calorimetry and fluorimetry measurements of monoclonal antibodies and reference proteins: Effect of scanning rate and dye selection. Biotechnol. Prog. 2017, 33, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Shan, P. A reinforcement learning based method for protein’s differential scanning calorimetry signal separation. Measurement 2022, 188, 110391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, Y.; Acevedo, N.C. Effects of pre-heating soybean protein isolate and transglutaminase treatments on the properties of egg-soybean protein isolate composite gels. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, T.-H.; Tan, S.-S.; Xue, Y.-L. The amino acid composition, solubility and emulsifying properties of sweet potato protein. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 1002–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, A.C.B.; Medeiros, G.B.; do Carmo Vieira, D.; Garcia, F.P.; Nakamura, C.V.; Muniz, E.C.; Corradini, E. Influence of process variables on the yield and diameter of zein-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) fiber blends obtained by electrospinning. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 292, 109971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, E.; Selling, G.W.; Campanella, O.H.; Jones, O.G. Incorporation of Plasticizers and Co-proteins in Zein Electrospun Fibers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 14610–14619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Song, X.; Li, Q.; Zheng, F.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Huang, M.; Sun, B. Characterization of prolamin recycled from the byproduct of the Baijiu brewing industry (Jiuzao) by SDS-PAGE, multispectral analysis, and morphological analysis. Food Biosci. 2022, 49, 101854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantino, A.B.T.; Garcia-Rojas, E.E. Proteins from pseudocereal seeds: Solubility, extraction, and modifications of the physicochemical and techno-functional properties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 2630–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Tong, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, H. Functional Properties of Corn Byproduct-Based Emulsifier Prepared by Hydrothermal–Alkaline. Molecules 2023, 28, 665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bing, J.; Xiao, X.; McClements, D.J.; Biao, Y.; Chongjiang, C. Protein corona formation around inorganic nanoparticles: Food plant proteins-TiO2 nanoparticle interactions. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, M.A.; Habibi Najafi, M.B.; Movaffagh, J.; Ghorani, B. Encapsulation of Ascorbyl Palmitate in Zein by Electrospinning Technique. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 29, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Amino Acid | Zein | Prolamins from Highland Barley |
|---|---|---|
| Aspartic acid/Asp | 5.95 ± 0.22 b | 2.10 ± 0.10 a |
| Glutamic acid/Glu | 26.49 ± 0.95 a | 41.12 ± 1.83 b |
| Serine/Ser | 6.04 ± 0.19 b | 3.74 ± 0.21 a |
| Glycine/Gly | 1.16 ± 0.04 a | 1.10 ± 0.11 a |
| Histidine/His | 1.09 ± 0.07 a | 1.14 ± 0.05 a |
| Arginine/Arg | 2.09 ± 0.11 a | 2.52 ± 0.39 b |
| Threonine/Thr | 2.16 ± 0.15 b | 1.80 ± 0.11 a |
| Alanine/Ala | 9.43 ± 0.31 b | 1.50 ± 0.10 a |
| Proline/Pro | 7.75 ± 0.30 a | 15.89 ± 0.87 b |
| Tyrosine/Tyr | 4.03 ± 0.02 b | 2.61 ± 0.09 a |
| Valine/Val | 2.38 ± 0.07 a | 2.13 ± 0.15 a |
| Methionine/Met | 0.11 ± 0.01 a | 0.11 ± 0.01 a |
| Cystine/Cys | 0.28 ± 0.02 b | 0.16 ± 0.06 a |
| Isoleucine/Ile | 1.89 ± 0.12 a | 2.02 ± 0.03 a |
| Leucine/Leu | 15.59 ± 0.34 b | 5.03 ± 0.16 a |
| Tryptophan/Trp | 5.12 ± 0.16 a | 5.62 ± 0.19 a |
| Lysine/Lys | 0.10 ± 0.01 a | 0.58 ± 0.04 b |
| Hydrophobic amino acids | 42.29 ± 0.59 b | 32.31 ± 1.05 a |
| Hydrophilic amino acids | 12.55 ± 0.77 b | 8.31 ± 0.45 a |
| Acidic amino acids | 32.44 ± 1.25 a | 43.22 ± 1.93 b |
| Basic amino acids | 3.28 ± 0.09 a | 4.24 ± 0.46 b |
| Ratio of acidic-to-basic amino acids | 9.87 ± 0.21 a | 10.24 ± 0.72 b |
| Property | Zein | Prolamins from Highland Barley |
|---|---|---|
| Surface hydrophobicity index | 407.25 ± 35.08 b | 338.54 ± 21.80 a |
| Thermal properties | ||
| T0 (°C) | 55.87 ± 1.40 a | 62.02 ± 1.85 b |
| Tp (°C) | 103.74 ± 3.01 b | 112.41 ± 2.45 a |
| ΔH (°C) | −32.58 ± 2.40 b | −55.95 ± 1.72 a |
| Water holding capacity (g/g) | 0.81 ± 0.09 a | 1.27 ± 0.13 b |
| Oil absorption capacity (mL/g) | 4.85 ± 0.22 b | 3.18 ± 0.17 a |
| Emulsifying activity index (m2/g) | 9.29 ± 0.81 a | 14.58 ± 1.05 b |
| Emulsifying stability (min) | 24.52 ± 4.19 a | 37.20 ± 2.41 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, P. The Composition, Structure, and Functionalities of Prolamins from Highland Barley. Molecules 2023, 28, 5334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145334
Xing J, Li Z, Zhang W, Wang P. The Composition, Structure, and Functionalities of Prolamins from Highland Barley. Molecules. 2023; 28(14):5334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145334
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Jinjin, Zhaomin Li, Wenhui Zhang, and Pengjie Wang. 2023. "The Composition, Structure, and Functionalities of Prolamins from Highland Barley" Molecules 28, no. 14: 5334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145334
APA StyleXing, J., Li, Z., Zhang, W., & Wang, P. (2023). The Composition, Structure, and Functionalities of Prolamins from Highland Barley. Molecules, 28(14), 5334. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145334





