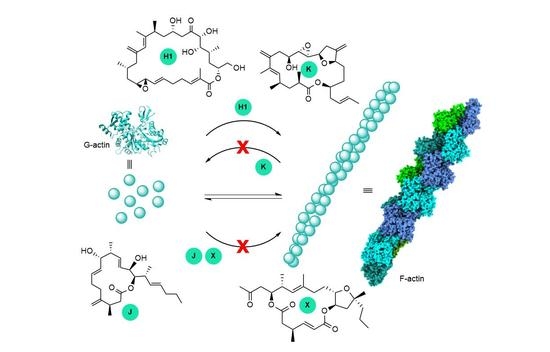
Actin-Interacting Amphidinolides: Syntheses and Mechanisms of Action of Amphidinolides X, J, and K
Abstract
1. Introduction
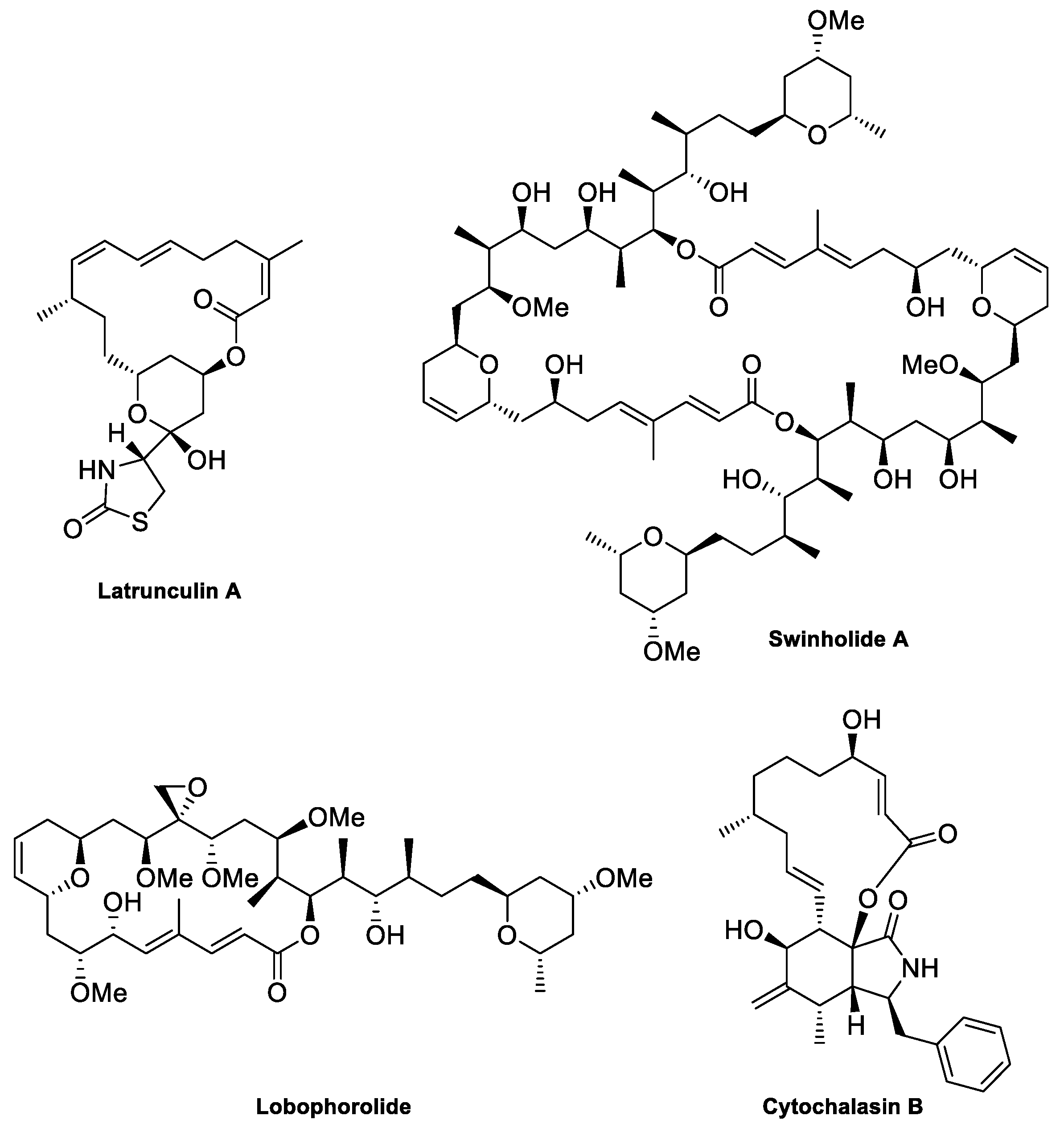
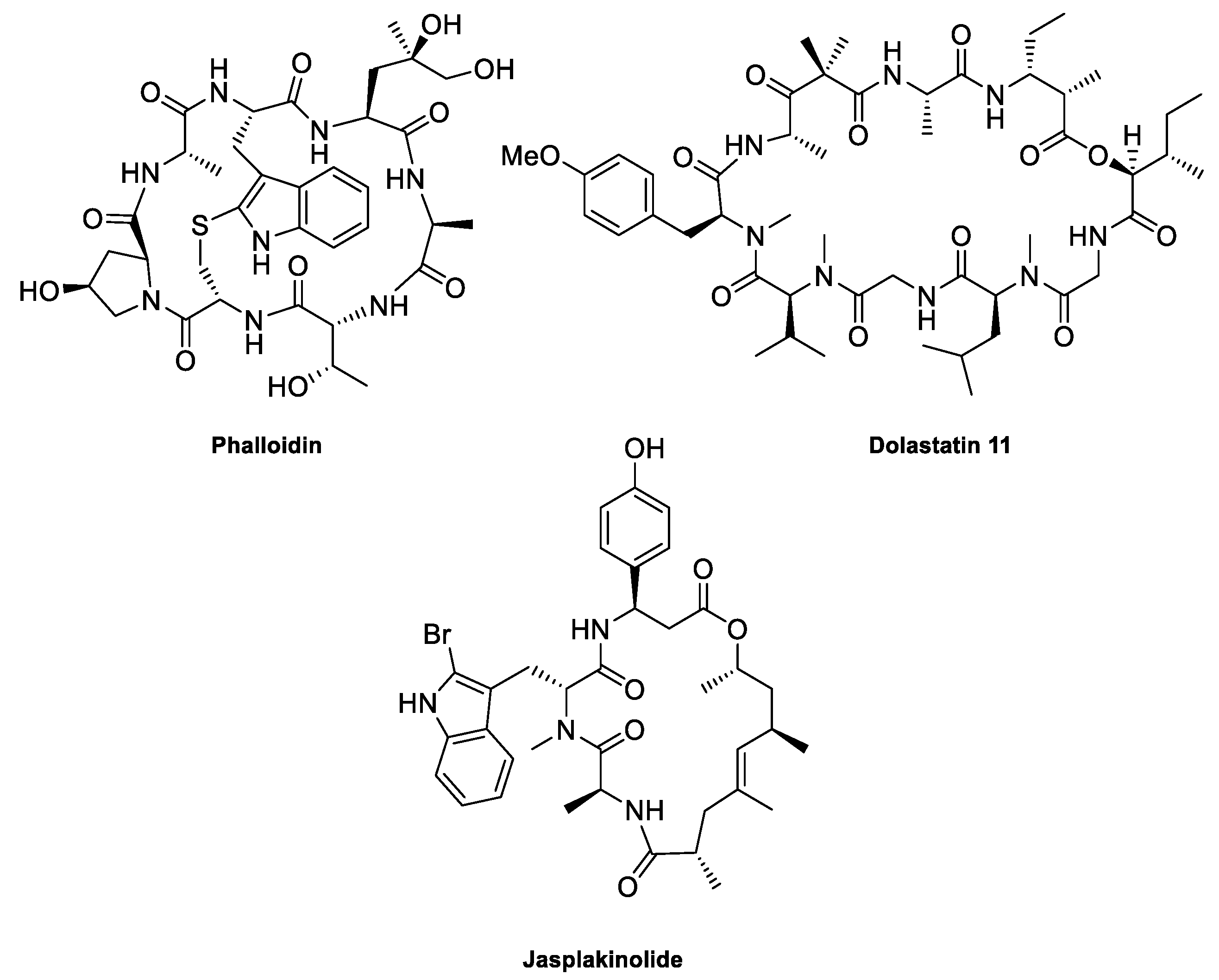
2. The Actin Cytoskeleton
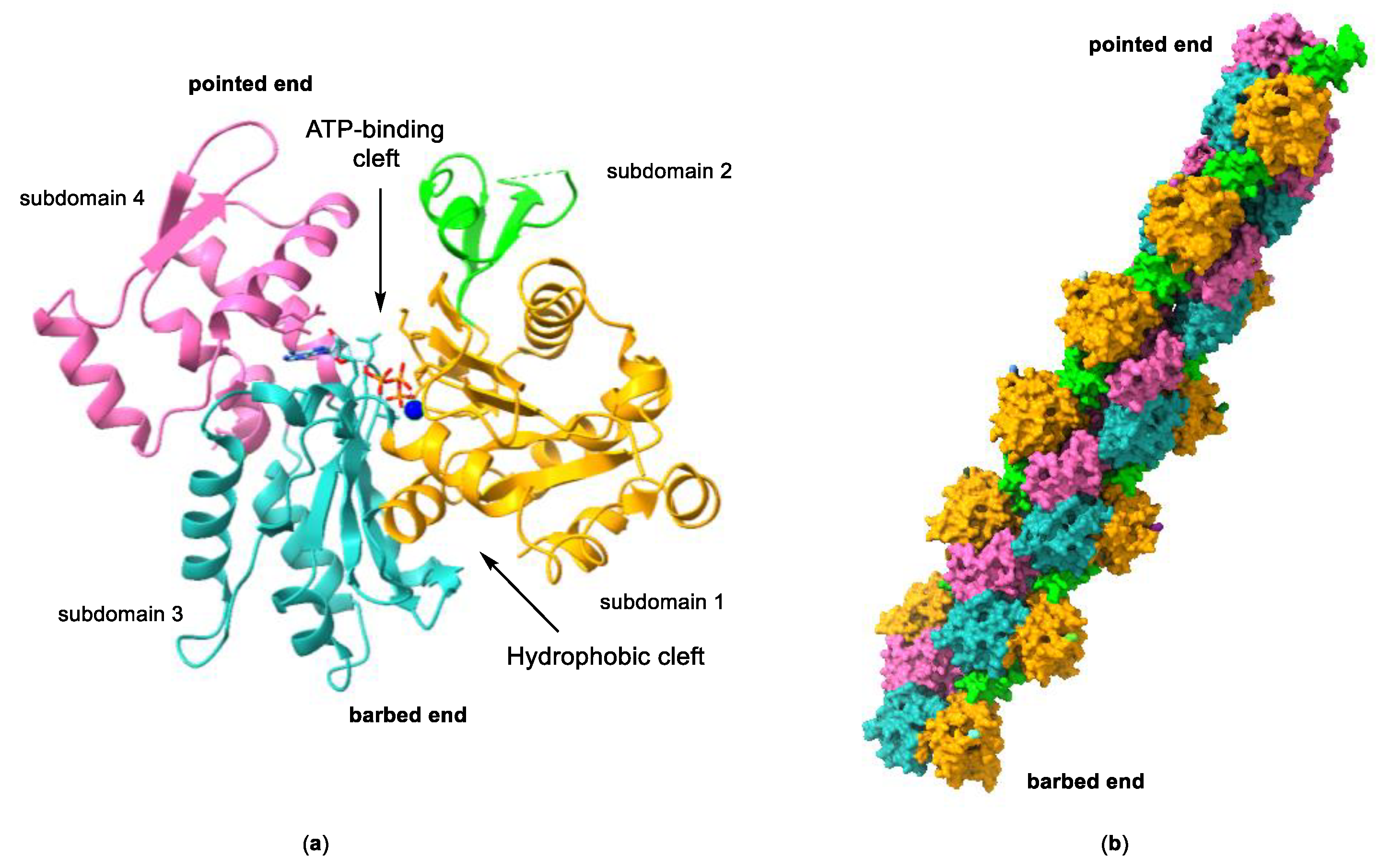
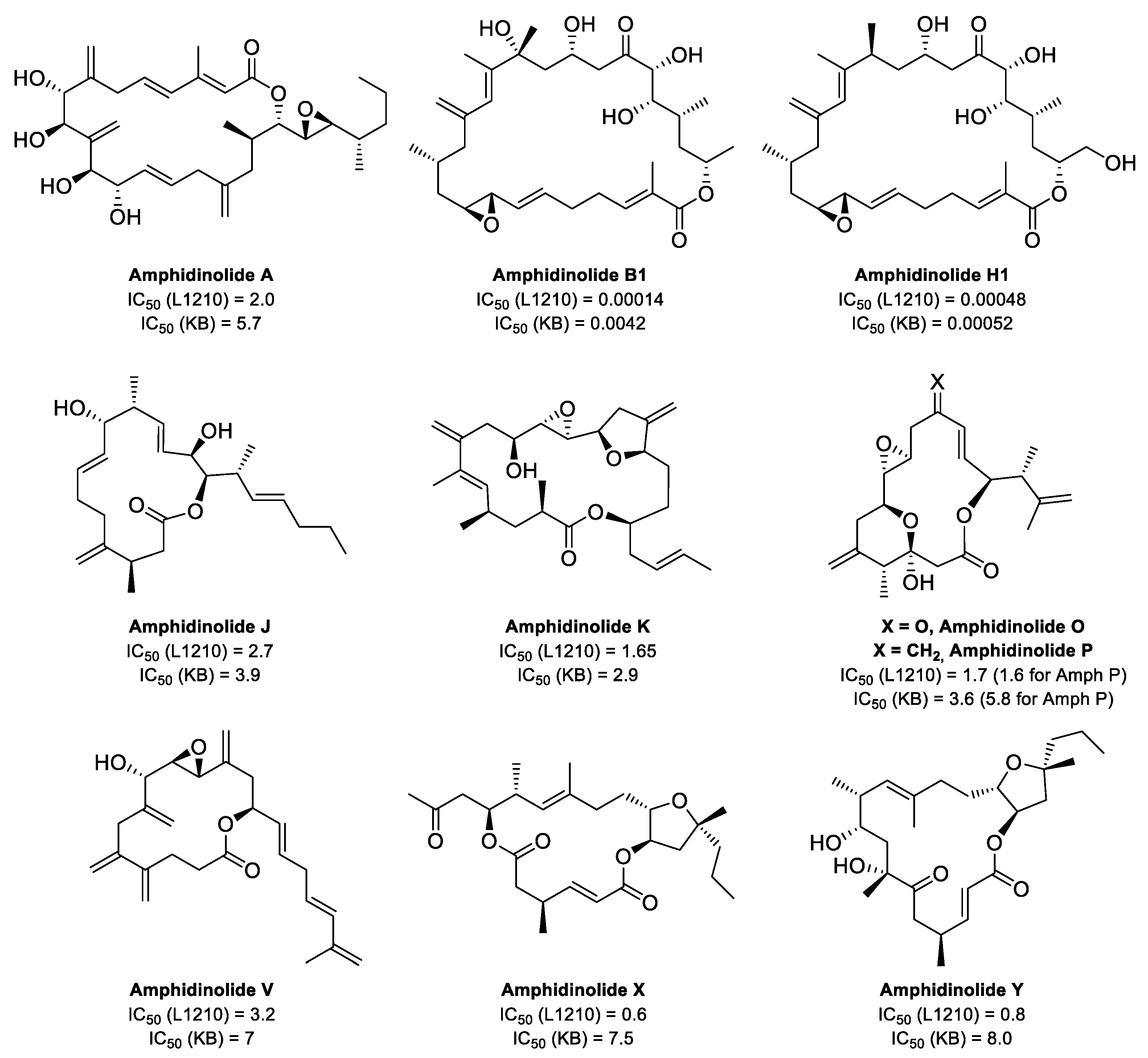
3. Interaction of Amphidinolides B1 and H1 with Actin
4. Total Syntheses of Amphidinolides X, J, and K Aimed at Elucidating Their Mechanisms of Action
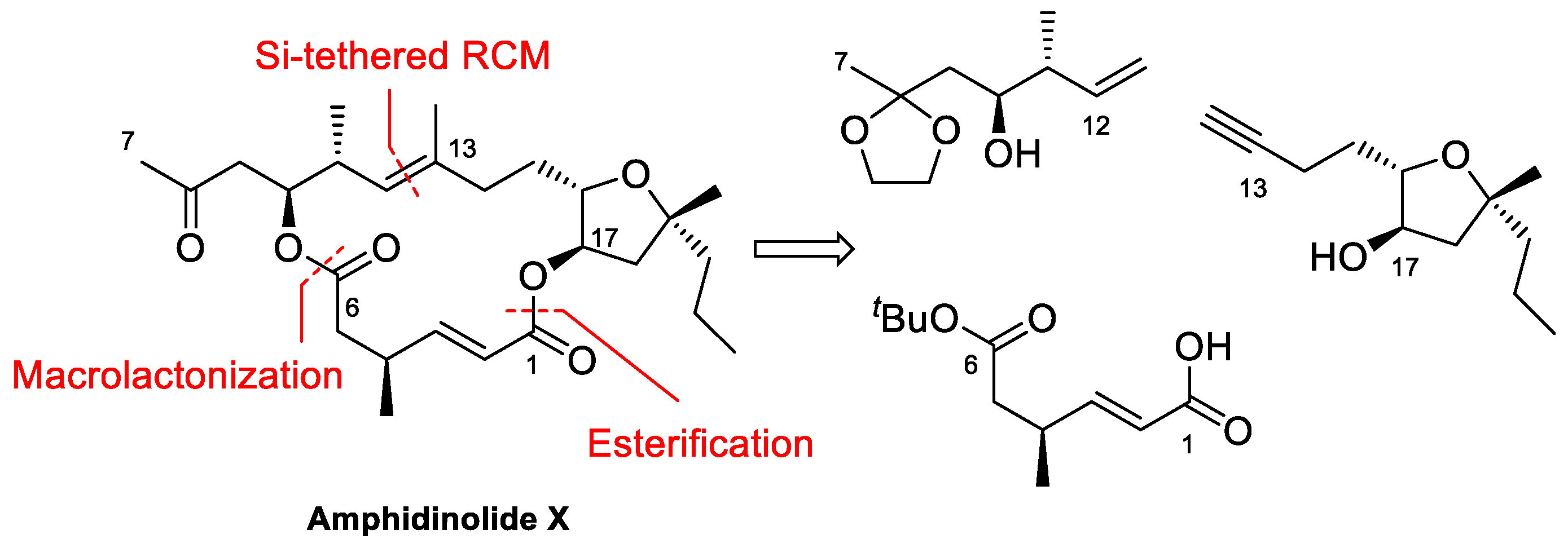
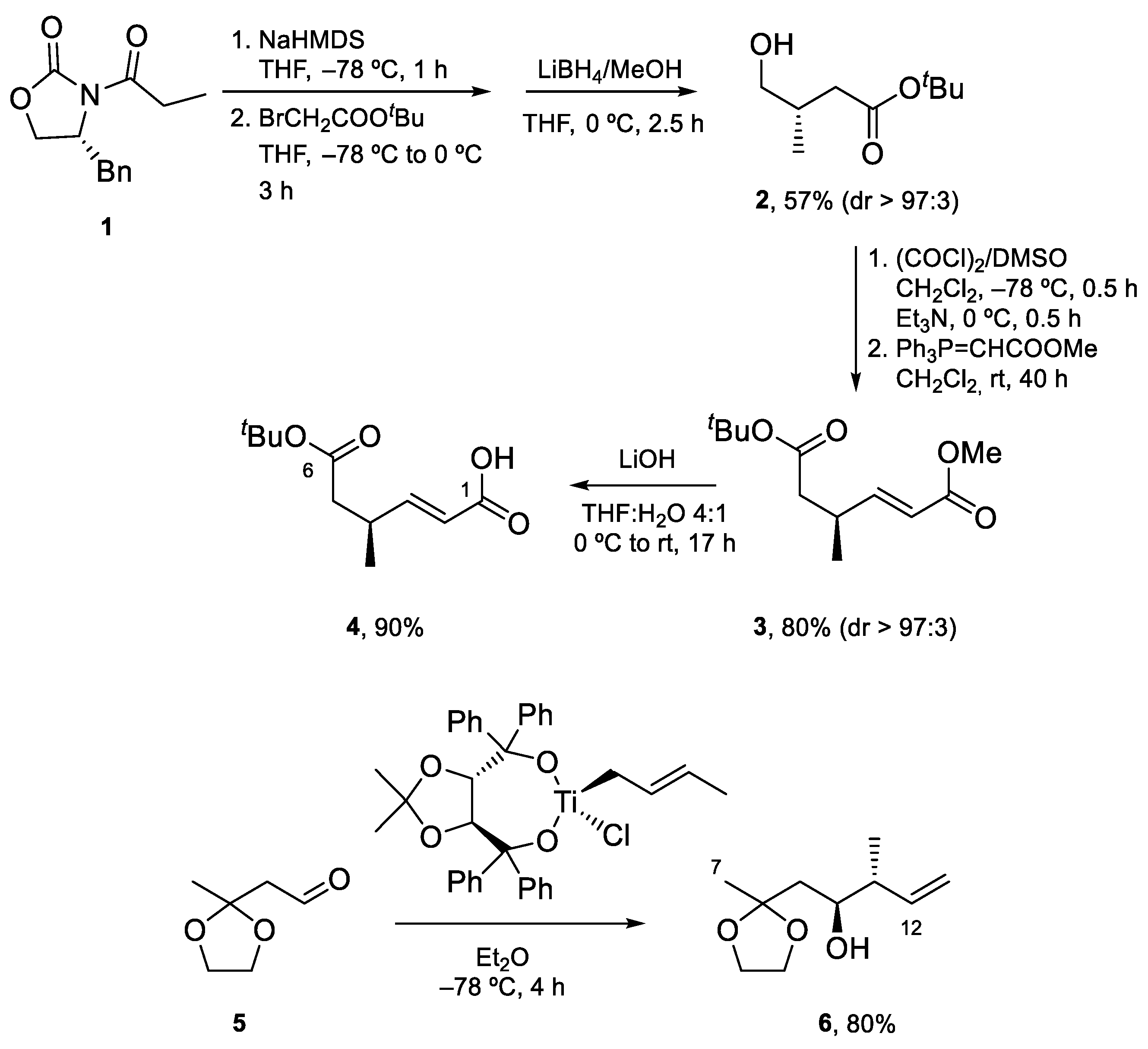
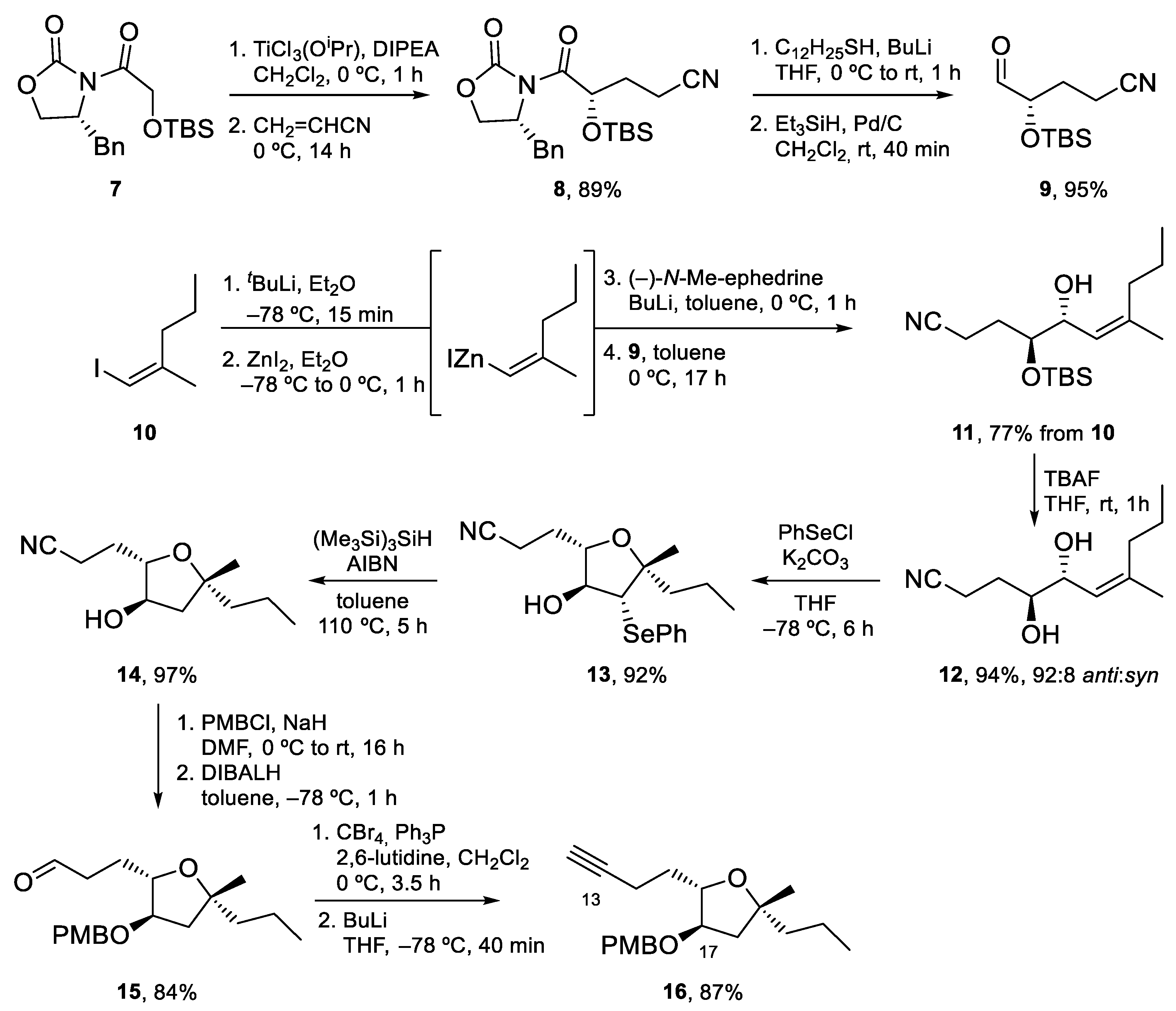
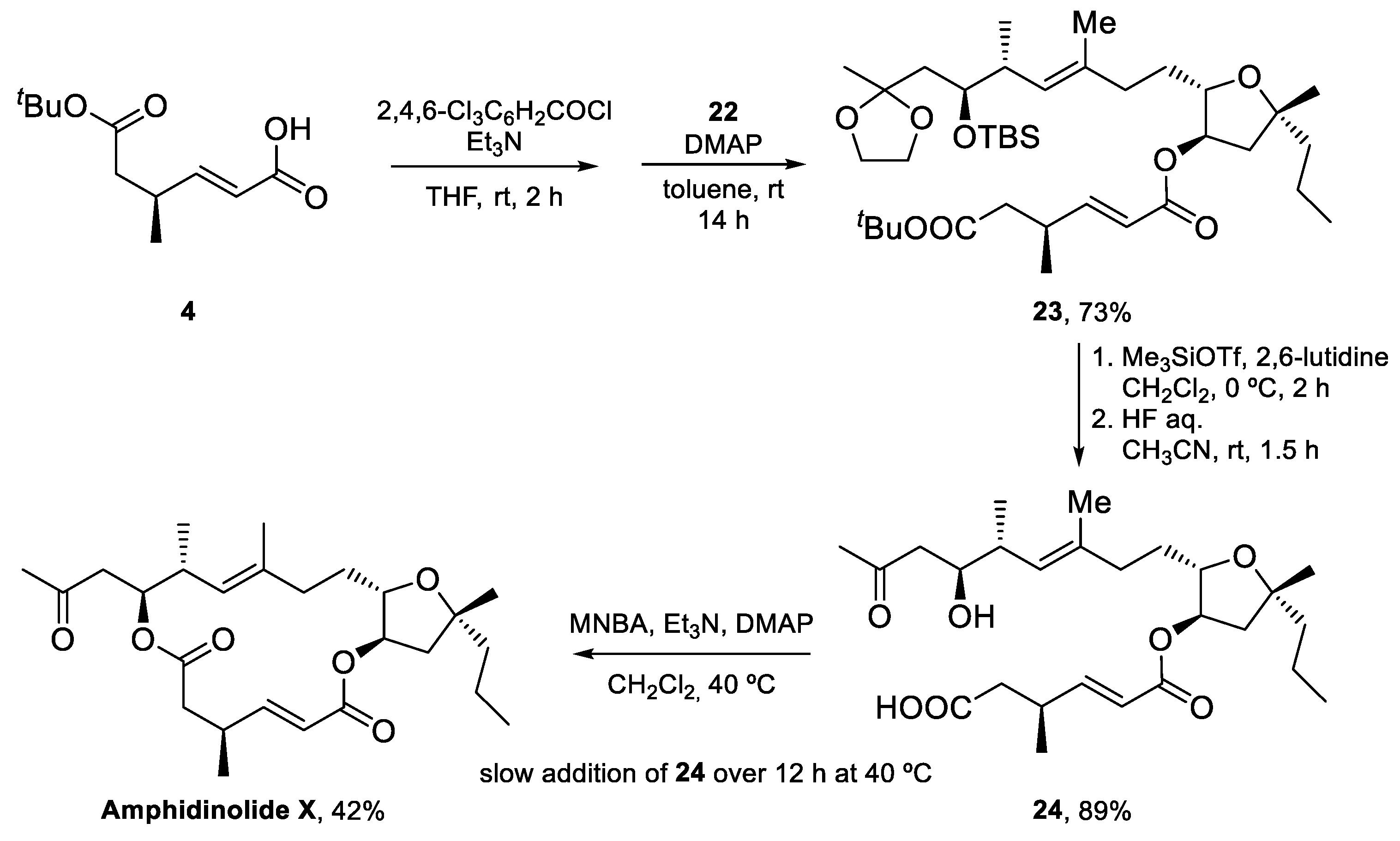
4.1. Total Synthesis of Amphidinolide X
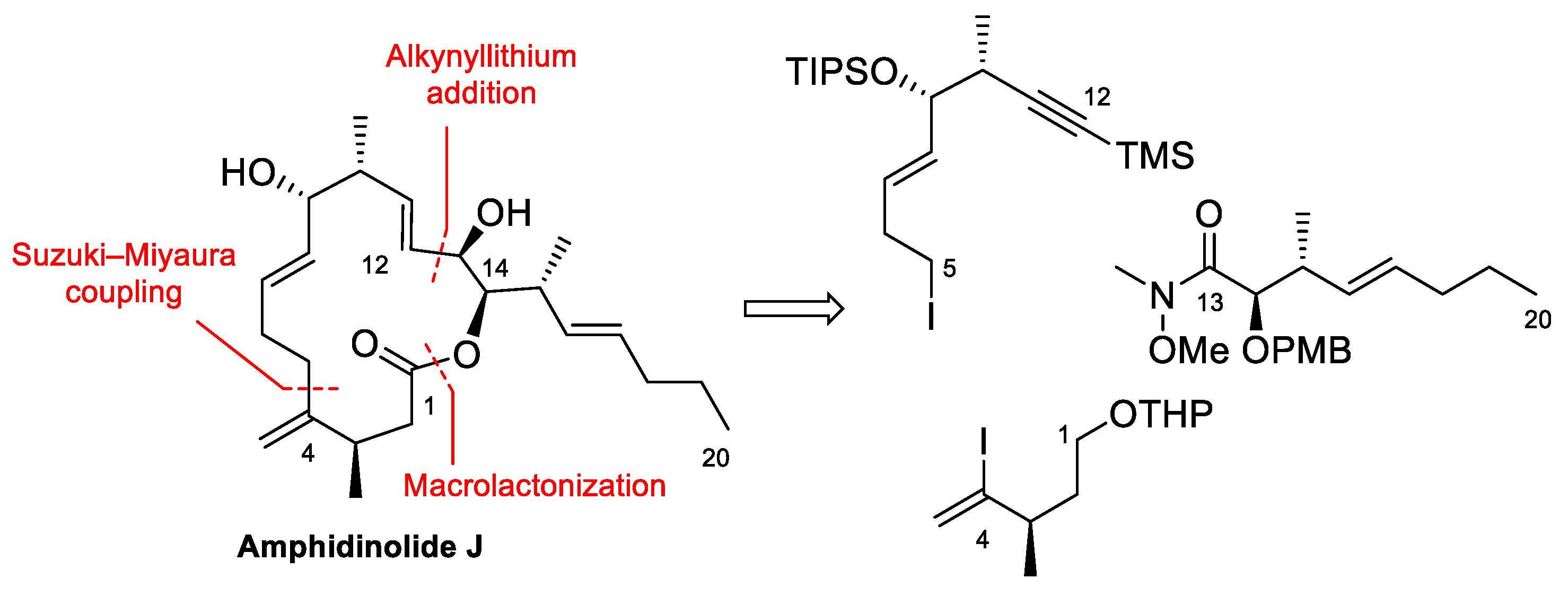
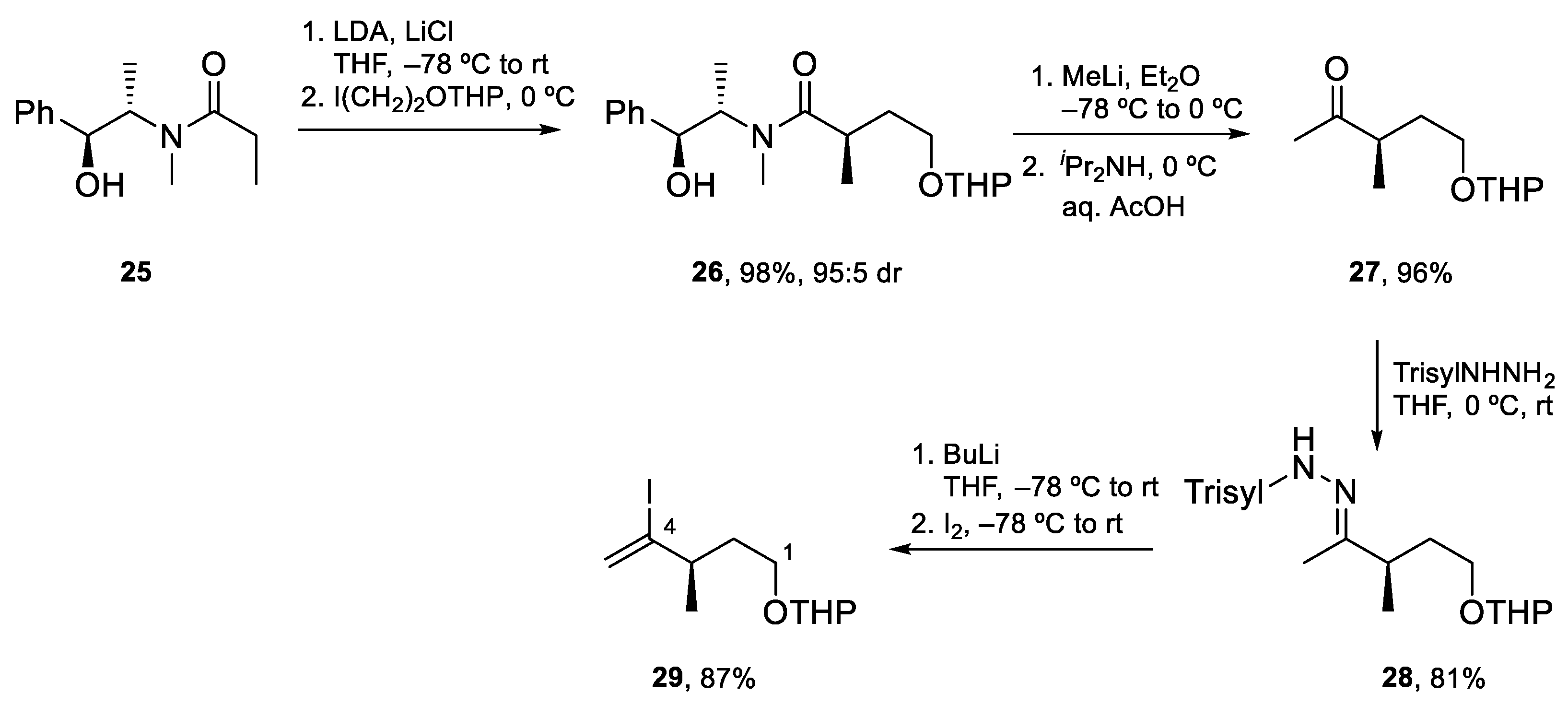
4.2. Total Synthesis of Amphidinolide J
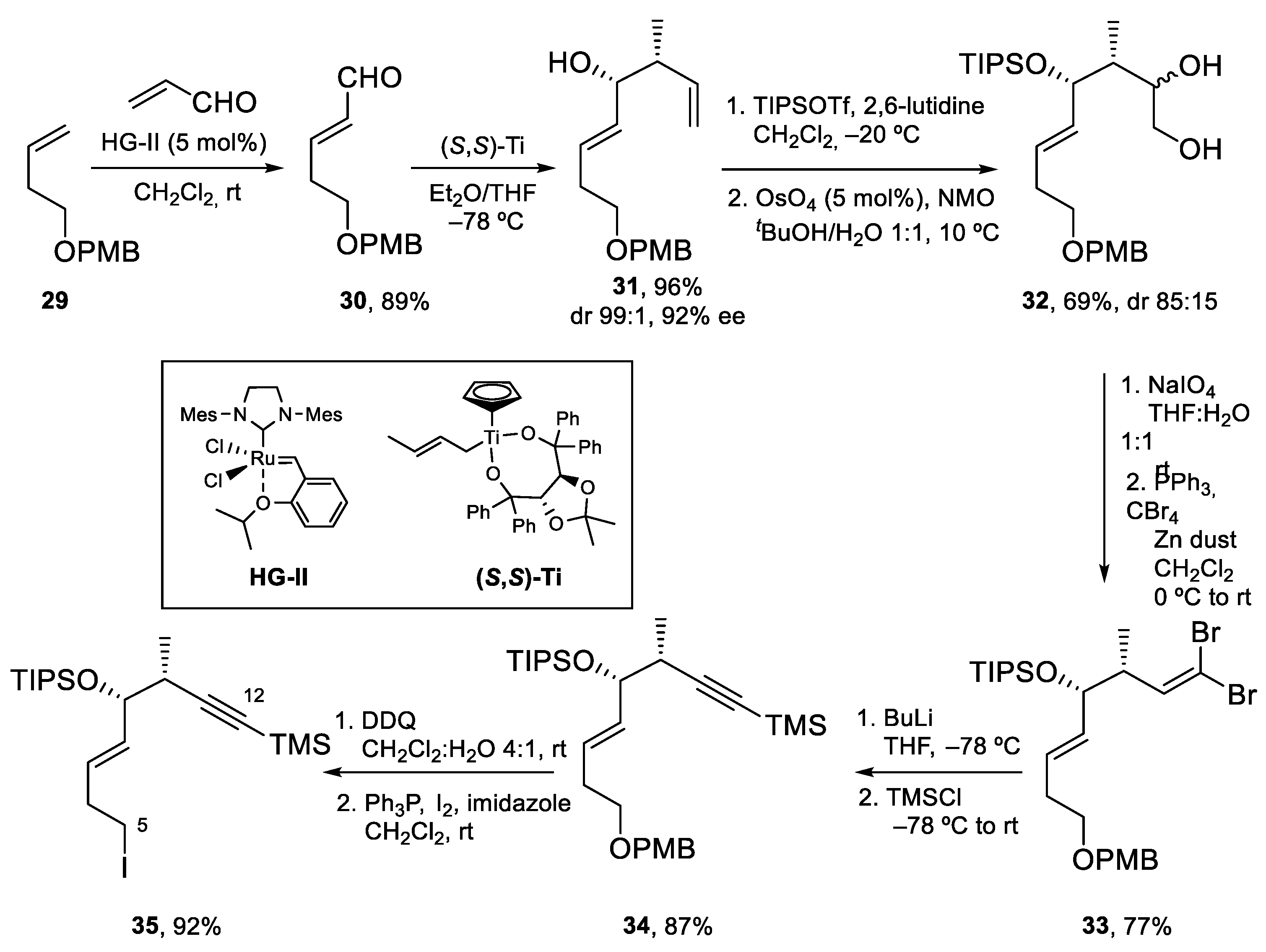
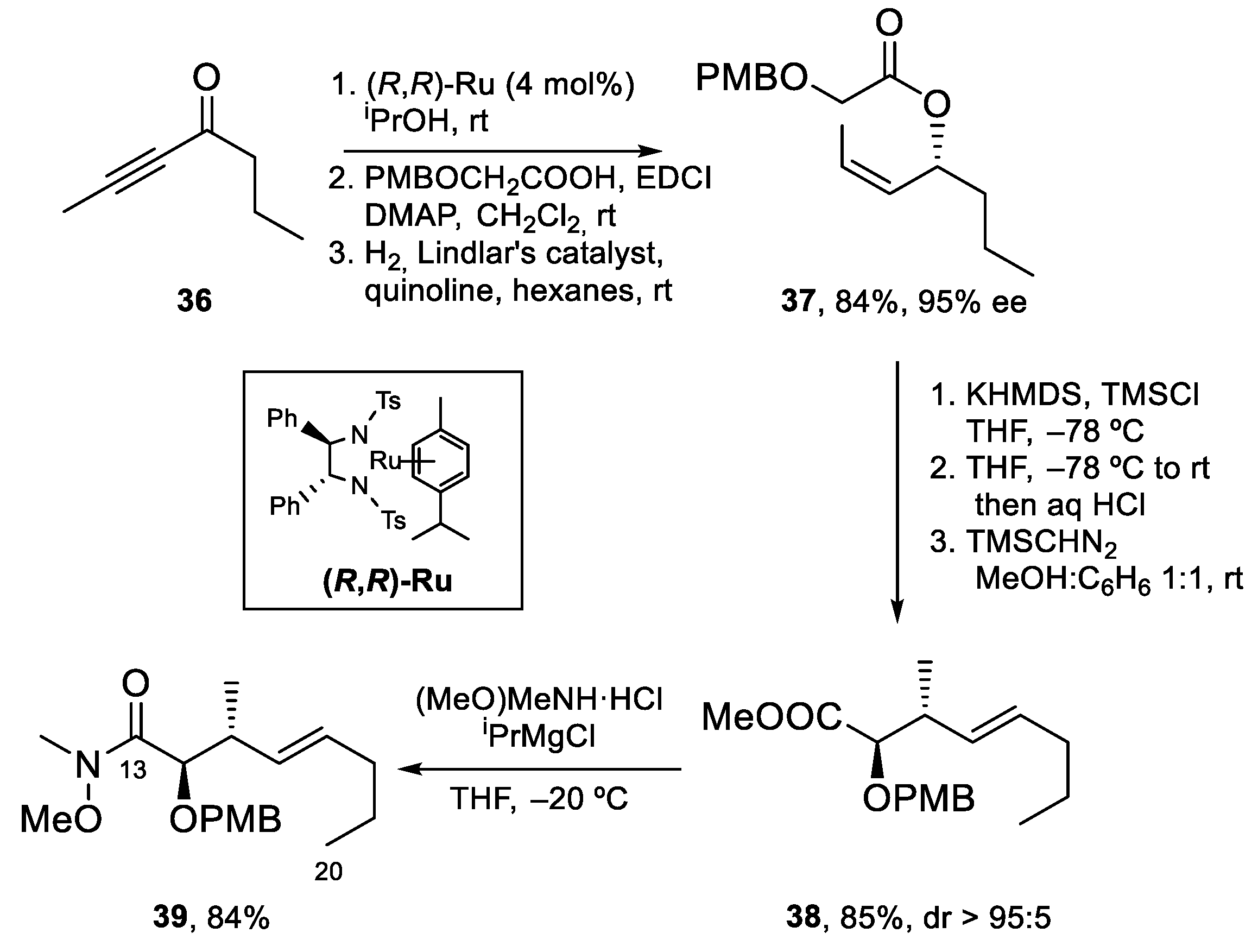
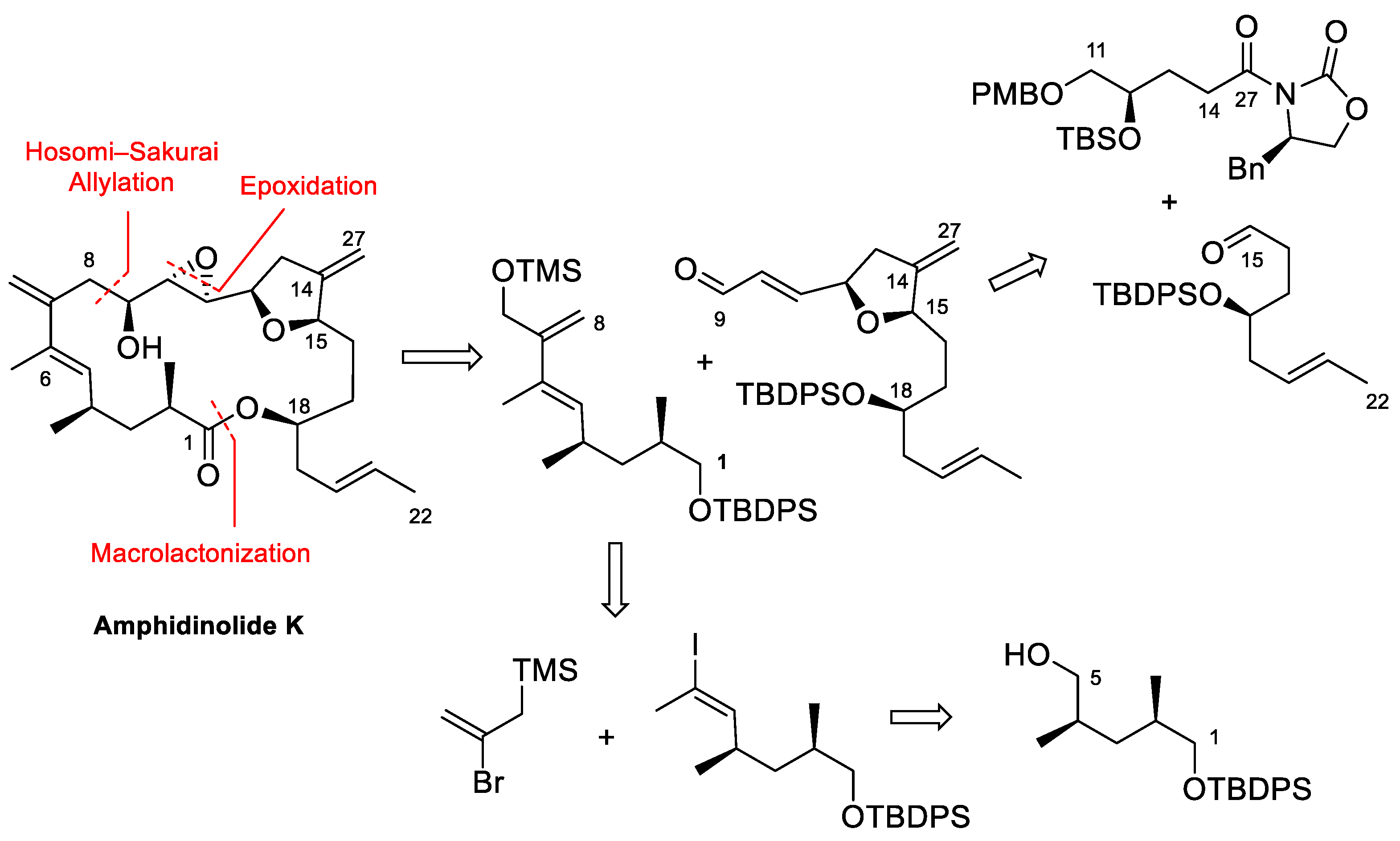
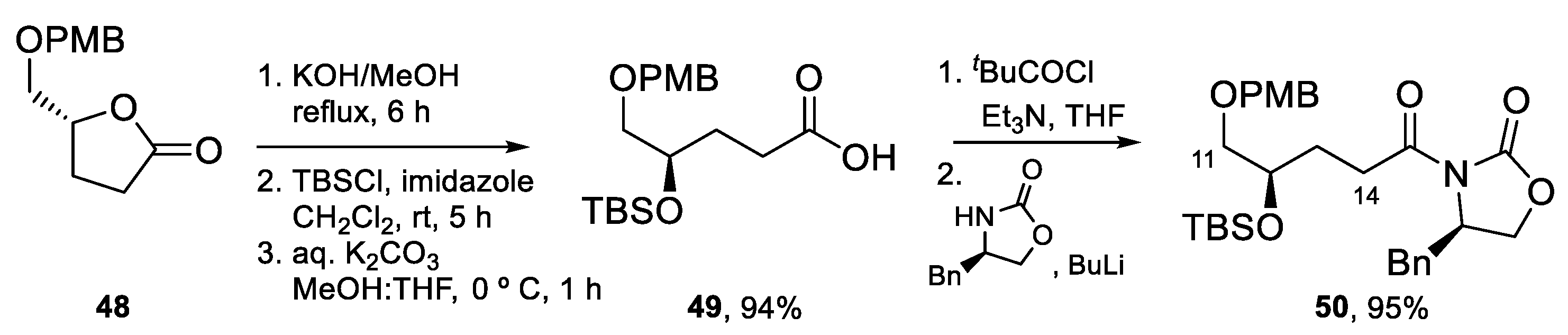
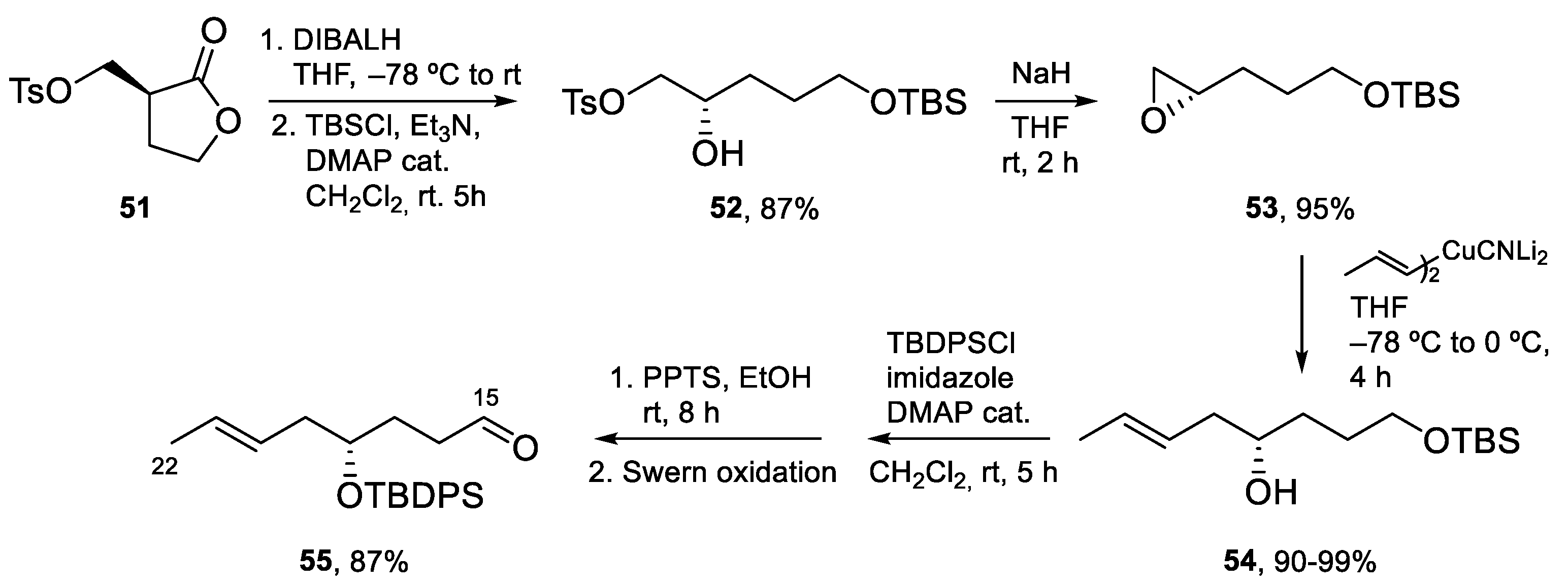
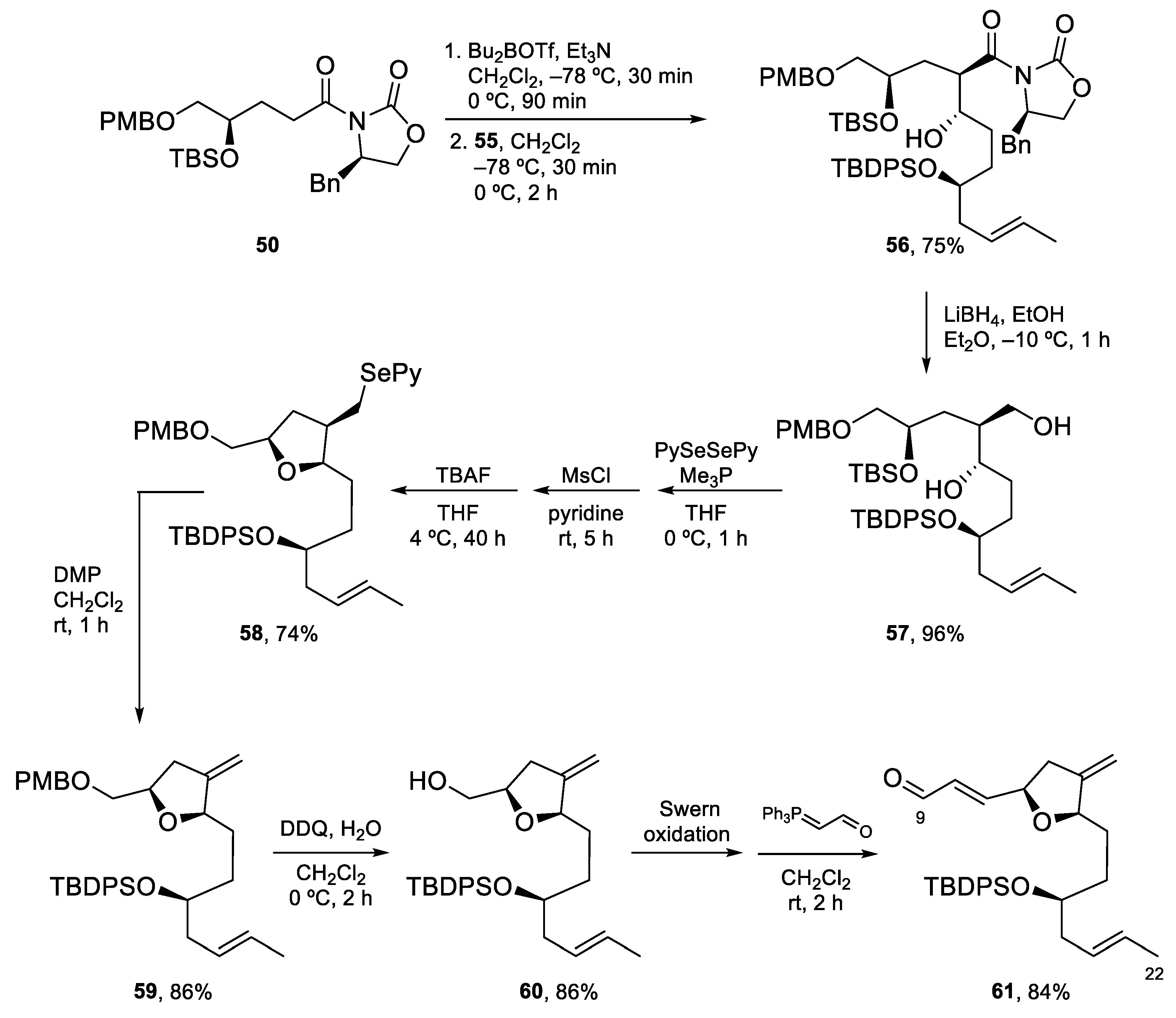
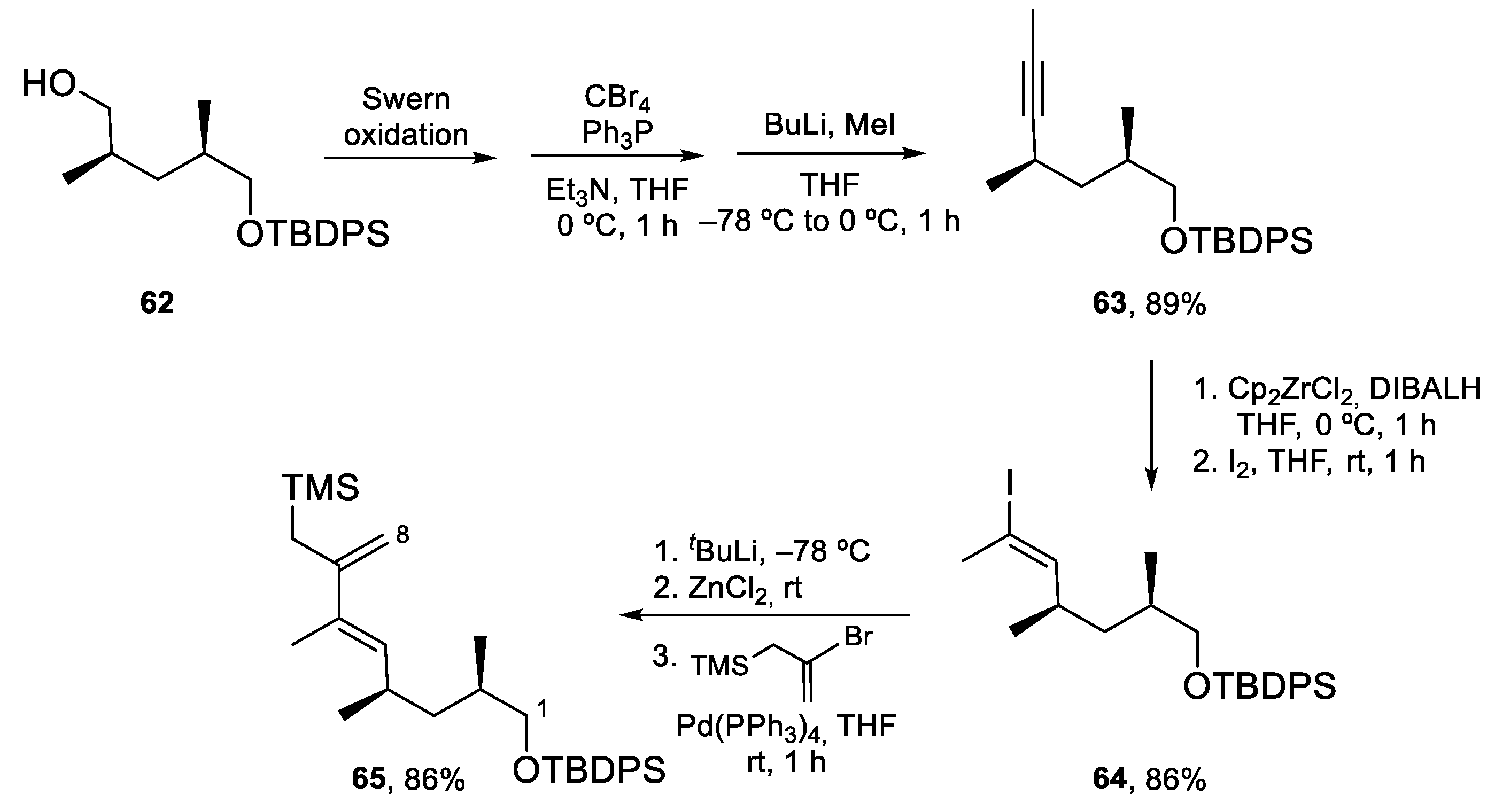
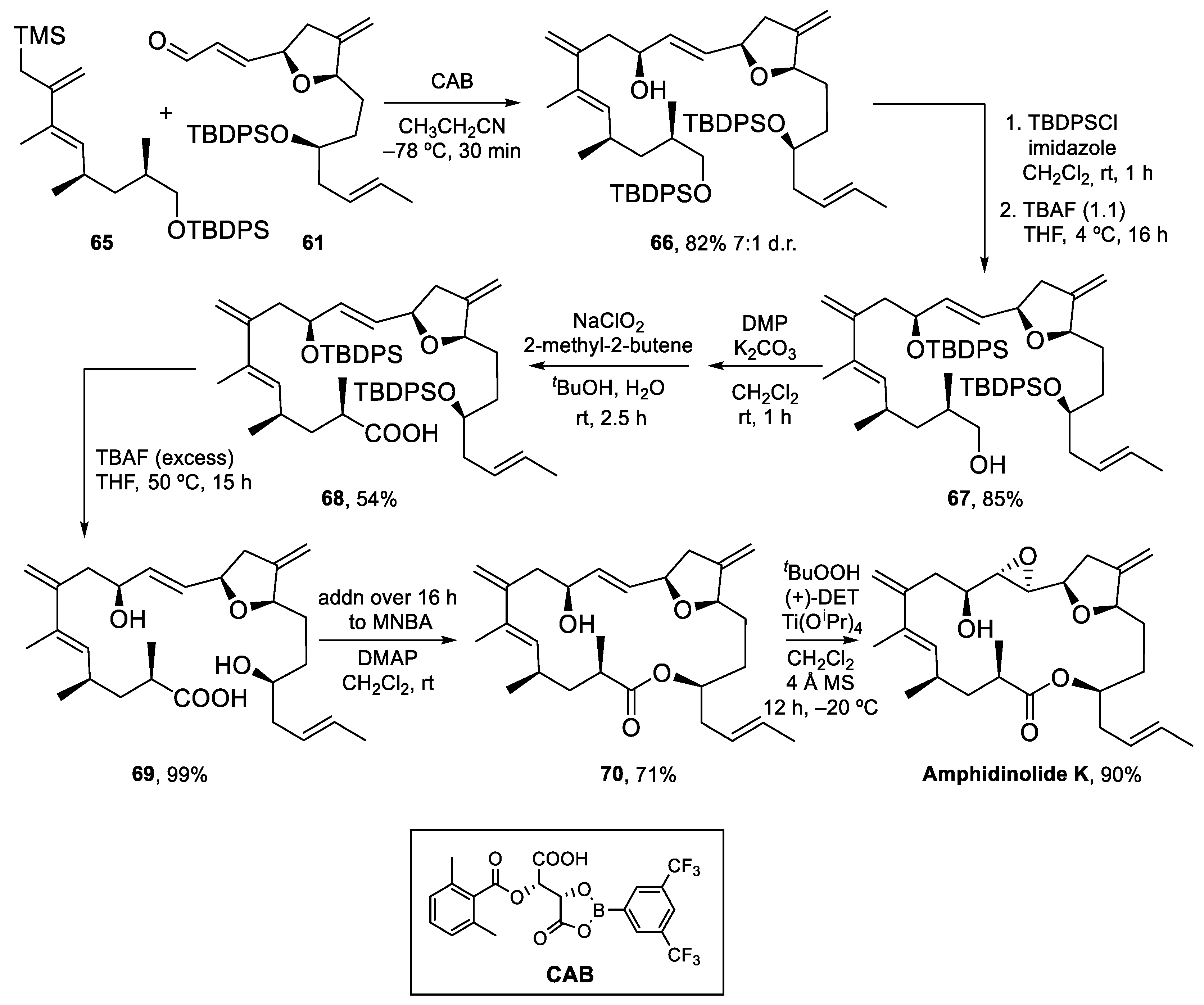
4.3. Total Synthesis of Amphidinolide K
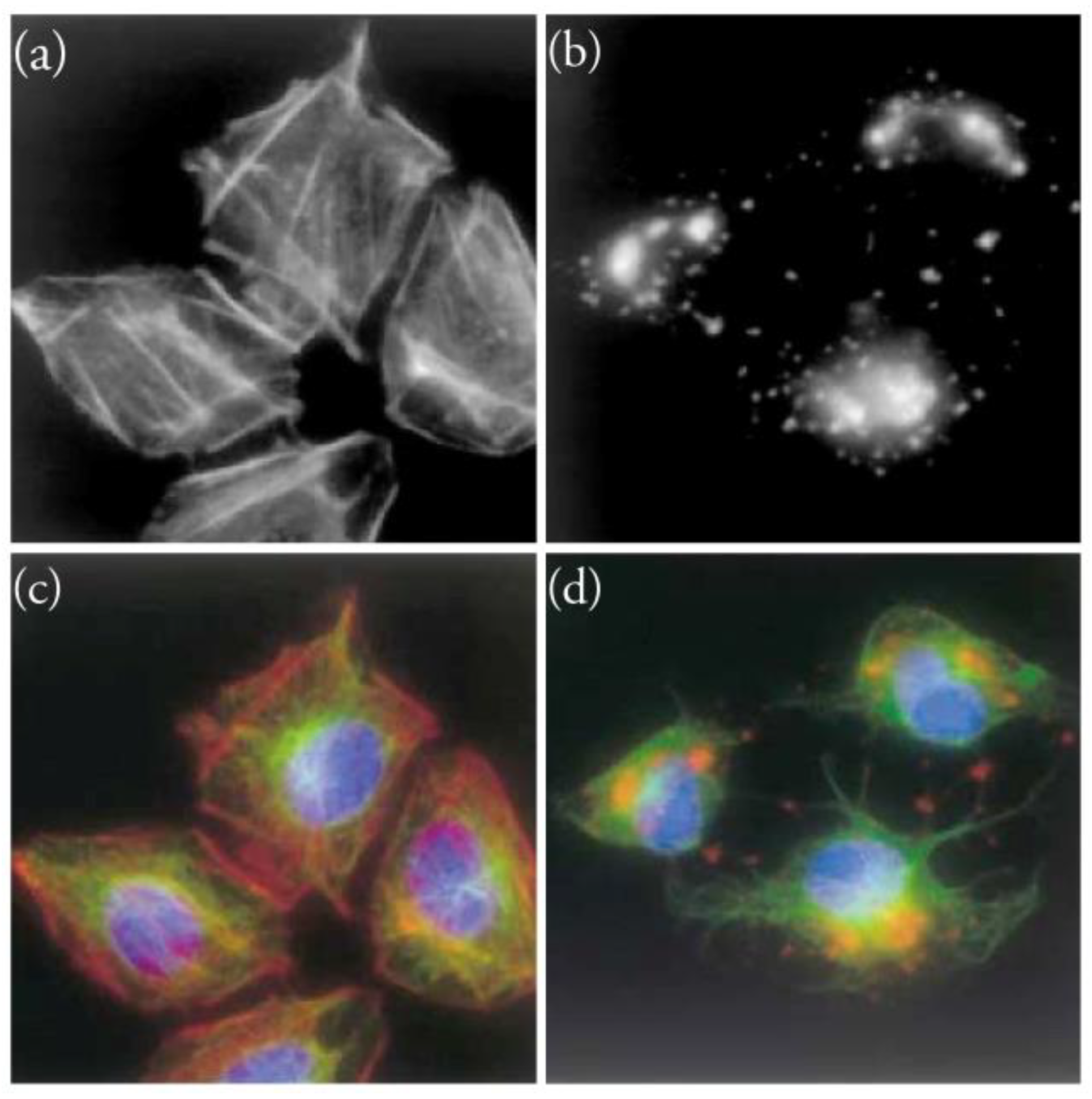
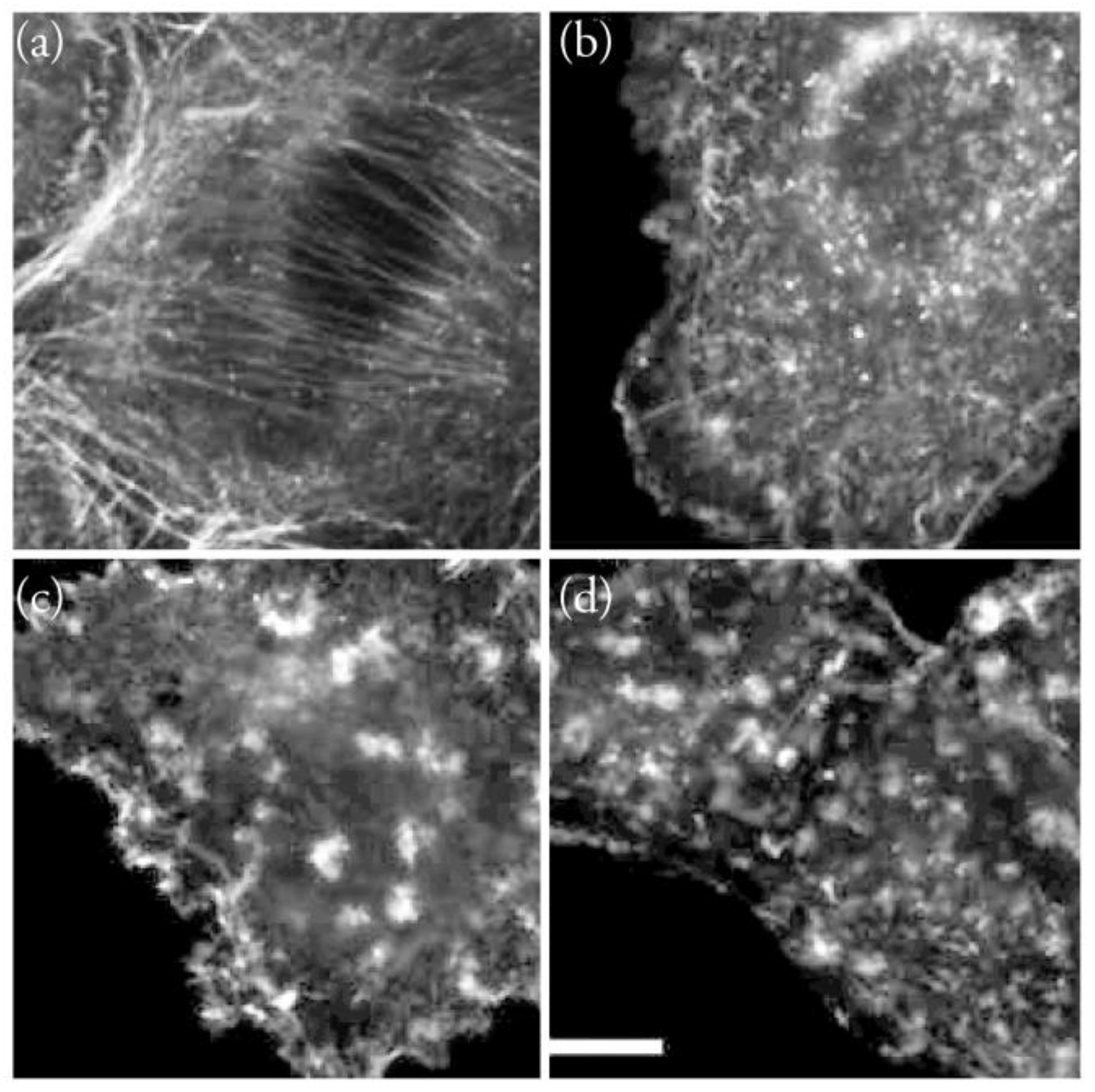
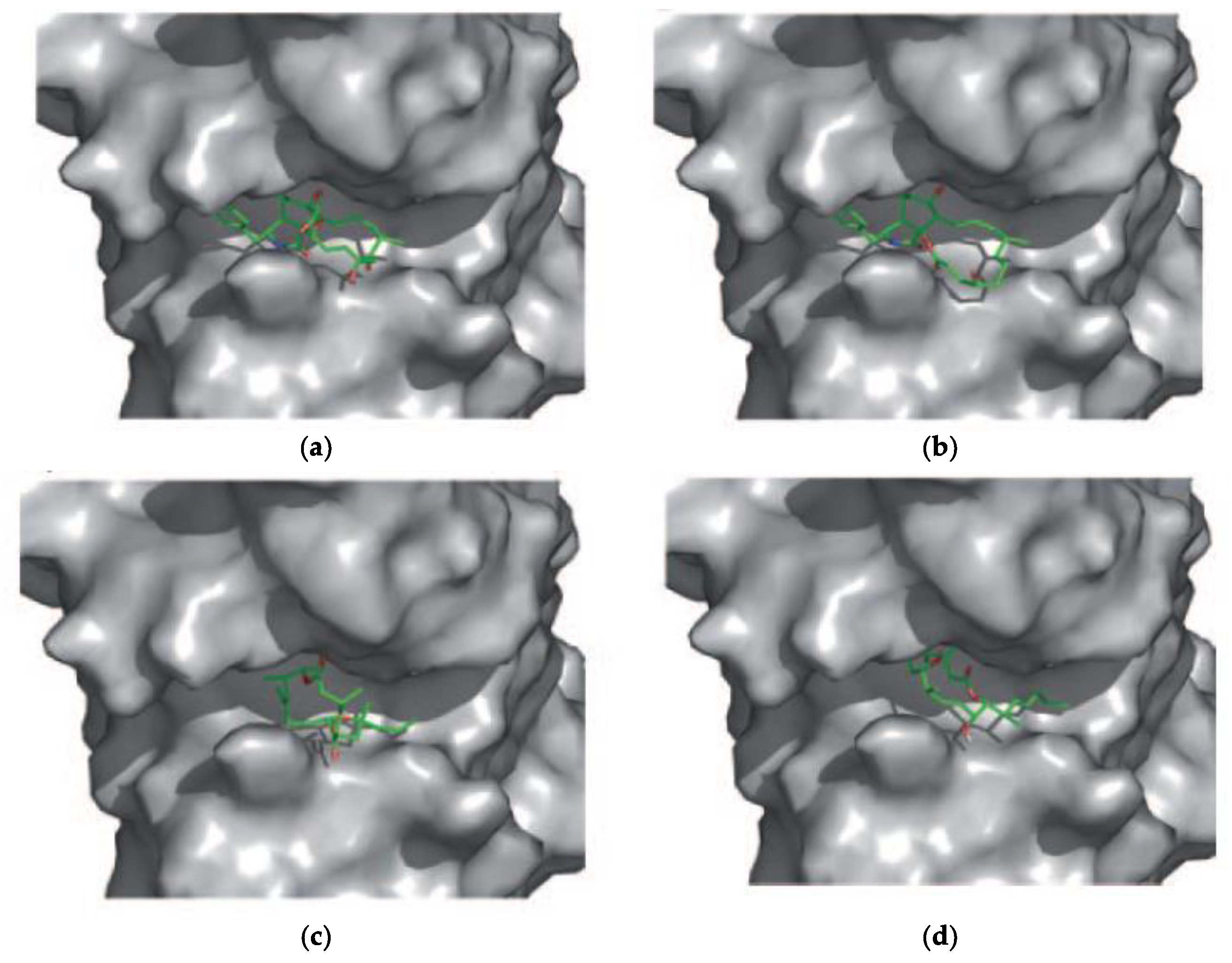
5. Interaction of Amphidinolides J, X, and K with Actin
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Kobayashi, J. Amphidinolides and Its Related Macrolides from Marine Dinoflagellates. J. Antibiot. 2008, 61, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, J.; Kubota, T. Bioactive Macrolides and Polyketides from Marine Dinoflagellates of the Genus Amphidinium. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, J.; Tsuda, M. Amphidinolides, Bioactive Macrolides from Symbiotic Marine Dinoflagellates. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 21, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, T.K.; Das, S. Chemistry of Potent Anti-Cancer Compounds, Amphidinolides. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti-Cancer Agents 2001, 1, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, J.; Ishibashi, M.; Nakamura, H.; Ohizumi, Y.; Yamasu, T.; Sasaki, T.; Hirata, Y. Amphidinolide-A, a Novel Antineoplastic Macrolide from the Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986, 27, 5755–5758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstner, A.; Flügge, S.; Larionov, O.; Takahashi, Y.; Kubota, T.; Kobayashi, J. Total Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Amphidinolide V and Analogues. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 4011–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furstner, A.; Kattnig, E.; Kelter, G.; Fiebig, H.H. Molecular Editing and Biological Evaluation of Amphidinolide X and Y. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 4030–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, D.; Andreou, T.; Costa, A.M.; Meyer, K.G.; Williams, D.R.; Barasoain, I.; Díaz, J.F.; Lucena-Agell, D.; Vilarrasa, J. Total Synthesis of Amphidinolide K, a Macrolide That Stabilizes F-Actin. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 8511–8519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, K.; Nakatani, K.; Ishibashi, M.; Kobayashi, J.; Ohizumi, Y. Amphidinolide B, a Powerful Activator of Actomyosin ATPase Enhances Skeletal Muscle Contraction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1427, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigili, C.; Pera, B.; Barbazanges, M.; Cossy, J.; Meyer, C.; Pineda, O.; Rodríguez-Escrich, C.; Urpí, F.; Vilarrasa, J.; Díaz, J.F.; et al. Mechanism of Action of the Cytotoxic Macrolides Amphidinolide X and J. ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 1027–1030, Corrigendum in ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, T.; Kazami, S.; Dohmae, N.; Mashimo, Y.; Kondo, H.; Tsuda, M.; Terasaki, A.G.; Ohashi, K.; Kobayashi, J.; Osada, H. Amphidinolide H, a Potent Cytotoxic Macrolide, Covalently Binds on Actin Subdomain 4 and Stabilizes Actin Filament. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.Y.; Feng, J.; Kira, A.; Kobayashi, J.; Ohizumi, Y. Amphidinolide H, a Novel Type of Actin-Stabilizing Agent Isolated from Dinoflagellate. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 320, 961–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Remedios, C.G.; Chhabra, D.; Kekic, M.; Dedova, I.V.; Tsubakihara, M.; Berry, D.A.; Nosworthy, N.J. Actin Binding Proteins: Regulation of Cytoskeletal Microfilaments. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 433–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, I.M. Actin Isoforms. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1993, 5, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, B.J.; Ervasti, J.M. The Actin Gene Family: Function Follows Isoform. Cytoskeleton 2010, 67, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, U.B.; Joel, P.B.; Wan, Q.; Lowey, S.; Rould, M.A.; Trybus, K.M. Crystal Structures of Monomeric Actin Bound to Cytochalasin D. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 384, 848–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Yasunaga, T.; Noguchi, T.Q.P.; Gomibuchi, Y.; Ngo, K.X.; Uyeda, T.Q.P.; Wakabayashi, T. Structural Basis for Actin Assembly, Activation of ATP Hydrolysis, and Delayed Phosphate Release. Cell 2010, 143, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risinger, A.L.; Du, L. Targeting and Extending the Eukaryotic Druggable Genome with Natural Products: Cytoskeletal Targets of Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 634–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unzue, A.; Cribiú, R.; Hoffman, M.M.; Knehans, T.; Lafleur, K.; Caflisch, A.; Nevado, C. Iriomoteolides: Novel Chemical Tools to Study Actin Dynamics. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 3793–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenteany, G.; Zhu, S. Small-Molecule Inhibitors of Actin Dynamics and Cell Motility. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2003, 3, 593–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, K.-S.; Paterson, I. Actin-Binding Marine Macrolides: Total Synthesis and Biological Importance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 4632–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spector, I.; Braet, F.; Shochet, N.R.; Bubb, M.R. New Anti-Actin Drugs in the Study of the Organization and Function of the Actin Cytoskeleton. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1999, 47, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melak, M.; Plessner, M.; Grosse, R. Actin Visualization at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izdebska, M.; Zielińska, W.; Hałas-Wiśniewska, M.; Grzanka, A. Involvement of Actin and Actin-Binding Proteins in Carcinogenesis. Cells 2020, 9, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, W.M.; Ayscough, K.R.; McLaughlin, P.J. Latrunculin Alters the Actin-Monomer Subunit Interface to Prevent Polymerization. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 376–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coué, M.; Brenner, S.L.; Spector, I.; Korn, E.D. Inhibition of Actin Polymerization by Latrunculin A. FEBS Lett. 1987, 213, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, I.; Shochet, N.R.; Kashman, Y.; Groweiss, A. Latrunculins: Novel Marine Toxins That Disrupt Microfilament Organization in Cultured Cells. Science 1983, 219, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allingham, J.S.; Klenchin, V.A.; Rayment, I. Actin-Targeting Natural Products: Structures, Properties and Mechanisms of Action. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 2119–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean-Fletcher, S.; Pollard, T.D. Mechanism of Action of Cytochalasin B on Actin. Cell 1980, 20, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.A. Effects of Cytochalasin and Phalloidin on Actin. J. Cell Biol. 1987, 105, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubb, M.R.; Spector, I.; Bershadsky, A.D.; Korn, E.D. Swinholide A Is a Microfilament Disrupting Marine Toxin That Stabilizes Actin Dimers and Severs Actin Filaments. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 3463–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klenchin, V.A.; King, R.; Tanaka, J.; Marriott, G.; Rayment, I. Structural Basis of Swinholide a Binding to Actin. Chem. Biol. 2005, 12, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blain, J.C.; Mok, Y.-F.; Kubanek, J.; Allingham, J.S. Two Molecules of Lobophorolide Cooperate to Stabilize an Actin Dimer Using Both Their “Ring” and “Tail” Region. Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Crane, Z.D.; Dicus, C.W.; Sufi, B.A.; Bates, R.B. Dolastatin 11 Connects Two Long-Pitch Strands in F-Actin to Stabilize Microfilaments. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 328, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, M.; Ohizumi, Y.; Hamashima, M.; Nakamura, H.; Hirata, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, J. Amphidinolide-B, a Novel Macrolide with Potent Antineoplastic Activity from the Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1987, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, I.; Maranda, L.; Shimizu, Y.; Peterson, R.W.; Cornell, L.; Steiner, J.R.; Clardy, J. The Structures of Amphidinolide B Isomers: Strongly Cytotoxic Macrolides Produced by a Free-Swimming Dinoflagellate, Amphidinium sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 2657–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Shigemori, H.; Ishibashi, M.; Yamasu, T.; Hirota, H.; Sasaki, T. Amphidinolides G and H: New Potent Cytotoxic Macrolides from the Cultured Symbiotic Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 5221–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, W.; Carter, R.G. Total Synthesis of Cytotoxic Macrolide Amphidinolide B1 and the Proposed Structure of Amphidinolide B2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7253–7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, W.; Nam, S.; Horne, D.A.; Jove, R.; Carter, R.G. Amphidinolide B: Total Synthesis, Structural Investigation, and Biological Evaluation. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 130, 2213–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstner, A.; Bouchez, L.C.; Morency, L.; Funel, J.-A.; Liepins, V.; Porée, F.-H.; Gilmour, R.; Laurich, D.; Beaufils, F.; Tamiya, M. Total Syntheses of Amphidinolides B1, B4, G1, H1 and Structure Revision of Amphidinolide H2. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 3983–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstner, A.; Bouchez, L.C.; Funel, J.-A.; Liepins, V.; Porée, F.-H.; Gilmour, R.; Beaufils, F.; Laurich, D.; Tamiya, M. Total Syntheses of Amphidinolide H and G13. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 9265–9270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Escrich, C.; Urpí, F.; Vilarrasa, J. Stereocontrolled Total Synthesis of Amphidinolide X via a Silicon-Tethered Metathesis Reaction. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 5191–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbazanges, M.; Meyer, C.; Cossy, J. Total Synthesis of Amphidinolide J. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4489–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, M.; Izui, N.; Shimbo, K.; Sato, M.; Fukushi, E.; Kawabata, J.; Katsumata, K.; Horiguchi, T.; Kobayashi, J. Amphidinolide X, a Novel 16-Membered Macrodiolide from Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 5339–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepage, O.; Kattnig, E.; Fürstner, A. Total Synthesis of Amphidinolide X. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15970–15971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fürstner, A.; Kattnig, E.; Lepage, O. Total Syntheses of Amphidinolide X and Y. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9194–9204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.-M.; Chen, Y.; Jin, J.; Wu, J.; Lou, J.; He, Q. Total Synthesis of Amphidinolide X and Its 12Z-Isomer by Formation of the C12-C13 Trisubstituted Double Bond via Ring-Closing Metathesis. Synlett 2008, 2008, 1737–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, E. Expedient Synthesis of (−)-Amphidinolide X. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5698–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Escrich, C.; Olivella, A.; Urpí, F.; Vilarrasa, J. Toward a Total Synthesis of Amphidinolide X and Y. The Tetrahydrofuran-Containing Fragment C12–C21. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Sato, M.; Ishibashi, M. Amphidinolide J: A Cytotoxic Macrolide from the Marine Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. Determination of the Absolute Stereochemistry. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 2645–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.R.; Kissel, W.S. Total Synthesis of (+)-Amphidinolide J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 11198–11199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, M.; Sato, M.; Kobayashi, J. Amphidinolide K, a New 19-Membered Macrolide from the Cultured Symbiotic Dinoflagellate Amphidinium sp. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 6928–6929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.R.; Meyer, K.G. Total Synthesis of (+)-Amphidinolide K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 765–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.M.; Lee, C.W.; Kwon, H.K.; Chung, H.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Chung, Y.K.; Lee, E. Total Synthesis of (–)-Amphidinolide K. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 2364–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, T.; Costa, A.M.; Esteban, L.; Gonzàlez, L.; Mas, G.; Vilarrasa, J. Synthesis of (–)-Amphidinolide K Fragment C9-C22. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 4083–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, T.; Burés, J.; Vilarrasa, J. Reaction of Dess–Martin Periodinane with 2-(Alkylselenyl)Pyridines. Dehydration of Primary Alcohols under Extraordinarily Mild Conditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 1863–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Mouri, M.; Gao, Q.; Maruyama, T.; Furuta, K.; Yamamoto, H. Catalytic Asymmetric Allylation Using a Chiral (Acyloxy)Borane Complex as a Versatile Lewis Acid Catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 11490–11495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A Visualization System for Exploratory Research and Analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, A.M. Actin-Interacting Amphidinolides: Syntheses and Mechanisms of Action of Amphidinolides X, J, and K. Molecules 2023, 28, 5249. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135249
Costa AM. Actin-Interacting Amphidinolides: Syntheses and Mechanisms of Action of Amphidinolides X, J, and K. Molecules. 2023; 28(13):5249. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135249
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Anna M. 2023. "Actin-Interacting Amphidinolides: Syntheses and Mechanisms of Action of Amphidinolides X, J, and K" Molecules 28, no. 13: 5249. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135249
APA StyleCosta, A. M. (2023). Actin-Interacting Amphidinolides: Syntheses and Mechanisms of Action of Amphidinolides X, J, and K. Molecules, 28(13), 5249. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135249