Adsorption Performance of Magnetic Covalent Organic Framework Composites for Bisphenol A and Ibuprofen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
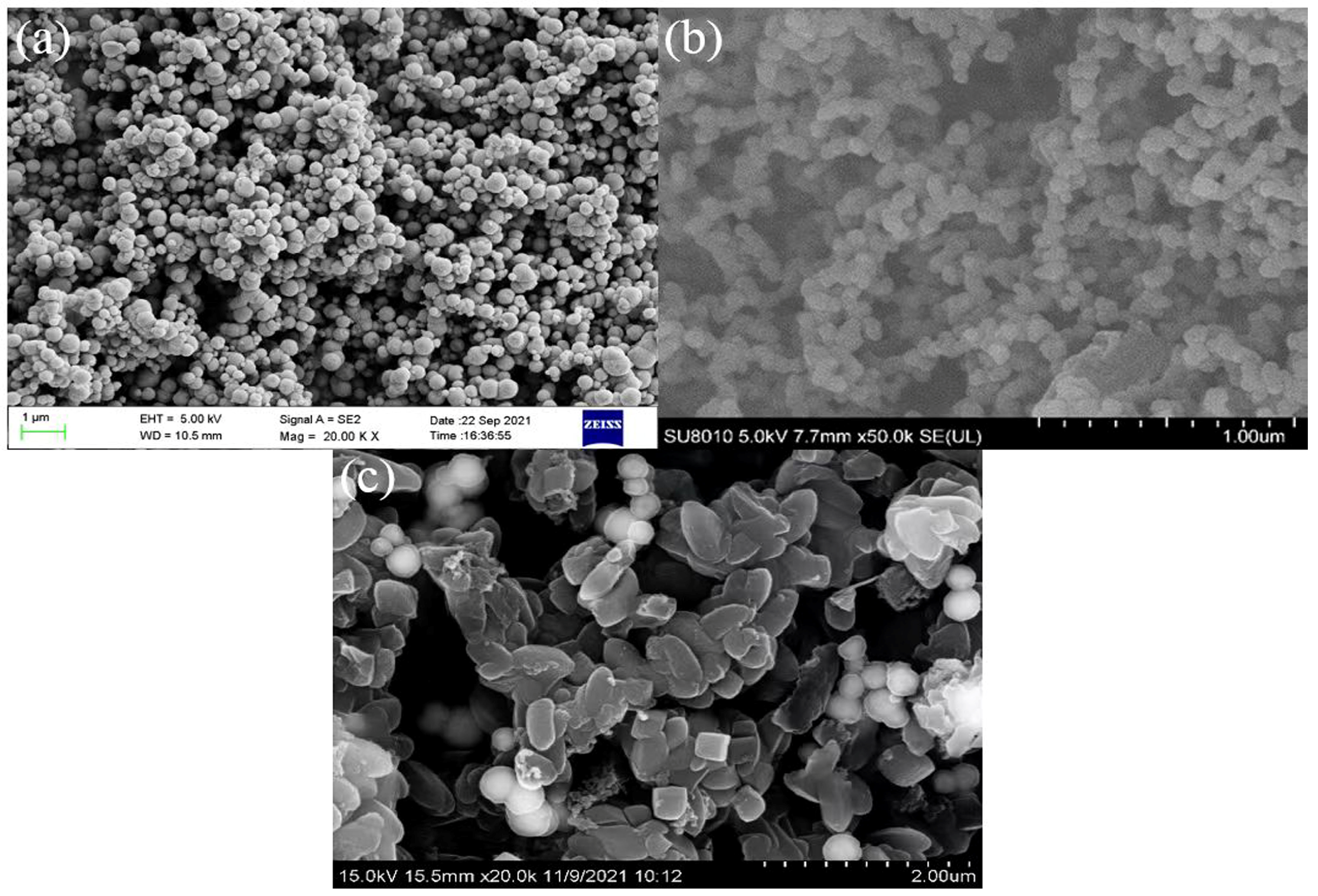
2.1. Characterization of Fe3O4@COF-300
2.2. Adsorption Experiment
2.2.1. Effect of pH on Removal Efficiency
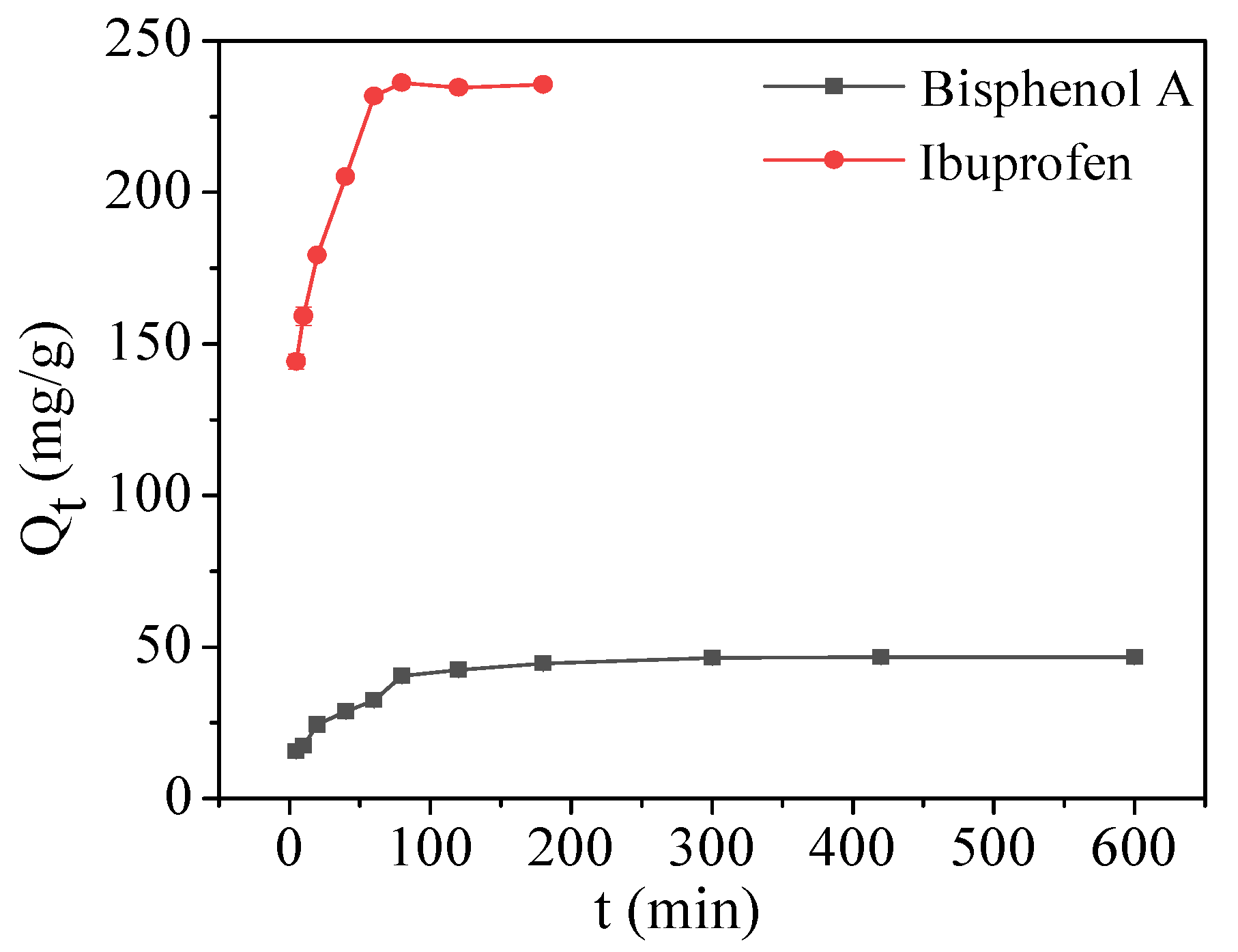
2.2.2. Adsorption Kinetics
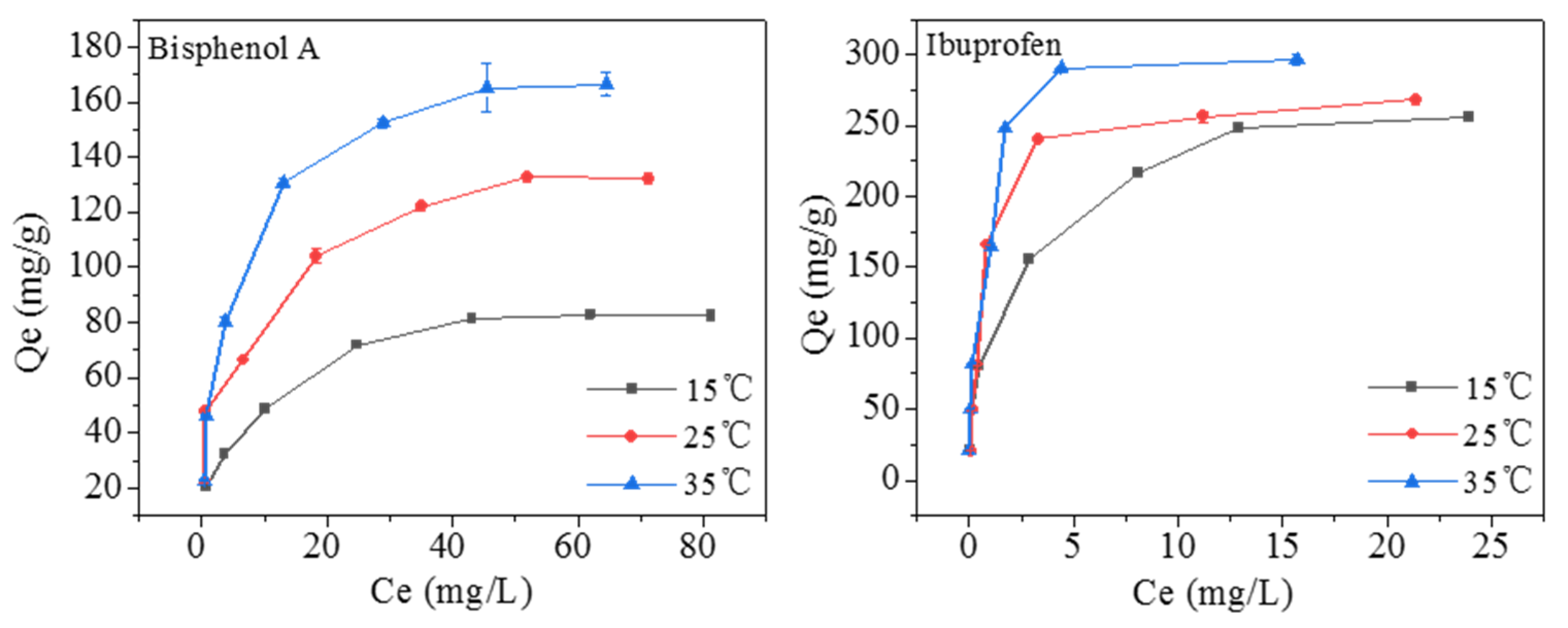
2.2.3. Adsorption Isotherms
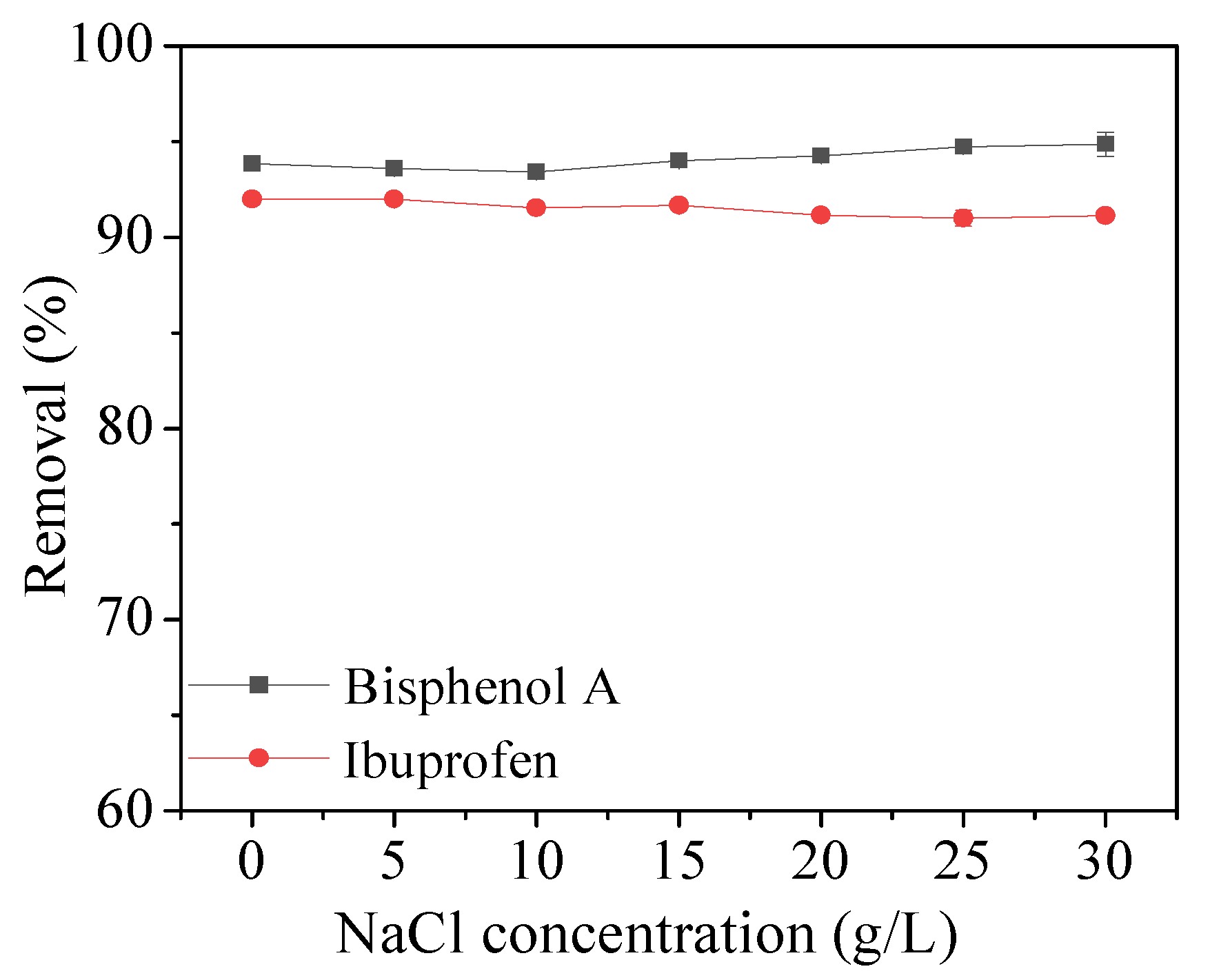
2.2.4. Effect of Ionic Strength
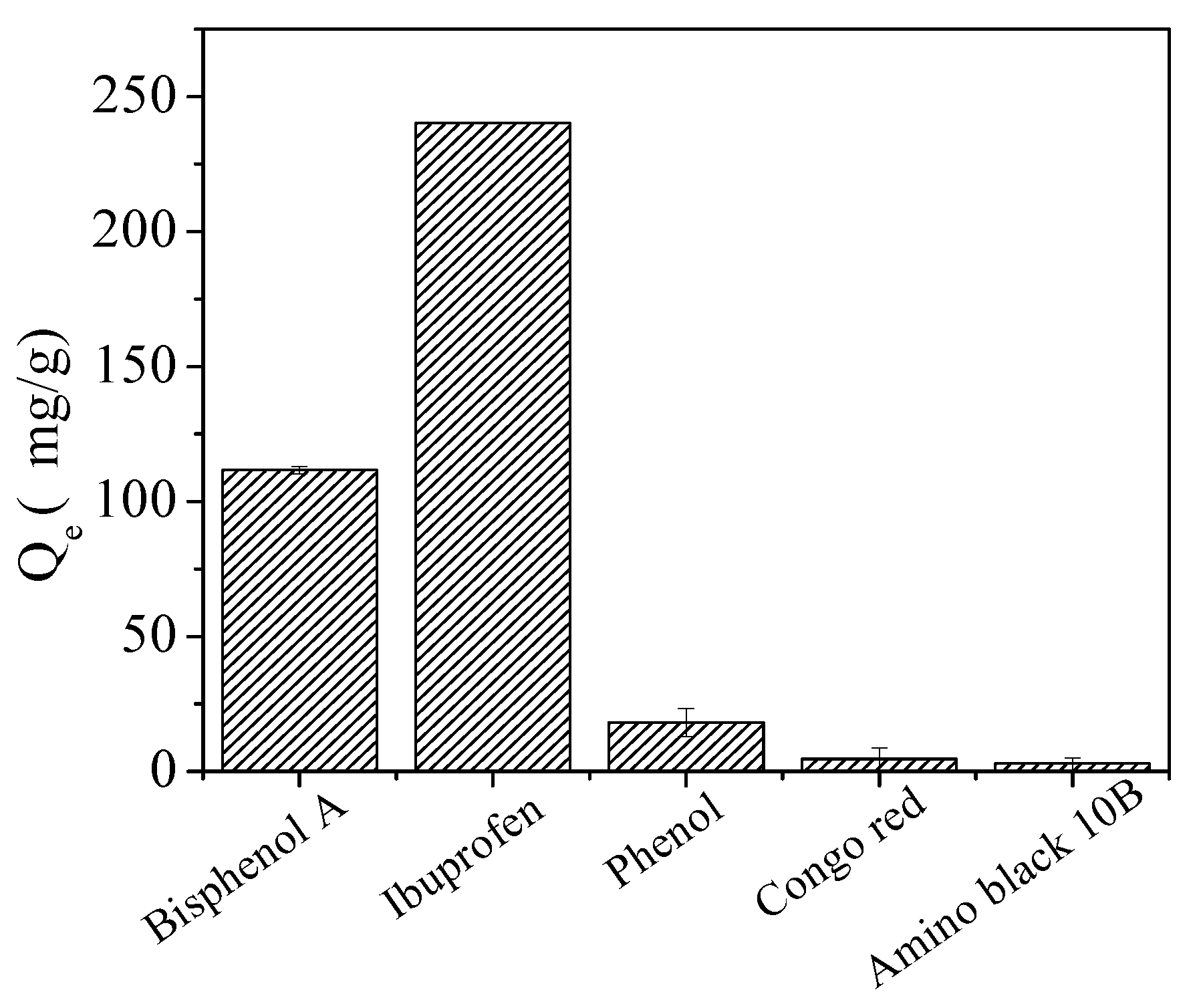
2.3. Selective Adsorption
2.4. Environmental Implications
2.5. Regeneration Property of Fe3O4@COF-300
2.6. Adsorption Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of Fe3O4@COF-300
3.3. Adsorption Experiment
3.4. Analysis Methods
3.5. Preparation of Simulated Water Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Bandura, L.; Białoszewska, M.; Malinowski, S.; Franus, W. Adsorptive performance of fly ash-derived zeolite modified by β-cyclodextrin for ibuprofen, bisphenol A and caffeine removal from aqueous solutions-equilibrium and kinetic study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 562, 150160–150170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, O.M.L.; Basheer, A.A.; Khattab, R.A.; Ali, I. Health and environmental effects of persistent organic pollutants. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 263, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seachrist, D.D.; Bonk, K.W.; Ho, S.-M.; Prins, G.S.; Soto, A.M.; Keri, R.A. A review of the carcinogenic potential of bisphenol A. Reprod. Toxicol 2016, 59, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanveer, M.; Guyer, G.T.; Abbas, G. Photocatalytic degradation of ibuprofen in water using TiO2 and ZnO under artificial UV and solar irradiation. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brillas, E. A critical review on ibuprofen removal from synthetic waters, natural waters, and real wastewaters by advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131849–131876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Al-Othman, Z.A.; Alwarthan, A. Synthesis of composite iron nano adsorbent and removal of ibuprofen drug residue from water. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 219, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin Simsek, E.; Kilic, B.; Asgin, M.; Akan, A. Graphene oxide based heterojunction TiO2–ZnO catalysts with outstanding photocatalytic performance for bisphenol-A, ibuprofen and flurbiprofen. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 59, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, S.N.; Ighalo, J.O.; Aniagor, C.O.; Igwegbe, C.A. Removal of ibuprofen from aqueous media by adsorption: A comprehensive review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146608–146630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharrazi, S.M.; Soleimani, M.; Jokar, M.; Richards, T.; Pettersson, A.; Mirghaffari, N. Pretreatment of lignocellulosic waste as a precursor for synthesis of high porous activated carbon and its application for Pb (II) and Cr (VI) adsorption from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 180, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Xu, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Ji, L.; Qu, Z.; Yan, N. Surface protection method for the magnetic core using covalent organic framework shells and its application in As(III) depth removal from acid wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 115, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.; Yan, N.; Qu, Z. Utilization of Ag nanoparticles anchored in covalent organic frameworks for mercury removal from acidic waste water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 151824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khataei, M.M.; Yamini, Y.; Asiabi, H.; Shamsayei, M. Covalent organic framework and montomorillonite nanocomposite as advanced adsorbent: Synthesis, characterization, and application in simultaneous adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 1555–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Cheng, J.; Yuan, X.; Tian, Y. Covalent organic framework-graphene oxide composite: A superior adsorption material for solid phase microextraction of bisphenol A. Talanta 2021, 222, 121501–121507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Lu, Z.; Liang, W.; Hu, B. Incorporating bimetal oxide MnFe2O4 onto covalent organic frameworks for the removal of UO22+ ion from aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 556, 149581–149592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Kapustin, E.A.; Yin, S.X.; Liang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Niu, J.; Li, L.-H.; Wang, Y.; Su, J.; Li, J.; et al. Single-crystal x-ray diffraction structures of covalent organic frameworks. Science 2018, 361, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Hunt, J.R.; Furukawa, H.; Klöck, C.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. A Crystalline Imine-Linked 3-D Porous Covalent Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4570–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.E.; Haji Shabani, A.M.; Dadfarnia, S.; Emami, S. Effective removal of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions using magnetic metal–organic framework sorbents: Mechanisms, isotherms and kinetics. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2016, 13, 1617–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Di, S.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.; Zhao, H.; Qi, P.; Ding, W. Facile synthesis of a core-shell structured magnetic covalent organic framework for enrichment of organophosphorus pesticides in fruits. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1101, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, S.; Khataee, A.; Bagheri, N.; Kobya, M.; Şenocak, A.; Demirbas, E.; Karaoğlu, A.G. Degradation of diazinon pesticide using catalyzed persulfate with Fe3O4@MOF-2 nanocomposite under ultrasound irradiation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 77, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Lv, W.; Sun, Y.; Dai, H.; Chen, H.; Chen, X. In situ fabrication of 3D COF-300 in a capillary for separation of aromatic compounds by open-tubular capillary electrochromatography. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Jiao, C.; Song, L. Preparation and thermal properties of a novel flame-retardant coating. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2007, 92, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Velamakanni, A.; Bozoklu, G.; Park, S.; Stoller, M.; Piner, R.D.; Stankovich, S.; Jung, I.; Field, D.A.; Ventrice, C.A., Jr.; et al. Chemical analysis of graphene oxide films after heat and chemical treatments by X-ray photoelectron and Micro-Raman spectroscopy. Carbon 2009, 47, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, P.; Cai, D.; Shan, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Qin, P.; Tan, T. Boosting pervaporation performance by promoting organic permeability and simultaneously inhibiting water transport via blending PDMS with COF-300. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 579, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, A.; Gharibi, H.; Kakavandi, B.; Ghanizadeh, G.; Javid, A.; Mahvi, A.H.; Sharafi, K.; Khosravia, T. Magnetic adsorption separation process: An alternative method of mercury extracting from aqueous solution using modified chitosan coated Fe3O4 nanocomposites. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedidi, H.; Reinert, L.; Lévêque, J.-M.; Soneda, Y.; Bellakhal, N.; Duclaux, L. The effects of the surface oxidation of activated carbon, the solution pH and the temperature on adsorption of ibuprofen. Carbon 2013, 54, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaheri, F.; Kheshti, Z.; Ghasemi, S.; Altaee, A. Enhancement of Cd2+ removal from aqueous solution by multifunctional mesoporous silica: Equilibrium isotherms and kinetics study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 224, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.H.; Karri, R.R.; Alimohammadi, M.; Nazmara, S.; Zarei, A.; Saeedi, Z. Insights into endocrine-disrupting Bisphenol-A adsorption from pharmaceutical effluent by chitosan immobilized nanoscale zero-valent iron nanoparticles. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 311, 113317–113329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-Y. Comparison with as-grown and microwave modified carbon nanotubes to removal aqueous bisphenol A. Desalination 2009, 249, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Liu, Z.; Hu, J.Q.; Cai, Q.W.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, W.; Faraj, Y.; Ju, X.J.; Xie, R.; Chu, L.Y. β-Cyclodextrin-modified graphene oxide membranes with large adsorption capacity and high flux for efficient removal of bisphenol A from water. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117510–117517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Tran, L. Simultaneous adsorption of Cd2+ and BPA on mphoteric surfactant activated montmorillonite. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, M.; Ahmed, A.; Ji, Z.; Yu, B.; Shen, Y.; Cong, H. Environmentally friendly fabrication of new β-Cyclodextrin/ZrO2 nanocomposite for simultaneous removal of Pb(II) and BPA from water. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147207–147218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadra, B.N.; Ahmed, I.; Kim, S.; Jhung, S.H. Adsorptive removal of ibuprofen and diclofenac from water using metal-organic framework-derived porous carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 314, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, A.C.; Foletto, E.L.; Dotto, G.L. Preparation and characterization of NiFe2O4/activated carbon composite as potential magnetic adsorbent for removal of ibuprofen and ketoprofen pharmaceuticals from aqueous solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, S.; Shuang, C.; Mu, Y.; Li, A.; Tan, L. The effect of incorporating inorganic materials into quaternized polyacrylic polymer on its mechanical strength and adsorption behaviour for ibuprofen removal. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5188–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phasuphan, W.; Praphairaksit, N.; Imyim, A. Removal of ibuprofen, diclofenac, and naproxen from water using chitosan-modified waste tire crumb rubber. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 294, 111554–111561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollarahithlu, S.C.; Balakrishnan, R.M. Adsorption of ibuprofen using cysteine-modified silane-coated magnetic nanomaterial. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 34117–34126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Deng, S.; Huang, Q.; Nie, Y.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Regenerable granular carbon nanotubes/alumina hybrid adsorbents for diclofenac sodium and carbamazepine removal from aqueous solution. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4139–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, H.; Tang, H.; Ma, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Liang, X. Iron-based metal–organic framework as an effective sorbent for the rapid and efficient removal of illegal dyes. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 15351–15358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zeng, Q.; Su, W.; Zhang, M.; Hou, L.; Wang, Z.L. Adsorption of Bisphenol A on Peanut Shell Biochars: The Effects of Surfactants. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 2428505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Adsorbates | Adsorbents | Qmax (mg·g–1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bisphenol A | nZVI–chitosan | 65.16 | [27] |
| modified carbon nanotubes | 69.93 | [28] | |
| β-Cyclodextrin-modified graphene oxide membranes | 25.50 | [29] | |
| modified montmorillonite (BS–Mt) | 80.77 | [30] | |
| β-Cyclodextrin/ZrO2 | 174.90 | [31] | |
| Ibuprofen | ZIF–8 derived porous carbon | 320.00 | [32] |
| NiFe2O4/AC | 261.35 | [33] | |
| MAP | 269.61 | [34] | |
| chitosan modified rubber | 70.00 | [35] | |
| cysteine-modified silane-coated magnetic nanomaterial | 138.10 | [36] |
| Pollutant | C0 (mg/L) | Ce (mg/L) | ΔSθ (J/mol/K) | ΔHθ (kJ/mol) | ΔGθ (kJ/mol) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 288 K | 298 K | 308 K | 288 K | 298 K | 308 K | ||||
| Bisphenol A | 100 | 81.65 | 71.86 | 64.99 | 120.62 | 34.69 | −0.07 | −1.27 | −2.48 |
| Ibuprofen | 75 | 23.90 | 21.39 | 15.68 | 92.07 | 20.96 | −24.43 | −25.35 | −26.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Tian, Y.; Gao, X.; Zheng, H.; Niu, Y.; Liu, J. Adsorption Performance of Magnetic Covalent Organic Framework Composites for Bisphenol A and Ibuprofen. Molecules 2023, 28, 5214. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135214
Zhang B, Tian Y, Gao X, Zheng H, Niu Y, Liu J. Adsorption Performance of Magnetic Covalent Organic Framework Composites for Bisphenol A and Ibuprofen. Molecules. 2023; 28(13):5214. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135214
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Beibei, Ye Tian, Xuezhen Gao, Hui Zheng, Yuzhong Niu, and Junshen Liu. 2023. "Adsorption Performance of Magnetic Covalent Organic Framework Composites for Bisphenol A and Ibuprofen" Molecules 28, no. 13: 5214. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135214
APA StyleZhang, B., Tian, Y., Gao, X., Zheng, H., Niu, Y., & Liu, J. (2023). Adsorption Performance of Magnetic Covalent Organic Framework Composites for Bisphenol A and Ibuprofen. Molecules, 28(13), 5214. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28135214





