A Novel LSTM-Based Machine Learning Model for Predicting the Activity of Food Protein-Derived Antihypertensive Peptides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
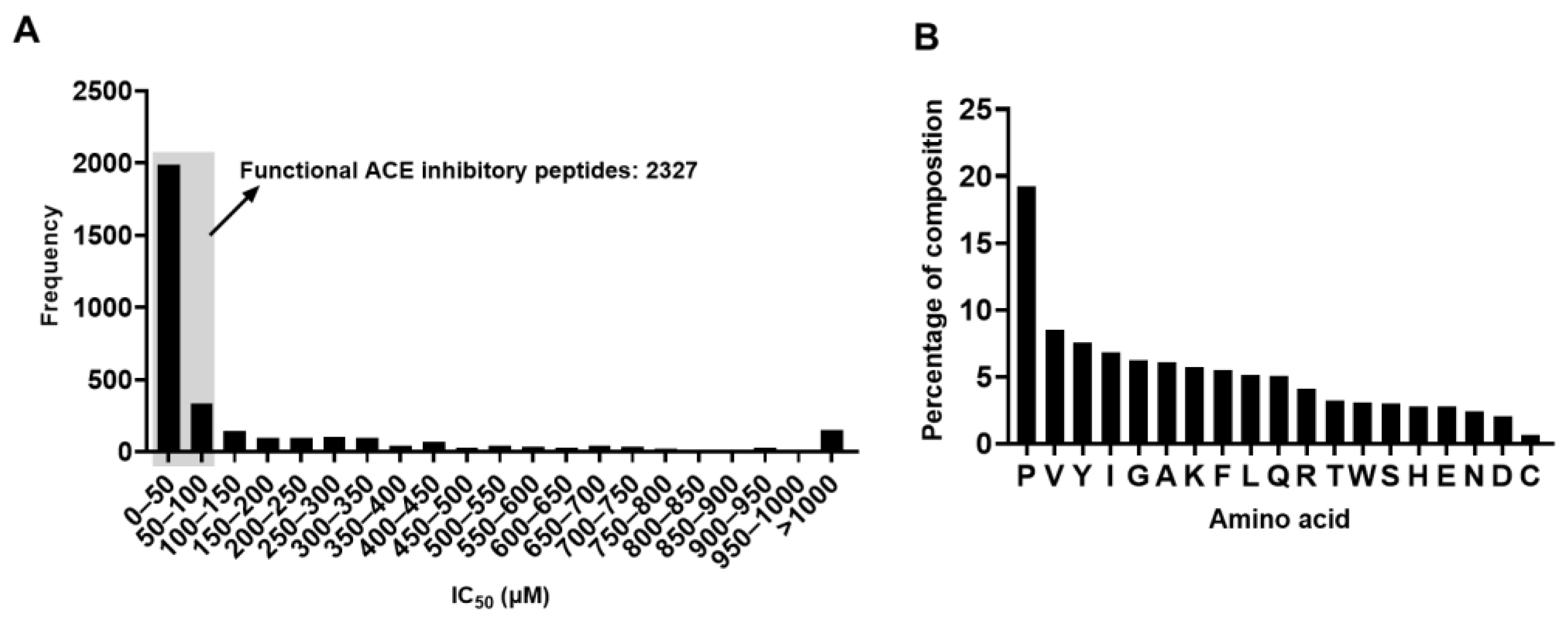
2.1. An Overview of the Dataset
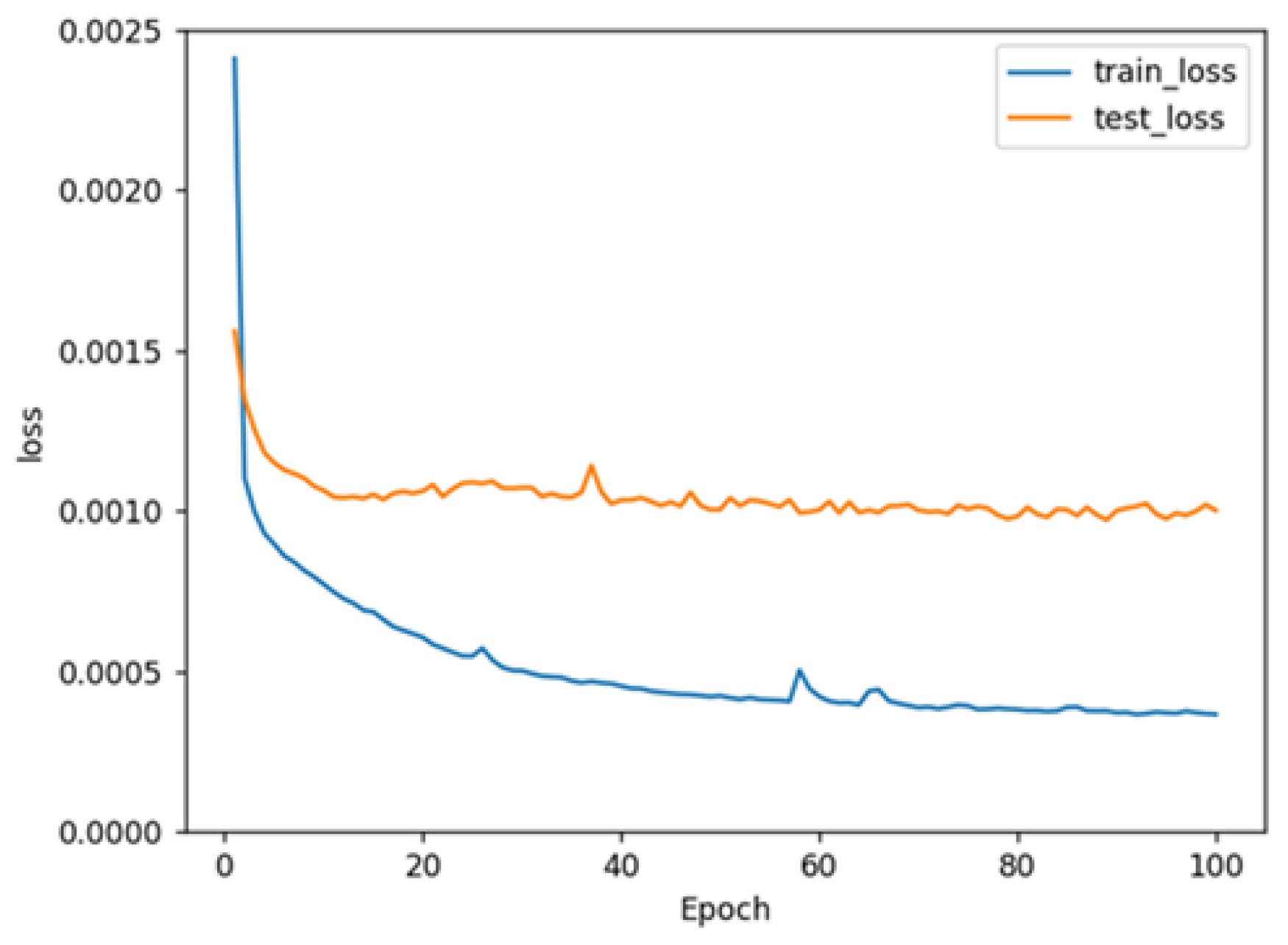
2.2. Performance Evaluation of the Model
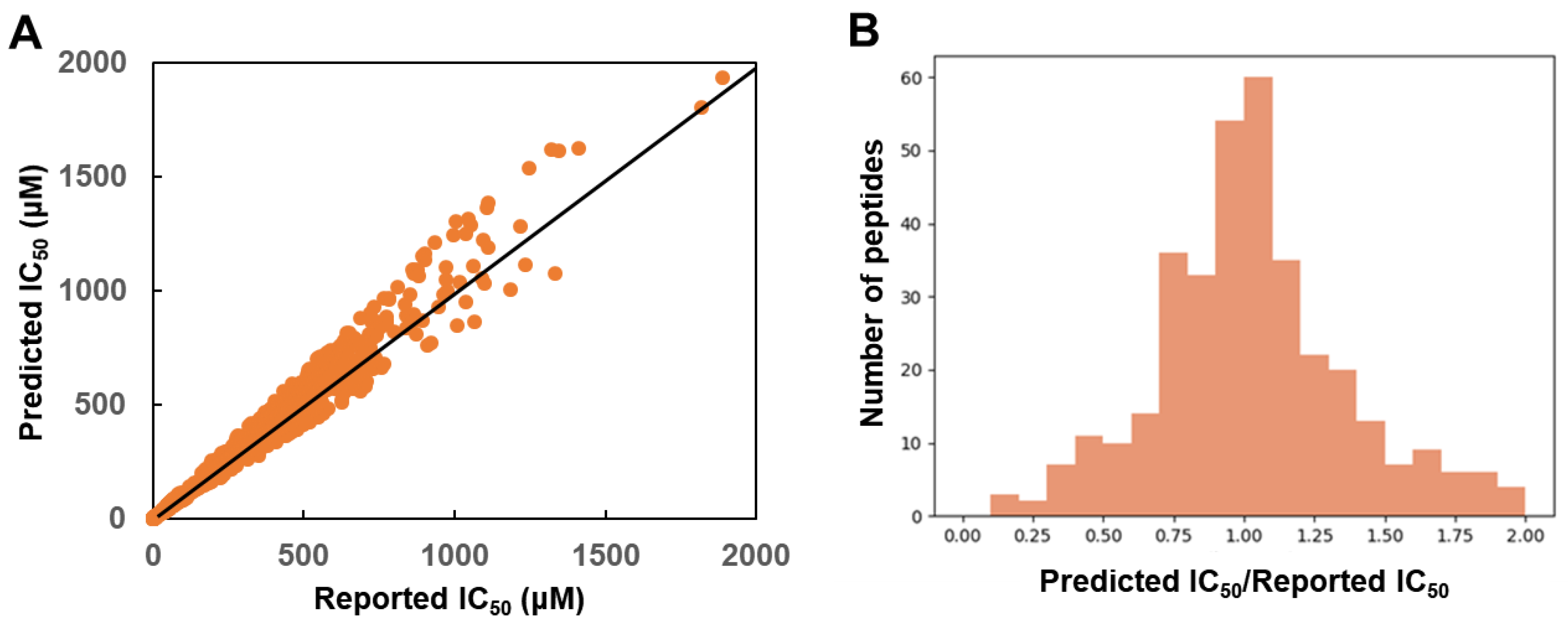
2.3. Model Validations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Benchmark Dataset
4.2. Literature Searching Strategy
4.3. Representation of the Peptide Sequence
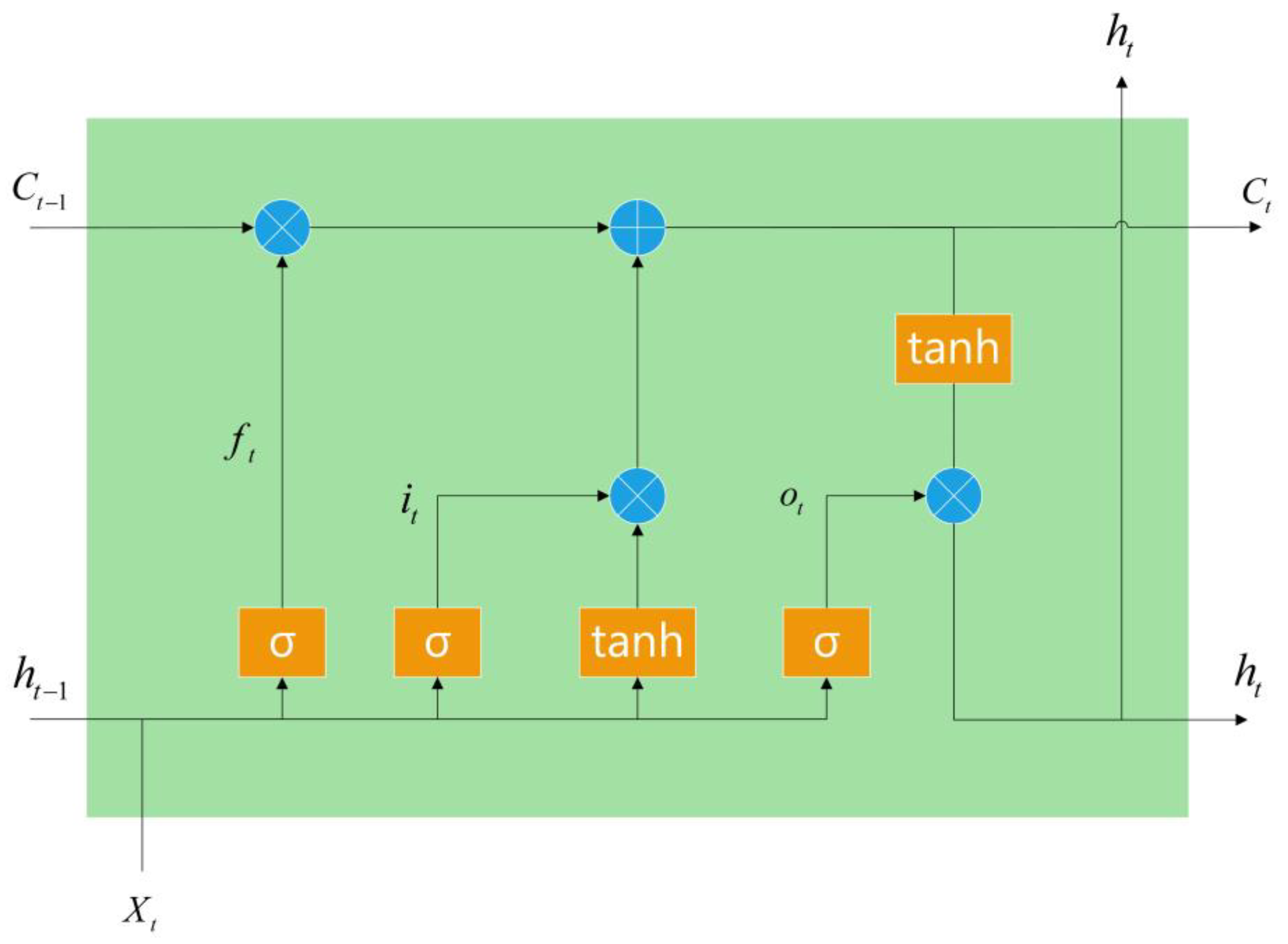
4.4. Machine Learning Algorithms
4.5. Model Evaluations
4.6. The In Vitro ACE Inhibitory Assay
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Makki, A.; DiPette, D.; Whelton, P.K.; Murad, M.H.; Mustafa, R.A.; Acharya, S.; Beheiry, H.M.; Champagne, B.; Connell, K.; Cooney, M.T.; et al. Hypertension Pharmacological Treatment in Adults: A World Health Organization Guideline Executive Summary. Hypertension 2022, 79, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, S.J.; Booz, G.W.; Sigmund, C.D.; Coffman, T.M.; Kawai, T.; Rizzo, V.; Scalia, R.; Eguchi, S. Angiotensin II Signal Transduction: An Update on Mechanisms of Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1627–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.M.; Musini, V.M.; Gill, R. First-line drugs for hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 8, CD001841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhle, Y.S. How ACE inhibitors transformed the renin–angiotensin system. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 2657–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluko, R.E. Antihypertensive Peptides from Food Proteins. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 235–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liao, W.; Udenigwe, C.C. Revisiting the mechanisms of ACE inhibitory peptides from food proteins. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.-M.; Wang, X.-Q. Identifying anticancer peptides by using improved hybrid compositions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, R.; Soltani, S.; Barzegar, A. A review of QSAR studies to predict activity of ACE peptide inhibitors. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 20, 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Learnings from quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) studies with respect to food protein-derived bioactive peptides: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 75400–75413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, C.; Chi, K.; Gao, Q.; Bai, X.; Xu, Y.; Guo, N. Development of a machine learning-based predictor for identifying and discovering antioxidant peptides based on a new strategy. Food Control 2022, 131, 108439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, T.H.; Yesiltas, B.; Marin, F.I.; Pertseva, M.; García-Moreno, P.J.; Gregersen, S.; Overgaard, M.T.; Jacobsen, C.; Lund, O.; Hansen, E.B. AnOxPePred: Using deep learning for the prediction of antioxidative properties of peptides. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manavalan, B.; Basith, S.; Shin, T.H.; Choi, S.; Kim, M.O.; Lee, G. MLACP: Machine-learning-based prediction of anticancer peptides. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 77121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Sutherland, D.; Hammond, S.A.; Yang, C.; Taho, F.; Bergman, L.; Houston, S.; Warren, R.L.; Wong, T.; Hoang, L. AMPlify: Attentive deep learning model for discovery of novel antimicrobial peptides effective against WHO priority pathogens. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouktif, S.; Fiaz, A.; Ouni, A.; Serhani, M.A. Optimal deep learning lstm model for electric load forecasting using feature selection and genetic algorithm: Comparison with machine learning approaches. Energies 2018, 11, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Shrivastava, S.; Kumar Singh, S.; Kumar, A.; Saxena, S.; Kumar Singh, R. Deep-ABPpred: Identifying antibacterial peptides in protein sequences using bidirectional LSTM with word2vec. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Niu, D.; Wang, X.; Khan, J.; Shen, Q.; Xue, Y. A Novel Machine Learning Strategy for the Prediction of Antihypertensive Peptides Derived from Food with High Efficiency. Foods 2021, 10, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, T.; Sevilla, M.A.; Montero, M.J.; Carron, R.; Malcata, F.X. Acute effect of whey peptides upon blood pressure of hypertensive rats, and relationship with their angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity. Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 2012, 56, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Tian, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Ng, T.B. A Tricholoma matsutake Peptide with Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitory and Antioxidative Activities and Antihypertensive Effects in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, D.; Ogura, K.; Miyakoshi, M.; Ishii, F.; Kawanishi, H.; Kurumazuka, D.; Kwak, C.-J.; Ikemura, K.; Takaoka, M.; Moriguchi, S.; et al. Antihypertensive Effect of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides from a Sesame Protein Hydrolysate in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, F.I.; Mas-Capdevila, A.; López-Fernández-Sobrino, R.; Torres-Fuentes, C.; Mulero, M.; Alcaide-Hidalgo, J.M.; Muguerza, B. Identification of novel antihypertensive peptides from wine lees hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaide-Hidalgo, J.M.; Romero, M.; Duarte, J.; López-Huertas, E. Antihypertensive Effects of Virgin Olive Oil (Unfiltered) Low Molecular Weight Peptides with ACE Inhibitory Activity in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liao, W.; Fan, H.; Wu, J. Optimization and Scale-Up Preparation of Egg White Hydrolysate with Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Activity. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1762–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suetsuna, K.; Maekawa, K.; Chen, J.-R. Antihypertensive effects of Undaria pinnatifida (wakame) peptide on blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2004, 15, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, K.; Chakrabarti, S.; Morton, J.S.; Panahi, S.; Kaufman, S.; Davidge, S.T.; Wu, J. Egg-Derived Tri-Peptide IRW Exerts Antihypertensive Effects in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetsuna, K. Isolation and characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitor dipeptides derived from Allium sativum L. (garlic). J. Nutr. Biochem. 1998, 9, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, K.; Chakrabarti, S.; Morton, J.S.; Panahi, S.; Kaufman, S.; Davidge, S.T.; Wu, J. Egg-derived ACE-inhibitory peptides IQW and LKP reduce blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 13, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobako, N.; Ogawa, Y.; Ishikado, A.; Harada, K.; Kobayashi, E.; Suido, H.; Kusakari, T.; Maeda, M.; Suwa, M.; Matsumoto, M.; et al. A Novel Antihypertensive Peptide Identified in Thermolysin-Digested Rice Bran. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balti, R.; Bougatef, A.; Sila, A.; Guillochon, D.; Dhulster, P.; Nedjar-Arroume, N. Nine novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) muscle protein hydrolysates and antihypertensive effect of the potent active peptide in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Hao, L.; Cao, J.; Sun, Y.; Pan, D. In vitro and in vivo studies on the angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity peptides isolated from broccoli protein hydrolysate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6757–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonklin, C.; Alashi, M.A.; Laohakunjit, N.; Kerdchoechuen, O.; Aluko, R.E. Identification of antihypertensive peptides from mung bean protein hydrolysate and their effects in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.-J.; Jung, W.-K.; Lee, S.-H.; Byun, H.-G.; Kim, S.-K. Antihypertensive effect of an angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana Shaw) muscle protein in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, K.H.; Yoshida, C.; Suzuki, K.M.; Maruyama, H.; Futamura, Y.; Araki, Y.; Mishima, S. Antihypertensive Effect of Peptides from Royal Jelly in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyanto, A.D.; Doerksen, R.J.; Chang, C.-I.; Sung, W.-C.; Widjanarko, S.B.; Kusnadi, J.; Lin, Y.-C.; Wang, T.-C.; Hsu, J.-L. Screening, discovery, and characterization of angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from proteolytic hydrolysate of bitter melon seed proteins. J. Proteom. 2015, 128, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel, M.; Gómez-Ruiz, J.Á.; Recio, I.; Aleixandre, A. Changes in arterial blood pressure after single oral administration of milk-casein-derived peptides in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Yu, J.; Song, J.; Wang, S.; Cao, T.; Liu, Z.; Gao, X.; Wei, Y. The antihypertensive effect and mechanisms of bioactive peptides from Ruditapes philippinarum fermented with Bacillus natto in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 79, 104411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kıvrık, M.; Süfer, Ö.; Bozok, F. A Research on Quality Evaluation of Eight Wild Edible Macrofungi Collected from East Mediterranean Region of Turkey. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202100967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Chen, L.; Liang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Cai, M.; Li, Y. Pilot-scale production of low molecular weight peptides from corn wet milling byproducts and the antihypertensive effects in vivo and in vitro. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, M.A.G.; Amaral, N.O.; Álvares, A.C.M.; de Oliveira, S.A.; Mehdad, A.; Honda, D.E.; Bessa, A.S.M.; Ramada, M.H.S.; Naves, L.M.; Pontes, C.N.R.; et al. Blood pressure-lowering effects of a Bowman-Birk inhibitor and its derived peptides in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Aluko, R.E.; Nakai, S. Structural Requirements of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides: Quantitative Structure—Activity Relationship Study of Di- and Tripeptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Chaudhary, K.; Singh Chauhan, J.; Nagpal, G.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, M.; Raghava, G.P. An in silico platform for predicting, screening and designing of antihypertensive peptides. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, B.; Basith, S.; Shin, T.H.; Wei, L.; Lee, G. mAHTPred: A sequence-based meta-predictor for improving the prediction of anti-hypertensive peptides using effective feature representation. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 2757–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhan, P. A deep neural network model for short-term load forecast based on long short-term memory network and convolutional neural network. Energies 2018, 11, 3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Wu, J. The ACE2/Ang (1–7)/MasR axis as an emerging target for antihypertensive peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2572–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyan, G.; Junghare, V.; Khan, M.F.; Pal, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Guha, S.; Majumder, K.; Chakrabarty, S.; Hazra, S. Anti-hypertensive peptide predictor: A machine learning-empowered web server for prediction of food-derived peptides with potential angiotensin-converting enzyme-I inhibitory activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 14995–15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minkiewicz, P.; Iwaniak, A.; Darewicz, M. BIOPEP-UWM database of bioactive peptides: Current opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyayai, T.; Ngamphiw, C.; Tongsima, S.; Mhuantong, W.; Limsripraphan, W.; Choowongkomon, K.; Sawatdichaikul, O. FeptideDB: A web application for new bioactive peptides from food protein. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Chen, H.; Xue, J.; Guo, X.; Liang, M.; Chen, M. BioPepDB: An integrated data platform for food-derived bioactive peptides. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 69, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, D.; Rossi, F.; Wertz, V.; Verleysen, M. Resampling methods for parameter-free and robust feature selection with mutual information. Neurocomputing 2007, 70, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantidis, N.; Karlis, D.; Giakoumakis, E.A. Unsupervised stratification of cross-validation for accuracy estimation. Artif. Intell. 2000, 116, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Liao, W.; Wu, J. Molecular interactions, bioavailability, and cellular mechanisms of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Wu, J. Purification and identification of novel ACE inhibitory and ACE2 upregulating peptides from spent hen muscle proteins. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Peptide Sequence | Predicted IC50 (μM) | Reported IC50 (μM) | Predicted IC50/ Reported IC50 | Reference Reporting the IC50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KGYGGVSLPEW | 0.23 | 0.70 | 0.33 | [17] |
| LLVTLKK | 0.42 | 0.95 | 0.44 | [18] |
| LKY | 0.36 | 0.78 | 0.46 | [19] |
| PAGELHP | 0.29 | 0.50 | 0.58 | [20] |
| DAQSAPLRVY | 7.60 | 12.20 | 0.62 | [17] |
| RDGGYCC | 0.56 | 0.84 | 0.67 | [21] |
| WV | 217.83 | 307.61 | 0.71 | [22] |
| KF | 20.08 | 28.30 | 0.71 | [23] |
| LVY | 1.30 | 1.80 | 0.72 | [19] |
| IRW | 0.44 | 0.61 | 0.72 | [24] |
| FY | 2.71 | 3.70 | 0.73 | [23] |
| LEEFCC | 1.36 | 1.85 | 0.73 | [21] |
| GF | 213.69 | 277.90 | 0.77 | [25] |
| MLPAY | 1.27 | 1.58 | 0.80 | [19] |
| IQW | 1.26 | 1.56 | 0.81 | [26] |
| LRA | 141.66 | 174.30 | 0.81 | [27] |
| KIDKVVK | 0.53 | 0.62 | 0.85 | [18] |
| LKP | 2.49 | 2.93 | 0.85 | [26] |
| AFVGYVLP | 12.62 | 14.41 | 0.88 | [28] |
| LAK | 42.46 | 48.00 | 0.88 | [29] |
| NF | 41.66 | 46.30 | 0.90 | [25] |
| VY | 10.24 | 11.30 | 0.91 | [23] |
| HLNVVHGN | 46.29 | 50.88 | 0.91 | [30] |
| DKVGINYW | 23.13 | 25.40 | 0.91 | [17] |
| EKSYELP | 16.54 | 18.02 | 0.92 | [28] |
| PGSGCAGTDL | 53.67 | 57.86 | 0.93 | [30] |
| LSA | 7.26 | 7.81 | 0.93 | [19] |
| GAAELPCSADWW | 10.25 | 10.95 | 0.94 | [31] |
| KY | 7.25 | 7.70 | 0.94 | [23] |
| IVY | 43.52 | 45.77 | 0.95 | [32] |
| KW | 10.28 | 10.80 | 0.95 | [23] |
| VW | 10.29 | 10.80 | 0.95 | [23] |
| VDSDVVK | 8.26 | 8.64 | 0.96 | [33] |
| VF | 42.00 | 43.70 | 0.96 | [23] |
| LRLESF | 5.21 | 5.39 | 0.97 | [30] |
| YY | 46.30 | 47.90 | 0.97 | [27] |
| LDSPSEGRAPG | 17.31 | 17.90 | 0.97 | [20] |
| VIY | 4.36 | 4.50 | 0.97 | [19] |
| VELYP | 5.23 | 5.22 | 1.00 | [28] |
| WQVLPNAVPAK | 1023.89 | 1010.00 | 1.01 | [34] |
| TFQGGlPPHGIQVER | 3.47 | 3.40 | 1.02 | [29] |
| VISDEDGVTH | 8.33 | 8.16 | 1.02 | [35] |
| RLSGQTIEVTSEYLFRH | 577.19 | 560.18 | 1.03 | [36] |
| ILSKLK | 4.28 | 4.02 | 1.07 | [18] |
| AY | 156.44 | 146.76 | 1.07 | [37] |
| IISKIK | 1.28 | 1.19 | 1.07 | [18] |
| CTFSIPAQC | 26.31 | 24.40 | 1.08 | [38] |
| IY | 2.96 | 2.70 | 1.09 | [23] |
| LT | 1.22 | 1.11 | 1.10 | [22] |
| TVTNPARIA | 16.33 | 14.50 | 1.13 | [20] |
| LVLPGELAK | 214.22 | 184.00 | 1.16 | [29] |
| LQP | 1.35 | 1.04 | 1.30 | [19] |
| IPPAYTK | 35.75 | 23.50 | 1.52 | [29] |
| LVLPGE | 20.79 | 13.50 | 1.54 | [29] |
| Peptide Sequence | Predicted IC50 (μM) | Experimental IC50 (μM) | Predicted IC50 /Experimental IC50 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LKPDQ | 0.70 | 0.88 | 0.79 |
| WD | 0.63 | 0.51 | 1.23 |
| GVPK | 0.61 | 0.25 | 2.44 |
| FI | 0.61 | 0.31 | 1.95 |
| PDFLI | 0.60 | 0.33 | 1.83 |
| HDHR | 0.59 | 0.59 | 1.00 |
| LKPNS | 0.56 | 0.5 | 1.12 |
| VYHEL | 0.55 | 0.38 | 1.45 |
| GPAY | 0.54 | 0.37 | 1.45 |
| LVL | 0.51 | 0.32 | 1.59 |
| LKL | 0.49 | 0.56 | 0.88 |
| FDKA | 0.47 | 0.6 | 0.79 |
| VAWKL | 0.46 | 0.23 | 2.00 |
| VHLAP | 0.46 | 0.33 | 1.39 |
| IQWCA | 0.46 | 0.1 | 4.59 |
| PLPLL | 0.55 | 0.2 | 1.75 |
| KLPAY | 0.44 | 0.12 | 3.63 |
| LKPI | 0.43 | 0.39 | 1.11 |
| FALPC | 0.42 | 0.16 | 2.65 |
| ALPD | 0.72 | 1.55 | 0.46 |
| Amino Acid | Representing Digit | Amino Acid | Representing Digit |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 2 | D | 11 |
| L | 3 | C | 12 |
| S | 4 | T | 13 |
| H | 5 | N | 14 |
| R | 6 | V | 15 |
| P | 7 | G | 16 |
| A | 8 | Q | 17 |
| W | 9 | K | 18 |
| F | 10 | Y | 19 |
| E | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, W.; Yan, S.; Cao, X.; Xia, H.; Wang, S.; Sun, G.; Cai, K. A Novel LSTM-Based Machine Learning Model for Predicting the Activity of Food Protein-Derived Antihypertensive Peptides. Molecules 2023, 28, 4901. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134901
Liao W, Yan S, Cao X, Xia H, Wang S, Sun G, Cai K. A Novel LSTM-Based Machine Learning Model for Predicting the Activity of Food Protein-Derived Antihypertensive Peptides. Molecules. 2023; 28(13):4901. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134901
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Wang, Siyuan Yan, Xinyi Cao, Hui Xia, Shaokang Wang, Guiju Sun, and Kaida Cai. 2023. "A Novel LSTM-Based Machine Learning Model for Predicting the Activity of Food Protein-Derived Antihypertensive Peptides" Molecules 28, no. 13: 4901. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134901
APA StyleLiao, W., Yan, S., Cao, X., Xia, H., Wang, S., Sun, G., & Cai, K. (2023). A Novel LSTM-Based Machine Learning Model for Predicting the Activity of Food Protein-Derived Antihypertensive Peptides. Molecules, 28(13), 4901. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28134901









