Vincamine Ameliorates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats; Targeting TGF-β/MAPK/Snai1 Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
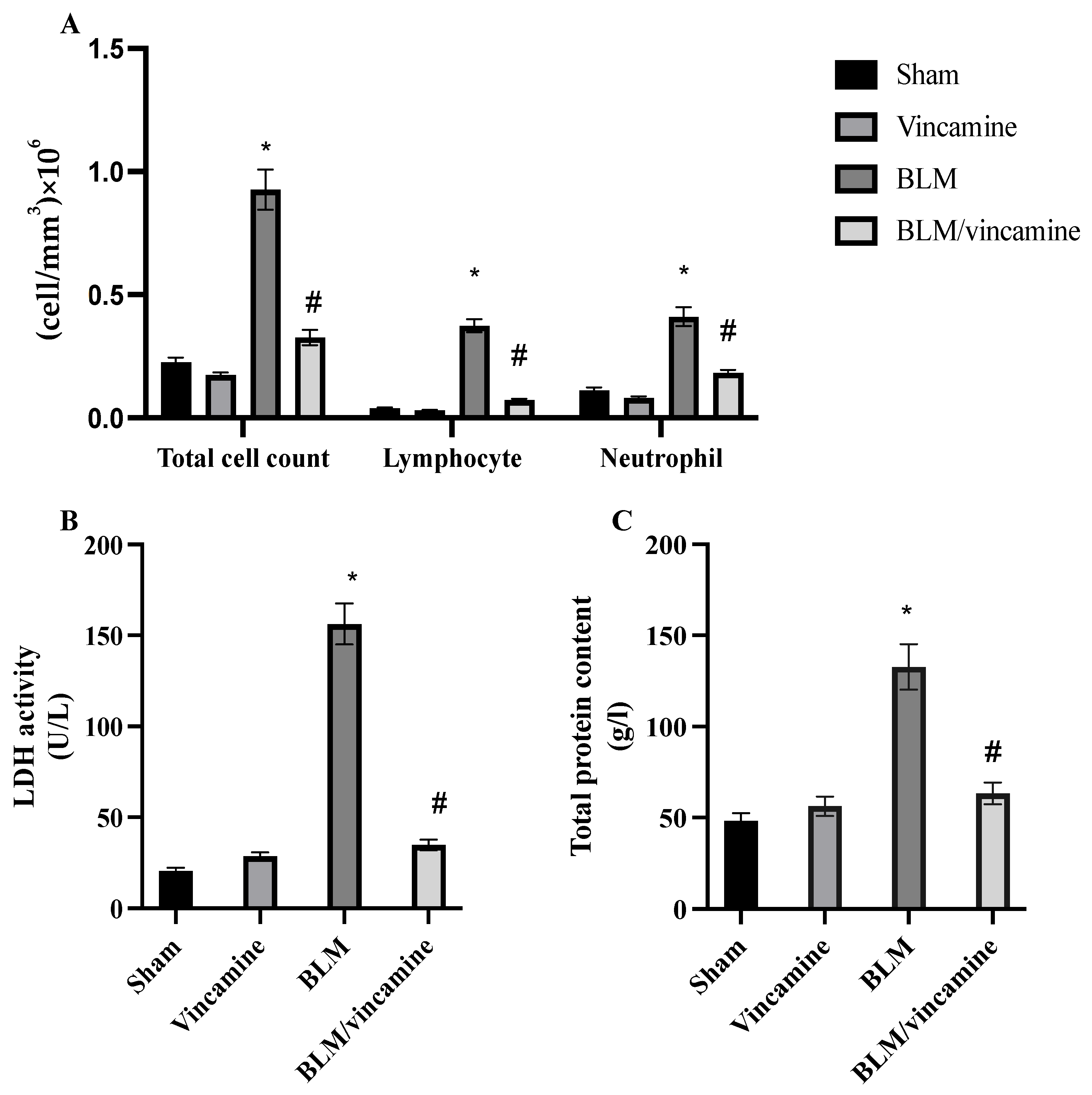
2.1. Total Cell Count, LDH Activity, and Total Protein Content
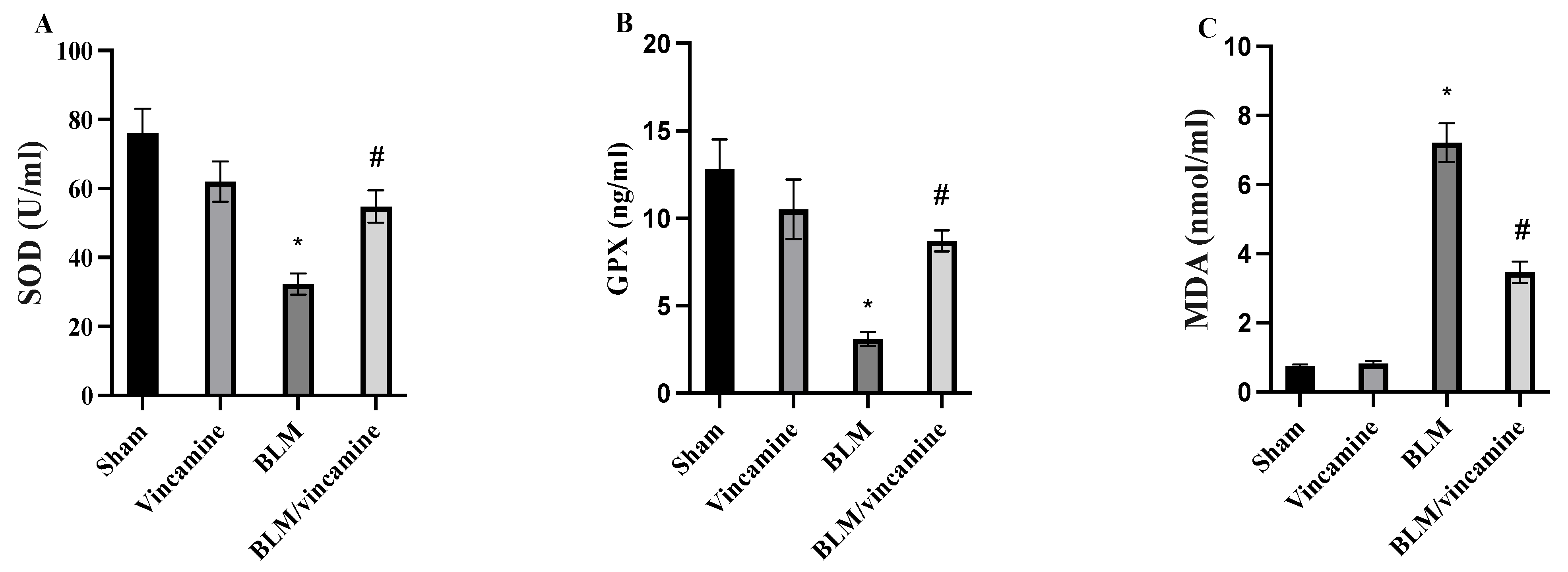
2.2. Measurement of Oxidative Stress
2.3. Evaluation of Fibronectin, N-Cadherin, and Collagen Levels
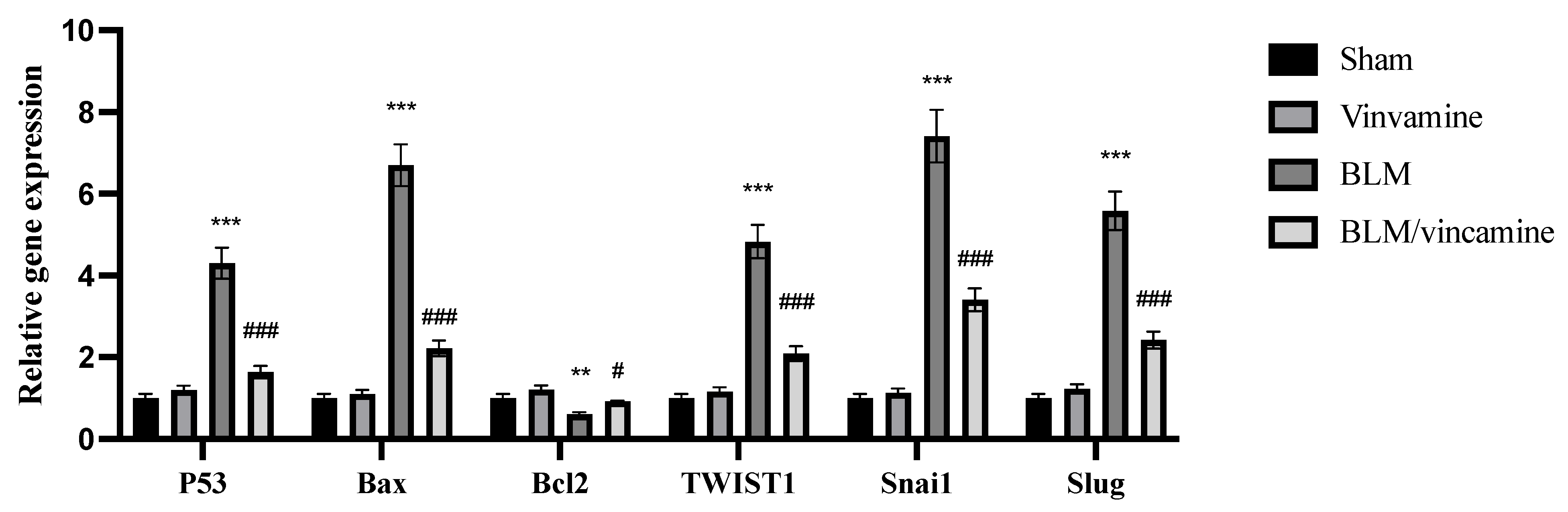
2.4. Gene Expression of p53, Bax, bcl2, TWIST1, Snai1, and Slug
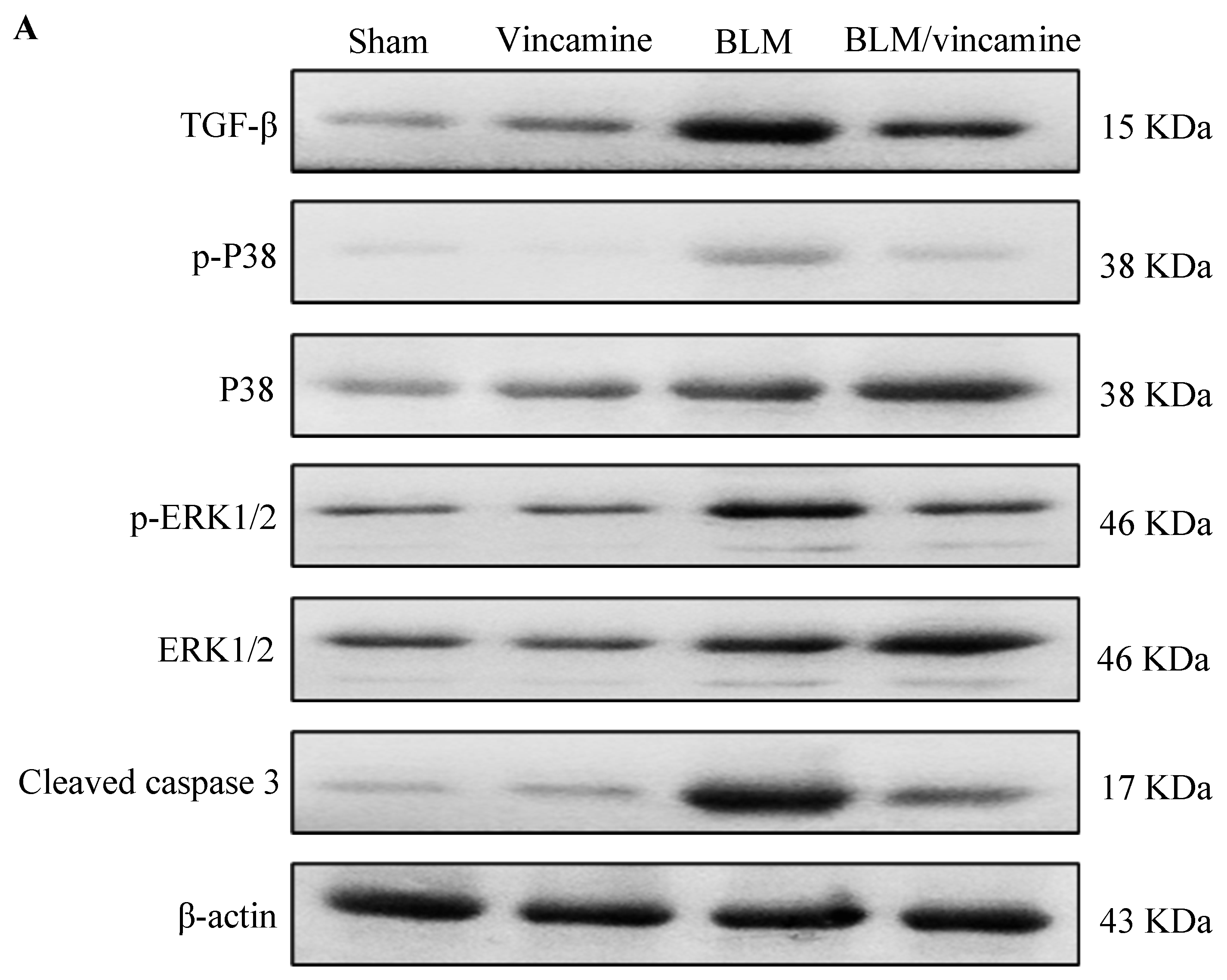
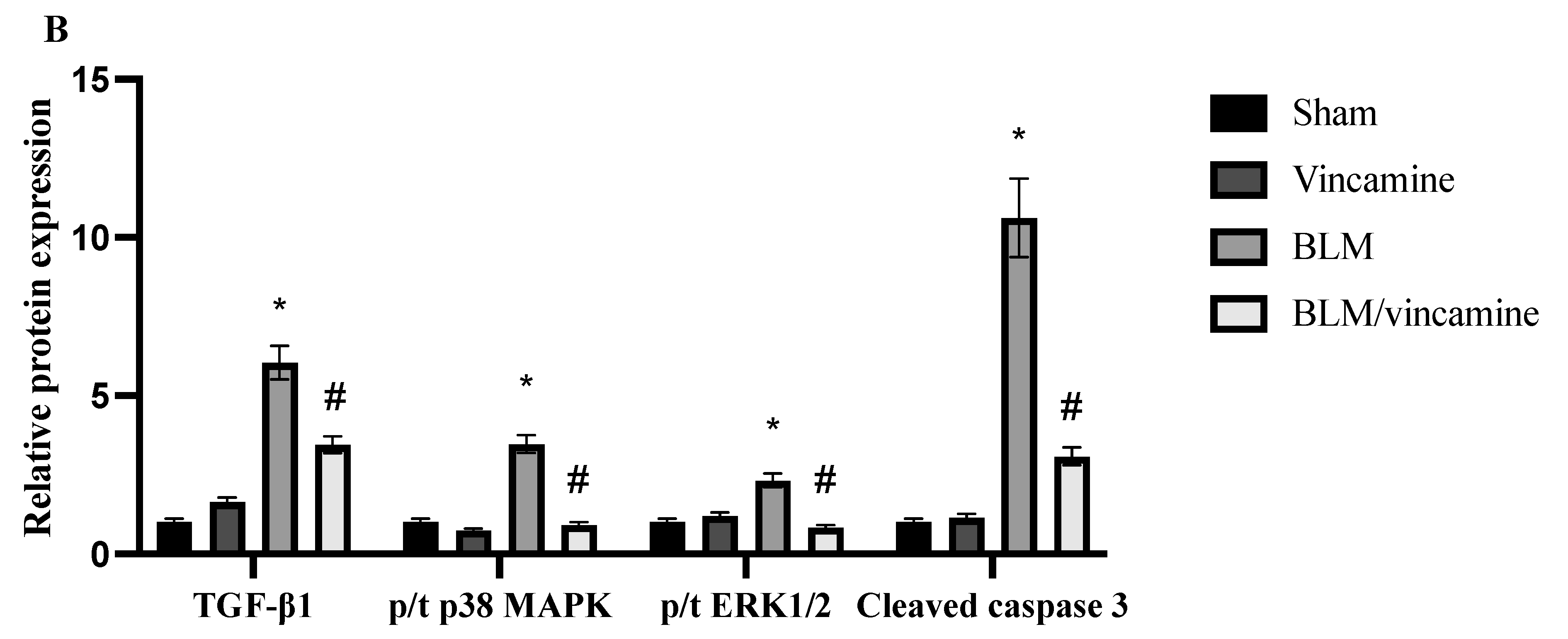
2.5. Expression of TGF-β1, p38 MAPK, ERK1/2, and Cleaved Caspase 3 Proteins
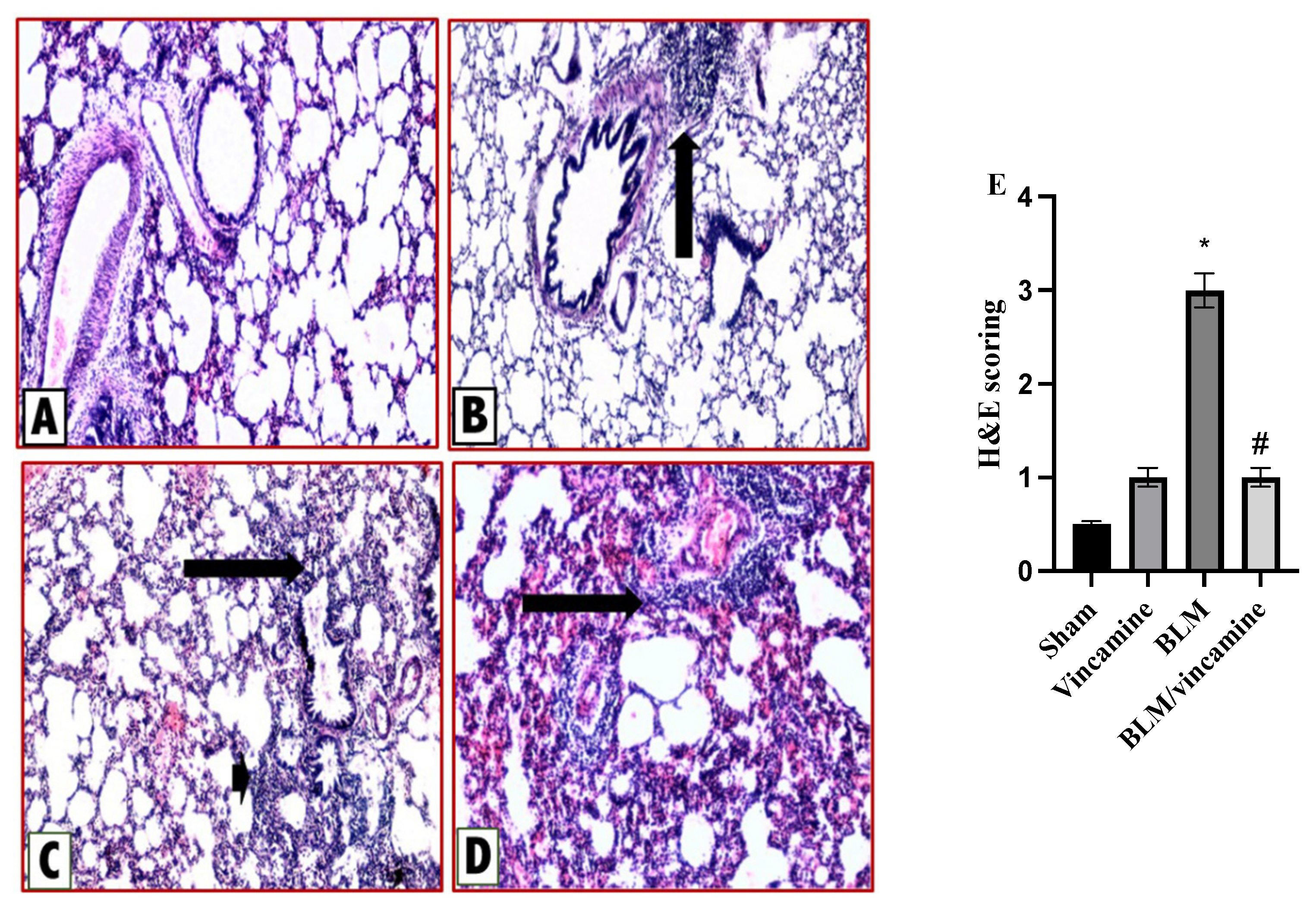
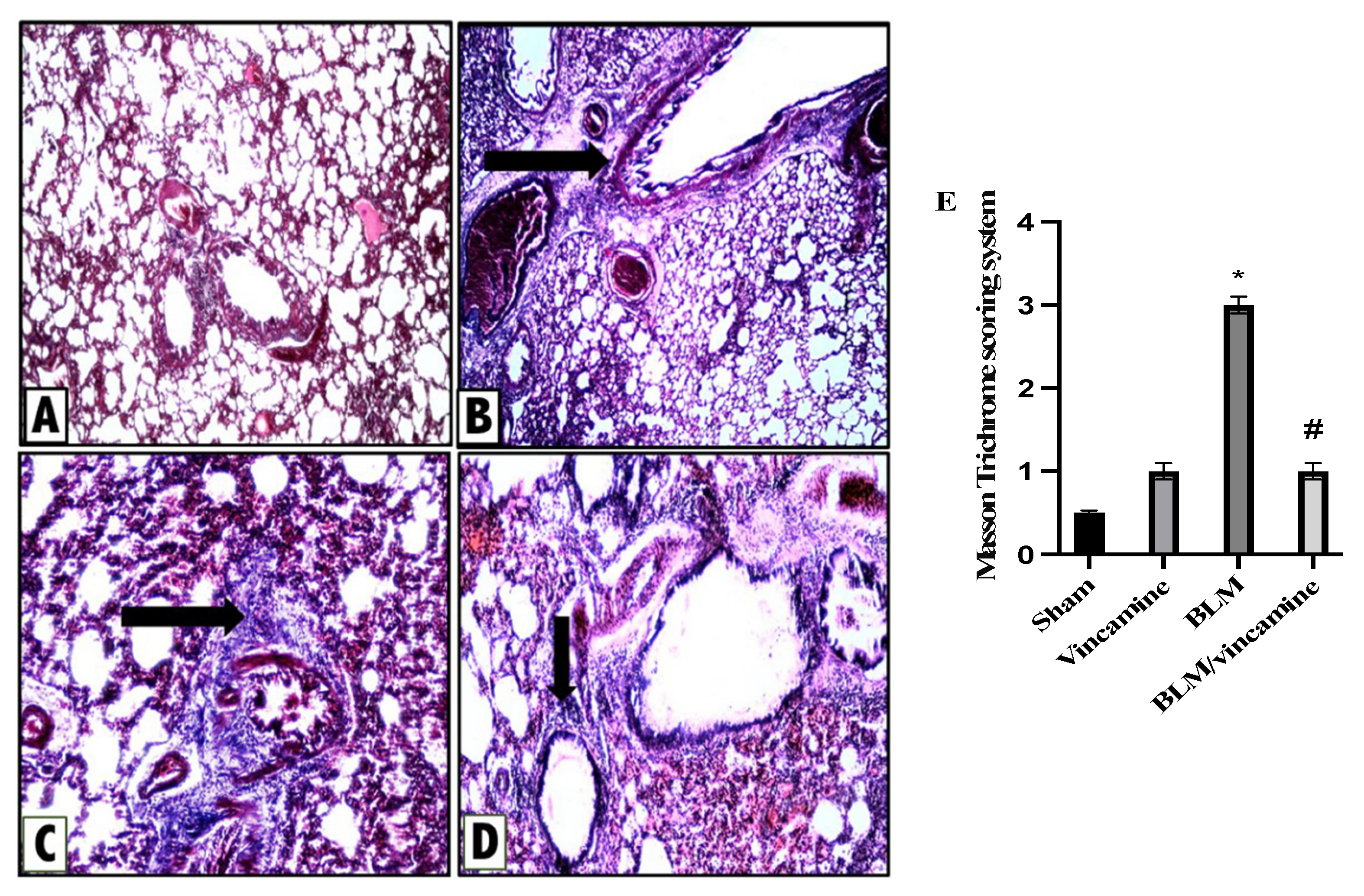
2.6. Histopathological Examination
2.6.1. Protective Activity of Vincamine against Lung Inflammation Induced by BLM
2.6.2. Protective Activity of Vincamine against Lung Fibrosis Induced by BLM
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs and Chemicals
4.2. Experimental Animals
4.3. Pulmonary Fibrosis Induction
4.4. Experimental Groups
- Group I (Sham group): An intratracheal injection of 0.9 NaCl was administrated on day 7 to animals. CMC was also orally administered to rats daily for 9 days.
- Group II (Vincamine group): Animals orally administrated (40 mg/kg) vincamine [20] daily from day 1 till the end of the experiment.
- Group III (BLM group): A single intratracheal injection of BLM (5 mg/kg in 0.9% NaCl) [57] was administrated to animals on the seventh day.
- Group IV (BLM-treated group with vincamine): BLM-induced animals were pretreated with vincamine (40 mg/kg) daily 7 days prior to BLM injection and till the end of the experiment [60].
4.5. Cell Count, LDH Activity, and Total Protein Content Evaluation
4.6. ELISA Analysis
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.8. Western Blotting Analysis
4.9. Pathological Examination
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Richeldi, L.; Collard, H.R.; Jones, M.G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuovo, G.J.; Hagood, J.S.; Magro, C.M.; Chin, N.; Kapil, R.; Davis, L.; Marsh, C.B.; Folcik, V.A. The distribution of immunomodulatory cells in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 416–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.J.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Development and Disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acloque, H.; Adams, M.S.; Fishwick, K.; Bronner-Fraser, M.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: The importance of changing cell state in development and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1438–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawzy, M.A.; Beshay, O.N.; Bekhit, A.A.; Abdel-Hafez, S.M.N.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Bin Jardan, Y.A.; Fathy, M. Nephroprotective effect of AT-MSCs against cisplatin-induced EMT is improved by azilsartan via attenuating oxidative stress and TGF-β/Smad signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 158, 114097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salton, F.; Volpe, M.C.; Confalonieri, M. Epithelial⁻Mesenchymal Transition in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Medicina 2019, 55, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaaeldin, R.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.A.; Zhao, Q.L.; Fathy, M. Modulation of Apoptosis and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition E-cadherin/TGF-beta/Snail/TWIST Pathways by a New Ciprofloxacin Chalcone in Breast Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 2383–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pain, M.; Bermudez, O.; Lacoste, P.; Royer, P.-J.; Botturi, K.; Tissot, A.; Brouard, S.; Eickelberg, O.; Magnan, A. Tissue remodelling in chronic bronchial diseases: From the epithelial to mesenchymal phenotype. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2014, 23, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, M.; Okabe, M.; Saad Eldien, H.M.; Yoshida, T. AT-MSCs Antifibrotic Activity is Improved by Eugenol through Modulation of TGF-beta/Smad Signaling Pathway in Rats. Molecules 2020, 25, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, J.; Okabe, M.; Yoshida, T.; Soko, C.; Fathy, M.; Amano, K.; Kobashi, D.; Wakasugi, M.; Okudera, H. Hyperdry human amniotic membrane application as a wound dressing for a full-thickness skin excision after a third-degree burn injury. Burn. Trauma 2020, 8, tkaa014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaaeldin, R.; Ali, F.E.M.; Bekhit, A.A.; Zhao, Q.-L.; Fathy, M. Inhibition of NF-kB/IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 Pathway and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer Cells by Azilsartan. Molecules 2022, 27, 7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, H.; Allen, J.T.; Mason, R.M.; Kamimura, T.; Zhang, Z. TGF-β1 induces human alveolar epithelial to mesenchymal cell transition (EMT). Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, N.W.; Luzina, I.G.; Atamas, S.P. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2012, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, N.; Berger, P.; Zenzmaier, C. Therapeutic targeting of redox signaling in myofibroblast differentiation and age-related fibrotic disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 458276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, M.A.; Huang, R.Y.-J.; Jackson, R.A.; Thiery, J.P. EMT: 2016. Cell 2016, 166, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyigit, L.P.; Aktas, E.C.; Senbas, Z.A.; Ozturk, A.B.; Ozturk, E.; Ergonul, M.O.; Tabak, L.; Ferhanoglu, B.; Cetiner, M.; Deniz, G. The role of atopy in the pathogenesis of bleomycin pulmonary toxicity. Respir. Med. 2019, 155, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-M.; Zhao, Y.; He, C.-C.; Li, J.-X. Preventive effects of Citrus reticulata essential oil on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats and the mechanism. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao 2012, 10, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandini, H.S.; Naik, P.R. Antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant effect of Vincamine, in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pharm. 2019, 843, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, R.R. A comparative evaluation of some blood sugar lowering agents of plant origin. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 67, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, R.M.; Abo El Gheit, R.E.; Badawi, G.A. Vincamine protects against cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 and hindering TLR4/ IFN-γ/CD44 cells inflammatory cascade. Life Sci. 2021, 272, 119224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ye, M.; Zhang, J. Vincamine prevents lipopolysaccharide induced inflammation and oxidative stress via thioredoxin reductase activation in human corneal epithelial cells. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 2195–2204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Dessouki, A.M.; El Fattah, M.A.; Awad, A.S.; Zaki, H.F. Zafirlukast and vincamine ameliorate tamoxifen-induced oxidative stress and inflammation: Role of the JNK/ERK pathway. Life Sci. 2018, 202, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaaeldin, R.; Abdel-Rahman, I.M.; Ali, F.E.; Bekhit, A.A.; Elhamadany, E.Y.; Zhao, Q.-L.; Cui, Z.-G.; Fathy, M. Dual Topoisomerase I/II Inhibition-Induced Apoptosis and Necro-Apoptosis in Cancer Cells by a Novel Ciprofloxacin Derivative via RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL Activation. Molecules 2022, 27, 7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaaeldin, R.; Bakkar, S.M.; Mohyeldin, R.H.; Ali, F.E.M.; Abdel-Maqsoud, N.M.R.; Fathy, M. Azilsartan Modulates HMGB1/NF-kappa;B/p38/ERK1/2/JNK and Apoptosis Pathways during Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. Cells 2023, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawzy, M.A.; Nasr, G.; Ali, F.E.M.; Fathy, M. Quercetin potentiates the hepatoprotective effect of sildenafil and/or pentoxifylline against intrahepatic cholestasis: Role of Nrf2/ARE, TLR4/NF-κB, and NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathways. Life Sci. 2023, 314, 121343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabra, R.T.; Abdellatef, A.A.; Abdel-Sattar, E.; Fathy, M.; Meselhy, M.R.; Hayakawa, Y. Russelioside A, a Pregnane Glycoside from Caralluma tuberculate, Inhibits Cell-Intrinsic NF-κB Activity and Metastatic Ability of Breast Cancer Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 45, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shytaj, I.L.; Fares, M.; Gallucci, L.; Lucic, B.; Tolba, M.M.; Zimmermann, L.; Adler, J.M.; Xing, N.; Bushe, J.; Gruber, A.D.; et al. The FDA-Approved Drug Cobicistat Synergizes with Remdesivir to Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication In Vitro and Decreases Viral Titers and Disease Progression in Syrian Hamsters. mBio 2022, 13, e0370521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A. Integrating mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnaser, M.; Alaaeldin, R.; Attya, M.E.; Fathy, M. Hepatoprotective potential of gabapentin in cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis; targeting oxidative stress, apoptosis, and NF-kB/MAPK signaling pathways. Life Sci. 2023, 320, 121562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, M.; Khalifa, E.; Fawzy, M.A. Modulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase pathway by eugenol and telmisartan in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in rats. Life Sci. 2019, 216, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, M.; Nikaido, T. In vivo attenuation of angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by Nigella sativa. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 48, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fawzy, M.A.; Maher, S.A.; Bakkar, S.M.; El-Rehany, M.A.; Fathy, M. Pantoprazole Attenuates MAPK (ERK1/2, JNK, p38)-NF-kappaB and Apoptosis Signaling Pathways after Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaaeldin, R.; Mustafa, M.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.A.; Fathy, M. In vitro inhibition and molecular docking of a new ciprofloxacin chalcone against SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Fundam. Clin. Pharm. 2022, 36, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaaeldin, R.; Nazmy, M.H.; Abdel-Aziz, M.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.A.; Fathy, M. Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Effect of 7-(4-(N-substituted carbamoylmethyl) piperazin-1-yl) Ciprofloxacin-derivative on HCT 116 and A549 Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 2739–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisa, M.A.; Fathy, M.; Abuo-Rahma, G.; Abdel-Aziz, M.; Nazmy, M.H. Anti-Proliferative and Pro-Apoptotic Activities of Synthesized 3,4,5 Tri-Methoxy Ciprofloxacin Chalcone Hybrid, through p53 Up-Regulation in HepG2 and MCF7 Cell Lines. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2021, 22, 3393–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathy, M.; Sun, S.; Zhao, Q.-L.; Abdel-Aziz, M.; Abuo-Rahma, G.E.-D.A.; Awale, S.; Nikaido, T. A New Ciprofloxacin-derivative Inhibits Proliferation and Suppresses the Migration Ability of HeLa Cells. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 5025–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdellatef, A.A.; Fathy, M.; Mohammed, A.E.I.; Bakr, M.S.A.; Ahmed, A.H.; Abbass, H.S.; El-Desoky, A.H.; Morita, H.; Nikaido, T.; Hayakawa, Y. Inhibition of cell-intrinsic NF-kappaB activity and metastatic abilities of breast cancer by aloe-emodin and emodic-acid isolated from Asphodelus microcarpus. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 75, 840–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaaeldin, R.; Abdel-Rahman, I.A.M.; Hassan, H.A.; Youssef, N.; Allam, A.E.; Abdelwahab, S.F.; Zhao, Q.L.; Fathy, M. Carpachromene Ameliorates Insulin Resistance in HepG2 Cells via Modulating IR/IRS1/PI3k/Akt/GSK3/FoxO1 Pathway. Molecules 2021, 26, 7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaaeldin, R.; Hassan, H.A.; Abdel-Rahman, I.M.; Mohyeldin, R.H.; Youssef, N.; Allam, A.E.; Abdelwahab, S.F.; Zhao, Q.L.; Fathy, M. A New EGFR Inhibitor from Ficus benghalensis Exerted Potential Anti-Inflammatory Activity via Akt/PI3K Pathway Inhibition. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 2967–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, M.; Fawzy, M.A.; Hintzsche, H.; Nikaido, T.; Dandekar, T.; Othman, E.M. Eugenol exerts apoptotic effect and modulates the sensitivity of HeLa cells to cisplatin and radiation. Molecules 2019, 24, 3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, M.; Nikaido, T. In vivo modulation of iNOS pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma by Nigella sativa. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2013, 18, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vereczkey, L. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of vincamine and related compounds. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 1985, 10, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlar Koprulu, R.E.; Okur, M.E.; Kolbasi, B.; Keskin, I.; Ozbek, H. Effects of Vincamine on Testicular Dysfunction in Alloxan-induced Diabetic Male Rats. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2023, 21, e132265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, M.A.; Maher, S.A.; El-Rehany, M.A.; Welson, N.N.; Albezrah, N.K.A.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Fathy, M. Vincamine Modulates the Effect of Pantoprazole in Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Attenuating MAPK and Apoptosis Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2022, 27, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zou, Q.; Zhang, J. Vincamine exerts protective effect on spiral ganglion neurons in endolymphatic hydrops guinea pig models. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 3650–3663. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Judge, J.L.; Nagel, D.J.; Owens, K.M.; Rackow, A.; Phipps, R.P.; Sime, P.J.; Kottmann, R. Prevention and treatment of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis with the lactate dehydrogenase inhibitor gossypol. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, H.H.; Omran, M.M.; Hasan, H.F.; El Kiki, S.M. Modulation of bleomycin-induced oxidative stress and pulmonary fibrosis by N-acetylcysteine in rats via AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κβ. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 1943–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Dou, Y.-N.; Zhao, Q.-W.; Zhang, J.-Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Xia, Y.-F.; Dai, Y.; Wei, Z.-F. Paeoniflorin suppresses TGF-β mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary fibrosis through a Smad-dependent pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. The Role of Osthole on TGF-β-Induced Lung Epithelium Apoptosis Injury and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition-Mediated Airway Remodeling in Pediatric Asthma. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 7099097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Zhao, Q.; Han, B.; Zhu, H.-P.; Peng, C.; Zhan, G.; Huang, W. Indole-Based Small Molecules as Potential Therapeutic Agents for the Treatment of Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 845892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Law, B.K.; Chytil, A.M.; Brown, K.A.; Aakre, M.E.; Moses, H.L. Activation of the Erk pathway is required for TGF-beta1-induced EMT in vitro. Neoplasia 2004, 6, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, D.; Otterbein, H.; Förster, M.; Giehl, K.; Zeiser, R.; Lehnert, H.; Ungefroren, H. Negative regulation of TGF-β1-induced MKK6-p38 and MEK-ERK signalling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by Rac1b. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Biekemitoufu, H.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Ma, Y. Expression of Twist, Slug and Snail in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and their prognostic significance. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.L.; Yang, D.; Cao, X.; Wang, F.; Hong, D.Y.; Wang, J.; Shen, X.C.; Chen, Y. Fibronectin induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells via activation of calpain. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3889–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.Y.; Chai, J.Y.; Tang, T.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chong, P.P.; Looi, C.Y. The E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Signaling, Therapeutic Implications, and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessen, H.; Hoyer, N.; Prior, T.S.; Frederiksen, P.; Karsdal, M.A.; Leeming, D.J.; Bendstrup, E.; Sand, J.M.B.; Shaker, S.B. Turnover of type I and III collagen predicts progression of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Gao, Y.-Q.; Wang, J.-F.; Niu, J.-Z.; Zhang, X.-X. Apoptosis of type II alveolar epithelial cell induced by bleomycin in lung fibrotic rat. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao Acta Acad. Med. Sin. 2007, 29, 782–786. [Google Scholar]
- Borzone, G.; Moreno, R.; Urrea, R.; Meneses, M.; Oyarzun, M.; Lisboa, C. Bleomycin-induced chronic lung damage does not resemble human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 1648–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.M.; Hoffman, W.; Tomlinson, K.; Lee, H.-Y. Refinement of the dosage and dosing schedule of ketoprofen for postoperative analgesia in Sprague-Dawley rats. Lab Anim. 2008, 37, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Dhull, D.K.; Joshi, J.; Kaur, S.; Kumar, A. Neuroprotective potential of azilsartan against cerebral ischemic injury: Possible involvement of mitochondrial mechanisms. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 132, 104604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelzaher, W.Y.; Abdel-Hafez, S.M.N.; Rofaeil, R.R.; Ali, A.H.S.A.; Hegazy, A.; Bahaa, H.A. The protective effect of fenofibrate, triptorelin, and their combination against premature ovarian failure in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, R.D.; Harmer, D.W.; Coleman, R.A.; Clark, B.J. GAPDH as a housekeeping gene: Analysis of GAPDH mRNA expression in a panel of 72 human tissues. Physiol. Genom. 2005, 21, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenfield, E.A. Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kseibati, M.O.; Shehatou, G.S.; Sharawy, M.H.; Eladl, A.E.; Salem, H.A. Nicorandil ameliorates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats through modulating eNOS, iNOS, TXNIP and HIF-1α levels. Life Sci. 2020, 246, 117423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, T.; Simpson, J.M.; Timbrell, V. Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J. Clin. Pathol. 1988, 41, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer | Sequence of the Primer |
|---|---|
| TWIST1 | Forward: 5′-CTCAGCTACGCCTTCTCCGT-3′ Reverse: 5′-TGACATCTAGGTCTCCGGCCT-3′ |
| Snai1 | Forward: 5′-ACCTCCAGACCCACTCGGAT-3′ Reverse: 5′-GAGGTAGCAGGGTCAGCGAG-3′ |
| Slug | Forward: 5′-ATTCCTGGTGCGTGTCCCAT-3′ Reverse: 5′-GCAACGTGTGGGTCCGAATG-3´ |
| P53 | Forward: 5′-AGCGACTACAGTTAGGGGGT-3′ Reverse: 5′-ACAGTTATCCAGTCTTCAGGGG-3′ |
| Bax | Forward: 5′-CGTCTGCGGGGAGTCAC-3′ Reverse: 5′-AGCCATCCTCTCTGCTCGAT-3′ |
| Bcl2 | Forward: 5′-TTCTCTCTTTCGGGCCGTGG-3′ Reverse: 5′-CCACTCGTAGCCCCTCTGTG-3′ |
| GAPDH | Forward: 5´-AACCTGCCAAGTATGATGACATCA-3′ Reverse: 5′-TTCCACTGATATCCCAGCTGCT-3′ |
| Severity Score | Histology |
|---|---|
| (0) None | No |
| (1) Mild | <20% of the tissue |
| (2) Moderate | 20–50% of the tissue |
| (3) Severe | >50% of the tissue |
| Fibrosis Score | Histological Findings |
|---|---|
| 0 1 | Normal Lung |
| Minimal fibrous thickening of bronchial or alveolar walls | |
| 2 3 | Moderate walls thickening without clear lung architecture damage |
| 4 5 | Increased lung structures fibrosis definite damage with formation of small fibrous masses or fibrous bands |
| 6 7 | Severe structure distortion and great areas of fibrosis (honeycomb lung) |
| 8 | Total field fibrous obliteration |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alaaeldin, R.; Mohyeldin, R.H.; Bekhit, A.A.; Gomaa, W.; Zhao, Q.-L.; Fathy, M. Vincamine Ameliorates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats; Targeting TGF-β/MAPK/Snai1 Pathway. Molecules 2023, 28, 4665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124665
Alaaeldin R, Mohyeldin RH, Bekhit AA, Gomaa W, Zhao Q-L, Fathy M. Vincamine Ameliorates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats; Targeting TGF-β/MAPK/Snai1 Pathway. Molecules. 2023; 28(12):4665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124665
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlaaeldin, Rania, Reham H. Mohyeldin, Amany Abdlrehim Bekhit, Wafaey Gomaa, Qing-Li Zhao, and Moustafa Fathy. 2023. "Vincamine Ameliorates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats; Targeting TGF-β/MAPK/Snai1 Pathway" Molecules 28, no. 12: 4665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124665
APA StyleAlaaeldin, R., Mohyeldin, R. H., Bekhit, A. A., Gomaa, W., Zhao, Q.-L., & Fathy, M. (2023). Vincamine Ameliorates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis in Rats; Targeting TGF-β/MAPK/Snai1 Pathway. Molecules, 28(12), 4665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28124665







