6-Methylcoumarin Promotes Melanogenesis through the PKA/CREB, MAPK, AKT/PI3K, and GSK3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
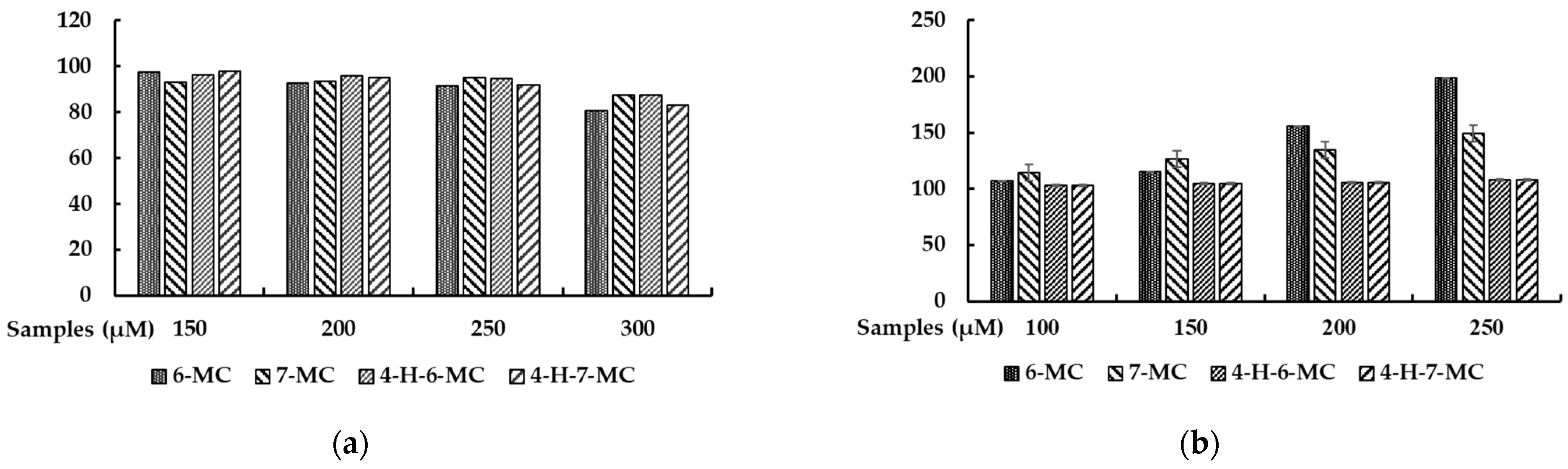
2.1. Effect of Methylcoumarin Derivatives on the Viability of B16F10 Cells
2.2. Effect of Methylcoumarin Derivatives on Melanin Production of B16F10 Cells
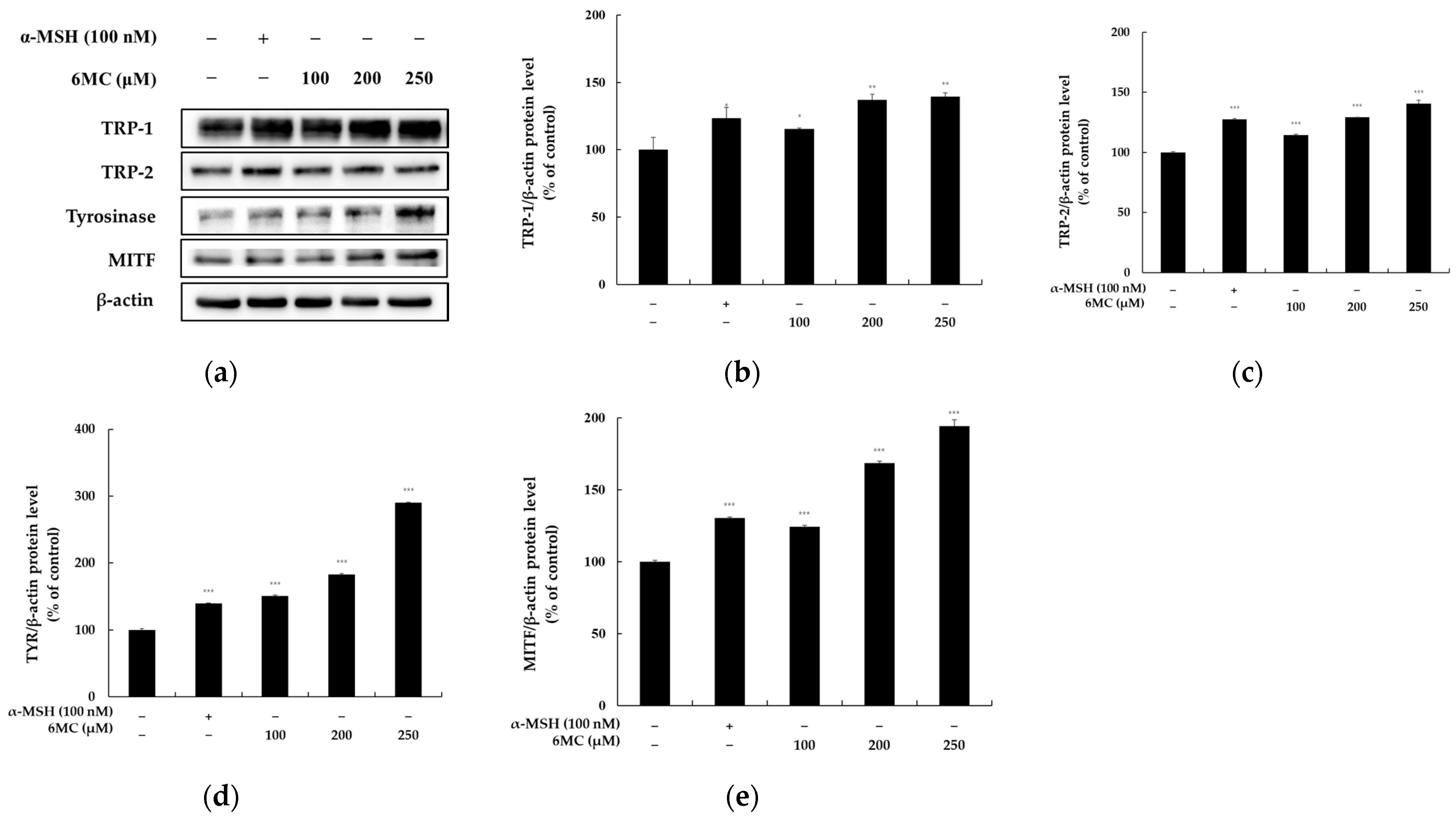
2.3. Effect of 6-Methylcoumarin on the Expression of Melanogenesis-Related Proteins in B16F10 Cells
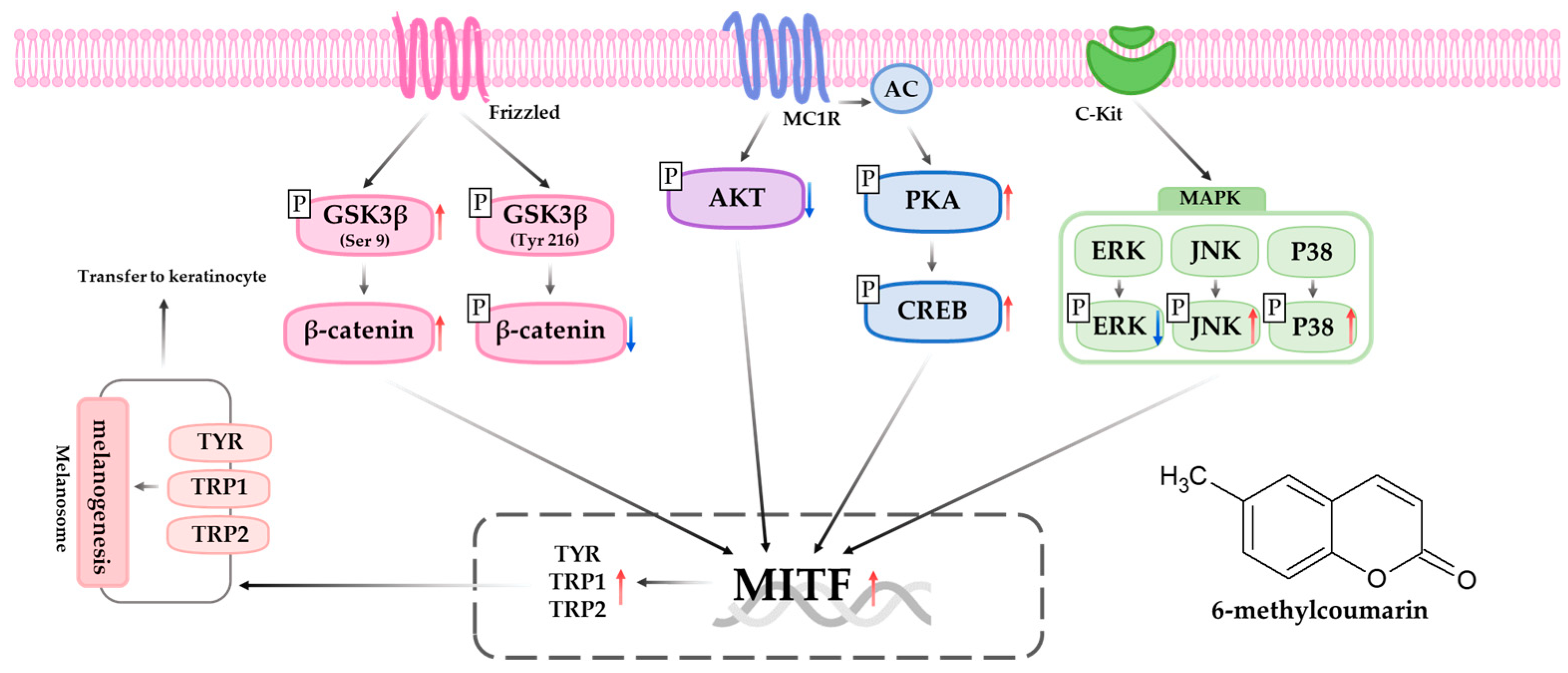
2.4. 6-Methylcoumarin Activated Melanogenesis in B16F10 Cells through the PKA/CREB Signaling Pathway
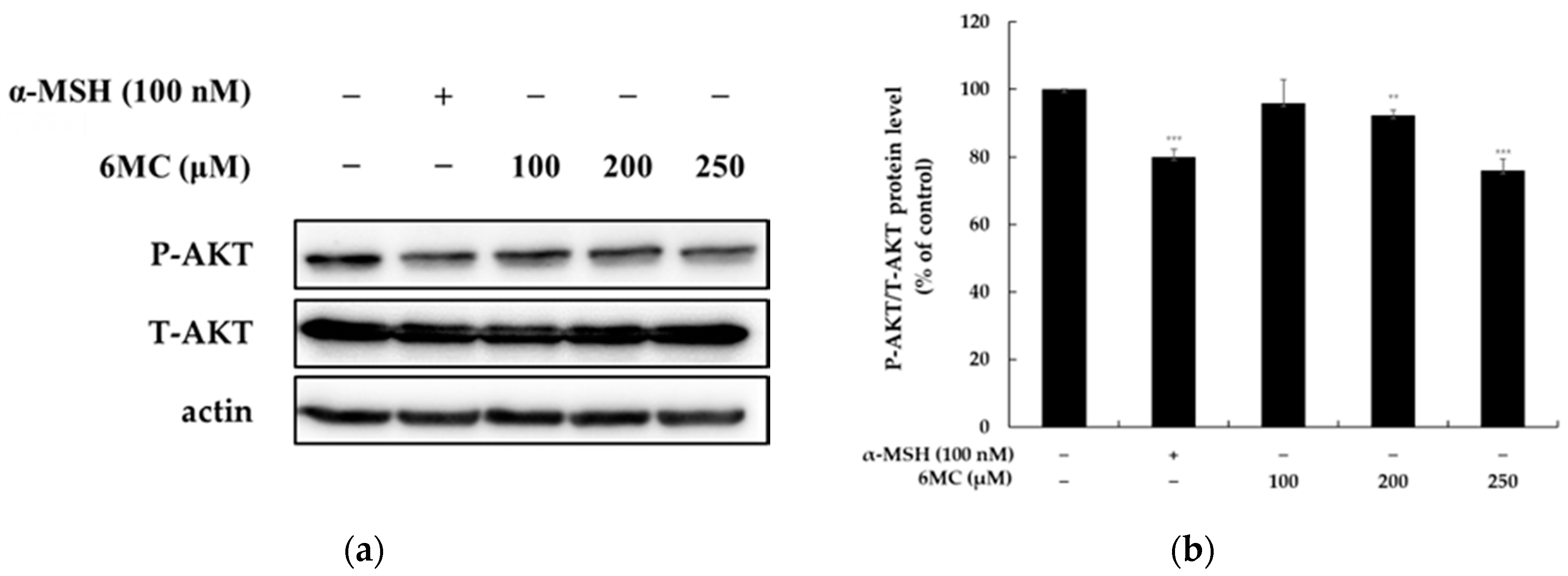
2.5. 6-Methylcoumarin Stimulated Melanogenesis in B16F10 Cells through PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathways
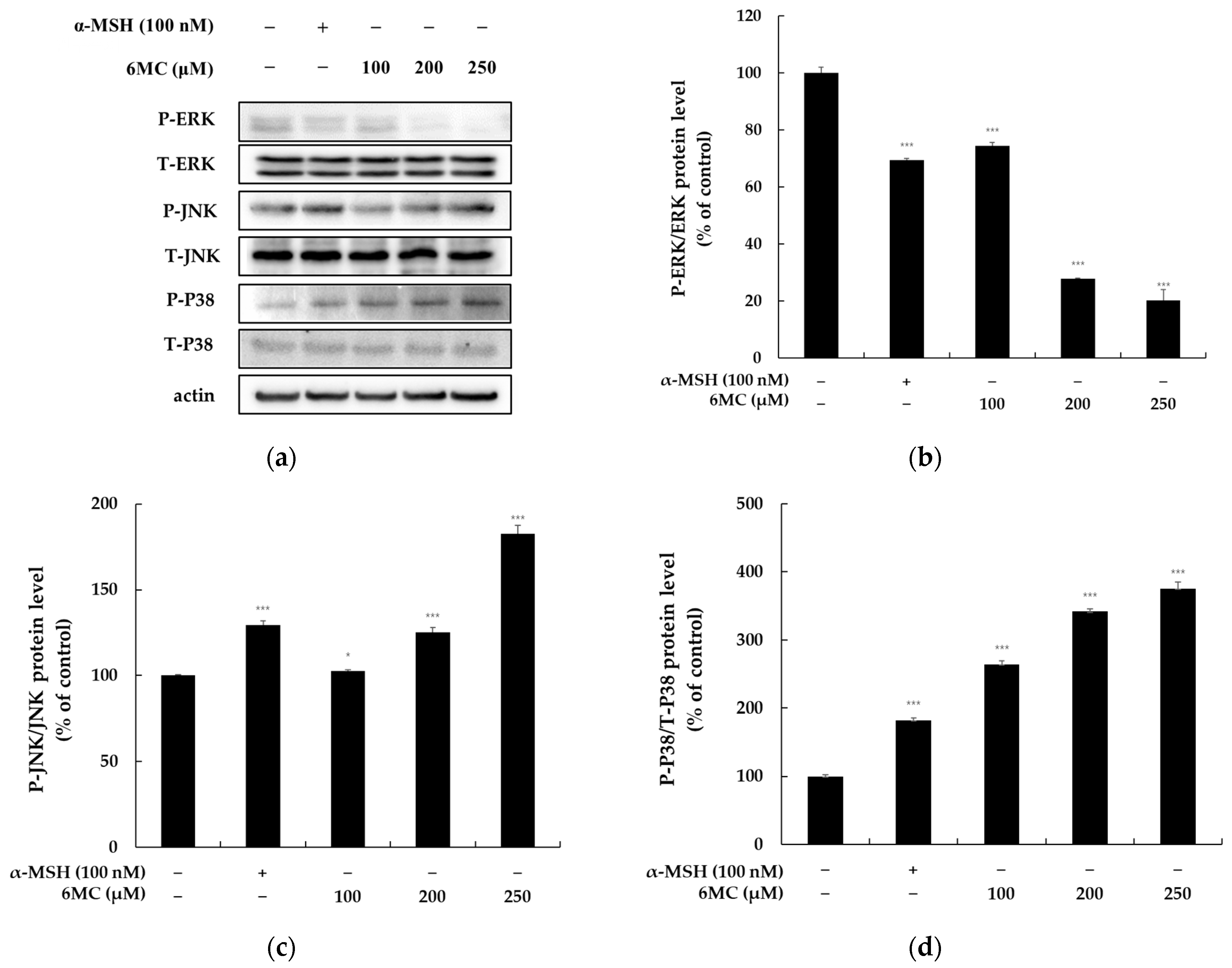
2.6. 6-Methylcoumarin Stimulated Melanogenesis in B16F10 Cells through the MAPK Signaling Pathway
2.7. 6-Methylcoumarin Stimulated Melanogenesis in B16F10 Cells through GSK-3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
2.8. 6-Methylcoumarin Is Safe for Human Skin
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viabilities
4.4. Determination of Cellular Melanin Contents
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Human Skin Irritation Test
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arora, N.; Siddiqui, E.M.; Mehan, S. Involvement of adenylate cyclase/cAMP/CREB and SOX9/MITF in melanogenesis to prevent vitiligo. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2021, 476, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.M.; Qu, L.Q.; Ng, J.P.L.; Zeng, W.; Yu, L.; Song, L.L.; Wong, V.K.W.; Xia, C.L.; Law, B.Y.K. Natural Citrus flavanone 5-demethylnobiletin stimulates melanogenesis through the activation of cAMP/CREB pathway in B16F10 cells. Phytomedicine 2022, 98, 153941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuerxuntayi, A.; Abulikemu, T.; Niu, C. Mechanisms of 4-Dimethylamino-4′-Methoxy Chalcone in Promoting Melanin Synthesis. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2022, 17, 1934578X221086895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, R.; Shang, J.; Zhong, H. The Great Capacity on Promoting Melanogenesis of Three Compatible Components in Vernonia anthelmintica (L.) Willd. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadeniz, F.; Oh, J.H.; Seo, Y.; Yang, J.; Lee, H.; Kong, C.S. Quercetin 3-O-Galactoside Isolated from Limonium tetragonum Inhibits Melanogenesis by Regulating PKA/MITF Signaling and ERK Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.Y.; Akter, K.M.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, K.D.; Yoo, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Hwangbo, C. Fraxinol Stimulates Melanogenesis in B16F10 Mouse Melanoma Cells through CREB/MITF Signaling. Molecules 2022, 27, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Hyun, C.G. Miglitol, an Oral Antidiabetic Drug, Downregulates Melanogenesis in B16F10 Melanoma Cells through the PKA, MAPK, and GSK3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2022, 28, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.H.; Yang, S.H.; Park, W.K.; Shin, H.J. Bamboo Lignin Fractions with In Vitro Tyrosinase Inhibition Activity Downregulate Melanogenesis in B16F10 Cells via PKA/CREB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Fu, M.; Pei, S.; Zhou, L.; Shang, J. R-Fluoxetine Increases Melanin Synthesis Through a 5-HT1A/2A Receptor and p38 MAPK Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.; Ko, J.; Kim, M.; Song, N.; Park, K. Morin Induces Melanogenesis via Activation of MAPK Signaling Pathways in B16F10 Mouse Melanoma Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phacharapiyangkul, N.; Thirapanmethee, K.; Sa-ngiamsuntorn, K.; Panich, U.; Lee, C.-H.; Chomnawang, M.T. The Ethanol Extract of Musa sapientum Linn. Peel Inhibits Melanogenesis through AKT Signaling Pathway. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.S.; Gu, G.E.; Jo, A.R.; Bang, J.S.; Yun, H.Y.; Baek, K.J.; Kwon, N.S.; Park, K.C.; Kim, D.S. Baicalin-induced Akt activation decreases melanogenesis through downregulation of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor and tyrosinase. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 761, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.C.; Yen, H.; Lu, J.Y.; Chang, T.M.; Hii, C.H. Theophylline enhances melanogenesis in B16F10 murine melanoma cells through the activation of the MEK 1/2, and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 137, 111165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.I.; Jung, K.E.; Shin, Y.B.; Kim, C.D.; Yoon, T.J. Sorafenib induces pigmentation via the regulation of β-catenin signalling pathway in melanoma cells. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 31, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Kim, K.B.; Hyun, C.G. A 7-Hydroxy 4-Methylcoumarin Enhances Melanogenesis in B16-F10 Melanoma Cells. Molecules 2023, 28, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Hyun, C.G. Imperatorin Positively Regulates Melanogenesis through Signaling Pathways Involving PKA/CREB, ERK, AKT, and GSK3β/β-Catenin. Molecules 2022, 27, 6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Chung, Y.C.; Hyun, C.G. Induction of Melanogenesis by Fosfomycin in B16F10 Cells through the Upregulation of P-JNK and P-p38 Signaling Pathways. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heghes, S.C.; Vostinaru, O.; Mogosan, C.; Miere, D.; Iuga, C.A.; Filip, L. Safety Profile of Nutraceuticals Rich in Coumarins: An Update. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 803338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, F.; Pinna, C.; Dallavalle, S.; Tamborini, L.; Pinto, A. An Overview of Coumarin as a Versatile and Readily Accessible Scaffold with Broad-Ranging Biological Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, A.; Sharma, R.; Jaswal, V.S.; Nepovimova, E.; Chaudhary, A.; Kuca, K. Psoralen: A Biologically Important Coumarin with Emerging Applications. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1838–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Hsouna, A.; Sadaka, C.; Generalić Mekinić, I.; Garzoli, S.; Švarc-Gajić, J.; Rodrigues, F.; Morais, S.; Moreira, M.M.; Ferreira, E.; Spigno, G.; et al. The Chemical Variability, Nutraceutical Value, and Food-Industry and Cosmetic Applications of Citrus Plants: A Critical Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Wang, S.R.; Li, T.; Zhang, G.C.; Yang, J. Antifungal Activity of 6-Methylcoumarin against Valsa mali and Its Possible Mechanism of Action. J. Fungi 2022, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Xiao, Q.; Han, S.; Jia, Z.; Li, S.; Ding, W. Discovery of a novel plant-derived agent against Ralstonia solanacearum by targeting the bacterial division protein FtsZ. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 177, 104892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.K.; Chung, Y.C.; Hyun, C.G. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of 6-Methylcoumarin in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Macrophages via Regulation of MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2021, 26, 5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.J.; Hyun, C.G. Acenocoumarol Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Activity via the Suppression of NF-κB and MAPK Pathways in RAW 264.7 Cells. Molecules 2023, 28, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Hyun, C.G. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Psoralen Derivatives on RAW264.7 Cells via Regulation of the NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Hyun, C.G. Mechanistic Insights into the Ameliorating Effect of Melanogenesis of Psoralen Derivatives in B16F10 Melanoma Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.C.; Hyun, C.G. Inhibitory Effects of Pinostilbene on Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes: A Study of Possible Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, W.J.; Kim, E.Y.; Park, J.E.; Jo, S.Y.; Bang, S.H.; Chang, E.J.; Chang, S.E. Microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 is involved in melanogenesis via regulation of MITF expression in melanocytes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | Test Sample | No. of Respondents | 20 min after Removal | 24 h after Removal | Reaction Grade (R) * | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 24 h | 48 h | Mean | |||
| 1 | 6-MC (125 μM) | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 6-MC (250 μM) | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | Squalene | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.; Kang, J.-K.; Hyun, C.-G. 6-Methylcoumarin Promotes Melanogenesis through the PKA/CREB, MAPK, AKT/PI3K, and GSK3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways. Molecules 2023, 28, 4551. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114551
Kim T, Kang J-K, Hyun C-G. 6-Methylcoumarin Promotes Melanogenesis through the PKA/CREB, MAPK, AKT/PI3K, and GSK3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways. Molecules. 2023; 28(11):4551. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114551
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Taejin, Jin-Kyu Kang, and Chang-Gu Hyun. 2023. "6-Methylcoumarin Promotes Melanogenesis through the PKA/CREB, MAPK, AKT/PI3K, and GSK3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways" Molecules 28, no. 11: 4551. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114551
APA StyleKim, T., Kang, J.-K., & Hyun, C.-G. (2023). 6-Methylcoumarin Promotes Melanogenesis through the PKA/CREB, MAPK, AKT/PI3K, and GSK3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways. Molecules, 28(11), 4551. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114551







