Is It Still Relevant to Discover New ACE Inhibitors from Natural Products? YES, but Only with Comprehensive Approaches to Address the Patients’ Real Problems: Chronic Dry Cough and Angioedema
Abstract
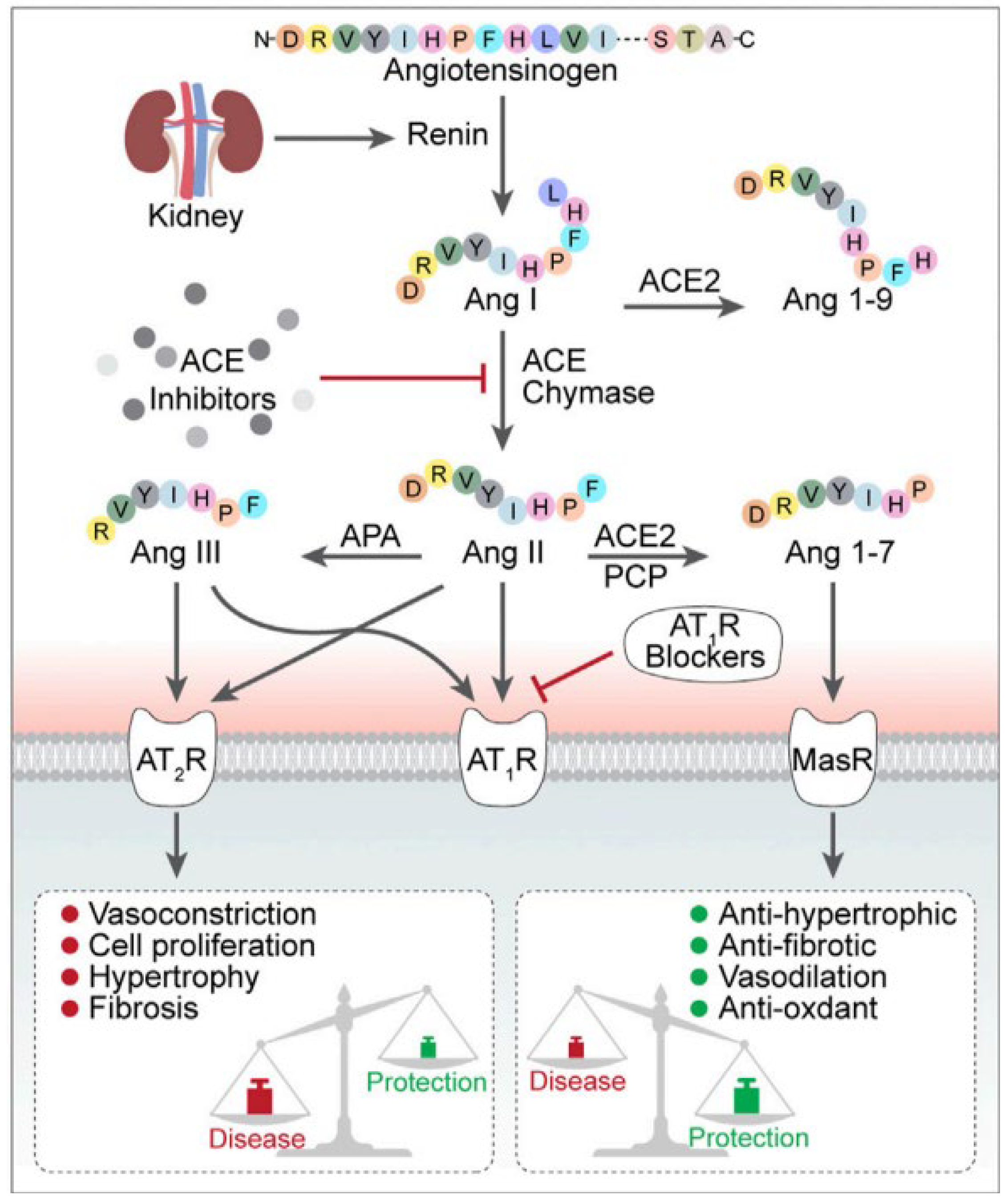
1. Introduction
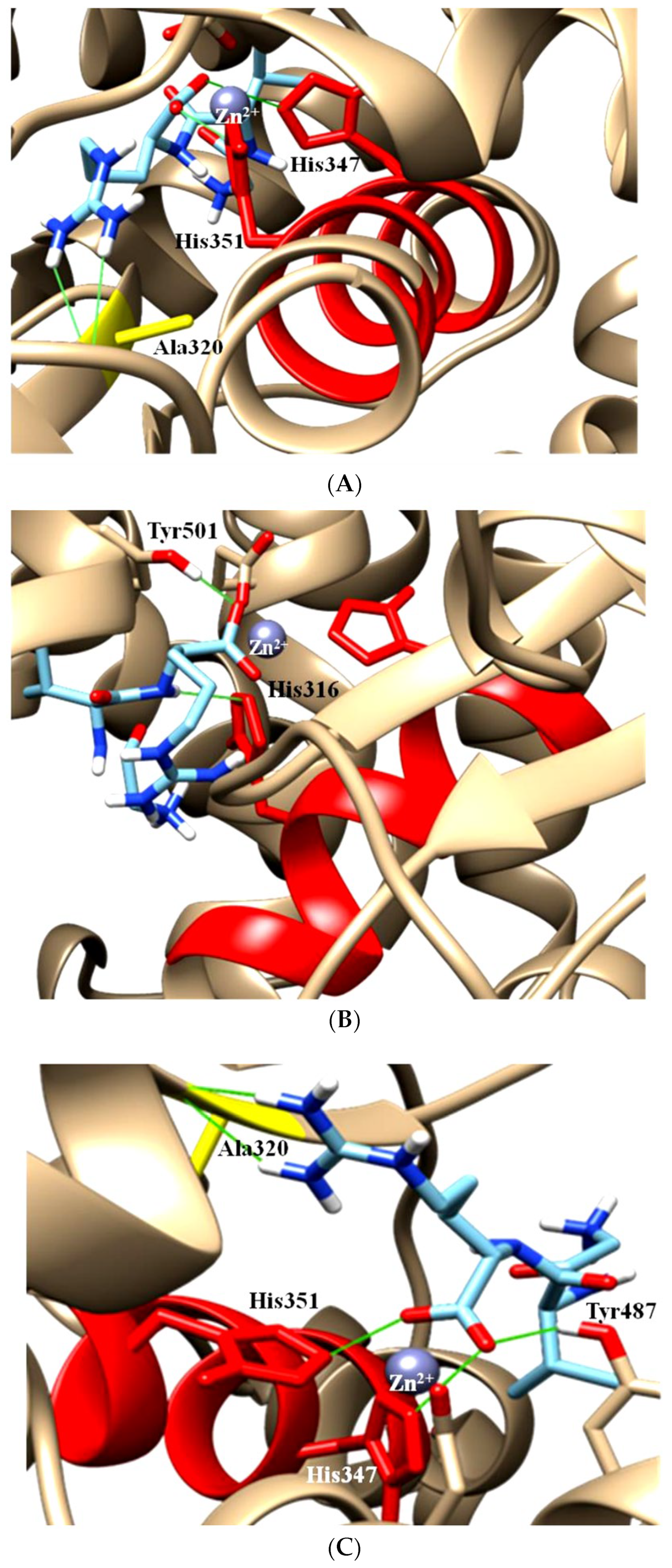
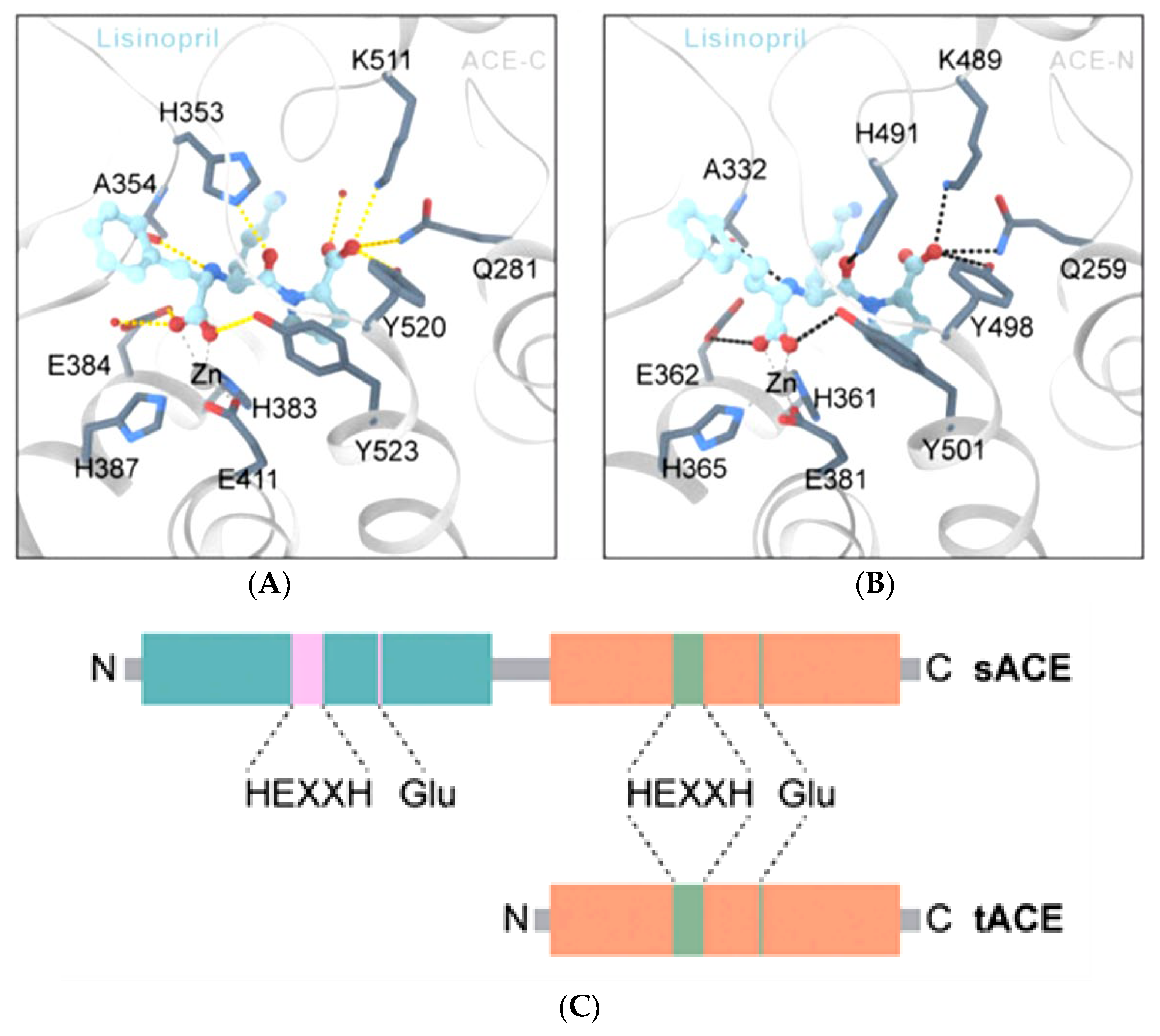
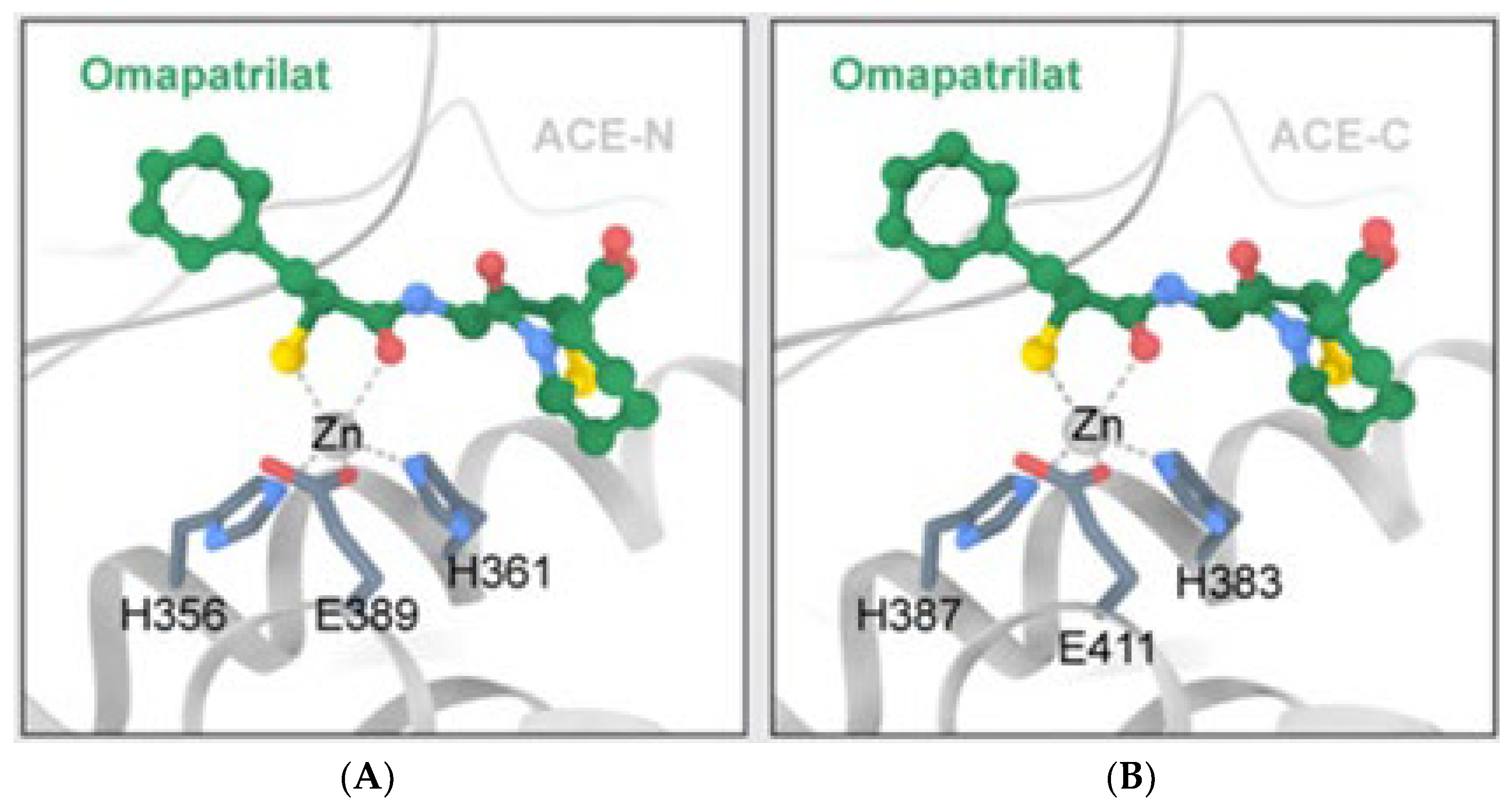
2. The ACE, Type of ACE, and Its Characteristics
3. ACE Inhibitors, Development of Dry Cough and Angioedema, and Possible Alternative Treatments to Address ACE Inhibitor-Induced Cough
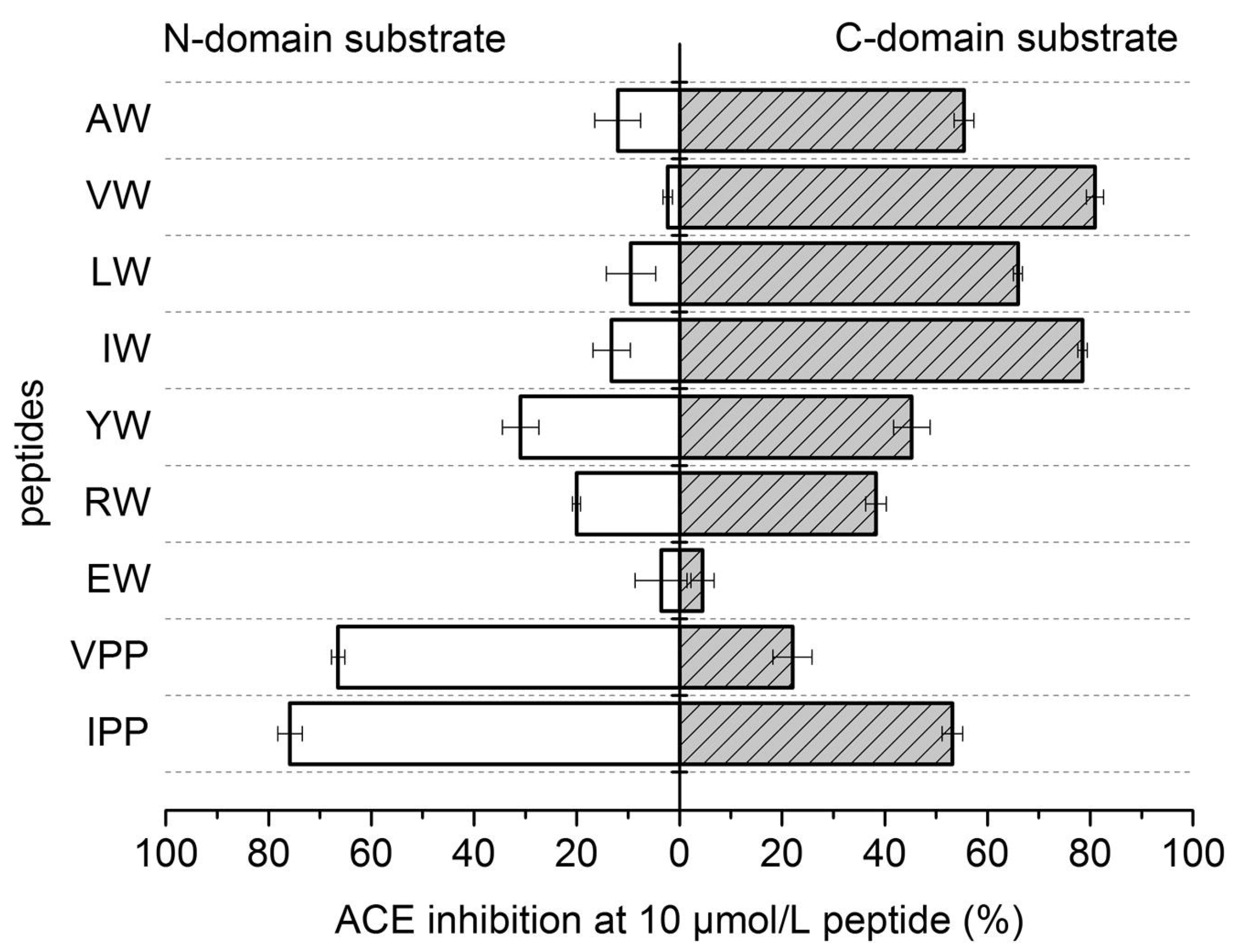
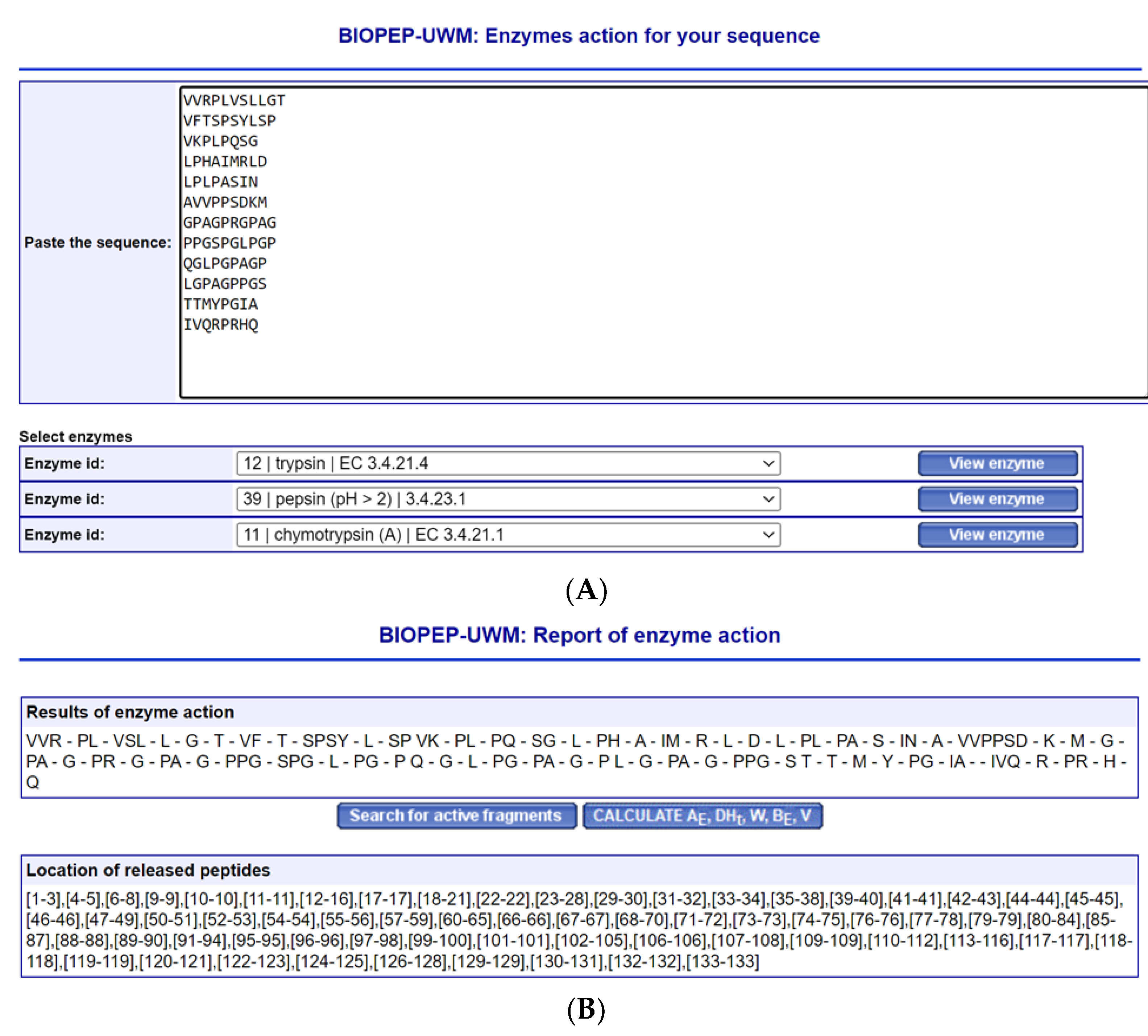
4. Peptides’ Stability against Gastrointestinal Enzymes and Its ACE Domain-Specific Inhibition
5. Function of Neprilysin and Chymase
6. Challenges Working with Naturally Derived Peptide-Based ACE Inhibitors
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anthony, C.S.; Masuyer, G.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Structure based drug design of angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, L.P.; Goh, P.S. Incidence of discontinuation of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors due to cough, in a primary healthcare centre in Singapore. Singap. Med. J. 2014, 55, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, D.S.; Kwong, J.; Rezvani, F.; Coates, A.O. Angiotensin-converting enzyme related cough among Chinese-Americans. Am. J. Med. 2010, 123, 183.e11–183.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Donald, S.; Howlett, J. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors. Cardiology Advisor, 20 January 2019. Available online: https://www.thecardiologyadvisor.com/home/decision-support-in-medicine/cardiology/angiotensin-converting-enzyme-inhibitors/ (accessed on 26 February 2023).
- Gallo, G.; Volpe, M.; Rubattu, S. Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in the Management of Hypertension: A Real-World Perspective and Current Recommendations. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2022, 18, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, L.A. Hypertension: Which First-Line Medication Is Best? Medical News Today. 27 July 2021. Available online: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/hypertension-which-first-line-medication-is-best (accessed on 21 February 2023).
- Li, E.C.; Heran, B.S.; Wright, J.M. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors versus angiotensin receptor blockers for primary hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD009096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naha, S.; Gardner, M.J.; Khangura, D.; Khangura, D.; Kurukulasuriya, R.L.; Sowers, J.R. Hypertension in Diabetes. In Endotext; Updated 2021; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279027 (accessed on 17 November 2022).
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Han, F.; Li, X.; He, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, J. Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers on all-cause mortality, cardiovascular deaths, and cardiovascular events in patients with diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014, 174, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Song, Q.; Zhao, Q. Comparison of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers on cardiovascular outcomes in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e0256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Fan, S.; Shi, X.; Gong, X.; Zhao, J.; Fan, G. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors versus angiotensin II receptor blockers on insulin sensitivity in hypertensive patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yun, J.; Wu, S.; Bi, Y.; Zhao, F. Optimisation and Characterisation of Novel Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Prepared by Double Enzymatic Hydrolysis from Agaricus bisporus Scraps. Foods 2022, 11, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Tian, E.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Yang, P.; Tian, K.; Liao, W.; Li, J.; Ren, C. Small molecule angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors: A medicinal chemistry perspective. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 968104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, S.; Shuib, A.S.; Abdullah, N. Structural characteristics and antihypertensive effects of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides in the renin-angiotensin and kallikrein kinin systems. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 14, 383–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.K.S. Angiotensin Converting Enzymes. In Handbook of Hormones; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 505–518. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, C.S.; Corradi, H.R.; Schwager, S.L.; Redelinghuys, P.; Georgiadis, D.; Dive, V.; Acharya, K.R.; Sturrock, E.D. The N domain of human angiotensin-I-converting enzyme: The role of N-glycosylation and the crystal structure in complex with an N domain-specific phosphinic inhibitor, RXP407. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 35685–35693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluf-Meiken, L.C.; Fernandes, F.B.; Aragão, D.S.; Ronchi, F.A.; Andrade, M.C.; Franco, M.C.; Febba, A.C.; Plavnik, F.L.; Krieger, J.E.; Mill, J.G.; et al. N-domain isoform of Angiotensin I converting enzyme as a marker of hypertension: Populational study. Int. J. Hypertens. 2012, 2012, 581780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunow, D.; Kaiser, S.; Rückriemen, J.; Pohl, C.; Henle, T. Tryptophan-containing dipeptides are C-domain selective inhibitors of angiotensin converting enzyme. Food Chem. 2015, 166, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, S.; Shuib, A.S.; Abdullah, N.; Ridzwan, N.F.W.; Mohamad, S.B. Molecular Docking Analysis of Human Somatic and Testicular Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Complexed with a Novel Compound Gly-Val-Arg. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. 2022, 10, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Esch, J.H.; Tom, B.; Dive, V.; Batenburg, W.W.; Georgiadis, D.; Yiotakis, A.; van Gool, J.M.; de Bruijn, R.J.; de Vries, R.; Danser, A.H. Selective angiotensin-converting enzyme C-domain inhibition is sufficient to prevent angiotensin I-induced vasoconstriction. Hypertension 2005, 45, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, D.; Beau, F.; Czarny, B.; Cotton, J.; Yiotakis, A.; Dive, V. Roles of the two active sites of somatic angiotensin-converting enzyme in the cleavage of angiotensin I and bradykinin: Insights from selective inhibitors. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersanetti, P.A.; Sabatini, R.A.; Matos, B.S.; Douglas, R.G.; Nchindam, A.; Juliano, M.A.; Pesquero, J.B.; Sturrock, E.D.; Carmona, A.K. Characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme N-domain selectivity using positional-scanning combinatorial libraries of fluorescence resonance energy transfer peptides. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACE Inhibitors. Cleveland Clinic. 2021. Available online: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/21934-ace-inhibitors (accessed on 26 February 2023).
- Yılmaz, İ. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors Induce Cough. Turk. Thorac. J. 2019, 20, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, B.; Jadhav, U.; Singhai, P.; Sadhanandham, S.; Shah, N. ACEI-induced cough: A review of current evidence and its practical implications for optimal CV risk reduction. Indian Heart J. 2020, 72, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.; Gonzalez, J.; Monteleone, C. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor-induced angioedema: A review of the literature. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2017, 19, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.C.; Park, S.W.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, K.P. Iron supplementation inhibits cough associated with ACE inhibitors. Hypertension 2001, 38, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malini, P.L.; Strocchi, E.; Zanardi, M.; Milani, M.; Ambrosioni, E. Thromboxane antagonism and cough induced by angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor. Lancet 1997, 350, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsen, E.; Reem, A. Fosinopril for Potential Resolution of Cough Associated with an Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor. Endocr. Pract. 2005, 11, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, M.N.; Evans, B.L.; Pylypchuk, G.B. Cough induced by quinapril with resolution after changing to fosinopril. Ann. Pharmacother. 1994, 28, 720–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, D.; Jallad, N.; Germino, F.W.; Willett, M.S.; de Silva, J.; Weidner, S.M.; Mills, D.J. A Comparison of the Cough Profile of Fosinopril and Enalapril in Hypertensive Patients with a History of ACE Inhibitor-Associated Cough. Am. J. Ther. 1995, 2, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germino, F.W.; Lastra, J.; Pool, P.; Punzi, H.; Spinowitz, B.; Smith, W.; Wallace, S.; Willett, M.; Mills, D.; De Silva, J.; et al. Evaluation of the cough profile of fosinopril in hypertensive patients with ACE inhibitor associated cough-A pilot study. Curr. Ther. Res. 1993, 54, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, S.; Shuib, A.S.; Abdullah, N.; Mohamad, S.B.; Aminudin, N. Characterisation of novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory tripeptide, Gly-Val-Arg derived from mycelium of Pleurotus pulmonarius. Process Biochem. 2017, 62, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, S.; Shuib, A.S.; Abdullah, N.; Ashrafzadeh, A.; Kabir, N. Gly-Val-Arg, an angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory tripeptide ameliorates hypertension on spontaneously hypertensive rats. Process Biochem. 2018, 69, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, M.M.; Dong, D.; O’Neill, P.M.; Amigues, E.; Matziari, M. Design, Synthesis, and Study of a Novel RXPA380-Proline Hybrid (RXPA380-P) as an Antihypertensive Agent. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 35035–35043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningrum, S.; Sutrisno, A.; Hsu, J.L. An exploration of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides derived from gastrointestinal protease hydrolysate of milk using a modified bioassay-guided fractionation approach coupled with in silico analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 1913–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhedi, O.; Nasri, R.; Mora, L.; Jridi, M.; Toldrá, F.; Nasri, M. In silico analysis and molecular docking study of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from smooth-hound viscera protein hydrolysates fractionated by ultrafiltration. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaniak, A.; Minkiewicz, P.; Darewicz, M. Food-Originating ACE Inhibitors, Including Antihypertensive Peptides, as Preventive Food Components in Blood Pressure Reduction. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkiewicz, P.; Iwaniak, A.; Darewicz, M. BIOPEP-UWM Virtual-A Novel Database of Food-Derived Peptides with In Silico-Predicted Biological Activity. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-Lopes, R.; Montezano, A.C.; Neves, K.B.; Harvey, A.; Rios, F.J.; Skiba, D.S.; Arendse, L.B.; Guzik, T.J.; Graham, D.; Poglitsch, M.; et al. Selective Inhibition of the C-Domain of ACE (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme) Combined with Inhibition of NEP (Neprilysin): A Potential New Therapy for Hypertension. Hypertension 2021, 78, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Cozier, G.E.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Molecular Basis for Omapatrilat and Sampatrilat Binding to Neprilysin-Implications for Dual Inhibitor Design with Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 5488–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.C.; Abdullah, N.; Shuib, A.S. Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from an edible mushroom, Pleurotus cystidiosus O.K. Miller identified by LC-MS/MS. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Varagic, J.; VonCannon, J.L.; Groban, L.; Collawn, J.F.; Dell’Italia, L.J.; Ferrario, C.M. Primacy of cardiac chymase over angiotensin converting enzyme as an angiotensin-(1-12) metabolizing enzyme. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, B. Clinical trials of angiotensin receptor blockers in heart failure: What do we know and what will we learn? Am. J. Hypertens. 2002, 15, 22S–27S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Agyei, D.; Udenigwe, C.C. Structural Basis of Bioactivity of Food Peptides in Promoting Metabolic Health. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 84, 145–181. [Google Scholar]
- Craik, D.J.; Fairlie, D.P.; Liras, S.; Price, D. The future of peptide-based drugs. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X.; Yan, Z.; Shao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Fu, C. Therapeutic peptides: Current applications and future directions. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manoharan, S. Is It Still Relevant to Discover New ACE Inhibitors from Natural Products? YES, but Only with Comprehensive Approaches to Address the Patients’ Real Problems: Chronic Dry Cough and Angioedema. Molecules 2023, 28, 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114532
Manoharan S. Is It Still Relevant to Discover New ACE Inhibitors from Natural Products? YES, but Only with Comprehensive Approaches to Address the Patients’ Real Problems: Chronic Dry Cough and Angioedema. Molecules. 2023; 28(11):4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114532
Chicago/Turabian StyleManoharan, Sivananthan. 2023. "Is It Still Relevant to Discover New ACE Inhibitors from Natural Products? YES, but Only with Comprehensive Approaches to Address the Patients’ Real Problems: Chronic Dry Cough and Angioedema" Molecules 28, no. 11: 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114532
APA StyleManoharan, S. (2023). Is It Still Relevant to Discover New ACE Inhibitors from Natural Products? YES, but Only with Comprehensive Approaches to Address the Patients’ Real Problems: Chronic Dry Cough and Angioedema. Molecules, 28(11), 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114532



