Preparation of a Series of Highly Efficient Porous Adsorbent PGMA-N Molecules and Its Application in the Co-Removal of Cu(II) and Sulfamethoxazole from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
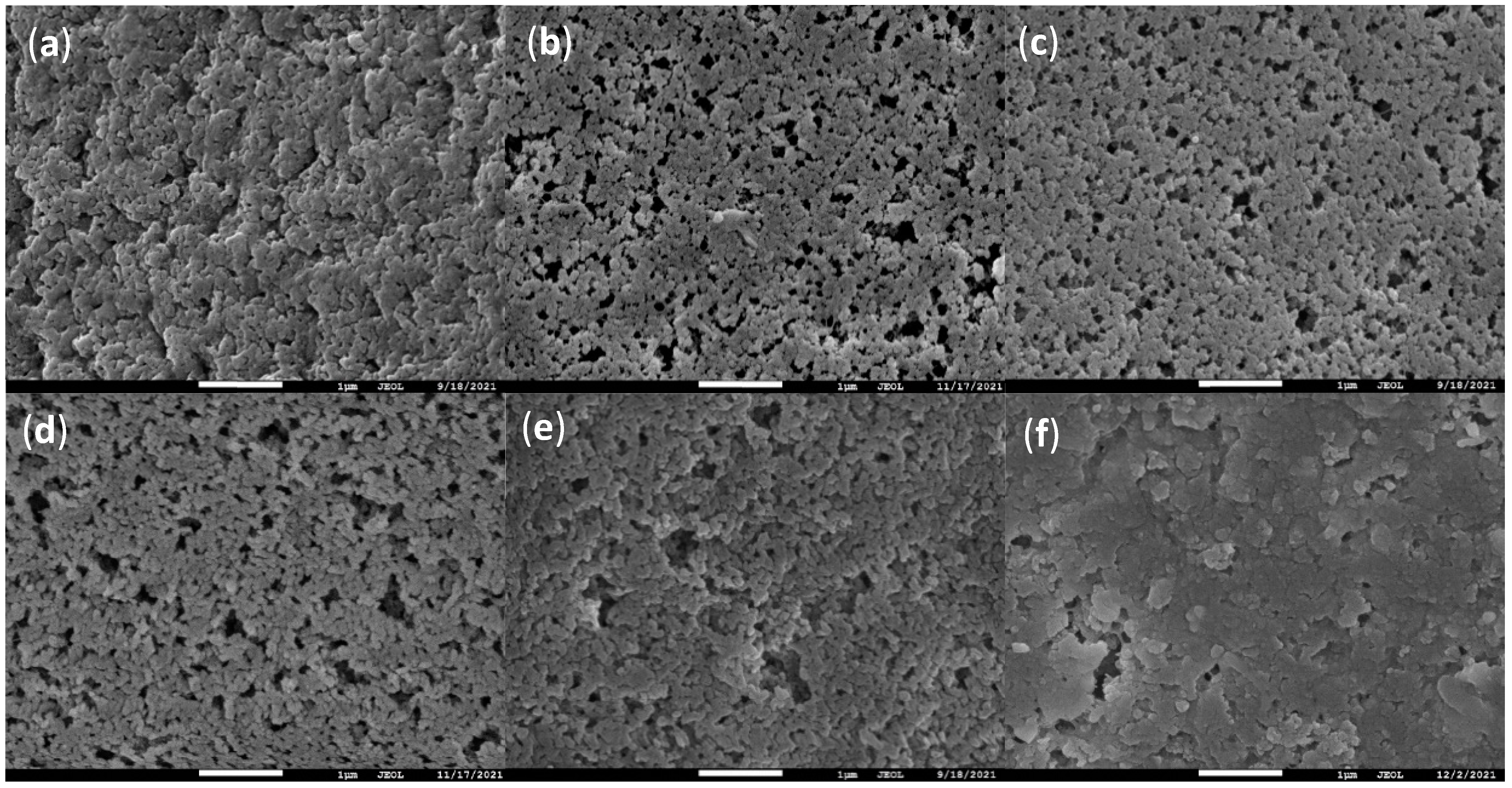
2.1. Characterizations
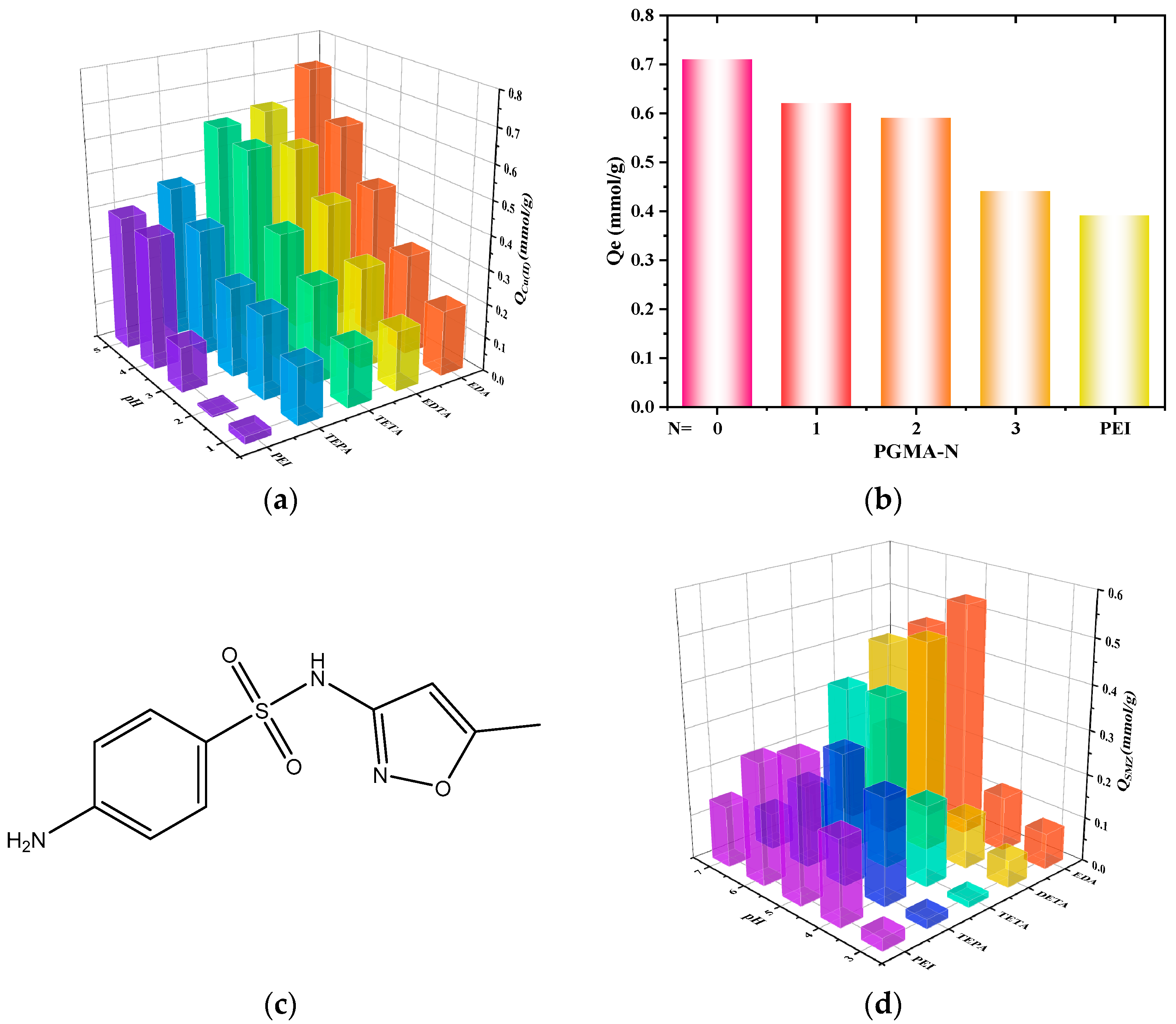
2.2. Single-Group Adsorption Behavior
2.3. Co-Adsorption Behavior of Cu(II) and SMZ Composite System
2.4. Cu(II) Adsorption Isotherms
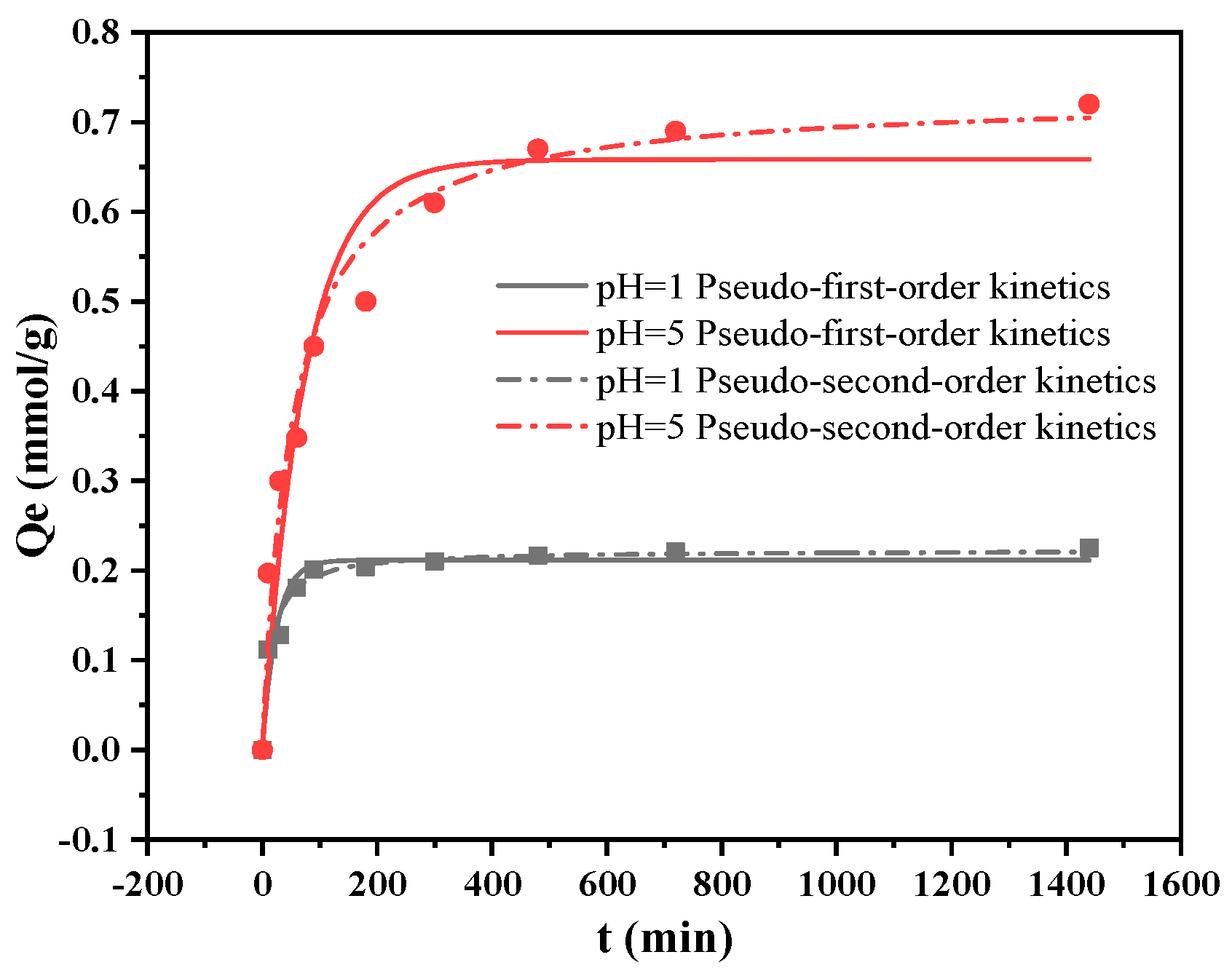
2.5. Cu(II) Adsorption Kinetics
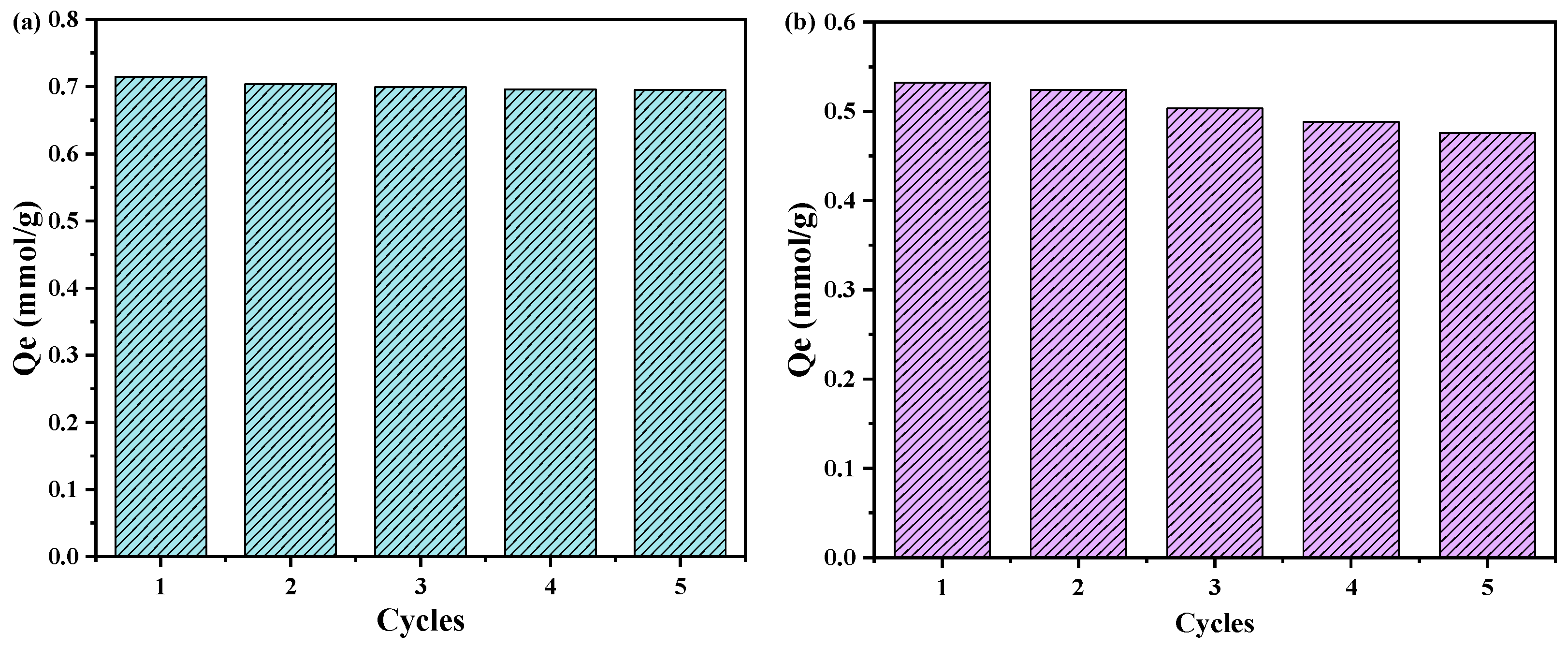
2.6. Adsorption Agent Recycling Performance
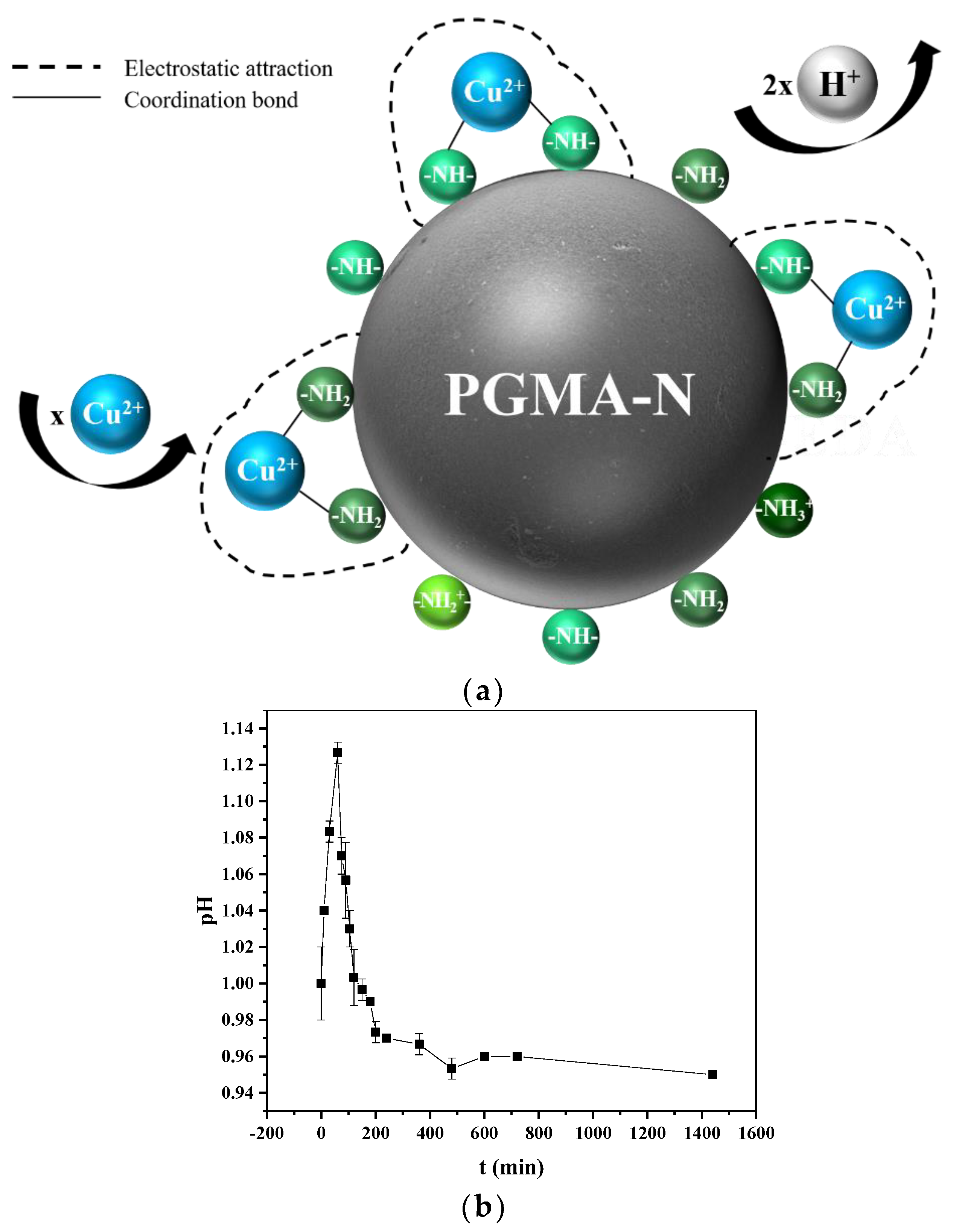
2.7. Adsorption Mechanism
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
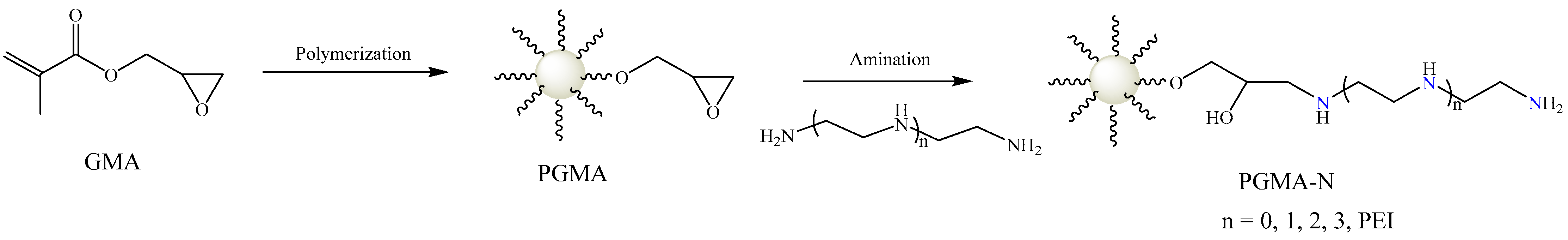
3.2. Preparation of PGMA-N Series Adsorbents
3.3. Characterizations of PGMA-N
3.4. Batch Adsorption
3.4.1. Influence of Solution pH
3.4.2. Isothermal Equilibrium Adsorption Behavior
3.4.3. Kinetic Adsorption Behavior
3.4.4. Influence of Co-Adsorption of Cu(II) and SMZ and Their Mutual Adsorption Effects
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Zhao, K.; Wang, Q.; Qian, S.; Li, F. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of antibiotics and heavy metals in the Yitong River basin and ecological risk assessment. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Xu, Z.; Fan, L. Response of heavy metal and antibiotic resistance genes and related microorganisms to different heavy metals in activated sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, C.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.G.J. Co-occurrence of resistance genes to antibiotics, biocides and metals reveals novel insights into their co-selection potential. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Das, K.R.; Naik, M.M. Co-selection of multi-antibiotic resistance in bacterial pathogens in metal and microplastic contaminated environments: An emerging health threat. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danner, M.-C.; Robertson, A.; Behrends, V.; Reiss, J. Antibiotic pollution in surface fresh waters: Occurrence and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 664, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Fu, Y.-H.; Sheng, H.-J.; Topp, E.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Tiedje, J.M. Antibiotic resistance in the soil ecosystem: A One Health perspective. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2021, 20, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainab, S.M.; Junaid, M.; Xu, N.; Malik, R.N. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistant genes (ARGs) in groundwater: A global review on dissemination, sources, interactions, environmental and human health risks. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsène, M.M.J.; Davares, A.K.L.; Viktorovna, P.I.; Andreevna, S.L.; Sarra, S.; Khelifi, I.; Sergueïevna, D.M. The public health issue of antibiotic residues in food and feed: Causes, consequences, and potential solutions. Vet. World 2022, 15, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothwal, R.; Shashidhar, T. Air, Water, Antibiotic pollution in the environment: A review. Clean 2015, 43, 479–489. [Google Scholar]
- Pruden, A.; Larsson, D.J.; Amézquita, A.; Collignon, P.; Brandt, K.K.; Graham, D.W.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Suzuki, S.; Silley, P.; Snape, J.R.; et al. Management options for reducing the release of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes to the environment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Yan, X.-T.; Zhai, Y.-Q.; Guo, Z.; Li, N.; Ying, G.-G. Antibiotic pollution in lakes in China: Emission estimation and fate modeling using a temperature-dependent multimedia model. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taoufik, N.; Boumya, W.; Janani, F.Z.; Elhalil, A.; Mahjoubi, F.Z.; Barka, N. Removal of emerging pharmaceutical pollutants: A systematic mapping study review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hena, S.; Gutierrez, L.; Croue, J.P. Removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) from wastewater using microalgae: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 124041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.C.; Hugie, C.N.; Kile, M.L.; Navab-Daneshmand, T. Association between heavy metals and antibiotic-resistant human pathogens in environmental reservoirs: A review. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, A.W.; Power, A.; Hansen, M.; Brandt, K.; Piliposian, G.; Appleby, P.; O’neill, P.; Jones, R.; Sierocinski, P.; Koskella, B.; et al. Heavy metal pollution and co-selection for antibiotic resistance: A microbial palaeontology approach. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, P.P.; Hurd, C.L.; Sander, S.G.; Armstrong, E.; Fernández, P.A.; Suhrhoff, T.J.; Roleda, M.Y. Copper pollution exacerbates the effects of ocean acidification and warming on kelp microscopic early life stages. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Negrete-Bolagay, D.; Figueroa, F.; Zamora-Ledezma, E.; Ni, M.; Alexis, F.; Guerrero, V.H. Heavy metal water pollution: A fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefnawy, A.; El-Khaiat, H.M. The importance of copper and the effects of its deficiency and toxicity in animal health. Int. J. Livest. Res. 2015, 5, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracioso, L.H.; Peña-Bahamonde, J.; Karolski, B.; Borrego, B.B.; Perpetuo, E.A.; do Nascimento, C.A.O.; Hashiguchi, H.; Juliano, M.A.; Robles Hernandez, F.C.; Rodrigues, D.F. Copper mining bacteria: Converting toxic copper ions into a stable single-atom copper. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, V.; Kaler, S.G. Role of copper in human neurological disorders. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 855S–858S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, H.; Peng, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, C. The molecular mechanisms of copper metabolism and its roles in human diseases. Pflug. Arch. 2020, 472, 1415–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grass, G.; Rensing, C.; Solioz, M. Metallic copper as an antimicrobial surface. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, M.; Singh, G.; Jadeja, R. Physical and Chemical Methods for Heavy Metal Removal. In Pollutants and Water Management: Resources, Strategies and Scarcity; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 377–397. [Google Scholar]
- Renu; Agarwal, M.; Singh, K. Methodologies for removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: An overview. Interdiscip. Environ. Rev. 2017, 18, 124–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, N.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. NPJ Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Seth, A.; Singh, A.K.; Rajput, M.S.; Sikandar, M. Remediation strategies for heavy metals contaminated ecosystem: A review. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2021, 12, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeeswara Reddy, B.; Pala, S.L.; Biftu, W.K.; Suneetha, M.; Ravindhranath, K. Effective removal of Cu2+ ions from polluted water using new bio-adsorbents. Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 16, 566–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wołowiec, M.; Komorowska-Kaufman, M.; Pruss, A.; Rzepa, G.; Bajda, T. Removal of heavy metals and metalloids from water using drinking water treatment residuals as adsorbents: A review. Minerals 2019, 9, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Mustaqeem, M.; Khaled, M. Water treatment technologies in removing heavy metal ions from wastewater: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, J.; Gan, Z.; Yang, P. Occurrence and fate of antibiotics and heavy metals in sewage treatment plants and risk assessment of reclaimed water in Chengdu, China. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdan, A.M.; Abd-El-Mageed, H.; Ghanem, N. Biological treatment of hazardous heavy metals by Streptomyces rochei ANH for sustainable water management in agriculture. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Mendoza-Castillo, D.I.; Reynel-Ávila, H.E. Adsorption Processes for Water Treatment and Purification; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 256. [Google Scholar]
- Eckenfelder, W.W. Industrial Water Pollution Control; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Rashed, M.N. Adsorption technique for the removal of organic pollutants from water and wastewater. In Organic Pollutants-Monitoring, Risk and Treatment; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013; Volume 7, pp. 167–194. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Wu, J.; Liang, H.; Yuan, Q. Preparation of poly (glycidyl methacrylate)(PGMA) and amine modified PGMA adsorbents for purification of glucosinolates from cruciferous plants. Molecules 2020, 25, 3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Yang, D.; Wang, N.; Sun, S.; Nie, J.; Ma, G. Polymers, Polyethylenimine grafted chitosan nanofiber membrane as adsorbent for selective elimination of anionic dyes. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, F.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, A.; He, L.; Xing, B. technology, High adsorption of sulfamethoxazole by an amine-modified polystyrene–divinylbenzene resin and its mechanistic insight. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10015–10023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Ling, C.; Yuan, R.; Liu, F.; Li, A. Bridging effects behind the coadsorption of copper and sulfamethoxazole by a polyamine-modified resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Liu, F.-Q.; Xu, C.; Chen, T.-P.; Li, A.-M. An integrative technique based on synergistic coremoval and sequential recovery of copper and tetracycline with dual-functional chelating resin: Roles of amine and carboxyl groups. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 11808–11817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.; Li, C.; Yu, J.; Xu, Q.; Wei, S.; Tian, Z.; Yang, Z.; Yang, W.; Shen, J. Insight into adsorption of combined antibiotic-heavy metal contaminants on graphene oxide in water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 236, 116278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, F.-Q.; Gao, J.; Li, L.-J.; Bai, Z.-P.; Ling, C.; Zhu, C.-Q.; Chen, D.; Li, A.-M. Enhancement mechanisms behind exclusive removal and selective recovery of copper from salt solutions with an aminothiazole-functionalized adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Bai, R.; San Ly, Q. Selective removal of copper and lead ions by diethylenetriamine-functionalized adsorbent: Behaviors and mechanisms. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

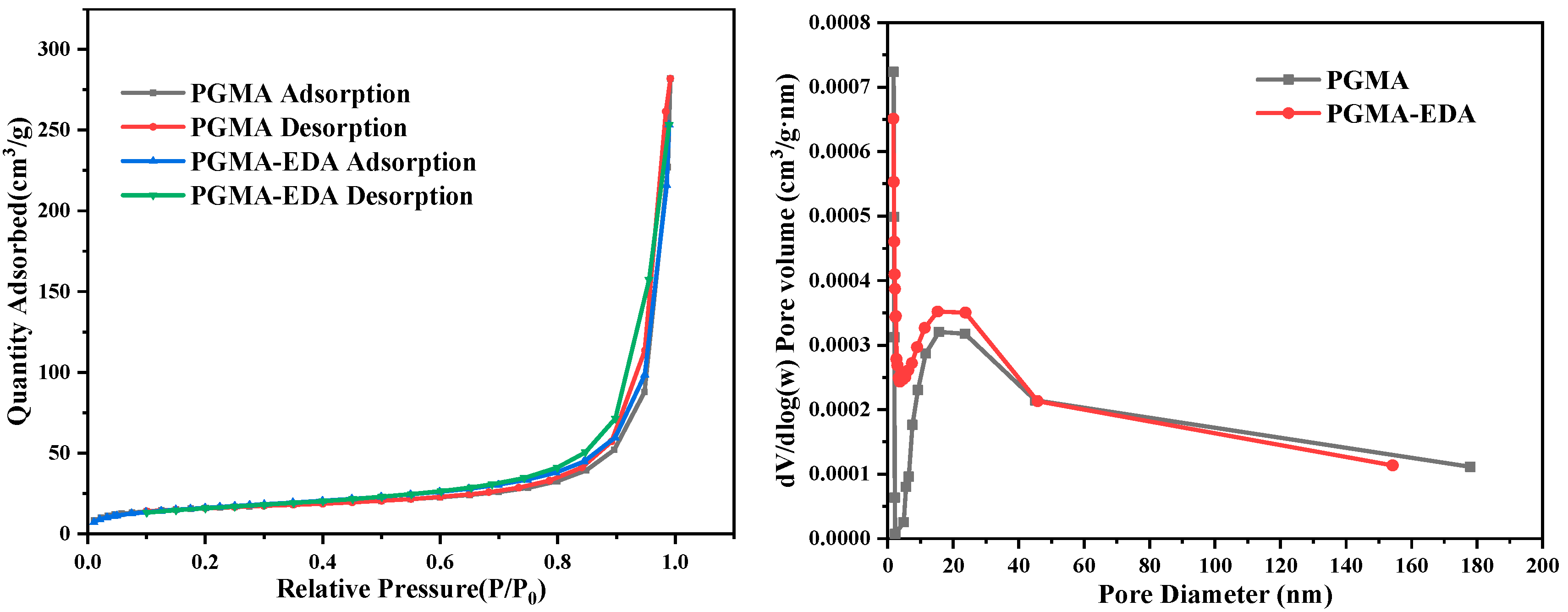


| Adsorption Material Type | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| PGMA | 60.284 | 34.11 |
| PGMA-EDA | 59.4897 | 24.98 |
| Adsorption Material Type | C (%) | H (%) | N (%) | S (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PGMA | 60.284 | 7.226 | 0.065 | 0.039 |
| PGMA-EDA | 36.175 | 7.969 | 4.006 | 0.052 |
| Ions | pH | Langmuir Equation | Freundlich Equation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm/(mmol·g−1) | b | RL2 | Kf | n | RF2 | ||
| Cu(II) | 5 | 0.794 | 0.33 | 0.988 | 0.573 | 4.762 | 0.859 |
| 1 | 0.244 | 1.837 | 0.990 | 0.155 | 3.717 | 0.876 | |
| Ions | pH | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetics | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k2/ (g·mmol−1·min−1) | Qe (mmol·g−1) | r2 | k1/min−1 | Qe/ (mmol·g−1) | r2 | ||
| Cu(II) | 5 | 0.0264 | 0.73 | 0.971 | 0.0135 | 0.658 | 0.928 |
| 1 | 0.324 | 0.223 | 0.977 | 0.0411 | 0.212 | 0.941 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, T.; Zhu, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, D. Preparation of a Series of Highly Efficient Porous Adsorbent PGMA-N Molecules and Its Application in the Co-Removal of Cu(II) and Sulfamethoxazole from Water. Molecules 2023, 28, 4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114420
Sun S, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Sun T, Zhu L, Shi Z, Zhang D. Preparation of a Series of Highly Efficient Porous Adsorbent PGMA-N Molecules and Its Application in the Co-Removal of Cu(II) and Sulfamethoxazole from Water. Molecules. 2023; 28(11):4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114420
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Shishu, Xiaopeng Zhang, Yan Zhang, Tianyi Sun, Linhua Zhu, Zaifeng Shi, and Dashuai Zhang. 2023. "Preparation of a Series of Highly Efficient Porous Adsorbent PGMA-N Molecules and Its Application in the Co-Removal of Cu(II) and Sulfamethoxazole from Water" Molecules 28, no. 11: 4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114420
APA StyleSun, S., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Sun, T., Zhu, L., Shi, Z., & Zhang, D. (2023). Preparation of a Series of Highly Efficient Porous Adsorbent PGMA-N Molecules and Its Application in the Co-Removal of Cu(II) and Sulfamethoxazole from Water. Molecules, 28(11), 4420. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28114420






