Biosynthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Tribulus terrestris Seeds: Revealed Promising Antidiabetic Potentials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
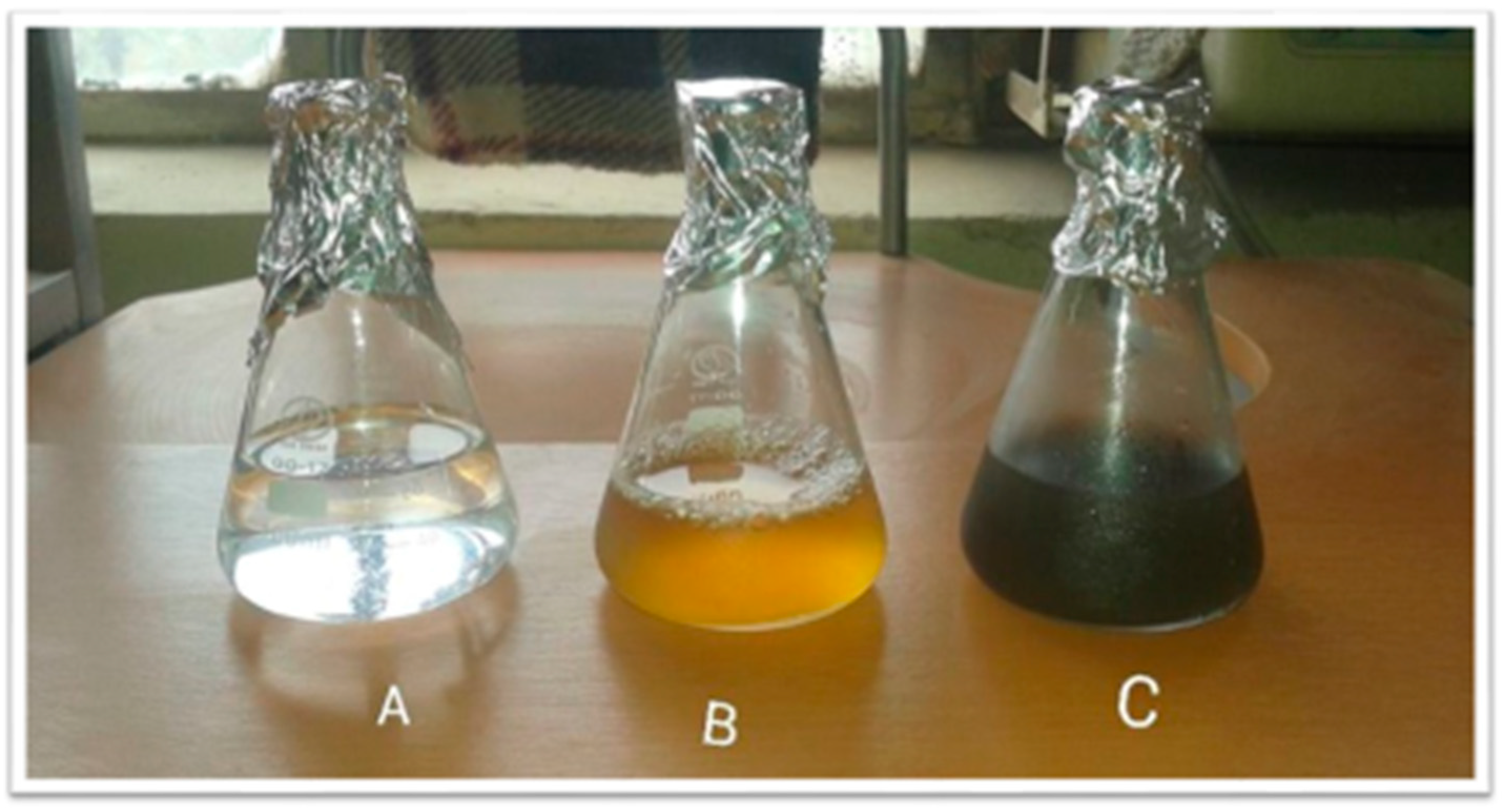
2.1. Synthesizing of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)
2.2. Characterization of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles
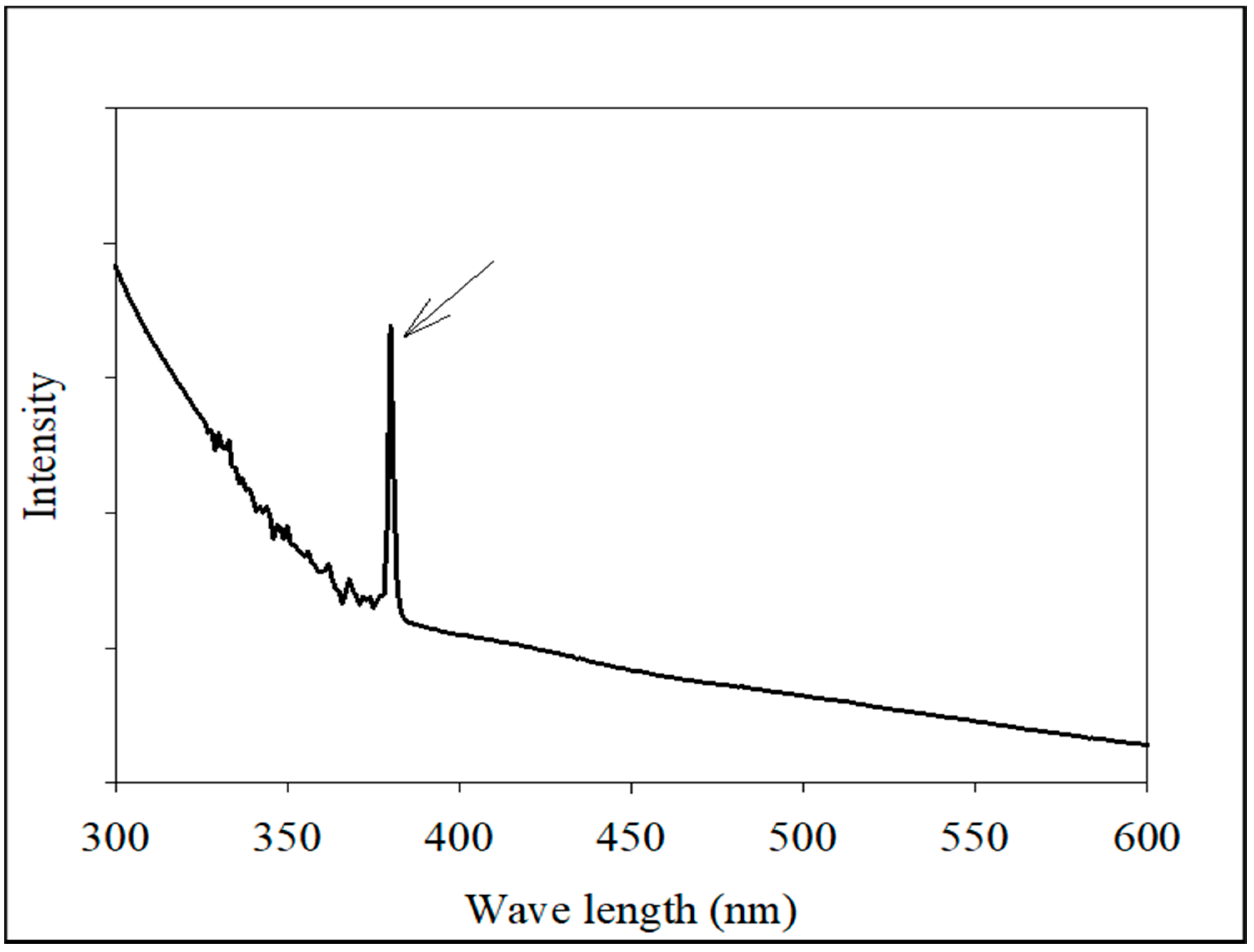
2.2.1. Analysis of the UV-Visible Spectrum
2.2.2. Analysis of Functional Groups Using FTIR Spectroscopy
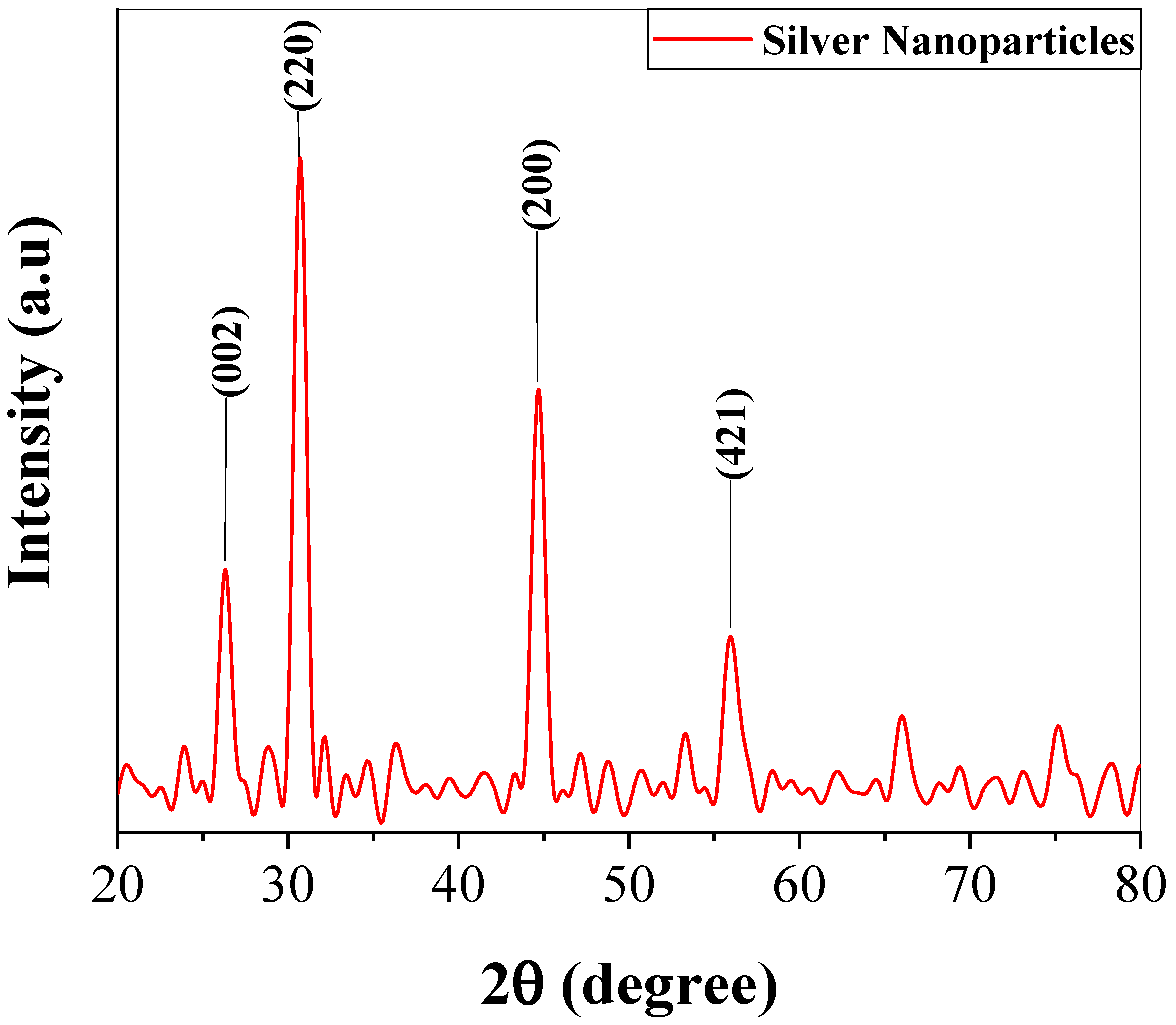
2.2.3. XRD Analysis
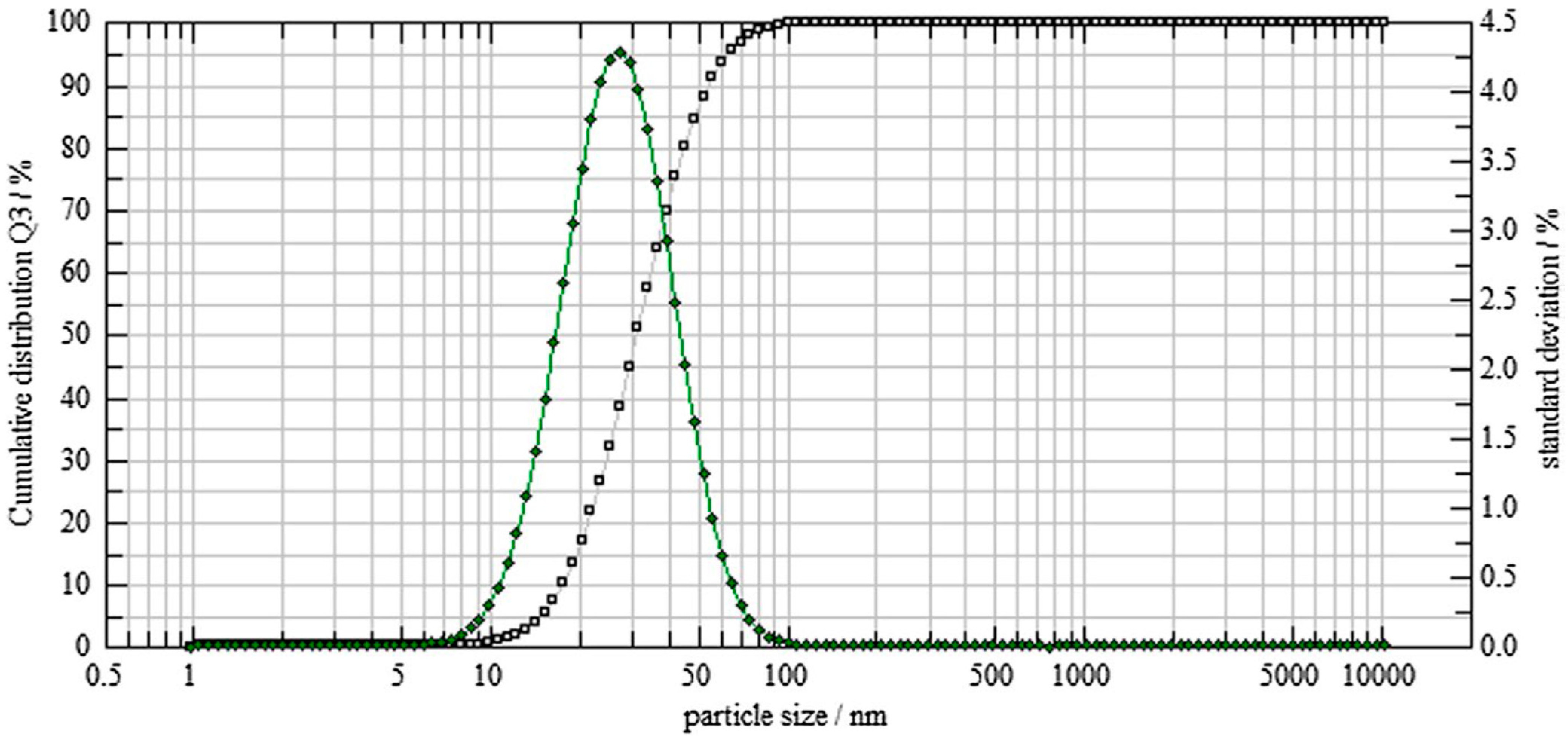
2.2.4. SEM Morphological Analysis of Biosynthesized TT-AgNPs
2.3. In Vitro Anti-Diabetic Assays
2.3.1. Effects of TT-AgNPs on Uptake of Glucose by Yeast Cells in a 5 mM Glucose Solution
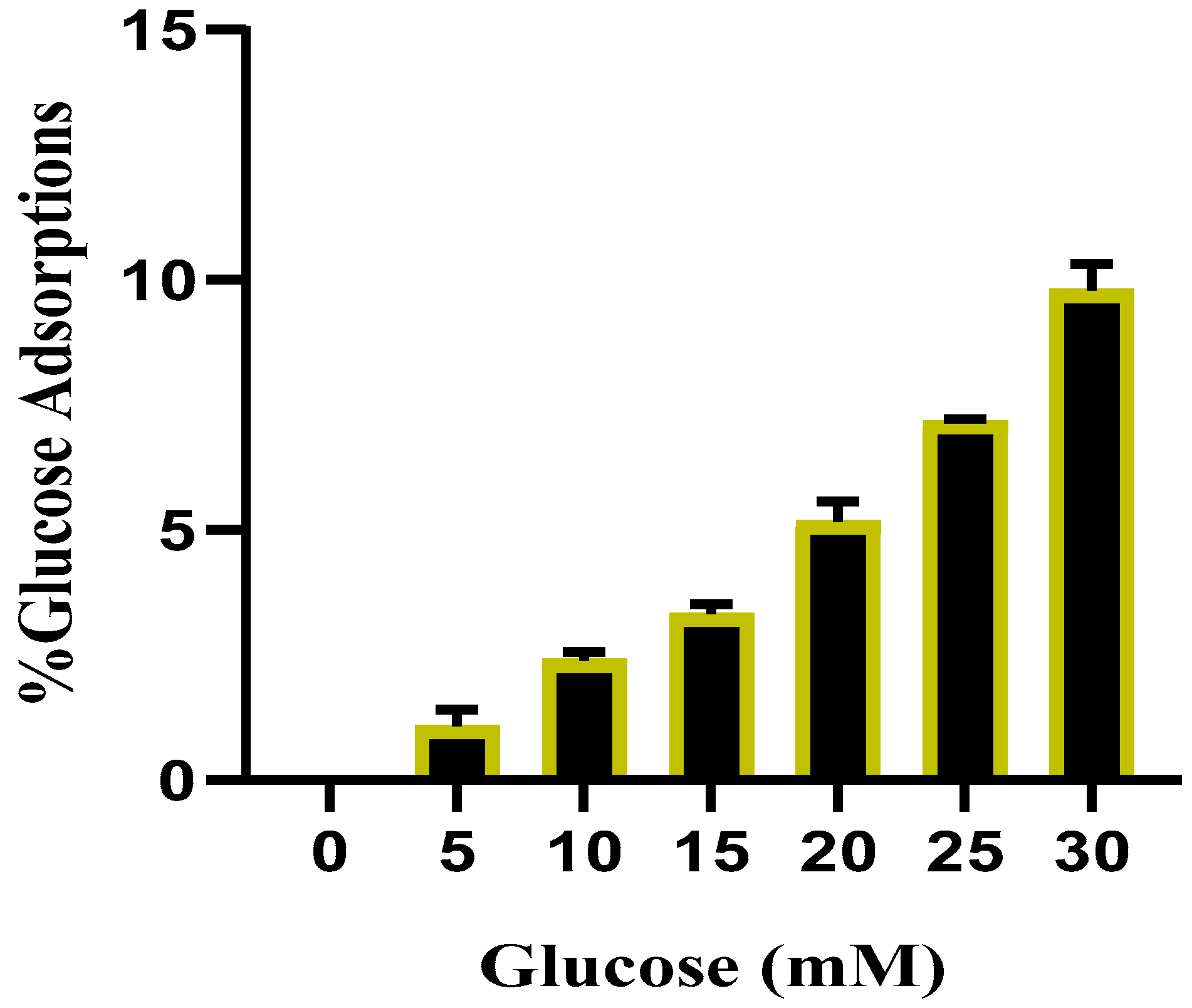
2.3.2. Effects of TT-AgNPs on Glucose Adsorption
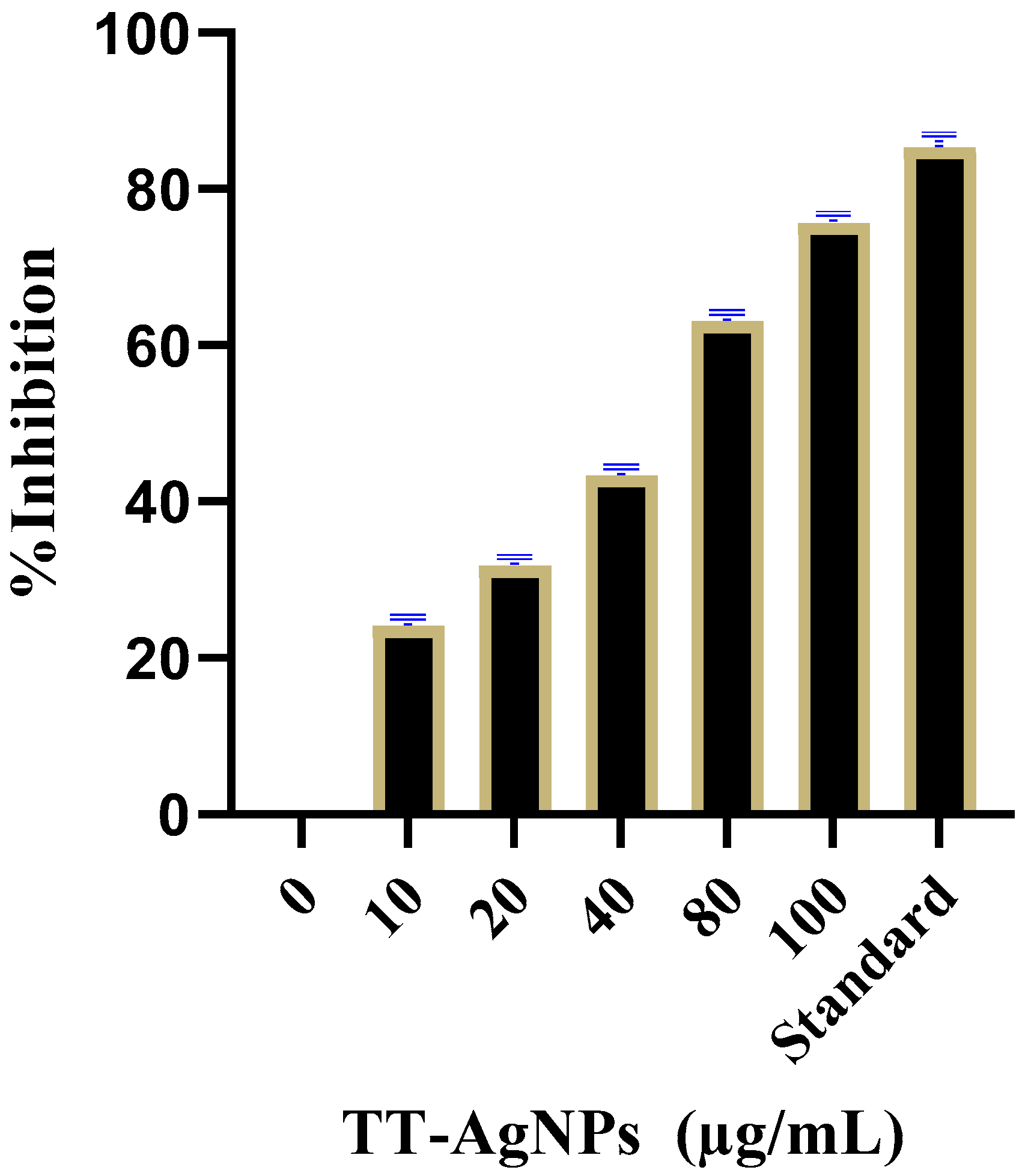
2.3.3. Effects of TT-AgNPs on Inhibition of α-Amylase Inhibition
2.4. In Vivo Antidiabetic Assay Results
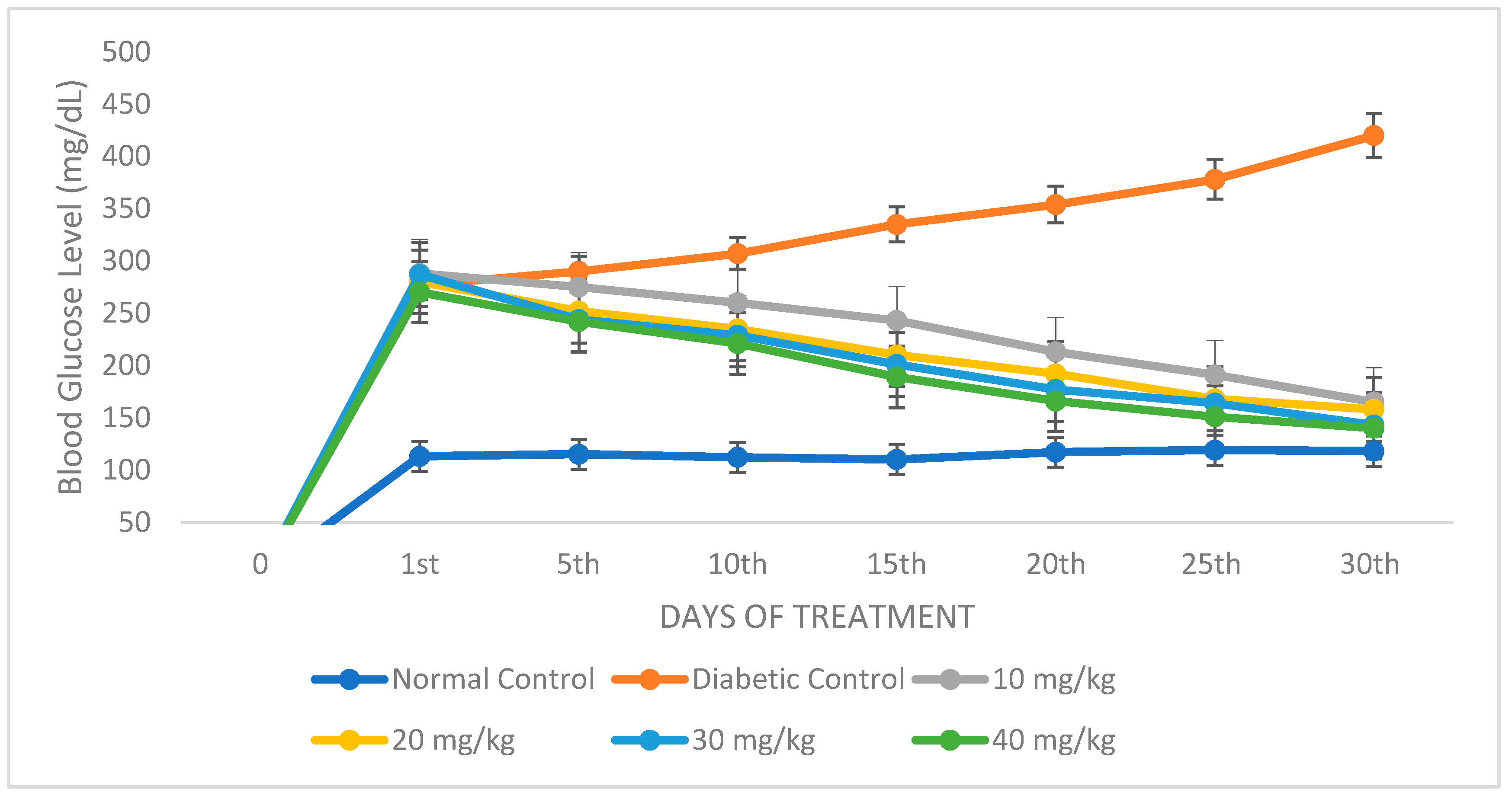
2.4.1. Assessment of Blood Glucose Level and Body Weight of Experimental Animals Administered with TT-AgNPs
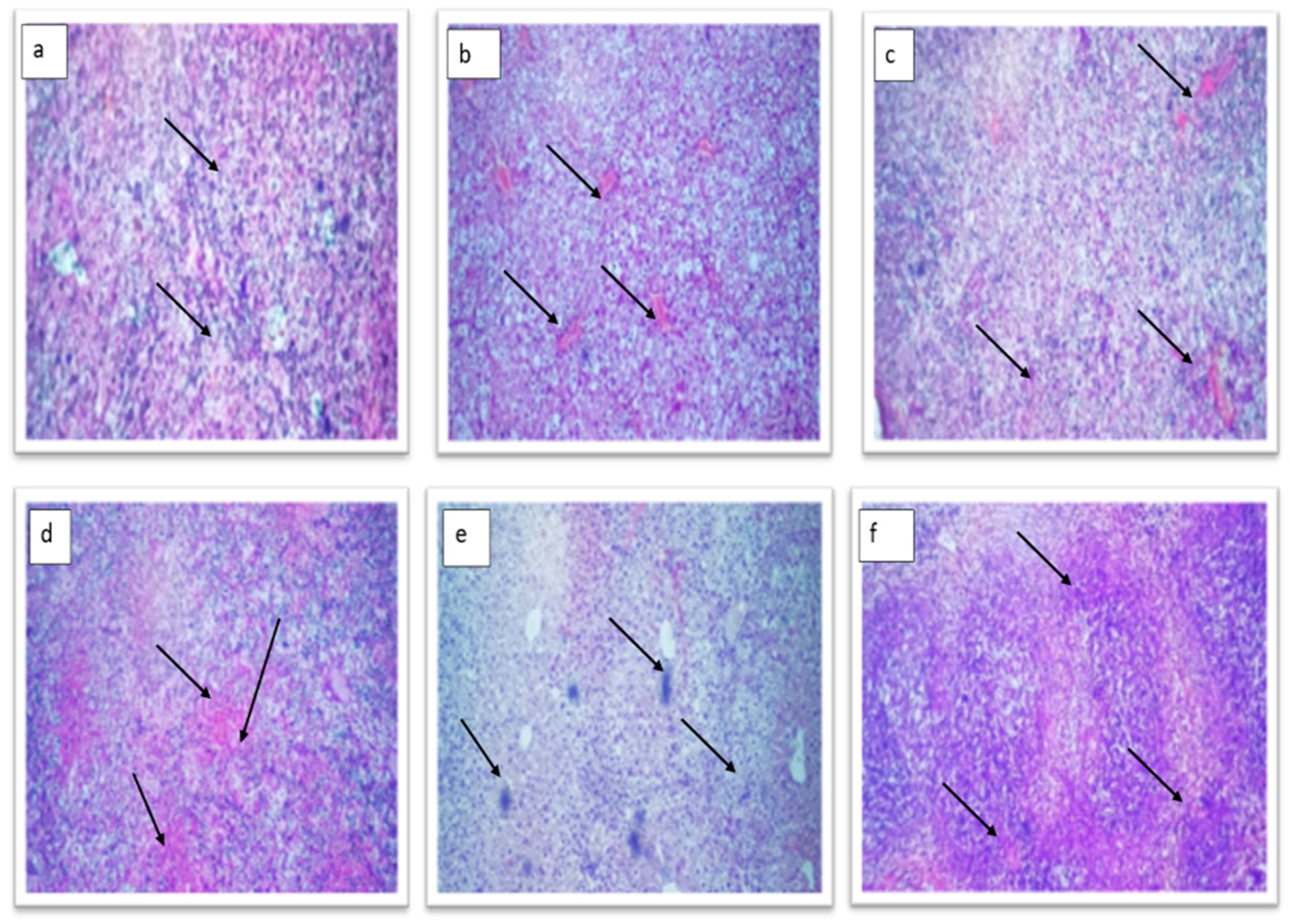
2.4.2. Histopathological Examination of the Liver
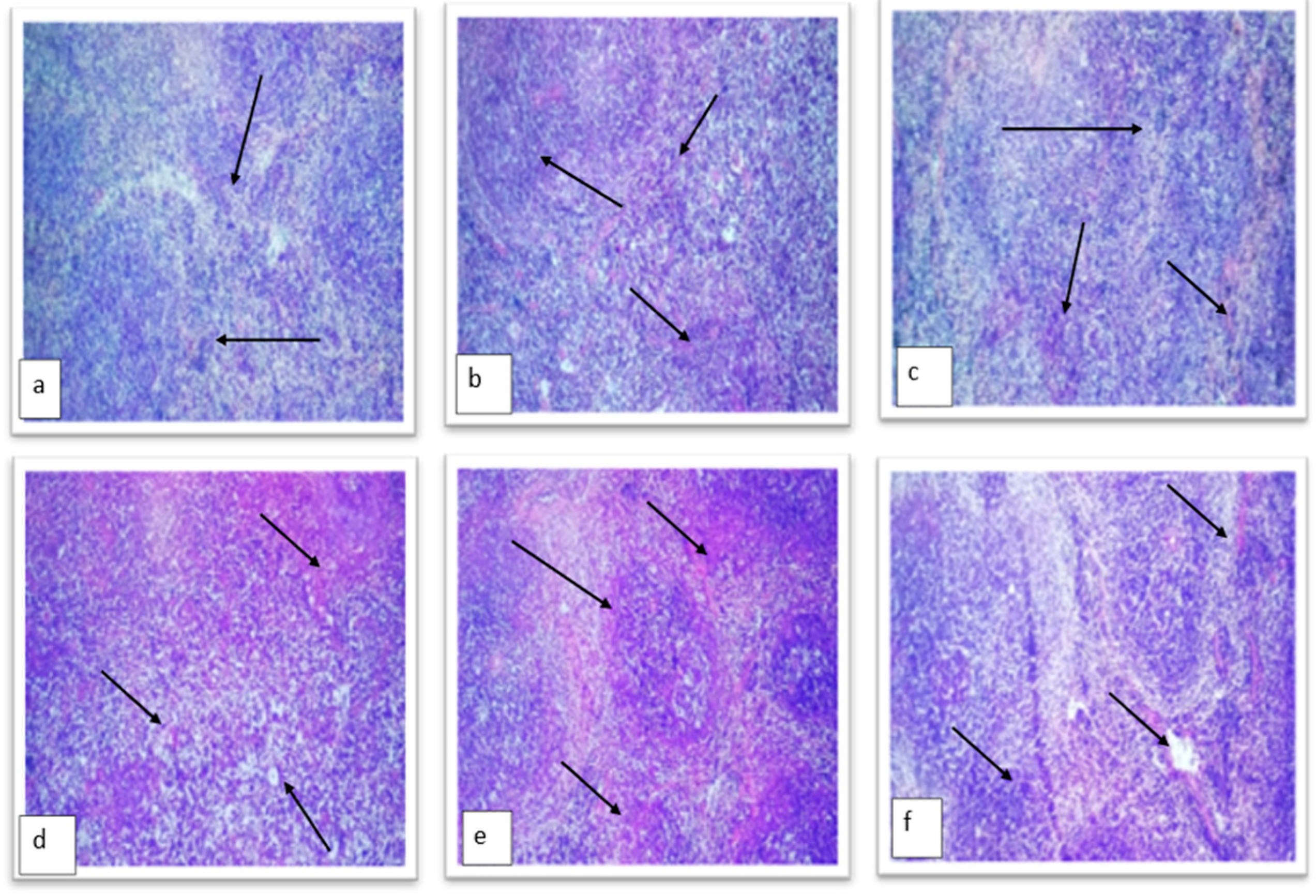
2.4.3. Histopathological Examination of Diabetic Mice Pancreas
3. Discussion
4. Methods and Materials
4.1. Extract Preparation of TT Seed
4.2. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)
4.3. Characterization of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles
4.3.1. UV-Visible Spectral Analysis
4.3.2. FTIR Spectral Analysis
4.3.3. X-ray Diffraction Technique
4.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX) Analysis
4.4. Anti-Diabetic Assays (In Vitro)
4.4.1. Uptake of Glucose by Yeast Cell Assay
4.4.2. Glucose Adsorption Assay
4.4.3. α-Amylase Inhibition Assay
4.5. In Vivo Anti-Diabetic Activity
4.5.1. Experimental Animals and Conditions
4.5.2. Inducing Diabetes in Mice
4.5.3. Experimental Design
4.5.4. Assessment of Body Weight and Blood Sugar Level
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saratale, R.G.; Shin, H.S.; Kumar, G.; Benelli, G.; Kim, D.-S.; Saratale, G.D. Exploiting antidiabetic activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Punica granatum leaves and anticancer potential against human liver cancer cells (HepG2). Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabapathi, N.; Ramalingam, S.; Aruljothi, K.N.; Lee, J.; Barathi, S. Characterization and Therapeutic Applications of Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Cassia auriculate Flower Extract. Plants 2023, 12, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ramamneh, E.A.D.M.; Ghrair, A.M.; Shakya, A.K.; Alsharafa, K.Y.; Al-Ismail, K.; Al-Qaraleh, S.Y.; Mojski, J.; Naik, R.R. Efficacy of Sterculia diversifolia leaf extracts: Volatile compounds, antioxidant and anti-Inflammatory activity, and green synthesis of potential antibacterial silver nanoparticles. Plants 2022, 11, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, G.; Shin, H.-S.; Patra, J.K. Comparative Bio-Potential Effects of Fresh and Boiled Mountain Vegetable (Fern) Extract Mediated Silver Nanoparticles. Plants 2022, 11, 3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiti, P.; Sarkar, S.; Singha, T.; Dutta Roy, S.; Mahato, M.; Karmakar, P.; Paul, S.; Paul, P.K. Enhancement of Fluo-Rescence Mediated by Silver Nanoparticles: Implications for Cell Imaging. Langmuir 2023, 39, 6713–6729. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, R.M.; Morawski, F.M.; Pessanha, E.C.; de Lima, S.L.S.; da Costa, D.S.; Ribeiro, G.A.C.; Val, J.; Mouta, R.; Tanaka, A.A.; Liu, L.; et al. Facile Gram-Scale Synthesis of NiO Nanoflowers for Highly Selective and Sensitive Electrocatalytic Detection of Hydrazine. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 11978–11986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahy, K.M.; Eiken, M.K.; Baumgartner, K.V.; Leung, K.Q.; Anderson, S.E.; Berggren, E.; Bouzos, E.; Schmitt, L.R.; Asuri, P.; Wheeler, K.E. Silver Nanoparticle Surface Chemistry Determines Interactions with Human Serum Albumin and Cytotoxic Responses in Human Liver Cells. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 3310–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouzahim, M.; Eddarai, E.; Eladaoui, S.; Guenbour, A.; Bellaouchou, A.; Zarrouk, A.; Boussen, R. Effect of Kaolin clay and Ficus carica mediated silver nanoparticles on chitosan food packaging film for fresh apple slice preservation. Food Chem. 2023, 410, 135470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, F.; Al-Homaidan, A.A.; Al-Sabri, A.; Almansob, A.; AlNAdhari, S. Anti-oxidant, anti-fungal and cytotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles synthesized using marine fungus Cladosporium halotolerans. Appl. Nanosci. 2023, 13, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahuman, H.B.H.; Dhandapani, R.; Narayanan, S.; Palanivel, V.; Paramasivam, R.; Subbarayalu, R.; Thangavelu, S.; Muthupandian, S. Medicinal plants mediated the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 16, 115–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhu, L.; Bai, Y.; Li, F.; Yu, X. Green one-step synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biosafety and anti-bacterial properties. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2022, 15, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Xu, Y. Sunlight-Induced Synthesis of Non-Target Biosafety Silver Nanoparticles for the Control of Rice Bacterial Diseases. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thandapani, G.; Arthi, K.; Pazhanisamy, P.; John, J.J.; Vinothini, C.; Rekha, V.; Santhanalakshmi, K.; Sekar, V. Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Spinacia oleracea leaf extract and evaluation of biological applications: Antioxidant, antibacterial, larvicidal and biosafety assay. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niloy, M.S.; Hossain, M.; Takikawa, M.; Shakil, S.; Polash, S.A.; Mahmud, K.M.; Uddin, F.; Alam, M.; Shubhra, R.D.; Shawan, M.M.A.K.; et al. Synthesis of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Using Caesalpinia digyna and Investigation of Their Antimicrobial Activity and In Vivo Biocompatibility. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 7722–7733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.R.; Prakash, J.; Shekhar, H.; Dwivedy, A.K.; Patel, V.K.; Tiwari, S.; Vishwakarma, N.K. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Eranthemum Pulchellum (Blue Sage) aqueous leaves extract: Characterization, evaluation of antifungal and antioxidant properties. Biomed. Biotechnol. Res. J. (BBRJ) 2021, 5, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lala, M. Characterization of Firmiana colorata (Roxb.) leaf extract and its silver nanoparticles reveal their antioxidative, anti-microbial, and anti-inflammatory properties. Int. Nano Lett. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S.; Nasir, J.A.; Sarwar, A.; Nasr, N.; Javed, A.; Majeed, R.; Salam, M.A.; Billah, B. Prevalence of diabetes and pre-diabetes in Bangladesh: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e036086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, B.; Ata, A.; Anil Kumar, N.V.; Sharopov, F.; Ramírez-Alarcón, K.; Ruiz-Ortega, A.; Abdulmajid Ayatollahi, S.; Valere Tsouh Fokou, P.; Kobarfard, F.; Amiruddin Zakaria, Z.; et al. Antidiabetic potential of medicinal plants and their active components. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, P.; Chen, L.; Mei, Z. Antidiabetic activities of entagenic acid in type 2 diabetic db/db mice and L6 myotubes via AMPK/GLUT4 pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 211, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhinge, S.; Bhutkar, M.A.; Randive, D.; Wadkar, G.H.; Hasabe, T.S. In vitro hypoglycemic effects of unripe and ripe fruits of Musa sapientum. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 53, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautela, A.; Rani, J.; Debnath (Das), M. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Tectona grandis seeds extract: Charac-terization and mechanism of antimicrobial action on different microorganisms. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications, and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambale, E.K.; Nkanga, C.I.; Mutonkole, B.-P.I.; Bapolisi, A.M.; Tassa, D.O.; Liesse, J.-M.I.; Krause, R.W.; Memvanga, P.B. Green synthesis of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extracts from three Congolese plant species (Brillantaisia patula, Crossopteryx febrifuga and Senna siamea). Heliyon 2020, 6, e04493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Husen, A.; Rao, R.A.K. A review on biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biocidal properties. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veera, S.; Chirumamilla, P.; Dharavath, S.B.; Maduru, N.; Taduri, S. Facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Corallocarpus epigaeus leaf extract: Structural, photoluminescence and antibacterial properties. Chem. Data Collect. 2023, 45, 101032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.J.; Custódio, L.; Lopes, A.; Oliveira, M.; Neng, N.R.; Nogueira, J.M.F.; Martins, A.; Rauter, A.P.; Varela, J.; Barreira, L. Unlocking the in vitro anti-inflammatory and antidiabetic potential of Polygonum maritimum. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 1348–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, P.; Satapathy, M.; Mukhopahayay, A.; Das, P. Leaf extract mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from widely available Indian plants: Synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial property and toxicity analysis. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2014, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, K.D.; Annamalai, S.K. Chrysopogon zizanioides aqueous extract mediated synthesis characterization of crystalline silver and gold nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2375–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elumalai, D.; Hemavathi, M.; Deepaa, C.V.; Kaleena, P.K. Evaluation of phytosynthesised silver nanoparticles from leaf extracts of Leucas aspera and Hyptis suaveolens and their larvicidal activity against malaria, dengue and filariasis vectors. Parasite Epidemiol. Control. 2017, 2, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, A.; Bhaskar, S.; Reddy, N.; Ramamurthy, S.S. Cellphone-Aided Attomolar Zinc Ion Detection Using Silkworm Protein-Based Nanointerface Engineering in a Plasmon-Coupled Dequenched Emission Platform. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 14959–14974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffar, S.S.; Saallah, S.; Misson, M.; Siddiquee, S.; Roslan, J.; Lenggoro, W. Green Synthesis of Flower-Like Carragee-nan-Silver Nanoparticles and Elucidation of Its Physicochemical and Antibacterial Properties. Molecules 2023, 28, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, Z.; Ali, M.N.; Qureshi, Z.; Mohsin, M. In vitro investigation and evaluation of novel drug based on pol-yherbal extract against type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 7357482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, K.; Aiswarya, D.; Sureshkumar, P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticle using Tephrosia tinctoria and its antidiabetic activity. Mater. Lett. 2015, 138, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azantsa, B.G.K.; Takuissu, G.R.; Tcheumeni, E.J.; Martin, F.; Edwige, R.K.; Judith, L.N. Antihyperglycemic mechanisms of Allium sativum, Citrus sinensis and Persea americana Extracts: Effects on inhibition of digestive enzymes, glucose adsorption and absorption on yeast cells and psoas muscles. Diabetes Res. Open J. 2019, 5, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Bhutkar, M.; Bhinge, S.; Randive, D.; Wadkar, G.; Todkar, S. Studies on glucose adsorption capacity of some indigenous plants. Glob. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singarapriyavardhanan, S.T.; Shanmugam, P.S.T.; Narayana, S.K.K.; Ammari, A.A.; Amran, R.A.; Alhimaidi, A.R. Mimosa pudica alleviates streptozotocin-induced diabetes, glycemic stress and glutathione depletion in Wistar Albino Rats. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2022, 34, 102037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpagam, S.; Amudha, P. Anti-Diabetic Activity of Salacia Chinensis Stem Extract. 2019. Available online: https://wjpr.s3.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com/article_issue/1556883273.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Prabhu, S.; Vinodhini, S.; Elanchezhiyan, C.; Rajeswari, D. Retracted: Evaluation of antidiabetic activity of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles using Pouteria sapota in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Diabetes 2018, 10, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, H.; Ullah, I.; Rehman, G.; Hamayun, M.; Ali, S.; Rahman, A.; Lee, I.-J. Magnesium and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Datura alba Improve Cognitive Impairment and Blood Brain Barrier Leakage. Molecules 2022, 27, 4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, V.P. Mechanism of glucose transport across the yeast cell membrane. J. Bacteriol. 1962, 84, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.; Kwok, K.-C.; Li, Y.; Fu, L. In Vitro Study of Possible Role of Dietary Fiber in Lowering Postprandial Serum Glucose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 1026–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shai, L.; Masoko, P.; Mokgotho, M.; Magano, S.; Mogale, A.; Boaduo, N.; Eloff, J. Yeast alpha glucosidase inhibitory and antioxidant activities of six medicinal plants collected in Phalaborwa, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2010, 76, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Wave Number (cm−1) | Functional Group |
|---|---|
| 3422 | O-H stretching |
| 2921 | C-H stretching of aromatic compounds |
| 2856 | C-H stretching of aromatic compounds |
| 1631 | C-N and C-C stretching indicate the presence of proteins |
| 1450 | N-H stretch showing amide linkage of proteins |
| 596 | C-X stretch indicated the presence of an alkyl halide |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, A.; Rehman, G.; Shah, N.; Hamayun, M.; Ali, S.; Ali, A.; Shah, S.k.; Khan, W.; Shah, M.I.A.; Alrefaei, A.F. Biosynthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Tribulus terrestris Seeds: Revealed Promising Antidiabetic Potentials. Molecules 2023, 28, 4203. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104203
Rahman A, Rehman G, Shah N, Hamayun M, Ali S, Ali A, Shah Sk, Khan W, Shah MIA, Alrefaei AF. Biosynthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Tribulus terrestris Seeds: Revealed Promising Antidiabetic Potentials. Molecules. 2023; 28(10):4203. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104203
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Abdur, Gauhar Rehman, Nasrullah Shah, Muhammad Hamayun, Sajid Ali, Abid Ali, Said karim Shah, Waliullah Khan, Muhammad Ishaq Ali Shah, and Abdulwahed Fahad Alrefaei. 2023. "Biosynthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Tribulus terrestris Seeds: Revealed Promising Antidiabetic Potentials" Molecules 28, no. 10: 4203. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104203
APA StyleRahman, A., Rehman, G., Shah, N., Hamayun, M., Ali, S., Ali, A., Shah, S. k., Khan, W., Shah, M. I. A., & Alrefaei, A. F. (2023). Biosynthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Tribulus terrestris Seeds: Revealed Promising Antidiabetic Potentials. Molecules, 28(10), 4203. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104203








