Levocetirizine-Loaded Electrospun Fibers from Water-Soluble Polymers: Encapsulation and Drug Release
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
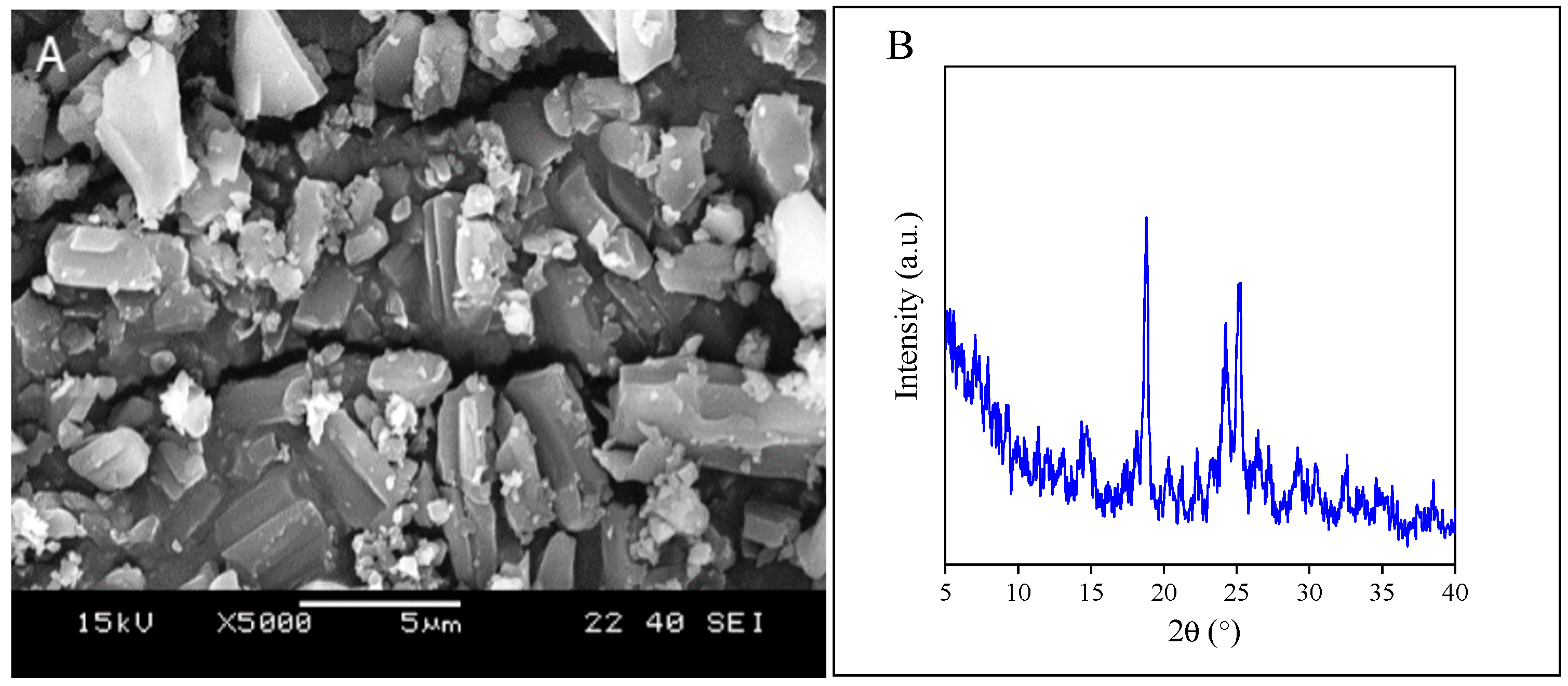
2.1. Component Properties
2.2. Interactions and Solubility
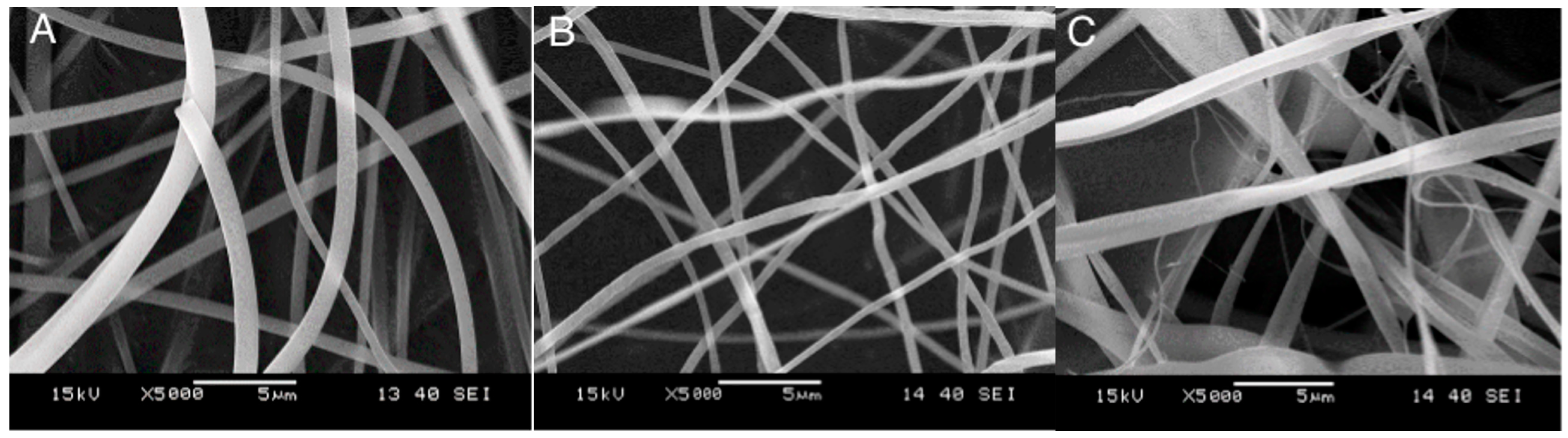
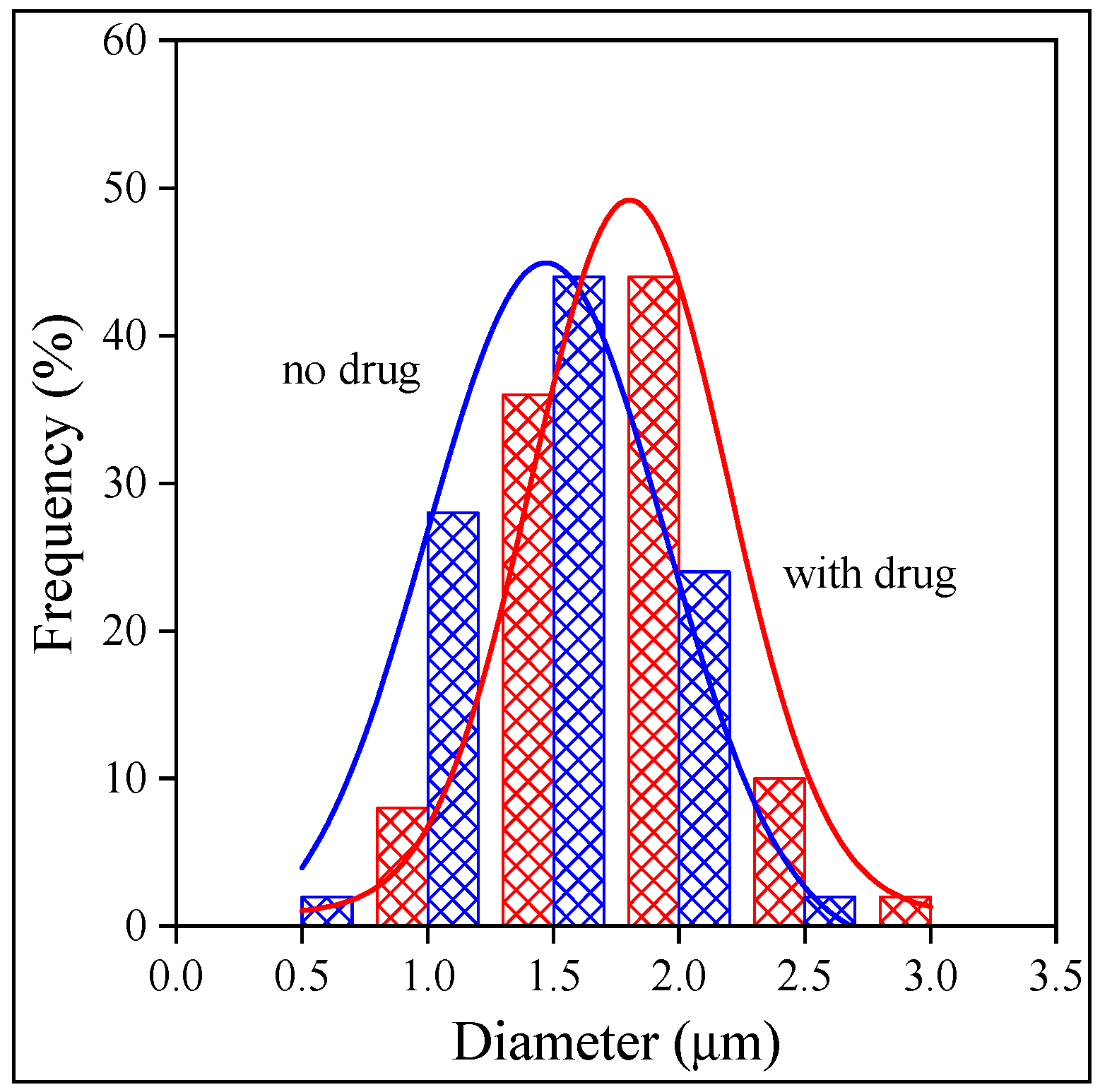
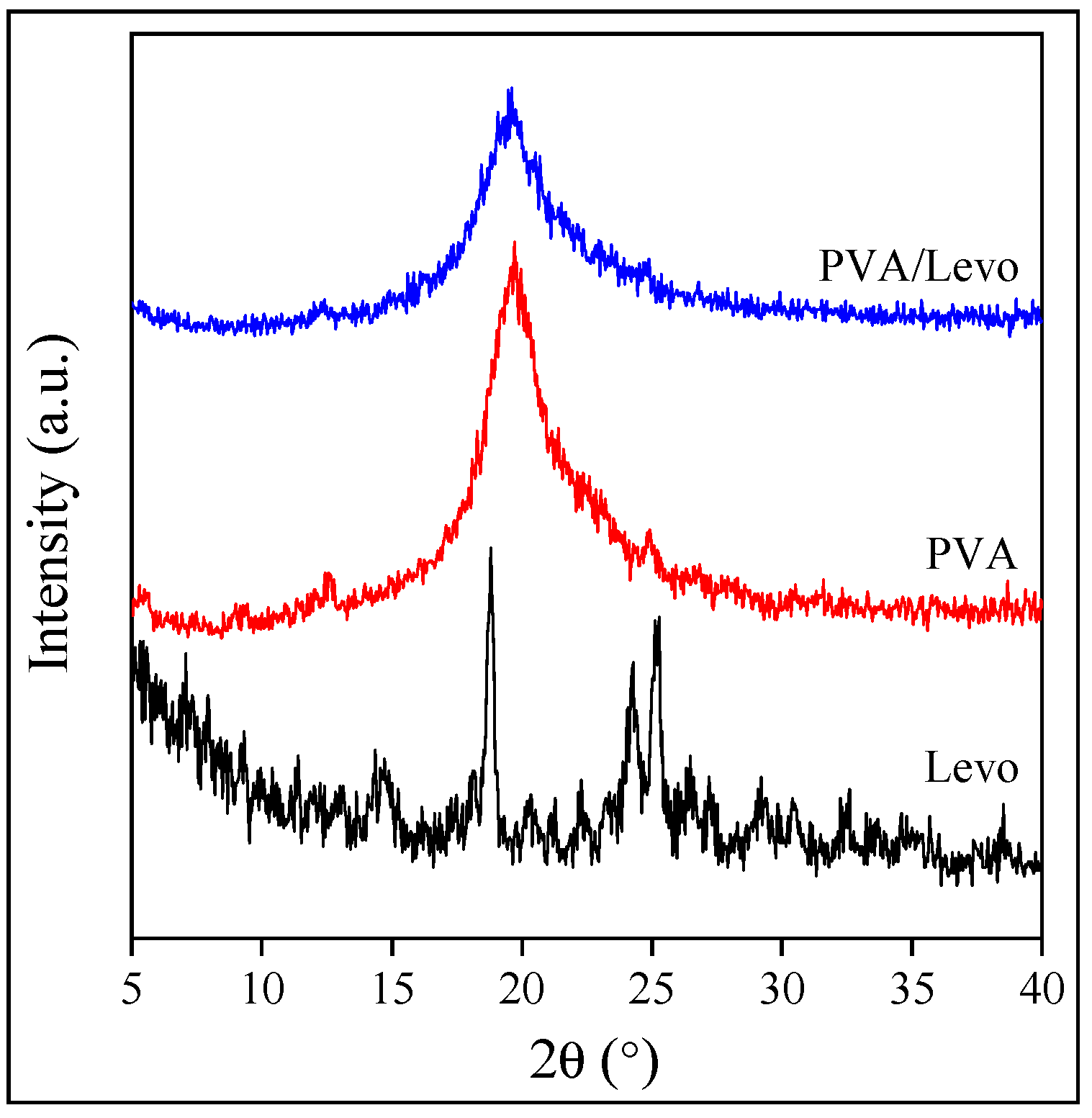
2.3. Fiber Characteristics and Morphology
2.4. Distribution, Location
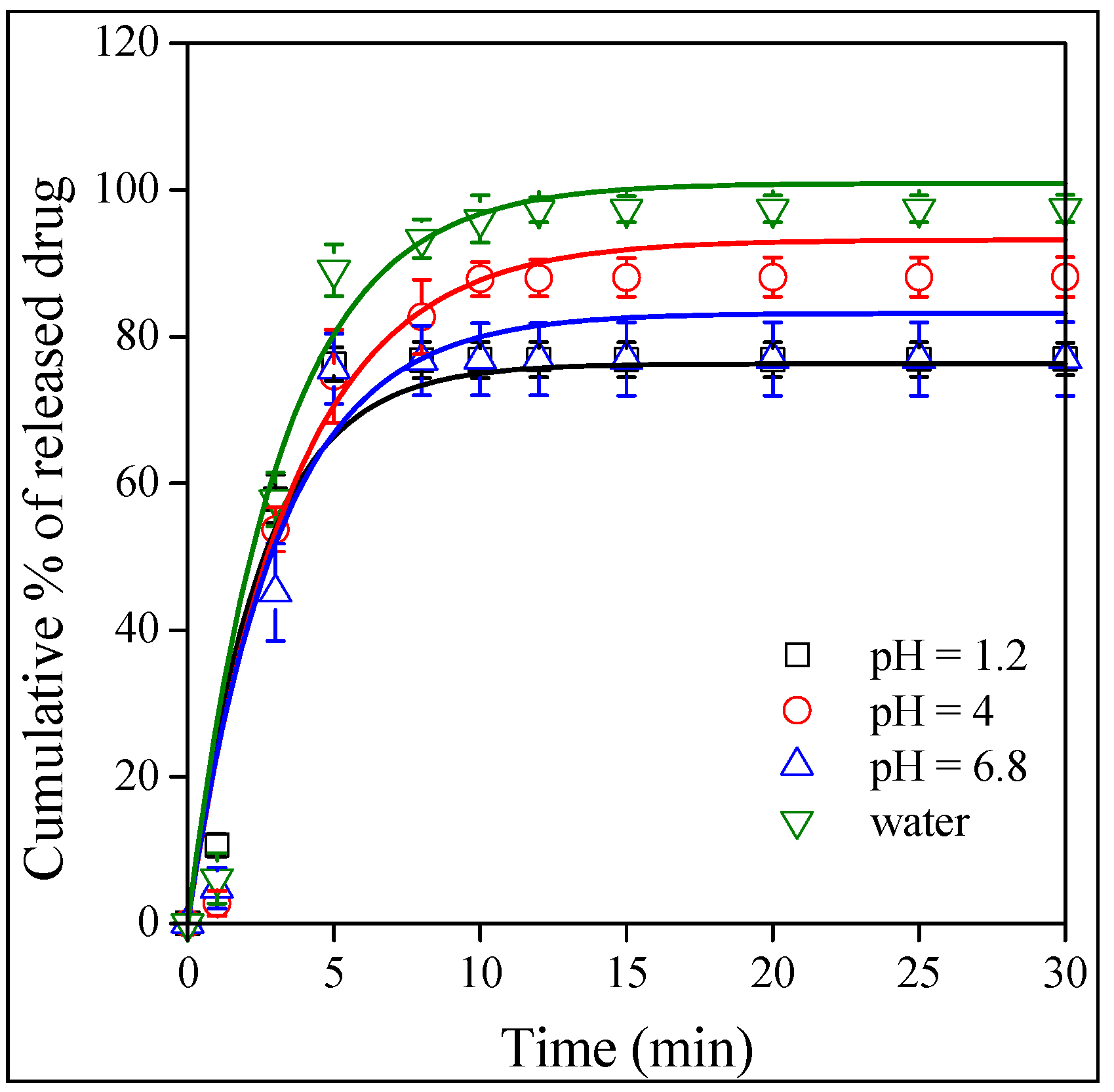
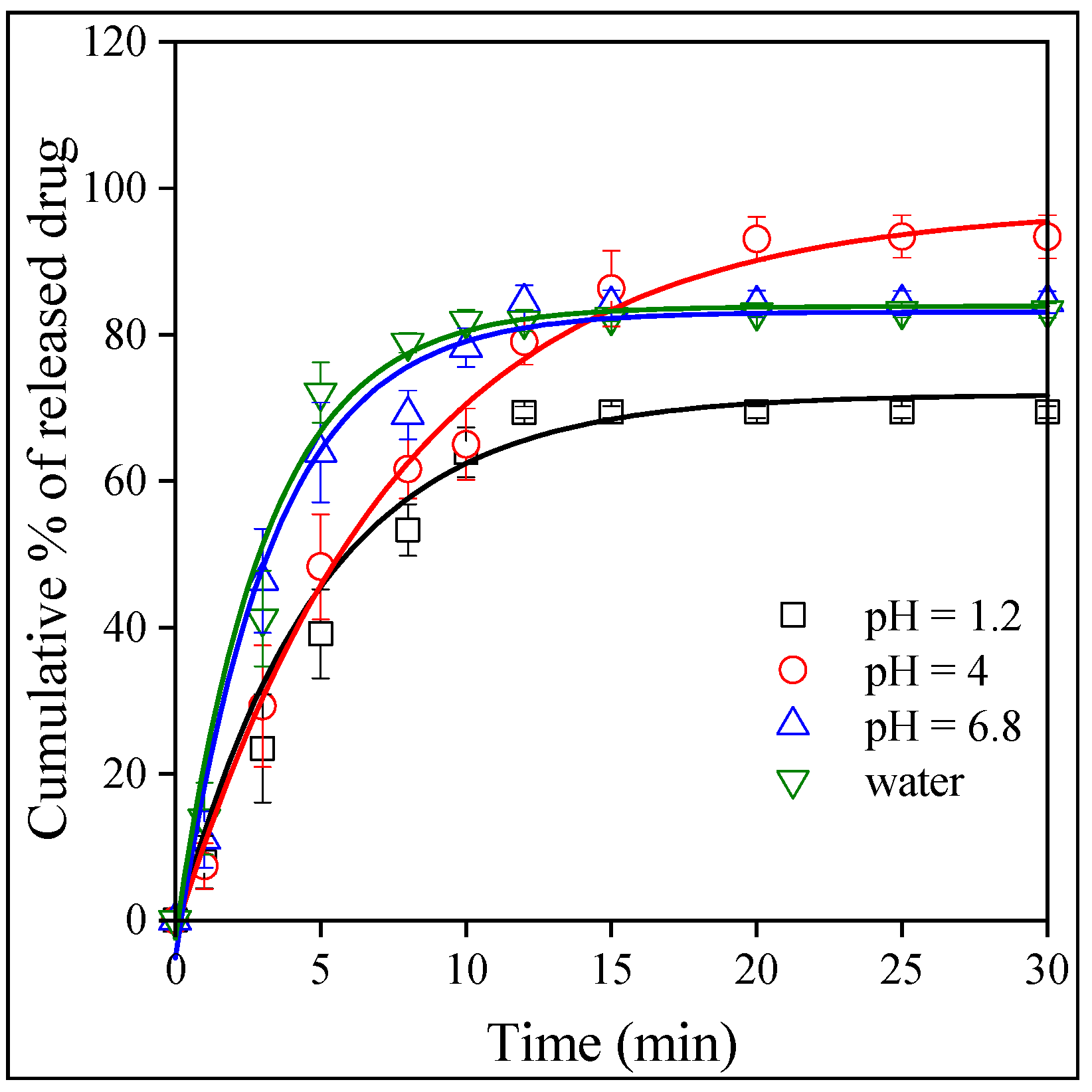
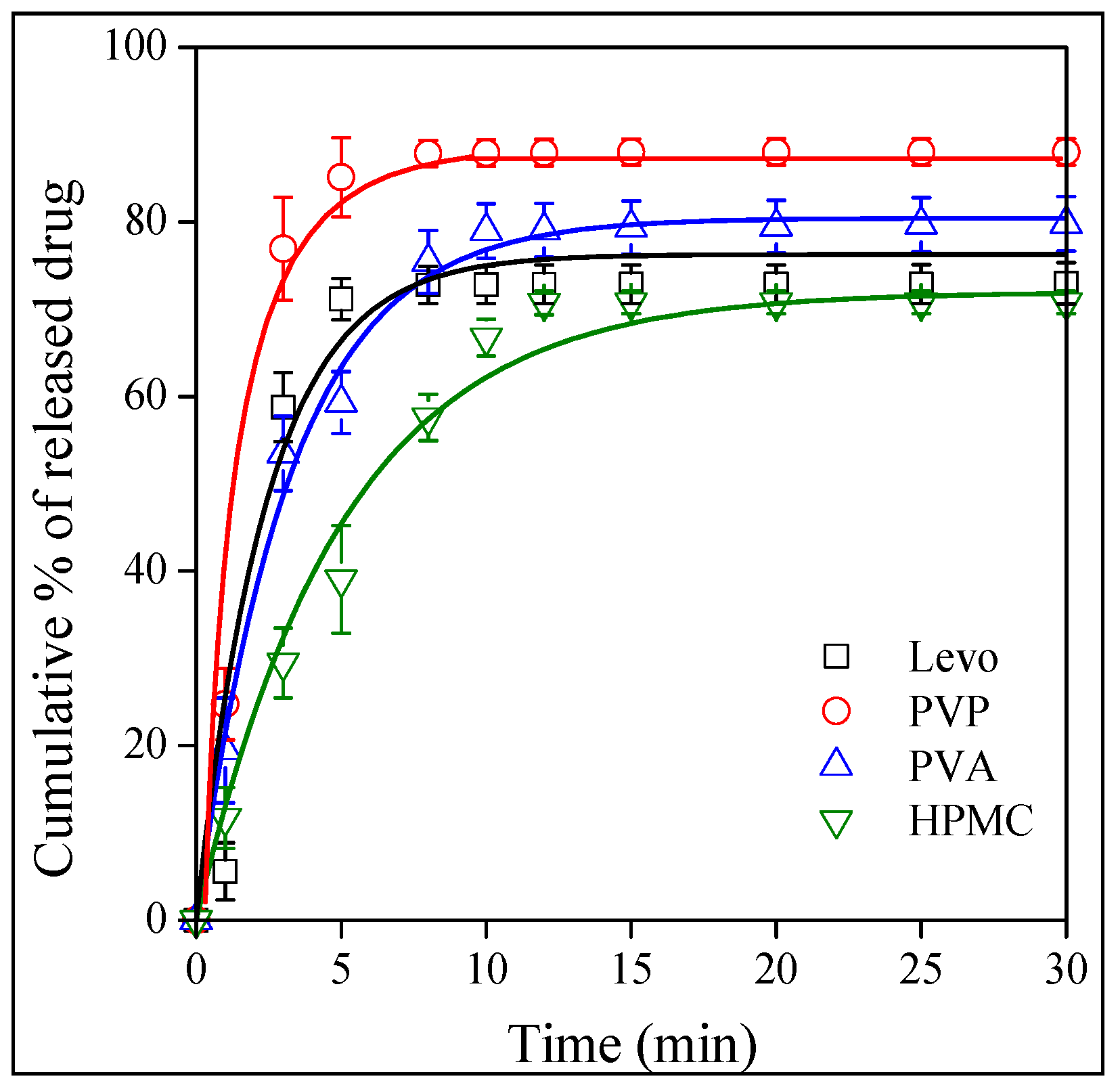
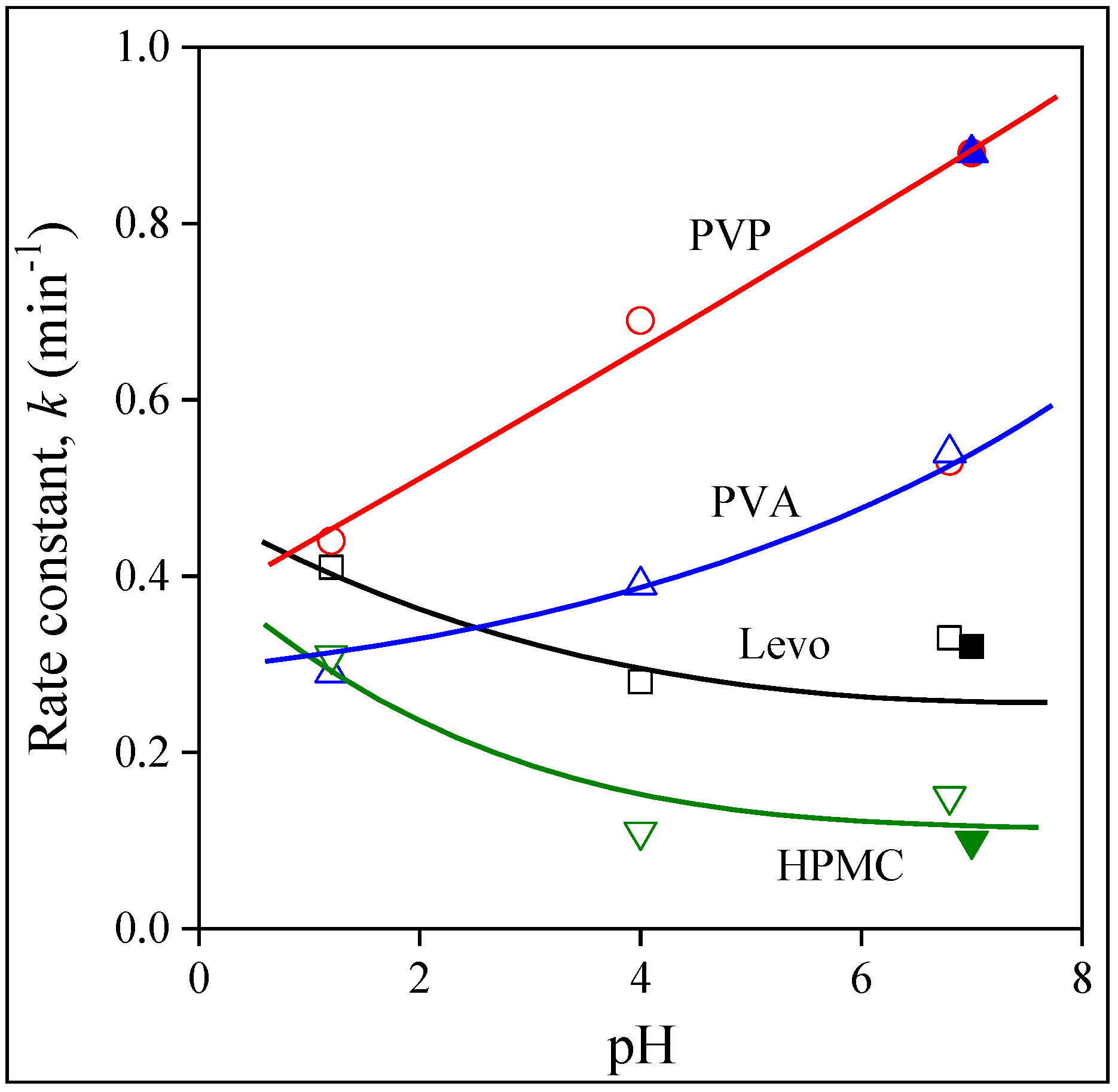
2.5. Release and Dissolution
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Solutions
3.3. Electrospinning
3.4. Release Experiments
3.5. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Sahoo, D.; Bandaru, R.; Samal, S.K.; Naik, R.; Kumar, P.; Kesharwani, P.; Dandela, R. Chapter 9—Oral drug delivery of nanomedicine. In Theory and Applications of Nonparenteral Nanomedicines; Kesharwani, P., Taurin, S., Greish, K., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2021; pp. 181–207. [Google Scholar]
- Indurkhya, A.; Patel, M.; Sharma, P.; Abed, S.N.; Shnoudeh, A.; Maheshwari, R.; Deb, P.K.; Tekade, R.K. Chapter 6—Influence of Drug Properties and Routes of Drug Administration on the Design of Controlled Release System. In Dosage form Design Considerations; Tekade, R.K., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; Volume I, pp. 179–223. [Google Scholar]
- Rewatkar, P.; Kumeria, T.; Popat, A. Chapter 5—Size, shape and surface charge considerations of orally delivered nanomedicines. In Nanotechnology for Oral Drug Delivery; Martins, J.P., Santos, H.A., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2020; pp. 143–176. [Google Scholar]
- Koenigsknecht, M.J.; Baker, J.R.; Wen, B.; Frances, A.; Zhang, H.; Yu, A.; Zhao, T.; Tsume, Y.; Pai, M.P.; Bleske, B.E.; et al. In Vivo Dissolution and Systemic Absorption of Immediate Release Ibuprofen in Human Gastrointestinal Tract under Fed and Fasted Conditions. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 4295–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Abeele, J.; Brouwers, J.; Mattheus, R.; Tack, J.; Augustijns, P. Gastrointestinal Behavior of Weakly Acidic BCS Class II Drugs in Man—Case Study of Diclofenac Potassium. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hens, B.; Brouwers, J.; Corsetti, M.; Augustijns, P. Gastrointestinal behavior of nano- and microsized fenofibrate: In vivo evaluation in man and in vitro simulation by assessment of the permeation potential. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 77, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hens, B.; Corsetti, M.; Brouwers, J.; Augustijns, P. Gastrointestinal and Systemic Monitoring of Posaconazole in Humans After Fasted and Fed State Administration of a Solid Dispersion. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2904–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwers, J.; Geboers, S.; Mols, R.; Tack, J.; Augustijns, P. Gastrointestinal behavior of itraconazole in humans—Part 1: Supersaturation from a solid dispersion and a cyclodextrin-based solution. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 525, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwers, J.; Tack, J.; Lammert, F.; Augustijns, P. Intraluminal drug and formulation behavior and integration in in vitro permeability estimation: A case study with amprenavir. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwald, R.B.; Conover, C.D.; Choe, Y.H. Poly (ethylene glycol) conjugated drugs and prodrugs: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2000, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-S.; Jo, B.-W. Enhanced paclitaxel bioavailability after oral administration of pegylated paclitaxel prodrug for oral delivery in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 280, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagden, N.; de Matas, M.; Gavan, P.T.; York, P. Crystal engineering of active pharmaceutical ingredients to improve solubility and dissolution rates. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serajuddin, A.T. Solid dispersion of poorly water-soluble drugs: Early promises, subsequent problems, and recent breakthroughs. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marano, S.; Barker, S.A.; Raimi-Abraham, B.T.; Missaghi, S.; Rajabi-Siahboomi, A.; Craig, D.Q.M. Development of micro-fibrous solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble drugs in sucrose using temperature-controlled centrifugal spinning. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 103, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, G.; Qu, Y.-L.; Yu, D.-G. Electrospun 4th-generation solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble drug utilizing two different processes. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 2012140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghel, S.; Cathcart, H.; O’Reilly, N.J. Polymeric Amorphous Solid Dispersions: A Review of Amorphization, Crystallization, Stabilization, Solid-State Characterization, and Aqueous Solubilization of Biopharmaceutical Classification System Class II Drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. 1. Drug solubilization and stabilization. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 85, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasenack, N.; Müller, B.W. Dissolution rate enhancement by in situ micronization of poorly water-soluble drugs. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 1894–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasenack, N.; Müller, B.W. Micron-size drug particles: Common and novel micronization techniques. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2004, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Duchêne, D. Cyclodextrins and their pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 329, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Lee, S.-E.; Pyo, Y.-C.; Tran, P.; Park, J.-S. Solubility enhancement and application of cyclodextrins in local drug delivery. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, N.; Delgadillo, R.M.V. Design, fabrication and drug release potential of dual stimuli-responsive composite hydrogel nanoparticle interfaces. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 204, 111819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamady Hussein, M.A.; Guler, E.; Rayaman, E.; Cam, M.E.; Sahin, A.; Grinholc, M.; Sezgin Mansuroglu, D.; Sahin, Y.M.; Gunduz, O.; Muhammed, M.; et al. Dual-drug delivery of Ag-chitosan nanoparticles and phenytoin via core-shell PVA/PCL electrospun nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 270, 118373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, N.; Delgadillo, R.M.V.; Castrejón, J.V. Unconventional and facile production of a stimuli-responsive multifunctional system for simultaneous drug delivery and environmental remediation. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 2081–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadinejad, R.; Madamsetty, V.S.; Kumar, A.; Varzandeh, M.; Dehshahri, A.; Zarrabi, A.; Sharififar, F.; Mohammadi, M.; Fahimipour, A.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun nanocarriers for delivering natural products for cancer therapy. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 887–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, N.; Zuníga, A.E.; Villela-Castrejón, J. Engineering and evaluation of forcespun functionalized carbon nano-onions reinforced poly (ε-caprolactone) composite nanofibers for pH-responsive drug release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, N.; Velasco Delgadillo, R.M.; Barrera, E.V. Covalently functionalized carbon nano-onions integrated gelatin methacryloyl nanocomposite hydrogel containing γ-cyclodextrin as drug carrier for high-performance pH-triggered drug release. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, H.W.; Woo, H.; Kim, I.-C.; Lee, K.H. Fish gelatin nanofibers prevent drug crystallization and enable ultrafast delivery. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 40411–40417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cheng, S.; Lu, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yao, Q. Electrospun fibers and their application in drug controlled release, biological dressings, tissue repair, and enzyme immobilization. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 25712–25729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ma, J.; Chen, S.; Wu, S. Designing an innovative electrospinning strategy to generate PHBV nanofiber scaffolds with a radially oriented fibrous pattern. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, F.; Li, T.; Wang, B.; Su, W.; Shang, D.; Wu, S. A simple, quick, and cost-effective strategy to fabricate polycaprolactone/silk fibroin nanofiber yarns for biotextile-based tissue scaffold application. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 186, 111863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, N.; Guo, L.; Yan, F.; Wang, H.; Kong, L. Effect of processing parameters on the electrospinning of cellulose acetate studied by response surface methodology. J. Agric. Food Res. 2020, 2, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budai-Szűcs, M.; Léber, A.; Cui, L.; Józó, M.; Vályi, P.; Burián, K.; Kirschweng, B.; Csányi, E.; Pukánszky, B. Electrospun PLA fibers containing metronidazole for periodontal disease. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Molnár, J.R.; Budai-Szűcs, M.; Szécsényi, M.; Burián, K.; Vályi, P.; Berkó, S.; Pukánszky, B. Physical–chemical aspects of the preparation and drug release of electrospun scaffolds. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samvedna, S.; Jindal, S.; Mishra, G.; Madan, J.R.; Gupta, G.; Awasthi, R.; Pinto, T.D.J.A.; Dua, K.; Kulkarni, G.T. Formulation and characterization of oral rapid disintegrating tablets of levocetirizine. Polim. Med. 2018, 48, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kirimlioğlu, G.Y.; Öztürk, A.A. Levocetirizine dihydrochloride-loaded chitosan nanoparticles: Formulation and in vitro evaluation. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 17, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revathi, V. Fast Dissolving drug delivery system. Pharma Times 2007, 39, 22–23. [Google Scholar]
- Heer, D.; Aggarwal, G.; Kumar, S.H. Recent trends of fast dissolving drug delivery system–an overview of formulation technology. Pharmacophore 2013, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhu, P.; Malli, R.; Koland, M.; Vijaynarayana, K.; D’Souza, U.; Harish, N.; Shastry, C.; Charyulu, R. Formulation and evaluation of fast dissolving films of levocitirizine di hydrochloride. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2011, 1, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, P.K.; Sridharan, A.; Sreekanth, J. Formulation development of fast releasing oral thin films of levocetrizine dihydrochloride with Eudragit® Epo and optimization through Taguchi orthogonal experimental design. Asian J. Pharm. 2011, 5, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangir, M.A.; Saleem, M.; Patel, H.R.; Kazmi, I.; Muheem, A.; Ahmad, K. Formulation and evaluation of oral fast dissolving films of levocetirizine. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 3, 1310–1323. [Google Scholar]
- Levocetirizine. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Levocetirizine#section=Experimental-Properties (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Józó, M.; Simon, N.; Yi, L.; Móczó, J.; Pukánszky, B. Improved Release of a Drug with Poor Water Solubility by Using Electrospun Water-Soluble Polymers as Carriers. Pharmaceutics 2021, 14, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billingham, N.C.; Calvert, P.D.; Manke, A.S. Solubility of phenolic antioxidants in polyolefins. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1981, 26, 3543–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Krevelen, D.W.; Te Nijenhuis, K. Properties of Polymers: Their Correlation with Chemical Structure; Their Numerical Estimation and Prediction from Additive Group Contributions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kirschweng, B.; Bencze, K.; Sárközi, M.; Hégely, B.; Samu, G.; Hári, J.; Tátraaljai, D.; Földes, E.; Kállay, M.; Pukánszky, B. Melt stabilization of polyethylene with dihydromyricetin, a natural antioxidant. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 133, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Component | Solubility Parameter, δ (MPa1/2) | Solubility (wt%) |
|---|---|---|
| PVA | 33.0 | 0.78 |
| PVP | 26.0 | 2.00 |
| HPMC | 28.6 | 0.77 |
| Levocetirizine | 22.9 | n.a. |
| Dichloromethane | 20.2 | 6.7 |
| Ethanol | 25.7 | 50 |
| Water | 47.9 | 96 |
| Polymer | Concentration (wt%) | Voltage (kV) | Feeding Rate (μL/s) | Collector Distance (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVP | 40 | 18 | 0.5 | 100 |
| PVA | 15 | 15 | 0.2 | 140 |
| HPMC | 10 | 18 | 0.5 | 125 |
| Polymer | Average Diameter (µm) | |
|---|---|---|
| No Drug | With Drug | |
| HPMC | 2.7 ± 1.5 | 2.9 ± 1.9 |
| PVP | 3.1 ± 0.1 | 4.2 ± 0.2 |
| PVA | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, L.; Cui, L.; Cheng, L.; Móczó, J.; Pukánszky, B. Levocetirizine-Loaded Electrospun Fibers from Water-Soluble Polymers: Encapsulation and Drug Release. Molecules 2023, 28, 4188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104188
Yi L, Cui L, Cheng L, Móczó J, Pukánszky B. Levocetirizine-Loaded Electrospun Fibers from Water-Soluble Polymers: Encapsulation and Drug Release. Molecules. 2023; 28(10):4188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104188
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Lan, Lu Cui, Linrui Cheng, János Móczó, and Béla Pukánszky. 2023. "Levocetirizine-Loaded Electrospun Fibers from Water-Soluble Polymers: Encapsulation and Drug Release" Molecules 28, no. 10: 4188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104188
APA StyleYi, L., Cui, L., Cheng, L., Móczó, J., & Pukánszky, B. (2023). Levocetirizine-Loaded Electrospun Fibers from Water-Soluble Polymers: Encapsulation and Drug Release. Molecules, 28(10), 4188. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104188






