Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation to Remove Cadmium from Rice and Its Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Growth Curve of L. plantarum and Results of Ultrasound Application on Its Growth
2.2. Determination of Fermentation Conditions
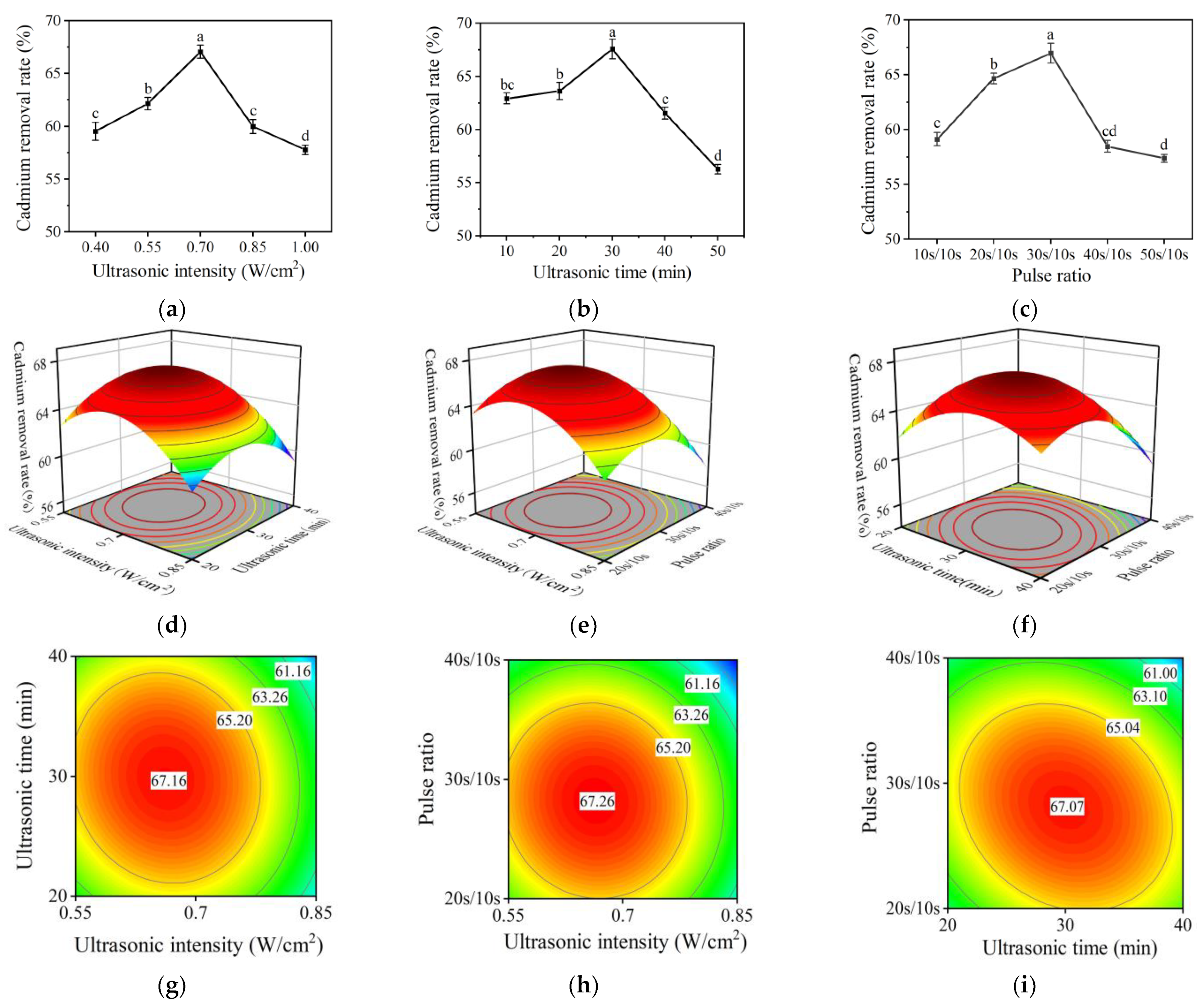
2.3. Single Factor Experimental Results of Ultrasonic-Assisted Fermentation Method
2.4. Response Surface Test Results of the Ultrasoound-Assisted Fermentation Method
2.4.1. Response Surface Design and Results
2.4.2. Interaction Analysis
2.5. Effect of Low-Intensity Ultrasonication on L. plantarum
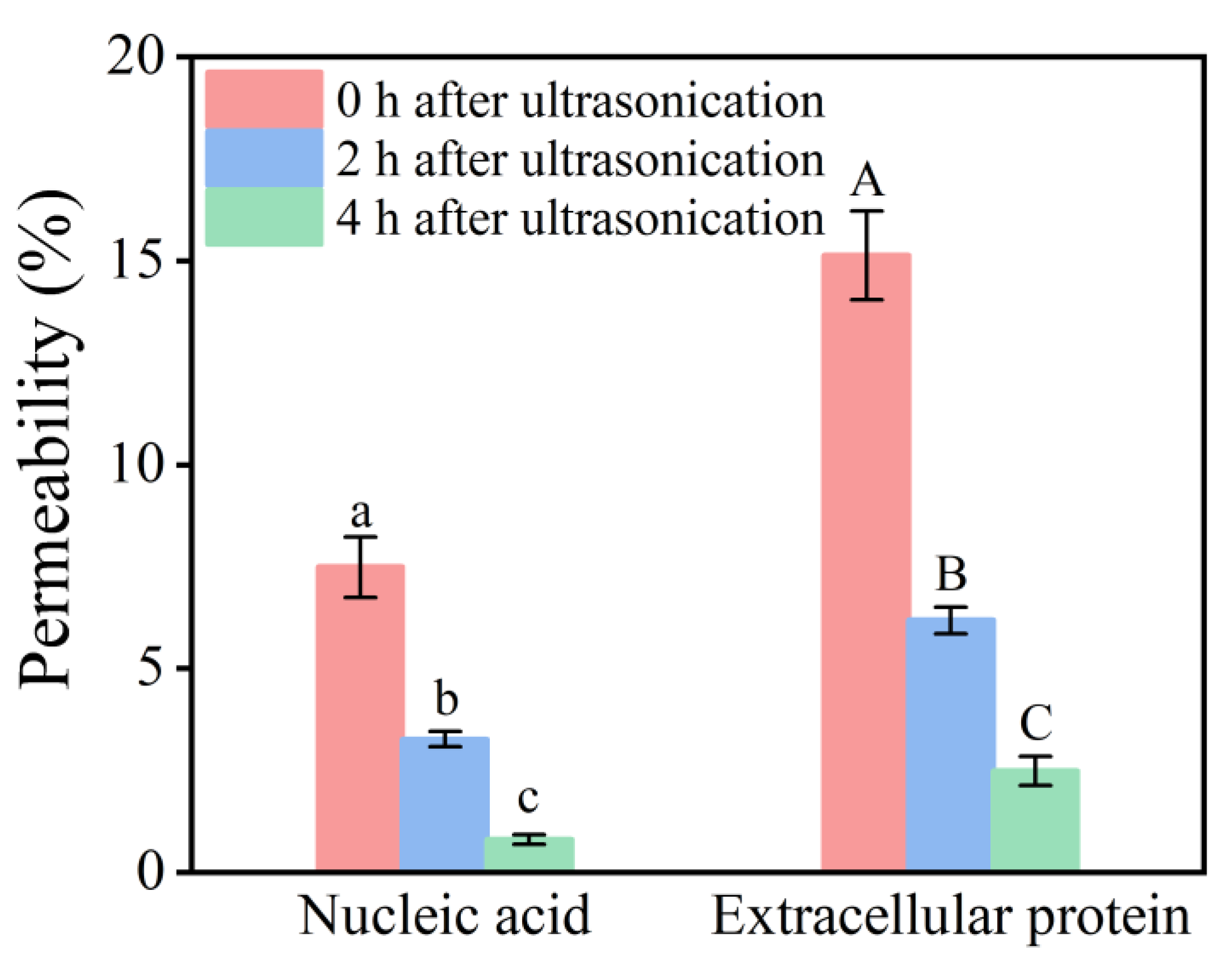
2.5.1. Changes in Cell Membrane Permeability
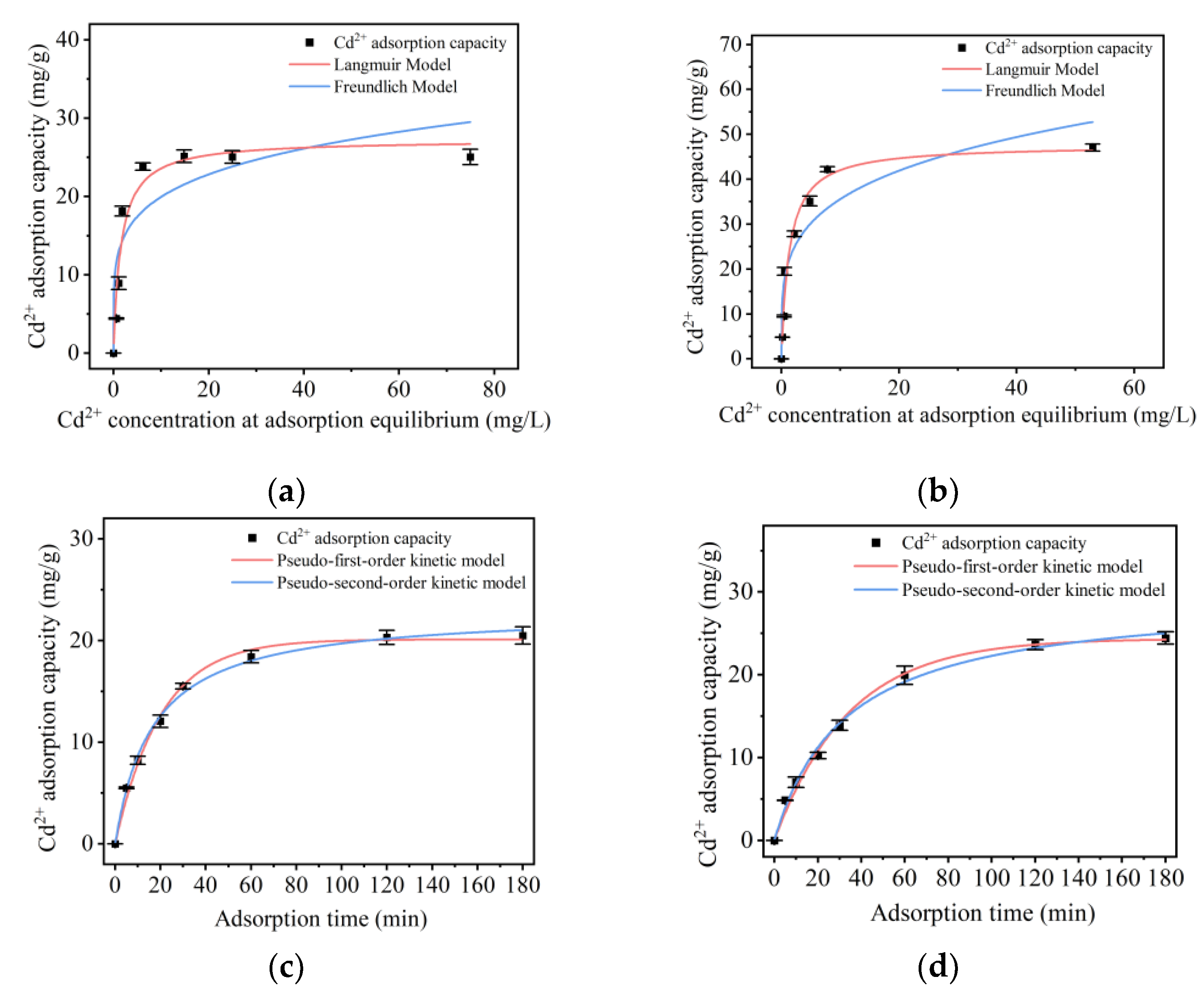
2.5.2. Isothermal Adsorption Model of Cd
2.5.3. Adsorption Kinetics of Cd
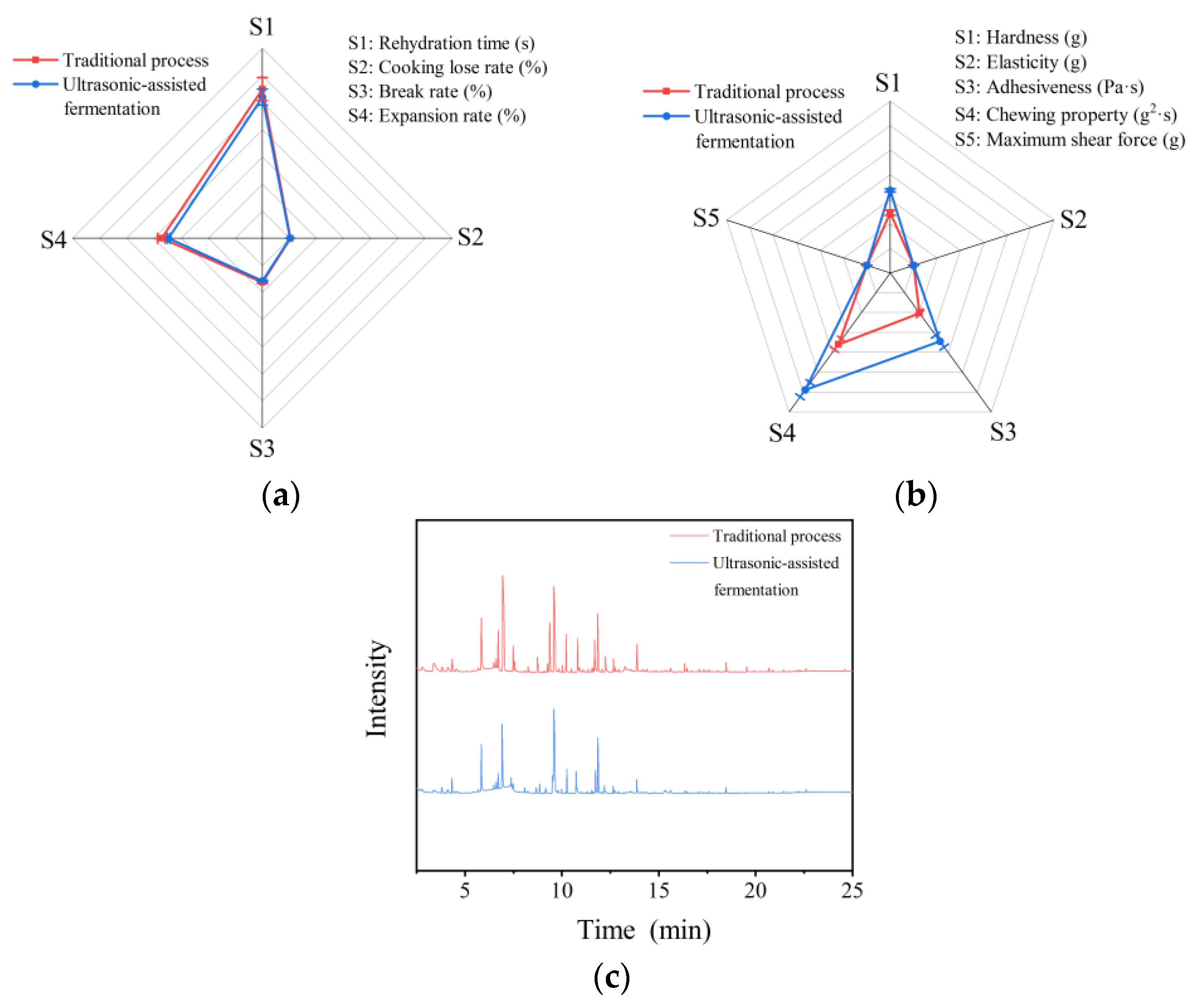
2.6. Quality Comparison of Rice Noodles
2.6.1. Cooking Quality and Texture Quality
2.6.2. Volatile Components
2.6.3. Sensory Evaluation Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Strain and Raw Materials
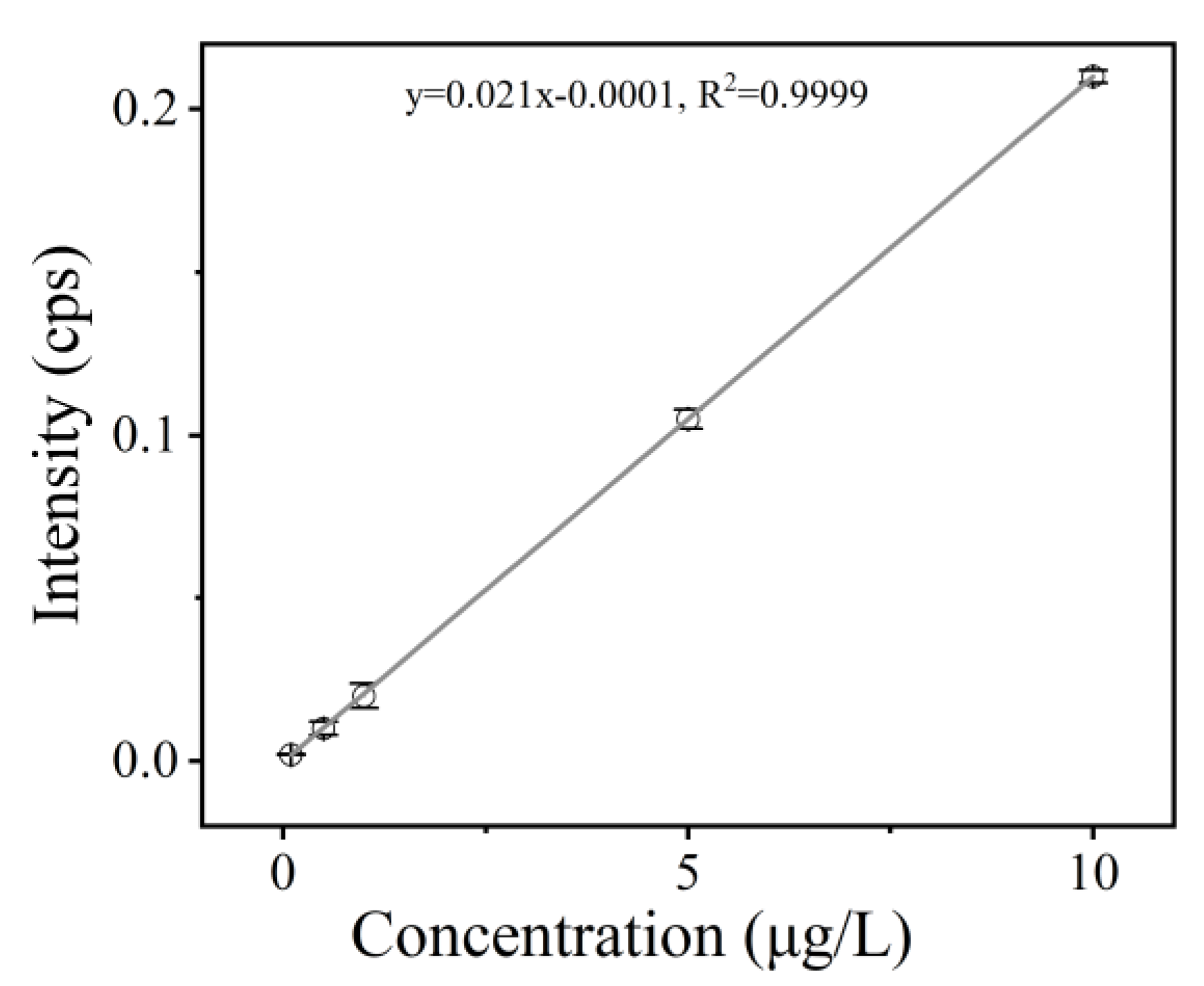
4.2. Method for the Determination of the Cd Content
4.3. Activation of L. plantarum and Growth Curve Determination
4.4. Determination of the Ultrasonic Intervention Stage
4.5. Determination of the Fermentation Conditions
4.6. Single-Factor Experiment of Ultrasonic Assisted Fermentation
4.7. Response Surface Experiment of Ultrasonic Assisted Fermentation
4.8. Research Methods to Determine the Cell Membrane Permeability of L. plantarum
4.9. Study of the Adsorption of Cd by L. plantarum
4.10. Determination Method for the Cooking Quality of the Rice Noodles
4.11. Determination Method of the Texture Quality of the Rice Noodles
4.12. Determination Method of the Flavor of the Rice Noodles
4.13. Sensory Evaluation Method of the Rice Noodles
4.14. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Appendix A
| CAS | Name | Formula | Odor Characteristic | Relative Content (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional | Ultrasonic-Assisted Fermentation | ||||
| 106-42-3 | p−Xylene | C8H10 | Almond | 4.052 | 5.911 |
| 95-47-6 | o−Xylene | C8H10 | 1.778 | − | |
| 540-18-1 | Butanoic acid, pentyl ester | C9H18O2 | 13.459 | − | |
| 98-01-1 | Furfural | C5H4O2 | 5.412 | − | |
| 108-05-4 | Acetic acid ethenyl ester | C4H6O2 | Fruit | 2.090 | 3.110 |
| 66-25-1 | Hexanal | C6H12O | 5.432 | 9.615 | |
| 71-41-0 | 1−Pentanol | C5H12O | 0.900 | 1.427 | |
| 124-13-0 | Octanal | C8H16O | 0.488 | 1.066 | |
| 513-86-0 | Acetoin | C4H8O2 | 4.462 | 3.346 | |
| 111-27-3 | 1−Hexanol | C6H14O | 2.231 | 3.508 | |
| 64-19-7 | Acetic acid | C2H4O2 | 2.620 | 4.647 | |
| 124-19-6 | Nonanal | C9H18O | Citrus | 2.156 | 3.733 |
| 112-31-2 | Decanal | C10H20O | 1.244 | 1.272 | |
| 100-52-7 | Benzaldehyde | C7H6O | Cherry | 0.791 | 1.096 |
| 64-17-5 | Ethanol | C2H6O | Wine | 3.361 | − |
| 100-41-4 | Ethylbenzene | C8H10 | Spicy | 1.300 | − |
| 111-13-7 | 2−Octanone | C8H16O | Milk | 0.048 | 1.054 |
| 107-92-6 | Butanoic acid | C4H8O2 | Cheese | 2.519 | 0.519 |
| 108-24-7 | Acetic anhydride | C4H6O3 | Vinegar | 6.837 | 3.284 |
| 3913-02-8 | 1−Octanol, 2−butyl− | C12H26O | Herb | 1.613 | − |
References
- Tedone, L.; Alhajj, A.S.; Verdni, L.; De Mastro, G. Nitrogen management strategy for optimizing agronomic and environmental performance of rainfed durum wheat under Mediterranean climate. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 2058–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Han, Y.; Manickam, S.; Show, P.L. Application of ultrasonication at different microbial growth stages during apple juice fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum: Investigation on the metabolic response. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 73, 105486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankit; Saha, L.; Kumar, V.; Tiwari, J.; Sweta; Rawat, S.; Singh, J.; Bauddh, K. Electronic waste and their leachates impact on human health and environment: Global ecological threat and management. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M.; Micali, A.; Marini, H.; Adamo, E.B.; Puzzolo, D.; Pisani, A.; Trichilo, V.; Altavilla, D.; Squadrito, F.; Minutoli, L. Cadmium, Organ Toxicity and Therapeutic Approaches: A Review on Brain, Kidney and Testis Damage. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 3879–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordberg, G.F.; Bernard, A.; Diamond, G.L.; Duffus, J.H.; Illing, P.; Nordberg, M.; Jin, T.; Skerfving, S. Risk assessment of effects of cadmium on human health (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2018, 90, 755–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Y.; Ren, J.Y.; Lin, Q.L.; Qu, L.L. Research progress in the process technology of removal of cadmium from rice. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2018, 39, 332–334, 341. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Q.Y.; Guo, Y.; Tang, X.S.; Tian, F.W.; Zhao, J.X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Removal of cadmium from rice by Lactobacillus planta-rum fermentation. Food Control 2019, 96, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Q.; Li, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.R. Influence of different fermentation microorganisms on physicochemical properties of rice and eating quality of rice noodles. J. Henan Univ. Technol. 2010, 31, 4–8+13. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderschueren, R.; De Mesmaeker, V.; Mounicou, S.; Isaure, M.-P.; Doelsch, E.; Montalvo, D.; Delcour, J.A.; Chavez, E.; Smolders, E. The impact of fermentation on the distribution of cadmium in cacao beans. Food Res. Int. 2020, 127, 108743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wei, F.; Chen, L. In vitro destructive effect of ultrasound on Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 2016, 20, 364–369. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, C.; Xiong, F.; He, R.; Zhang, W.; Ma, H. Effects of low-intensity ultrasound on the growth, cell membrane permeability and ethanol tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 36, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewe, J.A.; Wan, A.W.N.; Bhat, R.; Karim, A.A.; Liong, M.-T. Enhanced growth of lactobacilli and bioconversion of isoflavones in biotin-supplemented soymilk upon ultrasound-treatment. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.H.; Li, G.Q.; Li, K.M.; Razmovski-Naumovski, V.; Chan, K. Optimisation of Pueraria isoflavonoids by response surface methodology using ultrasonic-assisted extraction. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagn, J.; Hou, G.; Wu, L.; Cao, H.; Zheng, G.; Tang, Y. A novel adsorbent of three-dimensional ordered macro/mesoporous carbon for removal of malachite green dye. J. Cent. South Univ. 2020, 27, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.-Y.; Ke, X.; Liu, Y.-C.; Ha, Z.-H.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, T.C. A novel electrolytic-manganese-residues-and-serpentine-based composite (S-EMR) for enhanced Cd(II) and Pb(II) adsorption in aquatic environment. Rare Met. 2023, 42, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.G.; Chang, X.H.; Wu, J.H.; Qi, L.; Zhang, B.; Guo, F.J. Effect of Dynamic High Pressure Microfluidization Modified Polydextrose on Retrogradation of Rice Starch Gel. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2020, 35, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.Y.; Sang, P.T.; Guo, Y.H.; Jin, P.; Cheng, Y.L.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.F.; Yao, W.R.; Qian, H. Cadmium in food: Source, distribution and removal. Food Chem. 2022, 405, 134666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihucz, V.G.; Silversmit, G.; Szalóki, I.; de Samber, B.; Schoonjans, T.; Tatar, E.; Vincze, L.; Virag, I.; Yao, J.; Zaray, G. Removal of some elements from washed and cooked rice studied by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and synchrotron based confocal micro-X-ray fluorescence. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.N.; Gong, Z.Y. Optimization of Removal of Cadmium from Rice Flour by Water Soaking and Its Effect on Quality. Food Sci. 2019, 40, 272–278. [Google Scholar]
- Shindoh, K.; Yasui, A. Changes in Cadmium Concentration in Rice during Cooking. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2003, 9, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Feng, F.; Chen, Z.G.; Wu, T.; Wang, Z.H. Green and efficient removal of cadmium from rice flour using natural deep eutectic solvents. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Wang, T.; Dong, T.; Xu, P.C.; Zhang, T.Q.; Luo, X.H.; Wang, L.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z.X. Removal of cadmium from rice proteins by soaking with hydrochloric acid or ethylene diamine tetraacetic disodium solutions. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 85, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas Lima, A.; Ferreira de Moura, G.; Barbosa de Lima, M.A.; Mendes de Souza, P.; Alves da Silva, C.A.; De Campos Takaki, G.M.; Do Nascimento, A.E. Role of the Morphology and Polyphosphate in Trichoderma harzianum Related to Cadmium Removal. Molecules 2011, 16, 2486–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera-Bernal, M.; Martínez-Espinosa, R.M. Insights on Cadmium Removal by Bioremediation: The Case of Haloarchaea. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 12, 354–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Lv, C.; Wu, W.G.; Qin, S. Study on optimization of removing cadmium by lactobacillus fermentation and its effect on physi-cochemical and quality properties of rice noodles. Food Control 2019, 106, 106740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.P.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.G.; Wang, J.T. Optimization of acid leaching process combined fermentation technology for cadmium removal in rice. China Brew. 2015, 10, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Karizza, F.C.; Kingsley, K. Determination of Heavy Metals in Cannabinoid-Based Food Products Using Microwave-Assisted Digestion and ICP-MS. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 2537–2546. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.L.; Zhen, X.M.; Wang, G.W. Uncertainty evaluation of determination of cadmium by ICP-MS. China Food Saf. Mag. 2020, 12, 130–131. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Yoon, Y.-W.; Kim, M.-S.; Lee, M.-H.; Kim, G.-A.; Bae, K.; Yoon, S.-S. Gamma-aminobutyric acid fermentation in MRS-based medium by the fructophilic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Y7. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Hu, C.-H.; Ren, L.-Q.; Wang, D.-C.; Ye, B.-C. Enhancement of bile resistance by maltodextrin supplementation in Lactobacillus plantarum Lp-115. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Shi, N.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yan, M.; Li, Y. Response surface methodology optimization and HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS analysis on ultrasonic-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) and their antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, D.H.; Liu, L.; Zhou, S.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, X.; Tong, L.-T. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum Inoculum on the Fermentation Rate and Rice Noodle Quality. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Y.; Qiu, T.Q.; Huang, Z.L. Effects of different treatments on yeast cell membrane permeability. J. South Clrina Agiicultural. Univ. 2004, 1, 74–76. [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarty, R.; Banerjee, P.C. Mechanism of cadmium binding on the cell wall of an acidophilic bacterium. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 108, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.N.; Ma, Z.Q.; Li, H.H.; Tian, X.H.; Fang, Y.; Tan, B. Nutritional and cooking quality improvement of brown rice noodles prepared with extruded rice bran. Cereal Chem. 2021, 98, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasunmala, I.G.G.; Navaratne, S.B.; Wickramasinghe, I. Effect of process modifications and binding materials on textural properties of rice noodles. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2020, 21, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, K.; Liu, L. Comparative flavor analysis of four kinds of sweet fermented grains by sensory analysis combined with GC-MS. Int. J. Food Eng. 2022, 18, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, Y.K.; Effarizah, M.E.; Cheng, L.H. Factors Influencing Rice Noodles Qualities. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 8, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| A Ultrasonic Intensity (W/cm2) | B Ultrasonic Time (min) | C Pulse Ratio | Y Cd Removal Rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −1 (0.55) | −1 (20) | 0 | 62.004 |
| 2 | −1 | 0 (30) | −1 (20 s/10 s) | 63.022 |
| 3 | −1 | 1 (40) | 0 (30 s/10 s) | 63.656 |
| 4 | −1 | 0 | 1 (40 s/10 s) | 61.580 |
| 5 | 1 (0.85) | −1 | 0 | 59.679 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 60.471 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 59.558 |
| 8 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 57.786 |
| 9 | 0 (0.70) | 0 | 0 | 65.600 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67.816 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 68.046 |
| 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 65.568 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 67.774 |
| 14 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 61.806 |
| 15 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 62.924 |
| 16 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 62.356 |
| 17 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 58.220 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 159.71 | 9 | 17.75 | 13.64 | 0.0012 |
| A-Ultrasonic intensity | 20.37 | 1 | 20.37 | 15.66 | 0.0055 |
| B-Ultrasonic time | 0.28 | 1 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.6590 |
| C-Pulse ratio | 11.00 | 1 | 11.00 | 8.46 | 0.0227 |
| AB | 0.79 | 1 | 0.79 | 0.60 | 0.4623 |
| AC | 0.39 | 1 | 0.39 | 0.30 | 0.6027 |
| BC | 4.31 | 1 | 4.31 | 3.31 | 0.1115 |
| A2 | 42.43 | 1 | 42.43 | 32.61 | 0.0007 |
| B2 | 27.64 | 1 | 27.64 | 21.25 | 0.0025 |
| C2 | 39.74 | 1 | 39.74 | 30.54 | 0.0009 |
| Residual | 9.11 | 7 | 1.30 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 2.75 | 3 | 0.92 | 0.58 | 0.6608 |
| Pure Error | 6.36 | 4 | 1.59 | ||
| Cor Total | 168.82 | 16 | |||
| R2 = 0.9461 | R2adj = 0.8767 |
| Isothermal Adsorption Model | Blank | Ultrasonication | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorption Coefficients | Fitting Degree (R2) | Adsorption Coefficients | Fitting Degree (R2) | |
| Langmuir () | Qmax = 30.840 ± 3.718 | 0.943 | Qmax = 49.130 ± 2.917 | 0.986 |
| bL = 0.321 ± 0.068 | bL = 0.630 ± 0.055 | |||
| Freundlich () | KF = 6.473 ± 1.106 | 0.889 | KF = 11.022 ± 1.197 | 0.933 |
| nF = −0.409 ± 0.072 | nF = −0.427 ± 0.045 | |||
| Adsorption Kinetics Model | Blank | Ultrasonication | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorption Coefficients | Fitting Degree (R2) | Adsorption Coefficients | Fitting Degree (R2) | |
| Pseudo-first-order kinetic model [ln(qe − qt) = lnqe − k1t] | Qe = 18.605 ± 0.774 | 0.997 | Qe = 21.995 ± 2.012 | 0.997 |
| k1 = 0.068 ± 0.005 | k1 = 0.049 ± 0.005 | |||
| Pseudo-second-order kinetic model [t/qt = 1/k22qe2 + t/qe] | Qe = 23.271 ± 0.558 | 0.999 | Qe = 26.666 ± 1.664 | 0.999 |
| k2 = 0.003 ± 0.0002 | k2 = 0.002 ± 0.0002 | |||
| Rice Noodle | Sensory Index | A | B | C | D | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditionally processed rice noodle | Chewiness | 11 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Smoothness | 11 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |
| Gumminess | 12 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Color | 12 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| Flavor | 11 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| Ultrasound-assisted fermentation-treated rice noodle | Chewiness | 11 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Smoothness | 10 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |
| Gumminess | 9 | 6 | 5 | 0 | 0 | |
| Color | 10 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | |
| Flavor | 12 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Factor | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | |
| A-Ultrasonic intensity (W/cm2) | 0.55 | 0.70 | 0.85 |
| B-Ultrasonic time (min) | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| C-Pulse ratio | 20 s/10 s | 30 s/10 s | 40 s/10 s |
| Sensory Index (Weight) | Standard | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| Chewiness (0.23) | Chewy and moderate hardness | A, B, C, D, E |
| Smoothness (0.20) | Taste smooth | A, B, C, D, E |
| Gumminess (0.20) | Not sticky or half-cooked | A, B, C, D, E |
| Color (0.17) | White, uniform color, not variegated | A, B, C, D, E |
| Flavor (0.20) | Rice aroma and no peculiar smell | A, B, C, D, E |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Yin, J.; Guo, Y.; Yu, H.; Yuan, S.; Qian, H.; Yao, W.; Song, J. Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation to Remove Cadmium from Rice and Its Application. Molecules 2023, 28, 4127. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104127
Yang X, Yin J, Guo Y, Yu H, Yuan S, Qian H, Yao W, Song J. Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation to Remove Cadmium from Rice and Its Application. Molecules. 2023; 28(10):4127. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104127
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiaotong, Jie Yin, Yahui Guo, Hang Yu, Shaofeng Yuan, He Qian, Weirong Yao, and Jiangfeng Song. 2023. "Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation to Remove Cadmium from Rice and Its Application" Molecules 28, no. 10: 4127. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104127
APA StyleYang, X., Yin, J., Guo, Y., Yu, H., Yuan, S., Qian, H., Yao, W., & Song, J. (2023). Ultrasound-Assisted Fermentation to Remove Cadmium from Rice and Its Application. Molecules, 28(10), 4127. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104127







