Selecting Nanobodies Specific for the Epidermal Growth Factor from a Synthetic Nanobody Library
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
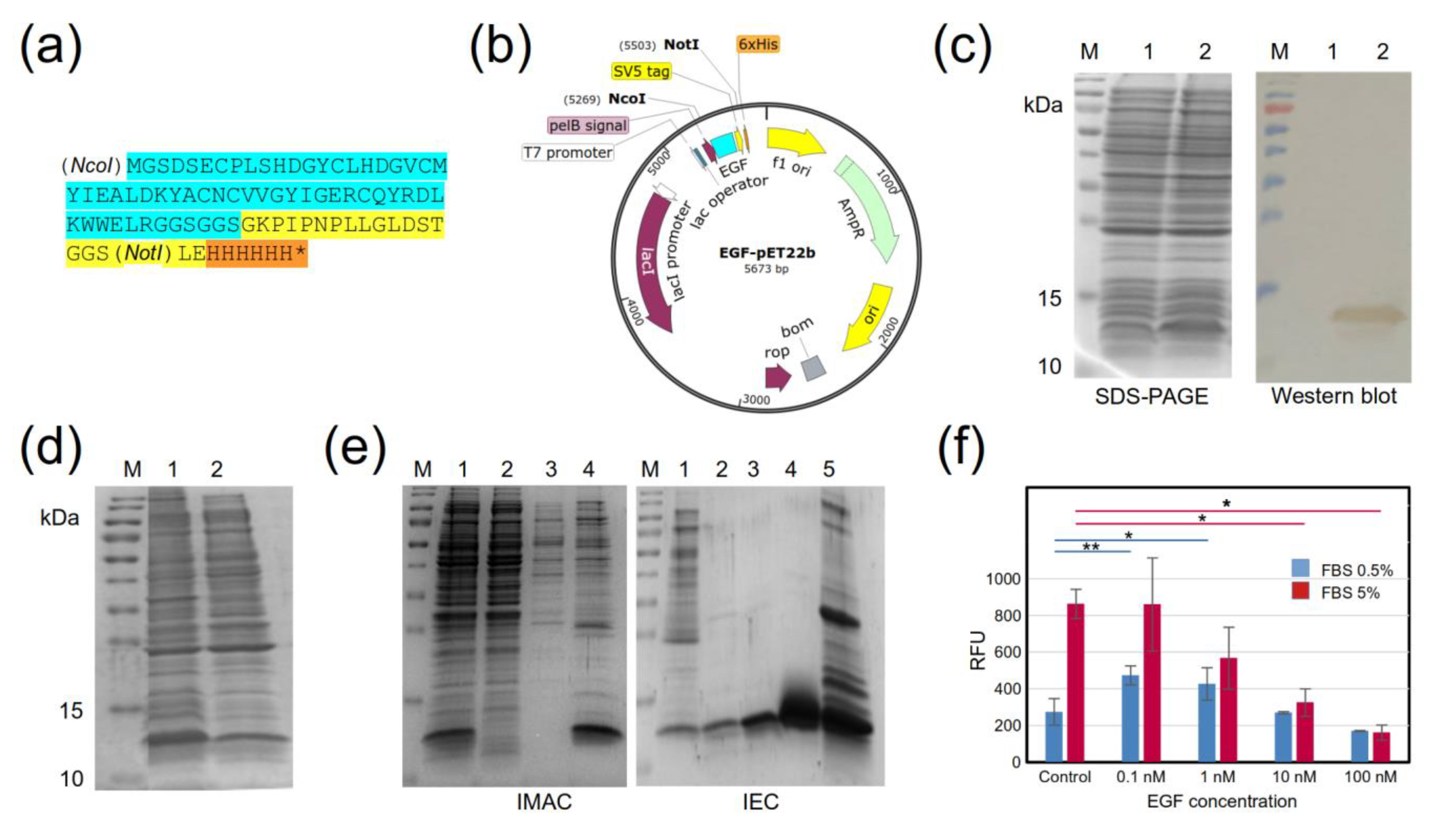
2.1. Design and Production of a Recombinant EGF Protein
2.2. Selection of EGF-Binding Phages
2.3. Sequences of Selected Clones
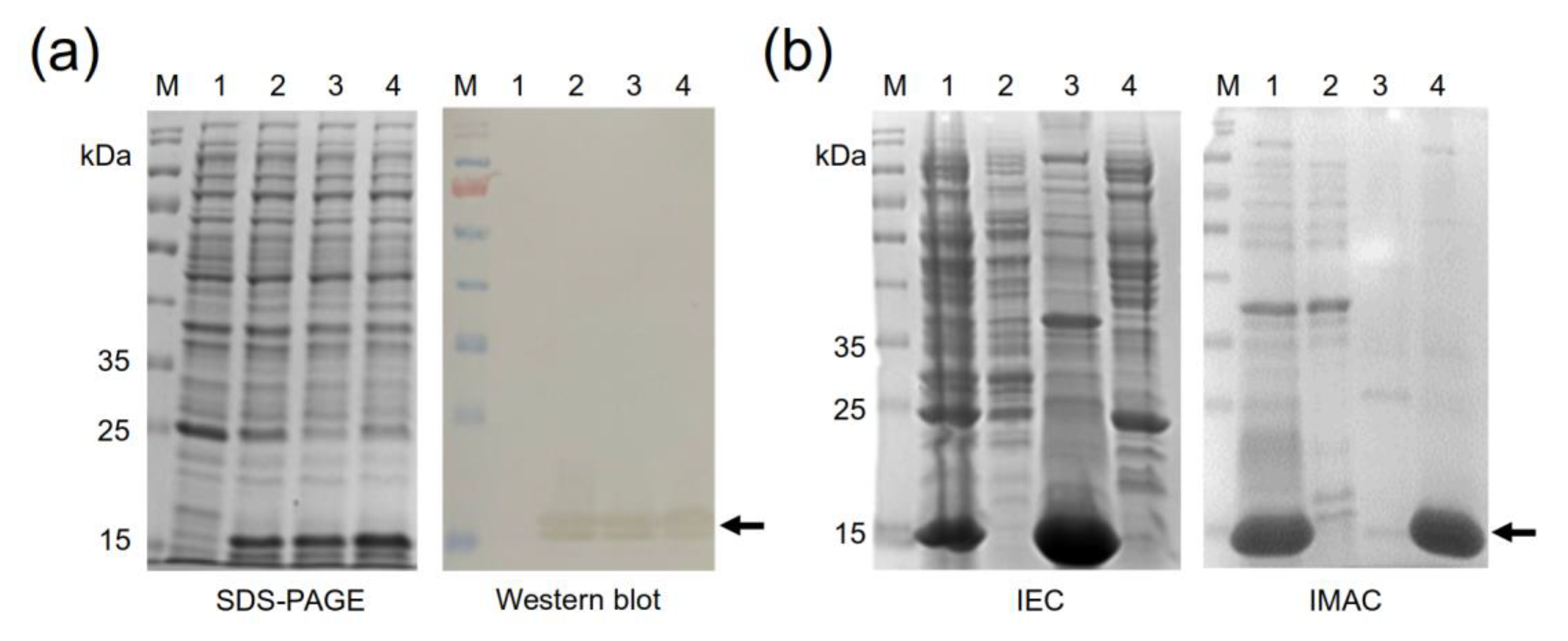
2.4. Production of the Four Recombinant Anti-EGF Nanobodies
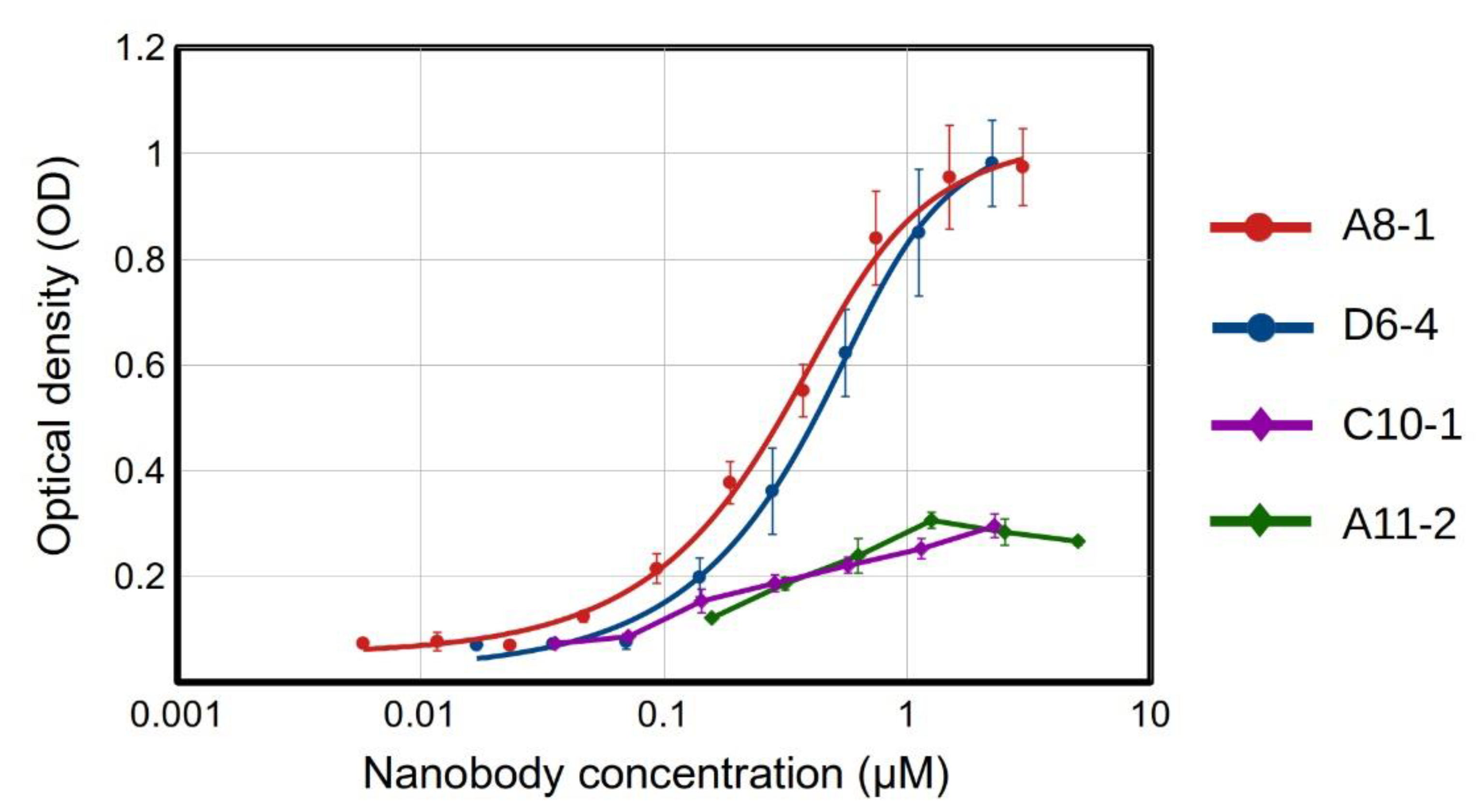
2.5. Binding Assays for Selected Recombinant Anti-EGF Nanobodies
2.6. Concluding Remarks
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthetic Library Production
3.2. Production and Purification of a Recombinant EGF Protein
3.3. Biological Activity of Recombinant EGF
3.4. Selection of EGF-Binding Phages
3.5. Enrichment of Positive Phages
3.6. Indirect ELISA for Detecting Positive Phage Clones
3.7. Sequencing
3.8. Production of Selected Recombinant Anti-EGF Nanobodies
3.9. Nanobody Purification
3.10. Nanobody Biotinylation
3.11. ELISA for Bilotinylated Anti-EGF Nanobodies
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Cohen, S.; Carpenter, G. Human Epidermal Growth Factor: Isolation and Chemical and Biological Properties. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Carpenter, G.; Coffey, R.J. EGF Receptor Ligands: Recent Advances. F1000Research 2016, 5, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudomi, T. Molecular Epidemiology of Lung Cancer and Geographic Variations with Special Reference to EGFR Mutations. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tahara, E.; Sumiyoshi, H.; Hata, J.; Yasui, W.; Taniyama, K.; Hayashi, T.; Nagae, S.; Sakamoto, S. Human Epidermal Growth Factor in Gastric Carcinoma as a Biologic Marker of High Malignancy. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1986, 77, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.-C.; Jin, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K. Role of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Lung Cancer and Targeted Therapies. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheaito, K.; Bahmad, H.F.; Jalloul, H.; Hadadeh, O.; Msheik, H.; El-Hajj, A.; Mukherji, D.; Al-Sayegh, M.; Abou-Kheir, W. Epidermal Growth Factor Is Essential for the Maintenance of Novel Prostate Epithelial Cells Isolated from Patient-Derived Organoids. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 571677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The Basics of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerboth, S.; Housman, G.; Leary, M.; Longacre, M.; Byler, S.; Lapinska, K.; Willbanks, A.; Sarkar, S. EMT and Tumor Metastasis. Clin. Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, G.; Montero, E.; Leon, K.; Cohen, I.R.; Lage, A. Autoimmunization to Epidermal Growth Factor, a Component of the Immunological Homunculus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2002, 1, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, D.; Crombet, T. CIMAvax-EGF: A New Therapeutic Vaccine for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, B.; Neninger, E.; de la Torre, A.; Leonard, I.; Martínez, R.; Viada, C.; González, G.; Mazorra, Z.; Lage, A.; Crombet, T. Effective Inhibition of the Epidermal Growth Factor/Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Binding by Anti–Epidermal Growth Factor Antibodies Is Related to Better Survival in Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with the Epidermal Growth Factor Cancer Vaccine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muyldermans, S. Nanobodies: Natural Single-Domain Antibodies. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 775–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, C. Nanobody Approval Gives Domain Antibodies a Boost. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 485–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyldermans, S. A Guide to: Generation and Design of Nanobodies. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 2084–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés-Tresanco, M.S.; Molina-Zapata, A.; Pose, A.G.; Moreno, E. Structural Insights into the Design of Synthetic Nanobody Libraries. Molecules 2022, 27, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keam, S.J. Ozoralizumab: First Approval. Drugs 2023, 83, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guardiola, S.; Varese, M.; Sánchez-Navarro, M.; Vincke, C.; Teixidó, M.; García, J.; Muyldermans, S.; Giralt, E. Blocking EGFR Activation with Anti-EGF Nanobodies via Two Distinct Molecular Recognition Mechanisms. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 13843–13847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiola, S.; Sánchez-Navarro, M.; Rosell, R.; Giralt, E.; Codony-Servat, J. Anti-EGF Nanobodies Enhance the Antitumoral Effect of Osimertinib and Overcome Resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Cellular Models. Med. Oncol. 2022, 39, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, M.A.; Serrano-Rivero, Y.; González-Pose, A.; Salazar-Uribe, J.; Rubio-Carrasquilla, M.; Soares-Alves, M.; Parra, N.C.; Camacho-Casanova, F.; Sánchez-Ramos, O.; Moreno, E. Design and Construction of a Synthetic Nanobody Library: Testing Its Potential with a Single Selection Round Strategy. Molecules 2023, 28, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigler, H.; Ash, J.F.; Singer, S.J.; Cohen, S. Visualization by Fluorescence of the Binding and Internalization of Epidermal Growth Factor in Human Carcinoma Cells A-431. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1978, 75, 3317–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamoto, T.; Sato, J.D.; Le, A.; Polikoff, J.; Sato, G.H.; Mendelsohn, J. Growth Stimulation of A431 Cells by Epidermal Growth Factor: Identification of High-Affinity Receptors for Epidermal Growth Factor by an Anti-Receptor Monoclonal Antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, T.; Virmani, N.; Bera, B.C.; Vaid, R.K.; Vashisth, M.; Bardajatya, P.; Kumar, A.; Tripathi, B.N. Phage Display Technique as a Tool for Diagnosis and Antibody Selection for Coronaviruses. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, G.; Pupo, A.; Gómez, S.; Krengel, U.; Moreno, E. Engineering the Binding Site of an Antibody against N-Glycolyl GM3: From Functional Mapping to Novel Anti-Ganglioside Specificities. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wu, J.; Lv, H.; Ji, X.; Muyldermans, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Identification of Serum Ferritin-Specific Nanobodies and Development towards a Diagnostic Immunoassay. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, B.; Lv, H.; Ji, X.; Lu, Y.; et al. Selection of Specific Nanobodies against Peanut Allergen through Unbiased Immunization Strategy and the Developed Immuno-Assay. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, J.Z.; Skottrup, P.D. Selection and Characterization of Camelid Nanobodies towards Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 65, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakzaei, M.; Rasaee, M.J.; Fazaeli, A.A.; Aminian, M. A Comparison of Three Strategies for Biopanning of Phage-scFv Library against Diphtheria Toxin. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 9486–9494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulpakko, J.; Juusti, V.; Rannikko, A.; Hänninen, P.E. Detecting Disease Associated Biomarkers by Luminescence Modulating Phages. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunder, M.; Bratkovič, T.; Urleb, U.; Kreft, S.; Štrukelj, B. Ultrasound in Phage Display: A New Approach to Nonspecific Elution. Biotechniques 2008, 44, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donatan, S.; Yazici, H.; Bermek, H.; Sarikaya, M.; Tamerler, C.; Urgen, M. Physical Elution in Phage Display Selection of Inorganic-Binding Peptides. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrath, K.E.; Lauwereys, M.; Galleni, M.; Matagne, A.; Frère, J.-M.; Kinne, J.; Wyns, L.; Muyldermans, S. β-Lactamase Inhibitors Derived from Single-Domain Antibody Fragments Elicited in the Camelidae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 2807–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Marco, A. Recombinant Expression of Nanobodies and Nanobody-Derived Immunoreagents. Protein Expr. Purif. 2020, 172, 105645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amcheslavsky, A.; Wallace, A.L.; Ejemel, M.; Li, Q.; McMahon, C.T.; Stoppato, M.; Giuntini, S.; Schiller, Z.A.; Pondish, J.R.; Toomey, J.R.; et al. Anti-CfaE Nanobodies Provide Broad Cross-Protection against Major Pathogenic Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli Strains, with Implications for Vaccine Design. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy-Fazekas, D.; Stráner, P.; Ecsédi, P.; Taricska, N.; Borbély, A.; Nyitray, L.; Perczel, A. A Novel Fusion Protein System for the Production of Nanobodies and the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD in a Bacterial System. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salema, V.; Fernández, L.Á. High Yield Purification of Nanobodies from the Periplasm of E. coli as Fusions with the Maltose Binding Protein. Protein Expr. Purif. 2013, 91, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariuki, C.K.; Magez, S. Improving the Yield of Recalcitrant Nanobodies® by Simple Modifications to the Standard Protocol. Protein Expr. Purif. 2021, 185, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eble, J.A. Titration ELISA as a Method to Determine the Dissociation Constant of Receptor Ligand Interaction. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 2018, 57334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, L.; Walt, D.R. Evaluation of Antibody Biotinylation Approaches for Enhanced Sensitivity of Single Molecule Array (Simoa) Immunoassays. Bioconjug Chem. 2018, 29, 3452–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.; Forte, N.; Baker, J.R. Site-Selective Lysine Conjugation Methods and Applications towards Antibody–Drug Conjugates. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 10689–10702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, J.D.; Domagala, T.; Rothacker, J.; Catimel, B.; Nice, E. Use of Thiazolidine-Mediated Ligation for Site Specific Biotinylation of Mouse EGF for Biosensor Immobilisation. Lett. Pept. Sci. 2001, 8, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, K.M.; Berger, M.B.; Mendrola, J.M.; Cho, H.-S.; Leahy, D.J.; Lemmon, M.A. EGF Activates Its Receptor by Removing Interactions That Autoinhibit Ectodomain Dimerization. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, W.-T.; Lin, W.-C.; Chang, K.-C.; Huang, J.-Y.; Yen, K.-C.; Young, I.-C.; Sun, Y.-J.; Lin, F.-H. Quantitative Analysis of Ligand-EGFR Interactions: A Platform for Screening Targeting Molecules. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moutel, S.; Bery, N.; Bernard, V.; Keller, L.; Lemesre, E.; De Marco, A.; Ligat, L.; Rain, J.C.; Favre, G.; Olichon, A.; et al. NaLi-H1: A Universal Synthetic Library of Humanized Nanobodies Providing Highly Functional Antibodies and Intrabodies. eLife 2016, 5, e16228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Predonzani, A.; Arnoldi, F.; López-Requena, A.; Burrone, O.R. In Vivosite-Specific Biotinylation of Proteins within the Secretory Pathway Using a Single Vector System. BMC Biotechnol. 2008, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Pacheco, A.F.; Monsalve, Y.; Serrano-Rivero, Y.; Salazar-Uribe, J.; Moreno, E.; Orozco, J. Engineered Synthetic Nanobody-Based Biosensors for Electrochemical Detection of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serrano-Rivero, Y.; Salazar-Uribe, J.; Rubio-Carrasquilla, M.; Camacho-Casanova, F.; Sánchez-Ramos, O.; González-Pose, A.; Moreno, E. Selecting Nanobodies Specific for the Epidermal Growth Factor from a Synthetic Nanobody Library. Molecules 2023, 28, 4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104043
Serrano-Rivero Y, Salazar-Uribe J, Rubio-Carrasquilla M, Camacho-Casanova F, Sánchez-Ramos O, González-Pose A, Moreno E. Selecting Nanobodies Specific for the Epidermal Growth Factor from a Synthetic Nanobody Library. Molecules. 2023; 28(10):4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104043
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerrano-Rivero, Yunier, Julieta Salazar-Uribe, Marcela Rubio-Carrasquilla, Frank Camacho-Casanova, Oliberto Sánchez-Ramos, Alaín González-Pose, and Ernesto Moreno. 2023. "Selecting Nanobodies Specific for the Epidermal Growth Factor from a Synthetic Nanobody Library" Molecules 28, no. 10: 4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104043
APA StyleSerrano-Rivero, Y., Salazar-Uribe, J., Rubio-Carrasquilla, M., Camacho-Casanova, F., Sánchez-Ramos, O., González-Pose, A., & Moreno, E. (2023). Selecting Nanobodies Specific for the Epidermal Growth Factor from a Synthetic Nanobody Library. Molecules, 28(10), 4043. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104043





