Tailoring of Mesoporous Silica-Based Materials for Enhanced Water Pollutants Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
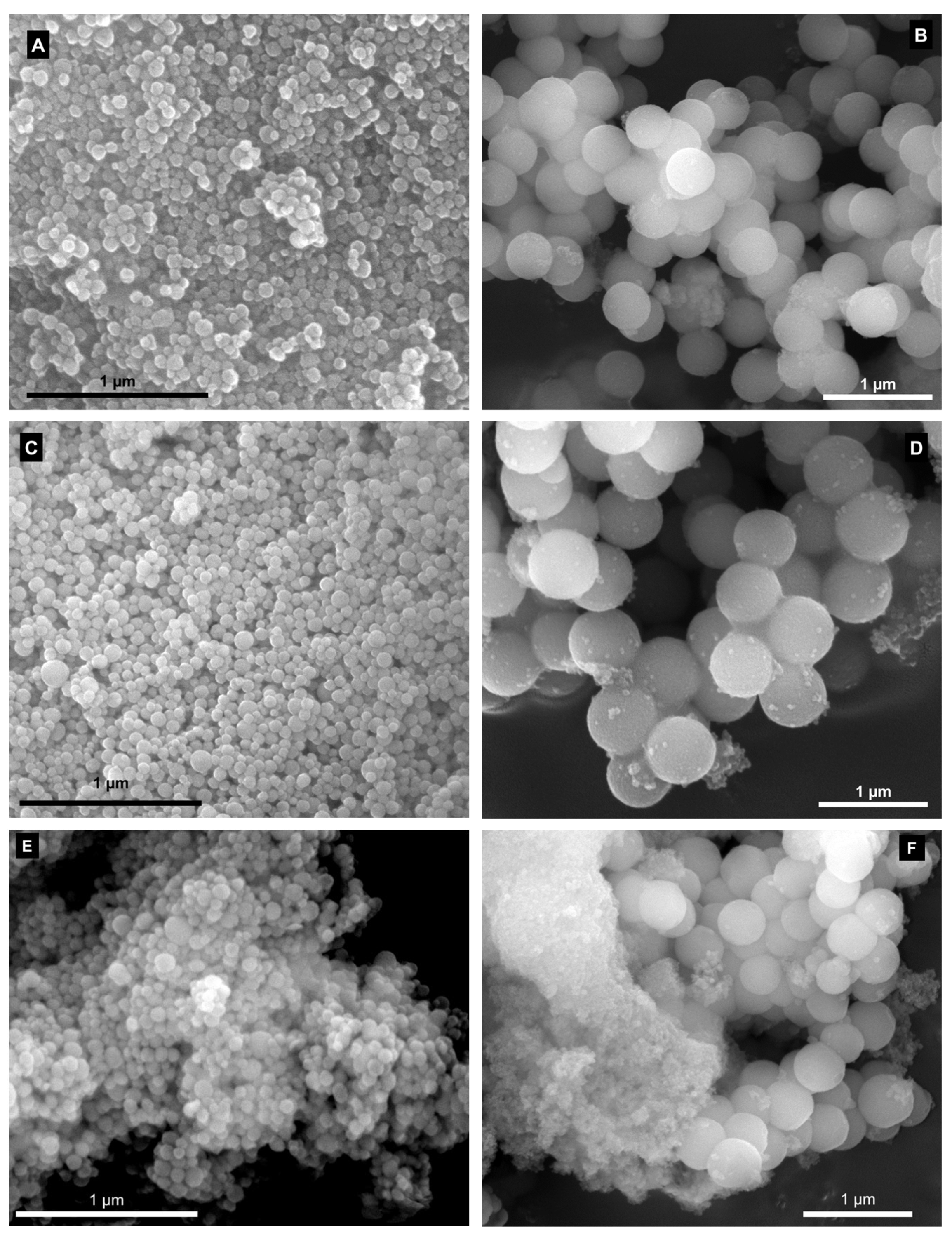
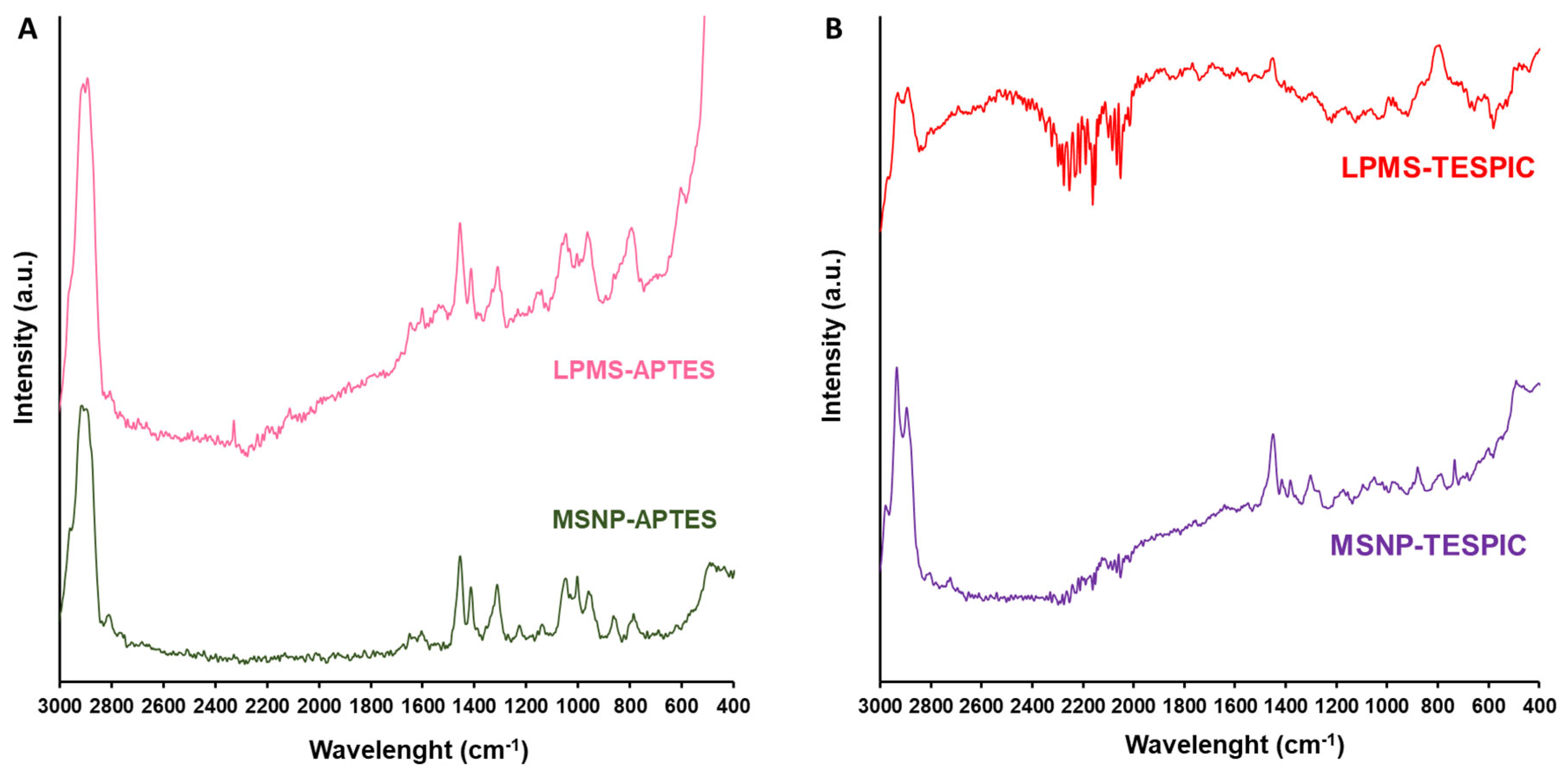
2.1. Characterisation of the Materials
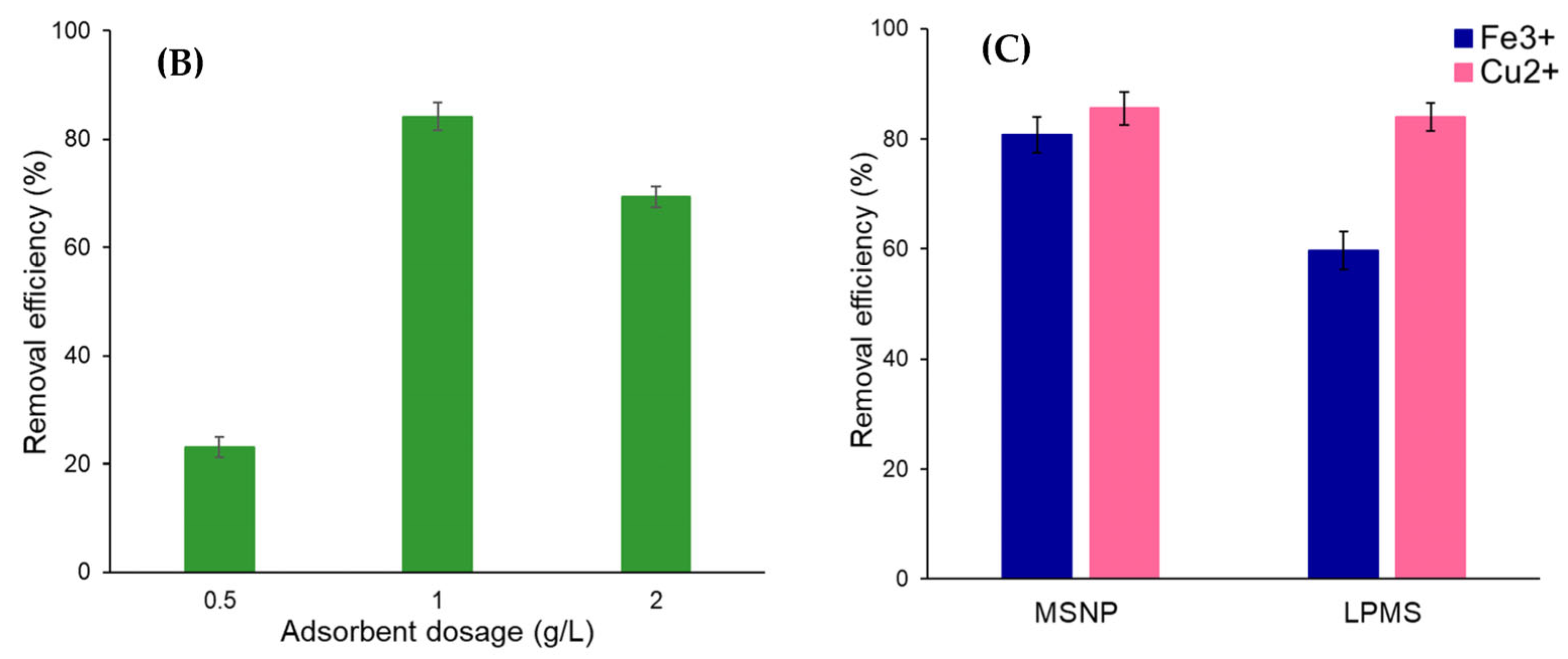
2.2. Metal Ions Adsorption Studies
2.3. Dye Adsorption Studies
2.3.1. Adsorption Kinetics
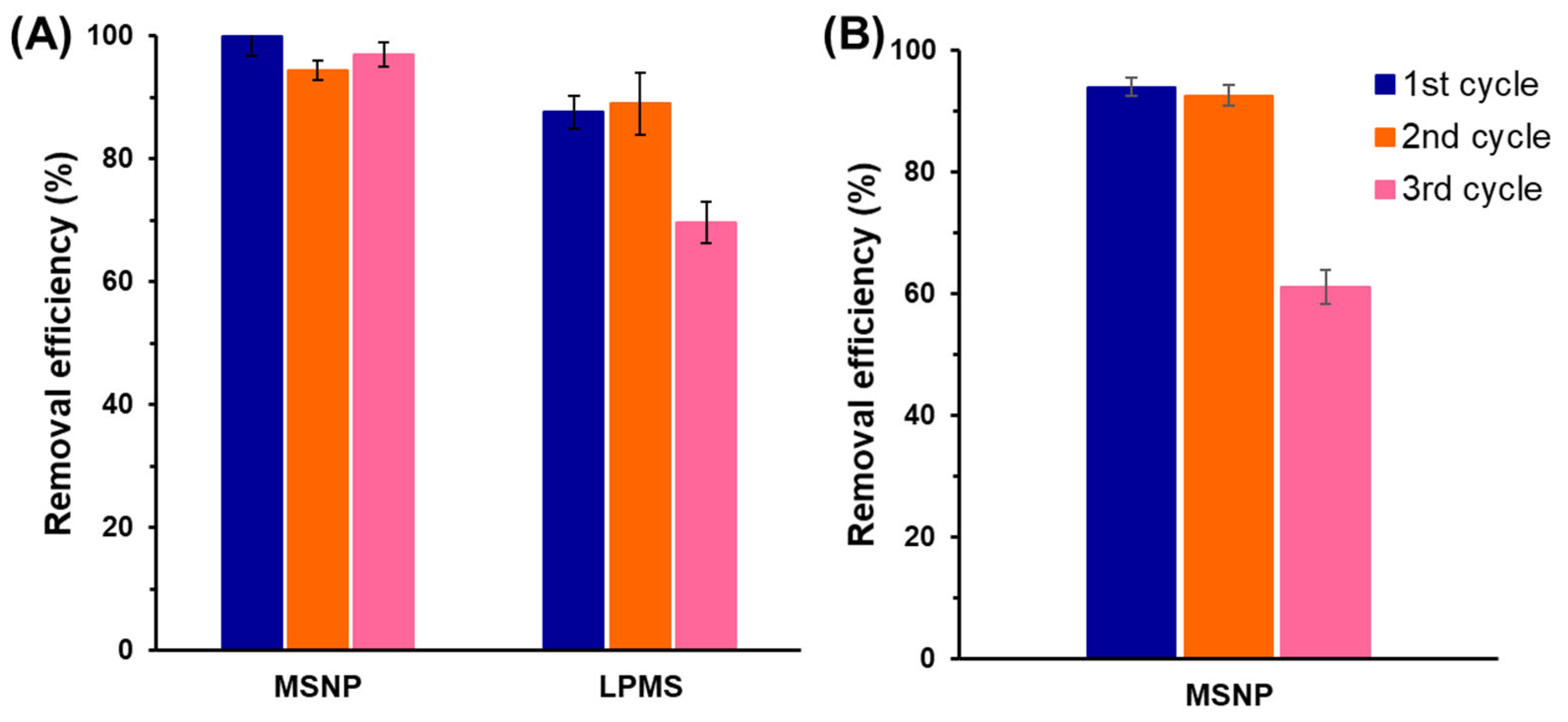
2.3.2. Recyclability and Stability of the Adsorbents
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Methods
3.2. Preparation of the Materials
3.2.1. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSNPs)
3.2.2. Large-Pore Mesoporous Silica (LPMS)
3.2.3. Functionalisation of Mesoporous Silica
3.3. Adsorption Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howarth, A.; Liu, Y.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. Metal–organic frameworks for applications in remediation of oxyanion/cation-contaminated water. CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 7245–7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-sayed, M.E.A. Nanoadsorbents for water and wastewater remediation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Xu, J.; Bu, X.-H. Recent advances about metal–organic frameworks in the removal of pollutants from wastewater. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 378, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Pan, X.; Fang, Z.; Li, J.; Bryan, B.A. Bryan, Future global urban water scarcity and potential solutions. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Astruc, D. Nanocatalysts and other nanomaterials for water remediation from organic pollutants. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 408, 213180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, G.; Chen, H.; Hu, X.; Niu, Z.; Ma, S. Functionalized metal–organic framework as a new platform for efficient and selective removal of cadmium(ii) from aqueous solution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 15292–15298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, G.; Chen, C.; Chai, Z.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Metal–organic framework-based materials: Superior adsorbents for the capture of toxic and radioactive metal ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2322–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksoud, M.I.A.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Farrell, C.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.A.H.; Rooney, D.W.; Osman, A.I. Insight on water remediation application using magnetic nanomaterials and biosorbents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 403, 213096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Shen, Y.; Xu, L.; Xiang, G.; Ni, Z. Highly efficient and rapid adsorption of methylene blue dye onto vinyl hybrid silica nano-cross-linked nanocomposite hydrogel. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 613, 126050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radi, S.; El Abiad, C.; Carvalho, A.P.; Santos, S.M.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Moura, N.M.M. An efficient hybrid adsorbent based on silica-supported amino penta-carboxylic acid for water purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 13096–13109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, F.D.; Attia, M.F.; Whitehead, D.C.; Alexis, F. Nanotechnology for Environmental Remediation: Materials and Applications. Molecules 2018, 23, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, H.-C.; Sharma, V.K. Water-stable metal-organic frameworks for aqueous removal of heavy metals and radionuclides: A review. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Shi, Z.; Lian, M.; Li, H.; Yin, J. Mechanically strong graphene oxide/sodium alginate/polyacrylamide nanocomposite hydrogel with improved dye adsorption capacity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 7433–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiyadh, S.S.; AlSaadi, M.A.; Jaafar, W.Z.; AlOmar, M.K.; Fayaed, S.S.; Mohd, N.S.; Hin, L.S.; El-Shafie, A. Review on heavy metal adsorption processes by carbon nanotubes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-X.; Wang, K.-Z.; Li, X.-J.; Liu, D.; Ma, L.-F.; Liu, L.-L. Highly Efficient and Facile Removal of Pb2+ from Water by Using a Negatively Charged Azoxy-Functionalized Metal–Organic Framework. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 5251–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zou, J.; Han, Y.; Liao, Z.; Lu, P.; Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A.; Liu, J.; Peng, Y. Recent advances in Al(iii)/In(iii)-based MOFs for the detection of pollutants. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 19577–19592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y.; Singh, A.; Trivedi, M.; Kumar, A.; Liu, J. Metal organic frameworks as efficient adsorbents for drugs from wastewater. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Rao, C.; Tan, X.; Ling, Y.; Singh, A.; Kumar, A.; Li, B.; Liu, J. Cobalt-seamed C-methylpyrogallol[4]arene nanocapsules-derived magnetic carbon cubes as advanced adsorbent toward drug contaminant removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.; Lu, C.; Liu, D.; Pan, Y.; Sakiyama, H.; Muddassir, M.; Liu, J. A new magnetic adsorbent of eggshell-zeolitic imidazolate framework for highly efficient removal of norfloxacin. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 18016–18026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mon, M.; Bruno, R.; Ferrando-Soria, J.; Armentano, D.; Pardo, E. Metal–organic framework technologies for water remediation: Towards a sustainable ecosystem. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 4912–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Cai, Y.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Wei, J.; Li, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D. Multifunctional Mesoporous Composite Microspheres with Well-Designed Nanostructure: A Highly Integrated Catalyst System. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8466–8473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirante, F.; Gomes, N.; Branco, L.C.; Cunha-Silva, L.; Almeida, P.L.; Pillinger, M.; Gago, S.; Granadeiro, C.M.; Balula, S.S. Mesoporous nanosilica-supported polyoxomolybdate as catalysts for sustainable desulfurization. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 275, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcarius, A.; Mercier, L. Mesoporous organosilica adsorbents: Nanoengineered materials for removal of organic and inorganic pollutants. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 4478–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, H.; Guo, M.; Shi, W.; Qiu, S. Novel mesoporous silica spheres with ultra-large pore sizes and their application in protein separation. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 2013–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecilia, J.A.; Tost, R.M.; Millán, M.R. Mesoporous Materials: From Synthesis to Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Cañas, M.C.; Corredor, L.M.; Quintero, H.I.; Manrique, E.; Bohórquez, A.R. Morphological and Structural Properties of Amino-Functionalized Fumed Nanosilica and Its Comparison with Nanoparticles Obtained by Modified Stöber Method. Molecules 2020, 25, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieszczycka, K.; Filipowiak, K.; Dudzinska, P.; Nowicki, M.; Siwińska-Ciesielczyk, K.; Jesionowski, T. Novel Mesoporous Organosilicas with Task Ionic Liquids: Properties and High Adsorption Performance for Pb(II). Molecules 2022, 27, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putz, A.-M.; Ciopec, M.; Negrea, A.; Grad, O.; Ianăşi, C.; Ivankov, O.I.; Milanović, M.; Stijepović, I.; Almásy, L. Comparison of Structure and Adsorption Properties of Mesoporous Silica Functionalized with Aminopropyl Groups by the Co-Condensation and the Post Grafting Methods. Materials 2021, 14, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da’na, E. Adsorption of heavy metals on functionalized-mesoporous silica: A review. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 247, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Zhu, G.; Wang, X.; Wei, Y.; Yuan, J.; Gao, C. Preparation of amidoxime functionalized SBA-15 with platelet shape and adsorption property of U(VI). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 174, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Cheng, S.; Li, H.Y. Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cu(II) metal ions on functionalized large-pore mesoporous silica. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paula, F.D.C.; Effting, L.; Arízaga, G.G.C.; Giona, R.M.; Tessaro, A.L.; Bezerra, F.M.; Bail, A. Spherical mesoporous silica designed for the removal of methylene blue from water under strong acidic conditions. Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 2278–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirante, F.; Alves, A.C.; Julião, D.; Almeida, P.L.; Gago, S.; Valença, R.; Ribeiro, J.C.; de Castro, B.; Granadeiro, C.M.; Balula, S.S. Large-pore silica spheres as support for samarium-coordinated undecamolybdophosphate: Oxidative desulfurization of diesels. Fuel 2020, 259, 116213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, L.S.; Ribeiro, S.M.; Granadeiro, C.; Pereira, E.; Feio, G.; Cunha-Silva, L.; Balula, S.S. Novel polyoxometalate silica nano-sized spheres: Efficient catalysts for olefin oxidation and the deep desulfurization process. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 9518–9528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Yan, B. Lanthanide (Eu3+, Tb3+) Centered Hybrid Materials using Modified Functional Bridge Chemical Bonded with Silica: Molecular Design, Physical Characterization, and Photophysical Properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 10898–10907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majoul, N.; Aouida, S.; Bessaïs, B. Progress of porous silicon APTES-functionalization by FTIR investigations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 331, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarshin, S.; Moghadasi, J.; Aboosadi, Z.A. Surface functionalization of silica nanoparticles to improve the performance of water flooding in oil wet reservoirs. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2017, 35, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, S.O.; Duarte, B.; De Castro, B.; Granadeiro, C.M.; Balula, S.S. Improving the Catalytic Performance of Keggin [PW12O40]3− for Oxidative Desulfurization: Ionic Liquids versus SBA-15 Composite. Materials 2018, 11, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, V.; Biju, S.; Varma, R.L.; Reddy, M.L.P. Highly efficient visible light sensitized red emission from europium tris[1-(4-biphenoyl)-3-(2-fluoroyl)propanedione](1,10-phenanthroline) complex grafted on silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 5220–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchoucha, M.; Côté, M.-F.; Gaudreault, R.C.; Fortin, M.-A.; Kleitz, F. Size-Controlled Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Tunable Drug Release and Enhanced Anti-Tumoral Activity. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 4243–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, J.; Elouear, Z.; Ksibi, M.; Feki, M.; Montiel, A. A study on removal characteristics of copper from aqueous solution by sewage sludge and pomace ashes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.-Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Pan, N. Design and thermal insulation performance analysis of endothermic opacifiers doped silica aerogels. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 145, 105995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talreja, K.; Chauhan, I.; Ghosh, A.; Majumdar, A.; Butola, B.S. Functionalization of silica particles to tune the impact resistance of shear thickening fluid treated aramid fabrics. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 49787–49794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, L.; Illés, E.; Tombácz, E.; Dzhardimalieva, G.; Golubeva, N.; Tushavina, O.; Adachi, Y.; Kydralieva, K. Fabrication, Microstructure and Colloidal Stability of Humic Acids Loaded Fe3O4/APTES Nanosorbents for Environmental Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filote, C.; Volf, I.; Santos, S.C.R.; Botelho, C.M.S. Bioadsorptive removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by the biorefinery waste of Fucus spiralis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funakoshi, K.; Yoshizawa, S.; Matsuoka, M. Continuous Precipitation of Nickel Hydroxide by Addition of Ammonium Ions. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 1824–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, N.; Guo, X.; Liang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J. Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by chemically modified orange peel. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, G.; Kaur, A.; Umar, A.; Khan, M.A.; Algarni, H.; Kansal, S.K. Removal of fluoroquinolone drug, levofloxacin, from aqueous phase over iron based MOFs, MIL-100(Fe). J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 281, 121029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmavathy, K.S.; Madhu, G.; Haseena, P.V. A study on Effects of pH, Adsorbent Dosage, Time, Initial Concentration and Adsorption Isotherm Study for the Removal of Hexavalent Chromium (Cr (VI)) from Wastewater by Magnetite Nanoparticles. Procedia Technol. 2016, 24, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, G.T.; Gok, X.Y.; Yong, W.F. Adsorption of pollutants in wastewater via biosorbents, nanoparticles and magnetic biosorbents: A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usgodaarachchi, L.; Thambiliyagodage, C.; Wijesekera, R.; Bakker, M.G. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles derived from rice husk and surface-controlled amine functionalization for efficient adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.-S. Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Deng, Q.; Tu, W.; Dai, G.; Zeng, Z.; Deng, S. Enhanced Cr(VI) removal by polyethylenimine- and phosphorus-codoped hierarchical porous carbons. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 523, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Liu, K.; Hu, L.; Teng, F.; Yu, P.; Zhu, Y. Superior Adsorption and Regenerable Dye Adsorbent Based on Flower-Like Molybdenum Disulfide Nanostructure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robati, D. Pseudo-second-order kinetic equations for modeling adsorption systems for removal of lead ions using multi-walled carbon nanotube. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2013, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.H.; Ahmad, A.L.; Latiff, K.N.A. Adsorption of basic dye (methylene blue) onto activated carbon prepared from rattan sawdust. Dye. Pigment. 2007, 75, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrah, A.; Farhadi, S. K6P2W18O62 encapsulated into magnetic Fe3O4/MIL-101 (Cr) metal–organic framework: A novel magnetically recoverable nanoporous adsorbent for ultrafast treatment of aqueous organic pollutants solutions. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 37976–37992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, S.K.; Liu, L. Fabrication of a Nanoporous Silica Hydrogel by Cross-Linking of SiO2–H3BO3–Hexadecyltrimethoxysilane for Excellent Adsorption of Azo Dyes from Wastewater. Langmuir 2021, 37, 8753–8764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almethen, A.A.; Alotaibi, K.M.; Alhumud, H.S.; Alswieleh, A.M. Highly Efficient and Rapid Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution Using Folic Acid-Conjugated Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Processes 2022, 10, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Niu, J.; Yang, H.; Tian, S.; Zhu, J.; Lu, M. Highly Efficient, Rapid, and Simultaneous Removal of Cationic Dyes from Aqueous Solution Using Monodispersed Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as the Adsorbent. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, M.; Dinari, M. Synthesis of new imine-linked covalent organic framework as high efficient absorbent and monitoring the removal of direct fast scarlet 4BS textile dye based on mobile phone colorimetric platform. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, N.; Afshari, M.; Dinari, M. Synthesis and characterization of a novel fluorene-based covalent triazine framework as a chemical adsorbent for highly efficient dye removal. Polymer 2020, 195, 122430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, R.; Zhang, C.; Xia, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Luo, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, C. Efficient adsorption of methylene blue by mesoporous silica prepared using sol-gel method employing hydroxyethyl cellulose as a template. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 606, 125425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Tang, Z.; Liu, P. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution with silica nano-sheets derived from vermiculite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, A.G.; Matos, L.C.; Manrique, Y.A.; Loureiro, J.M.; Mendes, A.; Ferreira, A.F.P. Adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes into shaped MCM-41. Adsorption 2020, 26, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lu, Q.; Fu, W.H.; Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Xu, N.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.M.; Chen, Z. Fabrication of mesoporous Al-SBA-15 as a methylene blue capturer via a spontaneous infiltration route. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, H. Structure directed reversible adsorption of organic dye on mesoporous silica in aqueous solution. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 97, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alardhi, S.M.; Albayati, T.M.; Alrubaye, J.M. Adsorption of the methyl green dye pollutant from aqueous solution using mesoporous materials MCM-41 in a fixed-bed column. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjomandi-Behzad, L.; Rofouei, M.K.; Badiei, A.; Ghasemi, J.B. Simultaneous removal of crystal violet and methyl green in water samples by functionalised SBA-15. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 5919–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material | Element Content (wt%) | Functional Group Content (mmol/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | N | ||
| MSNPs-APTES | 10.72 | 2.81 | 3.41 | 2.43 |
| MSNPs-TESPIC | 9.85 | 2.14 | 1.52 | 1.08 |
| LPMS-APTES | 6.10 | 1.57 | 1.90 | 1.35 |
| LPMS-TESPIC | 4.53 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.72 |
| Material | SBET (m2/g) | Vp (cm3/g) | Dp (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSNPs | 913 | 1.64 | 5.96 |
| MSNPs-APTES | 444 | 0.90 | 11.61 |
| MSNPs-TESPIC | 585 | 0.84 | 8.98 |
| LPMS | 138 | 0.75 | 16.36 |
| LPMS-APTES | 73 | 0.55 | 25.56 |
| LPMS-TESPIC | 109 | 0.64 | 19.99 |
| Material | pHPZC | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| As-Prepared | TESPIC | APTES | |
| MSNPs | 2.2 | 3.5 | 8.0 |
| LPMS | 2.1 | 4.9 | 9.2 |
| Adsorbent | Dye | qe,exp (mg g−1) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe,cal (mg g−1) | k1 (min−1) | R2 | qe,cal (mg g−1) | k2 (g mg−1 min−1) | R2 | |||
| MSNPs | MB | 4.0656 | 0.0680 | 0.0138 | 0.651 | 3.9851 | 0.3253 | 0.999 |
| MSNPs | MG | 5.6316 | 0.6245 | 0.0356 | 0.849 | 5.4910 | 0.1969 | 0.999 |
| LPMS | MB | 3.3226 | 1.5473 | 0.0375 | 0.980 | 3.3914 | 0.0751 | 0.999 |
| LPMS | MG | 2.1128 | 1.3473 | 0.0198 | 0.985 | 2.1730 | 0.0410 | 0.992 |
| Adsorbent | Dye | qe (mg/g) | te (min) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silica nanosheets | MB | 11.77 | 90 | [65] |
| MCM-41 | MB | 55.0 | 300 | [66] |
| SBA-15 | MB | 45.1 | 30 | [67] |
| MCM-41 | MB | 11.83 | 240 | [68] |
| MCM-48 | MB | 10.56 | 240 | [68] |
| MCM-41 | MG | 20.97 | 1000 | [69] |
| SBA-15-S4 | MG | 39.4 | 8 | [70] |
| MSNPs | MB | 4.07 | 20 | This work |
| MSNPs | MG | 5.63 | 20 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores, D.; Almeida, C.M.R.; Gomes, C.R.; Balula, S.S.; Granadeiro, C.M. Tailoring of Mesoporous Silica-Based Materials for Enhanced Water Pollutants Removal. Molecules 2023, 28, 4038. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104038
Flores D, Almeida CMR, Gomes CR, Balula SS, Granadeiro CM. Tailoring of Mesoporous Silica-Based Materials for Enhanced Water Pollutants Removal. Molecules. 2023; 28(10):4038. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104038
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores, Daniela, C. Marisa R. Almeida, Carlos R. Gomes, Salete S. Balula, and Carlos M. Granadeiro. 2023. "Tailoring of Mesoporous Silica-Based Materials for Enhanced Water Pollutants Removal" Molecules 28, no. 10: 4038. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104038
APA StyleFlores, D., Almeida, C. M. R., Gomes, C. R., Balula, S. S., & Granadeiro, C. M. (2023). Tailoring of Mesoporous Silica-Based Materials for Enhanced Water Pollutants Removal. Molecules, 28(10), 4038. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104038