The Potential of Ginkgo biloba as a Source of Biologically Active Compounds—A Review of the Recent Literature and Patents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Phytoconstituents of Plant
2.1. Terpenoids
2.2. Flavonoids
2.3. Carboxylic Acids
2.4. Lignins
2.5. Proanthocyanidins
2.6. Polyprenols
2.7. Polysaccharides
2.8. Alkylphenols and Alkylphenolic Acids
2.9. Other
3. Structure and Biosynthesis of Ginkgolides and Bilobalides
| Type of Activity | Substance | Result | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| anti-inflammatory | Ginkgolides |
| [54] |
| Extract |
| [55] | |
| Ginkgolides |
| [53] | |
| Leaf extract (EGb 761) |
| [51] | |
| Bilobalide |
| [52] | |
| Ethanol extract of flowers bilobetin isoginkgetin |
| [50] | |
| Ginkgolide B |
| [48] | |
| Amentoflavone |
| [57] | |
| GBSP3a (water-soluble polysaccharide) |
| [104] | |
| Ginkgolide A |
| [47] | |
| Extract EGb 761 |
| [10] | |
| Ginkgolide A |
| [46] | |
| Leaf extract (IGbE-761®) |
| [45] | |
| Ginkgo biloba leaf polysaccharides (PGBL) |
| [44] | |
| Ginkgolide A |
| [46] | |
| anti-bacterial | Leaf extract (GLE) |
| [73] |
| Leaf extract (GLE) |
| [63] | |
| Water extract Chloroform extract Methanol extract |
| [62] | |
| Ethanol extract of leaves |
| [64] | |
| Gelatin film with the addition of ginkgo extract (GBE) |
| [67] | |
| Ginkgetin |
| [117] | |
| Ginkgetin |
| [58] | |
| Leaf extracts (GLE) |
| [66] | |
| Amentoflavone |
| [57] | |
| Ginkgolic acid (GA) C15:1 monomer |
| [60] | |
| Polyprenol (GBP) |
| [61] | |
| Antioxidant | supernatant obtained after mixing the fermented seed powder and saline |
| [94] |
| hydroethanolic leaf extract and ingredients: flavone, ginkgolide, procyanidins, and organic acids |
| [21] | |
| Leaf extract (EGb 761) |
| [74] | |
| Ethanol extracts |
| [64] | |
| Leaf extract (EGb 761) |
| [51] | |
| Ethanol extract |
| [73] | |
| extract (GBE) |
| [67] | |
| Polysaccharides GBPS-2 and GBPS-3 |
| [72] | |
| ginkgo biloba (10 mg/kg/day) |
| [73] | |
| methanol extract from leaves ethanol (40%, 70% and 96% v/v) extracts from leaves |
| [70] | |
| polysaccharide monomers |
| [56] | |
| extract EGb 761 |
| [69] | |
| Anti-cancer | bilobol isolated from fruit |
| [87] |
| Ginkgetin (extract) |
| [83] | |
| Methanol extract from kernel |
| [82] | |
| Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb-761) |
| [81] | |
Substances isolated from fresh male flowers:
|
| [86] | |
| Ginkgolide B |
| [86] | |
| Leaf extract IDN 5933 |
| [80] | |
| Amentoflavone |
| [57] | |
| Methanolic extract from leaves |
| [79] | |
| Polysaccharide isolated from leaves (Se-GBLP) |
| [13] | |
| Extract EGb 761 |
| [78] | |
| Ginkgolide B (GB) |
| [85] | |
| Extract EGb 761 |
| [76] | |
| Extract EGb 761 |
| [77] | |
| Ginkgolide B (GKB) |
| [84] | |
| Extract EGb 761 |
| [35] | |
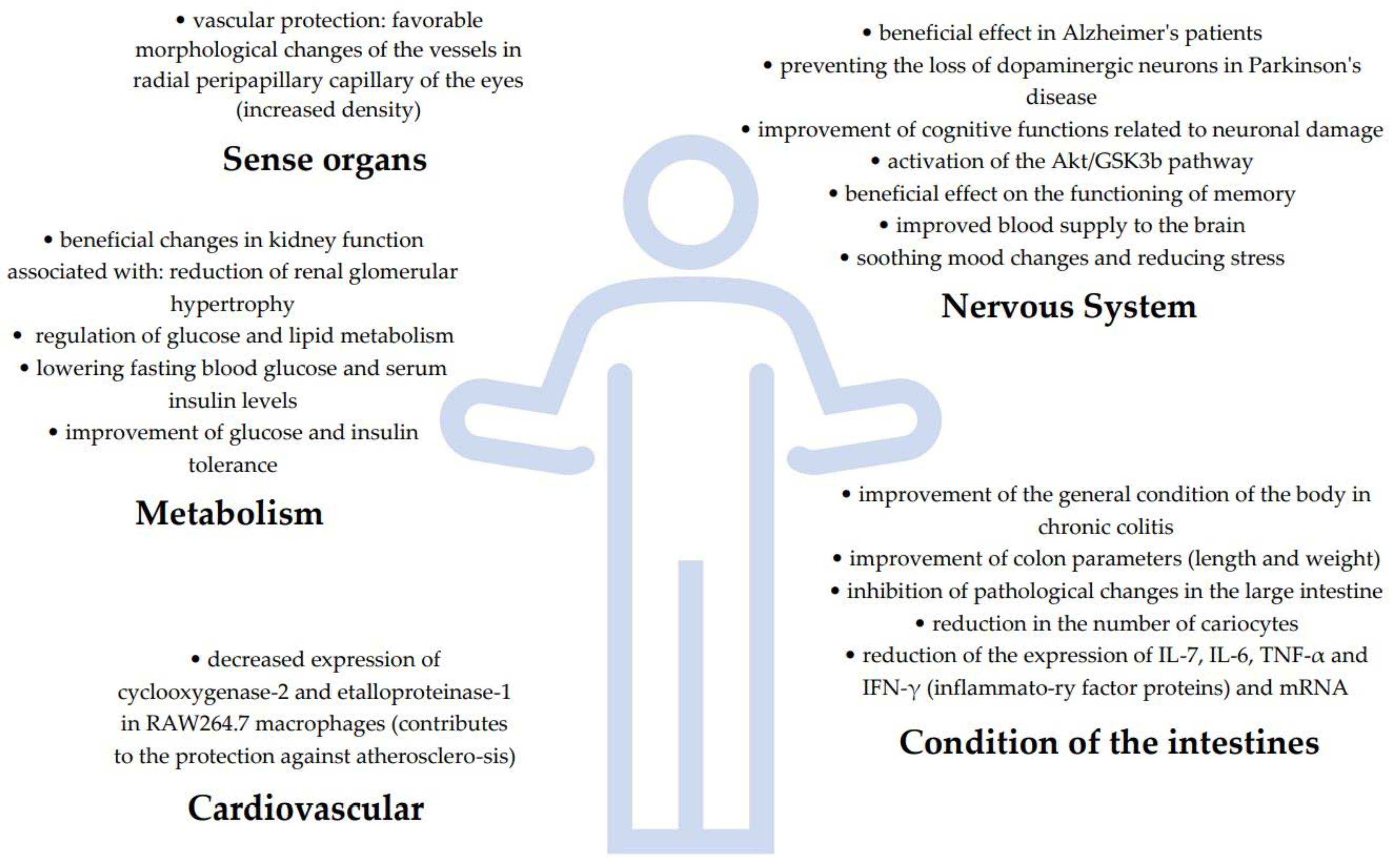
| Anti-obesity, anti-atherogenic and anti-diabetic | Leave extract (GbE) |
| [65] |
| Extract GbE |
| [90] | |
| Extract (GbE) |
| [55] | |
| Ginkgo biloba seeds (GBS) |
| [91] | |
| vinegar obtained from fermented coats of ginkgo seeds |
| [97] | |
| Extract GbE |
| [96] | |
| Extract GbE |
| [89] | |
| Ginkgo biloba leaves |
| [93] | |
| Ginkgolide B |
| [48] | |
| Ginkgolide C |
| [95] | |
| Ginkgo biloba leaves |
| [71] | |
| Ginkgolide B |
| [74] | |
| Extract GbE |
| [88] | |
| Neuroprotective and anti-neurodegenerative | Extract EGb |
| [106] |
| Extract EGb 761 |
| [103] | |
| Ginkgo biloba dropping pill (GBDP) Extract EGb 761 |
| [104] | |
| Extract EGb 761 |
| [74] | |
| Extracts (GB, EGb 761) Tablets |
| [105] | |
| Extract EGb 761 |
| [102] | |
| Ginkgolides |
| [53] | |
| Extract EGb |
| [3] | |
| Extract EGb 761 |
| [101] | |
| Extract EGb 761 |
| [98,100] | |
| Extract EGb 761 |
| [99] | |
| Protection of sense organs | GBE capsule (120 mg: 27% flavone glycosides + 6.8% terpene lactones from ginkgo) |
| [109] |
| Ginkgo leaf tablets |
| [107] | |
| Extract EGb 761 |
| [108] | |
| Cardiovascular protection | Ginkgolide B |
| [48] |
4. Pharmacological Activities
4.1. Anti-Inflammatory Effect
4.2. Anti-Microbial Activity
4.3. Antioxidant Activity
4.4. Antitumor Activity
4.5. Anti-Obesity, Anti-Atherogenic and Anti-Diabetic
4.6. Neuroprotective and Anti-Neurodegenerative
4.7. Protection of Other Organs
5. Toxicity
6. Interactions of Ginkgo biloba Extracts with Drugs
7. Patents
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Fu, C.; Wu, Z.; Xu, H.; Liu, H.; Schneider, H.; Lin, J. Ginkgo Biloba. Trends Genet. 2021, 37, 488–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Li, W.-H.; Lin, C.-F.; Wu, G.-R.; Zhao, Y.-P. International Biological Flora: Ginkgo biloba. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 951–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ye, M.; Guo, H. An Updated Review of Randomized Clinical Trials Testing the Improvement of Cognitive Function of Ginkgo biloba Extract in Healthy People and Alzheimer’s Patients. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhu, B.; Wang, R.; Cheng, Y. A strategy for identifying effective and risk compounds of botanical drugs with LC-QTOF-MS and network analysis: A case study of Ginkgo biloba preparation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 193, 113759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toghueo, R.M.K. Endophytes from Gingko biloba: The current status. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 743–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, I.D. A critical review of ginkgolic acids in Ginkgo biloba leaf extract (EGb): Toxicity and technologies to remove ginkgolic acids and their promising bioactivities. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 9226–9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S. Advances in the chemical constituents and chemical analysis of Ginkgo biloba leaf, extract, and phytopharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 193, 113704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Chio, C.; Ma, T.; Kognou, A.L.M.; Shrestha, S.; Chen, F.; Qin, W. Extracting flavonoid from Ginkgo biloba using lignocellulolytic bacteria Paenarthrobacter sp. and optimized via response surface methodology. Biotechnol. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 15, 867–878. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, P.; Sun, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Lou, Y.; Ju, Z.; Wei, X.; Wu, W.; Sun, N. Chemical constituents from Ginkgo biloba leaves and their cytotoxicity activity. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 74, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.-L.; Lin, S.; Wu, Q.-L.; Su, R.-X.; Wu, Z.-L.; Dong, H.-Y.; Li, H.-L.; Zhang, W.-D. A new bilobalide isomer and two cis-coumaroylated flavonol glycosides from Ginkgo biloba leaves. Fitoterapia 2020, 142, 104516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, N.-E.; Das, R.; Lami, M.S.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Mitra, S.; Tallei, T.E.; Idroes, R.; Mogamed, A.A.-R.; Hossain, J.; Dhama, K.; et al. Ginkgo biloba: A Treasure of Functional Phytochemicals with Multimedicinal Applications. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 8288818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisz, O.; Wolski, T.; Gerkowicz, M. Terapia zaburzeń krążenia obwodowego i mózgowego przy użyciu preparatów z miłorzębu dwuklapowego (Ginkgo biloba). Postępy Fitoter. 2005, 3–4, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Sun, S.; Cai, D.; Kong, G. Induction of mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in T24 cells by a selenium (Se)-containing polysaccharide from Ginkgo biloba L. leaves. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFeudis, F.V.; Papadopoulos, V.; Drieu, K. Ginkgo biloba extracts and cancer: A research area in its infancy. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 17, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Li, Y.; Chu, L.; Kuanhg, X.; Song, J.; Sun, C. Full-length sequencing of ginkgo transcriptomes for an in-depth understanding of flavonoid and terpenoid trilactone biosynthesis. Gene 2020, 758, 144961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, B.; Mau, X.; Lu, J.; Jin, B.; Wang, L. Liquid profiling in plants: Identification and analysis of extracellular metabolites and miRNAs in pollination drops of Ginkgo biloba. Tress Physiol. 2020, 40, 1420–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Cao, F.; Ma, G.; Su, E. Tailor-Made Deep Eutectic Solvents for Simultaneous Extraction of Five Aromatic Acids from Ginkgo biloba Leaves. Molecules 2018, 23, 3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gong, X.; Qu, H. Near-infrared spectroscopy and HPLC combined with chemometrics for comprehensive evaluation of six organic acids in Ginkgo biloba leaf extract. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2022, 74, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Ke, Z.; Xu, W.; Sun, L.; Ma, A.-C. A strategy for quality control of ginkgo biloba preparations based on UPLC fingerprint analysis and multi-component separation combined with quantitative analysis. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Chemical characterization of Ginkgo biloba L. and antioxidant properties of its extracts and dietary supplements. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 51, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, C.; Liu, X.; Su, E.; Cau, F.; Zhao, L. Study on Synergistic Antioxidant Effect of Typical Functional Components of Hydroethanolic Leaf Extract from Ginkgo Biloba In Vitro. Molecules 2022, 27, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Chen, H.; Zhao, H.; Wu, W.; Jin, Y. Structural features and antioxidant behavior of lignins successively extracted from ginkgo shells (Ginkgo biloba L). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulić, Ž.; Ritter, T.; Röck, B.; Elsäßer, J.; Schneider, H.; Germen, S. A Detailed View on the Proanthocyanidins in Ginkgo Extract EGb 761. Nat. Prod. Chem. Anal. Stud. 2022, 88, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boateng, I.D.; Yang, X.-M. Effect of different drying methods on product quality, bioactive and toxic components of Ginkgo biloba L. seed. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 3290–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.H.-W.; Li, M.-F.; Qi, Z.W.; Tao, R.; Ye, J.-Z.; Xue, X.-Y.; Wang, C.H.-Z. The construction of a green and efficient system for the separation of polyprenols from Ginkgo biloba leaves. Process Biochem. 2021, 100, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H.-W.; Wang, C.H.-Z.; Tao, R.; Ye, J.-Z. Separation of polyprenols from Ginkgo biloba leaves by a nano silica-based adsorbent containing silver ions. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1590, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, M. Extraction, structure and bioactivities of the polysaccharides from Ginkgo biloba: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, G.-Y.; Xu, J.-P.; Liu, J.-A.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Tan, Y. Research progress on polysaccharides from Ginkgo biloba. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, G.; Yu, W.; Cui, Q.; Lu, X.; Du, P.; An, L. Hair-growth promoting effect and anti-inflammatory mechanism of Ginkgo biloba polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, G.; Mohan, B.; Kishor, K.; Tewari, L.M.; Nailwal, T.K. Volatile constituents of Ginkgo biloba L. leaves from Kumaun: A source of (E)-nerolidol and phytol. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2015, 92, 1583–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Nwosu, O.; Okaka, A.N.C.; Ubaoji, K.I. Evaluation of Nutritional and Anti-nutritional Compositions of Leaves of (Maiden Hair) Tree Found in Nigeria. J. Exp. Res. 2018, 6, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Tomowa, T.; Slavova, I.; Tomov, D.; Kirova, G.; Argirova, M.D. Ginkgo biloba Seeds—An Environmental Pollutant or a Functional Food. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ChemSpider Search and Share Chemistry. Available online: http://www.chemspider.com/ (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Sarkar, C.; Quispe, C.; Jamaddar, S.; Hossain, R.; Ray, P.; Mondal, M.; Mohamed, Z.A.; Sani, M.; Salehi, B.; Islam, M.T.; et al. Therapeutic promises of ginkgolide A: A literature-based review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xiong, S.; Liu, P.; Liu, W.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tan, H.; Chen, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; et al. Polymeric Nanoparticles-Based Brain Delivery with Improved Therapeutic Efficacy of Ginkgolide B in Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 10453–10467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.H.; Baek, S.H.; Um, J.-Y.; Ahn, K.S. Anti-neoplastic Effect of Ginkgolide C through Modulating c-Met Phosphorylation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolshakov, S.; Dzyuba, S.V.; Decatur, J.; Nakanishi, K. A Concise Synthesis of Ginkgolide M, a Minor Component of a Terpene Trilactone Fraction from Ginkgo biloba Roots. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitolo, O.; Gong, B.; Cao, Z.; Ishii, H.; Jaracz, S.; Nakanishi, K.; Arancio, O.; Dzyuba, S.V.; Lefort, R.; Shelanski, M. Protection against β-amyloid induced abnormal synaptic function and cell death by Ginkgolide J. Neurobiol. Aging 2009, 30, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.-J.; Zheng, Y.-F.; Li, H.-Y.; Peng, G.-P. Two New Ginkgolides from the Leaves of Ginkgo biloba. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1818–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zou, W.; Chen, M.; Cao, L.; Ding, J.; Xiao, W.; Hu, G. Ginkgolide K promotes angiogenesis in a middle cerebral artery occlusion mouse model via activating JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 833, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Chai, Z.; Song, L.-J.; Wang, Q.; Song, G.-B.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.-Z.; Xiao, B.-G.; Ma, C.G. The neuroprotective effects and transdifferentiation of astrocytes into dopaminergic neurons of Ginkgolide K on Parkinson’ disease mice. J. Neuroimmunol. 2022, 364, 577806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-X.; Liu, X.-G.; Gan, Z.-Y.; Dong, X.; Lou, F.-C.; Li, P.; Yang, H. Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution study of ginkgolide L in rats by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 1006, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X. Transport of ginkgolides with different lipophilicities based on an hCMEC/D3 cell monolayer as a blood–brain barrier cell model. Life Sci. 2014, 114, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.D.; Zhang, L.H.; Zhang, X.T.; Fang, C.S.; Ma, J.R. Protective Effects of Ginkgolide N Against Glutamate-Induced Injury in PC12 Cells. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2015, 38, 1694–1698. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Xie, L.; Liu, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Dai, X.; Liang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, X. Bilobalide: A review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, toxicity, and safety. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 6114–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PubChem. National Center for Biotechnology Information. USA: National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Salehi, G.; Machin, L.; Monzote, L.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Ezzat, S.M.; Salem, M.A.; Merghany, R.M.; El Mahdy, N.M.; Kılıç, C.S.; Sytar, O.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin: New Insights and Perspectives for Human Health. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 11849–11872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Y.-L.; Zhou, H.-F.; Yang, J.; Wang, F.-X.; Dun, F.; Li, J.-Y. Biological Activities Underlying the Therapeutic Effect of Quercetin on Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 5665778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, K.P.; Malar, D.S.; Nabavi, S.F.; Sureda, A.; Xiao, J.; Nabavi, S.M.; Daglia, M. Kaempferol and inflammation: From chemistry to medicine. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, W.; Khan, H.; Shah, M.A.; Cauli, O.; Saso, L. Kaempferol as a Dietary Anti-Inflammatory Agent: Current Therapeutic Standing. Molecules 2020, 25, 4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, G.; Guan, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Ragman, K.; Wang, S.-J.; Zhou, S.; Luan, X.; Zhang, H. Isorhamnetin: A review of pharmacological effects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semwal, D.K.; Semwal, R.B.; Combrinck, S.; Viljoen, A. Myricetin: A Dietary Molecule with Diverse Biological Activities. Nutriens 2016, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Venditti, A.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Kręgiel, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B.; Novellino, E.; et al. The Therapeutic Potential of Apigenin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Ahi, R.; Wang, X.; Shen, H.-M. Luteolin, a Flavonoid with Potential for Cancer Prevention and Therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2008, 8, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Sun, Y.-W.; Ji, J.; Gan, L.; Zhang, C.-F.; Wang, C.-Z.; Yuan, C.-S. Genkwanin ameliorates adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats through inhibiting JAK/STAT and NF-κB signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2019, 63, 153036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, Y.-X.; Jalil, J.; Lam, K.-W.; Husain, K.; Premakumar, C.M. Genistein: A Review on its Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, M.; Basavaraj, B.V.; Murthy, K.N.C. Biological functions of epicatechin: Plant cell to human cell health. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 52, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idemura, M. Catechin in Human Health and Disease. Molecules 2019, 24, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, S.; Maqsood, M.; Mahtab, N.; Khan, M.I.; Sahar, A.; Zaib, S.; Gul, S. Epigallocatechin gallate: Phytochemistry, bioavailability, utilization challenges, and strategies. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carloth. Available online: https://www.carlroth.com (accessed on 14 March 2023).
- Park, C.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kang, K.S.; Hwang, G.S. Neuroprotective Effect of Gallocatechin Gallate on Glutamate-Induced Oxidative Stress in Hippocampal HT22 Cells. Molecules 2021, 26, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.-Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, M.F. Identification of the antiglycative components of Hong Dou Shan (Taxus chinensis) leaf tea. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Cui, M.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, P.; Ren, S.; Bao, J.; Gao, D.; Sun, R.; Wang, M.; Lin, J.; et al. Both baicalein and gallocatechin gallate effectively inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication by targeting M pro and sepsis in mice. Inflammation 2022, 45, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Li, Q.-Z.; Wang, R.-L. Flavonoid Components, Distribution, and Biological Activities in Taxus: A review. Molecules 2023, 28, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Tang, N.; Lai, X.; Zhang, J.; Wen, W.; Li, X.; Li, A.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z. Insights Into Amentoflavone: A Natural Multifunctional Biflavonoid. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 768708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-Y.; Lu, X.-Y.; Sun, J.-L.; Wang, Q.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Zhang, J.-B.; Fan, X.-H. Potential hepatic and renal toxicity induced by the biflavonoids from Ginkgo Biloba. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 17, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.K. Biological Importance of a Biflavonoid ‘Bilobetin’ in the Medicine: Medicinal Importance, Pharmacological Activities and Analytical Aspects. Infect. Disord.-Drug Targets 2022, 22, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, P.H.; Shieh, Y.D.; Hsu, L.C.; Kuo, L.M.Y.; Lin, J.H.; Liaw, C.C.; Kuo, Y.H. Naturally occurring cytotoxic [30→ 800-biflavonoidsfrom Podocarpus nakaii. J. Tradit. Compl. Med. 2012, 2, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adan, M.; Rasul, A.; Hussain, G.; Shah, M.A.; Zahoor, M.K.; Anwar, H.; Sarfraz, I.; Riaz, A.; Manzoor, M.; Adem, Ş.; et al. Ginkgetin: A natural biflavone with versatile pharmacological activities. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ding, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, M. Pharmacological Activities of Ginkgolic Acids in Relation to Autophagy. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Garg, M.; Makhija, P.; Kumar, A.P.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Zam, W.; Bishayee, A. Ginkgolic Acids Confer Potential Anticancer Effects by Targeting Pro- Inflammatory and Oncogenic Signaling Molecules. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 806–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa Leite, A.; Islam, M.T.; Paz, M.F.C.J.; Júnior, A.L.G.; da Silva Oliveira, G.L.; das Graças Lopes Cito, A.M.; de Carvalho Melo-Cavalcante, A.A.; Lopes, J.A.D. Cytogenotoxic and mutagenic profiling of cashew nut shell liquids and cardanol. Clin. Phytoscience 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, B.U.C.; Meza, A.; Beatriz, A.; Pesarini, J.R.; de Carvalho, P.C.; de Oliveira Mauro, M.; Karaziack, C.B.; Cunha-Laura, A.L.; Monreal, A.C.D.; Matuo, R.; et al. Cardanol: Toxicogenetic assessment and its effects when combined with cyclophosphamide. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2016, 39, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satooka, H.; Kubo, I. Prooxidative effect of cardols is involved in their cytotoxic activity against murine B16-F10 melanoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 609, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kustiawan, P.M.; Lirdprapamongkol, K.; Palaga, T.; Puthong, S.; Phuwapraisirisan, P.; Svasti, J.; Chanchao, C. Molecular mechanism of cardol, isolated from Trigona incisa stingless bee propolis, induced apoptosis in the SW620 human colorectal cancer cell line. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, B.; Gültekin-Özgüven, M.; Kırkın, C.; Özçelik, B.; Morais-Braga, M.F.B.; Carneiro, J.N.P.; Bezerra, C.F.; da Silva, T.G.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Amina, B.; et al. Anacardium Plants: Chemical, Nutritional Composition and Biotechnological Applications. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.O.; Bezerra, T.T.; Lima, N.M.A.; Sousa, A.F.; Trevisan, M.T.S.; Ribeiro, V.G.P.; Lomonaco, D.; Mazzetto, S.E. Cardol-Derived Organophosphorothioates as Inhibitors of Acetylcholinesterase for Dengue Vector Control. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 2634–2641. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Tai, Y.; Achanta, S.; Kaelberer, M.M.; Caceres, A.I.; Shao, X.; Fang, J.; Jordt, S.-E. IL-33/ST2 signaling excites sensory neurons and mediates itch response in a mouse model of poison ivy contact allergy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7572–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; He, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, S.; Cui, Z. Polyphenol-Enriched Extract of Lacquer Sap Used as a Dentine Primer with Benefits of Improving Collagen Cross-Linking and Antibacterial Functions. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 3741–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Qi, Z.; Xue, X.; Wang, C. Novel pH-Sensitive Urushiol-Loaded Polymeric Micelles for Enhanced Anticancer Activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 3851–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, T.A.; El Dib, R.A.; Al-Youssef, H.M.; Amina, M. Chemical composition and antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of Antidesm abunius L. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 32, 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, C.K.; Majid, N.I.; Yusof, H.M.; Zainol, K.M.; Mohamad, H.; Zin, Z.M. Catechin profile and hypolipidemic activity of Morinda citrifolia leaf water extract. Helion 2020, 6, e04337. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; He, Y.; Luo, C.; Feng, B.; Ran, F.; Xu, H.; Ci, Z.; Xu, R.; Han, L.; Zhang, D. New progress in the pharmacology of protocatechuic acid: A compound ingested in daily foods and herbs frequently and heavily. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 161, 105109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, M.G.; Carabin, I.G.; Burdock, G.A. Safety assessment of esters of p-hydroxybenzoic acid (parabens). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 985–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemini, C.; Silva, G.; Timossi, C.; Luque, D.; Valverde, A.; González Martínez, M.; Hernández, A.; Rubio Póo, C.; Chávez Lara, B.; Valenzuela, F. Estrogenic effects of p-hydroxybenzoic acid in CD1 mice. Environ. Res. 1997, 75, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugazhendhi, D.; Pope, G.S.; Darbre, P.D. Oestrogenic activity of p-hydroxybenzoic acid (common metabolite of paraben esters) and methylparaben in human breast cancer cell lines. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2005, 25, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksana, S.; Marian, B.; Mahendra, R.; Hong Bo, S. Plant phenolic compounds for food, pharmaceutical and cosmetics production. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 2526–2539. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Ma, L.; Li, J.; Shahzad, N.; Kim, C.K. Structure-antioxidant activity relationship of methoxy, phenolic hydroxyl, and carboxylic acid groups of phenolic acids. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-H.; Kim, S. In Vitro Antithrombotic, Hematological Toxicity, and Inhibitor Studies of Protocatechuic, Isovanillic, and p-Hydroxybenzoic Acids from Maclura tricuspidata (Carr.) Bur. Molecules 2022, 27, 3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.C.; Panchal, S.S. Safety Assessment of Vanillic Acid: Subacute Oral Toxicity Studies in Wistar Rats. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 17, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwini, S.I.; Megha, P.K.; Aishwarya, P.D.; Shital, M.K.; Piyusha, R.M.; Vaishali, D.T.; Om, R.L.; Aniket, P.N.; Yash, V.K.; Shatrughna, U.N.; et al. A Review of the Pharmacological Characteristics of Vanillic Acid. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2021, 11, 200–204. [Google Scholar]
- Istifli, E.S.; Sihoglu-Tepe, A.; Sarikurkcu, C.; Tepe, B. Molecular interactions of some phenolics with 2019-nCoV and related pathway elements. Int. J. Second. Metab. 2021, 8, 246–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.D.; Ahumada, M.C.; Saenz, M.T. Cytostatic Activity of Some Phenolic Acids of Scrophularia frutescens L. var. frutescens. Z. Für Nat. C 1998, 53, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, C.; Hou, Y.; Ai, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, X. Gallic acid: Pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms involved in inflammation-related diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiliç, I.; Yeşiloğlu, Y. Spectroscopic studies on the antioxidant activity of p-coumaric acid. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 115, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Ahmed, S.; Elasbali, A.M.; Adnan, M.; Alam, S.; Hassan, M.I.; Pasupuleti, V.R. Therapeutic Implications of Caffeic Acid in Cancer and Neurological Diseases. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 860508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Qiu, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, X.; Shao, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Reproductive and developmental toxicity study of caffeic acid in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 123, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandi, A.; Kalappan, V.M. Pharmacological and therapeutic applications of Sinapic acid—An updated review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 3733–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Rui, Y.-X.; Guo, S.D.; Luan, F.; Liu, R.; Zeng, N. Ferulic acid: A review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and derivatives. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Tian, Z.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, X. Chlorogenic acid: A comprehensive review of the dietary sources, processing effects, bioavailability, beneficial properties, mechanisms of action, and future directions. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3130–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gorkom, G.N.Y.; Lookermans, E.L.; Van Elssen, C.H.M.J.; Bos, G.M.J. The Effect of Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) in the Treatment of Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benali, T.; Bakrim, S.; Ghchime, R.; Benkhaira, N.; El Omari, N.; Balahbib, A.; Hasan, M.M.; Bibi, S.; Bouyahya, A. Pharmacological insights into the multifaceted biological properties of quinic acid. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2022, 19, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batory, M.; Rotsztejn, H. Shikimic acid in the light of current knowledge. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalibalta, S.; Majdalawieh, A.F.; Manjikian, H. Health benefits of sesamin on cardiovascular disease and its associated risk factors. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 1276–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Liang, J.; Qu, W. A new lignan from the roots of Ginkgo biloba. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2015, 51, 819–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Kwon, H.; Cho, E.; Jeon, J.; Kang, R.H.; Youn, K.; Jun, M.; Lee, Y.-C.; Ryu, J.-H.; Kim, D.-H. The effects of pinoresinol on cholinergic dysfunction-induced memory impairments and synaptic plasticity in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogungbe, I.V.; Crouch, R.A.; Demeritte, T. (−) Arctigenin and (+) Pinoresinol Are Antagonists of the Human Thyroid Hormone Receptor β. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 3051–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fini, L.; Hotchkiss, E.; Fogliano, V.; Graziani, G.; Romano, M.; De Vol, E.B.; Qin, H.; Selgrad, M. Chemopreventive properties of pinoresinol-rich olive oil involve a selective activation of the ATM-p53 cascade in colon cancer cell lines. Carcinogenesis 2014, 29, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikul, A.; Damsud, T.; Kataoka, K.; Phuwapraisirisan, P. (+)-Pinoresinol is a putative hypoglycemic agent in defatted sesame (Sesamum indicum) seeds though inhibiting α-glucosidase. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 5215–5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoi, Y.J.; Alishir, A.; Jang, T.; Kang, K.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.H. Antiskin Aging Effects of Indole Alkaloid N-Glycoside from Ginkgo Fruit (Ginkgo biloba fruit) on TNF-α-Exposed Human Dermal Fibroblasts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13651–13660. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Hydroquinone Health and Safety Guide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996; Volume 101, ISBN 92-4-151101.
- Chandra, M.; Levitt, J.; Pensabene, C.A. Hydroquinone Therapy for Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation Secondary to Acne: Not Just Prescribable by Dermatologists. Acta Derm Venereol. 2012, 92, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpofana, N.; Chibi, B.; Visser, T.; Paulse, M.; Finlayson, A.J.; Ghuman, S.; Gqaleni, N.; Hussein, A.A.; Dlova, N.C. Treatment of Melasma on Darker Skin Types: A Scoping Review. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hébert, M. Total Synthesis of (±)-Ginkgolide C and Formal Syntheses of (±)-Ginkgolide A and (±)-Ginkgolide B. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Major, R.T. The Ginkgo, the Most Ancient Living Tree: The resistance of Ginkgo biloba L. to pests accounts in part for the longevity of this species. Science 1967, 157, 1270–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Zhu, J.; Chen, L.; Wen, W.; Yu, R. Biosynthesis pathways of ginkgolides. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2013, 7, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Deng, Y.A. Ginkgetin in vitro and in vivo reduces Streptococcus suis virulence by inhibiting suilysin activity. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 1556–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Lin, L.; Li, G.; Ma, J.; Han, X.; Fei, R. PGBL inhibits the RAW 264.7 cells to express inflammatory factor. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 2015, 26, 2069–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.A.; Albaradie, R.S. Immunomodulation of Inflammatory Markers in Activated Macrophages by Leaf Extracts of Gingko Biloba. Adv. Neuroimmune Biol. 2015, 6, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Gao, C.; Cui, Z. Ginkgolide A reduces inflammatory response in high-glucose-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells through STAT3-mediated pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 25, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhaocheng, J.; Jinfeng, L.; Luchang, Y.; Yequan, S.; Feng, L.; Kai, W. Ginkgolide A inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in human coronary artery endothelial cells via downregulation of TLR4-NF-κB signaling through PI3K/Akt pathway. Pharmazie 2016, 71, 588–591. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yao, X.; Hao, F.; Yu, C.; Bao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Song, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, L.; et al. Ginkgolide A Ameliorates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses In Vitro and In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ansari, I.A.; Khan, M.S.; Han, S.; Feng, Y. Ginkgolide B ameliorates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced endothelial dysfunction via modulating Lectin-like ox-LDL-receptor-1 and NADPH oxidase 4 expression and inflammatory cascades. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2417–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.Q.; Li, L.; Xu, M.C.; Hu, H.H.; Zhou, H.; Yu, L.S.; Zeng, S. The metabolism and hepatotoxicity of ginkgolic acid (17:1) in vitro. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, B.; Hou, Y.; Tian, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, N.; Dong, J. Anti-inflammatory effects of chemical components from Ginkgo biloba L. male flowers on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, G.A.; de Marqui, S.V.; Matias, J.N.; Guiguer, E.L.; Barbalho, S.M. Effects of Ginkgo biloba on Diseases Related to Oxidative Stress. Planta Med. 2020, 86, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, N.; Yang, Z.; Fang, X.; Yang, X.; Li, H.; Hong, Z.; Ji, Z. Bilobalide Alleviated Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Experimental Colitis by Inhibiting M1 Macrophage Polarization Through the NF-kB Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, K.; Liu, S.; Aerqin, Q.; Wu, X. Role of Ginkgolides in The Inflammatory Immune Response of Neurological Diseases: A Review of Current Literatures. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, S.; Aerqin, Q.; Shen, D.; Wu, X.; Liu, K. The therapeutic effects of ginkgolides in Guillain-Barré syndrome and experimental autoimmune neuritis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 87, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.-T.; Chen, Y.-A.; Li, S.-Y.; Chen, J.-W. Nrf-2 mediated heme oxygenase-1 activation contributes to the anti-inflammatory and renal protective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract in diabetic nephropathy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 266, 113474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-W.; Wang, C.-Z.; Tao, R. Characterization and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides extracted from enzymatic hydrolysate of Ginkgo biloba leaves. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 41, e12352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Niu, X.; Li, G.; Deng, X.; Wang, J. Amentoflavone ameliorates Streptococcus suis-induced infection in vitro and in vivo. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01804-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ye, T.; Long, T.; Peng, X.B. Ginkgetin exerts anti-inflammatory effects on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury in a rat model via the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Wu, C.; Fan, G.; Tang, Z.; Cao, F. The antibacterial activity and mechanism of ginkgolic acid C15:1. BMC Biotechnol. 2017, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Wang, C.; Ye, J.; Zhou, H.; Chen, H. Polyprenols of Ginkgo biloba Enhance Antibacterial Activity of Five Classes of Antibiotics. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 4191938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, F.; Şahin, B.; Bülbül, A.S.; Ceylan, Y.; Kurt, E.; Tarakçı, M.F. Investigation of antimicrobial and antibiofilm effects of Ginkgo biloba L. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 13, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-K.; Choi, M.S.; Kim, J.-Y.; Yu, J.S.; Seo, J.I.; Yoo, H.H.; Kim, D.-H. Ginkgo biloba leaf extract suppresses intestinal human breast cancer resistance protein expression in mice: Correlation with gut microbiota. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ražná, K.; Sawinska, Z.; Ivanišová, E.; Vukovic, N.; Terentjeva, M.; Stričík, M.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Hlavačková, L.; Rovná, K.; Žiarovská, J.; et al. Properties of Ginkgo biloba L.: Antioxidant Characterization, Antimicrobial Activities, and Genomic MicroRNA Based Marker Fingerprints. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, D.; Yan, W.; Zhu, J.; Hao, H.; Wang, G.; Cao, L.; et al. Ginkgo biloba extract ameliorates atherosclerosis via rebalancing gut flora and microbial metabolism. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 2463–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Lan, W.; Wang, Q.; Sun, X.; Xie, J. Antibacterial mechanism of Ginkgo biloba leaf extract when applied to Shewanella putrefaciens and Saprophytic staphylococcus. Aquac. Fish. 2018, 3, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yuan, L.; Han, L.; Li, S.; Song, L. Characterization of antioxidant and antibacterial gelatin films incorporated with Ginkgo biloba extract. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 27449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sati, P.; Pandey, A.; Rawat, S.; Rani, A. Phytochemicals and antioxidants in leaf extracts of Ginkgo biloba with reference to location, seasonal variation and solvent system. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 7, 804–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Qi, Y.; Chen, T. Long-term pre-treatment of antioxidant Ginkgo biloba extract EGb-761 attenuates cerebral-ischemia-induced neuronal damage in aged mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 85, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Zielonka-Brzezicka, J.; Pechaiko, D.; Tkacz, M.; Klimowicz, A. Ocena właściwości antyoksydacyjnych liści Ginkgo biloba L. po zakończeniu wegetacji [The evaluation of the antioxidant properties of Ginkgo biloba L. leaves after the end of the growing season]. Pomeranian J. Life Sci. 2017, 63, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.A.; Assad, H.C.; Rabeea, I.S. Antihyperlipidemic, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Ginkgo Biloba in High Cholesterol Fed Rabbits. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 9, 2163–2167. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Q.; Chen, J.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, J.; Yang, S.; Ding, Z.; Dai, Q.; Ding, Z. In vitro antioxidant and immunostimulating activities of polysaccharides from Ginkgo biloba leaves. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 124, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gong, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Li, L. In vitro anti-aging activities of ginkgo biloba leaf extract and its chemical constituents. Food Sci. Technol. Camp. 2020, 40, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, Q.; Xie, S.; Wang, J.; Zuo, Z. Enhanced anti-amnestic effect of donepezil by Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) via further improvement in pro-cholinergic and antioxidative activities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 269, 113711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, M.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W.; Tang, C.; Cao, F.; Su, E. Improvement of quality of Ginkgo biloba seeds powder by solid-state fermentation with Eurotium cristatum for developing high-value ginkgo seeds products. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2022, 7, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Fang, X.-J.; Wang, C.-Y. Ginkgo biloba extract induce cell apoptosis and G0/G1 cycle arrest in gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 20977–20982. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.-Q.; Xu, C.-Y.; Qin, M.-B.; Tan, L.; Zhuge, C.-F.; Mao, Y.-B.; Lai, M.-Y.; Huang, J.-A. Ginkgo biloba extract enhances chemotherapy sensitivity and reverses chemoresistance through suppression of the KSR1-mediated ERK1/2 pathway in gastric cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2871–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Ahn, H.Y.; Kim, H.R.; Chung, K.H.; Oh, S.M. Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761-mediated inhibition of aromatase for the treatment of hormone-dependent breast cancer. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 87, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.H.; Shousha, W.G.; El-Mezayen, H.A.; El-Toumy, S.A.; Sayed, A.H.; Ramadan, A.R. Biochemical and molecular evidences for the antitumor potential of Ginkgo biloba leaves extract in rodents. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2017, 64, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonassi, S.; Prinzi, G.; Lamonaca, P.; Russo, P.; Paximadas, I.; Rasoni, G.; Rossi, R.; Ruggi, M.; Malandrino, S.; Sánchez-Flores, M.; et al. Clinical and genomic safety of treatment with Ginkgo biloba L. leaf extract (IDN 5933/Ginkgoselect®Plus) in elderly: A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial [GiBiEx]. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Lin, L.; Liu, S.; Qin, M.; He, S.; Zhu, L.; Huang, J. Ginkgo Biloba Extract Inhibits Metastasis and ERK/Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-kB) Signaling Pathway in Gastric Cancer. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 6836–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, Y.; Tomova, T.; Minchev, D.; Turiyski, V.; Draganov, M.; Argirova, M. Cytotoxic effect of Ginkgo biloba kernel extract on HCT116 and A2058 cancer cell lines. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, L.; Yin, W.; Nie, Y.; Zeng, P.; Yang, X. Anti-tumor effect of ginkgetin on human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines by inducing cell cycle arrest and promoting cell apoptosis. Cell Cycle 2022, 21, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; He, Z.; Ke, J.; Li, S.; Wu, X.; Lian, L.; He, X.; He, X.; Hu, J.; Zou, Y.; et al. PAF receptor antagonist Ginkgolide B inhibits tumourigenesis and angiogenesis in colitis-associated cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhi, Y.; Pan, J.; Shen, W.; He, P.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, X.; Lu, G.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Z. Ginkgolide B Inhibits Human Bladder Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion Through MicroRNA-223-3p. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, B.; Xia, Z.-M.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, D.; Rui, W.-J.; Dong, J.-X.; Xiao, F.-J. Anticancer Effects of Five Biflavonoids from Ginkgo Biloba L. Male Flowers In Vitro. Molecules 2019, 24, 1496. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-H.; Yim, S.-H. Effects of Bilobol from the Fruit Pulp of Ginkgo biloba on Cell Viability. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e57522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, B.K.S.; Banin, R.M.; Dornellas, A.P.S.; de Andrade, I.S.; Zemdegs, J.C.S.; Caperuto, L.C.; Oyama, L.M.; Ribeiro, E.B.; Telles, M.M. Ginkgo biloba Extract Improves Insulin Signaling and Attenuates Inflammation in Retroperitoneal Adipose Tissue Depot of Obese Rats. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 419106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, T.A.; Hussain, S.A.; Mahwi, T.O.; Ahmed, Z.A.; Rahman, H.S.; Rasedee, A. The efficacy and safety of Ginkgo biloba extract as an adjuvant in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients ineffectively managed with metformin: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banin, R.M.; Machado, M.M.F.; de Andrade, I.S.; Carvalho, L.O.T.; Hirata, B.K.S.; de Andrade, H.M.; Júlio, V.d.S.; de Souza Figueiredo Borges Ribeiro, J.; Cerutti, S.M.; Oyama, L.M.; et al. Ginkgo biloba extract (GbE) attenuates obesity and anxious/depressive like behaviours induced by ovariectomy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, F.-Y.; Zhou, Y.-Z.; Wang, H.-Y.; Yin, X.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Q. Enhancing antioxidant and anti-hyperglycaemic functions of gingko biloba L. seeds using thermal detoxification. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, S.; Kawazoe, Y.; Shiba, T.; Numazawa, S.; Manabe, A. Anti-Obesity Effect of Ginkgo Vinegar, a Fermented Product of Ginkgo Seed Coat, in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet and 3T3-L1 Preadipocyte Cells. Nutrients 2020, 12, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Jin, X.; Man, C.; Gong, D. Does Adjuvant Treatment With Ginkgo Biloba to Statins Have Additional Benefits in Patients With Dyslipidemia? Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Fang, J.; Chen, H.; Fan, S.; Huang, C. Ginkgolide B lowers body weight and ameliorates hepatic steatosis in high-fat diet-induced obese mice correlated with pregnane X receptor activation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 37858–37866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Liu, H.-C.; Wu, S.-J.; Liou, C.-J. Ginkgolide C reduced oleic acid-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, B.K.S.; Cruz, M.M.; de Sá, R.D.C.C.; Farias, T.S.M.; Machado, M.M.F.; Bueno, A.A.; Alonso-Vale, M.I.C.; Telles, M.M. Potential Anti-obesogenic Effects of Ginkgo biloba Observed in Epididymal White Adipose Tissue of Obese Rats. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, C.; Rojas-Castañeda, J.; Ruiz-Sánchez, E.; Montes, P.; Rojas, P. Antioxidant properties of a Ginkgo biloba leaf extract (EGb 761) in animal models of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Curr. Top. Nutraceutical Res. 2015, 13, 105–120. [Google Scholar]
- Hashiguchi, M.; Ohta, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Maruyama, J.; Mochizuki, M. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of Ginkgo biloba extract for the treatment of dementia. J. Pharm. Health Care Sci. 2015, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargouri, B.; Carstensen, J.; Bhatia, H.S.; Huell, M.; Dietz, G.P.H.; Fiebich, B.L. Anti-neuroinflammatory effects of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb761 in LPS-activated primary microglial cell. Phytomedicine 2018, 44, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meo, F.D.; Cuciniello, R.; Margarucci, S.; Bergamo, P.; Petillo, O.; Peluso, G.; Filosa, S.; Crispi, S. Ginkgo biloba Prevents Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis Blocking p53 Activation in Neuroblastoma Cells. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Kojder, K.; Zielonka-Brzezicka, J.; Wróbel, J.; Bosiacki, M.; Fabiańska, M.; Wróbel, M.; Sołek-Pastuszka, J.; Klimowicz, A. The Use of Ginkgo Biloba L. as a Neuroprotective Agent in the Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 1, 775034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Lu, X.; Fan, X. Neuroprotective effects of Ginkgo biloba dropping pills in Parkinson’s disease. J. Pharm. Anal. 2021, 11, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbalho, S.M.; Direito, R.; Laurindo, L.F.; Marton, L.T.; Guiguer, E.L.; Goulart, R.d.A.; Tofano, R.J.; Carvalho, A.C.A.; Flato, U.A.P.; Capelluppi Tofano, V.A.; et al. Ginkgo biloba in the Aging Process: A Narrative Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sochocka, M.; Ochnik, M.; Sobczyński, M.; Gębura, K.; Zambrowicz, A.; Naporowski, P.; Leszek, J. Ginkgo Biloba Leaf Extract Improves an Innate Immune Response of Peripheral Blood Leukocytes of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.F. Clinical effect of pills of six ingredients with Rehmannia combined with Ginkgo biloba on prevention and treatment of early retinopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Guoji Yanke Zazhi 2017, 17, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, M.A.; Sampaio, A.L.L.; Venosa, A.R.; de Alencar Meneses, E.; Oliveira, C.A.C.P. The chemopreventive effect of Ginkgo biloba extract 761 against cisplatin ototoxicity: A pilot study. Int. Tinnitus J. 2015, 9, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Sabaner, M.C.; Dogan, M.; Altin, S.S.; Balaman, C.; Yilmaz, C.; Omur, A.; Zeybek, I.; Palaz, M. Ginkgo Biloba affects microvascular morphology: A prospective optical coherence tomography angiography pilot study. Int. Ophthalmol. 2021, 41, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Bernart, M.W.; Nolan, G.S.; Lin, L.; Lindenmaier, M.P. High-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry study of ginkgolic acid in the leaves and fruits of the ginkgo tree (Ginkgo biloba). J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2000, 38, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, M.S. Biology and Ecology of Ginkgo biloba L. (GinkgoaceaeI); Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-63484-460-4. [Google Scholar]
- Gawron-Gzella, A.; Matławska, I. Efficacy and safety of preparations from Ginkgo Biloba. Farm. Klin. 2012, 1, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.; Alzahrani, T. Ginkgo Biloba 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK541024/ (accessed on 4 March 2023).
- Kajiyama, Y.; Fujii, K.; Takeuchi, H.; Manabe, Y. Ginkgo Seed Poisoning. Prediatrics 2002, 109, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, R.; Hanson, B.A.; Markosyan, R.M.; Gallo, E.S.; Narasipura, S.D.; Bhutta, M.; Shechter, O.; Lurain, N.S.; Cohen, F.S.; Al-Harthi, L.; et al. Ginkgolic acid inhibits fusion of enveloped viruses. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omindkhoda, S.F.; Razavi, B.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Protective effects of Ginkgo biloba L. against natural toxins chemical tocicities, and radiation: A comprehensive review. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 2821–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogacz, A.; Karasiewicz, M.; Dziekan, K.; Procyk, D.; Górska-Paukszta, M.; Kowalska, A.; Mikołajczyk, P.Ł.; Ożarowski, M.; Czerny, B. Impact of Panax ginseng and Ginkgo biloba extracts on expression level of transcriptional factors and xenobiotic-metabolizing cytochrome P450 enzymes. Herba Pol. 2016, 61, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędzia, B.; Alkiewicz, J. Interakcje pomiędzy lekami roślinnymi stosowanymi w inhalacjach a lekami syntetycznymi stosowanymi doustnie*. Postępy Fitoter. 2006, 2, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Hansten, P.D.; Horn, J.R. Top 100 Drug Interactions 2017; H&H Publications: Freeland, WA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lit, J.Z.; Shear, N.H. Drug Eruption & Reaction Manual; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, L.; Cohen, M. Essential Herbs & Natural Supplements; Elsevier: Chatswood, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Woroń, J.; Siwek, M. Unwanted effects of psychotropic drug interactions with medicinal products and diet supplements containing plant extracts. Psychiatr. Pol. 2018, 52, 983–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayroles, G.; Rossard, R.-M.; Cadiou, M. Method for Obtaining an Extract or Ginkgo biloba Leaves. U.S. Patent 4981688A, 1 January 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bombardelli, E.; Mustich, G.; Bertani, M. New Extracts of ginkgo biloba and Their Methods of Preparation. EP0360556A1, 21 April 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, T. Production of Essence of Ginkgo. JPH02193907A, 31 July 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Matsui, K.; Shinkawa, Y.; Tsuboi, M.; Kojima, H.; Ando, Y. Simple Production of Extract with High Content of Flavonoid from Ginkgo Leaf. JPH03227985A, 8 October 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe, K.-P. Extracts from Ginkgo biloba Leaves-with High Content of Flavone Glycoside(s) and Ginkgolide(s) but with Low Alkyl Phenol(s). DE3940095A1, 6 June 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Takane, Y. Extraction of Active Component of Ginkgo Leaf and Production of Glycoside Extract of Active Component of Ginkgo Leaf. JPH0391490A, 17 April 1991. [Google Scholar]
- O′Reilly, J.; Jaggy, H. Active Component Concentrates and New Active Component Combinations from ginkgo biloba Leaves, Their Method of Preparation and Pharmaceuticals Containing the Active Component Concentrates or the Active Component Combinations. US5389370A, 14 February 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Schwabe, K.-P. Extract from Ginkgo biloba Leaves, Its Method of Preparation and Pharmaceuticals Containing the Extract. US5399348A, 21 March 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, T. Health Tea Containing Ginkgo Extract. JPH057368B2, 28 January 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, T. Health Drink Containing Ginkgo Extract. JPH0563147B2, 9 September 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, T.; Matsumoto, A. Ginkgo Extract-Containing Chewing Gum. JPH0231648A, 1 February 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, T.; Matsumoto, A. Ginkgo Extract-Containing Chocolate. JPH0231646A, 1 February 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, T. Candy Containing Ginkgo Leaf. JPH0550254B2, 28 July 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Oschmann, R.; Waimer, F.; Hauer, H. Preparation of Ginkgo biloba Extract Used for Treating e.g. Dementia or Cerebral Disorder, Involves Extracting Aqueous Alcoholic Solution of Ginkgo biloba Leaves with Heptane to Remove Alkyl Phenol Compounds. DE102006019863A1, 16 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Erdelmeier, C.; Hauer, H.; Koch, E.; Lang, F.; Stumpf, K.-H. Method for Preparing a Ginkgo Extract Having a Reduced Content of 4′-O-Methyl Pyridoxine and/or Biflavones. WO2006117171A1, 9 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Erdelmeier, C.; Hauer, H.; Koch, E.; Lang, F. Method for Preparing Ginkgo Extracts Having a Low Content of 4′-O-Methyl Pyridoxine and/or Biflavones. US8642099B2, 4 February 2014. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, R. Fermentation Production Method for Efficiently Extracting Flavones from Ginkgo Leaves. CN107115367A, 30 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, L.; Guo, C.; Liu, L. Compound Gingko Health-Care Tea and Preparation Method Thereof. CN114766573A, 22 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Wang, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, R. Ginkgo Beer Production Method. CN105316145A, 3 February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Xuan, S.; Miao, Z. Production Technology of Ginkgo Short Bread. CN108391689A, 14 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, E. Ginkgo and Tartary Buckwheat Vinegar. CN103981077A, 13 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Cui, X.; Liu, G.; Lan, X.; He, Y. Ginkgo Beverage and Preparation Method Thereof. CN104473273B, 5 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, L. Preparation Method of Ginkgo Drink. CN104770812A, 15 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yunrong, K. Method for Extracting Gingko Powder from Gingkoes and Preparing Gingko Healthy Wine. CN101597553A, 9 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lyu, Q. Manufacturing Method of Ginkgo Health-Care Wine. CN103773660A, 7 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W. Brewing Method of Gingko Wine. CN113831990A, 24 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J. Gingko Wine and Production Method Thereof. CN113105986A, 13 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X. Process for Preparing Gingko Wine. CN114292718A, 8 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W. Ginkgo Healthful Drink. CN103054116A, 24 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Zhao, Q. Method for Preparing Gingko Powder from Fresh Gingko Fruits. CN114209048A, 22 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, T.; Yue, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, S. Ginkgo biloba Drink Containing Saffron Ingredient and Preparation Method Thereof. CN103584240A, 19 February 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, M. Ginkgo Fruit Drink. CN106901108A, 30 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Xu, R. Gingko Health Wine and Preparation Method Thereof. CN107974383A, 1 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Xu, F. Preparation Method of Gingko Sauce. CN106962870A, 21 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Yang, G.; Liang, J.; Chen, R. Gingko Herbal Extract, Fermented Yogurt and Preparation Method Thereof. CN106974286A, 25 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, L. Ginkgo and Aloe Compound Functional Tea Drink and Preparation Method Thereof. CN114766574A, 22 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, Y.C. Functional Foods Based on Ginkgo Nuts and the Making Method Thereof. KR20220015936A, 8 February 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, J.; Li, C.; Chen, A.H.; Cui, Y.; Dai, X.J.; Shao, Y.; Chen, S.L.; Wang, N.X.; Geng, Z.H. Ginkgo Leaf and Agaricus Bisporus Compound Health Drink and Method of Making Same. CN102488280A, 13 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, X.; Ge, X.; Zhang, S.; Fang, J.; Gao, W. Health-Promoting Functional Drink Suitable for People with Hypertension and Preparation Method Thereof. WO2016101319A1, 30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J. Gingko Health-Care Wine and Processing Method Thereof. CN113249182A, 13 August 2021. [Google Scholar]

| Compound | Structure | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight [g/mol] | Main Toxicological and/or Pharmacological Effects | Source of Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diterpenes | |||||
| Ginkgolide A | 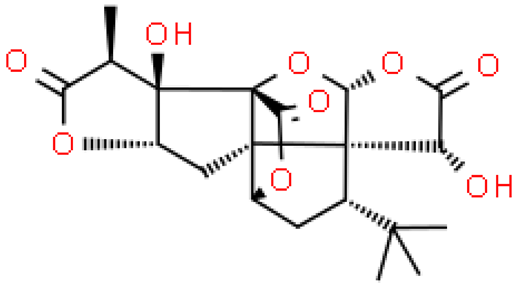 | C20H24O9 | 408.399 | No toxicity Anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating effect | [33,34] |
| Ginkgolide B | 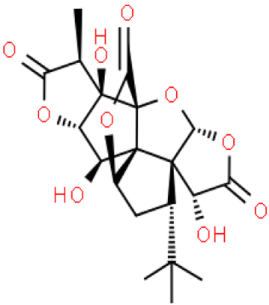 | C20H24O10 | 424.399 | No toxicity Beneficial effect on the functioning of the central nervous system | [33,35] |
| Ginkgolide C | 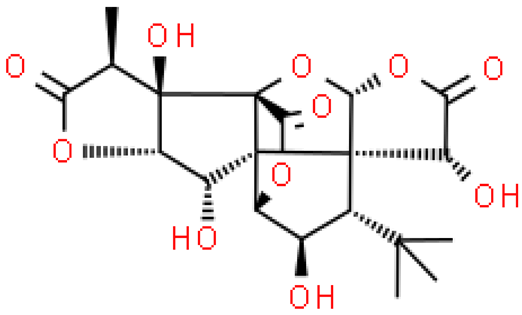 | C20H24O11 | 440.398 | No toxicity Reduces the accumulation of lipids, anti-cancer effect | [33,36] |
| Ginkgolide M | 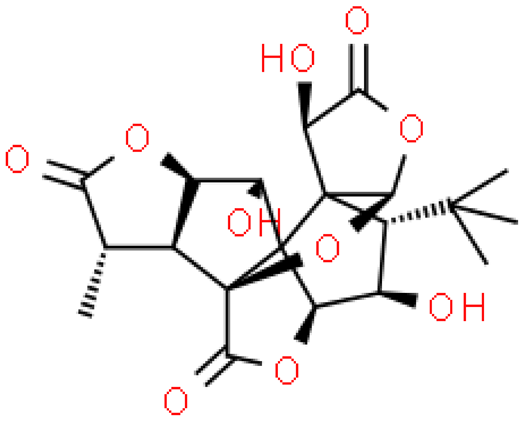 | C20H24O10 | 424.399 | No toxicity Inhibitor of ligand-gated ion channels in the central nervous system | [33,37] |
| Ginkgolide J | 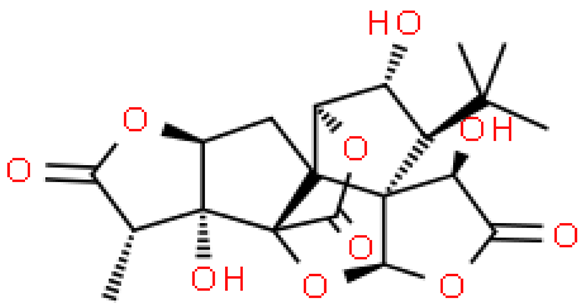 | C20H24O10 | 424.399 | No toxicity Dementia treatment | [33,38] |
| Ginkgolide P | 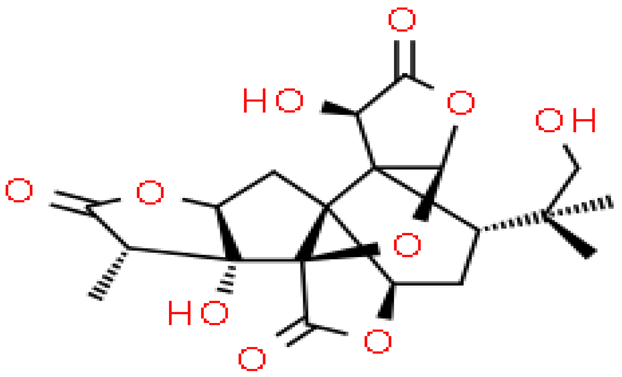 | C20H24O10 | 424.399 | No data | [33] |
| Ginkgolide Q |  | C20H24O11 | 463.126 | No data | [39] |
| Ginkgolide K | 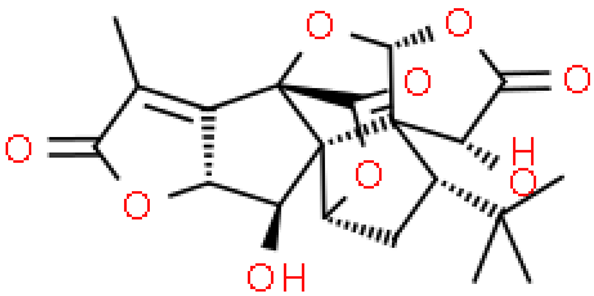 | C20H22O9 | 406.383 | No data Antioxidant, immunomodulatory and neuroprotective effects in ischemic stroke | [33,40,41] |
| Ginkgolide L | 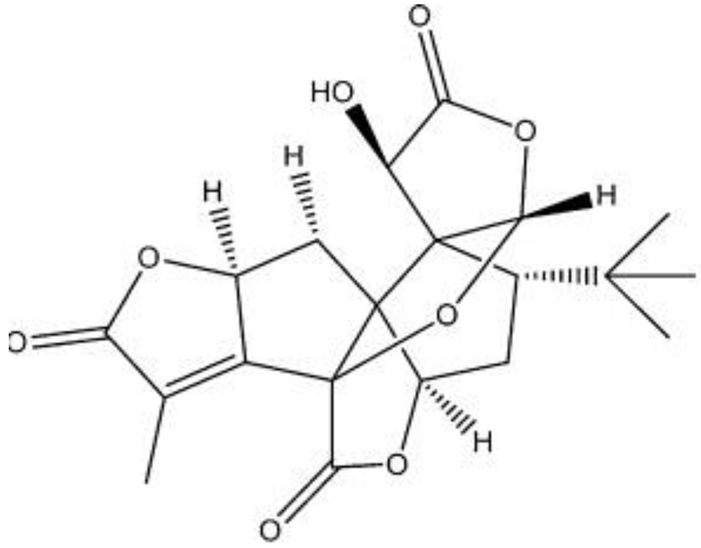 | C20H22O8 | No date | No data | [42] |
| Ginkgolide N | 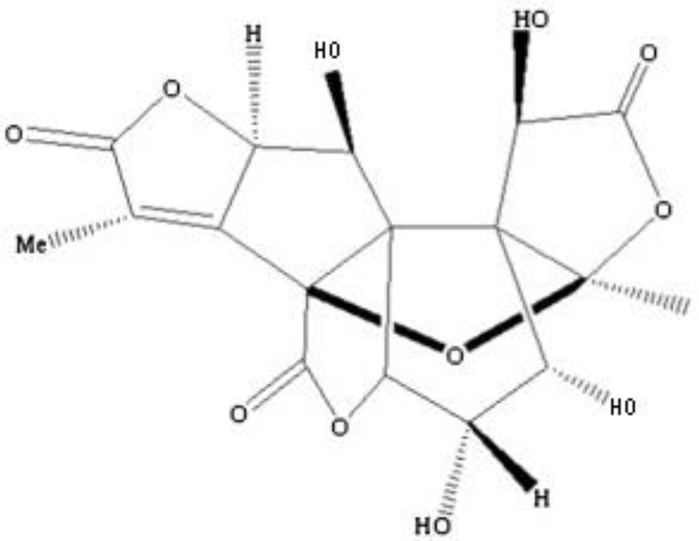 | C20H24O11 | No data | No toxicity Protective effect on damaged PC12 cells induced by glutamate | [43,44] |
| Sesquiterpenes | |||||
| Bilobalide | 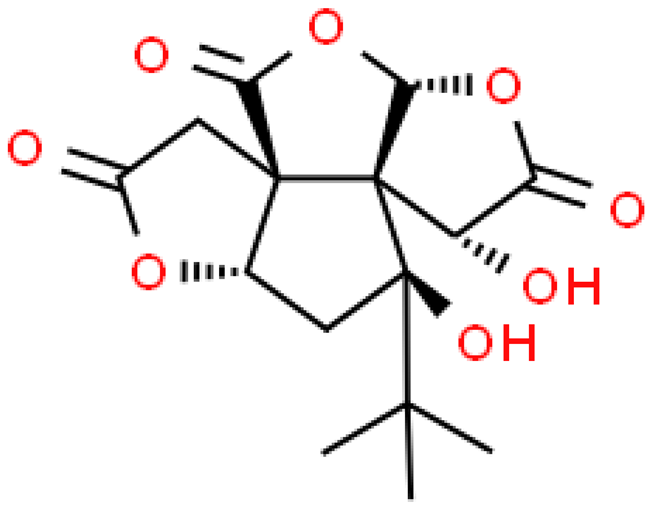 | C15H18O8 | 326.299 | May cause arrhythmia Neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-ischemic, protective effect on the circulatory system | [33,45] |
| Bilobalide isomer | 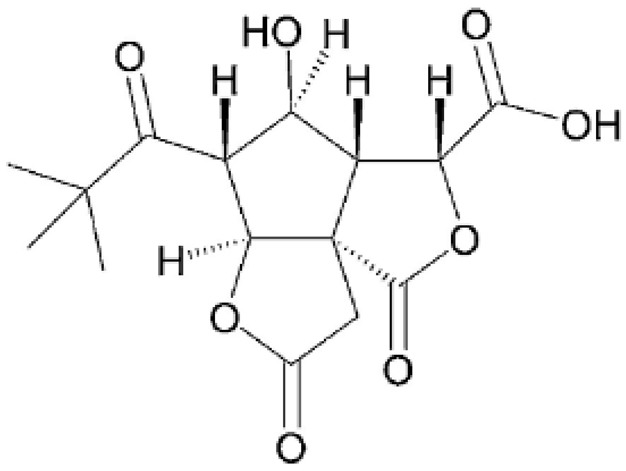 | No data | No data | No data | [46] |
| Flavonoids | |||||
| Quercetin | 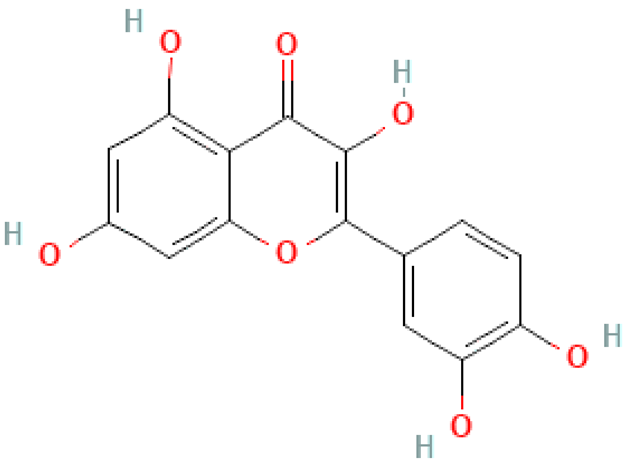 | C15H10O7 | 302.23 | Quercetin administration may cause cellular toxicity due to o-quinone/methide quinone side-production Anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-microbial, anti-cancer effect, supporting the functioning of the circulatory and nervous systems | [10,33,47,48] |
| Kaempferol | 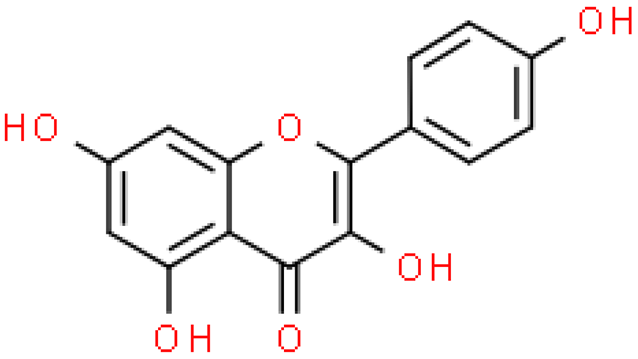 | C15H10O6 | 286.236 | Genotoxic and carcinogenic in vitro—no in vivo studies confirming this effect Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, ability to scavenge free radicals | [38,49,50] |
| Isorhamnetin | 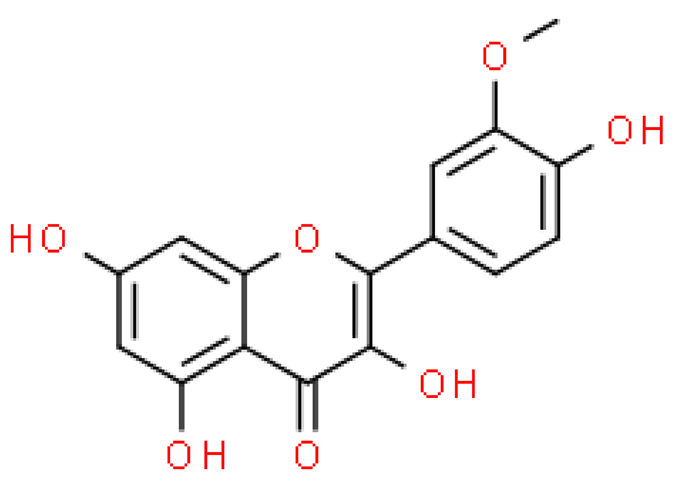 | C16H12O7 | 316.262 | No toxicity Protective effect on the circulatory and nervous systems, anti-atherosclerotic, hypotensive, hypoglycemic, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory effects | [33,51] |
| Myricetin | 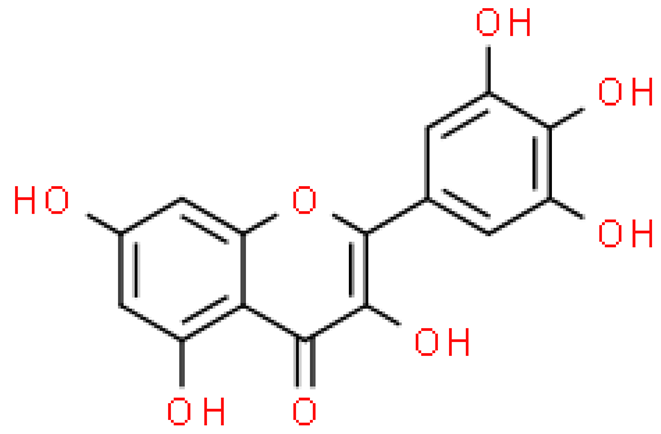 | C15H10O8 | 318.235 | No toxicity Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-photoaging, anti-cancer, anti-platelet aggregation, anti-hypertensive, immunostimulating effect | [33,52] |
| Apigenin | 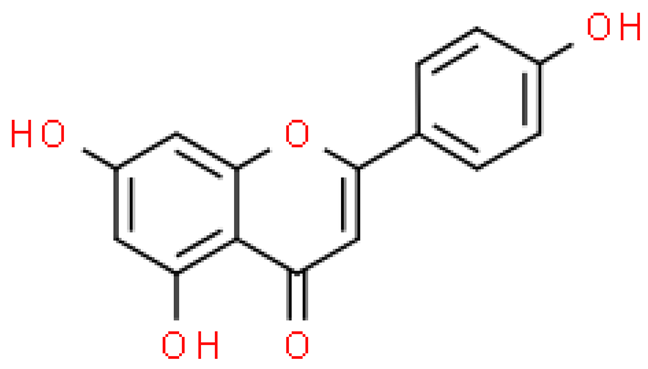 | C15H10O5 | 270.237 | No toxicity Anti-diabetic, anti-cancer, protective effect on the nervous system | [33,53] |
| Luteolin | 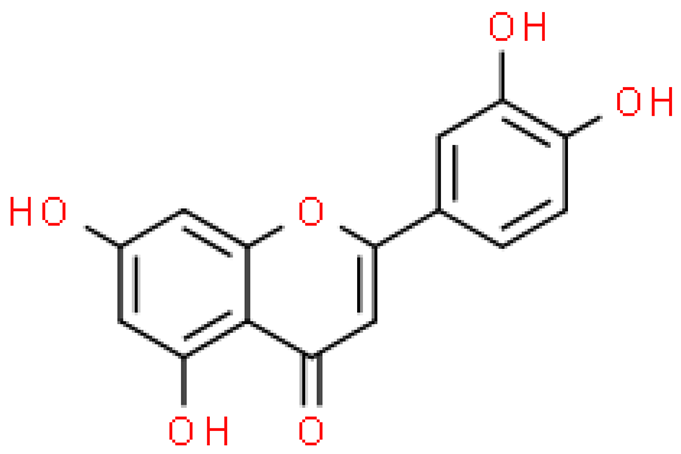 | C15H10O6 | 286.236 | No toxicity Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic and anti-cancer effect | [33,54] |
| Genkwanin | 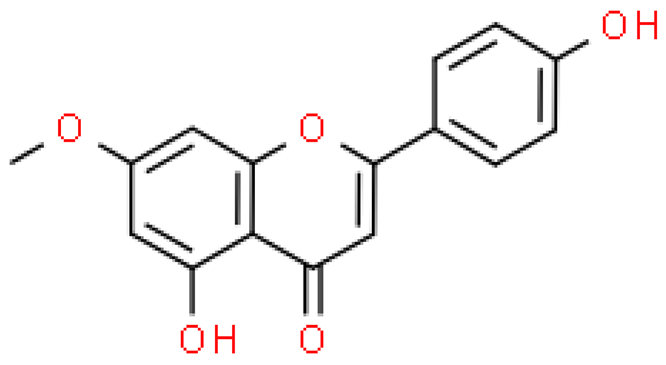 | C16H12O5 | 284.263 | No toxicity Anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, anti-bacterial, anti-rheumatic effect | [33,55] |
| Genistein | 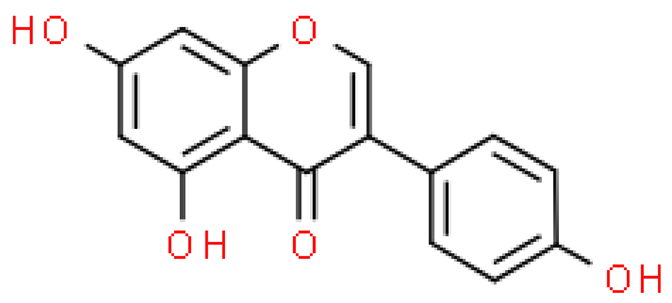 | C15H10O5 | 270.237 | A high dose of genistein has a strong teratogenic, endocrine-disrupting effect Anti-inflammatory effects, inhibition of nuclear factor Kappa-B, prostaglandins, pro-inflammatory cytokines, reactive oxygen species and free radical scavenging activity | [33,56] |
| Epicatechin | 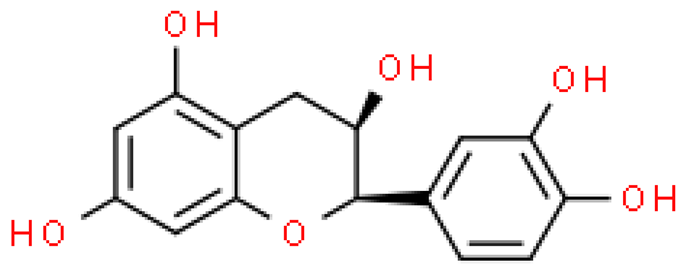 | C15H14O6 | 290.268 | No toxicity Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial, anti-diabetic, anti-cancer effect | [33,57] |
| Catechin | 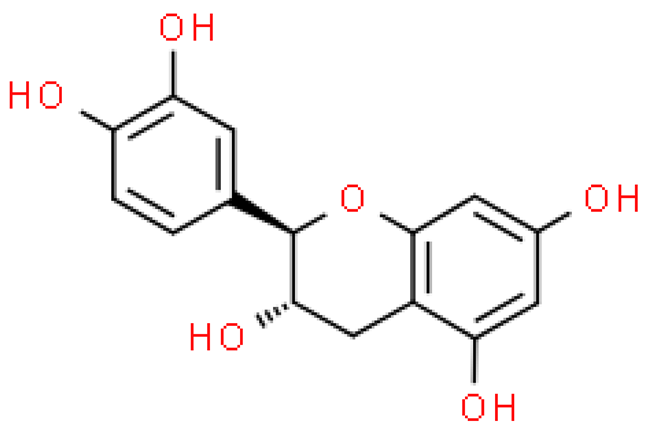 | C15H14O6 | 290.268 | Excessive dose may cause hepatitis Anti-cancer, anti-obesity, anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory, anti-cardiovascular, anti-infective, hepatoprotective and neuroprotective | [33,58] |
| Epigallocatechin | 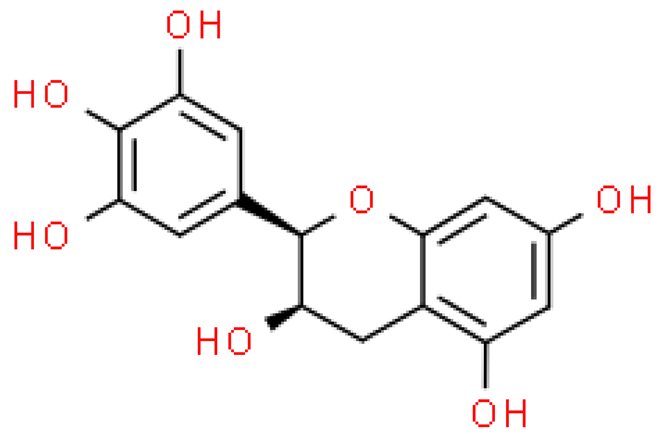 | C15H14O7 | 306.267 | Mild and acute health problems after using higher doses, i.e., skin irritation, hepatitis, hypoglycemia, dizziness—human and animal studies Anti-obesity, anti-microbial, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory effect | [33,59] |
| Gallocatechin | 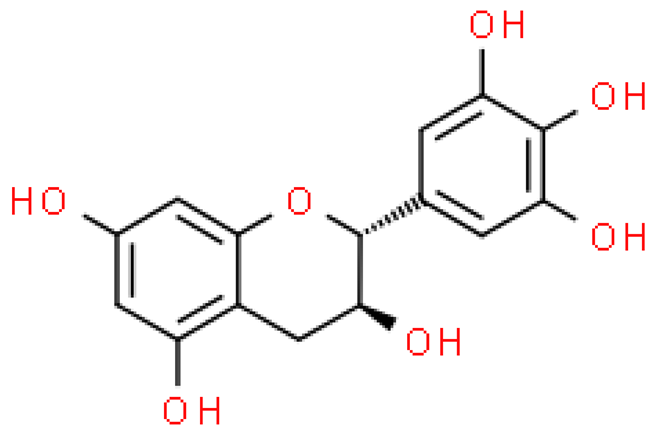 | C15H14O7 | 306.267 | May cause irritation of the respiratory tract (manifested by coughing and shortness of breath), skin and acute eye irritation Antioxidant and neuroprotective effect anti-diabetes, antivirus activities | [33,60,61,62,63,64] |
| Amentoflavone | 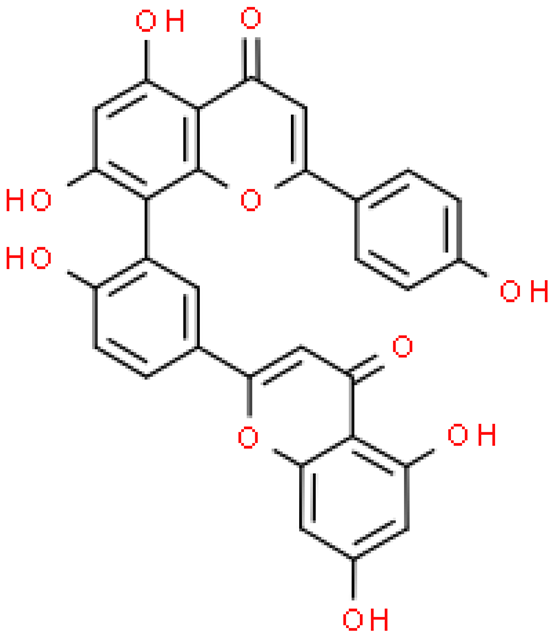 | C30H18O10 | 538.458 | It can be a strong inhibitor of some genes, e.g., CYP2C9 Anti-inflammatory, anti-microorganism, antioxidant, anti-angiogenesis, neuroprotective, musculoskeletal protection, radioprotection, metabolism regulation, anxiolytic/antidepressant, anti-cancer | [33,65] |
| Bilobetin |  | C31H20O10 | 552.484 | Extensive watery degeneration of hepatocytes Antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antihyperlipidemic and antiproliferative effects | [33,66,67] |
| Sequoiaflavone | 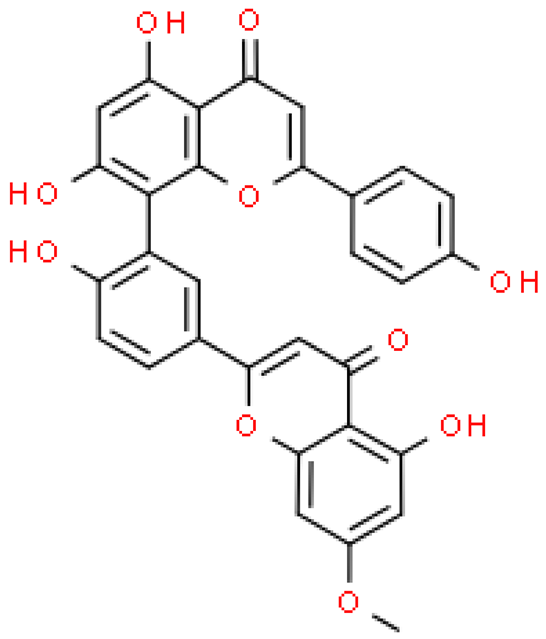 | C31H20O10 | 552.484 | LD toxicity in mice after oral and intraperitoneal administration at a dose above 3 gm/kg Anti-cancer activities | [33,46,64,68] |
| Ginkgetin | 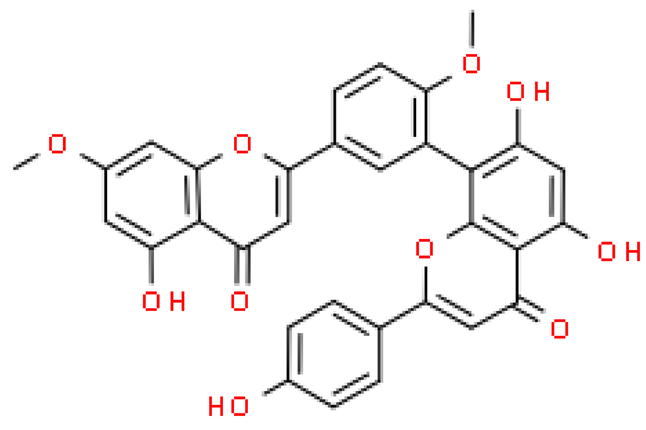 | C32H22O10 | 566.511 | Extensive watery degeneration of hepatocytes Anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial, anti-adipogenic and neuroprotective effect | [33,66,69] |
| Alkylophenolic acid | |||||
| Ginkgolic acid (C13:0) | 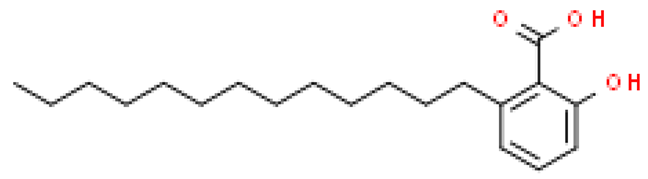 | C22H32O3 | 320.466 | Cytotoxic, mutagenic, genotoxic, allergenic and neurotoxic in high doses Anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer, anti-diabetic, anti-fibrotic, anti-bacterial, anti-viral and reno/neuroprotective effects | [6,33,70] |
| Ginkgolic acid (C15:1) | 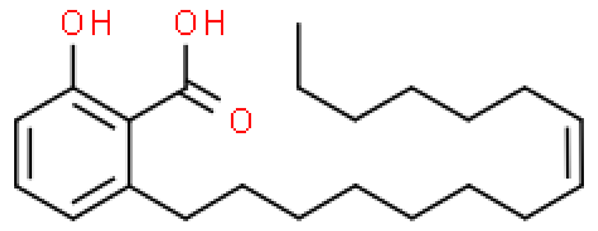 | C22H34O3 | 346.504 | Cytotoxic, mutagenic, genotoxic, allergenic and neurotoxic in high doses Anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer, anti-diabetic, anti-fibrotic, anti-bacterial, anti-viral and reno/neuroprotective effects | [6,33,70] |
| Ginkgolic acid (C17:1) | 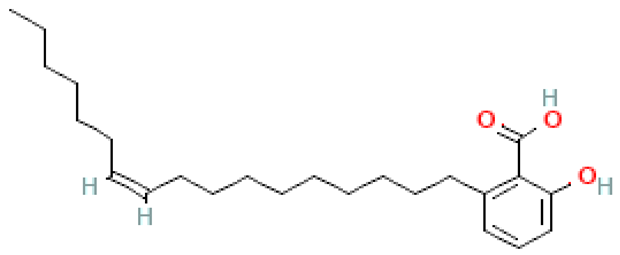 | C24H38O3 | 374.600 | Cytotoxic, mutagenic, genotoxic, allergenic and neurotoxic in high doses Anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer, anti-diabetic, anti-fibrotic, anti-bacterial, anti-viral and reno/neuroprotective effects | [6,33,70] |
| Ginkgolic acid (C17:2) |  | C24H36O3 | 372.500 | Cytotoxic, mutagenic, genotoxic, allergenic and neurotoxic in high doses Anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer | [6,33,71] |
| Alkylphenols | |||||
| Cardanols (C15:0) | 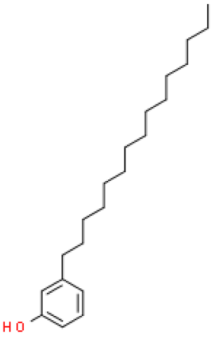 | C21H36O | 304.510 | No data | [33] |
| Cardanols (C15:1) | 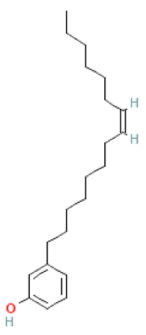 | C21H34O | 302.500 | At high doses genotoxic effects Antioxidant, anti-cancer and antimutagenic effect. At low dose DNA damage repair | [46,72,73] |
| Cardol (C15:0) | 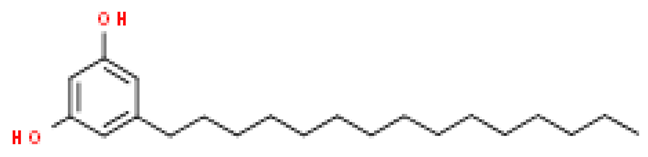 | C21H36O2 | 320.509 | Cytotoxic effect Anti-cancer effect—inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells and induces the death of cancer cells; antioxidant effect, neuroprotective effect | [33,74,75,76,77] |
| Cardol (C15:1) | 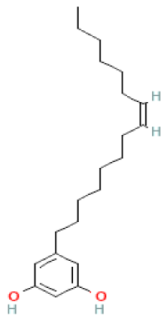 | C21H34O2 | 318.5000 | Cytotoxic effect No data | [46,74] |
| Urushiol (C15:0) | 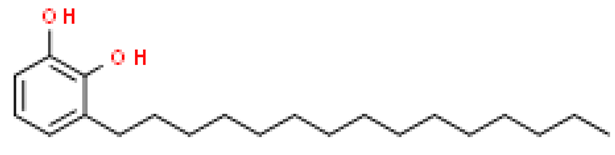 | C21H36O2 | 320.509 | Allergenic effect (acute inflammation of the skin) Anti-bacterial effect, anti-cancer effect (cytotoxic against tumor cells) | [33,78,79,80] |
| Proanthocyanidins | |||||
| Epicatechin-(4β→8)-catechin | 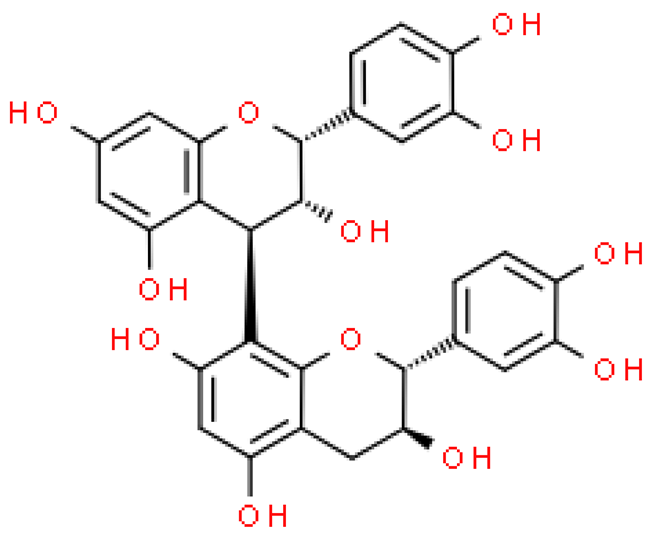 | C30H26O12 | 578.520 | Anti-microbial activity and strong cytotoxicity against tumor cells | [33,81] |
| Gallocatechin-(4β→8)-catechin | 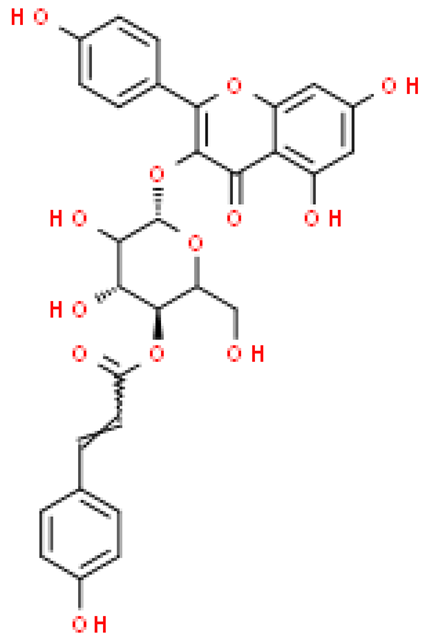 | C30H26O13 | 594.520 | No data | [33] |
| Epiallocatechin-(4β→8)-gallocatechin | 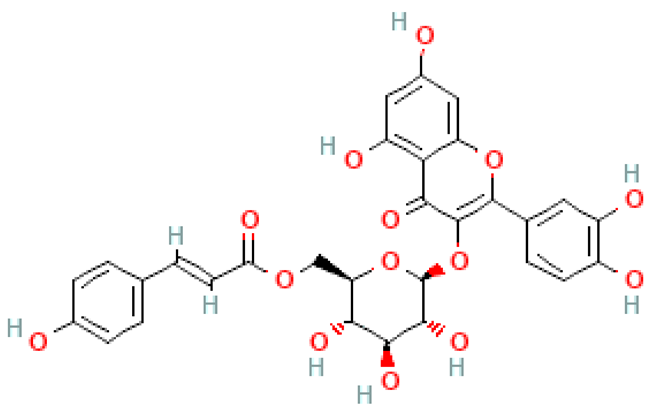 | C30H26O14 | 610.500 | No data Changes in fat metabolism in hyperlipidemia | [46,82] |
| Carboxylic acids | |||||
| Protocatechuic acid | 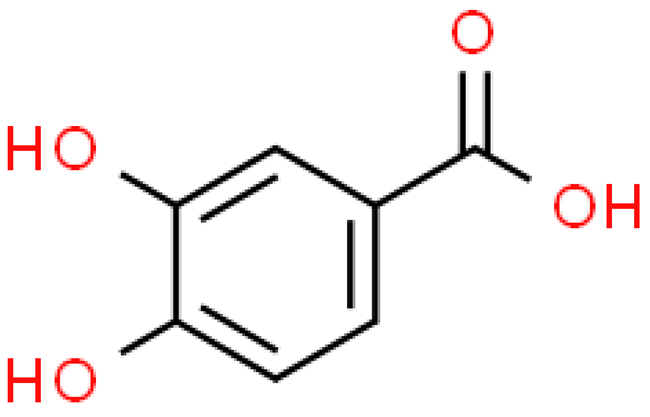 | C7H6O4 | 154.120 | Cytotoxic, genotoxic, carcinogenic, hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic at high doses Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, antihypertensive, anti-atherosclerotic, anti-aging, anti-cancer, neuroprotective, anti-bacterial, anti-viral effect and protective effect for organs | [33,83] |
| p-hydroxybenzoic acid | 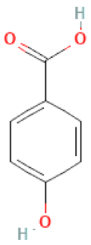 | C7H6O3 | 138.120 | Possible reproductive risk and potential involvement in breast cancer Antioxidant, anti-bacterial, antimutagenic, anti-thrombotic and estrogenic activity | [46,84,85,86,87,88,89] |
| Vanillic acid | 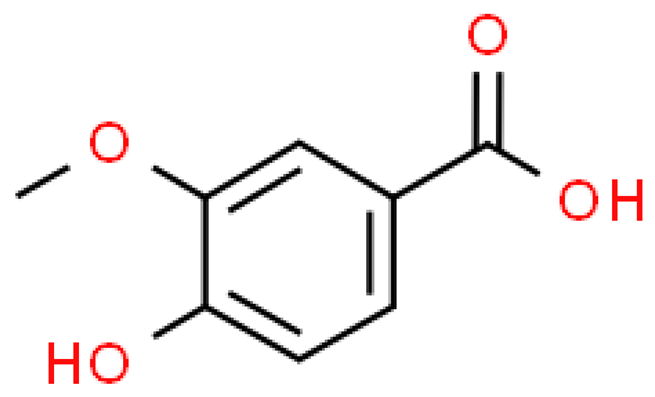 | C8H8O4 | 168.147 | No toxicity Sedative, anti-depressant, antioxidant, anti-hypertensive, anti-nociceptive, anti-cancer, anti-fungal, reducing the severity of ulcerative colitis, hepatoprotective, wound healing | [33,90,91] |
| Isovanillic acid |  | C8H8O | 168.147 | No toxicity Anti-thrombotic and cytostatic activity | [33,89,92,93] |
| Gallic acid | 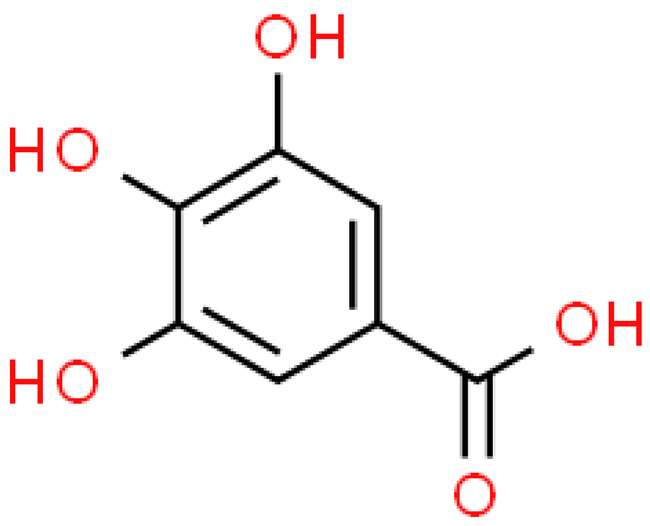 | C7H6O5 | 170.120 | At higher concentrations it can be toxic, e.g., cytotoxic effect. In vivo studies, the toxicity is relatively low Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-bacterial, anti-diabetic, anti-obesity, anti-microbial, anti-myocardial ischemia | [33,94] |
| p-coumaric acid | 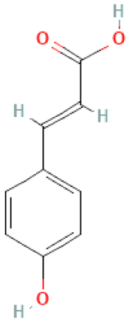 | C9H8O3 | 164.160 | No toxicity Anti-mutagenic, anti-genotoxic, antioxidant, anti-microbial activity, inhibits cellular melanogenesis and plays a role in immune regulation in humans | [46,95] |
| Caffeic acid | 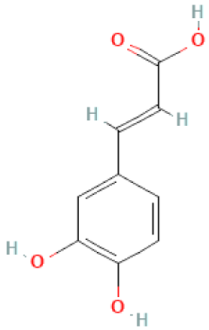 | C9H8O4 | 180.160 | It is anti-implantation during early pregnancy in mice at high doses Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-cancer, immunomodulatory and neuroprotective effect | [46,96,97] |
| Sinapic acid | 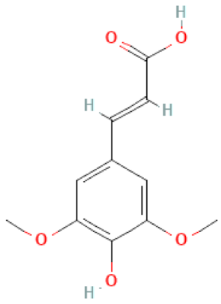 | C11H12O5 | 224.21 | May be cytotoxic at high doses Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, anti-hyperglycemic, anti-diabetic, anti-hypertensive, hepatoprotective, renoprotection, neuroprotective, anxiolytic, anti-bacterial effect | [46,98] |
| Ferulic acid | 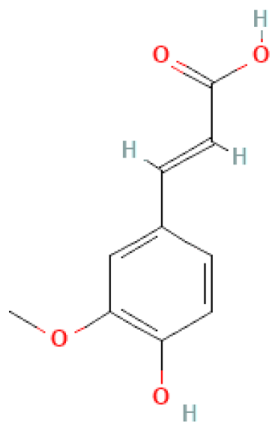 | C10H10O4 | 194.180 | Weak toxicity, e.g., on platelets, white and red blood cells Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, anti-apoptotic, anti-platelet, anti-bacterial, protective effect on vascular endothelial cells | [46,99] |
| Chlorogenic acid | 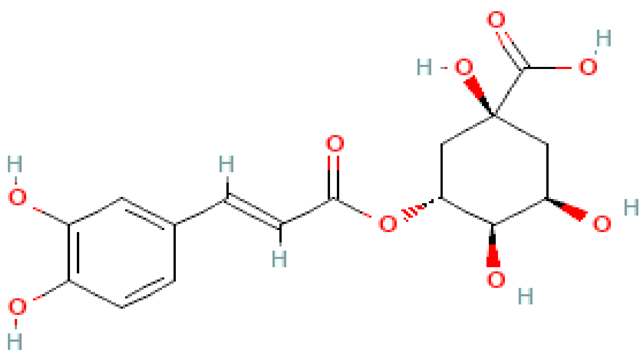 | C16H18O9 | 354.310 | No toxicity Neuroprotective, anti-cancer, anti-bacterial, protective effect on the circulatory system, renoprotection, protective effect on the digestive system, hepatoprotection, support in the treatment of metabolic syndrome | [46,100] |
| Ascorbic acid | 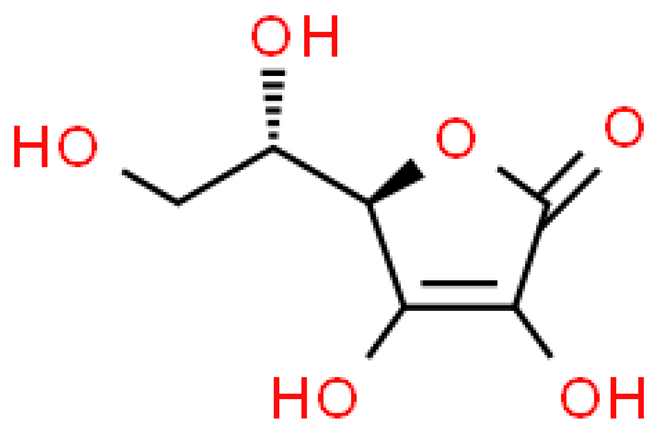 | C6H8O6 | 176.124 | No toxicity It has an antioxidant effect, stimulates the production and activation of immune cells | [33,101] |
| Quinic acid | 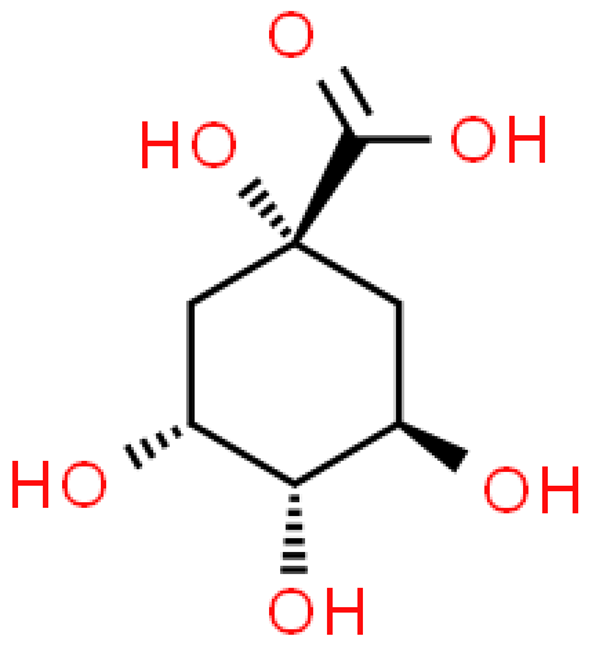 | C7H12O6 | 192.167 | No toxicity Antioxidant, anti-diabetic, anti-cancer, anti-microbial, anti-viral, anti-aging, protective and analgesic effects | [33,102] |
| Shikimic acid | 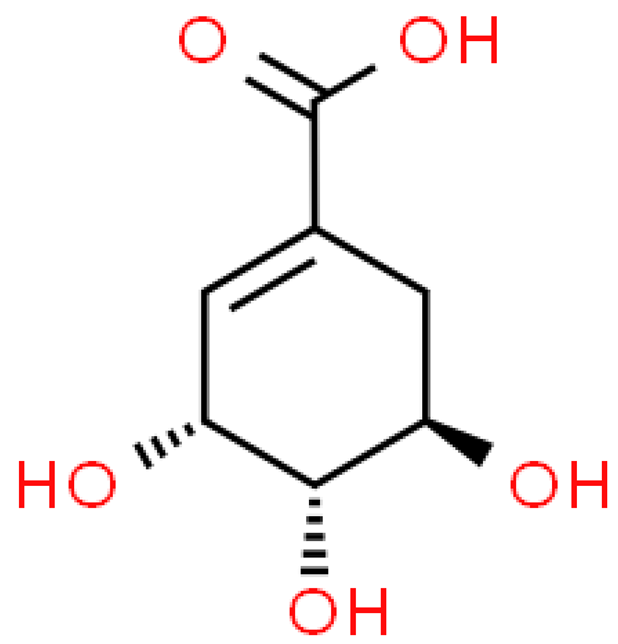 | C7H10O5 | 174.151 | No toxicity Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral, antifungal, exfoliating, anti-acne, whitening, moisturizing, anti-aging, sebum-regulating, hair growth stimulating | [33,103] |
| Lignans | |||||
| Sesamin | 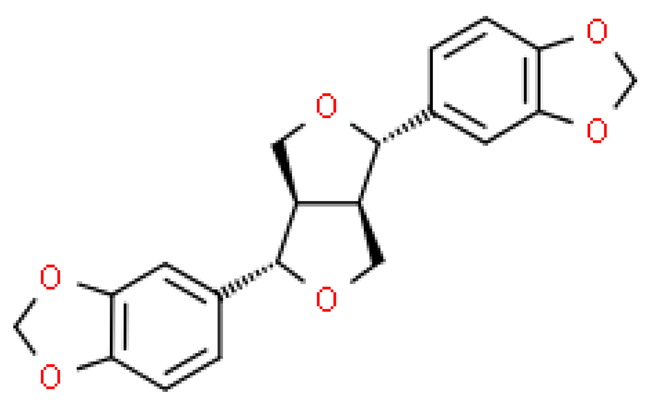 | C20H18O | 354.353 | In high doses, it can be a compound with a low and moderate degree of danger, e.g., it can cause loss of appetite, vomiting, diarrhea, hormone metabolism disorders Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory, anti-hypertensive, anti-atherosclerotic, lipolytic, anti-thrombotic, anti-diabetic and anti-obesity effects | [33,104] |
| Ginkgool |  | C20H24O7 | 376.000 | No data | [105] |
| Pinoresinol | 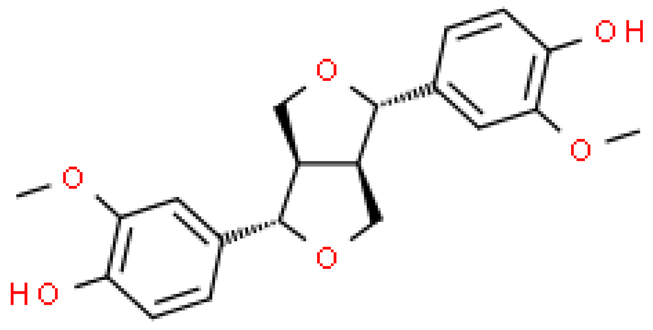 | C20H22O6 | 358.385 | No toxicity Hypoglycemic effect, improving memory and learning ability, anti-cancer effect (stimulation of cancer cell apoptosis) | [33,106,107,108,109] |
| Ginkgolide B | 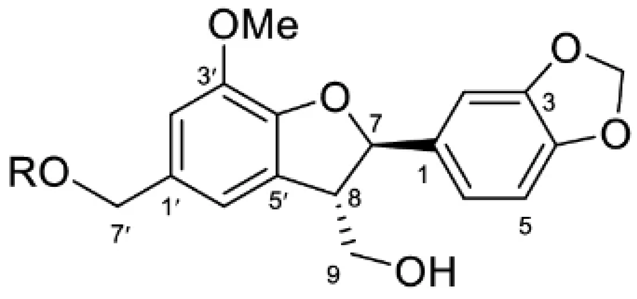 | C24H28O11 | 492.000 | No toxicity Anti-inflammatory and anti-aging effect | [9,110] |
| p-hydroxyphenyl | 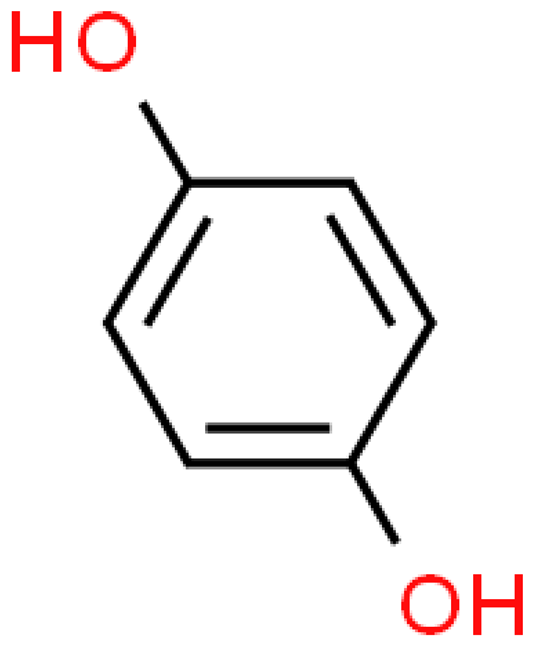 | C6H6O2 | 110.111 | Oral administration causes acute poisoning (abdominal pain, vomiting, tachycardia, convulsions, convulsions and coma) or formation of neoplastic lesions; skin contact may cause irritation (discoloration or erythema) and allergic dermatitis Treatment of melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation of the skin (tyrosinase inhibitor) | [33,111,112,113] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biernacka, P.; Adamska, I.; Felisiak, K. The Potential of Ginkgo biloba as a Source of Biologically Active Compounds—A Review of the Recent Literature and Patents. Molecules 2023, 28, 3993. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28103993
Biernacka P, Adamska I, Felisiak K. The Potential of Ginkgo biloba as a Source of Biologically Active Compounds—A Review of the Recent Literature and Patents. Molecules. 2023; 28(10):3993. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28103993
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiernacka, Patrycja, Iwona Adamska, and Katarzyna Felisiak. 2023. "The Potential of Ginkgo biloba as a Source of Biologically Active Compounds—A Review of the Recent Literature and Patents" Molecules 28, no. 10: 3993. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28103993
APA StyleBiernacka, P., Adamska, I., & Felisiak, K. (2023). The Potential of Ginkgo biloba as a Source of Biologically Active Compounds—A Review of the Recent Literature and Patents. Molecules, 28(10), 3993. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28103993






