Multifunctional Roles of Betulinic Acid in Cancer Chemoprevention: Spotlight on JAK/STAT, VEGF, EGF/EGFR, TRAIL/TRAIL-R, AKT/mTOR and Non-Coding RNAs in the Inhibition of Carcinogenesis and Metastasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Regulation of JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway
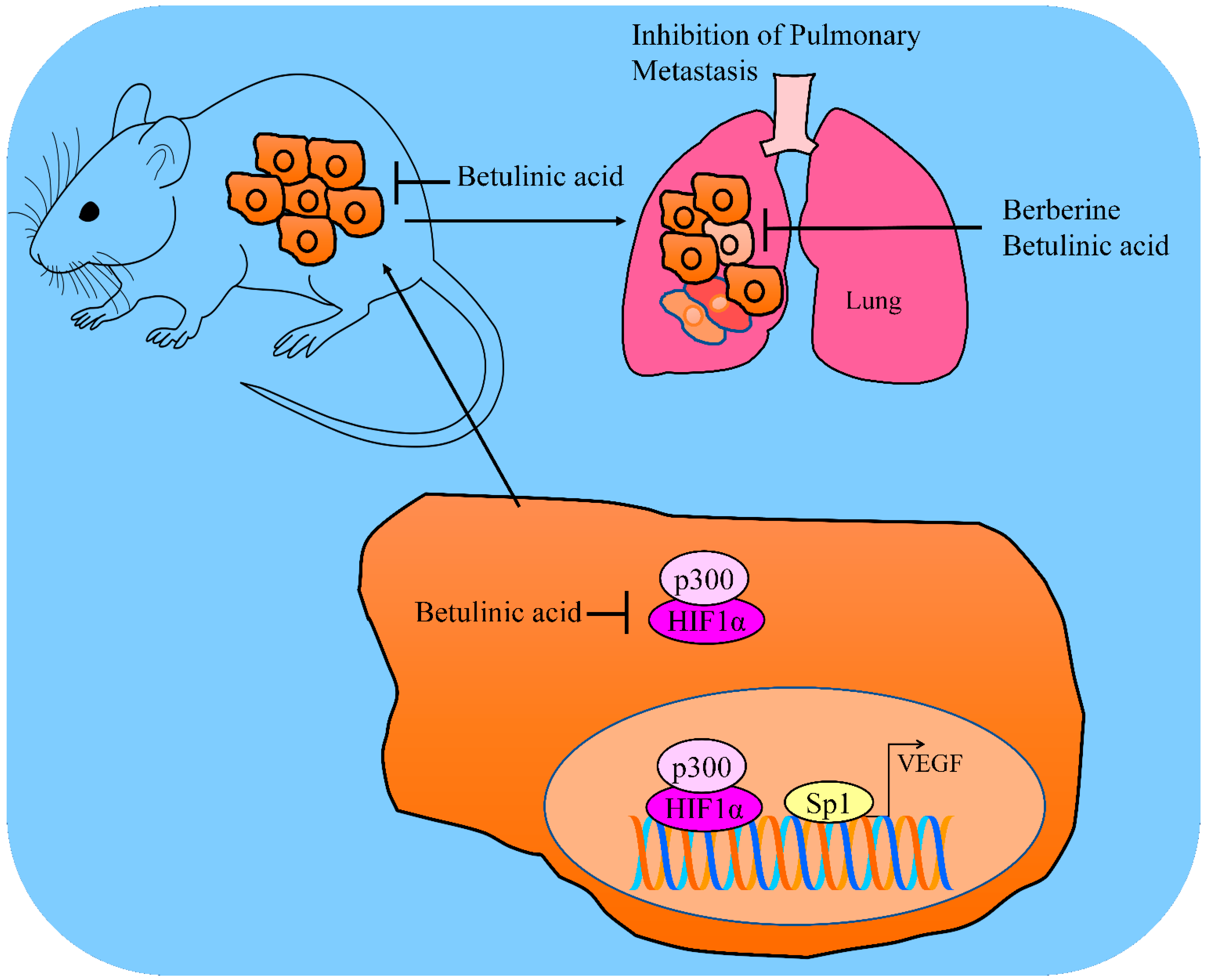
3. Regulation of VEGF
4. Regulation of EGFR
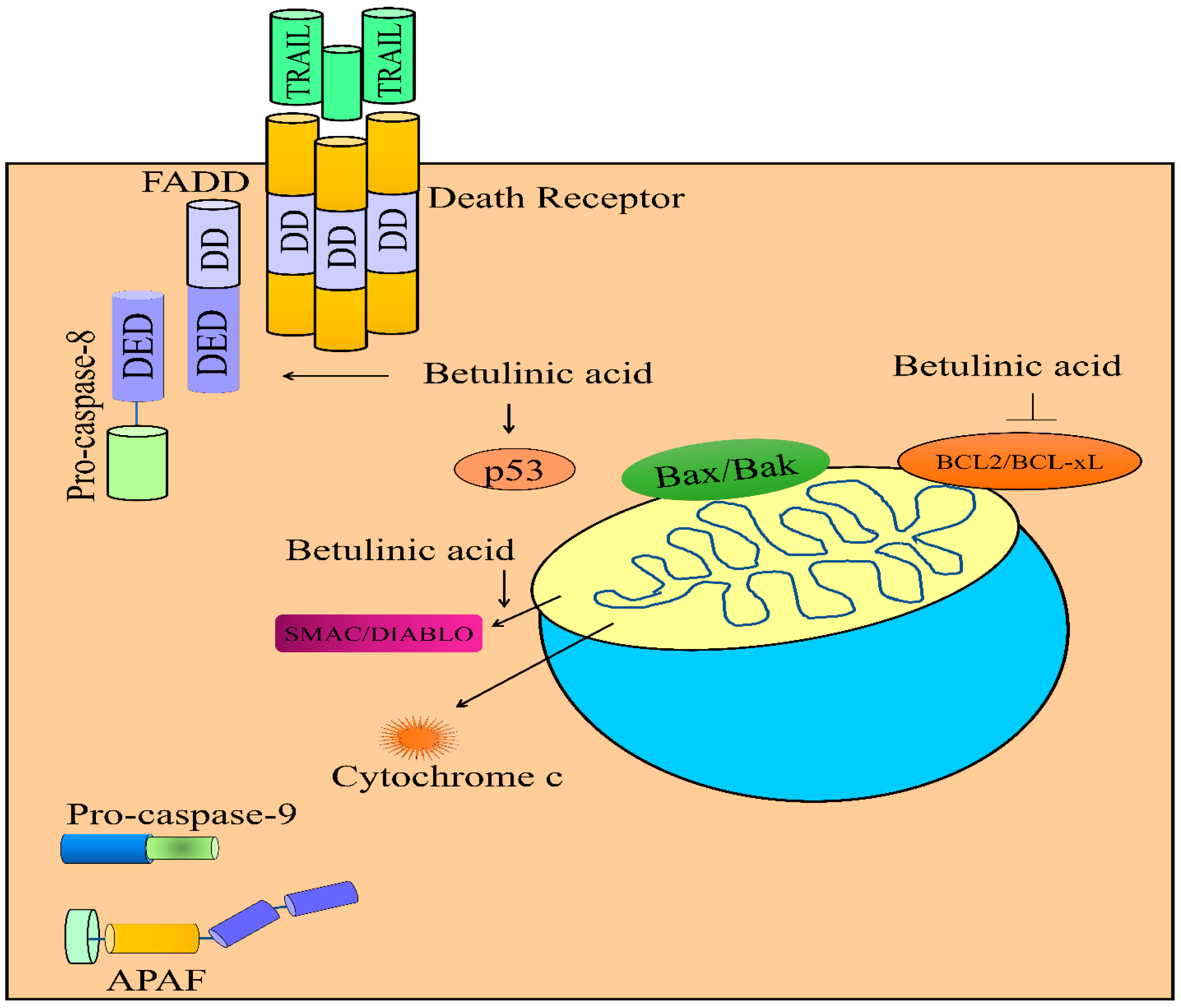
5. Regulation of TRAIL-Mediated Signaling
6. Regulation of Ubiquitination
7. Regulation of AKT/mTOR
8. Regulation of Non-Coding RNAs
9. Animal Models: Pharmacological Testing of Betulinic Acid in the Inhibition of Carcinogenesis and Metastasis
10. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puisieux, A.; Brabletz, T.; Caramel, J. Oncogenic roles of EMT-inducing transcription factors. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongre, A.; Weinberg, R.A. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valastyan, S.; Weinberg, R.A. Tumor metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell 2011, 147, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clardy, J.; Walsh, C. Lessons from natural molecules. Nature 2004, 432, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J. Natural products in cancer chemotherapy: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.; Reker, D.; Schneider, P.; Schneider, G. Counting on natural products for drug design. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehn, F.E.; Carter, G.T. The evolving role of natural products in drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.-Z.; Yang, X.-Z.; Wu, S.-N.; Wang, H.-G.; Shen, P.; Ma, T.-H. The protective effect of betulinic acid (BA) diabetic nephropathy on streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.-J.; Park, C.-H.; In, K.-R.; Kim, J.-B.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.; Chang, H.J. Antidiabetic effects of betulinic acid mediated by the activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase pathway. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-A.; Lee, J.-K.; Han, J.-S. Betulinic acid improves TNF-α-induced insulin resistance by inhibiting negative regulator of insulin signalling and inflammation-activated protein kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, G.A.-M.M.; Abu-Taweel, G.M.; Rajagopal, R.; Sun-Ju, K.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, Y.O.; Mothana, R.A.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Siddiqui, N.A.; et al. Betulinic acid lowers lipid accumulation in adipocytes through enhanced NCoA1–PPARγ interaction. J. Infect. Public Health 2019, 12, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-D.; Jung, H.-Y.; Ryu, H.; Kim, B.; Jeon, J.; Yoo, H.; Park, C.; Choi, B.-H.; Hyun, C.-K.; Fang, S.; et al. Betulinic acid inhibits high-fat diet-induced obesity and improves energy balance by activating AMPK. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-Y.; Won, K.-C.; Kim, B.-R.; Son, J.-K.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-W. Combined Treatment of Betulinic Acid, a PTP1B Inhibitor, with Orthosiphon stamineus Extract Decreases Body Weight in High-Fat–Fed Mice. J. Med. Food 2013, 16, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, C.L.; Queiroz, M.G.R.; Filho, A.C.V.A.; Rodrigues, A.M.; de Sousa, D.F.; Almeida, J.G.L.; Pessoa, O.D.L.; Silveira, E.R.; Menezes, D.B.; Melo, T.S.; et al. Betulinic Acid, a Natural Pentacyclic Triterpenoid, Prevents Abdominal Fat Accumulation in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 8776–8781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Han, B.H.; Choi, E.S.; Kho, M.C.; Park, J.H.; Ahn, Y.M.; Kim, H.Y.; Kang, D.G.; Lee, H.S. Protective effect of betulinic acid on early atherosclerosis in diabetic apolipoprotein-E gene knockout mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 796, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajala-Lawal, R.A.; Aliyu, N.O.; Ajiboye, T.O. Betulinic acid improves insulin sensitivity, hyperglycemia, inflammation and oxidative stress in metabolic syndrome rats via PI3K/Akt pathways. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 126, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathy, M.; Vijayan, A.; Daimary, U.D.; Girisa, S.; Radhakrishnan, K.V.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Betulinic acid: A natural promising anticancer drug, current situation, and future perspectives. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e23206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Li, X.; Dong, S.; Zhou, W. Betulinic acid in the treatment of tumour diseases: Application and research progress. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 111990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Bhadauria, A.S.; Singh, A.K.; Saha, S. Betulinic acid as apoptosis activator: Molecular mechanisms, mathematical modeling and chemical modifications. Life Sci. 2018, 209, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Fang, D.; Chu, P.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Z. Multiple molecular targets in breast cancer therapy by betulinic acid. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, E.A.; Walker, S.R.; Weisberg, E.; Bar-Natan, M.; Barrett, R.; Gashin, L.B.; Terrell, S.; Klitgaard, J.L.; Santo, L.; Addorio, M.R.; et al. The STAT5 inhibitor pimozide decreases survival of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells resistant to kinase inhibitors. Blood 2011, 117, 3421–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkson, J.; Ryan, D.; Kim, J.S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Haura, E.; Laudano, A.; Sebti, S.; Hamilton, A.D.; Jove, R. Phosphotyrosyl Peptides Block Stat3-mediated DNA Binding Activity, Gene Regulation, and Cell Transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 45443–45455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiquee, K.; Zhang, S.; Guida, W.C.; Blaskovich, M.A.; Greedy, B.; Lawrence, H.R.; Yip, M.L.R.; Jove, R.; McLaughlin, M.M.; Lawrence, N.J.; et al. Selective chemical probe inhibitor of Stat3, identified through structure-based virtual screening, induces antitumor activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7391–7396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, A.J.; Dai, W.; O’Mara, M.L.; Abankwa, D.; Chhabra, Y.; Pelekanos, R.A.; Gardon, O.; Tunny, K.A.; Blucher, K.M.; Morton, C.J.; et al. Mechanism of activation of protein kinase JAK2 by the growth hormone receptor. Science 2014, 344, 1249783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmes, S.; Hafer, M.; Vuorio, J.; Tucker, J.A.; Winkelmann, H.; Löchte, S.; Stanly, T.A.; Prieto, K.D.P.; Poojari, C.; Sharma, V.; et al. Mechanism of homodimeric cytokine receptor activation and dysregulation by oncogenic mutations. Science 2020, 367, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassman, C.R.; Tsutsumi, N.; Saxton, R.A.; Lupardus, P.J.; Jude, K.M.; Garcia, K.C. Structure of a Janus kinase cytokine receptor complex reveals the basis for dimeric activation. Science 2022, 376, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.-Q.; Yu, Y.; Yao, Y.-Q.; Yang, F.-F.; Liao, M.; Song, L.-J.; Li, Y.-L.; Li, Y.-J.; Deng, Y.-L.; Yang, S.-P.; et al. Betulinic acid impairs metastasis and reduces immunosuppressive cells in breast cancer models. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 3794–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Ye, X.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Ding, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Kuang, Y.; et al. CREPT/RPRD1B promotes tumorigenesis through STAT3-driven gene transcription in a p300-dependent manner. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Gao, Y.-Q.; Dai, W.-B.; Hu, Y.; Wu, Y.-F.; Mei, Q.-X. Helicteric Acid, Oleanic Acid, and Betulinic Acid, Three Triterpenes fromHelicteres angustifoliaL.; Inhibit Proliferation and Induce Apoptosis in HT-29 Colorectal Cancer Cells via Suppressing NF-κB and STAT3 Signaling. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 5180707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Xun, W.; Wei, K.; Zeng, G. Betulinic Acid Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma via Modulating ROS-Regulated p53 Signaling. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2017, 25, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Lee, H.-J.; Jung, D.-B.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, E.-O.; Lee, S.-G.; Shim, B.S.; Choi, S.H.; Ko, S.G.; Ahn, K.S.; et al. Suppression of STAT3 and HIF-1 Alpha Mediates Anti-Angiogenic Activity of Betulinic Acid in Hypoxic PC-3 Prostate Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, M.K.; Sung, B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Betulinic acid suppresses STAT3 activation pathway through induction of protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 in human multiple myeloma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintharlapalli, S.; Papineni, S.; Ramaiah, S.K.; Safe, S. Betulinic acid inhibits prostate cancer growth through inhibition of specificity protein transcription factors. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2816–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Jia, Z.; Kong, X.; Li, Q.; Chang, D.Z.; Wei, D.; Le, X.; Suyun, H.; Huang, S.; Wang, L.; et al. Combining Betulinic Acid and Mithramycin A Effectively Suppresses Pancreatic Cancer by Inhibiting Proliferation, Invasion, and Angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5182–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Huang, X.; Xie, W.; Xiang, W.; Yao, P. Combination of betulinic acid and chidamide inhibits acute myeloid leukemia by suppression of the HIF1α pathway and generation of reactive oxygen species. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 94743–94758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godugu, C.; Patel, A.R.; Doddapaneni, R.; Somagoni, J.; Singh, M. Approaches to Improve the Oral Bioavailability and Effects of Novel Anticancer Drugs Berberine and Betulinic Acid. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blume-Jensen, P.; Hunter, T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature 2001, 411, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirotnak, F.M.; Zakowski, M.F.; Miller, V.A.; Scher, H.I.; Kris, M.G. Efficacy of cytotoxic agents against human tumor xenografts is markedly enhanced by coadministration of ZD1839 (Iressa), an inhibitor of EGFR tyrosine kinase. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 4885–4892. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Baselga, J.; Masui, H.; Mendelsohn, J. Antitumor effect of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies plus cis-diamminedichloroplatinum on well established A431 cell xenografts. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 4637–4642. [Google Scholar]
- Ciardiello, F.; Caputo, R.; Bianco, R.; Damiano, V.; Pomatico, G.; De Placido, S.; Bianco, A.R.; Tortora, G. Antitumor effect and potentiation of cytotoxic drugs activity in human cancer cells by ZD-1839 (Iressa), an epidermal growth factor receptor-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chadalapaka, G.; Jutooru, I.; Burghardt, R.; Safe, S. Drugs that Target Specificity Proteins Downregulate Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Bladder Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.-L.; Lin, C.-H.; Chen, H.-C.; Hung, W.-H.; Chien, P.-J.; Chang, H.-Y.; Wang, B.-Y. Effects and mechanisms of betulinic acid on improving EGFR TKI-resistance of lung cancer cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, Q.; Di, W.; Jiang, Q.; Schefeller, E.; Derby, S.; Wanebo, H.; Yan, B.; Wan, Y. Transient activation of EGFR/AKT cell survival pathway and expression of survivin contribute to reduced sensitivity of human melanoma cells to betulinic acid. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 27, 823–830. [Google Scholar]
- Pitti, R.M.; Marsters, S.A.; Ruppert, S.; Donahue, C.J.; Moore, A.; Ashkenazi, A. Induction of Apoptosis by Apo-2 Ligand, a New Member of the Tumor Necrosis Factor Cytokine Family. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 12687–12690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, H.; Miller, R.E.; Ariail, K.; Gliniak, B.; Griffith, T.S.; Kubin, M.; Chin, W.; Jones, J.; Woodward, A.; Le, T.; et al. Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor–related apoptosis–inducing ligand in vivo. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; O’Rourke, K.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Gentz, R.; Ebner, R.; Ni, J.; Dixit, V.M. The Receptor for the Cytotoxic Ligand TRAIL. Science 1997, 276, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Franco, A.; Myers, K.; Gray, C.; Nguyen, T.; Hersey, P. Relation of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor and FLICE-inhibitory protein expression to TRAIL-induced apoptosis of melanoma. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 2747–2753. [Google Scholar]
- Gliniak, B.; Le, T. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand’s antitumor activity in vivo is enhanced by the chemotherapeutic agent CPT-11. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 6153–6158. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, W.; Isenmann, S.; Naumann, U.; Kügler, S.; Bähr, M.; Dichgans, J.; Ashkenazi, A.; Weller, M. Locoregional Apo2L/TRAIL eradicates intracranial human malignant glioma xenografts in athymic mice in the absence of neurotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999, 265, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Q.-J.; Feng, Y.-L.; Pan, F. Betulinic acid promotes TRAIL function on liver cancer progression inhibition through p53/Caspase-3 signaling activation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulda, S.; Jeremias, I.; Debatin, K.-M. Cooperation of betulinic acid and TRAIL to induce apoptosis in tumor cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7611–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulda, S.; Debatin, K.-M. Sensitization for Anticancer Drug-Induced Apoptosis by Betulinic Acid. Neoplasia 2005, 7, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Hong, M.; Yu, X.; Wei, S.; Fan, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; et al. Phytochemical library screening reveals betulinic acid as a novel Skp2-SCF E3 ligase inhibitor in non–small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 3218–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Cho, H.-S.; Ban, H.S.; Nakamura, H. Suppression of HIF-1α accumulation by betulinic acid through proteasome activation in hypoxic cervical cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 523, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.; Wang, C.; Hu, N.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Lei, Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, L.; Chen, C.; Lan, P.; et al. Inhibition of PINK1/Parkin-dependent mitophagy sensitizes multidrug-resistant cancer cells to B5G1, a new betulinic acid analog. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.-Y.; Meng, Z.; Xu, K.; Li, Q.-F.; Chen, C.; Li, K.-Y.; Zhang, B. Betulinic acid increases radiosensitization of oral squamous cell carcinoma through inducing Sp1 sumoylation and PTEN expression. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2360–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.-I.; Wang, M.-C.; Chen, S.-Y.; Huang, S.-T.; Yeh, Y.-M.; Su, W.-C.; Chang, W.-C.; Hung, J.-J. Betulinic Acid Decreases Specificity Protein 1 (Sp1) Level via Increasing the Sumoylation of Sp1 to Inhibit Lung Cancer Growth. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 82, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, S.; Qu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Chen, R.; Wei, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q. Betulinic acid induces autophagy-mediated apoptosis through suppression of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 6952–6964. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Zhu, H.; Weng, M.; Wang, C.; Sun, L. Chemopreventive effect of Betulinic acid via mTOR -Caspases/Bcl2/Bax apoptotic signaling in pancreatic cancer. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.G.; Ambs, S.; Cimmino, A.; Petrocca, F.; Visone, R.; Iorio, M.; Roldo, C.; Ferracin, M.; et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lytle, J.R.; Yario, T.A.; Steitz, J.A. Target mRNAs are repressed as efficiently by microRNA-binding sites in the 5’ UTR as in the 3’ UTR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9667–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khraiwesh, B.; Arif, M.A.; Seumel, G.I.; Ossowski, S.; Weigel, D.; Reski, R.; Frank, W. Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression by MicroRNAs. Cell 2010, 140, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabili, M.N.; Dunagin, M.C.; McClanahan, P.D.; Biaesch, A.; Padovan-Merhar, O.; Regev, A.; Rinn, J.L.; Raj, A. Localization and abundance analysis of human lncRNAs at single-cell and single-molecule resolution. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, M.K.; Niknafs, Y.S.; Malik, R.; Singhal, U.; Sahu, A.; Hosono, Y.; Barrette, T.R.; Prensner, J.R.; Evans, J.R.; Zhao, S.; et al. The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, M.; Amit, I.; Garber, M.; French, C.; Lin, M.F.; Feldser, D.; Huarte, M.; Zuk, O.; Carey, B.W.; Cassady, J.P.; et al. Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 2009, 458, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.-S.; Somvanshi, S.; Patel, E.; Chen, T.-W.; Singh, V.P.; Zorman, B.; Patil, S.L.; Pan, Y.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Sood, A.K.; et al. Pan-Cancer Analysis of lncRNA Regulation Supports Their Targeting of Cancer Genes in Each Tumor Context. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Qiu, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W. p53-p66shc/miR-21-Sod2 signaling is critical for the inhibitory effect of betulinic acid on hepatocellular carcinoma. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 238, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jutooru, I.; Lei, P.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.-O.; Brents, L.K.; Prather, P.L.; Safe, S. Betulinic Acid Targets YY1 and ErbB2 through Cannabinoid Receptor-Dependent Disruption of MicroRNA-27a:ZBTB10 in Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintharlapalli, S.; Papineni, S.; Lei, P.; Pathi, S.; Safe, S. Betulinic acid inhibits colon cancer cell and tumor growth and induces proteasome-dependent and -independent downregulation of specificity proteins (Sp) transcription factors. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; Chadalapaka, G.; Cho, S.-G.; Lee, S.-O.; Jin, U.-H.; Jutooru, I.; Choi, K.; Leung, Y.-K.; Ho, S.-M.; Safe, S.; et al. The Transcriptional Repressor ZBTB4 Regulates EZH2 Through a MicroRNA-ZBTB4-Specificity Protein Signaling Axis. Neoplasia 2014, 16, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhong, Z.; Tan, H.Y.; Guo, W.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, C.; Wang, N.; Ren, J.; Feng, Y. Suppression of lncRNA MALAT1 by betulinic acid inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting IAPs via miR-22-3p. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; He, N.; Zhou, X.; Wang, F.; Cai, H.; Huang, S.H.; Chen, X.; Hu, Z.; Jin, X. Betulinic acid induces autophagy-dependent apoptosis via Bmi-1/ROS/AMPK-mTOR-ULK1 axis in human bladder cancer cells. Aging 2021, 13, 21251–21267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Wei, D.; Yu, K.; Ma, D.; Xiong, J.; Fang, Q.; Wang, J. Betulinic acid restores imatinib sensitivity in BCR-ABL1 kinase−independent, imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia by increasing HDAC3 ubiquitination and degradation. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2020, 1467, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, W.-L.; Hsu, T.-I.; Yang, W.-B.; Kao, T.-J.; Wu, M.-H.; Huang, Y.-N.; Yeh, S.-H.; Chuang, J.-Y. Betulinic Acid-Mediated Tuning of PERK/CHOP Signaling by Sp1 Inhibition as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Glioblastoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, M.E.; Firek, M.; Chen, S.-T.; Amaar, Y.G. Evidence that RASSF1C Stimulation of Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation Depends on IGFBP-5 and PIWIL1 Expression Levels. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenmüller, M.; Hemmerlein, B.; Von Schweinitz, D.; Kappler, R. Betulinic acid induces apoptosis and inhibits hedgehog signalling in rhabdomyosarcoma. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, K.R.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, C.K.; Park, K.-K.; Chung, W.-Y. Betulinic acid, a bioactive pentacyclic triterpenoid, inhibits skeletal-related events induced by breast cancer bone metastases and treatment. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 275, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Lv, S.J.; Wu, Z.; Qian, M.; Xu, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, T.; Guo, W.; Hou, T.; Li, X.; et al. Role of betulinic acid derivative SH-479 in triple negative breast cancer and bone microenvironment. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.-I.; Chen, Y.-J.; Hung, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Lin, S.-J.; Su, W.-C.; Lai, M.-D.; Kim, S.-Y.; Wang, Q.; Qian, K.; et al. A novel derivative of betulinic acid, SYK023, suppresses lung cancer growth and malignancy. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 13671–13687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Du, Y.; Kong, X.; Li, Z.; Jia, Z.; Cui, J.; Gao, J.; Wang, G.; Xie, K. Lamin B1 Is a Novel Therapeutic Target of Betulinic Acid in Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4651–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, N.; Kataoka, K.; Kondo, K.; Arimochi, H.; Fujino, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Miyoshi, T.; Kuwahara, T.; Monden, Y.; Ohnishi, Y. Betulinic acid augments the inhibitory effects of vincristine on growth and lung metastasis of B16F10 melanoma cells in mice. Br. J. Cancer. 2004, 90, 1672–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, A.; Hua, H.; Liu, L.; Zhao, J. Betulinic acid induces apoptosis and inhibits metastasis of human colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 2546–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, T.; Li, D.; Huang, Y.; Li, Q.; Bai, G.; Shi, L. Betulinic acid induces apoptosis and suppresses metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines in vitro and in vivo. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- YaYang, C.; Li, Y.; Fu, L.; Jiang, T.; Meng, F. Betulinic acid induces apoptosis and inhibits metastasis of human renal carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 8611–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, J.; Jiang, W. 23-hydroxybetulinic acid reduces tumorigenesis, metastasis and immunosuppression in a mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma via disruption of the MAPK signaling pathway. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2022, 33, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farooqi, A.A.; Turgambayeva, A.; Tashenova, G.; Tulebayeva, A.; Bazarbayeva, A.; Kapanova, G.; Abzaliyeva, S. Multifunctional Roles of Betulinic Acid in Cancer Chemoprevention: Spotlight on JAK/STAT, VEGF, EGF/EGFR, TRAIL/TRAIL-R, AKT/mTOR and Non-Coding RNAs in the Inhibition of Carcinogenesis and Metastasis. Molecules 2023, 28, 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010067
Farooqi AA, Turgambayeva A, Tashenova G, Tulebayeva A, Bazarbayeva A, Kapanova G, Abzaliyeva S. Multifunctional Roles of Betulinic Acid in Cancer Chemoprevention: Spotlight on JAK/STAT, VEGF, EGF/EGFR, TRAIL/TRAIL-R, AKT/mTOR and Non-Coding RNAs in the Inhibition of Carcinogenesis and Metastasis. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):67. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010067
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarooqi, Ammad Ahmad, Assiya Turgambayeva, Gulnara Tashenova, Aigul Tulebayeva, Aigul Bazarbayeva, Gulnara Kapanova, and Symbat Abzaliyeva. 2023. "Multifunctional Roles of Betulinic Acid in Cancer Chemoprevention: Spotlight on JAK/STAT, VEGF, EGF/EGFR, TRAIL/TRAIL-R, AKT/mTOR and Non-Coding RNAs in the Inhibition of Carcinogenesis and Metastasis" Molecules 28, no. 1: 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010067
APA StyleFarooqi, A. A., Turgambayeva, A., Tashenova, G., Tulebayeva, A., Bazarbayeva, A., Kapanova, G., & Abzaliyeva, S. (2023). Multifunctional Roles of Betulinic Acid in Cancer Chemoprevention: Spotlight on JAK/STAT, VEGF, EGF/EGFR, TRAIL/TRAIL-R, AKT/mTOR and Non-Coding RNAs in the Inhibition of Carcinogenesis and Metastasis. Molecules, 28(1), 67. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010067







