A Renewable Biosensor Based on LNA-Aptamer Hybridization for the Detection of Salmonella enteritidis in Penaeus vannamei
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
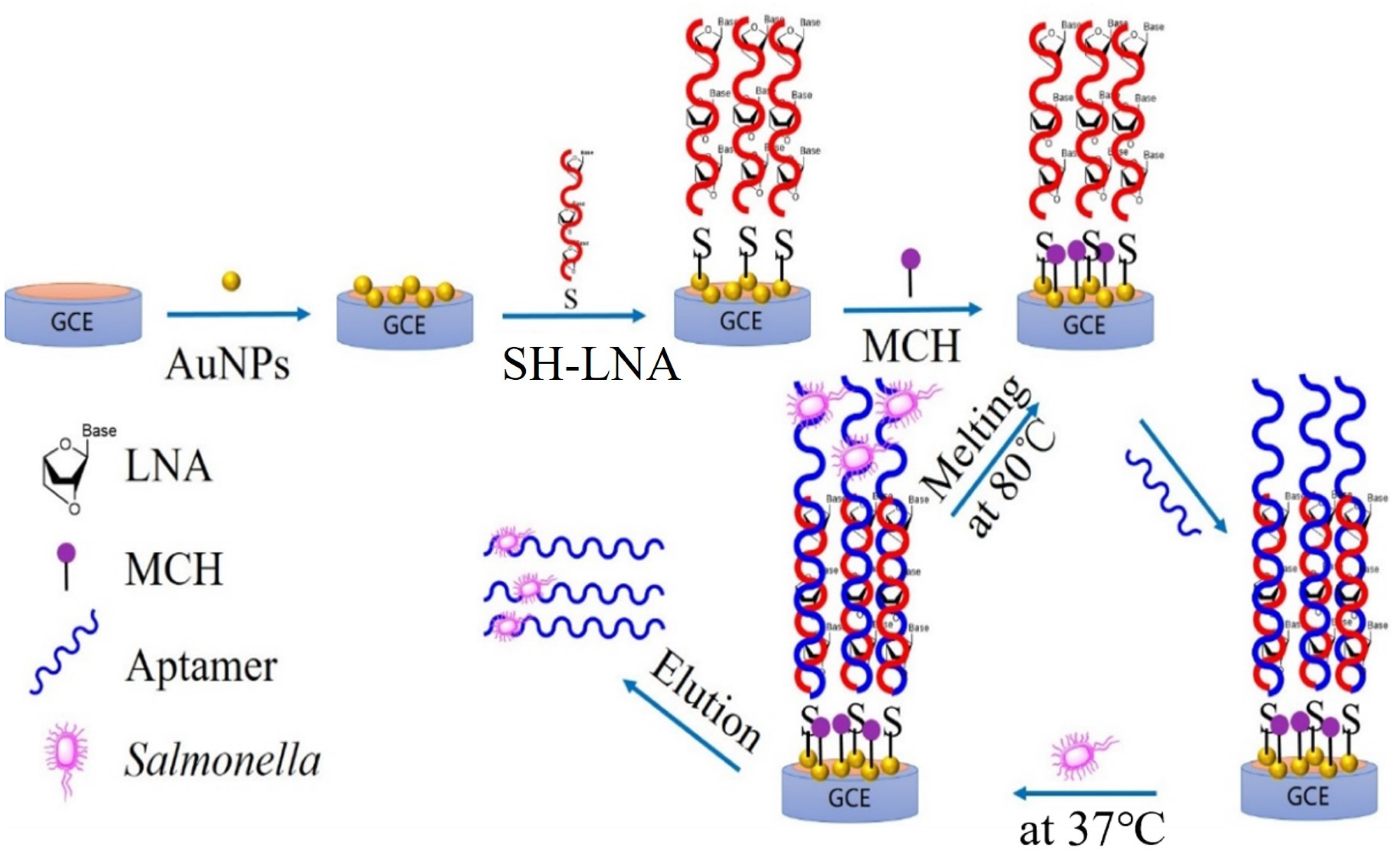
2.1. Working Principle of the Electrochemical Biosensor
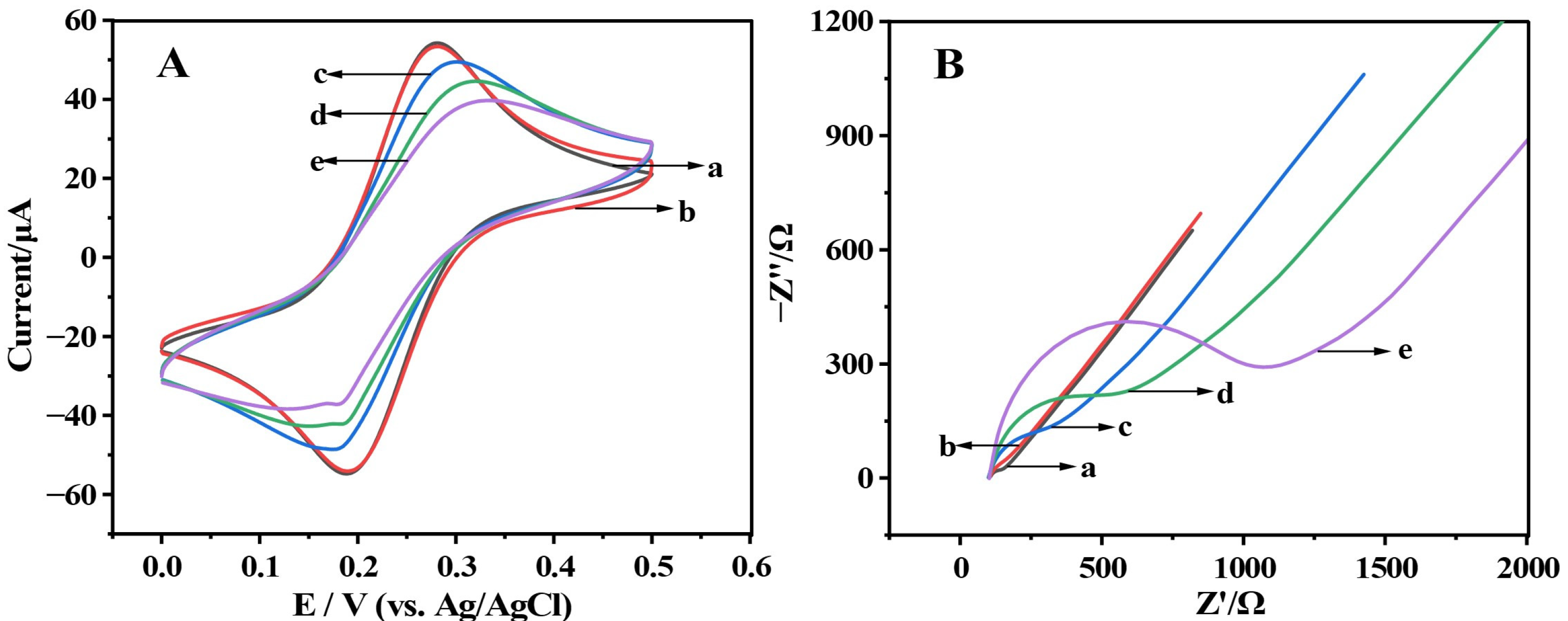
2.2. Characterization of Renewable Biosensor Based on LNA-Aptamer Hybridization
2.3. Optimization of Renewable Biosensor Performance
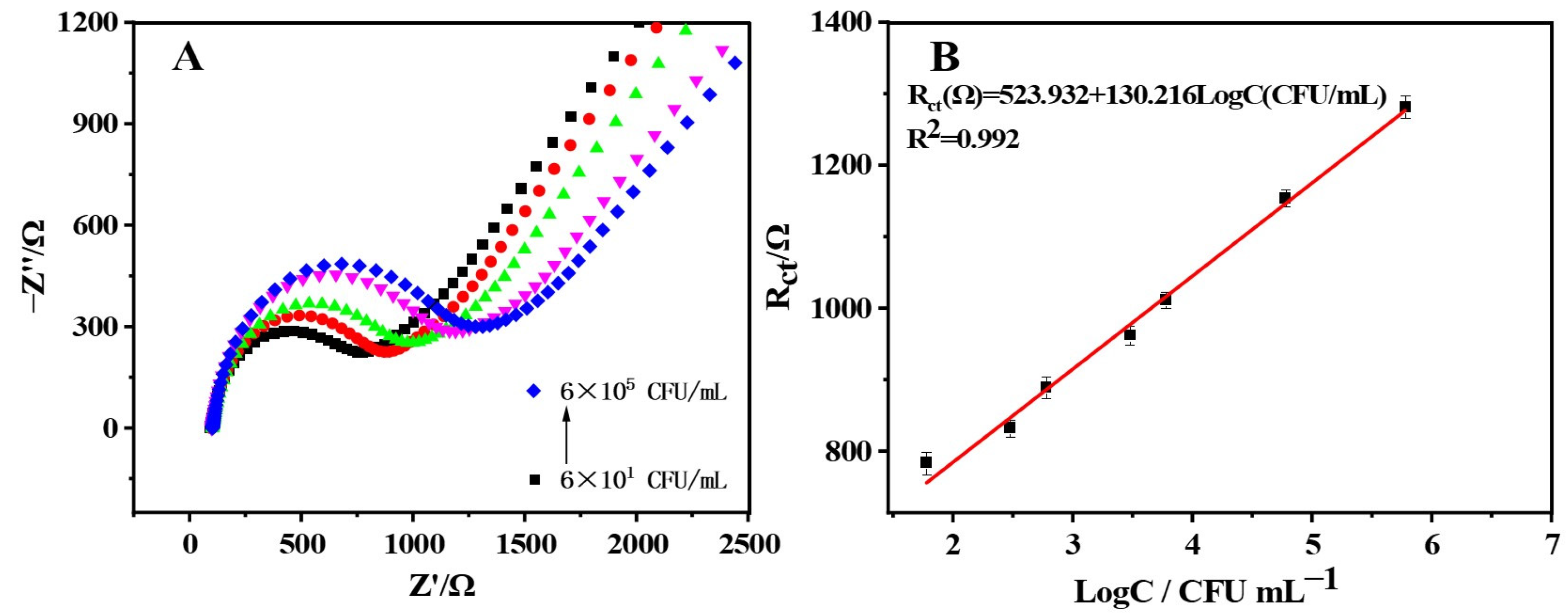
2.4. Salmonella enteritidis Quantitative Detection
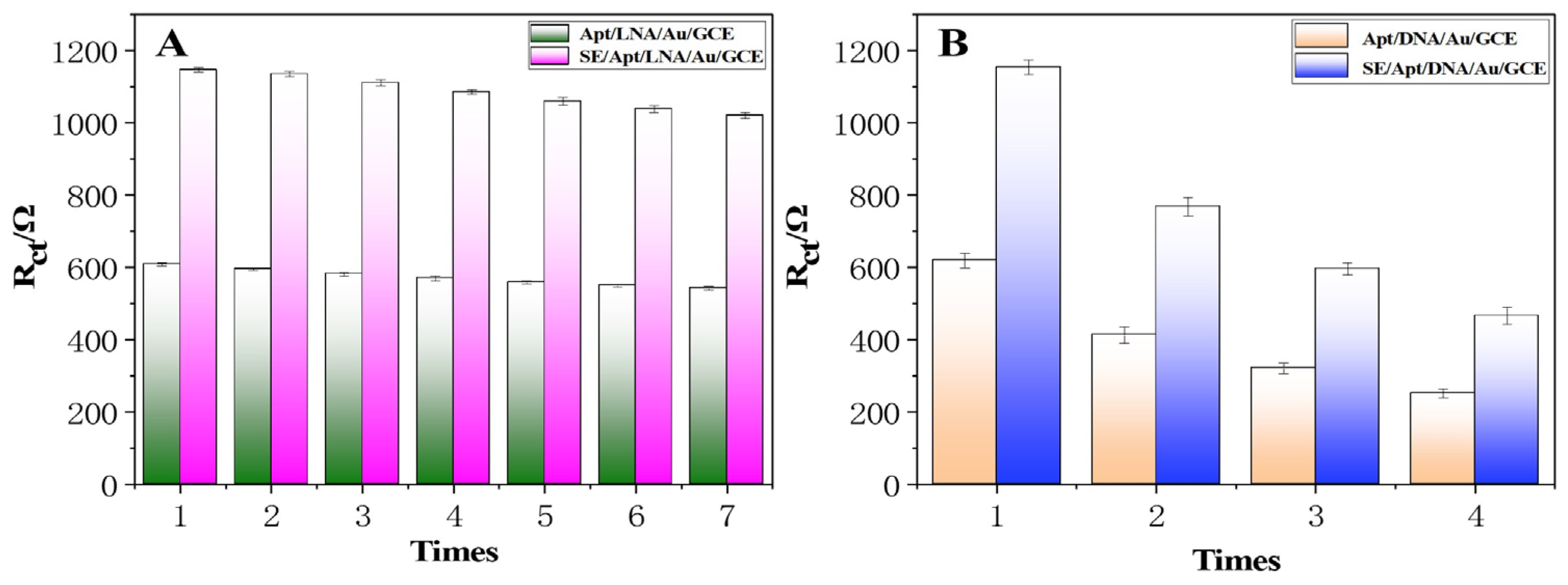
2.5. Stability, Repeatability, and Selectivity of the Renewable Biosensor
2.6. Renewability of the Renewable Biosensor
2.7. Real Sample Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Equipment
3.3. Preparation of Renewable Biosensor
3.4. Regeneration of Biosensor
3.5. Culture and Counting of Bacteria
3.6. Electrochemical Measurements
3.7. Recovery of Salmonella enteritidis in Penaeus vannamei
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perry, J.J.; Yousef, A.E. Salmonella Enteritidis in Shell Eggs. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 81, 243–274. [Google Scholar]
- Pulido-Landínez, M.; Sánchez-Ingunza, R.; Guard, J.; Nascimento, V.P.D. Presence of Salmonella Enteritidis and Salmonella Gallinarum in Commercial Laying Hens Diagnosed with Fowl Typhoid Disease in Colombia. Avian Dis. 2013, 58, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, A.; Stanaway, J.; Sarkar, K.; Crump, J. The Global Burden of Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Invasive Disease: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 101, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.W.F.; Ab Mutalib, N.S.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H. Rapid Methods for the Detection of Foodborne Bacterial Pathogens: Principles, Applications, Advantages and Limitations. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Dijk, S.; Bruins, M.J.; Ruijs, G.J.H.M. Evaluation and Implementation of a Chromogenic Agar Medium for Salmonella Detection in Stool in Routine Laboratory Diagnostics. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooks, B.W.; Lutze-Wallace, C.L.; Devenish, J.; Elmufti, M.; Burke, T. Comparison of an Antigen-Capture Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay with Bacterial Culture for Detection of Salmonella in Poultry-Hatchery Environmental Samples. Can. J. Vet. Res. Rev. Can. Rech. Vétérinaire 2014, 78, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Furrer, B.; Baumgartner, A.; Bommeli, W. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (Elisa) for the Detection of Antibodies against Salmonella Enteritidis in Chicken Blood or Egg Yolk. Zent. Bakteriol. 1993, 279, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khnouf, R.; Jaradat, M.A.K.; Karasneh, D.; Al-Shami, F.; Sawaqed, L.; Albiss, B.A. Simulation and Optimization of a Single Heater Convective Pcr Chip and Its Controller for Fast Salmonella Enteritidis Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 13186–13195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, M.; Bueno, D.; Colazo, J. A Comparative Study of Culture Methods and Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay for Salmonella Detection in Poultry Feed. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Yuan, F.; Ye, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yao, L.; Xue, F.; Chen, W.; Li, B. Aptamer-Based Technologies in Foodborne Pathogen Detection. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Justino, C.I.L.; Freitas, A.C.; Pereira, R.; Duarte, A.C.; Santos, T.A.P.R. Recent Developments in Recognition Elements for Chemical Sensors and Biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 68, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yu, Z.; Han, X.; Lai, R.Y. Electrochemical Aptamer-Based Sensors for Food and Water Analysis: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1051, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, F.; Yu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z. An Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for the Detection of Salmonella. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 98, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniandy, S.; Teh, S.J.; Appaturi, J.N.; Thong, K.L.; Lai, C.W.; Ibrahim, F.; Leo, B.F. A Reduced Graphene Oxide-Titanium Dioxide Nanocomposite Based Electrochemical Aptasensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Salmonella enterica. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 127, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braasch, D.A.; Corey, D.R. Locked Nucleic Acid (Lna): Fine-Tuning the Recognition of DNA and Rna. Cell Chem. Biol. 2001, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.K.; Koshkin, A.A.; Wengel, J.; Nielsen, P. Lna (Locked Nucleic Acids): Synthesis and High-Affinity Nucleic Acid Recognition. Chem. Commun. 1998, 455–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondensgaard, K.; Petersen, M.; Singh, S.K.; Rajwanshi, V.K.; Kumar, R.; Wengel, J.; Jacobsen, J.P. Structural Studies of Lna:Rna Duplexes by Nmr: Conformations and Implications for Rnase H Activity. Chem. A Eur. J. 2000, 6, 2687–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengel, J. Synthesis of 3′-C- and 4′-C-Branched Oligodeoxynucleotides and the Development of Locked Nucleic Acid (Lna). Acc. Chem. Res. 1999, 32, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, K.; Lin, X.; Huang, L.; Chen, G. Electrochemical Biosensor for Detection of Bcr/Abl Fusion Gene Using Locked Nucleic Acids on 4-Aminobenzenesulfonic Acid-Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8028–8034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlestedt, C.; Salmi, P.; Good, L.; Kela, J.; Johnsson, T.; Hökfelt, T.; Broberger, C.; Porreca, F.; Lai, J.; Ren, K.; et al. Potent and Nontoxic Antisense Oligonucleotides Containing Locked Nucleic Acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5633–5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, P.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, L.; Chen, G.; Fu, F. A Signal-on Electrochemiluminescence Aptamer Biosensor for the Detection of Ultratrace Thrombin Based on Junction-Probe. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2645–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Su, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Ni, X.; Chen, Z. A Sensitive Signal-on Electrochemical Assay for Mtase Activity Using Aunps Amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, C.M.A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy in the Characterisation and Application of Modified Electrodes for Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors. Molecules 2022, 27, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D. A Novel Multifunctional Electrochemical Platform for Simultaneous Detection, Elimination, and Inactivation of Pathogenic Bacteria Based on the Vancomycin-Functionalised Agnps/3d-Zno Nanorod Arrays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropero-Vega, J.L.; Redondo-Ortega, J.F.; Rodriguez-Caicedo, J.P.; Rondon-Villarreal, P.; Florez-Castillo, J.M. New Peptir-2.0 Peptide Designed for Use as Recognition Element in Electrochemical Biosensors with Improved Specificity towards E. coli O157:H7. Molecules 2022, 27, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, M.M.; Che-Engku-Chik, C.; Yusof, N.; Abdullah, J.; Othman, S.; Issa, R.; Noh, M.; Wasoh, H. DNA Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Iron Oxide/Nanocellulose Crystalline Composite Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode for Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Molecules 2020, 25, 3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, F.I.; Procura, F.; Bueno, D.J. Comparison of 7 Culture Methods for Salmonella Serovar Enteritidis and Salmonella Serovar Typhimurium Isolation in Poultry Feces. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 3826–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Added (CFU/mL) | Measured (CFU/mL) | Recovery (%) | The Relative Standard Deviations (RSD, %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6.520 × 101 | 8.763 × 101 | 134.82 | 7.830 |
| 6.520 × 102 | 6.578 × 102 | 101.20 | 7.110 |
| 6.520 × 103 | 6.424 × 103 | 98.84 | 16.270 |
| Name | Sequences |
|---|---|
| SH-LNA | 5′-HS-ALGAGTTCALAAAGCCCLTTC-3′ (L: 2′-O,4′-C-methylene-(D-ribofuranosyl) nucleotides LNA) |
| Aptamer | 5′-TTTTTGCGATCCAAGCTTCTTCAATTGGAGTGCTACCGAGATACATGGGTGGGCTCAAACAATCGTGGGCTCGCTTGATACTAGACTGCACATCTGAAGGGCTTTTGAACTCT-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Shi, J.; Zou, X. A Renewable Biosensor Based on LNA-Aptamer Hybridization for the Detection of Salmonella enteritidis in Penaeus vannamei. Molecules 2023, 28, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010450
Li Z, Zhao L, Wu Q, Zhang X, Huang X, Shi J, Zou X. A Renewable Biosensor Based on LNA-Aptamer Hybridization for the Detection of Salmonella enteritidis in Penaeus vannamei. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010450
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhihua, Ling Zhao, Qian Wu, Xue Zhang, Xiaowei Huang, Jiyong Shi, and Xiaobo Zou. 2023. "A Renewable Biosensor Based on LNA-Aptamer Hybridization for the Detection of Salmonella enteritidis in Penaeus vannamei" Molecules 28, no. 1: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010450
APA StyleLi, Z., Zhao, L., Wu, Q., Zhang, X., Huang, X., Shi, J., & Zou, X. (2023). A Renewable Biosensor Based on LNA-Aptamer Hybridization for the Detection of Salmonella enteritidis in Penaeus vannamei. Molecules, 28(1), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010450







