Study on Volatile Chemicals as Spoilage Indexes of Salmon by HS-SPME-GC-MS Technique during Non-Frozen Storage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
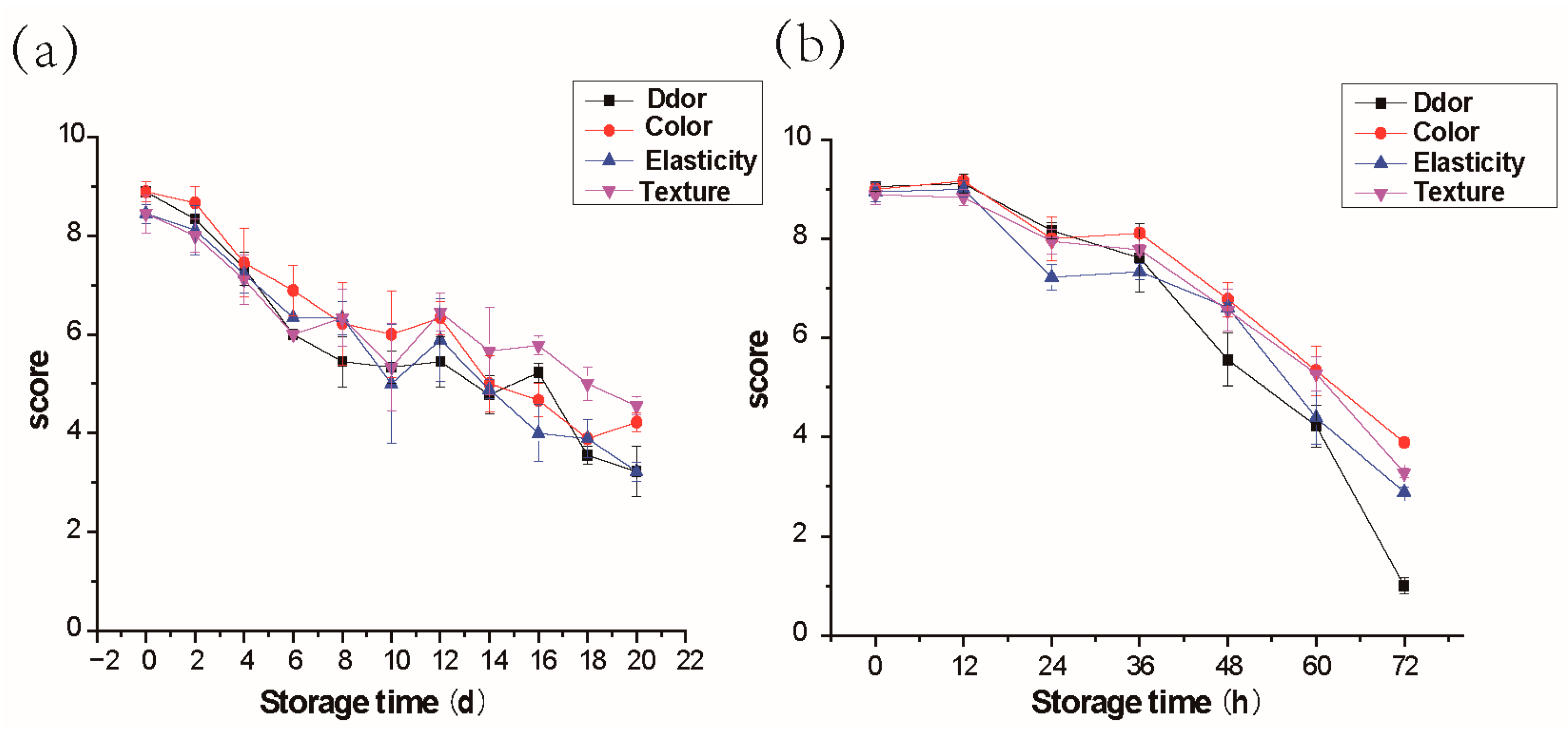
2.1. Sensory Analysis
2.2. Principal Component Analysis
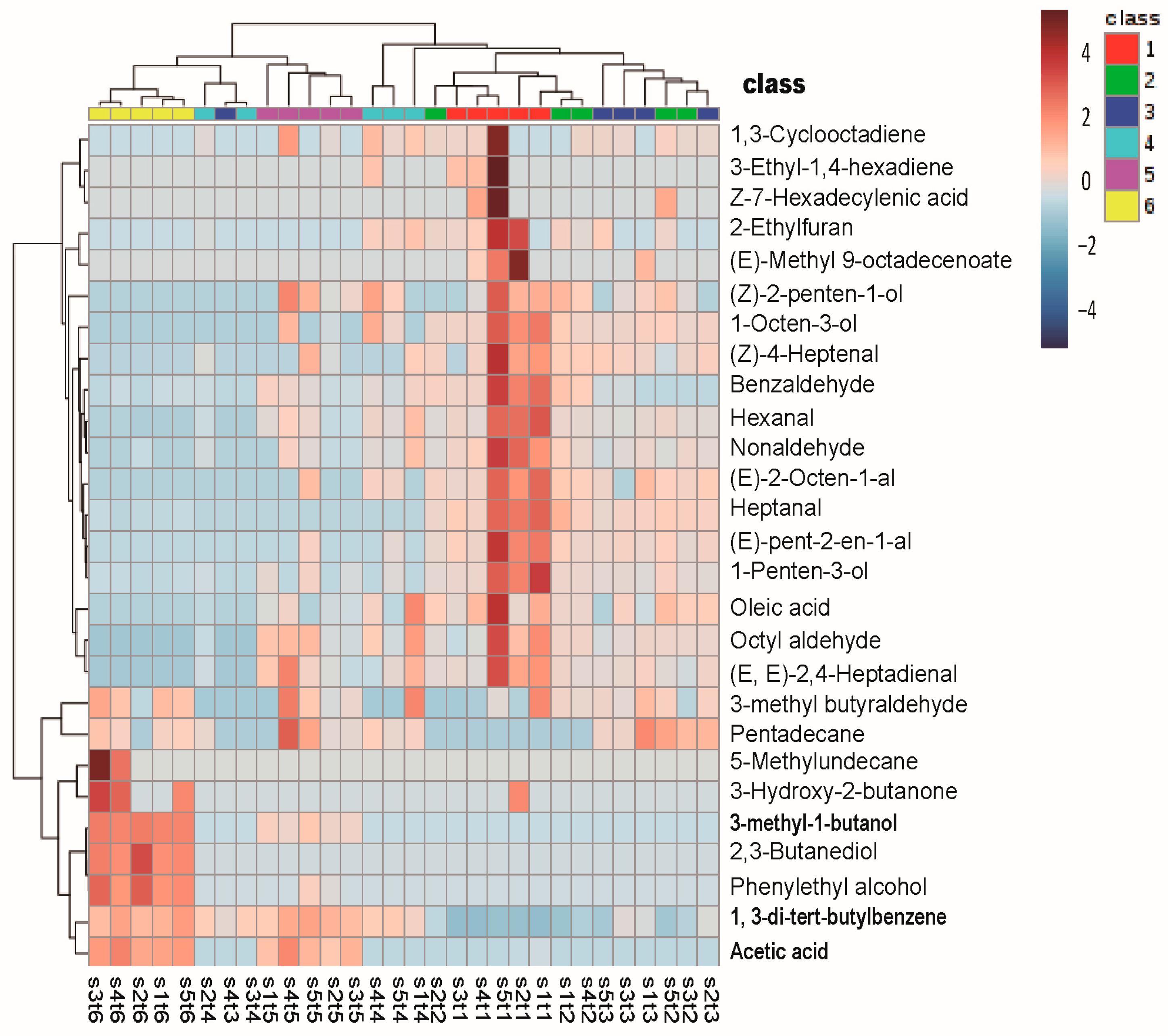
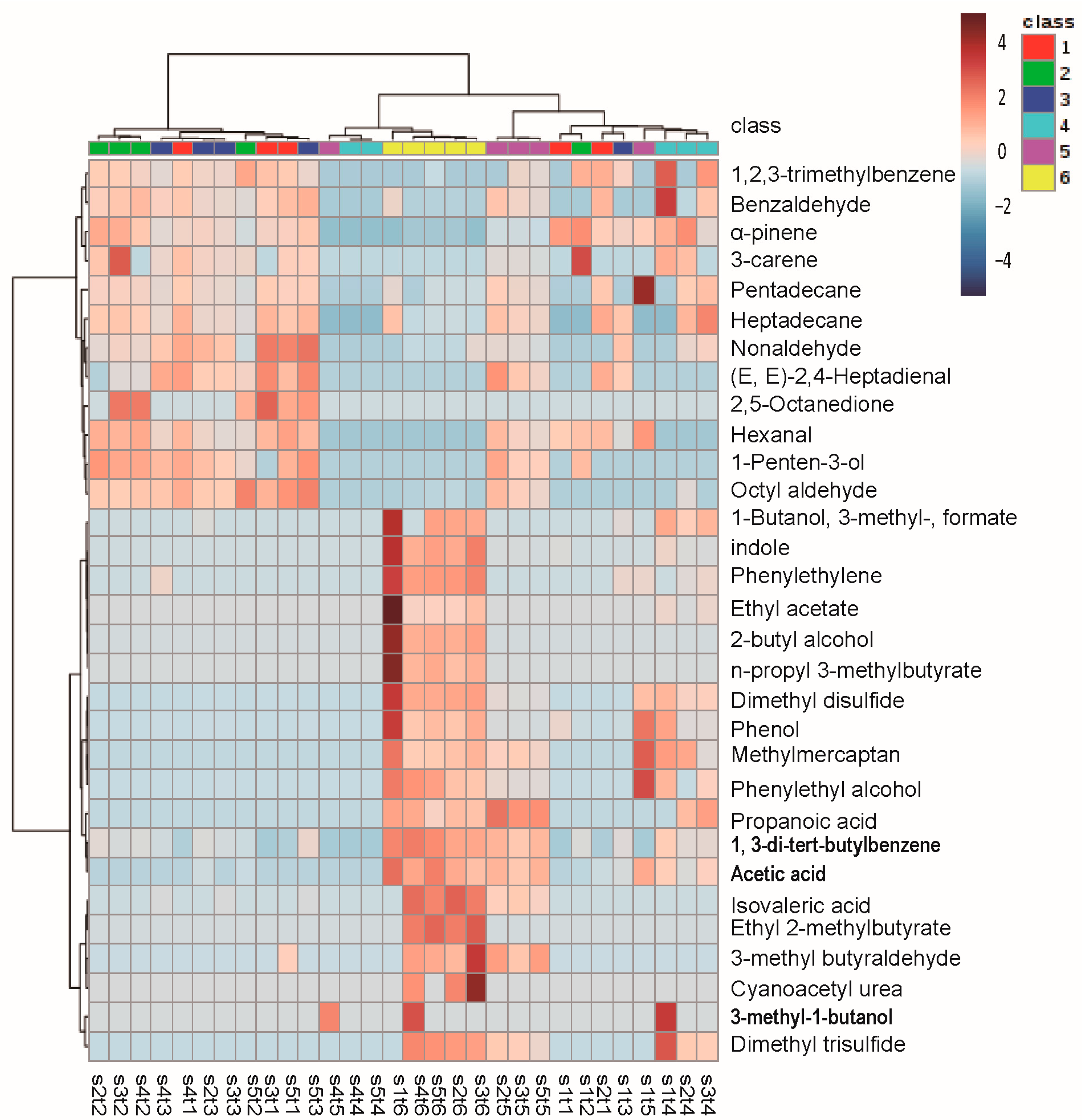
2.3. The Change of Volatile Organic Compounds (Non-Targeted Detection)
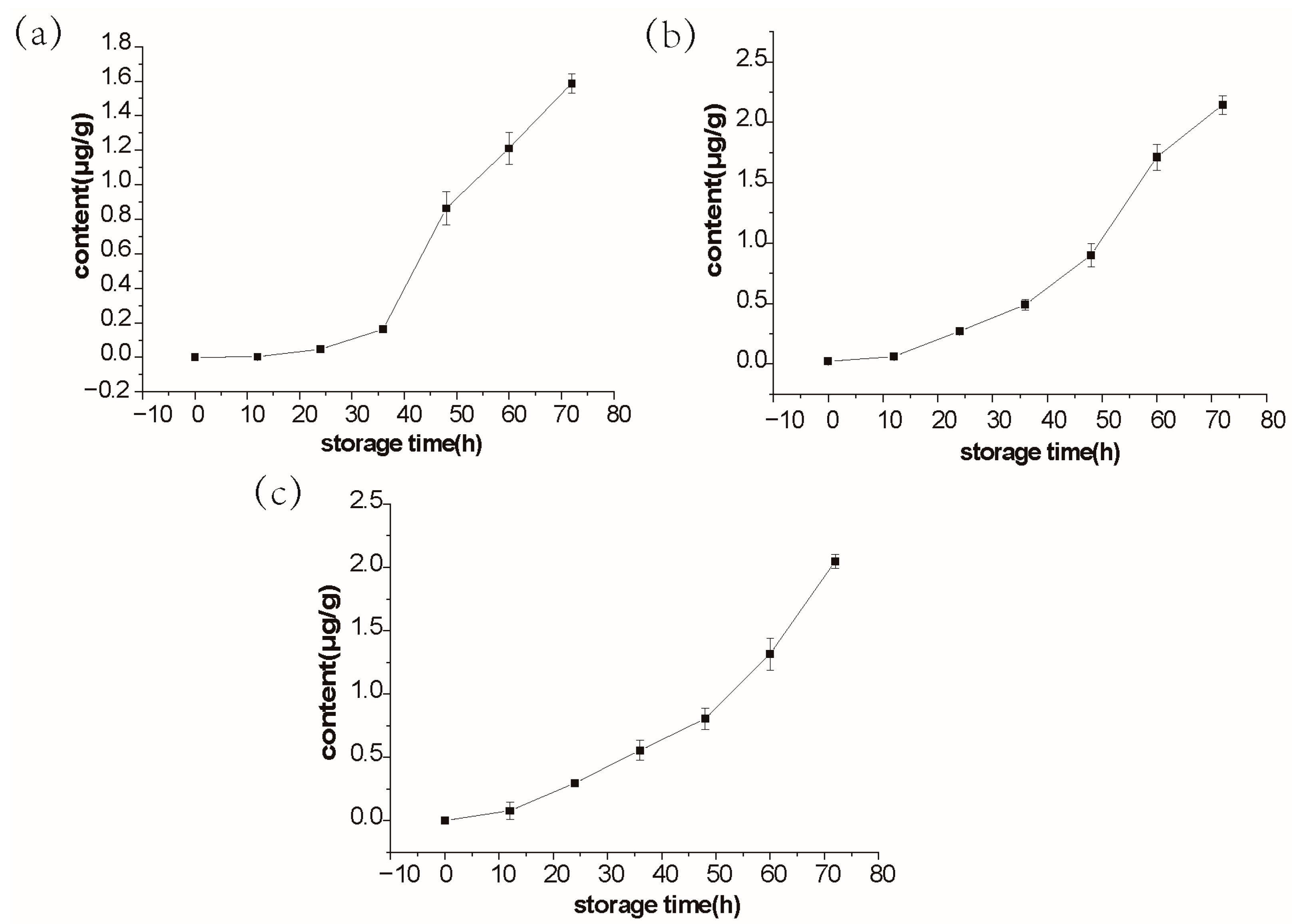
2.4. Quantitative Verification of Salmon Spoilage Indexes (Targeted Detection)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Sensory Evaluation
4.3. HS-SPME-GC-MS Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olafsdottir, G.; Nesvadba, P.; Di Natale, C.; Careche, M.; Oehlenschläger, J.; Tryggvadóttir, S.V.; Schubring, R.; Kroeger, M.; Heia, K.; Esaiassen, M.; et al. Multisensor for fish quality determination. In Trends in Food Science & Technology; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 15, p. 8693. [Google Scholar]
- Cléach, J.; Pasdois, P.; Marchetti, P.; Watier, D.; Duflos, G.; Goffier, E.; Lacoste, A.; Slomianny, C.; Grard, T.; Lencel, P. Mitochondrial activity as an indicator of fish freshness. Food Chem. 2019, 287, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.H.; Sun, D.W.; Han, Z.; Zeng, X.A. Texture and Structure Measurements and Analyses for Evaluation of Fish and Fillet Freshness Quality: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F 2014, 13, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, R. Technological processing of fresh gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata): A review of quality changes. Food Rev. Int. 2019, 35, 20–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, D.L.; Hites, R.A. Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Salmon and Salmon Feed: Global Differences and Bioaccumulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7389–7395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amit, S.K.; Uddin, M.M.; Rahman, R.; Islam, S.M.R.; Khan, M.S. A review on mechanisms and commercial aspects of food preservation and processing. Agric. Food Secur. 2017, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Bhandari, B. Freshness monitoring technology of fish products in intelligent packaging. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2021, 61, 1279–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrica, M.; Pavlovic, R.; Balzaretti, C.M.; Curone, G.; Brecchia, G.; Copelotti, E.; Panseri, S.; Pessina, D.; Arnoldi, C.; Chiesa, L.M. Effect of High-Pressure Processing on Physico-Chemical, Microbiological and Sensory Traits in Fresh Fish Fillets (Salmo salar and Pleuronectes platessa). Foods 2021, 10, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, Y.A.A.; Rosario, D.K.A.; Delgado, I.F.; Conte Junior, C.A. Fish Quality Index Method: Principles, weaknesses, validation, and alternatives—A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F 2020, 19, 2657–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, L.; Dalgaard, P. Fish Spoilage Bacteria—Problems and Solutions; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 13, pp. 262–266. [Google Scholar]
- Parlapani, F.F.; Mallouchos, A.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Boziaris, I.S. Microbiological spoilage and investigation of volatile profile during storage of sea bream fillets under various conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 189, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikš-Krajnik, M.; Yoon, Y.; Ukuku, D.O.; Yuk, H. Volatile chemical spoilage indexes of raw Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) stored under aerobic condition in relation to microbiological and sensory shelf lives. Food Microbiol. 2016, 53, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlapani, F.F.; Mallouchos, A.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Boziaris, I.S. Volatile organic compounds of microbial and non-microbial origin produced on model fish substrate un-inoculated and inoculated with gilt-head sea bream spoilage bacteria. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 78, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuuliala, L.; Abatih, E.; Ioannidis, A.G.; Vanderroost, M.; De Meulenaer, B.; Ragaert, P.; Devlieghere, F. Multivariate statistical analysis for the identification of potential seafood spoilage indicators. Food Control 2018, 84, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlapani, F.F.; Boziaris, I.S.; Meziti, A.; Michailidou, S.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Argiriou, A.; Karapanagiotidis, I.T. Microbiological status based on 454-pyrosequencing and volatilome analysis of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) fed on diets with hydrolyzed feather meal and poultry by-product meal as fishmeal replacers. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1409–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyasaki, T.; Hamaguchi, M.; Yokoyama, S. Change of volatile compounds in fresh fish meat during ice storage. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C1319–C1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, D.A.; Parlapani, F.F.; Mallouchos, A.; Angelidou, A.; Syropoulou, F.; Minos, G.; Boziaris, I.S. Volatile Organic Compounds and 16S Metabarcoding in Ice-Stored Red Seabream Pagrus major. Foods 2022, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Luo, L.; Chen, G. Study on seafood volatile profile characteristics during storage and its potential use for freshness evaluation by headspace solid phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 659, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, C.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid phase microextraction with thermal desorption using fused silica optical fibers. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 2145–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratini, G.; Lois, S.; Pazos, M.; Parisi, G.; Medina, I. Volatile profile of Atlantic shellfish species by HS-SPME GC/MS. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, F.; Tournayre, P.; Kondjoyan, N.; Mercier, F.; Malle, P.; Kol, O.; Berdagué, J.L.; Duflos, G. Evolution of volatile odorous compounds during the storage of European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Food Chem. 2012, 131, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, Y. Rapid classification of hairtail fish and pork freshness using an electronic nose based on the PCA method. Sensors 2012, 12, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Soufan, O.; Li, C.; Caraus, I.; Li, S.; Bourque, G.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 4.0: Towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2018, 46, W486–W494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, M.C.; Ma, L.M.; Doyle, M.P. Development of Models To Relate Microbiological and Headspace Volatile Parameters in Stored Atlantic Salmon to Acceptance and Willingness To Prepare the Product by Senior Consumers. J. Food Protect. 2015, 78, 2156–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugen, J.E.; Chanie, E.; Westad, F.; Jonsdottir, R.; Bazzo, S.; Labreche, S.; Marcq, P.; Lundby, F.; Olafsdottir, G. Rapid control of smoked Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) quality by electronic nose: Correlation with classical evaluation methods. Sens. Actuators. B Chem. 2006, 116, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edirisinghe, R.K.B.; Graffham, A.J.; Taylor, S.J. Characterisation of the volatiles of yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) during storage by solid phase microextraction and GC-MS and their relationship to fish quality parameters. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soncin, S.; Chiesa, L.M.; Panseri, S.; Biondi, P.; Cantoni, C. Determination of volatile compounds of precooked prawn (Penaeus vannamei) and cultured gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) stored in ice as possible spoilage markers using solid phase microextraction and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2009, 89, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, L.V.; Huss, H.H.; Dalgaard, P. Significance of Volatile Compounds Produced by Spoilage Bacteria in Vacuum-Packed Cold-Smoked Salmon (Salmo salar) Analyzed by GC-MS and Multivariate Regression. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2376–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierda, R.L.; Fletcher, G.; Xu, L.; Dufour, J. Analysis of Volatile Compounds as Spoilage Indicators in Fresh King Salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) During Storage Using SPME−GC−MS. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8480–8490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macé, S.; Joffraud, J.; Cardinal, M.; Malcheva, M.; Cornet, J.; Lalanne, V.; Chevalier, F.; Sérot, T.; Pilet, M.; Dousset, X. Evaluation of the spoilage potential of bacteria isolated from spoiled raw salmon (Salmo salar) fillets stored under modified atmosphere packaging. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 160, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaburi, A.; Piombino, P.; Nychas, G.; Villani, F.; Ercolini, D. Bacterial populations and the volatilome associated to meat spoilage. Food Microbiol. 2015, 45, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Fernández-García, E.; Nuñez, M. Production of volatile compounds in cheese by Pseudomonas fragi strains of dairy origin. J. Food Protect 2005, 68, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nychas, G.E.; Skandamis, P.N.; Tassou, C.C.; Koutsoumanis, K.P. Meat spoilage during distribution. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosansu, S.; Mol, S.; Ucok Alakavuk, D.; Ozturan, S. The Effect of Lemon Juice on Shelf Life of Sous Vide Packaged Whiting (Merlangius merlangus euxinus, Nordmann, 1840). Food Bioprocess Tech. 2013, 6, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Timira, V.; Zhao, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Z. Insight into the Characterization of Volatile Compounds in Smoke-Flavored Sea Bass (Lateolabrax maculatus) during Processing via HS-SPME-GC-MS and HS-GC-IMS. Foods 2022, 11, 2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xuan, G.; Guo, M.; Lin, H.; Sui, J.; Wang, J. Study on Volatile Chemicals as Spoilage Indexes of Salmon by HS-SPME-GC-MS Technique during Non-Frozen Storage. Molecules 2023, 28, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010013
Xuan G, Guo M, Lin H, Sui J, Wang J. Study on Volatile Chemicals as Spoilage Indexes of Salmon by HS-SPME-GC-MS Technique during Non-Frozen Storage. Molecules. 2023; 28(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleXuan, Guanhua, Miaorong Guo, Hong Lin, Jianxin Sui, and Jingxue Wang. 2023. "Study on Volatile Chemicals as Spoilage Indexes of Salmon by HS-SPME-GC-MS Technique during Non-Frozen Storage" Molecules 28, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010013
APA StyleXuan, G., Guo, M., Lin, H., Sui, J., & Wang, J. (2023). Study on Volatile Chemicals as Spoilage Indexes of Salmon by HS-SPME-GC-MS Technique during Non-Frozen Storage. Molecules, 28(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28010013





