Novel Inhibitors of 2′-O-Methyltransferase of the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Nsp16 Structure Preparation
2.2. Results of the Virtual Screening
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Ligands
3.2. Ligand Docking
3.3. Protein–Ligand Binding Enthalpy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ksiazek, T.G.; Erdman, D.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Zaki, S.R.; Peret, T.; Emery, S.; Tong, S.; Urbani, C.; Comer, J.A.; Lim, W.; et al. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1953–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, A.M.; van Boheemen, S.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Fouchier, R.A.M. Isolation of a Novel Coronavirus from a Man with Pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, L.R.; da Silva Santos-Júnior, P.F.; de Andrade Brandão, J.; Anderson, L.; Bassi, Ê.J.; Xavier de Araújo-Júnior, J.; Cardoso, S.H.; da Silva-Júnior, E.F. Druggable targets from coronaviruses for designing new antiviral drugs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, V.; Beer, J.C.; Sankaranarayanan, N.V.; Swanson-Mungerson, M.; Desai, U.R. Discovering small-molecule therapeutics against SARS-CoV-2. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, C.; Ginex, T.; Maestro, I.; Nozal, V.; Barrado-Gil, L.; Cuesta-Geijo, M.A.; Urquiza, J.; Ramirez, D.; Alonso, C.; Campillo, N.E.; et al. COVID-19: Drug Targets and Potential Treatments. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 12359–12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhong, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Li, M.; Li, X.; et al. Analysis of therapeutic targets for SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of potential drugs by computational methods. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 766–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.S.; Huang, Y.Y.; Jiang, M.Y.; Luo, H. Bin Therapeutic targets and potential agents for the treatment of COVID-19. Med. Res. Rev. 2021, 41, 1775–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazikeh-Lemeski, E.; Moradi, S.; Raoufi, R.; Shahlaei, M.; Janlou, M.A.M.; Zolghadri, S. Targeting SARS-COV-2 non-structural protein 16: A virtual drug repurposing study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 4633–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krafcikova, P.; Silhan, J.; Nencka, R.; Boura, E. Structural analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 methyltransferase complex involved in RNA cap creation bound to sinefungin. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, A.; Robb, G.B.; Chan, S.-H. mRNA capping: Biological functions and applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 7511–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferron, F.; Decroly, E.; Selisko, B.; Canard, B. The viral RNA capping machinery as a target for antiviral drugs. Antivir. Res. 2012, 96, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decroly, E.; Debarnot, C.; Ferron, F.; Bouvet, M.; Coutard, B.; Imbert, I.; Gluais, L.; Papageorgiou, N.; Sharff, A.; Bricogne, G.; et al. Crystal structure and functional analysis of the SARS-coronavirus RNA cap 2′-O-methyltransferase nsp10/nsp16 complex. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bobiļeva, O.; Bobrovs, R.; Kaņepe, I.; Patetko, L.; Kalniņš, G.; Šišovs, M.; Bula, A.L.; Gri Nberga, S.; Borodušķis, M.R.; Ramata-Stunda, A.; et al. Potent SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Cap Methyltransferase Inhibitors by Bioisosteric Replacement of Methionine in SAM Cosubstrate. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrovs, R.; Kanepe, I.; Narvaiss, N.; Patetko, L.; Kalnins, G.; Sisovs, M.; Bula, A.L.; Grinberga, S.; Boroduskis, M.; Ramata-Stunda, A.; et al. Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 Nsp14 and Nsp16 Methyltransferase Inhibitors by High-Throughput Virtual Screening. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hassab, M.A.; Ibrahim, T.M.; Al-Rashood, S.T.; Alharbi, A.; Eskandrani, R.O.; Eldehna, W.M. In silico identification of novel SARS-COV-2 2′-O-methyltransferase (nsp16) inhibitors: Structure-based virtual screening, molecular dynamics simulation and MM-PBSA approaches. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.; Alshawaf, E.; Marafie, S.K.; Abu-Farha, M.; Al-Mulla, F.; Abubaker, J. Molecular Simulation-Based Investigation of Highly Potent Natural Products to Abrogate Formation of the nsp10-nsp16 Complex of SARS-CoV-2. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halgren, T.A. Merck molecular force field. I. Basis, form, scope, parameterization, and performance of MMFF94. J. Comput. Chem. 1996, 17, 490–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulimov, A.V.; Kutov, D.C.; Oferkin, I.V.; Katkova, E.V.; Sulimov, V.B. Application of the docking program SOL for CSAR benchmark. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 1946–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulimov, V.B.; Ilin, I.S.; Kutov, D.C.; Sulimov, A. V Development of docking programs for Lomonosov supercomputer. J. Turkish Chem. Soc. Sect. A Chem. 2020, 7, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schrödinger, LLC. Available online: https://www.schrodinger.com (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Kutov, D.C.; Katkova, E.V.; Kondakova, O.A.; Sulimov, A.V.; Sulimov, V.B. Influence of the method of hydrogen atoms incorporation into the target protein on the protein-ligand binding energy. Bull. South Ural State Univ. Ser. Math. Model. Program. Comput. Softw. 2017, 10, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voevodin, V.V.; Antonov, A.S.; Nikitenko, D.A.; Shvets, P.A.; Sobolev, S.I.; Sidorov, I.Y.; Stefanov, K.S.; Voevodin, V.V.; Zhumatiy, S.A. Supercomputer Lomonosov-2: Large scale, deep monitoring and fine analytics for the user community. Supercomput. Front. Innov. 2019, 6, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, L.; Klug-Mcleod, J.; Rai, B.; Lunney, E.A. Kinase hinge binding scaffolds and their hydrogen bond patterns. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 6520–6527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLano, W.L. References. Hypertens. Res. 2014, 37, 362–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enamine Coronavirus Library. Available online: https://enamine.net/compound-libraries/targeted-libraries/coronavirus-library (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Madhavi Sastry, G.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and ligand preparation: Parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enamine Nucleoside Mimetics Library. Available online: https://enamine.net/compound-libraries/targeted-libraries/nucleoside-mimetic (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Brito-Arias, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Glycosides; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-387-26251-2. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, J.J.P. Stewart Computational Chemistry. MOPAC2016. Available online: http://openmopac.net/MOPAC2016.html (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Stewart, J.J.P. Optimization of parameters for semiempirical methods VI: More modifications to the NDDO approximations and re-optimization of parameters. J. Mol. Model. 2013, 19, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klamt, A.; Schüürmann, G. COSMO: A new approach to dielectric screening in solvents with explicit expressions for the screening energy and its gradient. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1993, 2, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
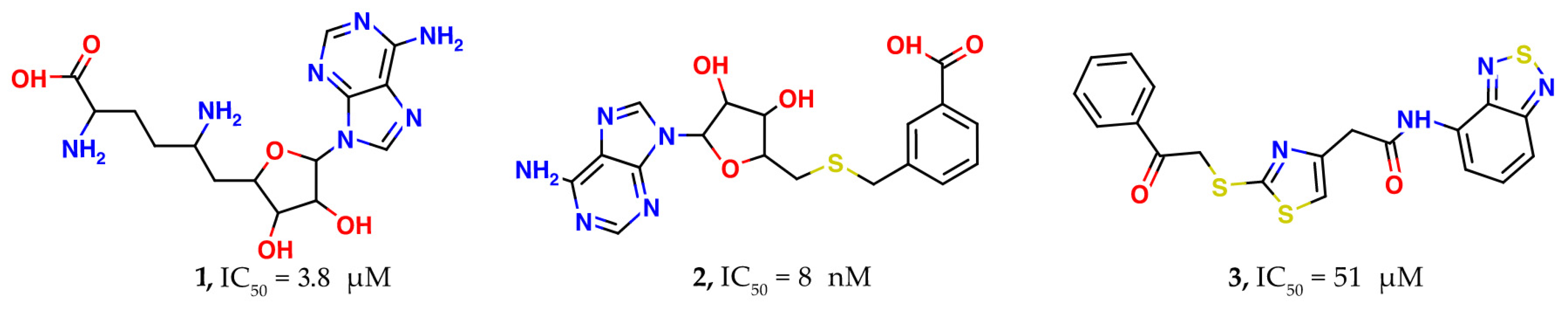
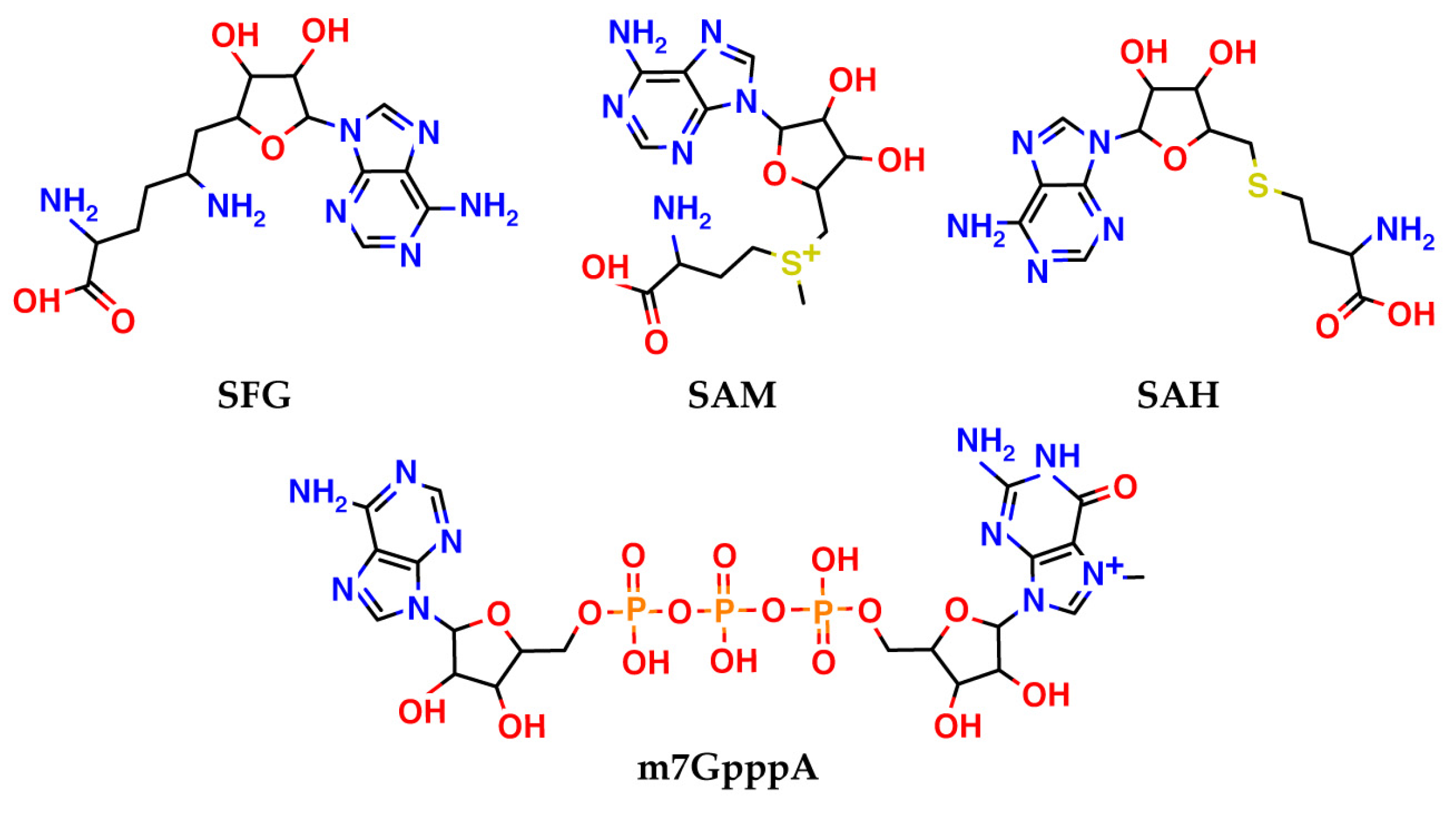
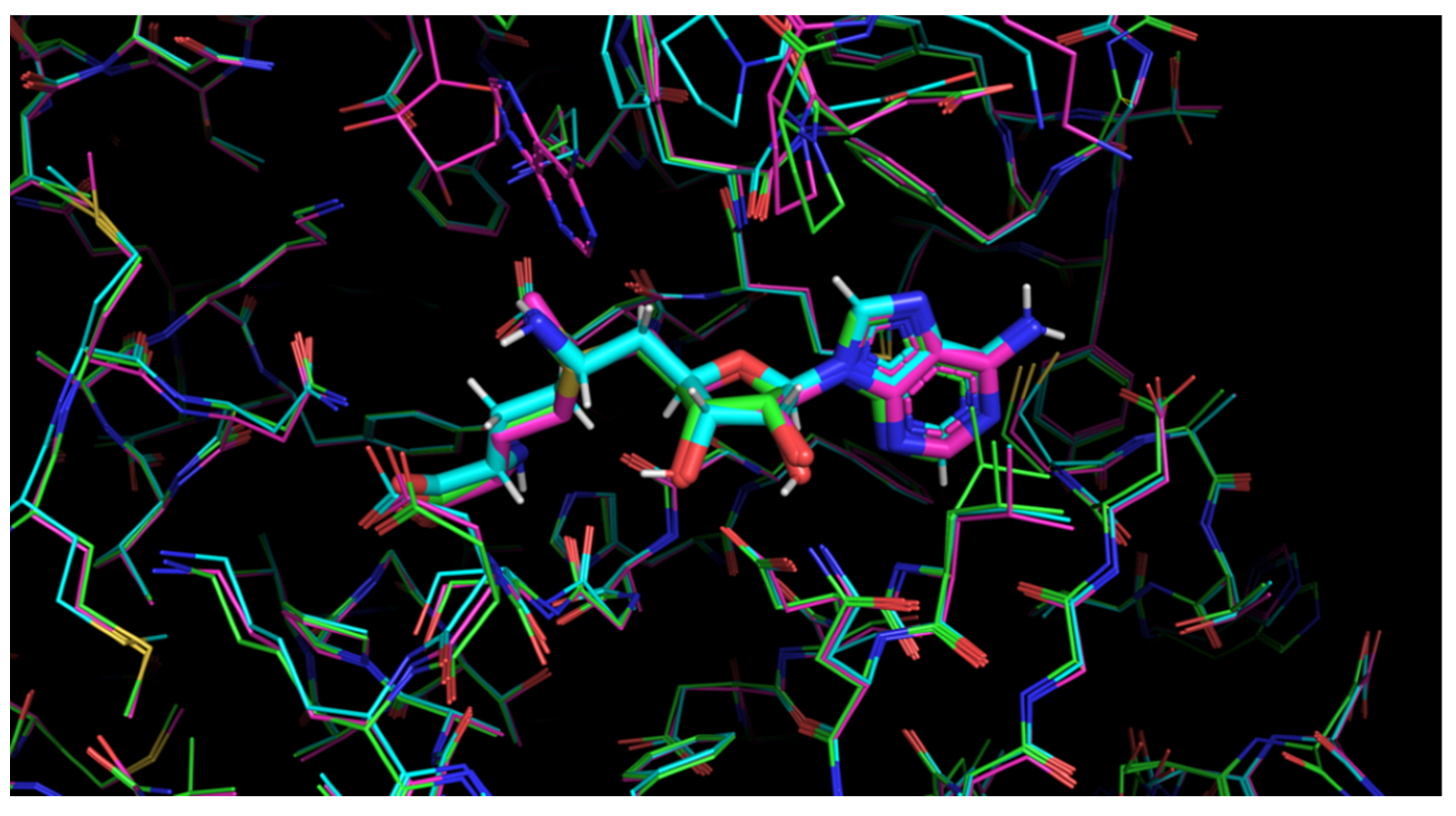
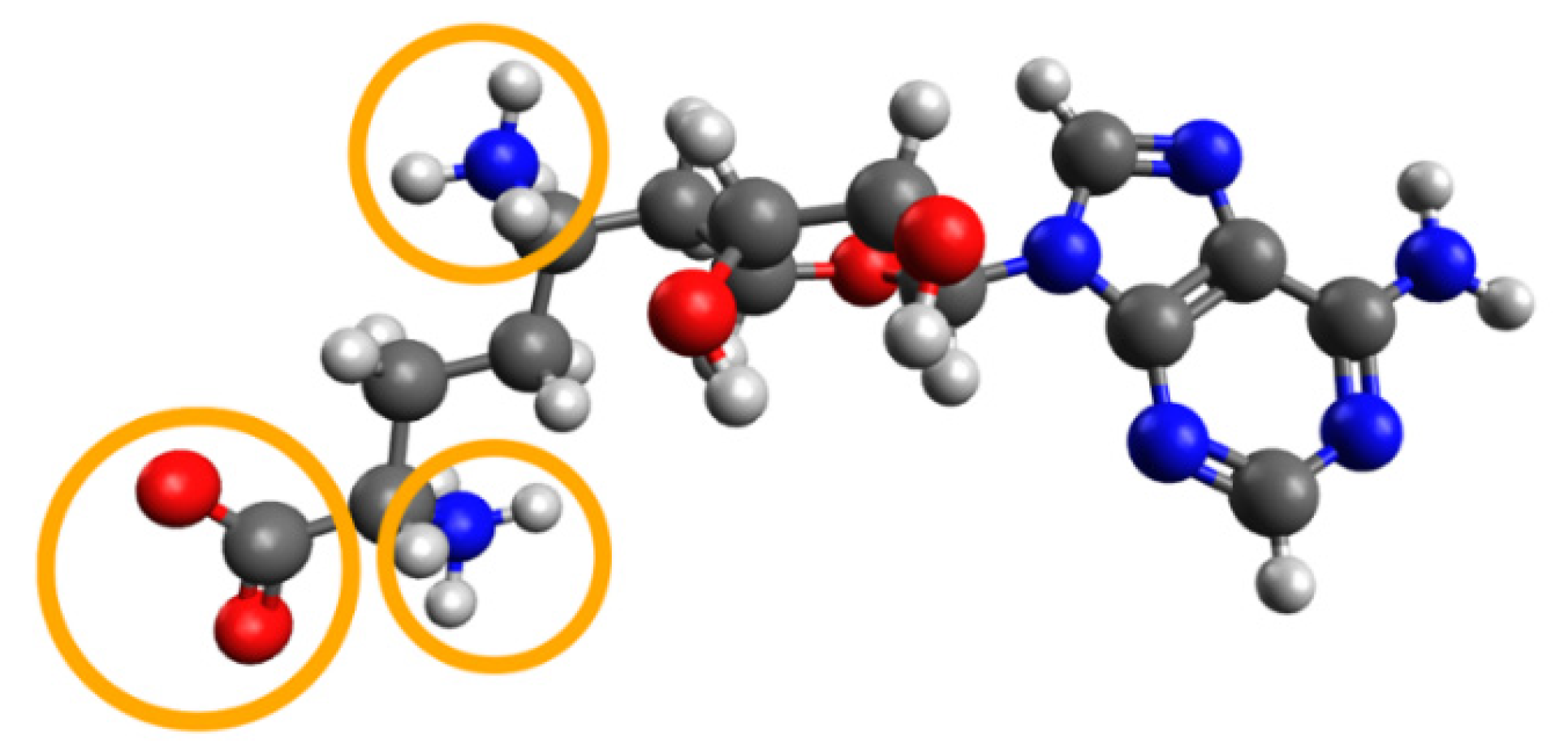
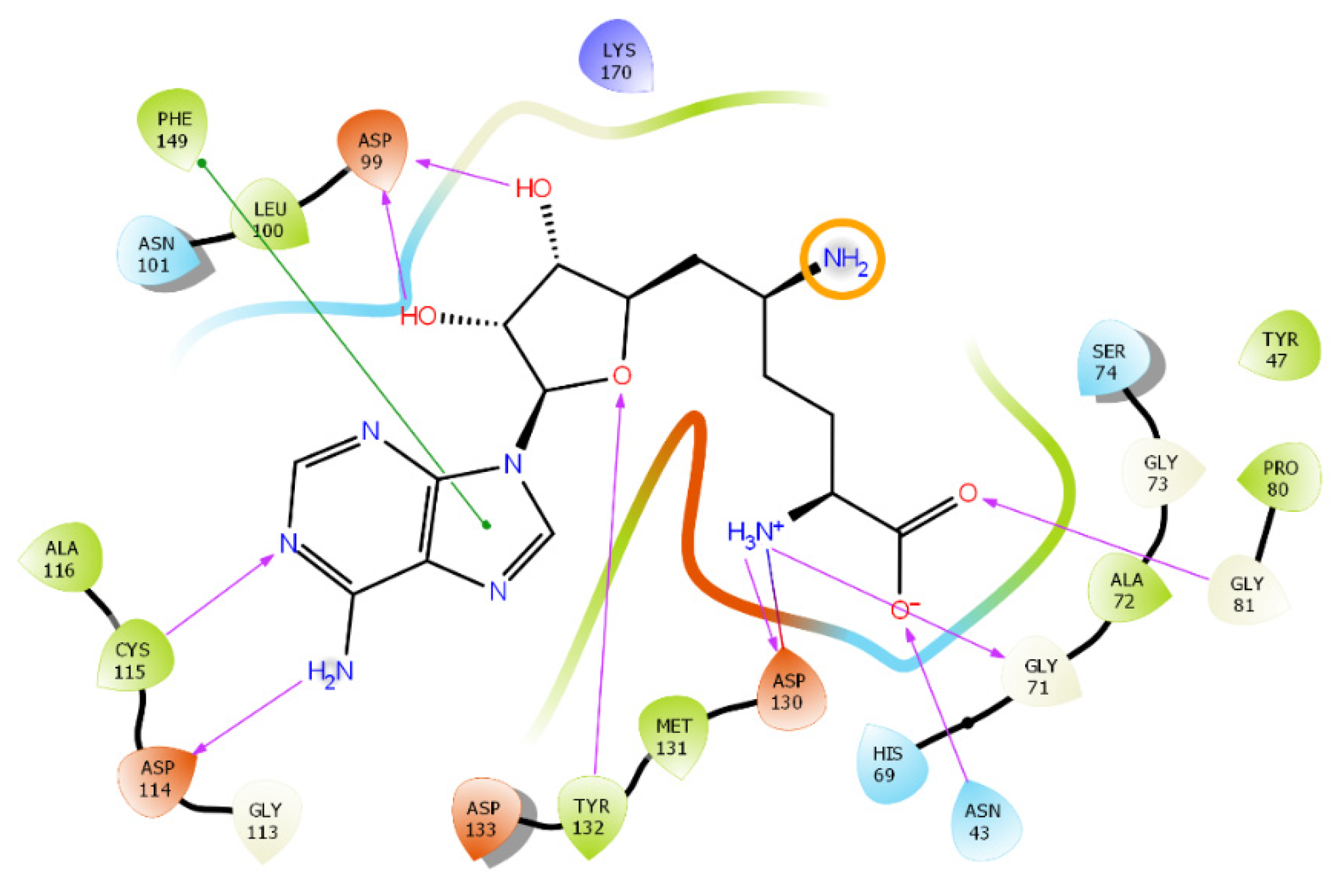
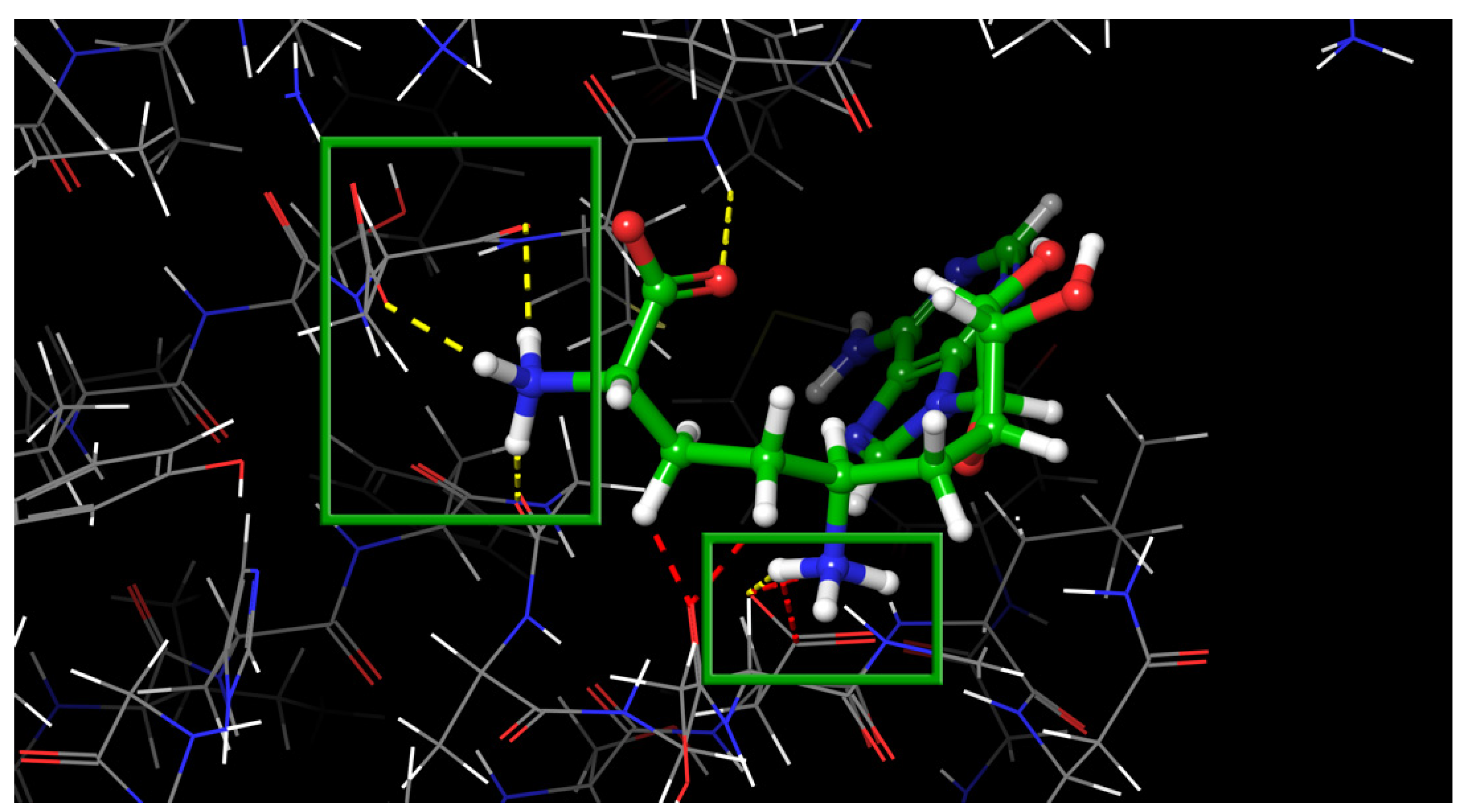
| PDB ID | Ligand | Resolution, Å |
|---|---|---|
| 6W4H | SAM | 1.8 |
| 6W61 | SAM | 2 |
| 6W75 | SAM | 1.95 |
| 7C2J | SAM | 2.8 |
| 6WKQ | SFG | 1.98 |
| 6YZ1 | SFG | 2.4 |
| 6WKS | SAM + RNA substrate | 1.8 |
| 6WJT | SAH | 2 |
| PDB ID | Resolution, Å | R-Value Work | Missing Elements |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6YZ1 | 2.4 | 0.187 | One residue on N- and C-terminus |
| 6WKQ | 1.98 | 0.162 | Four residues missed on N-terminus |
| Protein | Ligand | RMSD, Å | 1st Cluster Popul. | N. of Clusters | Score, kcal/mol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6YZ1 | SFG (fully charged) | 4.02 | 2 | 45 | −4.89 |
| 6WKQ | SFG (fully charged) | 10.28 | 2 | 42 | −4.66 |
| Protein | Ligand | RMSD, Å | 1st Cluster Popul. | N. of Clusters | Score, kcal/mol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6YZ1 | SFG (neutralized) | 4.0197 | 2 | 45 | −4.89 |
| 6WKQ | SFG (neutralized) | 0.87 | 1 | 38 | −7.05 |
| 6WKQ* | SFG (neutralized) | 0.87 | 8 | 36 | −7.07 |
| Protein | Ligand | RMSD, Å | 1st Cluster Popul. | N. of Clusters | Score, kcal/mol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6WKQ | SAH (quasi-native—from 6WJT complex) | 2.54 | 1 | 44 | −5.63 |
| 6WKQ* | SAH (quasi-native—from 6WJT complex) | 0.97 | 9 | 57 | −7.48 |
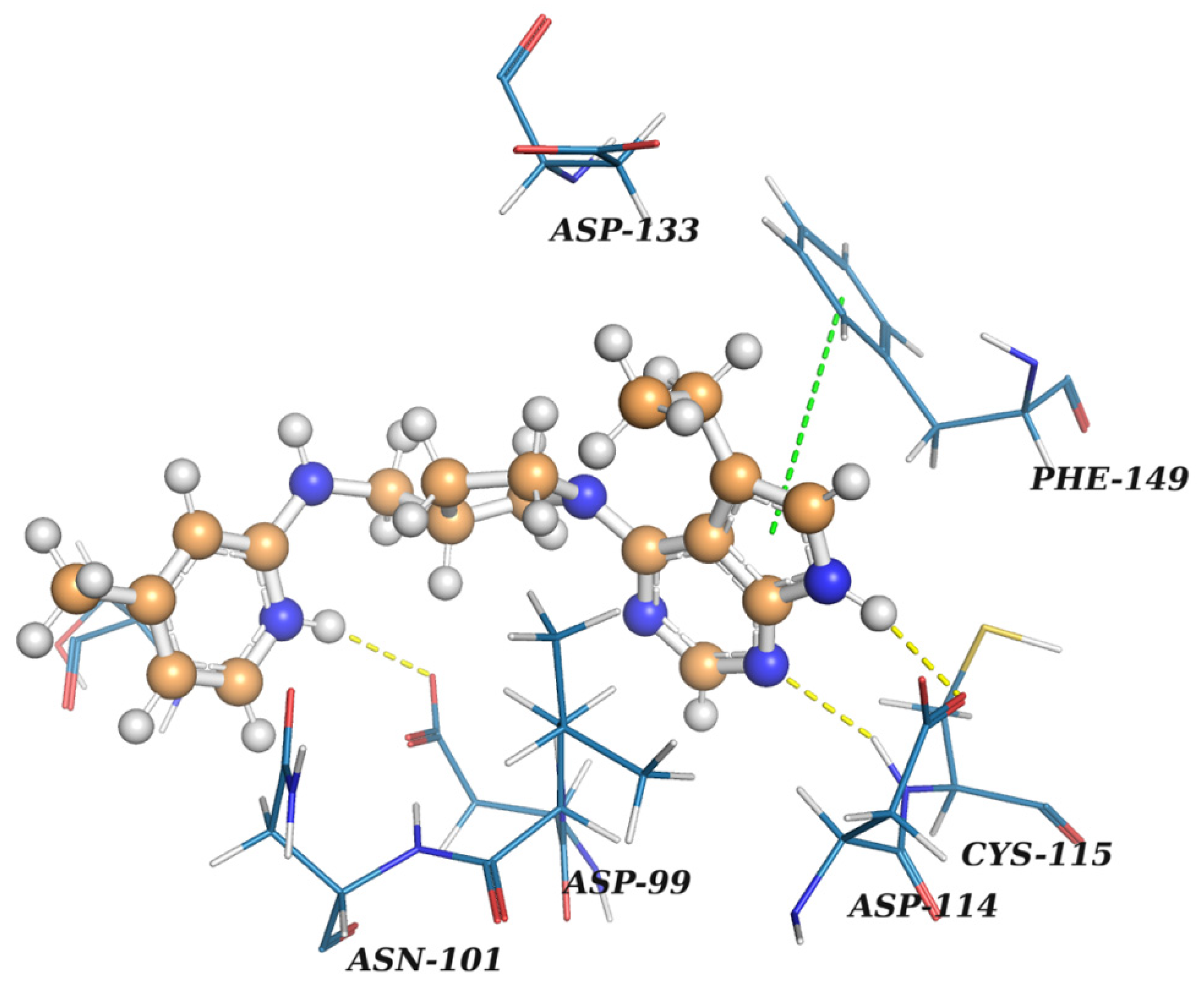
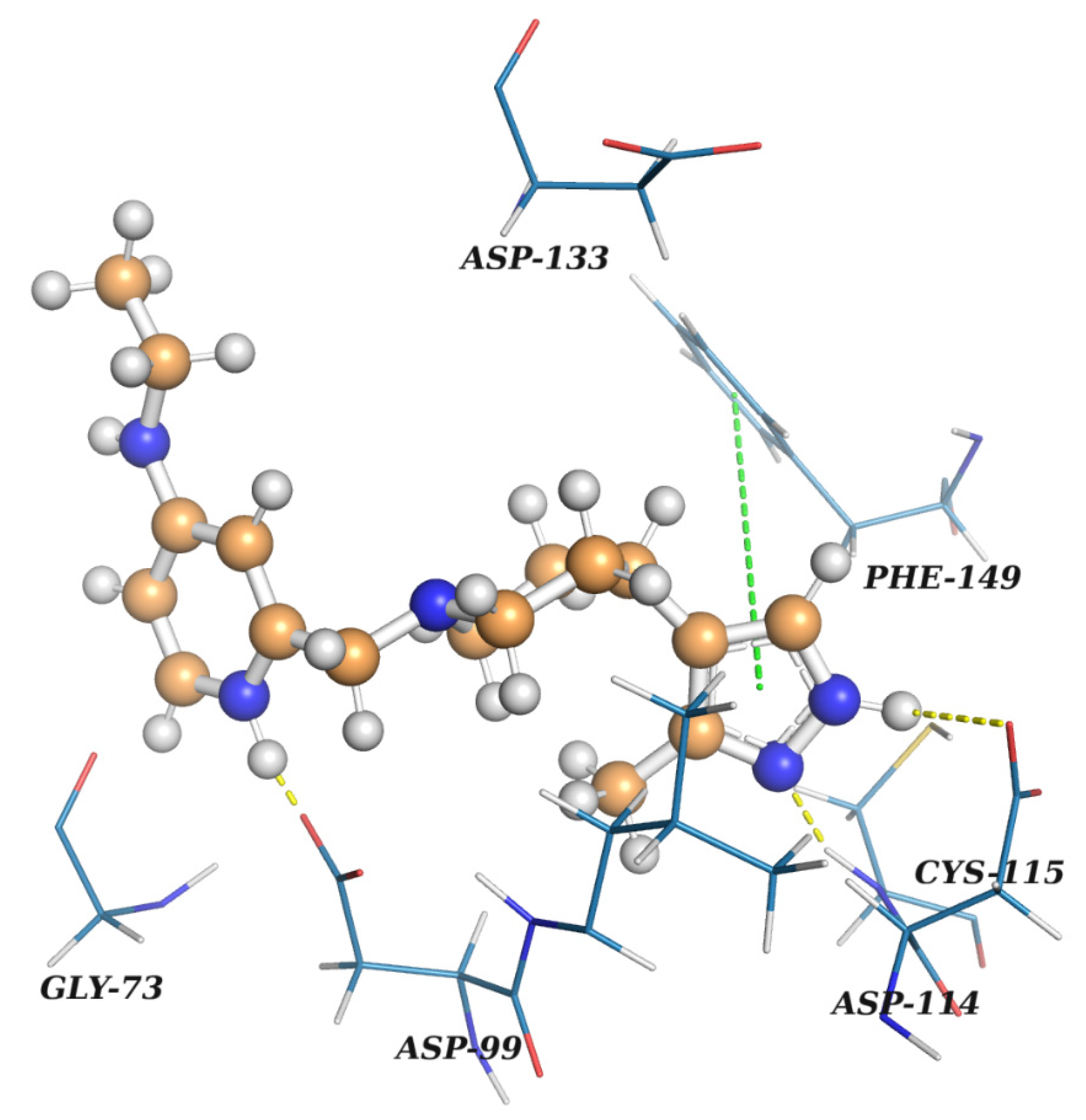
| Ligname | Score, kcal/mol | 1st Cluster Popul. | ΔH Bind, kcal/mol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reference (SFG) | −7.07 | 8 | −93.8 |
| Enamine Coronavirus Library | |||
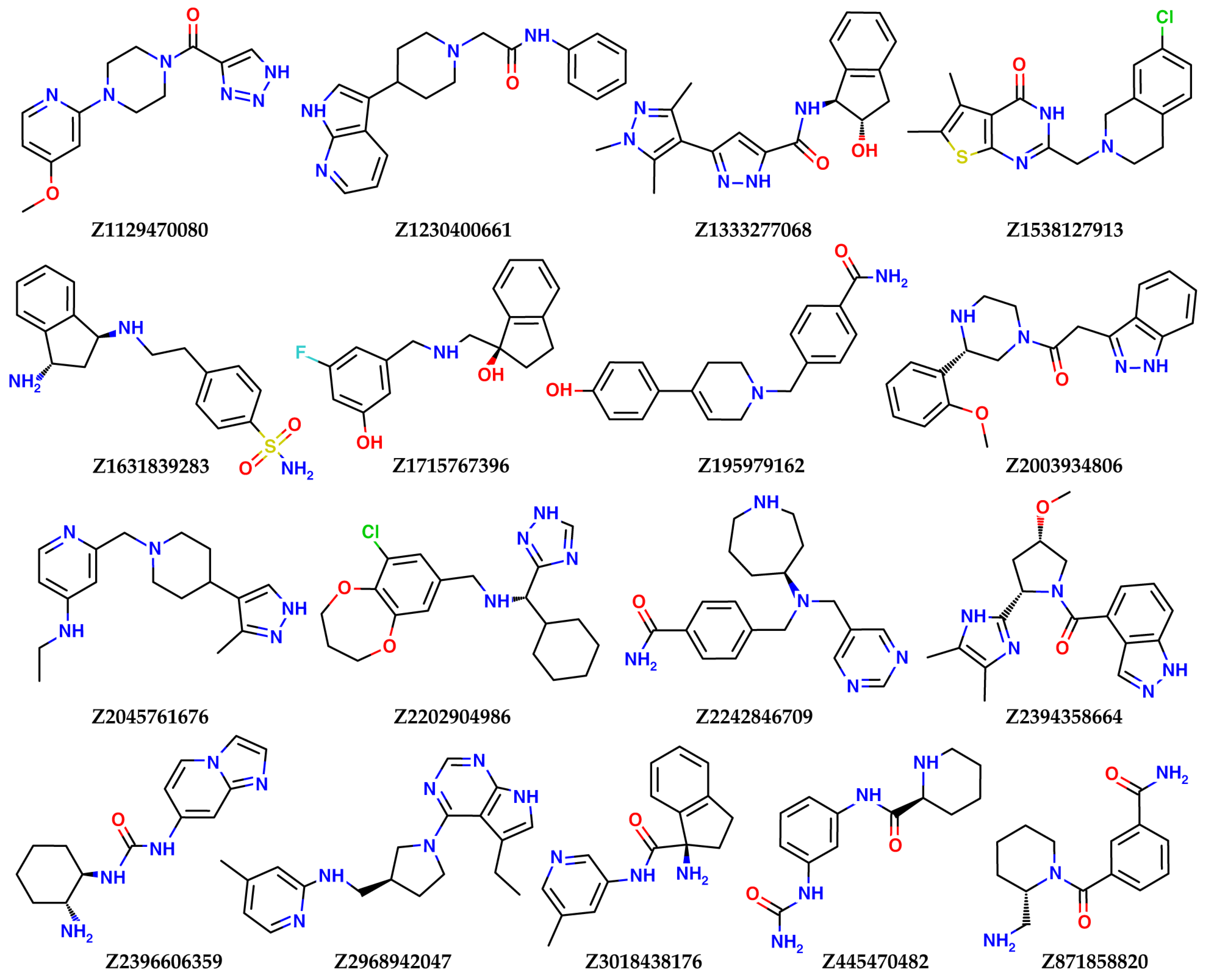
| Z1129470080 | −6.04 | 36 | −38.3 |
| Z1230400661 | −5.26 | 20 | −51.2 |
| Z1333277068 | −5.24 | 47 | −53.8 |
| Z1538127913 | −6.13 | 34 | −40.7 |
| Z1631839283 | −6.38 | 2 | −62.5 |
| Z1715767396 | −5.38 | 23 | −53.0 |
| Z195979162 | −5.24 | 40 | −53.4 |
| Z2003934806 | −6.41 | 30 | −44.8 |
| Z2045761676 | −6.76 | 4 | −30.8 |
| Z2202904986 | −5.94 | 17 | −60.8 |
| Z2242846709 | −5.51 | 30 | −61.6 |
| Z2394358664 | −6.11 | 32 | −51.6 |
| Z2396606359 | −5.81 | 30 | −54.5 |
| Z2968942047 | −6.15 | 17 | −55.4 |
| Z3018438176 | −6.43 | 12 | −42.3 |
| Z445470482 | −5.54 | 15 | −60.0 |
| Z871858820 | −5.70 | 38 | −54.7 |
| Chemdiv Nucleoside Analogue Library | |||
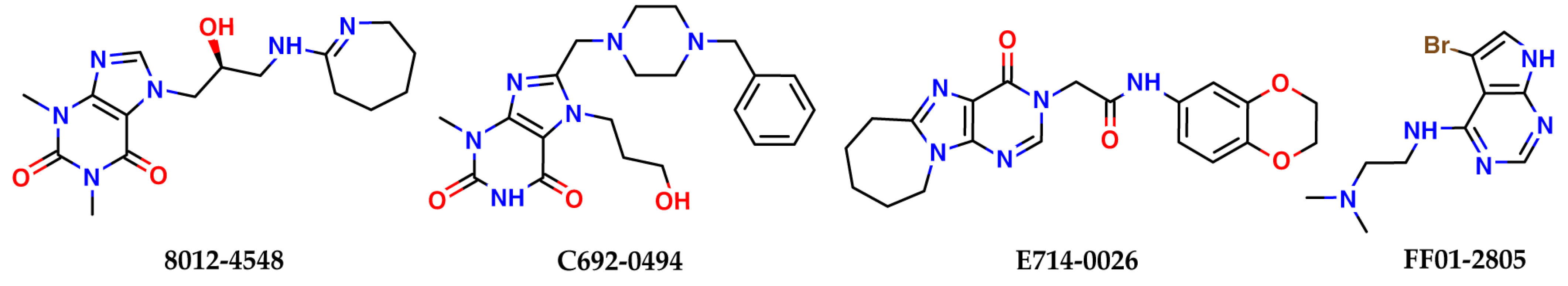
| 8012-4548 | −5.41 | 33 | −39.3 |
| C692-0494 | −5.27 | 10 | −48.4 |
| E714-0026 | −5.00 | 10 | −43.2 |
| FF01-2805 | −5.03 | 37 | −37.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sulimov, A.; Kutov, D.; Ilin, I.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Sulimov, V. Novel Inhibitors of 2′-O-Methyltransferase of the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus. Molecules 2022, 27, 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092721
Sulimov A, Kutov D, Ilin I, Xiao Y, Jiang S, Sulimov V. Novel Inhibitors of 2′-O-Methyltransferase of the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus. Molecules. 2022; 27(9):2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092721
Chicago/Turabian StyleSulimov, Alexey, Danil Kutov, Ivan Ilin, Yibei Xiao, Sheng Jiang, and Vladimir Sulimov. 2022. "Novel Inhibitors of 2′-O-Methyltransferase of the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus" Molecules 27, no. 9: 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092721
APA StyleSulimov, A., Kutov, D., Ilin, I., Xiao, Y., Jiang, S., & Sulimov, V. (2022). Novel Inhibitors of 2′-O-Methyltransferase of the SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus. Molecules, 27(9), 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092721






