Molecular Dynamics Simulation for the Demulsification of O/W Emulsion under Pulsed Electric Field
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
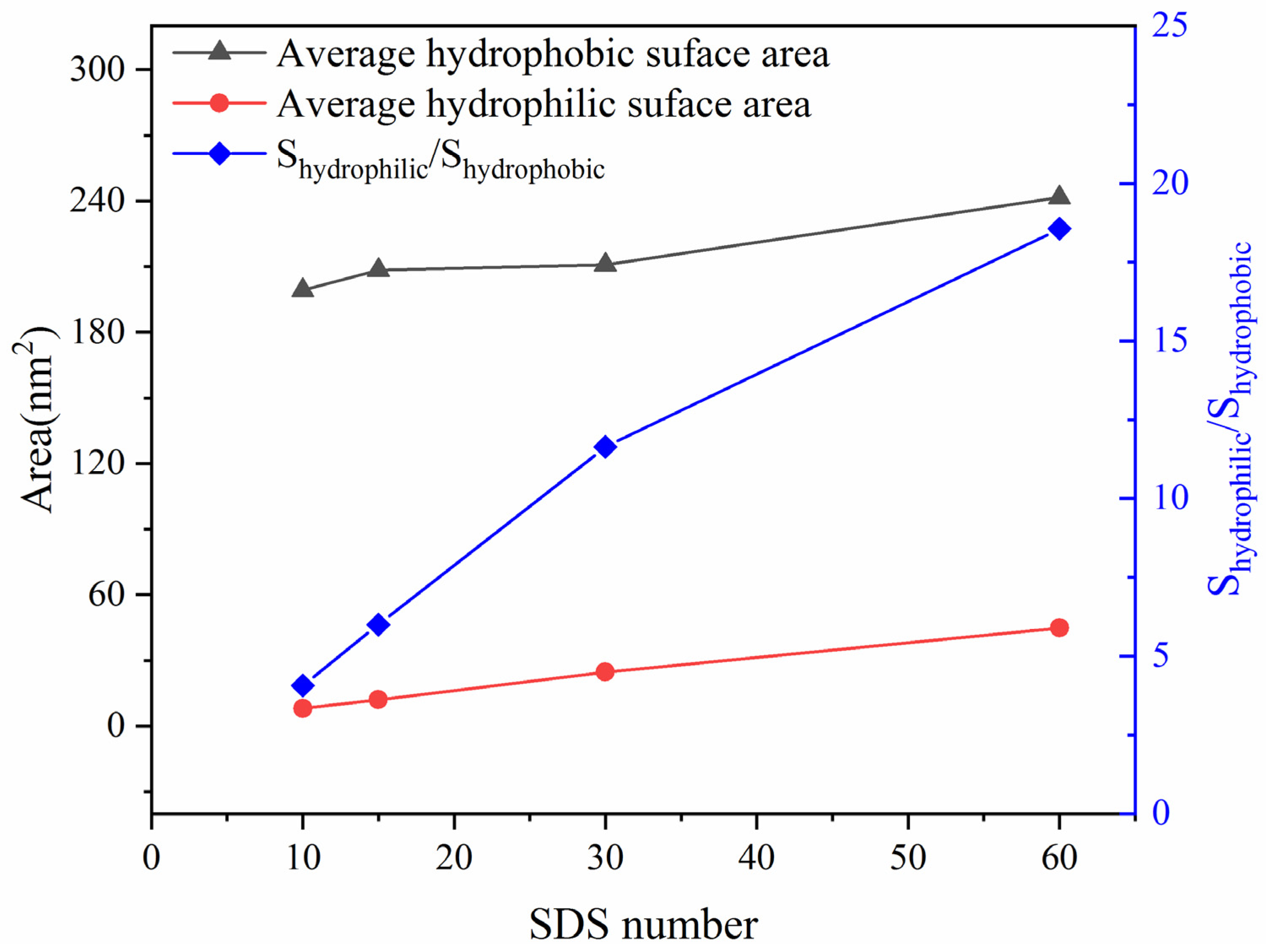
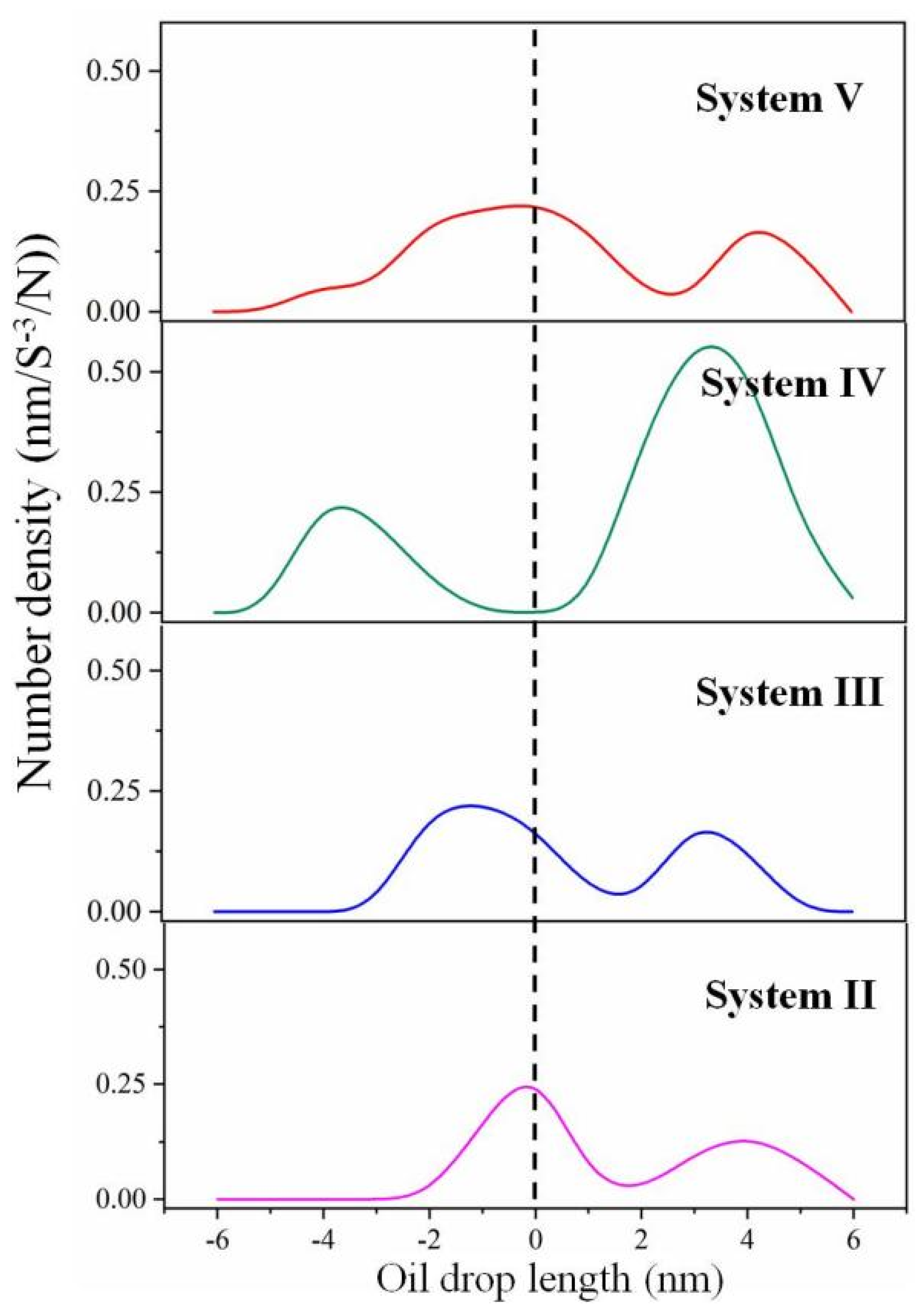
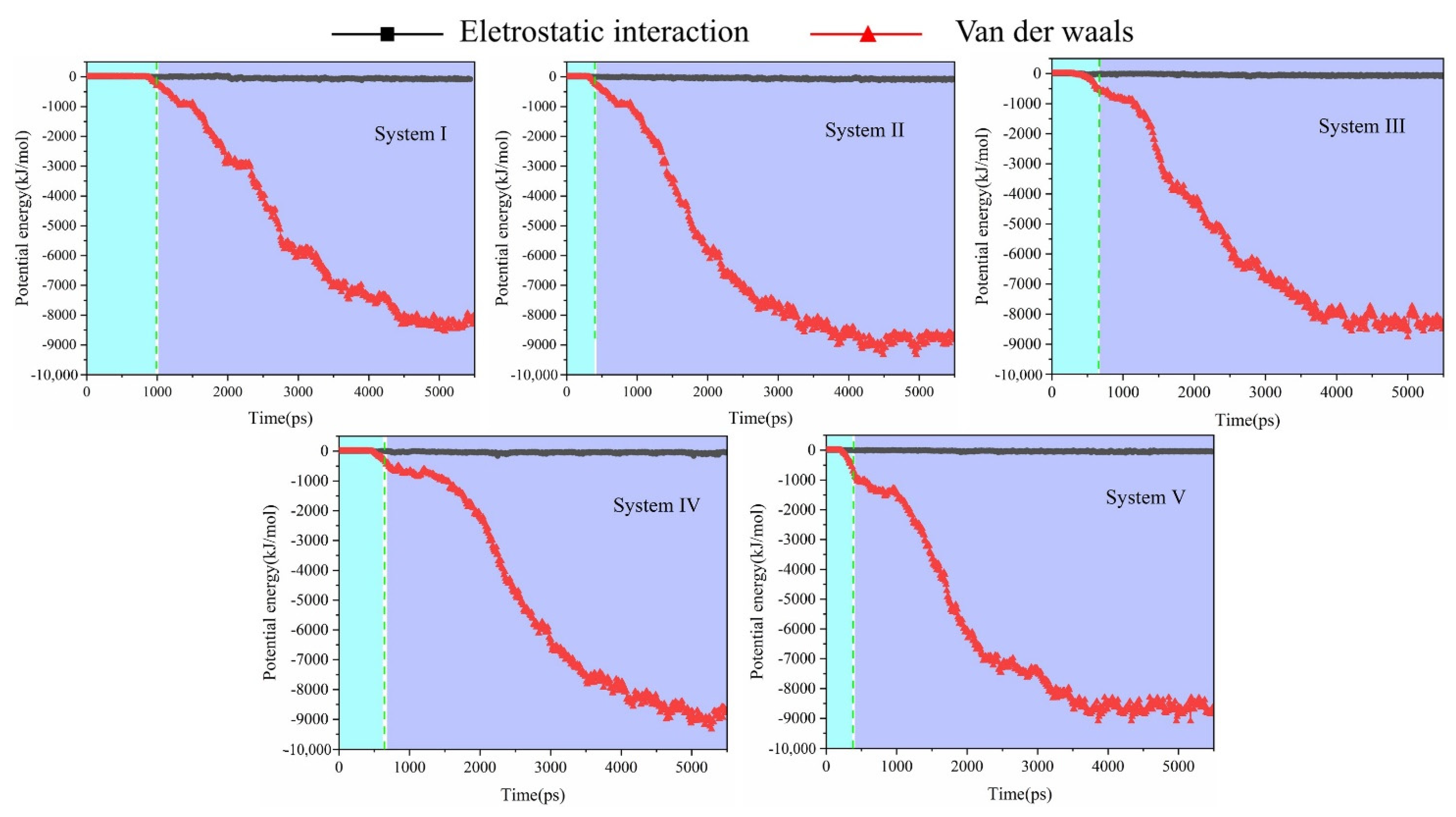
2.1. Emulsified Crude Oil Droplet
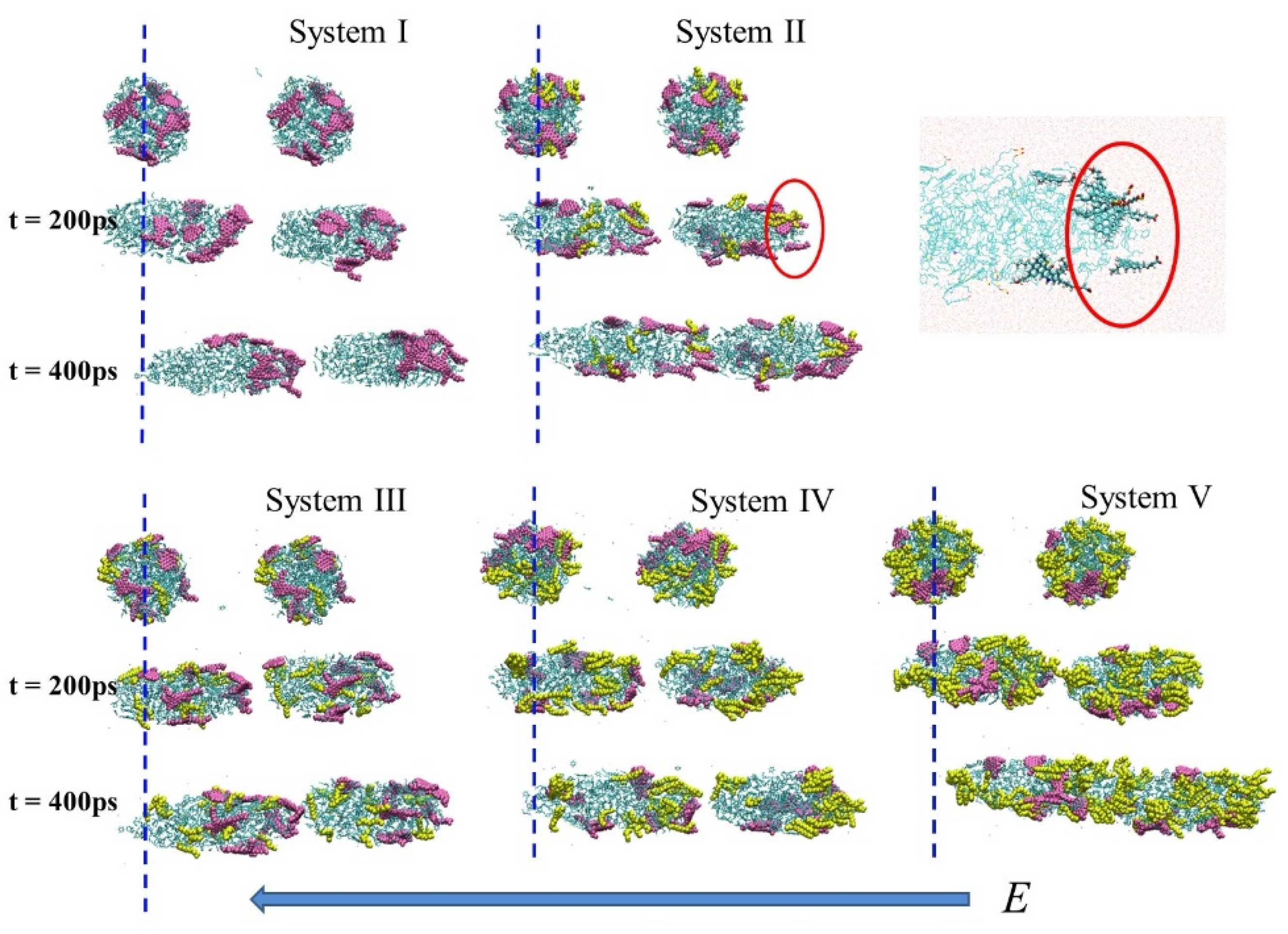
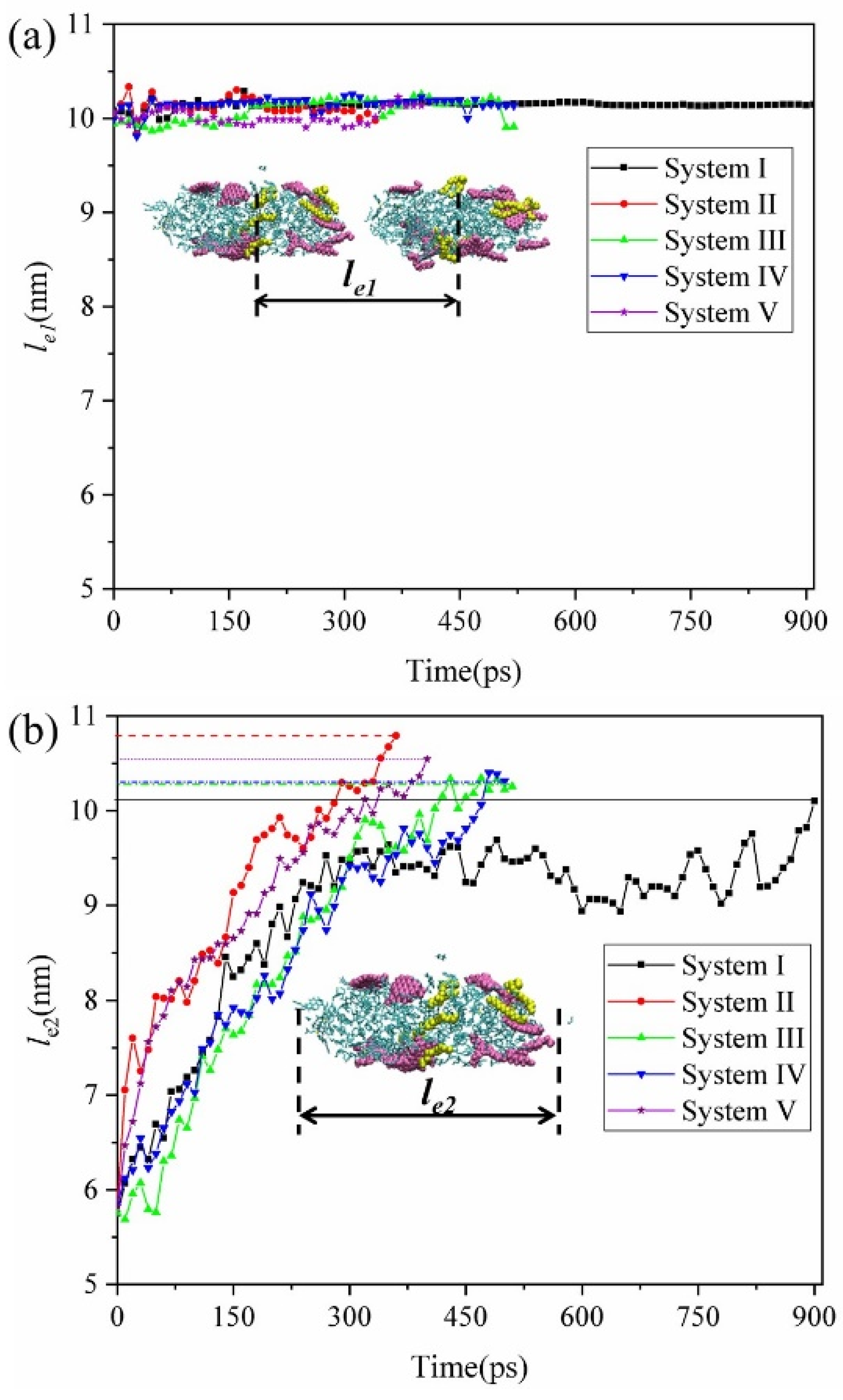
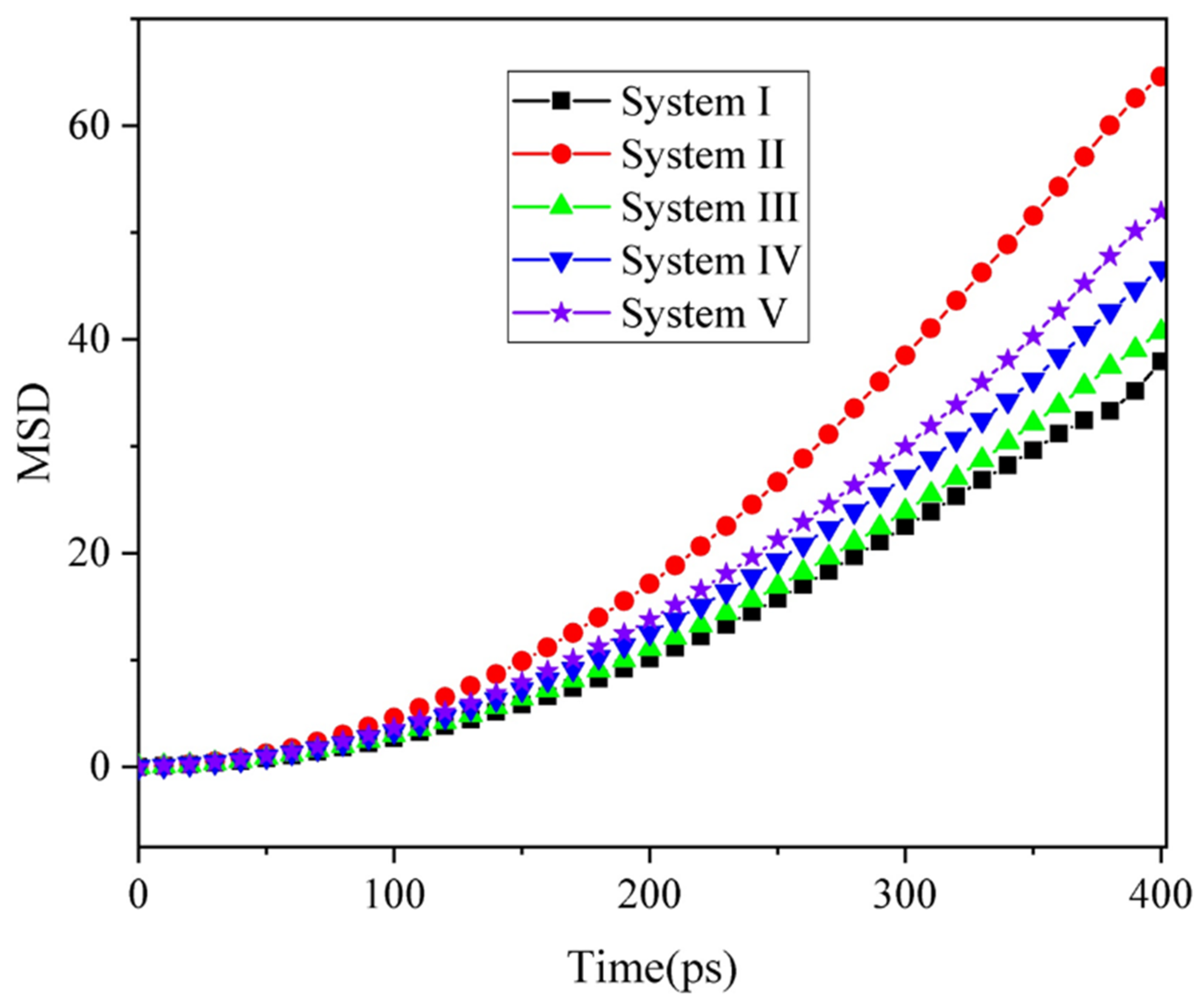
2.2. Dynamic Behavior of Oil Droplets under BPEF
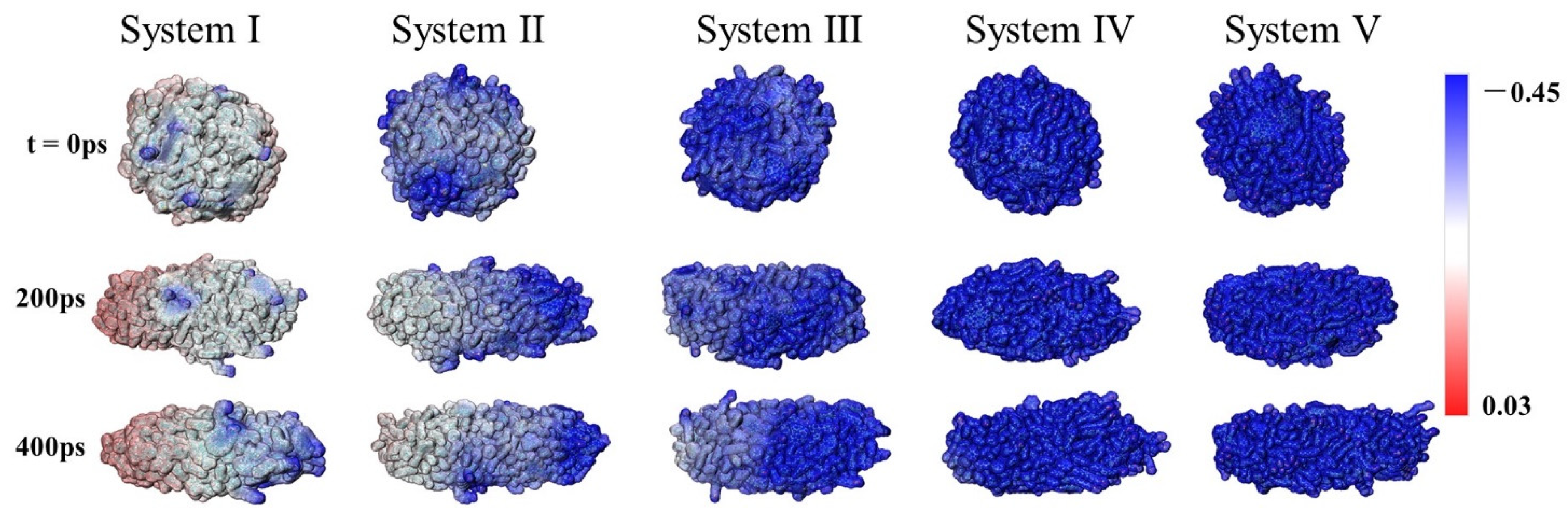
2.3. Surface Charge Distribution
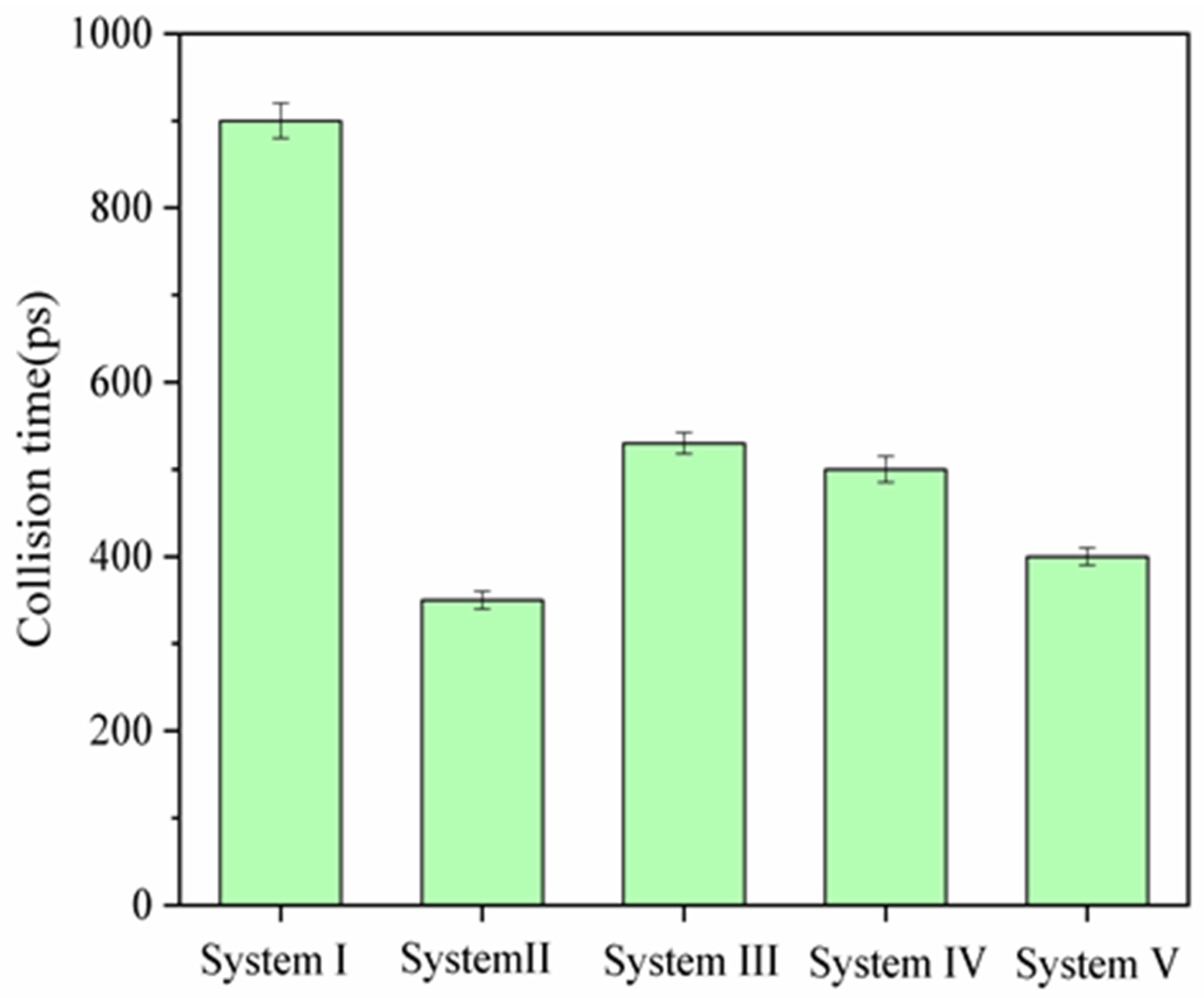
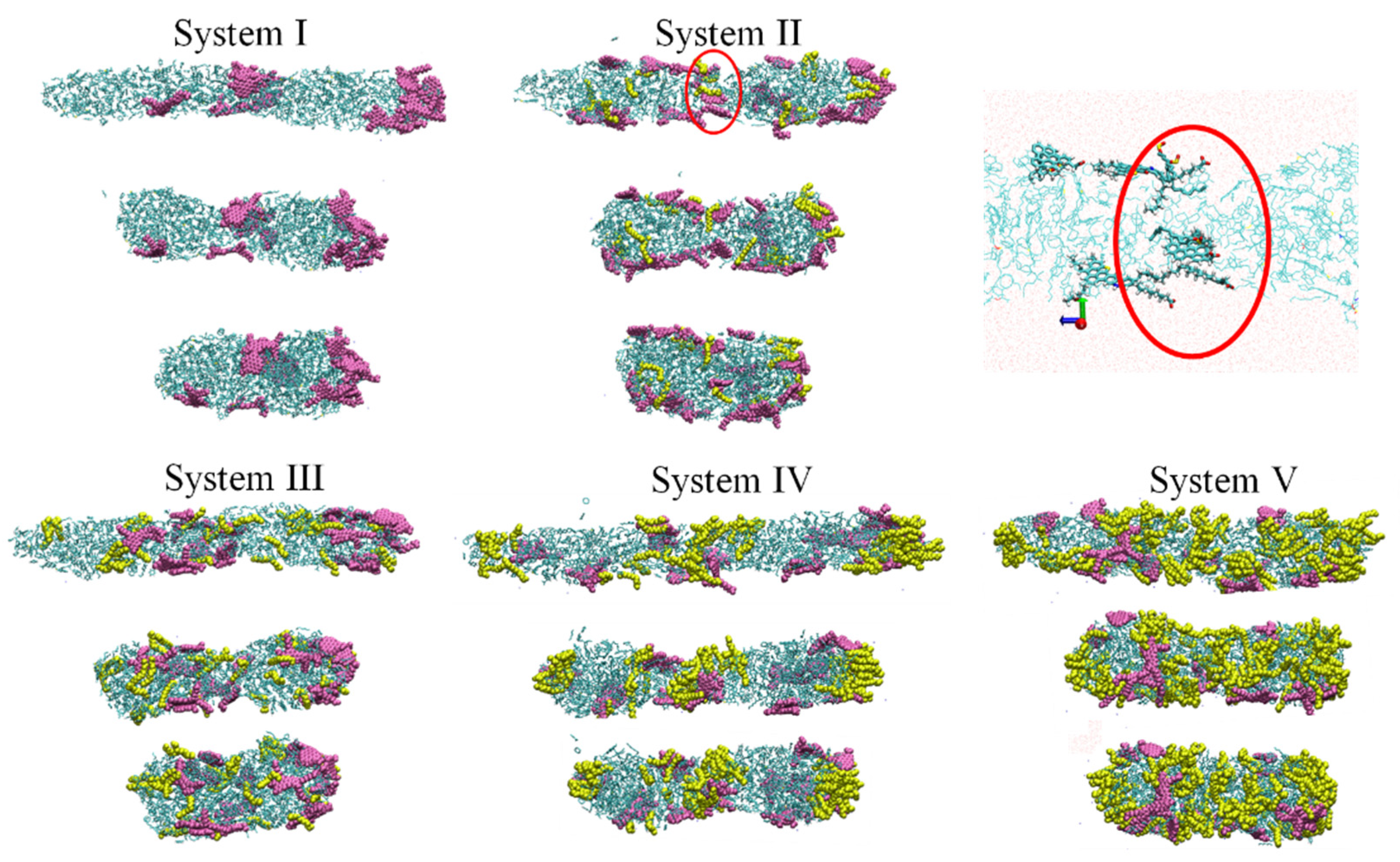
2.4. Aggregation Behavior of Oil Droplets
2.5. Mechanism of Aggregation of Oil Droplets
3. Methods and Materials
3.1. Simulation Details
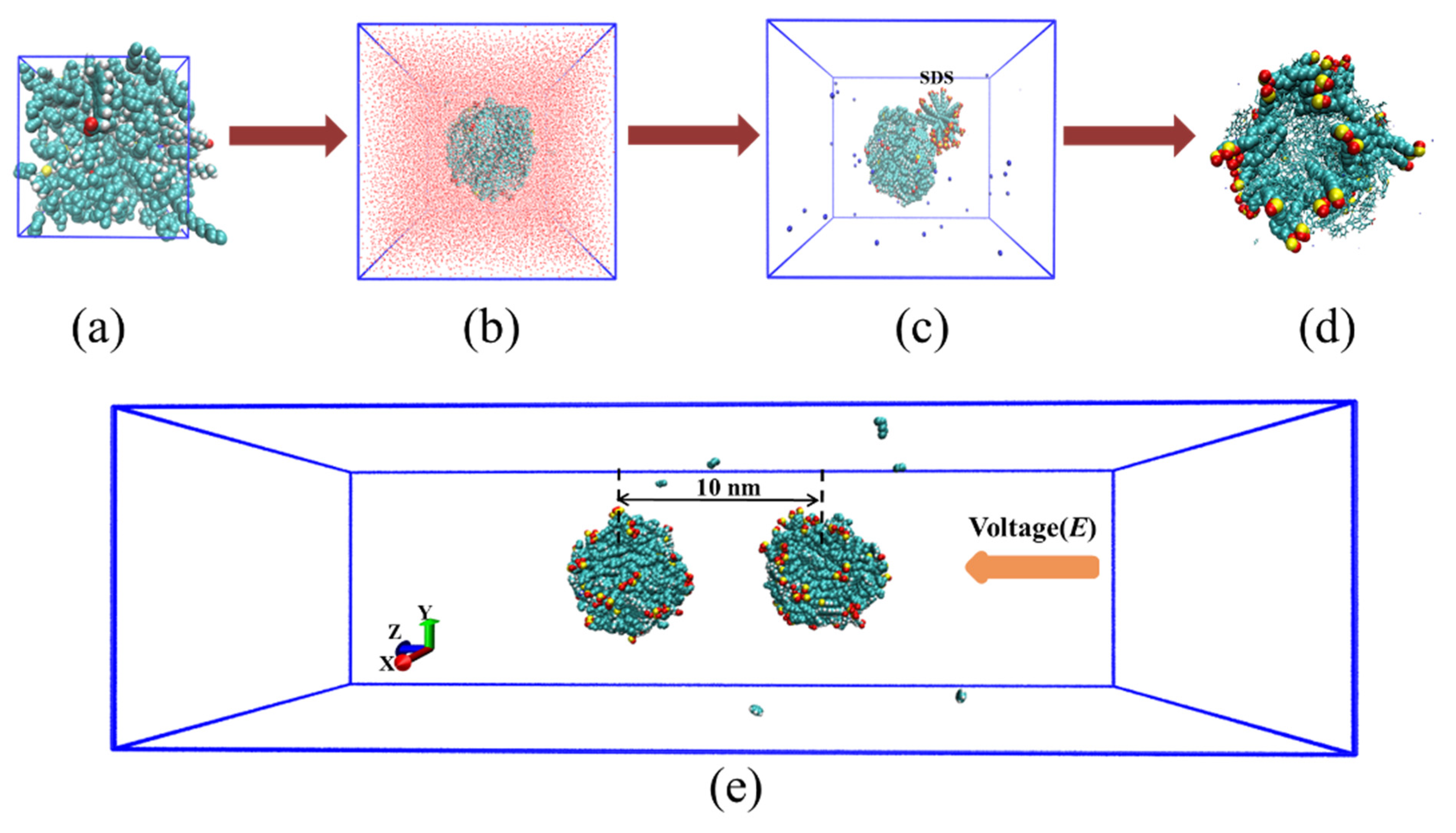
3.2. Simulation Systems
3.2.1. Molecular Models of Crude Oil
3.2.2. Emulsified Oil Droplet
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Ahmadun, F.L.R.; Pen Da Shteh, A.; Abdullah, L.C.; Biak, D.; Madaeni, S.S.; Abidin, Z.Z. Review of technologies for oil and gas produced water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 530–551. [Google Scholar]
- Wahi, R.; Chuah, L.A.; Choong, T.; Ngaini, Z.; Nourouzi, M.M. Oil removal from aqueous state by natural fibrous sorbent: An overview. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 113, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, D.; Jiang, L.; Jin, J. Recent progress in developing advanced membranes for emulsified oil/water separation. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.S.; Hilal, N.; Murali, R.S.; Padaki, M. Membrane technology enhancement in oil-water separation. A review. Desalin. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Desalt. Water Purif. 2015, 357, 197–207. [Google Scholar]
- Zolfaghari, R.; Fakhru’L-Razi, A.; Abdullah, L.C.; Elnashaie, S.; Pendashteh, A. Demulsification techniques of water-in-oil and oil-in-water emulsions in petroleum industry. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 170, 377–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, A.; Viraraghavan, T. Removal of oil by walnut shell media. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 8217–8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Chong, M.F.; Bhatia, S.; Ismail, S. Drinking water reclamation from palm oil mill effluent (POME) using membrane technology—ScienceDirect. Desalination 2006, 191, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonović, B.R.; Dragana, A.; Mića, J.; Branimir, K.; Aca, J. Removal of mineral oil and wastewater pollutants using hard coal. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2009, 15, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunov, I.; Uzunova, S.; Gigova, A.; Minchev, L. Kinetics of oil and oil products adsorption by carbonized rice husks. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 306–311. [Google Scholar]
- Annunciado, T.R.; Sydenstricker, T.; Amico, S.C. Experimental investigation of various vegetable fibers as sorbent materials for oil spills. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Pan, Z.; Miao, Z.; Xu, X.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, Q. Combination of electric field and medium coalescence for enhanced demulsification of oil-in-water emulsion. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2021, 6, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Sun, J.; Wu, K.; Hu, C. Enhanced oil droplet aggregation and demulsification by increasing electric field in electrocoagulation. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjblom, J.; Aske, N.; Auflem, I.H.; Brandal, Y.; Kallevik, H. Our current understanding of water-in-crude oil emulsions.: Recent characterization techniques and high pressure performance. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 100, 399–473. [Google Scholar]
- Mhatre, S.; Vivacqua, V.; Ghadiri, M.; Abdullah, A.M.; Al-Marri, M.J.; Hassanpour, A.; Hewakandamby, B.; Azzopardi, B.; Kermani, B. Electrostatic phase separation: A review. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 96, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Less, S.; Vilagines, R. The electrocoalescers’ technology: Advances, strengths and limitations for crude oil separation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2012, 81, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Kang, Y.; Wu, S.; Sheng, K. Demulsification performance of oil-in-water emulsion in bidirectional pulsed electric field with starlike electrodes arrangement. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, J.; An, S.; Luan, Z.; Liu, F.; Zhang, B. Dynamic demulsification of oil-in-water emulsions with electrocoalescence: Diameter distribution of oil droplets. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ptasinski, K.J.; Kerkhof, P.J.A.M. Electric Field Driven Separations: Phenomena and Applications. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1992, 27, 995–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mousavichoubeh, M.; Ghadiri, M.; Shariaty-Niassar, M. Electro-coalescence of an aqueous droplet at an oil–water interface. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2011, 50, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Lee, C.J.; Chan, C.C. Demulsification of Water-in-Oil Emulsions by Use of a High Voltage ac Field. Sep. Sci. 1994, 29, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Wasan, D.T.; Breen, P.J. A study of dynamic interfacial mechanisms for demulsification of water-in-oil emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1995, 95, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, G.; Lundgaard, L.E.; Abi-Chebel, N. Electrically stressed water drops in oil. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2010, 12, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, T.; Nakajima, Y. Rapid demulsification of dense oil-in-water emulsion by low external electric field.: II. Theory. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 242, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Shahavi, M.H.; Yakhkeshi, A. AC and DC-Currents for Separation of Nano-Particles by External Electric Field. Asian J. Chem. 2012, 24, 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Bailes, P.J.; Freestone, D.; Sams, G.W. Pulsed DC fields for electrostatic coalescence of water-in-oil emulsions. Chem. Eng. 1997, 38, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Bailes, P.J.; Larkai, S.K.L. An experimental investigation into the use of high voltage D.C. fields for liquid phase separation. Trans. Inst. Chem. Eng. 1981, 59, 229–237. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, B.; Kang, Y. Aggregation of oil droplets and demulsification performance of oil-in-water emulsion in bidirectional pulsed electric field—ScienceDirect. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.C.; Ma, J.; Xu, H.M.; Zhang, Y.J. The impact of ionic concentration on electrocoalescence of the nanodroplet driven by dieletrophoresis. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 290, 111214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hou, L.; Li, W.; Li, S. Influence of electric field on the viscosity of waxy crude oil and micro property of paraffin: A molecular dynamics simulation study. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 272, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, S.L.; Yang, Y.R.; Wang, X.D.; Chen, J.Q. Electro-coalescence of two charged droplets under pulsed direct current electric fields with various waveforms: A molecular dynamics study. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 312, 113429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Tamnanloo, J.; Mousavi, S.H.; Miandoab, E.S.; Hosseini, E.; Ghasemi, H.; Mozaffari, S. Discrete-Continuous Genetic Algorithm for Designing a Mixed Refrigerant Cryogenic Process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 7700–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, H.; Darjani, S.; Mazloomi, H.; Mozaffari, S. Preparation of stable multiple emulsions using food-grade emulsifiers: Evaluating the effects of emulsifier concentration, W/O phase ratio, and emulsification process. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Mozaffari, A.; Pablo, J.J.; Abbott, N. Active motion of multiphase oil droplets: Emergent dynamics of squirmers with evolving internal structure. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 312, 113429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Lædre, S.; Gawel, K. Review of Asphaltenes in an Electric Field. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 7285–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Kang, Y. Demulsification of Oil-in-water (O/W) Emulsion in Bidirectional Pulsed Electric Field. Langmuir 2018, 34, 8923–8931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oostenbrink, C.; Villa, A.; Mark, A.E.; Gunsteren, W. A biomolecular force field based on the free enthalpy of hydration and solvation: The GROMOS force-field parameter sets 53A5 and 53A6. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 25, 1656–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malde, A.K.; Zuo, L.; Breeze, M.; Stroet, M.; Poger, D.; Nair, P.C.; Oostenbrink, C.; Mark, A.E. An Automated Force Field Topology Builder (ATB) and Repository: Version 1.0. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziara, K.B.; Stroet, M.; De Mal, A.K.; Mark, A. Testing and validation of the Automated Topology Builder (ATB) version 2.0: Prediction of hydration free enthalpies. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des. 2014, 28, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wander, M.; Shuford, K.L. Molecular Dynamics Study of Interfacial Confinement Effects of Aqueous NaCl Brines in Nanoporous Carbon. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 20539–20546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, S.; Ghasemi, H.; Tchoukov, P.; Czarnecki, J.; Nazemifard, N. Lab-on-a-Chip Systems in Asphaltene Characterization: A Review of Recent Advances. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 9080–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Sho, J.; Cao, X.; Yuan, S. Molecular Dynamics Study on Aggregating Behavior of Asphaltene and Resin in Emulsified Heavy Oil Droplets with Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 12383–12393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lara, L.S.; Michelon, M.F.; Miranda, C.R. Molecular Dynamics Studies of Fluid/Oil Interfaces for Improved Oil Recovery Processes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 14667–14676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunieda, M.; Nakaoka, K.; Liang, Y.; Miranda, C.R.; Ueda, A.; Takahashi, S.; Okabe, H.; Matsuoka, T. Self-accumulation of aromatics at the oil-water interface through weak hydrogen bonding. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18281–18286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| System | Number of Molecules | Mass Fraction (SDS of Oil Droplet) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude Oil Droplet | SDS | Na+ | Water | ||
| I | 1 | 0 | 8 | 47,086 | 0.0% |
| II | 1 | 10 | 18 | 47,018 | 6.2% |
| III | 1 | 15 | 23 | 46,985 | 9.1% |
| IV | 1 | 30 | 38 | 46,883 | 16.6% |
| V | 1 | 60 | 68 | 46,680 | 28.5% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, H. Molecular Dynamics Simulation for the Demulsification of O/W Emulsion under Pulsed Electric Field. Molecules 2022, 27, 2559. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27082559
Liu S, Yuan S, Zhang H. Molecular Dynamics Simulation for the Demulsification of O/W Emulsion under Pulsed Electric Field. Molecules. 2022; 27(8):2559. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27082559
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shasha, Shiling Yuan, and Heng Zhang. 2022. "Molecular Dynamics Simulation for the Demulsification of O/W Emulsion under Pulsed Electric Field" Molecules 27, no. 8: 2559. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27082559
APA StyleLiu, S., Yuan, S., & Zhang, H. (2022). Molecular Dynamics Simulation for the Demulsification of O/W Emulsion under Pulsed Electric Field. Molecules, 27(8), 2559. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27082559






