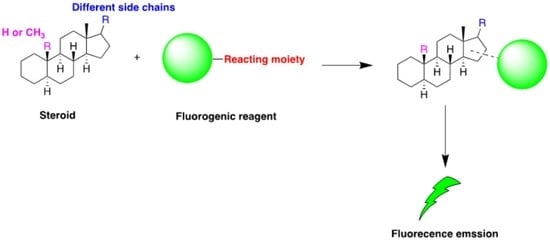
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with Fluorescence Detection for Quantification of Steroids in Clinical, Pharmaceutical, and Environmental Samples: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. HPLC-FLD Methods
3. Clinical Applications of HPLC-FLD Techniques
3.1. Detection of Glucocorticosteroids
3.2. Detection of Steroid Hormones
3.3. Detection of Endocrine Disruptive Chemicals (EDCs)
4. Pharmaceutical Applications
5. Environmental and Food Applications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benc, D.; Icin, T.; Pejakovic, S.; Bajkin, I.; Prodanovic, J.; Vukovic, B.; Novakovic-Paro, J.; Tomic-Naglic, D.; Zvezdin, B.; Mitrovic, M. Glucocorticoid therapy and adrenal suppression. Med. Pregl. 2017, 70, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, L.M.; Cornil, C.A.; Mittelman-Smith, M.A.; Rainville, J.R.; Remage-Healey, L.; Sinchak, K.; Micevych, P.E. Actions of steroids: New neurotransmitters. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 11449–11458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cole, T.J.; Short, K.L.; Hooper, S.B. The science of steroids. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019, 24, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makin, H.L.J.; Honour, J.W.; Shackleton, C.H.L.; Griffiths, W.J. General Methods for the Extraction, Purification, and Measurement of Steroids by Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry. Steroid Anal. 2010, 163–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, S.A.; Keith, T.L.; Verbrugge, D.A.; Snyder, E.M.; Gross, T.S.; Kannan, K.; Giesy, J.P. Analytical methods for detection of selected estrogenic compounds in aqueous mixtures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 2814–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varriale, A.; Pennacchio, A.; Pinto, G.; Oliviero, G.; D’Errico, S.; Majoli, A.; Scala, A.; Capo, A.; Pennacchio, A.; Di Giovanni, S.; et al. A Fluorescence Polarization Assay to Detect Steroid Hormone Traces in Milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9159–9164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.Y.; McCalley, D.V.; McEvoy, J. Analysis of estrogens in river water and effluents using solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography–negative chemical ionisation mass spectrometry of the pentafluorobenzoyl derivatives. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 923, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackleton, C. Clinical steroid mass spectrometry: A 45-year history culminating in HPLC-MS/MS becoming an essential tool for patient diagnosis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 121, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelblad, P.; Irgum, K. Separation and detection of neuroactive steroids from biological matrices. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 955, 151–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Namdev, K.K.; Verma, K.; Gururani, R.; Tiwari, A.; Kumar, P.; Dewangan, R.P.; Wabaidur, S.M.; Sharma, S.; Dwivedi, J. HPLC-UV and spectrofluorimetric methods for simultaneous estimation of fluticasone furoate and vilanterol in rabbit plasma: A pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2019, 1132, 121842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, B.; Kadioglu, Y. Determination of 17 β-estradiol in pharmaceutical preparation by UV spectrophotometry and high performance liquid chromatography methods. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1422–S1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsova-Sarafinovska, Z.; Ugrinova, L.; Starkoska, K.; Djordjev, D.; Dimitrovska, A. Determination of ethinylestradiol and levonorgestrel in oral contraceptives with HPLC methods with UV detection and UV/fluorescence detection. Maced. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 52, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsova-sarafinovska, Z.; Polozhani, A.; Dimitrovska, A. Determination of ethinylestradiol and drospirenone in oral contraceptives with HPLC method with UV and fluorescence detection Determination of ethinylestradiol and drospirenone in oral contraceptives with HPLC method with UV and fluorescence detection. Arch. Public Health 2009, 1, 67. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, S. Effect of heavy metal ions on steroid estrogen removal and transport in SAT using DLLME as a detection method of steroid estrogen. Water (Switzerland) 2020, 12, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nozaki, O. Steroid analysis for medical diagnosis. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 935, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.Y.; Praveena, S.M.; de Burbure, C.; Aris, A.Z.; Ismail, S.N.S.; Rasdi, I. Analytical techniques for steroid estrogens in water samples—A review. Chemosphere 2016, 165, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Liz, M.V.; Do Amaral, B.; Stets, S.; Nagata, N.; Peralta-Zamora, P. Sensitive estrogens determination in wastewater samples by HPLC and fluorescence detection. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2017, 28, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiros, L.; Queiroz, J.F.; Magalhães, L.M.; Silva, A.M.T.; Segundo, M.A. Analysis of 17-β-estradiol and 17-α-ethinylestradiol in biological and environmental matrices—A review. Microchem. J. 2016, 126, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowska-Tylingo, K.; Namieśnik, J.; Górecki, T. Determination of estrogenic endocrine disruptors in environmental samples-a review of chromatographic methods. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2010, 40, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozłowska-Tylingo, K.; Konieczka, P.; Gustaw, E.; Wasik, A.; Namieśnik, J. Comparison of High Performance Liquid Chromatography Methods with Different Detectors for Determination of Steroid Hormones in Aqueous Matrices. Anal. Lett. 2014, 47, 1449–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Shi, Y.E.; Li, M.; Zhang, T.D.; Gao, S. Simultaneous determination of four trace estrogens in feces, leachate, tap and groundwater using solid-liquid extraction/auto solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 3494–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que, A.H.; Palm, A.; Baker, A.G.; Novotny, M.V. Steroid profiles determined by capillary electrochromatography, laser-induced fluorescence detection and electrospray—Mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 887, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufartová, J.; Mahugo-Santana, C.; Sosa-Ferrera, Z.; Santana-Rodríguez, J.J.; Nováková, L.; Solich, P. Determination of steroid hormones in biological and environmental samples using green microextraction techniques: An overview. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 704, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toldrá, F.; Reig, M. Methods for rapid detection of chemical and veterinary drug residues in animal foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noppe, H.; Le Bizec, B.; Verheyden, K.; De Brabander, H.F. Novel analytical methods for the determination of steroid hormones in edible matrices. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 611, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.; Harrington, K.; Von Wandruszka, R. Determination of Steroids in Urine by Micellar HPLC with Detection by Sensitized Terbium Fluorescence. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 2346–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, K.; Nakagi, T. Studies on neurosteroids. IV. Quantitative determination of pregnenolone in rat brains using high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 1996, 19, 2593–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Loyo-Rosales, J.E.; Rice, C.P. A simple method for the determination of trace levels of alkylphenolic compounds in fish tissue using pressurized fluid extraction, solid phase cleanup, and high-performance liquid chromatography fluorescence detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Li, G.; Liu, S.; Hu, N.; Geng, D.; Chen, G.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, X.; Xia, L.; You, J. Monitoring the contents of six steroidal and phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals in chicken, fish and aquaculture pond water samples using pre-column derivatization and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction with the aid of experimental design metho. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarth, J.; Akre, C.; van Ginkel, L.; le Bizec, B.; de Brabander, H.; Korth, W.; Points, J.; Teale, P.; Kay, J. Presence and metabolism of endogenous androgenic-anabolic steroid hormones in meat-producing animals: A review. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2009, 26, 640–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbazi, Y.; Malekinejad, H.; Tajik, H. Determination of naturally occurring estrogenic hormones in cow’s and river buffalo’s meat by HPLC-FLD method. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsuda, T.; Suga, K.; Kaneda, E.; Ohsuga, M. Determination of 4-nonylphenol, nonylphenol monoethoxylate, nonylphenol diethoxylate and other alkylphenols in fish and shellfish by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2000, 746, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, N.; Akiyama, Y.; Takeda, N. Determination of α- and β-trenbolone in bovine muscle and liver by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2000, 739, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görög, S. Advances in the analysis of steroid hormone drugs in pharmaceuticals and environmental samples (2004-2010). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 55, 728–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejo-Rodríguez, R.; Lopez-Lopez, A.; Saldarriaga-Noreña, H.; Murillo-Tovar, M.; Hernández-Mena, L. Optimization of Analytical Conditions to Determine Steroids and Pharmaceuticals Drugs in Water Samples Using Solid Phase-Extraction and HPLC. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2011, 02, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socas-Rodríguez, B.; Asensio-Ramos, M.; Hernández-Borges, J.; Rodríguez-Delgado, M.Á. Analysis of oestrogenic compounds in dairy products by hollow-fibre liquid-phase microextraction coupled to liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, D.L.D.; Silva, C.P.; Otero, M.; Esteves, V.I. Low cost methodology for estrogens monitoring in water samples using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and HPLC with fluorescence detection. Talanta 2013, 115, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Yan, P.; Chu, M.; Gao, Y.Q.; Li, W.H.; Yang, X.L. A rapid and simple HPLC–FLD screening method with QuEChERS as the sample treatment for the simultaneous monitoring of nine bisphenols in milk. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Guijo, A.; Hartmann, M.F.; Shi, L.; Remer, T.; Wudy, S.A. Determination of free cortisol and free cortisone in human urine by on-line turbulent flow chromatography coupled to fused-core chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (TFC-HPLC-MS/MS). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Zhao, L.; Chu, B.; Feng, Q.; Yan, W.; Lin, J.M. Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for the selective determination of 17β-estradiol in fishery samples with high performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 2009, 78, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes-Alonso, R.; Santana-Viera, S.; Sosa-Ferrera, Z.; Santana-Rodríguez, J.J. Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled with ultra high performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection for the determination of estrogens and their metabolites in wastewater. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 3961–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Sun, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, D. Determination of environmental estrogens in human urine by high performance liquid chromatography after fluorescent derivatization with p-nitrobenzoyl chloride. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 522, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosawa, S.; Koike, T.; Yoshimura, T.; Kurosawa, T.; Tohma, M.; Chiba, H.; Kobayashi, K. Simultaneous determination of 18-oxygenated corticosteroids by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1995, 18, 2383–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Nonaka, M. Utility of cyclodextrin in mobile phase for high-performance liquid chromatographic separation of C21 steroids. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1991, 14, 2109–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Główka, F.K.; Kosicka, K.; Karaźniewicz-Łada, M. HPLC method for determination of fluorescence derivatives of cortisol, cortisone and their tetrahydro- and allo-tetrahydro-metabolites in biological fluids. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2010, 878, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, J.; Goto, N.; Shamsa, F.; Saito, M.; Komatsu, S.; Suzaki, K.; Nambara, T. New sensitive derivatization of hydroxysteroids for high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 1983, 147, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, N.; Hayakawa, T.; Takada, K.; Hoshino, N.; Minouchi, T.; Yamaji, A. Simultaneous determination of glucocorticoids in plasma or urine by high-performance liquid chromatography with precolumn fluorimetric derivatization by 9-anthroyl nitrile. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1998, 706, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haegele, A.D.; Wade, S.E. Ultrasensitive differential measurement of cortisol and cortisone in biological samples using fluorescent ester derivatives in normal phase hplc. J. Liq. Chromatogr. 1991, 14, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosicka, K.; Siemiątkowska, A.; Szpera-Goździewicz, A.; Krzyścin, M.; Bręborowicz, G.; Główka, F. High-performance liquid chromatography methods for the analysis of endogenous cortisol and cortisone in human urine: Comparison of mass spectrometry and fluorescence detection. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 56, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neufeld, E.; Chayen, R.; Stern, N. Fluorescence derivatisation of urinary corticosteroids for high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1998, 718, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamoh, K.; Omote, K.; Okamoto, N.; Takatsuto, S. High-performance liquid chromatography of brassinosteroids in plants with derivatization using 9-phenanthreneboronic acid. J. Chromatogr. A 1989, 469, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; You, J.; Sun, Z.; Song, C.; Ning, S.; Zhao, C.; Suo, Y. A sensitive method for extraction and determination of endocrine-disrupting compounds from wastewater using 10-ethyl-acridone-2-sulfonyl chloride as pre-column labeling reagent by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Microchem. J. 2012, 103, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, O.; Ohata, T.; Ohba, Y.; Moriyama, H.; Kato, Y. Determination of serum cortisol by reversed-phase liquid chromatography using precolumn sulphuric acid-ethanol fluorescence derivatization and column switching. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1991, 570, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, O.; Ohata, T.; Ohba, Y.; Moriyama, H.; Kato, Y. Determination of urinary free cortisol by high performance liquid chromatography with sulphuric acid–ethanol derivatization and column switching. Biomed. Chromatogr. 1992, 6, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudo, A. Analysis of corticosterone in rat urine by high-performance liquid chromatography and fluorimetry using post-column reaction with sulphuric acid. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1990, 528, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Xie, Q.; Jin, J.; Qiao, T.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Deng Huihua, H.; Lu, Z. HPLC-FLU detection of cortisol distribution in human hair. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 43, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saisho, Y.; Shimada, C.; Umeda, T. Determination of 7α-hydroxycholesterol in dog plasma by high- performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Anal. Biochem. 1998, 265, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, M.; Masuda, Y.; Taniguchi, H. Determination of corticosteroids in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography after pre-column derivatization with 2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1993, 612, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, M.; Sasaki, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Iwamoto, T.; Tanaka, M. Sensitive determination of bisphenol A and alkylphenols by high performance liquid chromatography with pre-column derivatization with 2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2001, 15, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, T.; Yamaguchi, Y. New fluorimetric determination of 17-hydroxycorticosteroids after high-performance liquid chromatography using post-column derivatization with benzamidine. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1984, 305, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Irie, M.; Kishikawa, N.; Wada, M.; Kuroda, N.; Nakashima, K. Determination of bisphenol A in human breast milk by HPLC with column-switching and fluorescence detection. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2004, 18, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, N.; Kinoshita, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wada, M.; Kishikawa, N.; Nakashima, K.; Makino, T.; Nakazawa, H. Measurement of bisphenol A levels in human blood serum and ascitic fluid by HPLC using a fluorescent labeling reagent. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 30, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Nakashima, M.N.; Takahashi, M.; Kuroda, N.; Nakashima, K. Determination of bisphenol A in rat brain by microdialysis and column switching high-performance liquid chromatrography with fluorescence detection. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2002, 16, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.F.B.; Uejo, Y.; Kishikawa, N.; Ohyama, K.; Kuroda, N. A selective and highly sensitive high performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence derivatization approach based on Sonogashira coupling reaction for determination of ethinyl estradiol in river water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1628, 461440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Ishida, J.; Yoshitake, T.; Nakamura, M. Determination of prednisolone and prednisone in plasma by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 1991, 242, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshitake, T.; Hara, S.; Yamaguchi, M.; Nakamura, M.; Ohkura, Y.; Görög, S. Measurement of 21-hydroxycorticosteroids in human and rat sera by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1989, 489, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YAMAGUCHI, M.; YOSHITAKE, T.; ISHIDA, J.; NAKAMURA, M. Determination of 21-hydroxycorticosteroids in human urine by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1989, 37, 3022–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katayama, M.; Nakane, R.; Matsuda, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Hara, I.; Sato, H. Determination of progesterone and 17-hydroxyprogesterone by high performance liquid chromatography after pre-column derivatization with 4,4-difluoro-5,7-dimethyl-4-bora-3a,4a- diaza-s-indacene-3-propionohydrazide. Analyst 1998, 123, 2339–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, S.A.G.; Smulders, C.J.G.M.; Gladdines, W.W.F.T.; Irth, H.; Van Der Graaf, P.H.; Danhof, M. High-performance liquid chromatography of the neuroactive steroids alphaxalone and pregnanolone in plasma using dansyl hydrazine as fluorescent label: Application to a pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic study in rats. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2000, 745, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.D.; Xu, D.H.; Jin, J.; Mei, X.T.; Lv, J.Y.; Xu, S.B. Determination of a new active steroid by high performance liquid chromatography with laser-induced fluorescence detection following the pre-column derivatization. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 337, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Maeda, M.; Tsuji, A. Determination of plasma and urinary cortisol by high-performance liquid chromatography using fluorescence derivatization with dansyl hydrazine. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1979, 163, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motegi, C.; Takatsuto, S.; Gamoh, K. Identification of brassinolide and castasterone in the pollen of orange (Citrus sinensis Osbeck) by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1994, 658, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wu, D.; Liu, J.; Hu, N.; Shi, X.; Dai, C.; Sun, Z.; Suo, Y.; Li, G.; Wu, Y. Magnetic covalent organic frameworks based on magnetic solid phase extraction for determination of six steroidal and phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals in food samples. Microchem. J. 2018, 143, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; You, J.; Suo, Y.; Song, C.; Sun, Z.; Xia, L.; Zhao, X.; Shi, J. A developed pre-column derivatization method for the determination of free fatty acids in edible oils by reversed-phase HPLC with fluorescence detection and its application to Lycium barbarum seed oil. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; You, J.; Zhang, S.; Song, C.; Ji, Z.; Zhuang, J.; Yu, Y. New fluorescent labeling reagent Benzimidazo[2,1-b]quinazoline-12(6H) -one-5-ethylimidazole ester and its application in the analysis of endocrine disrupting compounds in milk by high performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Microchem. J. 2018, 138, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, A.W.; Litwack, G. Hormones; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997; ISBN 9780125214414. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, S.R.; Ward, L.C.; Reilly, P.E.B. Fluorimetric detection of serum corticosterone using high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1992, 581, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, M.; Masuda, Y.; Taniguchi, H. Determination of alcohols by high-performance liquid chromatography after pre-column derivatization with 2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole. J. Chromatogr. A 1991, 585, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Wu, S.S.; Wu, H.L. Highly sensitive analysis of cholesterol and sitosterol in foods and human biosamples by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1156, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganà, A.; Marino, A. General and selective isolation procedure for high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of anabolic steroids in tissues. J. Chromatogr. A 1991, 588, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Gaurav; Heena; Malik, A.K.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Efficient analysis of selected estrogens using fabric phase sorptive extraction and high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1359, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Qiu, X.; Yang, Y. Determination of estrogens in human urine by vortex-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on floating organic acid droplet combined with high-performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2015, 38, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impens, S.; De Wasch, K.; Cornelis, M.; De Brabander, H.F. Analysis on residues of estrogens, gestagens and androgens in kidney fat and meat with gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 970, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Koyano, Y.; Takeda, Y.; Yamada, T. Migration of Bisphenol a from Polycarbonate Products. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Japan 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Chen, W.Y.; Hunter, D.J.; Stampfer, M.J.; Colditz, G.A.; Hankinson, S.E.; Willett, W.C. Red meat intake and risk of breast cancer among premenopausal women. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 2253–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noda, M.; Komatsu, H.; Sano, H. HPLC analysis of dental resin composites components. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 47, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vom Saal, F.S.; Cooke, P.S.; Buchanan, D.L.; Palanza, P.; Thayer, K.A.; Nagel, S.C.; Parmigiani, S.; Welshons, W.V. A Physiologically Based Approach To the Study of Bisphenol a and Other Estrogenic Chemicals On the Size of Reproductive Organs, Daily Sperm Production, and Behavior. Toxicol. Ind. Health 1998, 14, 239–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Główka, F.K.; Karaźniewicz, M.; Lipnicka, E. RP-HPLC method with fluorescence detection for determination of small quantities of triamcinolone in plasma in presence of endogenous steroids after derivatization with 9-anthroyl nitrile; pharmacokinetic studies. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2006, 839, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.B.; Galdos, A.A.G.; Mothe, C.M.A.; Pallastrelli, M.B.; Prado, M.S.A.; Singh, A.K.; Kedor-Hackmann, E.R.M.; Santoro, M.I.R.M. Simultaneous determination of ethinyl estradiol and drospirenone in oral contraceptive by high performance liquid chromatography. Brazilian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gatti, R.; Gotti, R.; Gioia, M.G.; Cavrini, V. HPLC analysis of pharmaceutical estrogens in raw materials and dosage forms. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1998, 17, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Kong, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Q. Analysis of oestrogenic hormones in chicken litter by HPLC with fluorescence detection. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2014, 94, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, R.L.; Escandar, G.M. Multivariate calibration-assisted high-performance liquid chromatography with dual UV and fluorimetric detection for the analysis of natural and synthetic sex hormones in environmental waters and sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 209, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrolecco, L.; Ademollo, N.; Grenni, P.; Tolomei, A.; Barra Caracciolo, A.; Capri, S. Simultaneous determination of human pharmaceuticals in water samples by solid phase extraction and HPLC with UV-fluorescence detection. Microchem. J. 2013, 107, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Westerhoff, P.; Snyder, S.A.; Esparza, M. HPLC-fluorescence detection and adsorption of bisphenol A, 17β-estradiol, and 17α-ethynyl estradiol on powdered activated carbon. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3530–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durhan, E.J.; Lambright, C.S.; Makynen, E.A.; Lazorchak, J.; Hartig, P.C.; Wilson, V.S.; Gray, L.E.; Ankley, G.T. Identification of metabolites of trenbolone acetate in androgenic runoff from a beef feedlot. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wen, Y.; Zhou, B.S.; Xu, Y.; Jin, S.W.; Feng, Y.Q. Analysis of estrogens in environmental waters using polymer monolith in-polyether ether ketone tube solid-phase microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1133, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, G.G.; Kookana, R.S.; Chen, Z. On-line solid-phase extraction and fluorescence detection of selected endocrine disrupting chemicals in water by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2002, 37, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Da, S.L.; Feng, Y.Q. Determination of endocrine disruptors in environmental waters using poly(acrylamide-vinylpyridine) monolithic capillary for in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled to high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Analyst 2005, 130, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, T.; Zhao, X.E.; Zhu, S.; Ji, Z.; Chen, G.; Sun, Z.; Song, C.; You, J.; Suo, Y. Development of an Efficient HPLC Fluorescence Detection Method for Brassinolide by Ultrasonic-Assisted Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Coupled with Derivatization. Chromatographia 2014, 77, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzymala, S.S.; Weiz, S.; Heinze, J.; Marten, S.; Prinz, C.; Zimathies, A.; Garbe, L.A.; Koch, M. Automated solid-phase extraction coupled online with HPLC-FLD for the quantification of zearalenone in edible oil. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 3489–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Cheng, X.; Guo, J.; Zhang, H.; Hao, X. Comparison of Two Ionic Liquid-Based Pretreatment Methods for Three Steroids’ Separation and Determination in Water Samples by HPLC. Chromatographia 2017, 80, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.N.; Benevides, A.P.; Cesar, D.V.; Luna, A.S.; de Gois, J.S. Magnetic solid-phase extraction and pre-concentration of 17β-estradiol and 17α-ethinylestradiol in tap water using maghemite-graphene oxide nanoparticles and determination via HPLC with a fluorescence detector. Microchem. J. 2020, 157, 104947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazza, G.; Merib, J.; Magosso, H.A.; Bittencourt, O.R.; Carasek, E. A hybrid material as a sorbent phase for the disposable pipette extraction technique enhances efficiency in the determination of phenolic endocrine-disrupting compounds. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1513, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louros, V.L.; Lima, D.L.D.; Leitão, J.H.; Esteves, V.I.; Nadais, H.G. Determination of estrone and 17α-ethinylestradiol in digested sludge by ultrasonic liquid extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 1585–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, M.; Jia, N.; Zhai, C.; Han, Y.; Yan, H. Graphene/multi-walled carbon nanotubes as an adsorbent for pipette-tip solid-phase extraction for the determination of 17β-estradiol in milk products. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1600, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, S. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) in the Pharmaceutical Analysis. In Pharmaceutical Sciences Encyclopedia: Drug Discovery, Development, and Manufacturing; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Argentine, M.D.; Owens, P.K.; Olsen, B.A. Strategies for the investigation and control of process-related impurities in drug substances. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, M.; Singh, S. Development of validated stability-indicating assay methods—Critical review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 28, 1011–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleicher, K.H.; Böhm, H.J.; Müller, K.; Alanine, A.I. Hit and lead generation: Beyond high-throughput screening. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolz-Pérez, I.; Sallam, M.A.; Masiá, E.; Morelló-Bolumar, D.; Pérez del Caz, M.D.; Graff, P.; Abdelmonsif, D.; Hedtrich, S.; Nebot, V.J.; Vicent, M.J. Polypeptide-corticosteroid conjugates as a topical treatment approach to psoriasis. J. Control. Release 2020, 318, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, S.; Lacorn, M.; Steinhart, H. Natural occurrence of steroid hormones in food. Food Chem. 1998, 62, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- STRUSIAK, S.H.; HOOGERHEIDE, J.G.; GARDNER, M.S. Determination of Ethinyl Estradiol in Solid Dosage Forms By High-Performance Liquid-Chromatography. J. Pharm. Sci. 1982, 71, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, L.; Harmatha, J.; Lafont, R. Chromatographic procedures for the isolation of plant steroids. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 935, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Feng, X.S. Sample Preparation and Analytical Methods for Steroid Hormones in Environmental and Food Samples: An Update Since 2012. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, T. Isolation and characterization of a new highly effective 17β-estradiol-degrading Gordonia sp. strain R9. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, T. Identification and genome analysis of Comamonas testosteroni strain JLU460ET, a novel steroid-degrading bacterium. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M.; Ishimaru, M.; Shibata, T.; Hatate, H.; Tanaka, R. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection for Simultaneous Analysis of Phytosterols (Stigmasterol, β-Sitosterol, Campesterol, Ergosterol, and Fucosterol) and Cholesterol in Plant Foods. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 2692–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobling, S.; Sumpter, J.P. Detergent components in sewage effluent are weakly oestrogenic to fish: An in vitro study using rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) hepatocytes. Aquat. Toxicol. 1993, 27, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobling, S.; Sheahan, D.; Osborne, J.A.; Matthiessen, P.; Sumpter, J.P. Inhibition of testicular growth in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) exposed to estrogenic alkylphenolic chemicals. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1996, 15, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
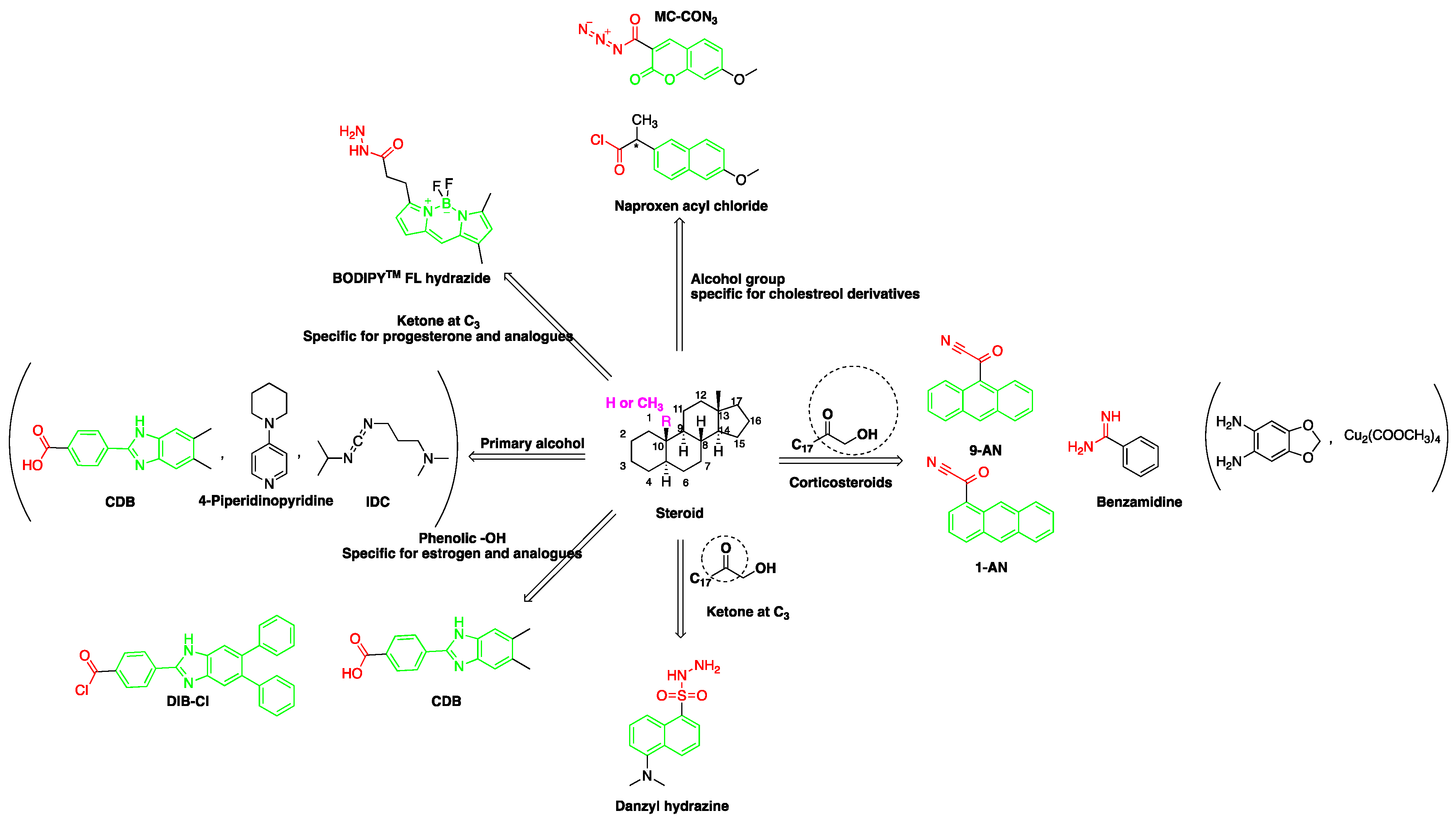




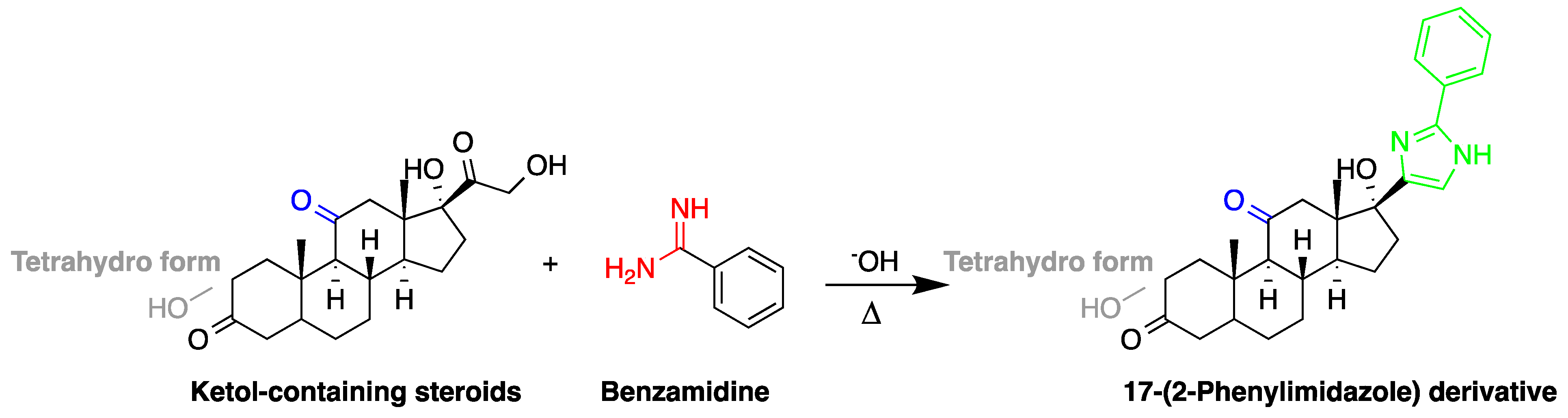
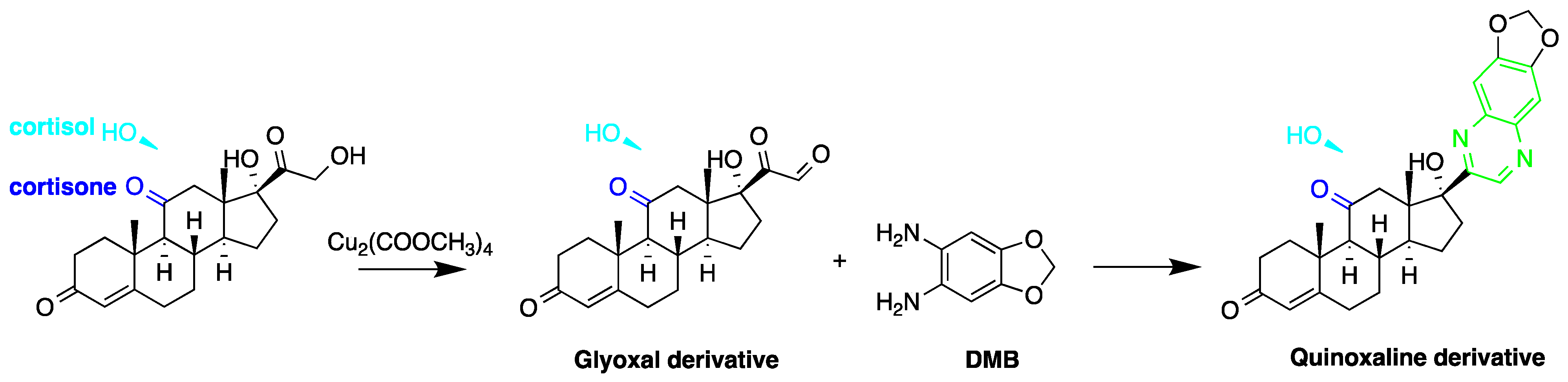
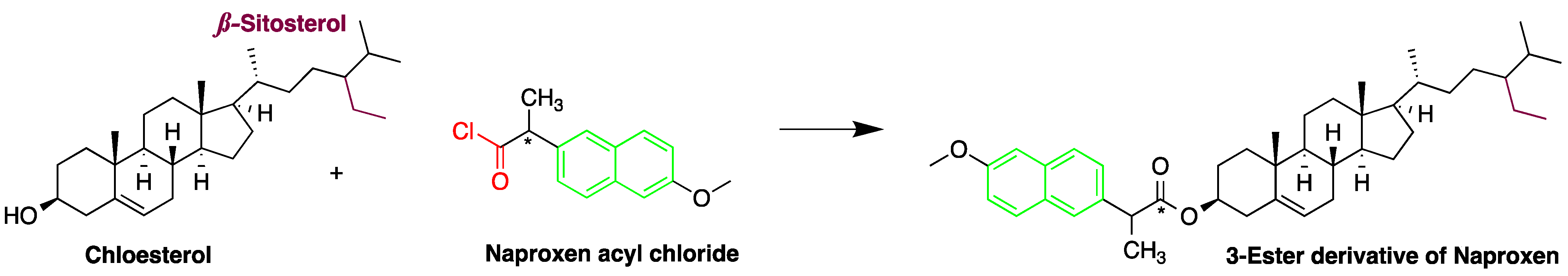
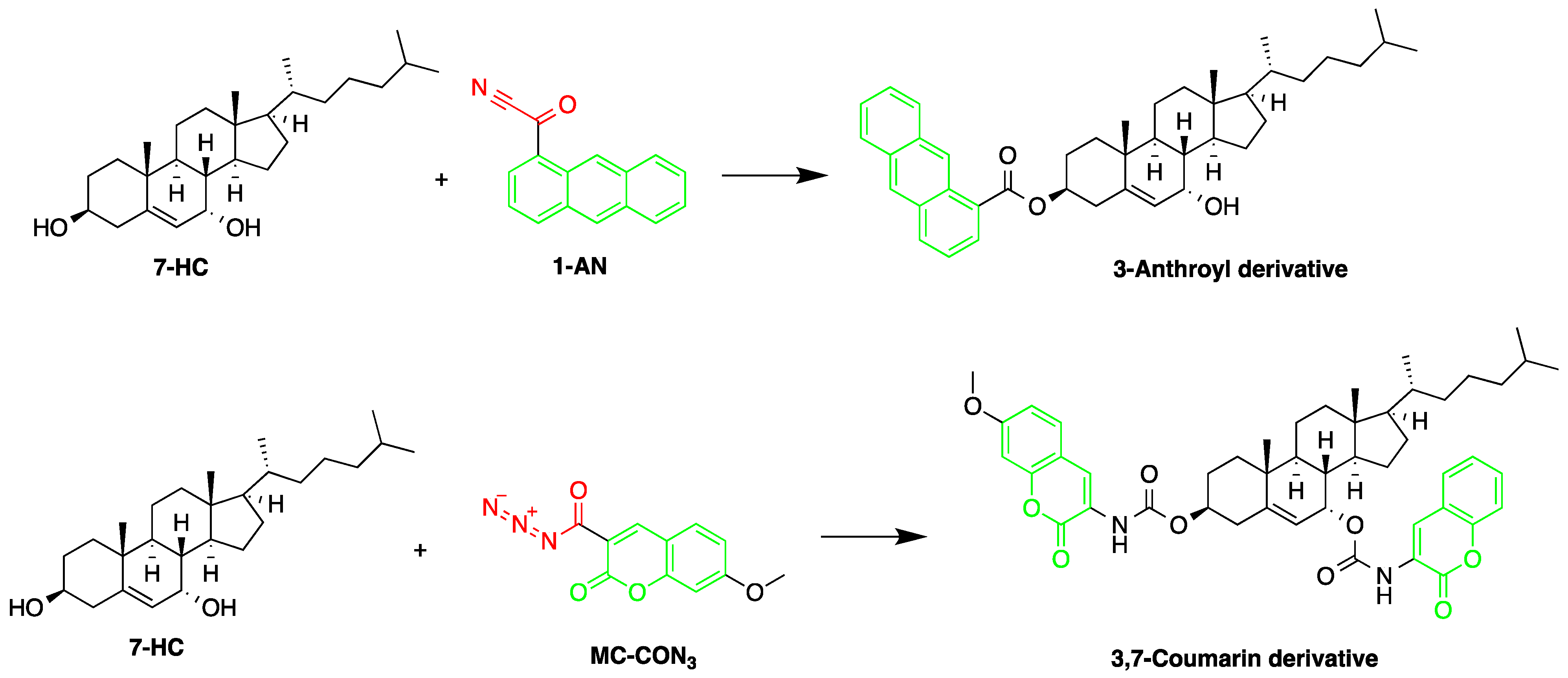
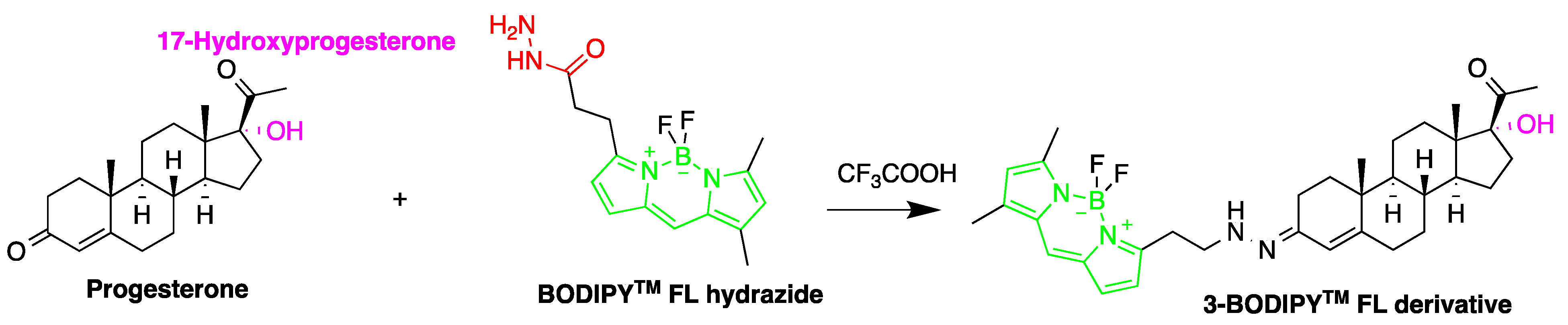

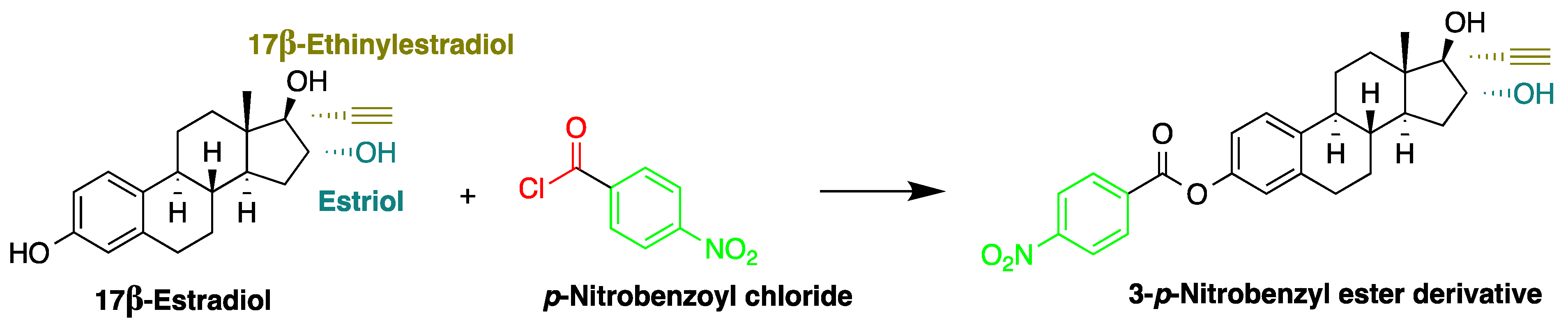
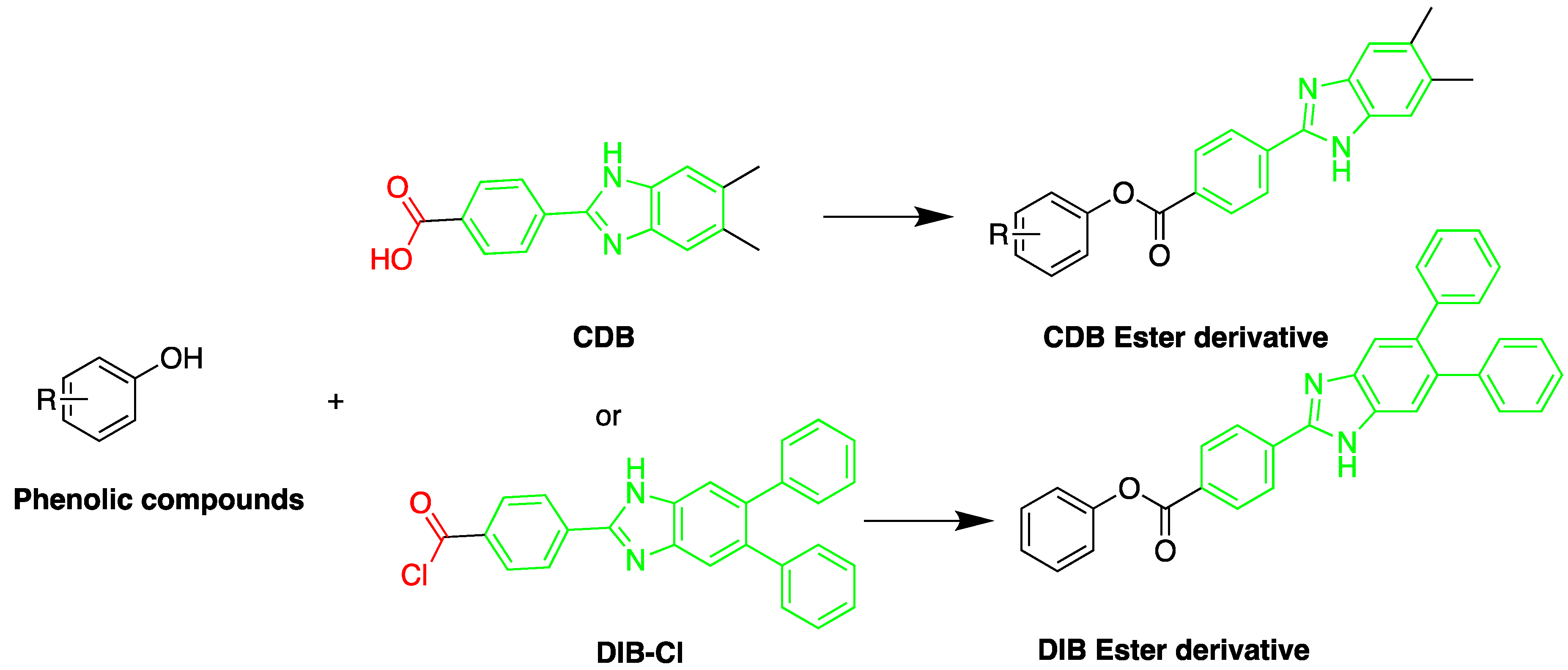
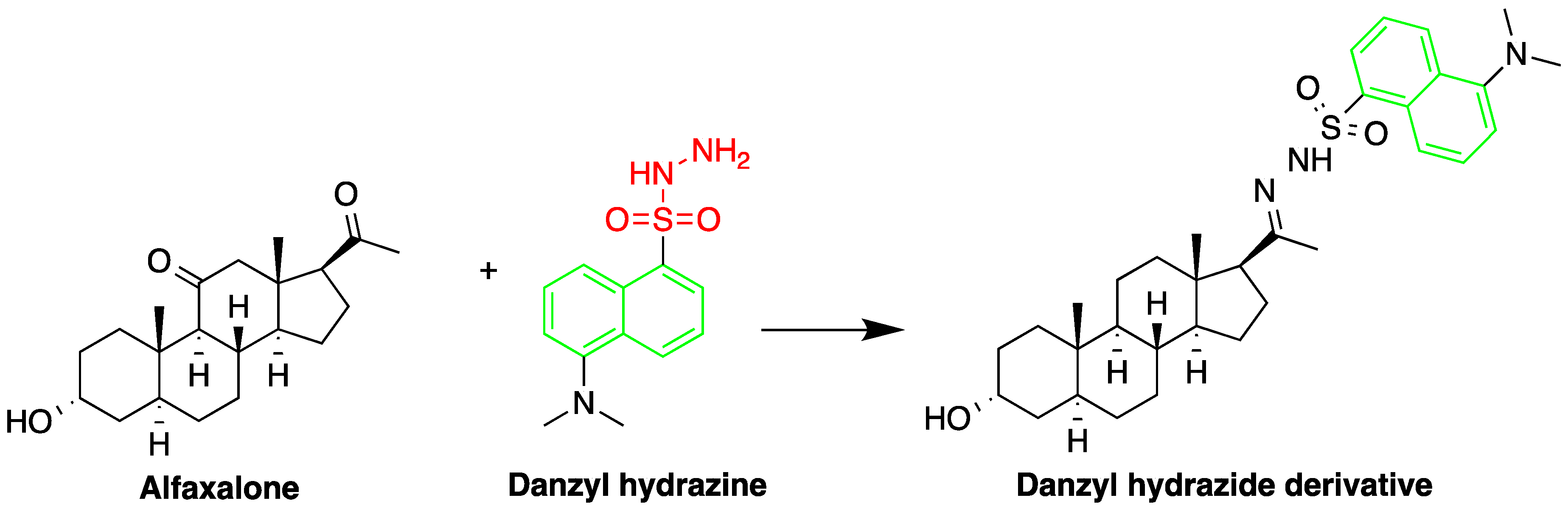
| Reagent | Target Steroid | Sample Preparation and Derivatization Conditions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
p-Nitrobenzoyl chloride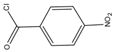 | Estrogens | Sample was extracted by SPE C18. Residue reacted with p-nitrobenzoyl chloride at 25 °C, 30 min | Mao et al. 2004 [42] |
1-Anthroyl nitrile (1-AN)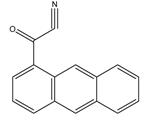 | 18-Oxygenated corticosteroids, 18-hydroxycortisol, 18-hydroxycortisone and 18-oxocortisol, Pregnenolone and C21 steroids; especially corticoids | Sample was extracted by SPE or LLE with a mixture of diethyl ether and dichloromethane. Extract reacted with 1-anthroyl nitrile in acetonitrile at room temperature for 10 min. | Kurosawa et al. 1995 [43] Shimada et al. 1996 [27] Shimada et al. 1991 [44] |
9-Anthroyl nitrile (9-AN) 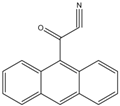 | Glucocorticoids; F and E, Hydroxysteroids Corticosteroids | Sample was extracted by LLE or SPE. Extracts reacted with 9-AN in a mixture of quinuclidine and triethylamine for 30 min at RT. | Glowka et al. 2009 [45] Goto et al. 1983 [46] Shibata et al. 1997 [47] Haegele et al. 1991 [48] Kosicka et al. 2018 [49] Neufeld et al. 1998 [50] Shimada et al. 1991 [44] |
2-(11H-Benzo[a]carbazole-11-yl) ethyl carbonochloridate (BCEC-Cl)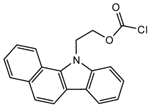 | E1, E2, E3, BPA, NP, OP | Sample was extracted by DLLME. Extracts were added to BCEC-Cl in a NaHCO3 buffer at pH 10; it was shaken for 10 s, and then allowed to stand for 14 min at 43 °C. | Wu et al. 2015 [29] |
| 9-Phenanthrene boronic acid 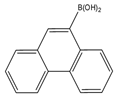 | Brassinosteroids | Sample was extracted by LLE. Extracts reacted with 9-phenanthrene-boronic acid in a mixture of pyridine and acetonitrile for 10 min at 70 °C. | Gamoh and Takatsuto. 1989 [51] |
| 10-Ethyl-acridone- 2-sulfonyl chloride (EASC) 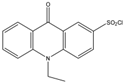 | Estrogens and Biogenic Amines (aliphatic amines) | Sample was extracted by LLE or SPE. Extracts reacted with EASC in anhydrous acetonitrile and NaHCO3 buffer pH (10.2), for 5 min at 60 °C. | Zhang et al. 2012 [52] |
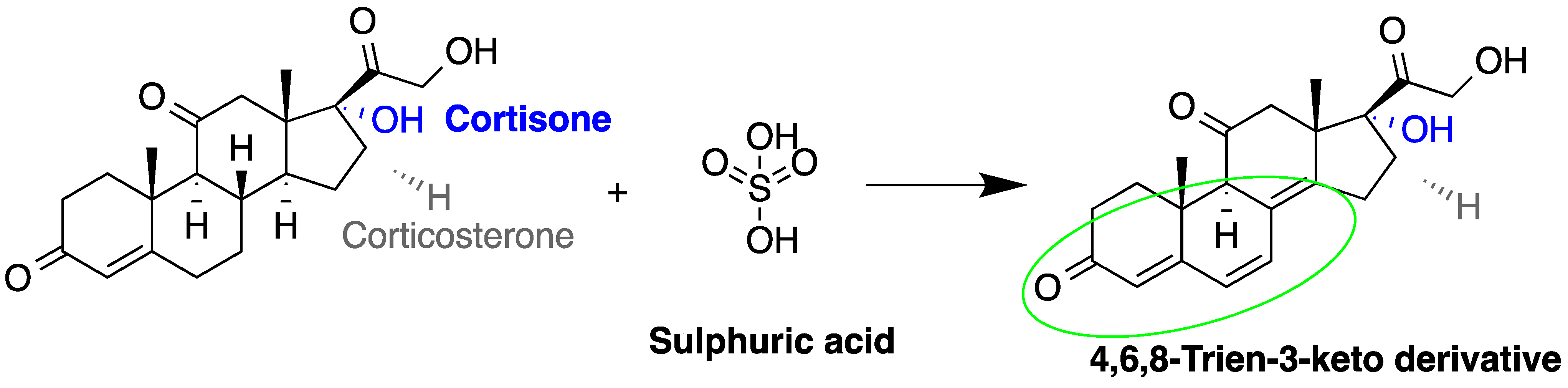
Sulfuric acid |
F and Corticosterone | Sample was extracted by SPE or LLE. Extracts reacted with sulfuric acid in ethanol; it was cooled in crushed ice for 15 min in the dark. | Nozaki et al. 1991 [53] Nozaki et al. 1992 [54] Sudo et al. 1990 [55]Gao et al. 2010 [56] |
7-Methoxycoumarin-3-carbonyl azide (MC-CON3)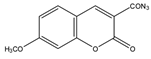 | 7α-hydroxycholesterol | Sample was extracted by LLE and purified by normal-phase SPE. Extracts reacted with MC-CON3 in ethyl acetate for 40 min at 140 °C. | Saisho et al. 1998 [57] |
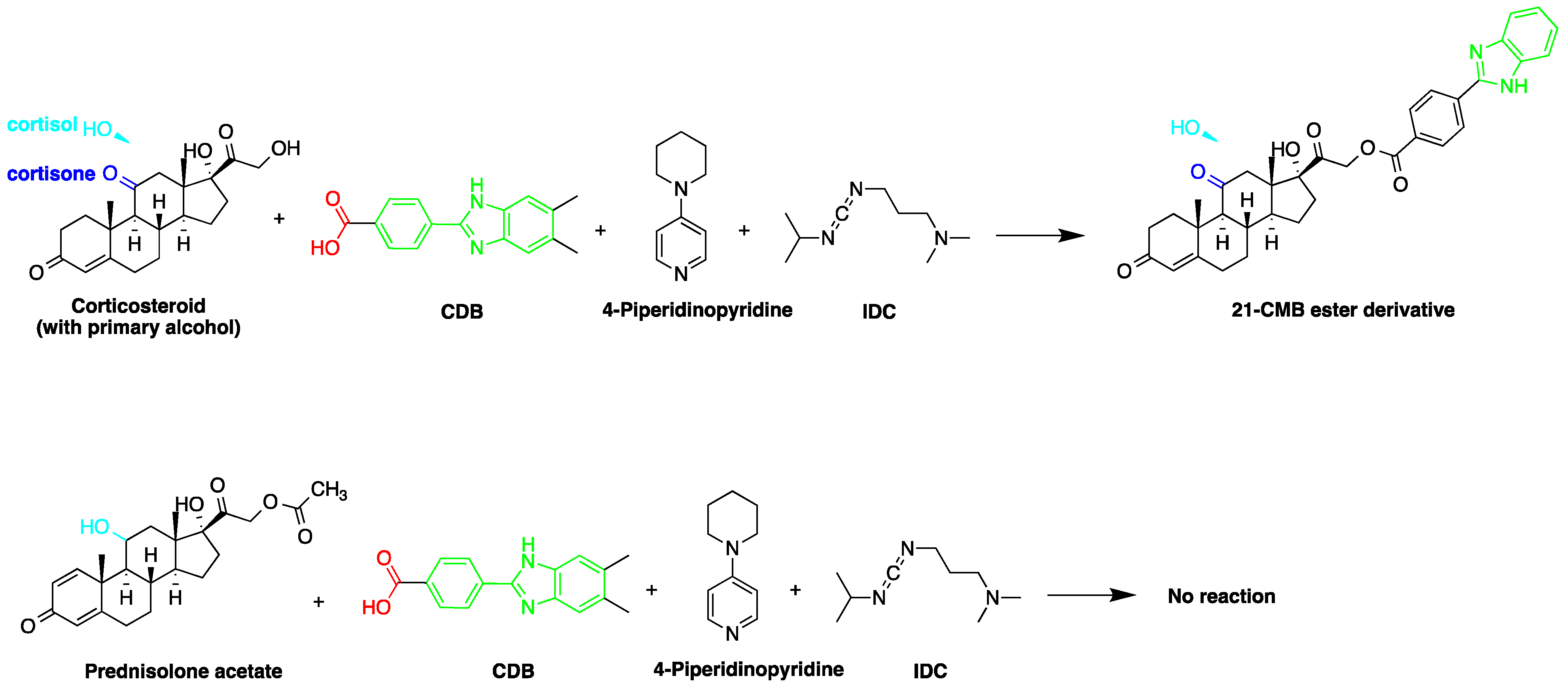
2-(4-Carboxyphenyl)-5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole(CDB) 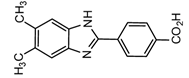 | Corticosteroids, BPA and alkylphenols | Sample was extracted by LLE. 0.02% w/v CDB solution, 2.0% w/v 1-isopropyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide perchlorate (IDC) solution, and 0.01% w/v (10 mg/mL) 4-piperidinopyridine, for 60 min at 40 °C. | Katayama et al. 1991 [58] Katayama et al. 1992 [58] Katayama et al. 2001 [59] |
Benzamidine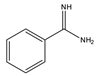 | 17-hydroxycorticosteroids | Sample was extracted by LLE. Extracts reacted with benzamidine in a basic medium of sodium hydroxide solution, with a mixture of propanol and water for 5 min at 95 °C. | Seki et al. 1984 [60] |
| 4-(4,5-Diphenyl-1H- imidazol-2-yl) benzoyl chloride (DIB-Cl) 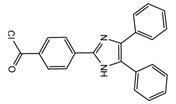 | BPA | Sample was extracted by LLE or SPE. Extracts reacted with DIB-Cl in a mixture of acetonitrile and triethylamine for 20 min at RT. | Sun et al. 2004 [61] Kuroda et al. 2003 [62] Sun et al. 2002 [63] |
4-(4,5-Diphenyl-1H-imidazol-2-yl) iodobenzene (DIB-I)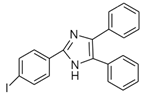 | EE | Sample was extracted by the SPE disc method (C18 SPE disk). A total of 50 μL of the extracts reacted with 50 μL of DIB-I (3.0 mM), in a mixture of 50 μL of solution containing 0.2 mM of PdCl2 and 0.3 mM of CuI, and 50 μL of DIPEA (3.0 mM). The vial contents were deoxygenated by N2 purge for 10 sec, heated at 100 °C for 40 min, cooled, then filtered through a 0.45-μm membrane filter before injection into the HPLC-FLD system. | Ali et al. 2020 [64] |
1,2-Diamino-4,5-methylenedioxybenzene (DMB)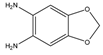 | α-Dicarbonyl compounds; prednisolone, PN and 21-hydroxycorticosteroids | Sample was extracted by LLE. Extracts reacted with DMB for 40 min at 60 °C. | Yamaguchi et al. 1991 [65] Yoshitake et al. 1989 [66] Yamaguchi et al. 1989 [67] |
2-(4-Carboxyphenyl)-5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole (BODIPY FL hydrazide) 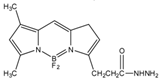 | Aldehydes and ketones; progesterone, 17-hydroxyprogesterone, and other 3-keto steroids. | Sample was extracted by LLE. Extracts reacted with BODIPY FL hydrazide in ethanol for 15 h at RT. | Katayama et al. 1998 [68] |
Dansyl hydrazine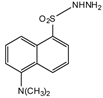 | F, Butane acid-(5-androsten-17-one-3beta-ol)-diester (A1998)[69], alfaxalone and pregnanolone [70] | Sample was extracted by LLE. Extracts reacted with dansyl hydrazine in organic solvent for 30 min at RT in acidic medium. | Kawasaki et al. 1979 [71] Visser et al. 2000 [69] Peng et al. 2007 [70] |
Naproxen acyl chloride in toluene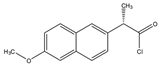 | Cholesterol and sitosterol | Sample was extracted by LLE. Extracts reacted with naproxen acyl chloride in toluene, while shaking for 1.5 h at 90 °C. Diethylamine in toluene was then added to inactivate the excess naproxen acyl chloride, while shaking for 5 min at 30 °C. | Lin et al. 2007 [38] |
Dansylaminophenylboronic acid | Brassinolide and castasterone | Sample was extracted by LLE. Extracts reacted with dansylaminophenylboronic acid in a mixture of pyridine and acetonitrile for 20 min at 70 °C. | Motegi et al. 1994 [72] |
9-Fluorenylmethyl chloroformate (Fmoc-Cl)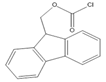 | E1, E2, E3, BPA, NP, OP | Samples were extracted by MSPE. Extracts were reacted with Fmoc-Cl in NaHCO3 (pH = 10.5) at 60 °C for 10 min, and then added to a mixture of aqueous acetic acid and acetonitrile. The mixture was cooled to RT. | Qianyu Li et al. 2018 [73] |
| 2-(11H-Benzo[a]carbazole-11-yl)- ethyl-4-methylbenzenesulfonate (BCETS)  | FFA | The samples were extracted by supercritical CO2 and organic solvent extraction. The extracted samples were derivatized in BCETS in a solution of K2CO3 at 84 °C; then the mixture was cooled down to RT and diluted with DMF. | Li et al. 2011 [74] |
Benzimidazo[2, 1-b]quinazoline-12(6H)-one-5-ethylimidazole ester (BQEIC)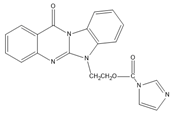 | OP, NP, TBP, BPA, E1, E2, E3 | The samples were extracted by LLE. BQEIC in a solvent of DMAP at 80 °C for 60 min. Finally, the mixture was cooled to RT and diluted with acetonitrile. | Liu et al. 2018 [75] |
| Detected Steroids | Sample Type | Column Chemistry | Mobile Phase (v/v) | Derivatization Agent | Excitation (λex) and Emission Wavelengths (λem) (nm) | Extraction Method | LOD | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PL and PN | Human plasma | C18 | MeOH:ACN:1.0 M ammonium acetate (38:25:45) | DMB | 350, 390 | LLE | 3 ng/mL | Yamaguchi et al. 1991 [65] |
| F and E | Biological samples | Keystone Hypersil | H2O:MeOH:ACN (50:33.3:16.7) | 9-AN | 305–395, 430–470 | SPE | F: 50 pg E: 70 pg | Haegele et al. 1991 [48] |
| F | Human serum | C18 | 1: 10 mM potassium biphthalate 2: ACN Tetrahydrofuran: 19 mM potassium biphthalate (40:6:54) Both adjusted to pH 1.85 with trifluoroacetic acid | Sulfuric acid-ethanol | 365, 520 | - | 0.30 pg/dL | Nozaki et al. 1991 [53] |
| F | Human urine | C18 | Gradient of ACN: 36.4 mmol/L phosphate (45:55; pH 1.85 with trifluoroacetic acid) | Sulfuric acid-ethanol | 365, 520 | SPE | 0.26 pg/dL | Nozaki et al. 1992 [54] |
| 7α-Hydroxycholesterol | Dog plasma | Develosil Ph-5 | Acetonitrile: Water (5:2) | 1-AN | 338, 411 | LLE | 4 pg | Saisho et al. 1998 [57] |
| Corticosteroids | Urine | Silica | 2-Propanol–hexane | 9-AN | 370, 470 | Enzyme hydrolysis, extraction with 0.5 M NaOH | NR | Neufeld et al. 1998 [50] |
| F and E | Human plasma | C18 | ACN: 0.3 mM ortho-phosphoric acid (470:530) | 9-AN | 360, 460 | SPE | 3.0 ng/mL | Glowka et al. 2009 [45] |
| Corticosterone | Rat urine | CN | ACN: H2O (24.5:75.5) | post-column reaction with sulfuric acid | 460, 510 | LLE | 0.5 pmol | Sudo et al. 1990 [55] |
| F | Human hair | C18 | MeOH:H2O 60:40 | sulfuric acid | 360, 480 | LLE | 1 pg/mg | Gao et al. 2010 [56] |
| EE2, E2, and BPA | Human urine and aqueous samples | C18 | ACN:MeOH:H2O (30:15:55) | - | 280, 310 | FPSE | E2: 20 pg/mL EE2: 36 pg/mL BPA: 42 pg/mL | Kumar et al. 2014 [81] |
| BPA, NP, E2, EE2, and E3 | Human urine | C18 | Gradient elution of ACN and H2O | p-nitrobenzoyl chloride | E2, E3: 282, 315 BPA, NP, EE2: 228, 316 | SPE | BPA and E2: 2.7 μg/L NP: 2.9 μg/L E2 and EE2: 4.6 μg/L E3: 8.3 μg/L | Mao et al. 2004 [42] |
| E, testosterone, methyltestosterone, bolasterone, testosterone acetate, progesterone | Urine | C18 | 0.01 M Tb(NO3)3, 0.1 M sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), and 20% acetonitrile | - | 245, 547 | SPE | Down to 100 pg/mL | Amin et al. 1993 [26] |
| BPA and 8 alkylphenols (4-sec-Butylphenol, 2-tert-Butylphenol, 3-tert-butylphenol, 4-tert-butylphenol, 4-n-Pentylphenol, 4-tert-pentylphenol, 4-n-hexylphenol, and 4-n-heptylphenol) | Rat plasma and blood | C18 | MeOH:Water (10:90) | 2-(4-carboxyphenyl)-5,6- dimethylbenzimidazole | Derivatized: 336, 440 Native: 275, 315 | LLE | BPA: 0.1 pg/mL Alkylphenol: 0.7–10 pg/mL | Katayama et al. 2001 [59] |
| progesterone and 17-hydroxyprogesterone dehydroepiandrosterone, androstenedione, testosterone and 17-methyltestosterone | Serum from pregnant and non-pregnant women | Wakosil 5C4 | Acetonitrile:Water (7:3) | BODIPY FL hydrazide | 495, 516 | LLE | 550–3700 fmol per 10 μL | Katayama et al. 1998 [68] |
| aldosterone, corticosterone, F, E, dexamethasone, fluocinolone acetonide, triamcinolone and triamcinolone acetonide | Human plasma | C18 | Water:MeOH (25:75) containing 5 mmol/L tetramethylammonium hydrogen sulphate | CDB | 334, 418 | LLE | 0.06–0.3 pg per 100 μL | Katayama et al. 1992 [58] |
| BPA | Breast Milk | C18 | 1: ACN:H2O:MeOH (72:13:15) 2: ACN:0.1 M acetate buffer (pH 5.5):MeOH (55:12:33) | DIB-Cl | 350, 475 | SPE then LLE | 0.11 ng/mL | Sun et al. 2004 [61] |
| BPA | Human blood serum and ascitic fluid samples | C18 | 1: ACN: H2O:MeOH (72:13:15) 2: ACN:0.1 M Acetate buffer (pH 5.5):MeOH (55:12:33) | DIB-Cl | 350, 475 | LLE | 0.04 ppb | Kuroda et al. 2003 [62] |
| BPA | Rat brain rat plasma | C18 | 1: ACN: H2O:MeOH:Tetrahydrofuran (55:10:35:2.5) 2: ACN:0.1 M Acetate buffer (pH 3.0):MeOH (35:10:55) | DIB-Cl | 350, 475 | LLE | 0.3 ppb in 60 μL rat brain 4.6 ppb in 50 μL rat plasma | Sun et al. 2002 [63] |
| F, E, PL, PN, 6β-OHF, 6β-OHP and 6β-OHE | Human plasma and urine | Cosmosil 5SL | diethylene dioxide: ethyl acetate:chloroform:n-hexane:pyridine (500:100:100:1400:21) | 9-AN | 360, 460 | LLE | F, E, PL and PN: 0.1 ng/mL 6β-OHF and 6β-OHP: 0.5 ng/mL | Shibata et al. 1997 [47] |
| Corticosterone | Rat serum | C18 | 60% MeOH: 40% 5 mM triethylamine, pH 3.3 | - | 375, 485 | LLE | 0.1 ng | Mason et al. 1992 [77] |
| 18-Oxygenated corticosteroids, 18-hydroxycortisol, 18- hydroxycortisone and 18-oxocortisol | Human urine | μBondasphere phenyl | A: 10 mM ammonium acetate: MeOH (50:50) B: ACN | 1-AN | 370, 470 | LLE and SPE | 0.1 pmol | Kurosawa et al. 1995 [43] |
| Cholesterol and sitosterol | Saliva and urine biosamples, Cow milk, and Soybean milk | C8 | MeOH:isopropanol:H2O (90:5:5) | naproxen acyl chloride | 231, 352 | LLE | 25 nM per 10 μL injected volume | Lin et al. 2007 [79] |
| Pregnenolone | Rat brain | C18 | MeOH:H2O (9:1) | 1-AN | 370, 470 | SPE | NR | Shimada et al. 1996 [27] |
| C21 steroids; corticoids | Steroid standards | C18 | MeOH:H2O:cyclodextrin | 1-AN | 360, 460 | NR | NR | Shimada et al. 1991 [44] |
| Triamcinolone | Human plasma | C18 | ACN and 0.3 mM ortho-phosphoric acid | 9-AN | 360, 460 | SPE | 1 ng/mL | Glowka et al. 2006 [88] |
| Butane acid-(5-androsten-17-one-3beta-ol)-diester (A1998) | Rat plasma | C18 | 25 mM acetate buffer (pH 3.7):ACN Alfaxalone: (45:55) Pregnanolone: (40:60) | Dansyl hydrazine | 332, 516 | LLE | 10 ng/mL | Visser et al. 2000 [69] |
| Alfaxalone and pregnanolone | Rat plasma | C18 | Gradient mixture of ACN and H2O | Dansyl Hydrazine | 350, 520 | - | 0.025 μg/mL | Peng et al. 2007 [70] |
| EED | Oral contraceptive tablets | STAR RP-18e | ACN:H2O (47:53) | - | EED: 285, 310 | - | EED: 0.0538 μg/ml | Sarafinovska et al. 2006 [12] |
| EED and drospirenone | Oral contraceptive tablets | STAR RP-18e RP | ACN:H2O (47:53) | - | 285, 310 | - | EED: 0.00065 μg/mL DROSP: 0.0774 μg/mL | Sarafinovska et al. 2009 [13] |
| EED | Coated tablets | LiChroCART 100RP | ACN:H2O (50:50) | - | 280, 310 | - | EED: 0.02 μg/mL | Silva et al. 2013 [89] |
| Sodium E1 sulphate, sodium equilin sulphate, E1 and equilin |
Raw materials and Pharmaceuticals | 5 ODS2 | TEA phosphate buffer (pH 4.0; 0.05 M):ACN 1— (70:30, v:v) 2—for unconjugated estrogens: (66:34) | Postcolumn on line photochemical derivatization | 280, 410 or 312 | - | 0.01–1.38 pmol | Gatti et al. 1998 [90] |
| E1, 17β-Estradiol, E3, BPA, NP, OP | Fish, chicken, aquaculture pond water sample | C18 | Gradient program of 1: H2O: 5% ACN 2: H2O: ACN | BCEC-Cl | 279, 380 | DLLME | 0.02–0.07 µg/L | Wu et al. 2015 [29] |
| E1, E2, and E3 | Cow and river Buffalo | C18 | 1: ACN:H2O:Formic Acid (40:60:0.4) 2: ACN:H2O:Formic Acid (90:10:0.4) | - | 280, 310 | LLE and SPE | 5–10 ng/kg | Shahbazi et al. 2016 [31] |
| α- and β-Trenbolone | Bovine muscle and liver | C18 | MeOH:H2O (60:40) | - | 364, 460 | LLE then SPE | bovine muscle: 0.2 ng/g liver: 1.0 ng/g | Yoshioka et al. 2000 [33] |
| NP, 4-nonylphenol mono-(NP1EO), diethoxylates (NP2EO), BPA, TBP, and OP | Fish and shellfish | Inertsil PH | Gradient program of A: H2O B: MeOH | - | 275, 300 | LLE | NP NP1EO and NP2EO : 2 ng/g BPA, BP and OP: 1 ng/g | Tsuda et al. 2000 [32] |
| Nonylphenol and its ethoxylates | Fish tissue | Hypersil APS | Hexane:ethanol (98:2) | - | 230, 300 | Pressurized fluid extraction | 4–15 ng/mL | Datta et al. 2002 [28] |
| E2 and EE2 | Poultry litter | C18 | Gradient program of A: H2O B: ACN | - | 280, 312 | LLE | E2: 4.0 μg/kg EE2: 2.6 μg/kg | Lu et al. 2014 [91] |
| E2 and EE2 | Waste Water | C18 | Gradient program of A: H2O B: ACN | - | 282, 306 | SPE | 2.5 ng/L | Liz et al. 2017 [17] |
| E3, E2, EE2, HEX, mestranol | Water, sediment | Poroshell 120 EC | H2O:ACN 50:50 | - | 275, 310 | SPE | Water: 6–24 ng/L Sediment: 0.1–0.9 ng/g | Perez et al. 2015 [92] |
| E2, 17α-EE2, and E1 | Water | C18 | Gradient program of A: ACN B: H2O acidified at pH 3.6 with glacial acetic acid | - | 230, 302 | SPE | 10 to 1100 ng/L | Patrolecco et al. 2013 [93] |
| OP, NP, BPA, diethylstilbestrol, E1, EE2, E2, and E3 | Wastewater samples | C18 | Gradient program of A: 5% ACN B: ACN | EASC | 262, 430 | SPE | 0.3–0.7 ng/L | Zhang et al. 2012 [52] |
| E2 and EE2 | Tap, surface and waste water | C18 | Water:acetonitrile mixture (50:50) | - | 280, 310 | DLLME | E2: 2.0 ng/L EE2: 6.5 ng/L | Lima et al. 2013 [37] |
| BPA, 17β-estradiol, and 17α-ethynyl estradiol | Drinking water | LiChro-sorbs RP18 | 10 mM H3PO4:55% MeOH (45:55) | - | 280, 310 | PAC | BPA: 201 ng/L E2: 313 ng/L EE2: 284.5 ng/L | Yoon et al. 2003 [94] |
| 17α- and 17β-Trenbolone | River water | C18 | Gradient program of MeOH:H2O | - | 359, 458 | SPE | 4 ng/L | Durhan et al. 2005 [95] |
| NP, OP, NP polyethoxylates | municipal wastewater treatment plants | C18 | Gradient program of H2O:ACN | - | 229, 310 | LLE | OP: 2 ng/L NP: 11 ng/L NPE: 52 ng/L | Snyder et al. 1999 [5] |
| E2, E3, BPA, and 17β-ethinylestradiol | environmental waters | C18 | ACN:0.02 mol/L phosphate solution (45:55) | - | 227, 315 | Synthesized in-tube SPME device | 0.006–0.10 ng/mL | Wen et al. 2006 [96] |
| E2, E3, EE2, 3-methyl ether EE2, NP, OP, POE(1-2) nonyl phenol and BPA | River water | C18 | Gradient program of Milli-Q H2O and ACN | - | 230, 290 | on-line SPE | 20–50 ng/L | Ying et al. 2002 [97] |
| Endocrine disruptors; BPA and EE2 | Environmental water samples | C18 | MeOH:0.025 mol/L Na2HPO4 buffer (70:30) | - | 220, 315 | A poly(acrylamide-vinylpyridine) monolithic capillary column | BPA: 0.064 ng/mL 17α-ethinylestradiol: 0.12 ng/mL | Fan et al. 2005 [98] |
| Brassinosteroids | Plant: (Vicia faba L.) | C18 | ACN: H2O (90:10) | 9-Phenanthreneboronic acid | 305, 375 | LLE | 50 pg | Gamoh et al. 1989 [51] |
| Brassinolide | Arabidopsis thaliana, Daucus carota and Brassica campestris L. leaves’ samples | C18 | Gradient program of A: H2O and ACN B: ACN and 0.1% Formic Acid | - | 305, 375 | UA-DLLME | 8.0 ng/L | Lv et al. 2014 [99] |
| Brassinolide and castasterone | Pollen of orange (Citrus sinensis Osbeck) | C18 | ACN:H2O (80:20) | Dansylaminophenylboronic acid | 345, 515 | LLE | NR | Motegi et al. 1994 [72] |
| Norgestrel, norethindrone, EE2, gestodene, and norethisterone acetate | Meat samples | Hypersil GOLD | Gradient program of (A) H2O containing 5% ACN (B)ACN | Fmoc-Cl | 250, 395 | MSPE | 1.4 × 103–8.7 × 103 | Qianyu Li et al. 2018 [73] |
| F and E | Human urine samples | C18 | ACN:0.3 mM orthophosphoric acid (470: 530) | 9-AN | 360, 460 | LLE | LLOQ: F: 27.6 nmol/L E: 27.7 nmol/L | Kosicka et al. 2018 [49] |
| FFA | Edible oils and foodstuff | C8 | Gradient system: A: H2O B: ACN/DMF (1:1) C: ACN (100%) | BCETS | 279, 380 | Supercritical CO2 and organic solvent extraction | 0.22–1.06 ng/mL | Li et al. 2011 [74] |
| OP, NP, TBP, BPA, E1, E2, E3 | Milk samples | C18 | Gradient program of A:5% ACN in H2O B: ACN | BQEIC | 302, 401 | LLE | 10.5–13.8 ng/L | Liu et al. 2018 [75] |
| E3, 2-OHE2, 17β-E2, 17α-E2, EE2, HEX | Dairy products | C18 | Gradient Flow A: 1 mM formic acid in ACN B: 1 mM formic acid at pH 3.50 | - | 280, 310/320 | HF-LPME | 0.23–14.8 μg/kg | Bárbara Socas-Rodríguez et al. 2014 [36] |
| Zearalenone | Edible oil | C18 | Gradient program of A: H2O, B: ACN | 274, 456 | SPE | 10 μg/kg | Drzymala et al. 2015 [100] | |
| EE2, E1, E2, E3, and progesterone | Drinking water and wastewater samples | C18 | Gradient program of A: H2O/CH3CN 90/10 v/v B: CH3CN | 200, 315 | SPE | Drinking water: 1–3.8 ng/L Sewage water: 3.8–7.5 ng/L | Kozłowska-Tylingo et al. 2015 [20] | |
| E3, E2, E1 | Human urine | C18 | Gradient program of A: H2O, B: ACN | 280, 310 | VA-DLLME-FOA | E3: 0.01 ng/mL β-E2: 0.01 ng/mL E1: 0.06 ng/mL | Wang et al. 2015 [82] | |
| 17-α-E2, 17-β-E2 benzoate and quinestrol | Environmental water samples | Zorbax Eclipse SB-C18 | Gradient program of A: ACN, B: H2O | 265, 311 | IF-IHLME | 17-α-Estradiol: 0.04 ng/mL E2 and Quinestrol: 0.05 ng/mL | Zhang et al. 2017 [101] | |
| E2 and EE2 | Tap water samples | Pursuit 5 C18 column | ACN:H2O (50:50), with 200 μL of H3PO4 | 230, 306 | Nanoparticles of graphene oxide/γ-Fe2O3 as a sorbent for SPE | E2: 2.7 ng/L EE2: 0.8 ng/L | Fernanda Nunes Ferreira et al. 2020 [102] | |
| 17-E2 and E3 | Water samples | C18 | H2O:MeOH:ACN (50:30:20) | 280, 310 | ultrasonication assisted DLLME | DLLME-HPLC/FLD: 7.16–69.22 ng/L | Zhang et al. 2020 [14] | |
| E2, 1,3,5(10)-Estratriene-3,17β-diol | Fish and prawn tissue samples | ODS C18 | H2O:MeOH (30:70) | 280,310 | MISPE | 0.023 mg/L | Jiang et al. 2009 [40] | |
| BPA, EE2, 4-t- OP, 4-OP, and 4-NP | River water | C18 | Gradient program of A: ACN B: H2O | 277, 307 | Disposable pipette extraction (DPX) | BPA, EE2, 4-OP and 4-NP: 0.30 μg/L 4-t-OP: 0.60 μg/L | Gabriela Corazza et al. 2017 [103] | |
| E1 and EE2 | Digested sludge | C18-PFP | A: H2O B: ACN E1: (50:50) EE2 (55:45) | 280, 310 | ultrasonic liquid extraction | E1: 0.305 μg/g EE2: 0.052 μg/g | Vitória L. Louros et al. 2019 [104] | |
| E2 | Milk sample | XDB-C18 | MeOH:H2O (70:30) | 280, 310 | SPE | 0.7 ng/mL | Yanan Yuan et al. 2019 [105] | |
| Nine BPs | milk samples | C18 | Gradient program of 0.1% formic acid: ACN | 230, 305 | ultrasonically with acetonitrile and cleaned using the QuEChERS technique. | 1.0–3.1 µg/kg | Xiong et al. 2017 [38] | |
| EE | river water samples | 5C18 MS-II | ACN: 5.0 mM Tris-HNO3 buffer, pH 7.4 (60:40) | 310, 400 | C18 SPE disk | 7.4 ng/L | Ali et al. 2020 [64] | |
| E3, 17β-estradiol glucuronide, 17β-E2, 17α-E2, 17β-E2-3-methyl ether | wastewater | UPLC C18 | Gradient program of water with 0.1% of ammonia: ACN | 280, 310 | Molecularly Imprinted SPE | 1.4 to 2.5 ng/mL | Rayco Guedes-Alonso et al. 2015 [41] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hameedat, F.; Hawamdeh, S.; Alnabulsi, S.; Zayed, A. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with Fluorescence Detection for Quantification of Steroids in Clinical, Pharmaceutical, and Environmental Samples: A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061807
Hameedat F, Hawamdeh S, Alnabulsi S, Zayed A. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with Fluorescence Detection for Quantification of Steroids in Clinical, Pharmaceutical, and Environmental Samples: A Review. Molecules. 2022; 27(6):1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061807
Chicago/Turabian StyleHameedat, Fatima, Sahar Hawamdeh, Soraya Alnabulsi, and Aref Zayed. 2022. "High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with Fluorescence Detection for Quantification of Steroids in Clinical, Pharmaceutical, and Environmental Samples: A Review" Molecules 27, no. 6: 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061807
APA StyleHameedat, F., Hawamdeh, S., Alnabulsi, S., & Zayed, A. (2022). High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) with Fluorescence Detection for Quantification of Steroids in Clinical, Pharmaceutical, and Environmental Samples: A Review. Molecules, 27(6), 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061807