Mimic Nature Using Chemotaxis of Ionic Liquid Microdroplets for Drug Delivery Purposes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Ionic Liquids
2.1. Composition and Properties of ILs
2.2. Classification of ILs
2.3. ILs as Promising Alternatives to Traditional Solvents
2.4. Cytotoxicity of ILs
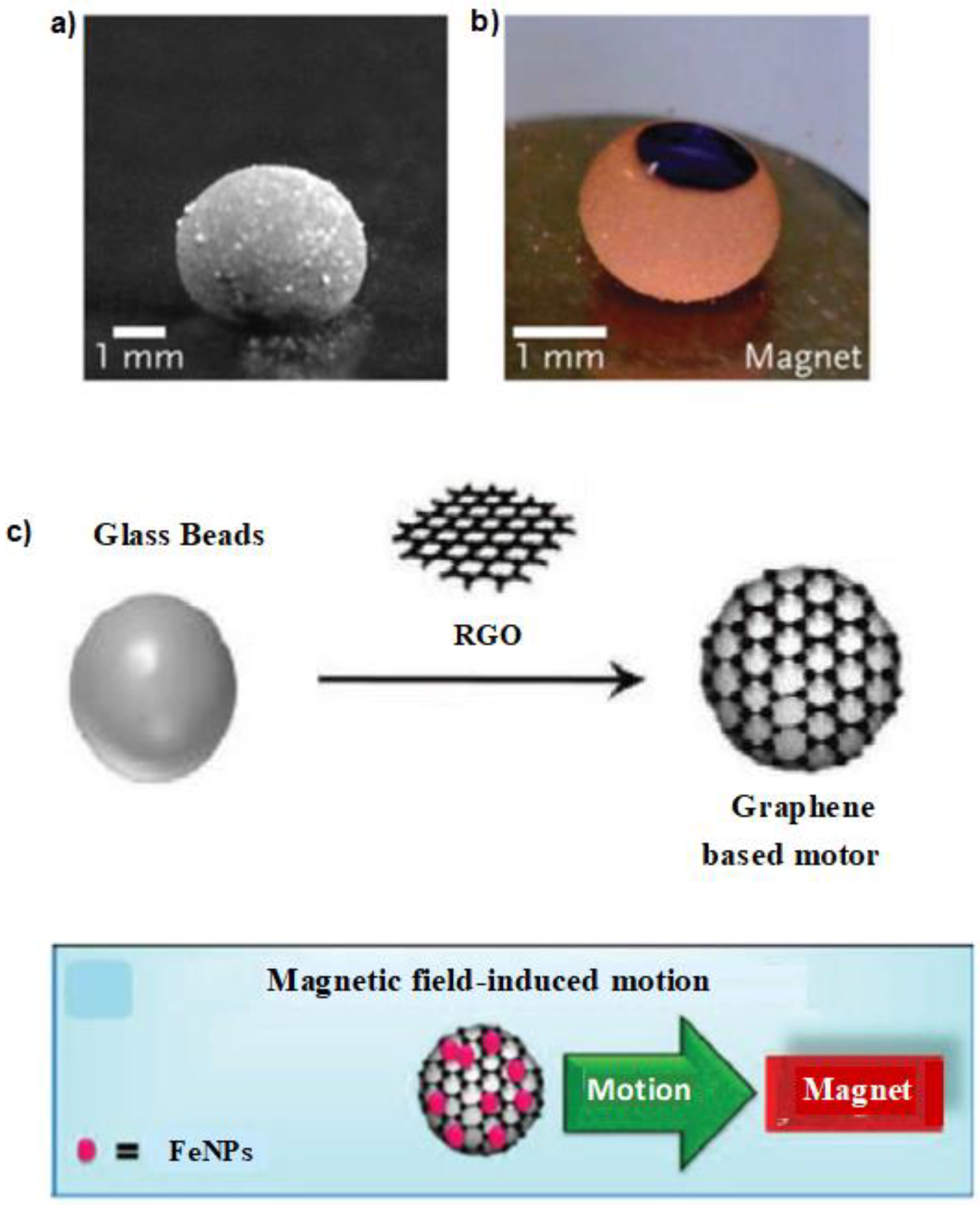
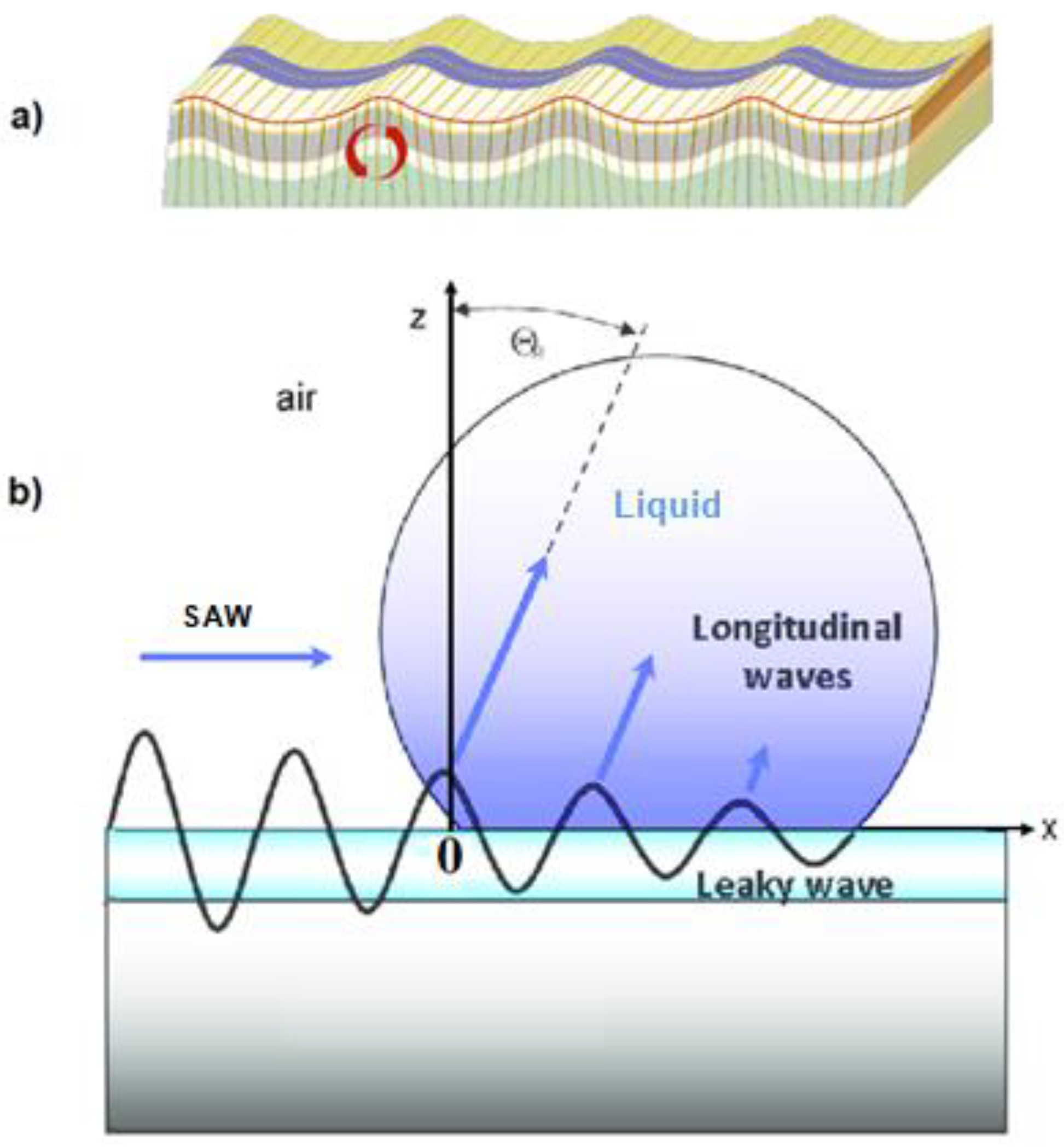
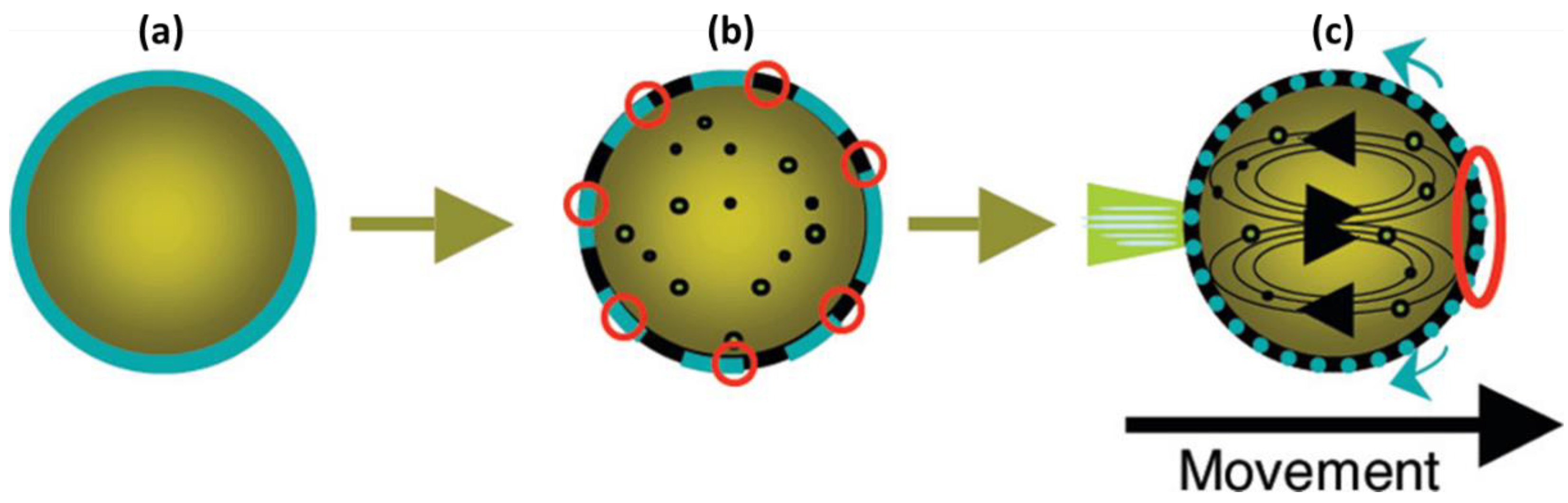
3. Self-Propelled Microdroplets
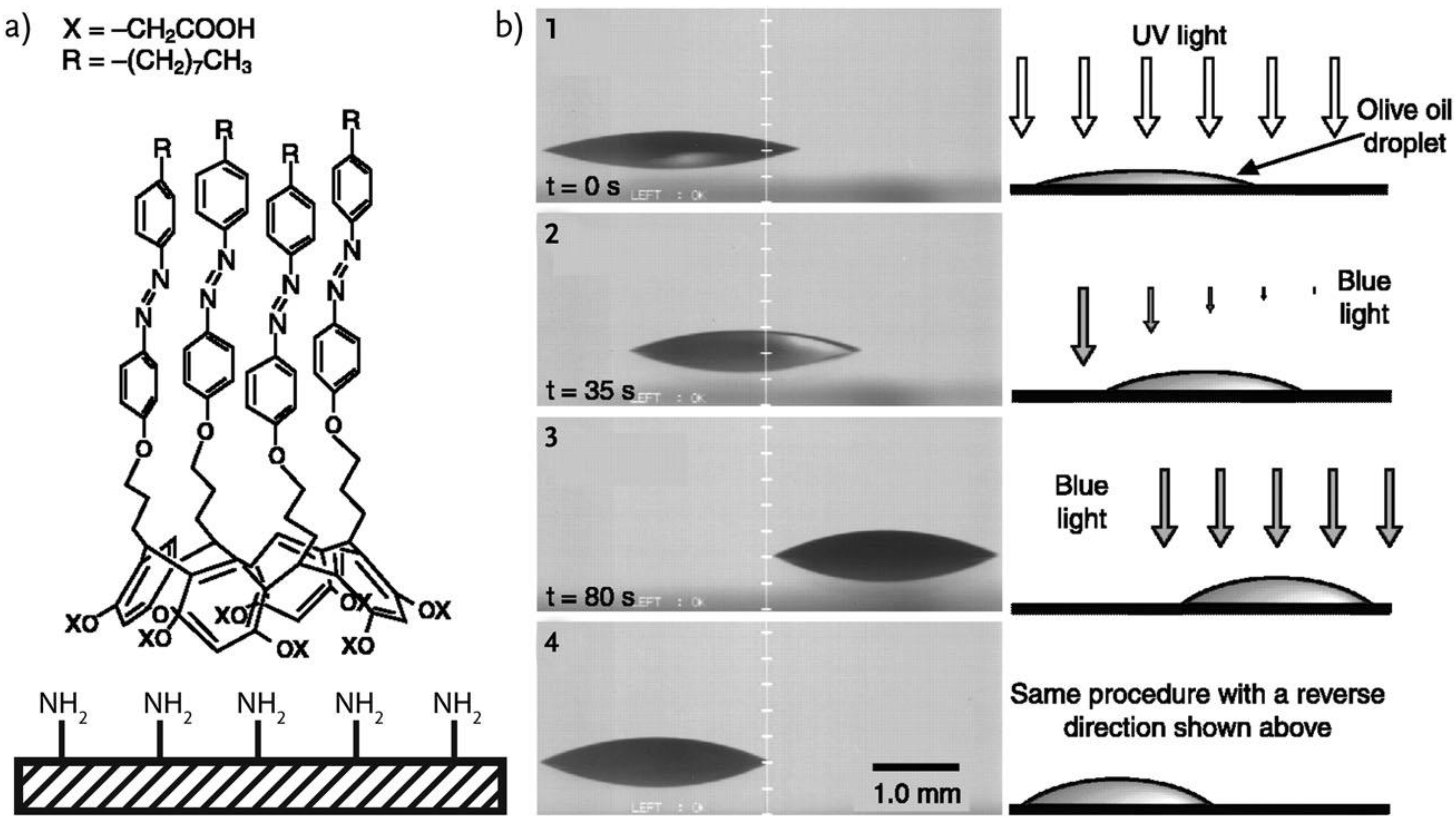
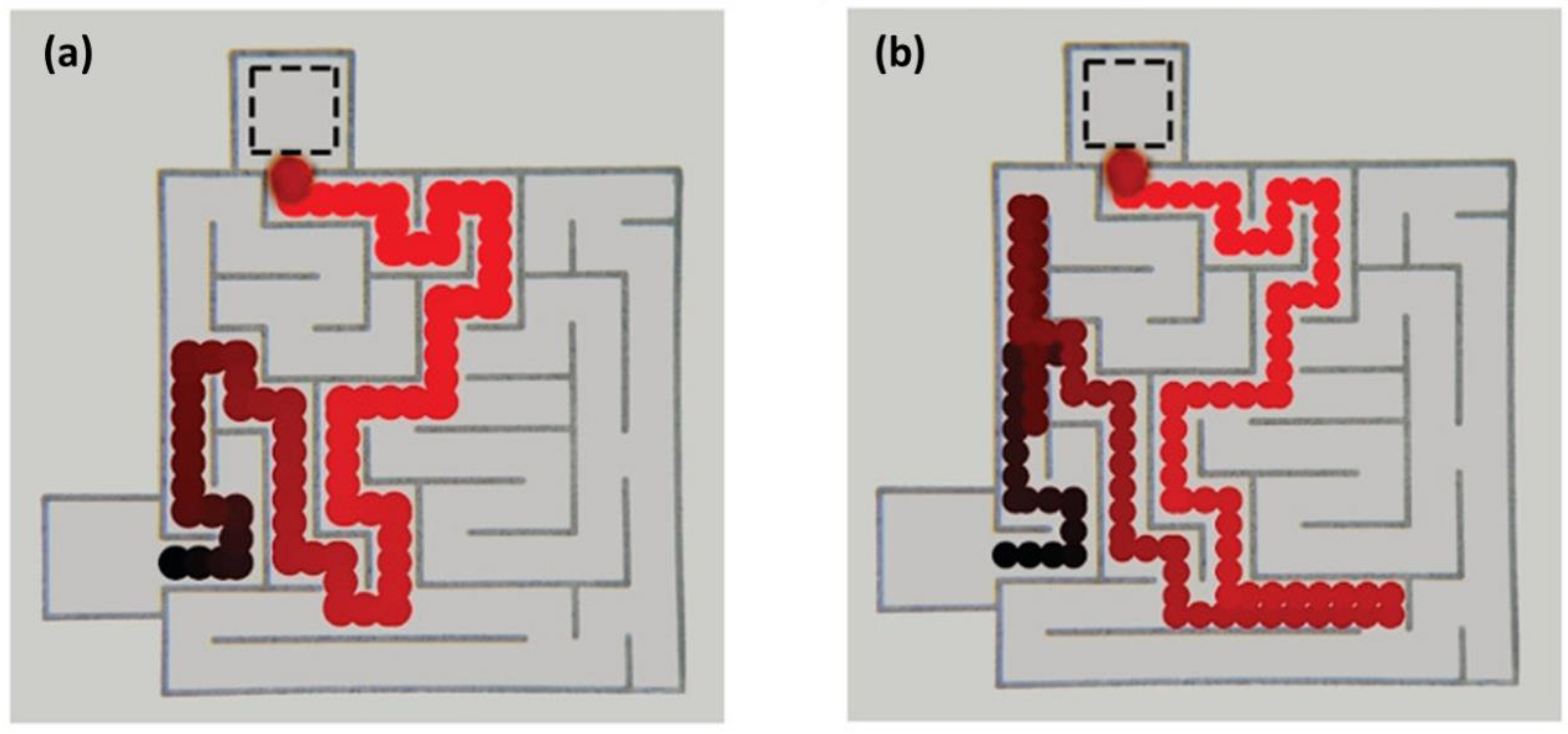
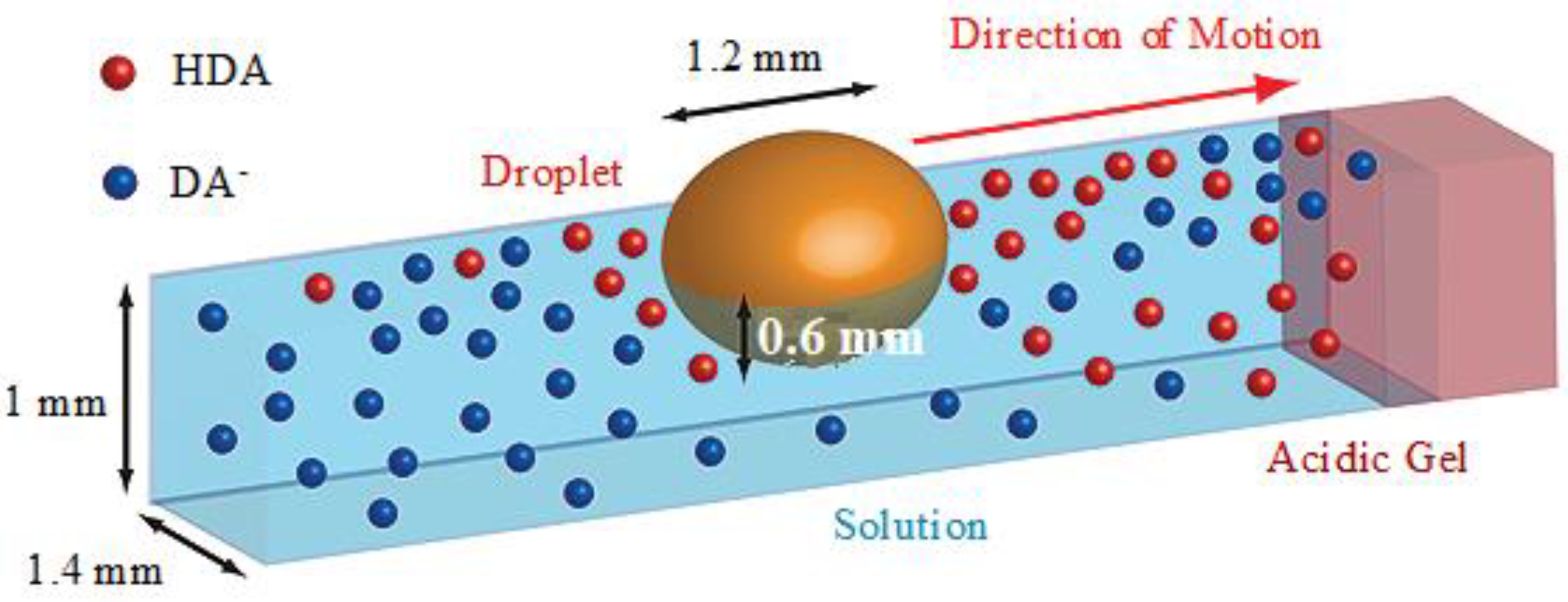
4. IL-Based Chemotaxis
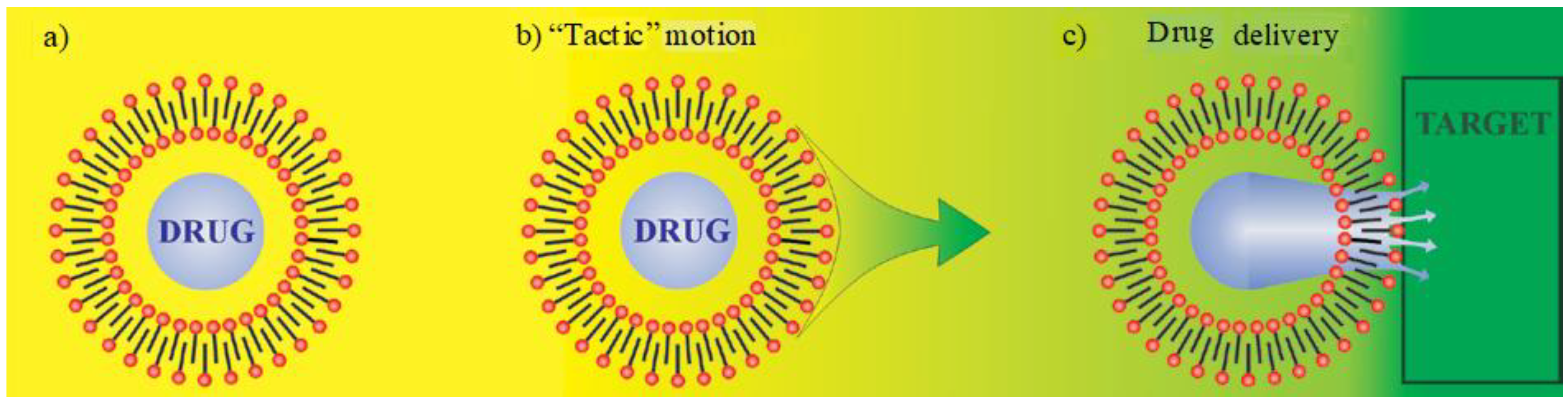
5. Smart Drug Delivery Using ILs
6. Conclusions and Future Trends
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adler, J. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Science 1966, 153, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Haastert, P.J.M.; Devreotes, P.N. Chemotaxis: Signalling the way forward. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spehr, M.; Gisselmann, G.; Poplawski, A.; Riffell Jeffrey, A.; Wetzel Christian, H.; Zimmer Richard, K.; Hatt, H. Identification of a testicular odorant receptor mediating human sperm chemotaxis. Science 2003, 299, 2054–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funamoto, S.; Meili, R.; Lee, S.; Parry, L.; Firtel, R.A. Spatial and temporal regulation of 3-phosphoinositides by PI 3-kinase and PTEN mediates chemotaxis. Cell 2002, 109, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li Jeon, N.; Baskaran, H.; Dertinger, S.K.W.; Whitesides, G.M.; Van De Water, L.; Toner, M. Neutrophil chemotaxis in linear and complex gradients of interleukin-8 formed in a microfabricated device. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Feng, L.; Park, H.-T.; Havlioglu, N.; Wen, L.; Tang, H.; Bacon, K.B.; Jiang, Z.-h.; Zhang, X.-c.; Rao, Y. The neuronal repellent Slit inhibits leukocyte chemotaxis induced by chemotactic factors. Nature 2001, 410, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury Manoj, K.; Whitesides George, M. How to make water run uphill. Science 1992, 256, 1539–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.D.; Dhiman, R.; Anand, S.; Reza-Garduno, E.; Cohen, R.E.; McKinley, G.H.; Varanasi, K.K. Droplet mobility on lubricant-impregnated surfaces. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 1772–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Kim, C.-J.C. All-electronic droplet generation on-chip with real-time feedback control for EWOD digital microfluidics. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, A.R.; Moon, H.; Bird, C.A.; Ogorzalek Loo, R.R.; Kim, C.-J.; Loo, J.A.; Garrell, R.L. Digital microfluidics with in-line sample purification for proteomics analyses with MALDI-MS. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Butts, C.P.; Eastoe, J. Stimuli-responsive surfactants. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 2365–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darhuber, A.A.; Valentino, J.P.; Troian, S.M.; Wagner, S. Thermocapillary actuation of droplets on chemically patterned surfaces by programmable microheater arrays. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2003, 12, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wixforth, A.; Strobl, C.; Gauer, C.; Toegl, A.; Scriba, J.; Guttenberg, Z.V. Acoustic manipulation of small droplets. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 379, 982–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Fang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Magnetic liquid marbles: Manipulation of liquid droplets using highly hydrophobic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, H.-S.; Kumar, A.; Wereley, S.T. Open optoelectrowetting droplet actuation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 064104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, M.G. Drops, liquid layers and the Marangoni effect. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 1998, 356, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roché, M.; Li, Z.; Griffiths, I.M.; Le Roux, S.; Cantat, I.; Saint-Jalmes, A.; Stone, H.A. Marangoni flow of soluble amphiphiles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 208302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diguet, A.; Guillermic, R.-M.; Magome, N.; Saint-Jalmes, A.; Chen, Y.; Yoshikawa, K.; Baigl, D. Photomanipulation of a droplet by the chromocapillary effect. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 9281–9284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florea, L.; Wagner, K.; Wagner, P.; Wallace, G.G.; Benito-Lopez, F.; Officer, D.L.; Diamond, D. Photo-chemopropulsion-light-stimulated movement of microdroplets. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7339–7345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagzi, I.; Soh, S.; Wesson, P.J.; Browne, K.P.; Grzybowski, B.A. Maze solving by chemotactic droplets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1198–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovic, M.; Seddon, K.R.; Rebelo, L.P.N.; Silva Pereira, C. Ionic liquids: A pathway to environmental acceptability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1383–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seddon, K.R. Ionic liquids for clean technology. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1997, 68, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, R.; Branco, L.C.; Prudêncio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Z. Ionic liquids as active pharmaceutical ingredients. ChemMedChem 2011, 6, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, H.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Ionic liquid solutions as extractive solvents for value-added compounds from biomass. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4786–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawała, J.; Dawidziuk, B.; Dziedzic, D.; Gordon, D.; Popiel, S. Applications of ionic liquids in analytical chemistry with a particular emphasis on their use in solid-phase microextraction. TrAC Trend Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G.; Cláudio, A.F.M.; Araújo, J.M.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Marrucho, I.M.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Rebelo, L.P.N. Aqueous biphasic systems: A boost brought about by using ionic liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4966–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Barber, P.S.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic liquids in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bica, K.; Shamshina, J.; Hough, W.L.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Rogers, R.D. Liquid forms of pharmaceutical co-crystals: Exploring the boundaries of salt formation. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2267–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, S. Room temperature ionic liquids: Different classes and physical properties. Curr. Org. Chem. 2005, 9, 959–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh; Sandhu, J.S. Recent advances in ionic liquids: Green unconventional solvents of this century: Part I. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2011, 4, 289–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, A.; Abdul Mutalib, M.; Leveque, J. A review on dicationic ionic liquids: Classification and application. Ind. Eng. Manag. 2016, 5, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Hal, R.V.; Bösmann, A. 1-n-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium ([bmim]) octylsulfate-an even ‘greener’ ionic liquid. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.-T.; Yang, Z.; Chen, C.-J. Room temperature ionic liquid as a novel medium for liquid/liquid extraction of metal ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 488, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradkar, R.P.; Williams, R.R. Micellar colorimetric determination of dithizone metal chelates. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 2752–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, A.E.; Swatloski, R.P.; Reichert, W.M.; Mayton, R.; Sheff, S.; Wierzbicki, A.; Davis, J.J.H.; Rogers, R.D. Task-specific ionic liquids for the extraction of metal ions from aqueous solutions. Chem. Commun. 2001, 1, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, P.; Marchand, G.; Fouillet, Y.; Berthier, J.; Douki, T.; Hassine, F.; Gmouh, S.; Vaultier, M. Ionic liquid droplet as e-microreactor. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4909–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Ragauskas, A.J. Ionic liquid as a green solvent for lignin. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2007, 27, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Li, M.; Zhao, L.; Lu, C.; de Rooy, S.L.; Warner, I.M. Highly efficient extraction of phenolic compounds by use of magnetic room temperature ionic liquids for environmental remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Lu, Y.; Hu, R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, Y. Application of ionic liquids based microwave-assisted extraction of three alkaloids N-nornuciferine, O-nornuciferine, and nuciferine from lotus leaf. Talanta 2010, 80, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Chu, K.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Chen, R.; Chen, L. Ionic liquid-based microwave-assisted extraction of flavonoids from Bauhinia championii (Benth.) Benth. Molecules 2012, 17, 14323–14335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Wang, Y.; Kong, J.; Nie, C.; Yuan, Y. Ionic liquid-based microwave-assisted extraction of rutin from Chinese medicinal plants. Talanta 2010, 83, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.A.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; MacFarlane, D.R. Distillable ionic liquid extraction of tannins from plant materials. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usuki, T.; Yasuda, N.; Yoshizawa-Fujita, M.; Rikukawa, M. Extraction and isolation of shikimic acid from Ginkgo biloba leaves utilizing an ionic liquid that dissolves cellulose. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10560–10562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhang, R.; Ren, R.; Li, N.; Zhang, H. Determination of the active constituents in Arnebia euchroma (Royle) Johnst. by ionic liquid-based ultrasonic-assisted extraction high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 1833–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; Kamiya, N.; Goto, M. Ionic liquid based microemulsion with pharmaceutically accepted components: Formulation and potential applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 352, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperato, G.; König, B.; Chiappe, C. Ionic green solvents from renewable resources. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 2007, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidiš, A.; Ohlin, C.A.; Laurenczy, G.; Küsters, E.; Sedelmeier, G.; Dyson, P.J. Rationalisation of solvent effects in the Diels-Alder reaction between cyclopentadiene and methyl acrylate in room temperature ionic liquids. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2005, 347, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, S.; Pegot, B.; Coleman, D.; Garcia, M.T.; Ferguson, D.; Quilty, B.; Gathergood, N. Biodegradable, non-bactericidal oxygen-functionalised imidazolium esters: A step towards ‘greener’ ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afouna, M.I.; Mehta, S.C.; Ghanem, A.-H.; Higuchi, W.I.; Kern, E.R.; De Clercq, E.; El-Shattawy, H.H. Assessment of correlation between skin target site free drug concentration and the in vivo topical antiviral efficacy in hairless mice for (E)-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2′-deoxyuridine and acyclovir formulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Penetration enhancers. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alade, S.L.; Brown, R.E.; Paquet, A., Jr. Polysorbate 80 and E-Ferol Toxicity. Pediatrics 1986, 77, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolte, S.; Matzke, M.; Arning, J.; Böschen, A.; Pitner, W.-R.; Welz-Biermann, U.; Jastorff, B.; Ranke, J. Effects of different head groups and functionalised side chains on the aquatic toxicity of ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorvee, J.R.; Derfus, A.M.; Bhatia, S.N.; Sailor, M.J. Manipulation of liquid droplets using amphiphilic, magnetic one-dimensional photonic crystal chaperones. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormashenko, E.; Pogreb, R.; Bormashenko, Y.; Musin, A.; Stein, T. New investigations on ferrofluidics: Ferrofluidic marbles and magnetic-field-driven drops on superhydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 2008, 24, 12119–12122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, K.; Oh, S.-K.; Nakagawa, M. Light-driven motion of liquids on a photoresponsive surface. Science 2000, 288, 1624–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, F.A.; Kettunen, M.I.; Day, S.E.; Hu, D.-E.; Ardenkjær-Larsen, J.H.; Zandt, R.i.t.; Jensen, P.R.; Karlsson, M.; Golman, K.; Lerche, M.H.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of pH in vivo using hyperpolarized 13C-labelled bicarbonate. Nature 2008, 453, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.T.; Hines, J.R.; Gordon, D. Intracellular hyperthermia a biophysical approach to cancer treatment via intracellular temperature and biophysical alterations. Med. Hypotheses 1979, 5, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, T.; Oosawa, H.; Sakai, M.; Syundou, Y.; Ban, T.; Shioi, A. Autonomous motion of vesicle via ion exchange. Langmuir 2010, 26, 1610–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanczyc, M.M.; Toyota, T.; Ikegami, T.; Packard, N.; Sugawara, T. Fatty acid chemistry at the oil–water interface: Self-propelled oil droplets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9386–9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyota, T.; Maru, N.; Hanczyc, M.M.; Ikegami, T.; Sugawara, T. Self-propelled oil droplets consuming “fuel” surfactant. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5012–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagzi, I. Chemical robotics-chemotactic drug carriers. Cent. Eur. J. Med. 2013, 8, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rösler, A.; Vandermeulen, G.W.M.; Klok, H.-A. Advanced drug delivery devices via self-assembly of amphiphilic block copolymers. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudimack, J.; Lee, R.J. Targeted drug delivery via the folate receptor. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2000, 41, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostak, J.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Luisi, P.L. Synthesizing life. Nature 2001, 409, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, W.; Fay, C.; Florea, L.; Diamond, D. Self-propelled chemotactic ionic liquid droplets. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2342–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, W.; Wagner, K.; Beirne, S.; Officer, D.L.; Wallace, G.G.; Florea, L.; Diamond, D. Electrotactic ionic liquid droplets. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrn, S.; Pfeiffer, R.; Ganey, M.; Hoiberg, C.; Poochikian, G. Pharmaceutical solids: A strategic approach to regulatory considerations. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giron, D.; Mutz, M.; Garnier, S. Solid-state of pharmaceutical compounds. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2004, 77, 709–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, K.S.; Gordeev, E.G.; Ananikov, V.P. Biological activity of ionic liquids and their application in pharmaceutics and medicine. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 7132–7189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastoe, J.; Gold, S.; Rogers, S.E.; Paul, A.; Welton, T.; Heenan, R.K.; Grillo, I. Ionic liquid-in-oil microemulsions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 7302–7303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, S.; Wakabayashi, R.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Kamiya, N.; Goto, M. Ionic liquid-mediated transcutaneous protein delivery with solid-in-oil nanodispersions. MedChemComm 2015, 6, 2124–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; Tamura, M.; Tahara, Y.; Kamiya, N.; Goto, M. Ionic liquid-in-oil microemulsion as a potential carrier of sparingly soluble drug: Characterization and cytotoxicity evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 400, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goindi, S.; Arora, P.; Kumar, N.; Puri, A. Development of novel ionic liquid-based microemulsion formulation for dermal delivery of 5-fluorouracil. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazylińska, U.; Kulbacka, J.; Wilk, K.A. Dicephalic ionic surfactants in fabrication of biocompatible nanoemulsions: Factors influencing droplet size and stability. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. 2014, 460, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Ghosh, S.; Banerjee, C.; Kuchlyan, J.; Banik, D.; Sarkar, N. A novel ionic liquid-in-oil microemulsion composed of biologically acceptable components: An excitation wavelength dependent fluorescence resonance energy transfer study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 3221–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mat Hadzir, N.; Basri, M.; Abdul Rahman, M.B.; Salleh, A.B.; Raja Abdul Rahman, R.N.Z.; Basri, H. Phase behaviour and formation of fatty acid esters nanoemulsions containing piroxicam. AAPS PharmSciTech 2013, 14, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mason, T.G.; Wilking, J.N.; Meleson, K.; Chang, C.B.; Graves, S.M. Nanoemulsions: Formation, structure, and physical properties. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, R635–R666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, M.; Tang, S.Y.; Tan, K.W. Cavitation technology—A greener processing technique for the generation of pharmaceutical nanoemulsions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 2069–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhadi, S.; Javadian, H.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. The effect of Na2SO4 concentration in aqueous phase on the phase inversion temperature of lemon oil in water nano-emulsions. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, N.; Ahmad, N.; Musa, S.H.; Hashim, R.; Tadros, T.F.; Basri, M. Nanoemulsion as a topical delivery system of antipsoriatic drugs. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 6234–6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvand, K.; Ghiasvand, A.; Gupta, V.; Paull, B. Chemotaxis-based smart drug delivery of epirubicin using a 3D printed microfluidic chip. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1162, 122456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, A.; Contini, C.; Cecchin, D.; Nyberg, S.; Ruiz-Perez, L.; Gaitzsch, J.; Fullstone, G.; Tian, X.; Azizi, J.; Preston, J.; et al. Chemotactic synthetic vesicles: Design and applications in blood-brain barrier crossing. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahamat Nor, S.B.; Woi, P.M.; Ng, S.H. Characterisation of ionic liquids nanoemulsion loaded with piroxicam for drug delivery system. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 234, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Ibsen, K.; Brown, T.; Chen, R.; Agatemor, C.; Mitragotri, S. Ionic liquids for oral insulin delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holler, S.; Porcelli, C.; Ieropoulos, I.A.; Hanczyc, M.M. Transport of live cells under sterile conditions using a chemotactic droplet. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielas, R.; Mielańczyk, A.; Skonieczna, M.; Mielańczyk, Ł.; Neugebauer, D. Choline supported poly(ionic liquid) graft copolymers as novel delivery systems of anionic pharmaceuticals for anti-inflammatory and anti-coagulant therapy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielas, R.; Łukowiec, D.; Neugebauer, D. Drug delivery via anion exchange of salicylate decorating poly(meth)acrylates based on a pharmaceutical ionic liquid. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 12801–12807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Flieger, M. Ionic liquids toxicity-Benefits and threats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy Pham, T.P.; Cho, C.-W.; Yun, Y.-S. Environmental fate and toxicity of ionic liquids: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramenko, N.; Kustov, L.; Metelytsia, L.; Kovalishyn, V.; Tetko, I.; Peijnenburg, W. A review of recent advances towards the development of QSAR models for toxicity assessment of ionic liquids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitch, A.C.; Abdelghany, T.M.; Probert, P.M.; Dunn, M.P.; Meyer, S.K.; Palmer, J.M.; Cooke, M.P.; Blake, L.I.; Morse, K.; Rosenmai, A.K.; et al. The toxicity of the methylimidazolium ionic liquids, with a focus on M8OI and hepatic effects. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 111069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
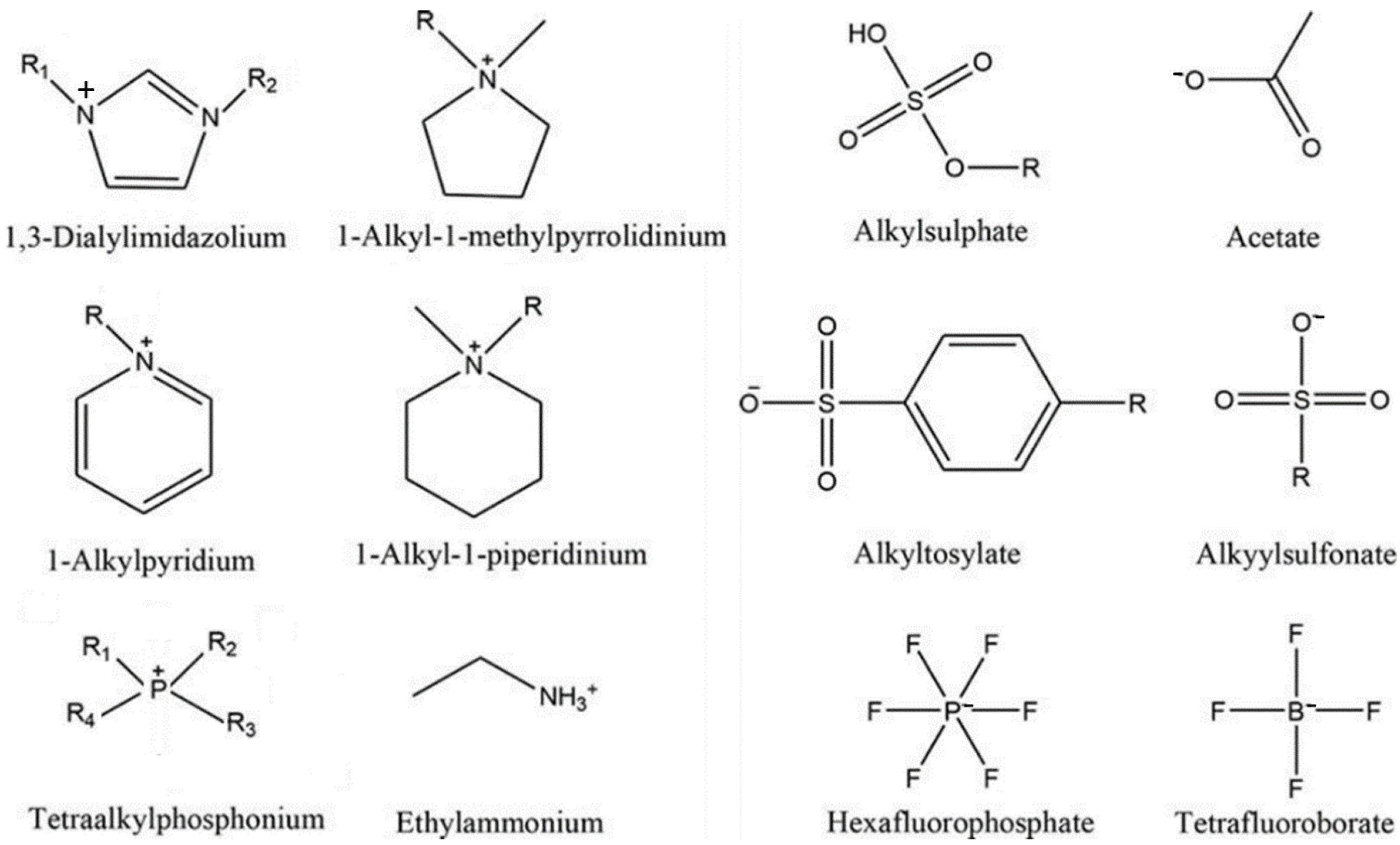
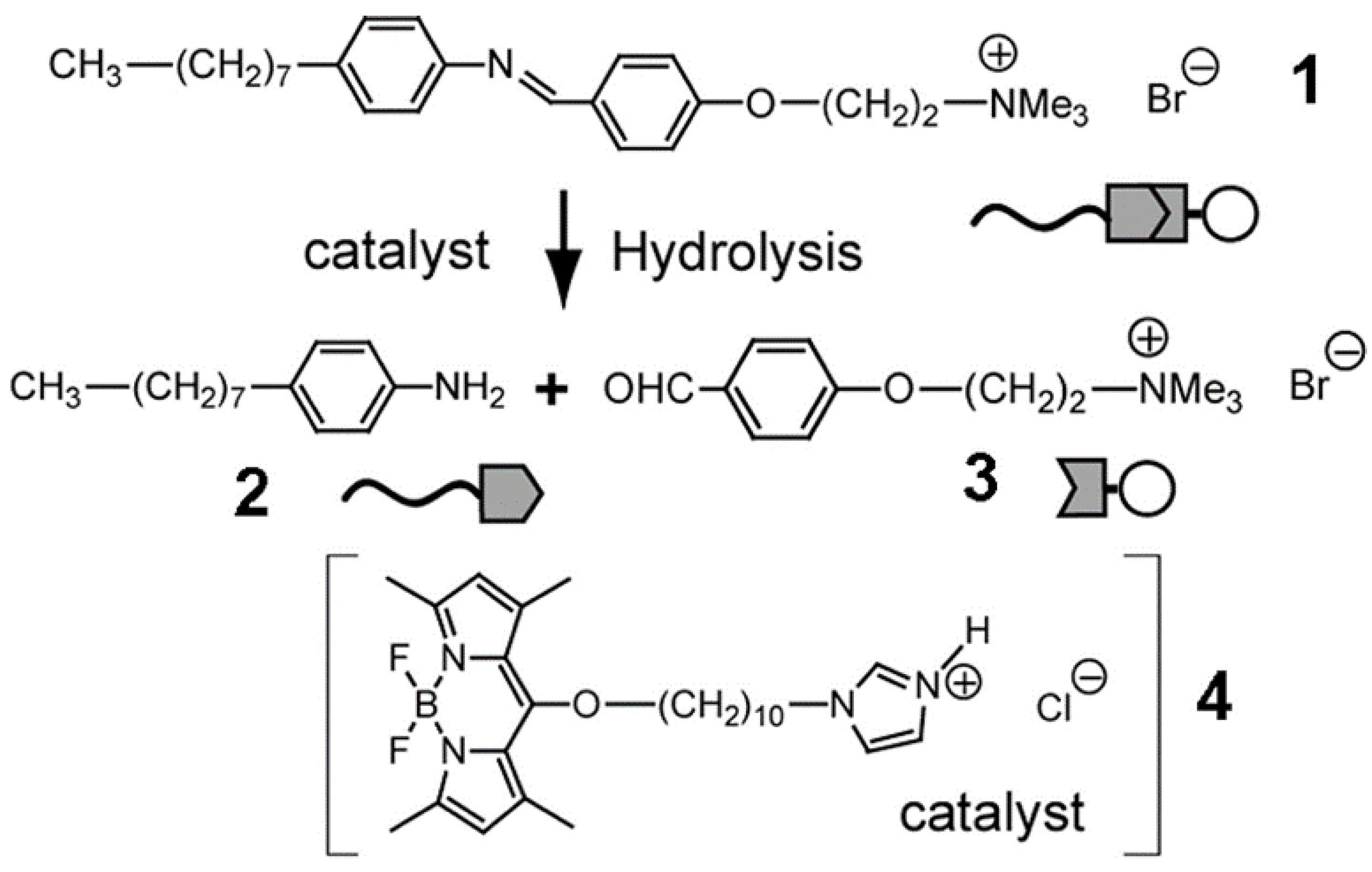
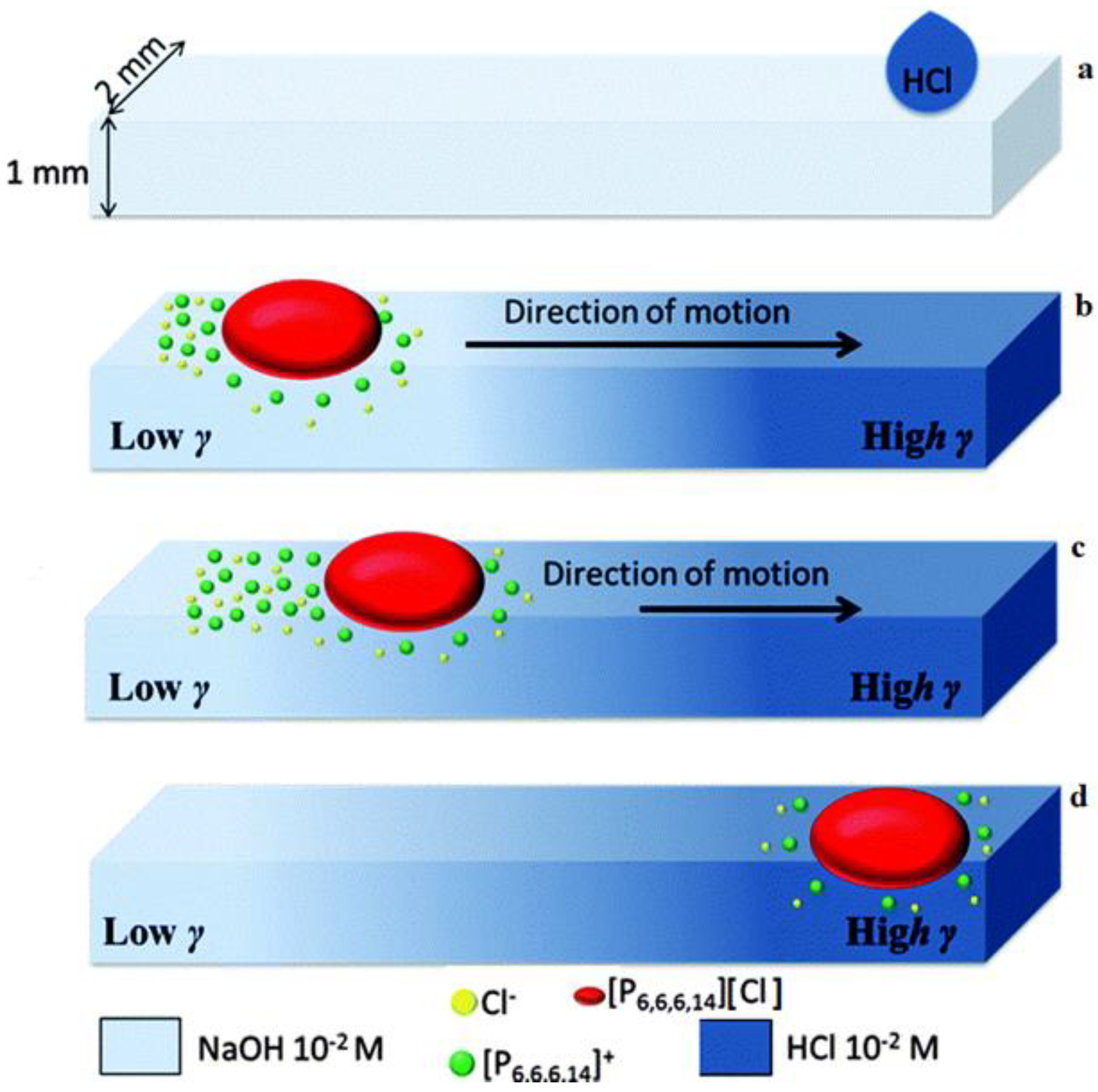
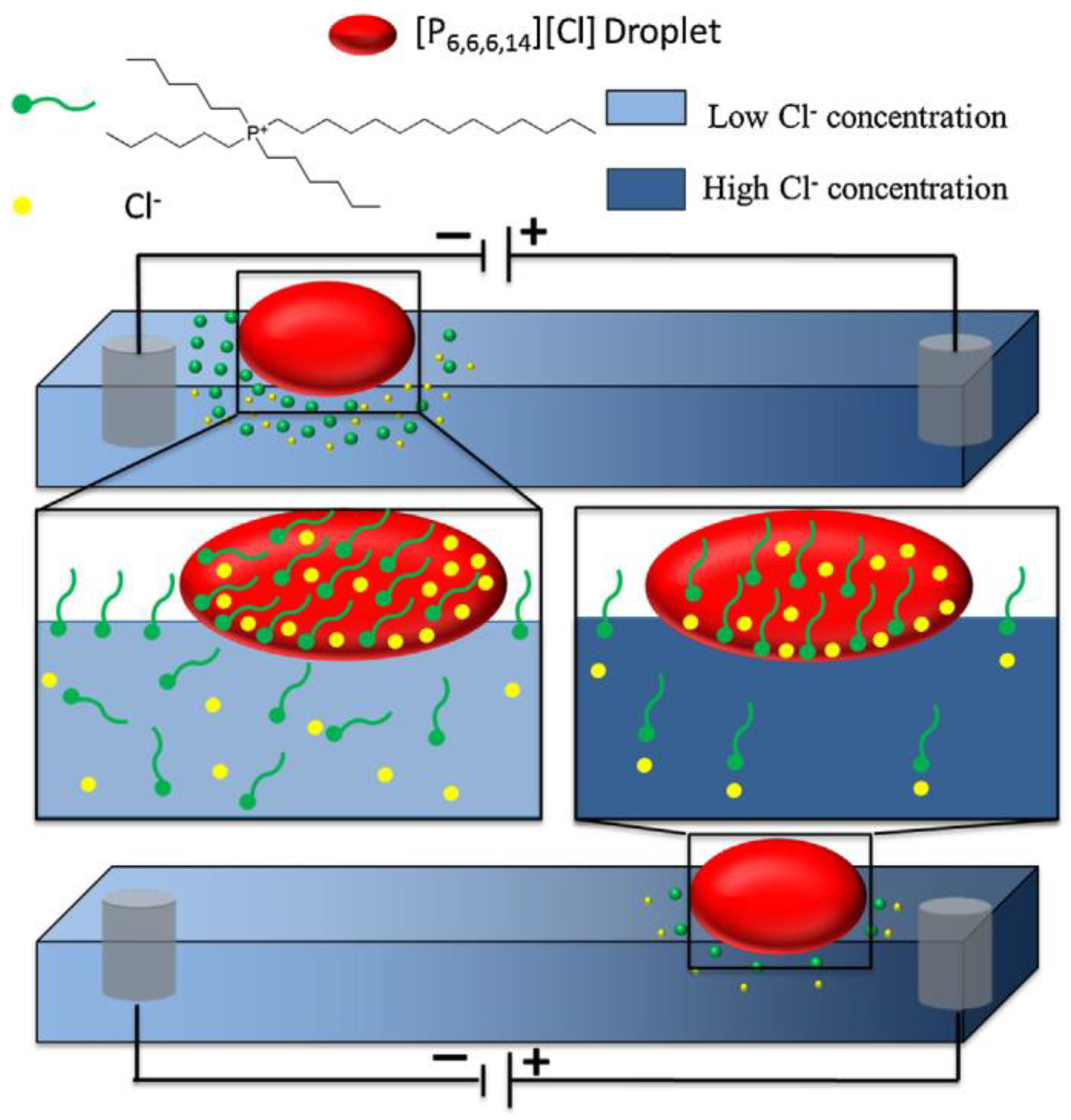
| Name | Abbreviation |
|---|---|
| triisobutyl (methyl) phosphonium tosylate | [P1,4,4,4][Tos] |
| tetrabutylphosphonium dicyanamide | [P4,4,4,4][DCA] |
| trihexyltetradecyl phosphonium dicyanamide | [P6,6,6,14][DCA] |
| trihexyltetradecyl phosphonium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide | [P6,6,6,14][Ntf2] |
| trihexyltetradecyl phosphonium dodecylbenzenesulfonate | [P6,6,6,14][DBSA] |
| trihexyltetradecyl phosphonium chloride | [P6,6,6,14][Cl] |
| 1-methyl-3-octylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate | [OMIM][BF4] |
| 1-ethyl-3-methyliidazolium methyl sulphate | [EMIM][MeSO4] |
| 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium ethyl sulfate | [EMIM][EtSO4] |
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hydrogen sulphate | [BMIM][HSO4] |
| 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium tetrafluoroborate | [EMIM][BF4] |
| 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium dicyanamide | [EMIM][DCA] |
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate | [BMIM][BF4] |
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate | [BMIM][PF6] |
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium dodecanesulfonate | [BMIM][DoS] |
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide | [BMIM][NTf2] |
| 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide | [HMIM][NTf2] |
| 1-buty1-butyl-4-methylpyridinum tetrafluoroborate | [BMPy][BF4] |
| Application | IL Name | IL Class | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Separation and extraction of heavy metal ions including Hg2+ and Cd2+ from aqueous solution into [C4mim][PF6] | 1-butyl-3 methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, [C4mim][PF6] | RTIL | [33] |
| Extraction and preconcentration of Cd2+ and Hg2+ from aqueous samples into a mixture of different TSILs and a RTIL, [C4mim][PF6] | Combinations of derivatized imidazolium cations with urea, thiourea, and thioether, mixed with 1-butyl-3 methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, [C4mim][PF6] | TSILs and RTILs | [35] |
| Synthesis of organic compounds by using ILs as electronic microreactor | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate, [bmim][BF4], and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, [bmim][PF6] | RTIL and RTIL | [36] |
| Dissolution of a softwood lignin in different ionic liquids as aprotic green solvents | 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoromethanesulfonate, [hmim][CF3SO3], 1,3-dimethylimidazolium methylsulfate, [mmim][MeSO4], and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium methylsulfate [bmim][MeSO4] | TSIL, RTIL, and RTIL | [37] |
| Removal of phenolic compounds such as pentachlorophenol by use of magnetic room-temperature ionic liquid (MRTIL) | trihexyltetradecyl phosphonium etrachloroferrate (III), [3C6PC14][FeCl4] | MRTIL | [38] |
| Extraction of three alkaloids from lotus leaf | 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide, ([C(6)MIM]Br) | TSIL | [39] |
| Extraction and determination of flavonoids from Bauhinia championii | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide, ([bmim]Br) | TSIL | [40] |
| Effective extraction of rutin from Chinese medicinal plants | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide, ([bmim]Br) | TSIL | [41] |
| Separation of tannins from plant materials | N,N-dimethylammonium N′N′-dimethylcarbamate, (DIMCARB) | TSIL | [42] |
| Extraction and isolation of shikimic acid from Ginkgo biloba leaves | 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride, ([bmim]Cl) | TSIL | [43] |
| Extraction of Shikonin and β,β’-dimethylacrylshikonin in Arnebia euchroma (Royle) Johnst | 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate, [C(6)MIM][BF4] | RTIL | [44] |
| Drug Delivery Application | Chemotactic System (IL Name) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Transdermal delivery of Acyclovir (to treat infections caused by certain types of viruses such as cold sores around the mouth) | dimethylimidazolium dimethylphosphate [C1mim][(MeO)2PO2] | [72] |
| Targeted delivery of Epirubicin (anticancer drug) | trihexyltetradecyl phosphonium chloride ([P6,6,6,14][Cl]) | [81] |
| Encapsulating of glucose oxidase alone or in combination with catalase into biocompatible nanoscopic asymmetric polymer vesicles (polymersomes), applications in blood–brain barrier crossing | asymmetric polymersomes: poly [(2-methacryloyl) ethyl phosphorylcholine]–poly[2-(diisopropylamino) ethyl methacrylate] (PMPC-PDPA) and poly[oligo (ethylene glycol) methyl methacrylate] (POEGMA-PDPA) | [82] |
| Delivery of Piroxicam (a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug), which is sparingly soluble in water | 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride [Hmim][Cl] and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate [Bmim][PF6] | [83] |
| Development of a highly effective oral insulin formulation and delivery | choline and geranate (CAGE) ionic liquid | [84] |
| Transport live cells protected in alginate capsules as a protective unit along chemical gradients | 1-decanol chemotactic droplets in an aqueous medium containing decanoate at high pH by chemical gradient in the external aqueous environment | [85] |
| Delivery of biologically active anionic pharmaceuticals for anti-inflammatory and anti-coagulant therapy | salicylate decorating poly (2-(trimethylammonium) ethyl methacrylate based on a pharmaceutical ionic liquid | [86,87] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khodarahmian, K.; Ghiasvand, A. Mimic Nature Using Chemotaxis of Ionic Liquid Microdroplets for Drug Delivery Purposes. Molecules 2022, 27, 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030786
Khodarahmian K, Ghiasvand A. Mimic Nature Using Chemotaxis of Ionic Liquid Microdroplets for Drug Delivery Purposes. Molecules. 2022; 27(3):786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030786
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhodarahmian, Kobra, and Alireza Ghiasvand. 2022. "Mimic Nature Using Chemotaxis of Ionic Liquid Microdroplets for Drug Delivery Purposes" Molecules 27, no. 3: 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030786
APA StyleKhodarahmian, K., & Ghiasvand, A. (2022). Mimic Nature Using Chemotaxis of Ionic Liquid Microdroplets for Drug Delivery Purposes. Molecules, 27(3), 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030786







