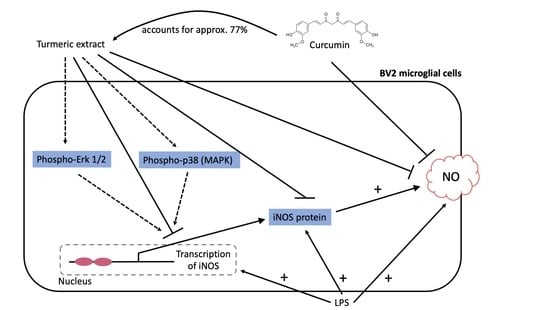
Turmeric Extract (Curcuma longa) Mediates Anti-Oxidative Effects by Reduction of Nitric Oxide, iNOS Protein-, and mRNA-Synthesis in BV2 Microglial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of TE and Its Constituents on Cell Viability
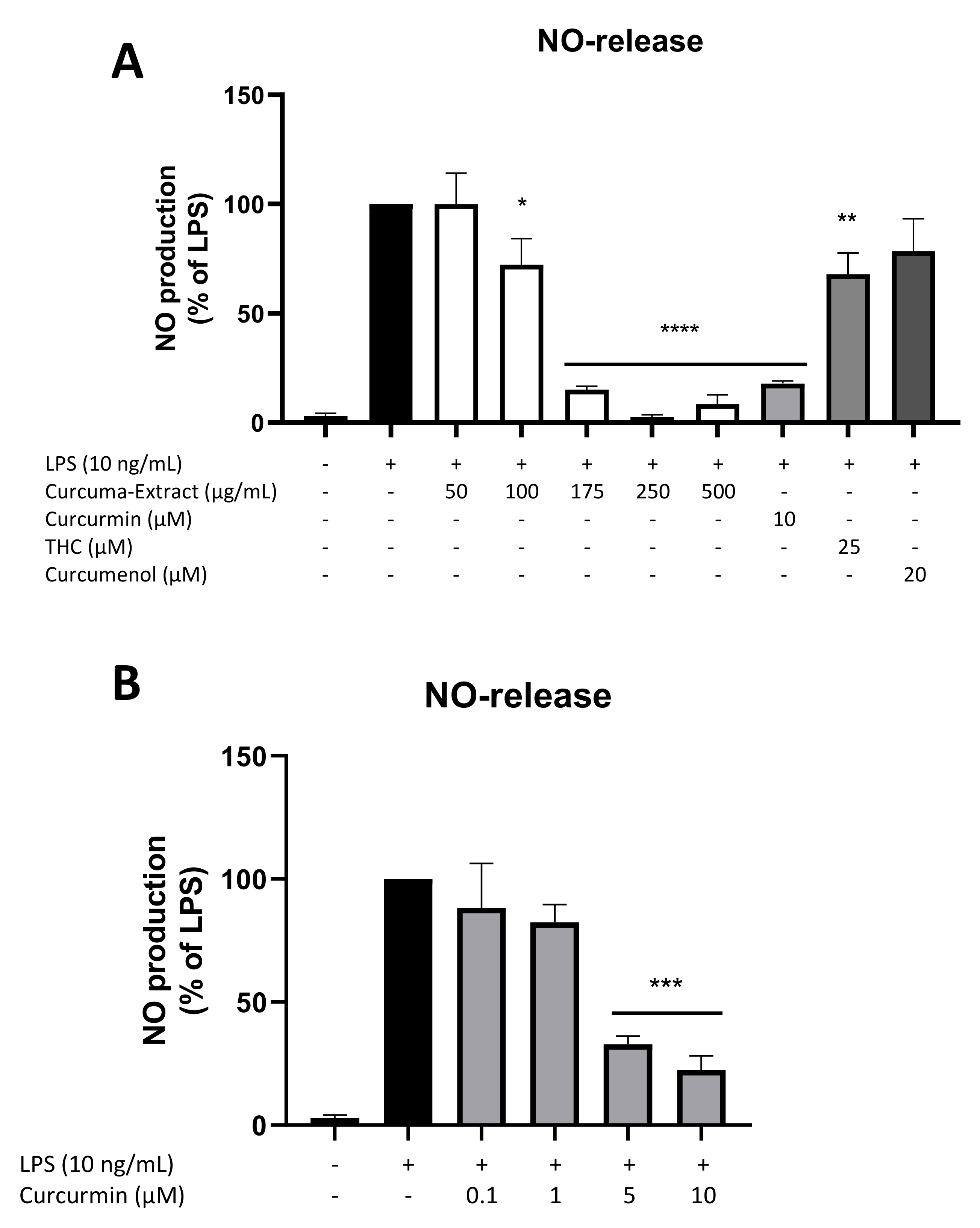
2.2. Effects of TE and Its Constituents on NO-Release
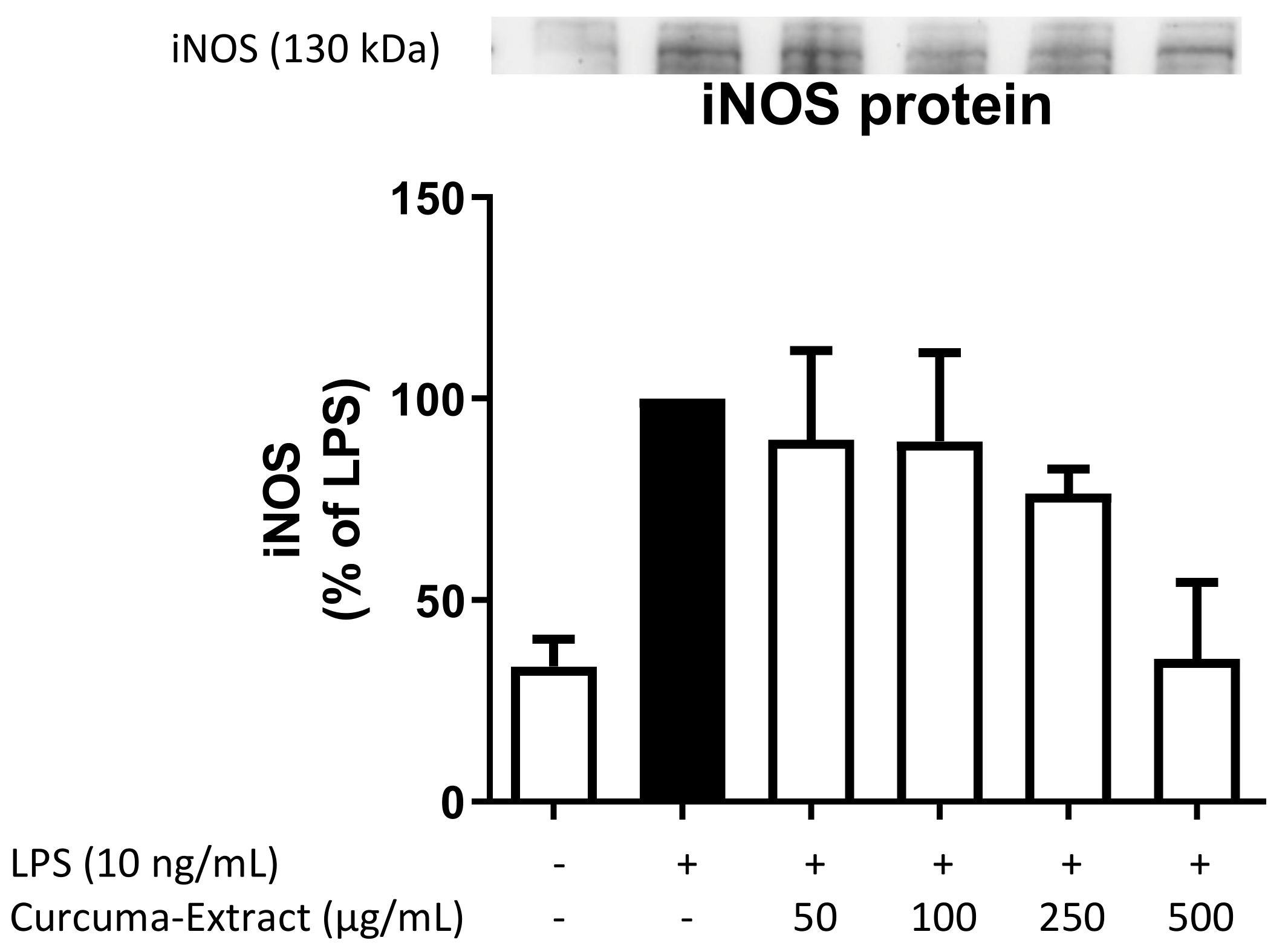
2.3. Effects of TE on iNOS-Protein Synthesis
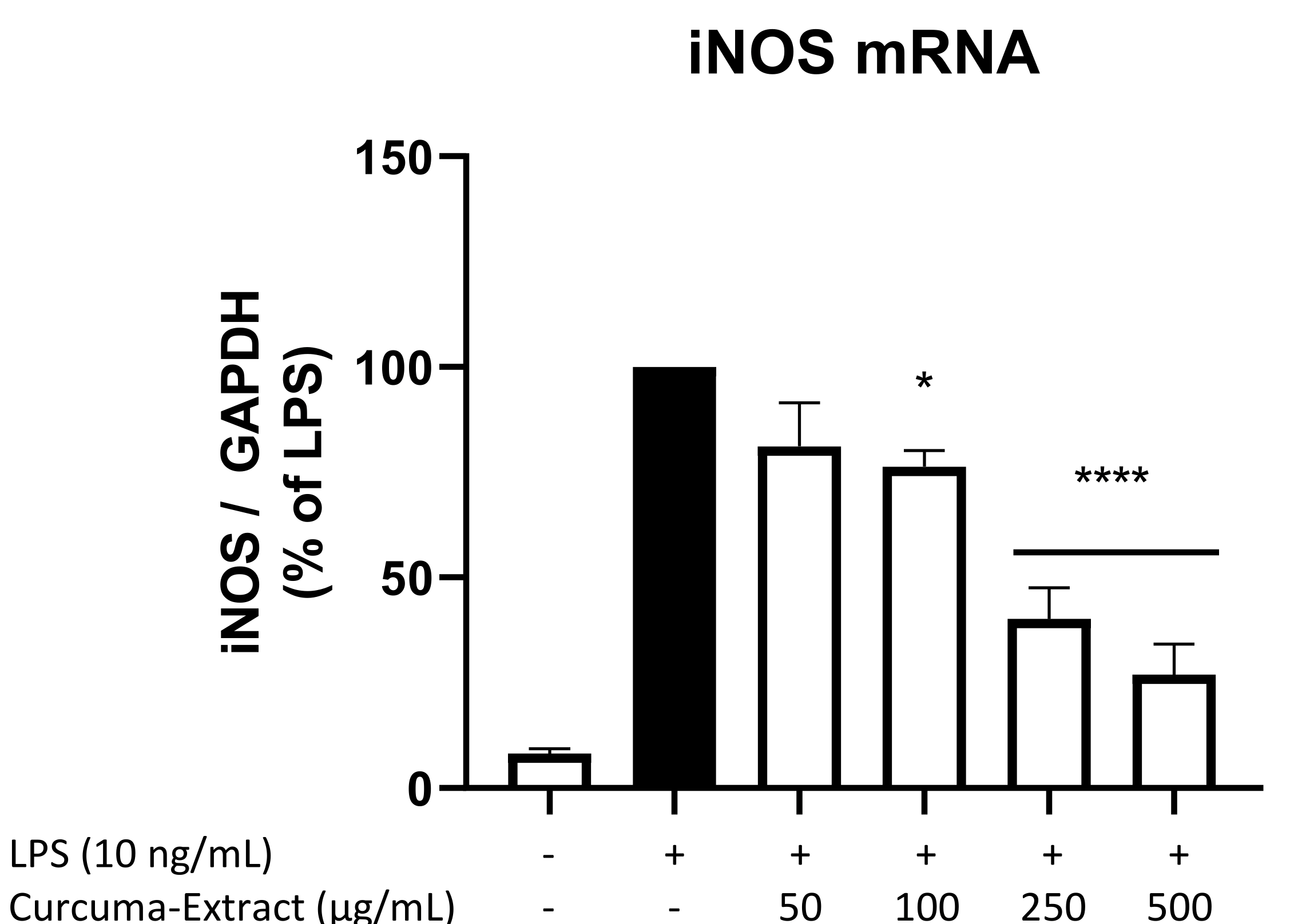
2.4. Effects of TE on iNOS-mRNA Expression
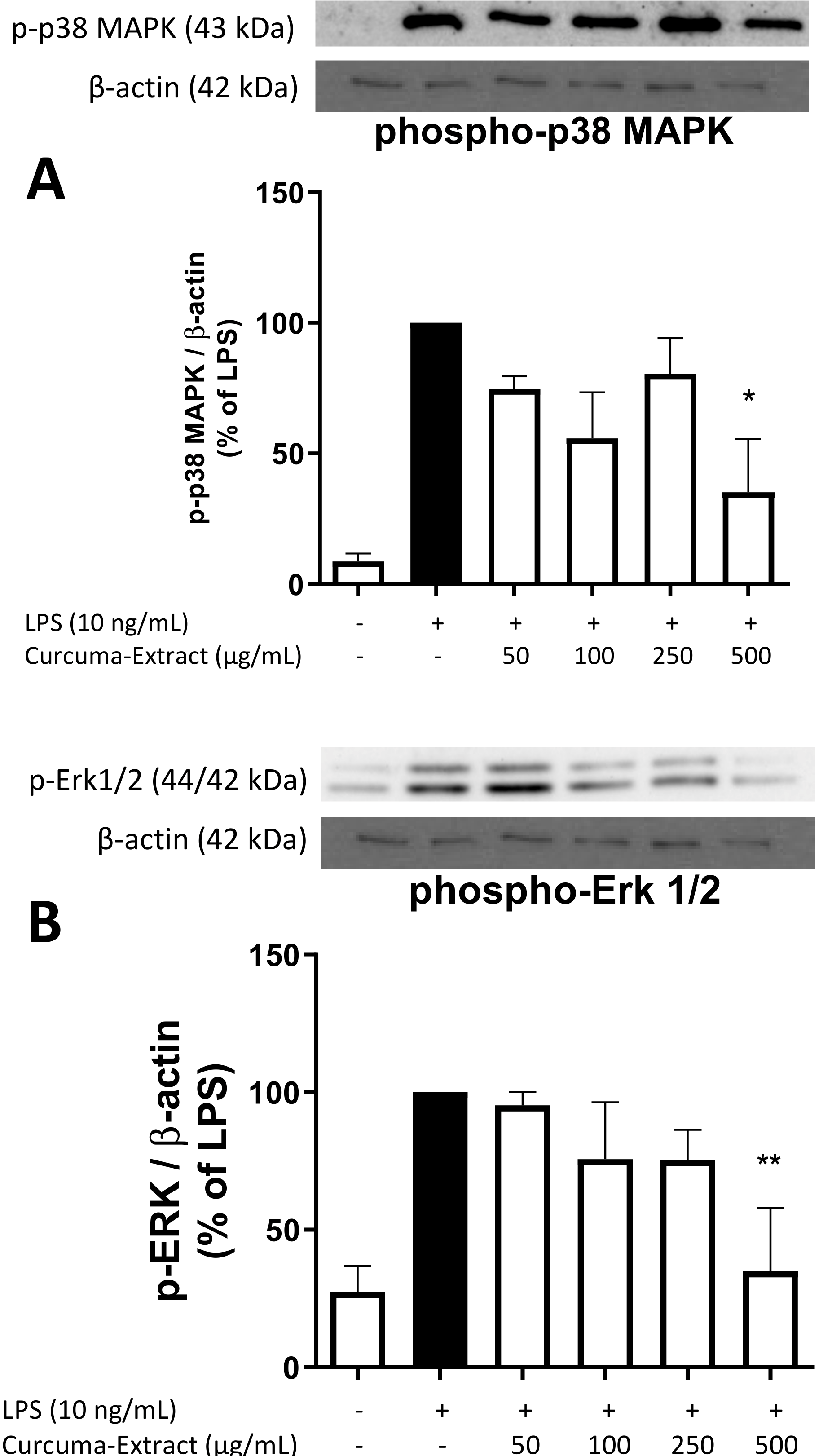
2.5. Effects of TE on MAPK Activation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Microglia Cell Culture
4.3. Determination of NO-Release from LPS-Activated BV2 Cells
4.4. Cell Viability Assays
4.5. RNA Isolation and Quantitative PCR
4.6. Immunoblotting
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Gupta, S.C.; Sung, B.; Kim, J.H.; Prasad, S.; Li, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Multitargeting by Turmeric, the Golden Spice: From Kitchen to Clinic. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1510–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Turmeric, the Golden Spice: From Traditional Medicine to Modern Medicine. In Herbal Medicine: Biomolecular and Clinical Aspects; Benzie, I.F.F., Wachtel-Galor, S., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-4398-0713-2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Miao, X.; Li, F.; Adhikari, B.K.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, R.; Cai, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. Curcuminoids: Implication for Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Diseases. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1302–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brundin, P.; Melki, R.; Kopito, R. Prion-like Transmission of Protein Aggregates in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozpędek-Kamińska, W.; Siwecka, N.; Wawrzynkiewicz, A.; Wojtczak, R.; Pytel, D.; Diehl, J.A.; Majsterek, I. The PERK-Dependent Molecular Mechanisms as a Novel Therapeutic Target for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amor, S.; Puentes, F.; Baker, D.; van der Valk, P. Inflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Immunology 2010, 129, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heppner, F.L.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Becher, B. Immune Attack: The Role of Inflammation in Alzheimer Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebay, L.E.; Robertson, H.; Durant, S.T.; Vitale, S.R.; Penning, T.M.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Hayes, J.D. Mechanisms of Activation of the Transcription Factor Nrf2 by Redox Stressors, Nutrient Cues, and Energy Status and the Pathways through Which It Attenuates Degenerative Disease. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 108–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, Q.; Yang, C. Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Retinopathy: Molecular Mechanisms, Pathogenetic Role and Therapeutic Implications. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzon dos Santos, J.; Schaan de Quadros, A.; Weschenfelder, C.; Bueno Garofallo, S.; Marcadenti, A. Oxidative Stress Biomarkers, Nut-Related Antioxidants, and Cardiovascular Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, S.J.; Scheller, L.F.; Marletta, M.A.; Seguin, M.C.; Klotz, F.W.; Slayter, M.; Nelson, B.J.; Nacy, C.A. Nitric Oxide: Cytokine-Regulation of Nitric Oxide in Host Resistance to Intracellular Pathogens. Immunol. Lett. 1994, 43, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Lu, X.; Tong, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, B.; Yang, R. Requirement for Endogenous Heat Shock Factor 1 in Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Induction in Murine Microglia. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathy, N.W.; Burleigh, O.; Kochvar, A.; Whiteford, E.R.; Behrens, M.; Marta, P.; Tian, C.; Gong, A.-Y.; Drescher, K.M.; Steyger, P.S.; et al. A Novel Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNA, Nostrill, Regulates INOS Gene Transcription and Neurotoxicity in Microglia. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anavi, S.; Tirosh, O. INOS as a Metabolic Enzyme under Stress Conditions. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 146, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Cho, H.J.; Calaycay, J.; Mumford, R.A.; Swiderek, K.M.; Lee, T.D.; Ding, A.; Troso, T.; Nathan, C. Cloning and Characterization of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase from Mouse Macrophages. Science 1992, 256, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banuls, C.; Rocha, M.; Rovira-Llopis, S.; Falcon, R.; Castello, R.; Herance, J.; Polo, M.; Blas-Garcia, A.; Hernandez-Mijares, A.; Victor, V. The Pivotal Role of Nitric Oxide: Effects on the Nervous and Immune Systems. CPD 2014, 20, 4679–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, A.; Navascués, J.; Cuadros, M.A.; Calvente, R.; Martín-Oliva, D.; Ferrer-Martín, R.M.; Martín-Estebané, M.; Carrasco, M.-C.; Marín-Teva, J.L. Expression of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (INOS) in Microglia of the Developing Quail Retina. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ransohoff, R.M. How Neuroinflammation Contributes to Neurodegeneration. Science 2016, 353, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, K.; Schwabenland, M.; Prinz, M. Microglia Metabolism in Health and Disease. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 130, 104331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, T.; Sershen, C.L.; May, E.E. Investigating the Role of TNF-α and IFN-γ Activation on the Dynamics of INOS Gene Expression in LPS Stimulated Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, L.; Karin, M. Mammalian MAP Kinase Signalling Cascades. Nature 2001, 410, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itokawa, H.; Shi, Q.; Akiyama, T.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Lee, K.-H. Recent Advances in the Investigation of Curcuminoids. Chin. Med. 2008, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.A.; Kitts, D.D. Turmeric and Its Bioactive Constituents Trigger Cell Signaling Mechanisms That Protect against Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2021, 476, 3785–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinyemi, A.J.; Adeniyi, P.A. Effect of Essential Oils from Ginger ( Zingiber Officinale ) and Turmeric ( Curcuma Longa ) Rhizomes on Some Inflammatory Biomarkers in Cadmium Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats. J. Toxicol. 2018, 2018, 4109491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pavlov, V.A.; Tracey, K.J. Controlling Inflammation: The Cholinergic Anti-Inflammatory Pathway. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 1037–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohare, P.; Varma, S.; Ray, M. Curcuma Oil Modulates the Nitric Oxide System Response to Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Nitric. Oxide. 2008, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J.; Wu, C.F.; Meng, X.L.; Yuan, D.; Cai, X.D.; Wang, Q.L.; Yang, J.Y. Comparison of Inhibitory Potency of Three Different Curcuminoid Pigments on Nitric Oxide and Tumor Necrosis Factor Production of Rat Primary Microglia Induced by Lipopolysaccharide. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 447, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas Garza, G.R.; Elizondo Luévano, J.H.; Bazaldúa Rodríguez, A.F.; Chávez Montes, A.; Pérez Hernández, R.A.; Martínez Delgado, A.J.; López Villarreal, S.M.; Rodríguez Rodríguez, J.; Sánchez Casas, R.M.; Castillo Velázquez, U.; et al. Benefits of Cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum (L.) Maton) and Turmeric (Curcuma conga L.) Extracts for Their Applications as Natural Anti-Inflammatory Adjuvants. Plants 2021, 10, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, V.; Mancuso, C.; Calvani, M.; Rizzarelli, E.; Butterfield, D.A.; Giuffrida Stella, A.M. Nitric Oxide in the Central Nervous System: Neuroprotection versus Neurotoxicity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.M.; Dahlin, J.L.; Bisson, J.; Graham, J.; Pauli, G.F.; Walters, M.A. The Essential Medicinal Chemistry of Curcumin: Miniperspective. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1620–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, N.; Piperi, C.; Psarra, V.; Lea, R.W.; Kalofoutis, A. Increased Plasma Levels of 8-Iso-PGF2α and IL-6 in an Elderly Population with Depression. Psychiatry Res. 2008, 161, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative Stress: A Key Modulator in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiurchiù, V.; Lanuti, M.; De Bardi, M.; Battistini, L.; Maccarrone, M. The Differential Characterization of GPR55 Receptor in Human Peripheral Blood Reveals a Distinctive Expression in Monocytes and NK Cells and a Proinflammatory Role in These Innate Cells. Int. Immunol. 2015, 27, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, C.S.; Jin, D.-Q.; Mok, H.; Oh, S.J.; Lee, J.U.; Hwang, J.K.; Ha, I.; Han, J.-S. Antioxidant and Antiinflammatory Activities of Xanthorrhizol in Hippocampal Neurons and Primary Cultured Microglia. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 82, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas Shytle, R.; Tan, J.; Bickford, P.C.; Rezai-zadeh, K.; Hou, L.; Zeng, J.; Sanberg, P.R.; Sanberg, C.D.; Alberte, R.S.; Fink, R.C.; et al. Optimized Turmeric Extract Reduces β-Amyloid and Phosphorylated Tau Protein Burden in Alzheimer’s Transgenic Mice. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2012, 9, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tommonaro, G. Curcumin and Cancer. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Yuan, W.; Li, S.; Gupta, S.C. Curcumin-Free Turmeric Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory and Anticancer Activities: Identification of Novel Components of Turmeric. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; Hsi, Y.-T.; Chang, C.-S.; Huang, L.-F.; Ho, C.-T.; Way, T.-D.; Kao, J.-Y. Chemical Constituents and Anticancer Activity of Curcuma Zedoaria Roscoe Essential Oil against Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11418–11427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Triste, N.E.; González-García, M.P.; Jiménez-Andrade, J.M.; Castañeda-Hernández, G.; Chávez-Piña, A.E. Pharmacological Evidence for the Participation of NO–CGMP–KATP Pathway in the Gastric Protective Effect of Curcumin against Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Injury in the Rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 730, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacher, P.; Beckman, J.S.; Liaudet, L. Nitric Oxide and Peroxynitrite in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 315–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apweiler, M.; Saliba, S.W.; Streyczek, J.; Hurrle, T.; Gräßle, S.; Bräse, S.; Fiebich, B.L. Targeting Oxidative Stress: Novel Coumarin-Based Inverse Agonists of GPR55. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apweiler, M.; Streyczek, J.; Saliba, S.W.; Ditrich, J.; Muñoz, E.; Fiebich, B.L. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidative Effects of AM404 in IL-1β-Stimulated SK-N-SH Neuroblastoma Cells. Front Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 789074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Streyczek, J.; Apweiler, M.; Sun, L.; Fiebich, B.L. Turmeric Extract (Curcuma longa) Mediates Anti-Oxidative Effects by Reduction of Nitric Oxide, iNOS Protein-, and mRNA-Synthesis in BV2 Microglial Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030784
Streyczek J, Apweiler M, Sun L, Fiebich BL. Turmeric Extract (Curcuma longa) Mediates Anti-Oxidative Effects by Reduction of Nitric Oxide, iNOS Protein-, and mRNA-Synthesis in BV2 Microglial Cells. Molecules. 2022; 27(3):784. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030784
Chicago/Turabian StyleStreyczek, Jana, Matthias Apweiler, Lu Sun, and Bernd L. Fiebich. 2022. "Turmeric Extract (Curcuma longa) Mediates Anti-Oxidative Effects by Reduction of Nitric Oxide, iNOS Protein-, and mRNA-Synthesis in BV2 Microglial Cells" Molecules 27, no. 3: 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030784
APA StyleStreyczek, J., Apweiler, M., Sun, L., & Fiebich, B. L. (2022). Turmeric Extract (Curcuma longa) Mediates Anti-Oxidative Effects by Reduction of Nitric Oxide, iNOS Protein-, and mRNA-Synthesis in BV2 Microglial Cells. Molecules, 27(3), 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030784