FNDC5/Irisin: Physiology and Pathophysiology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Irisin: Biosynthesis, Structure, and Downstream Signaling
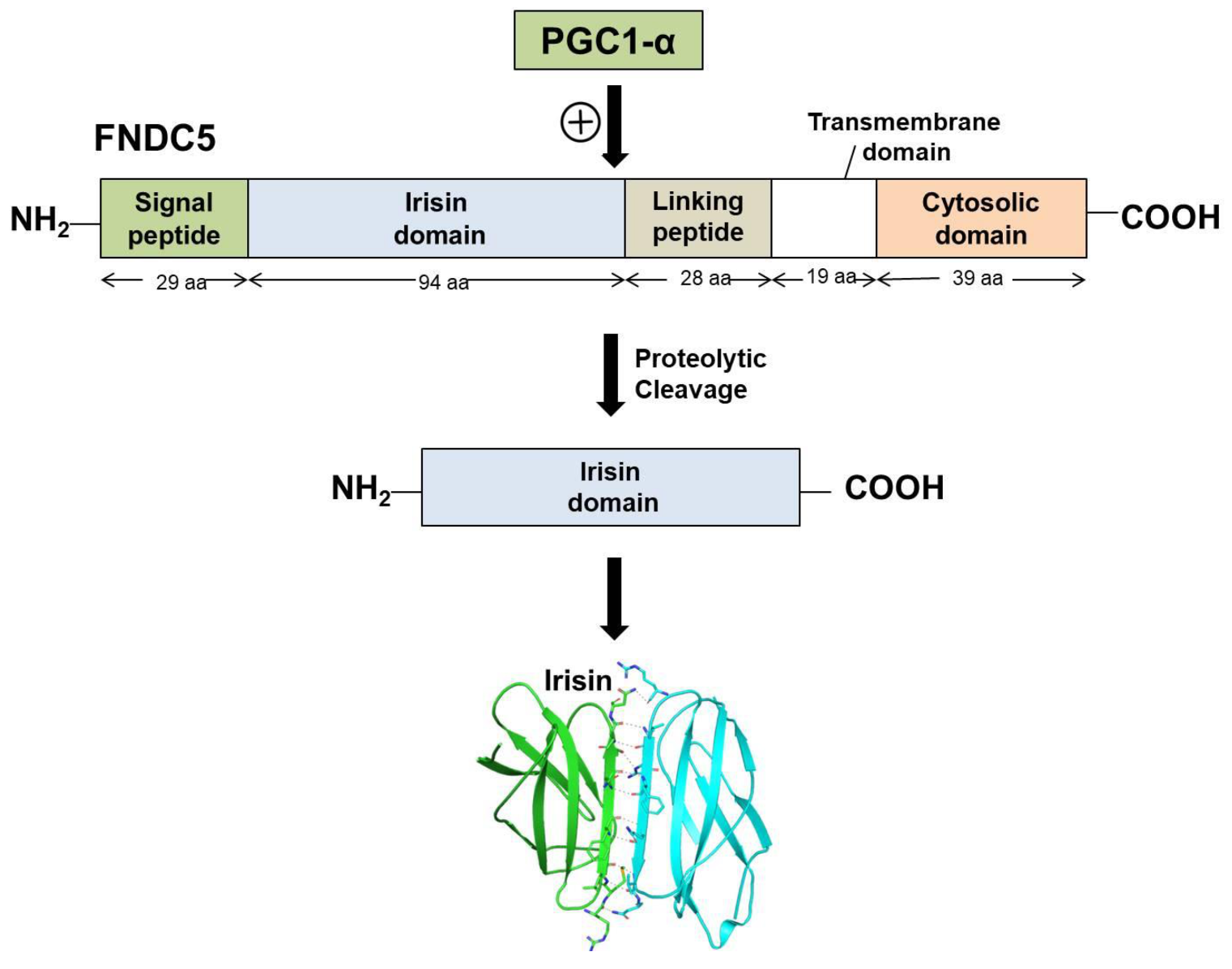
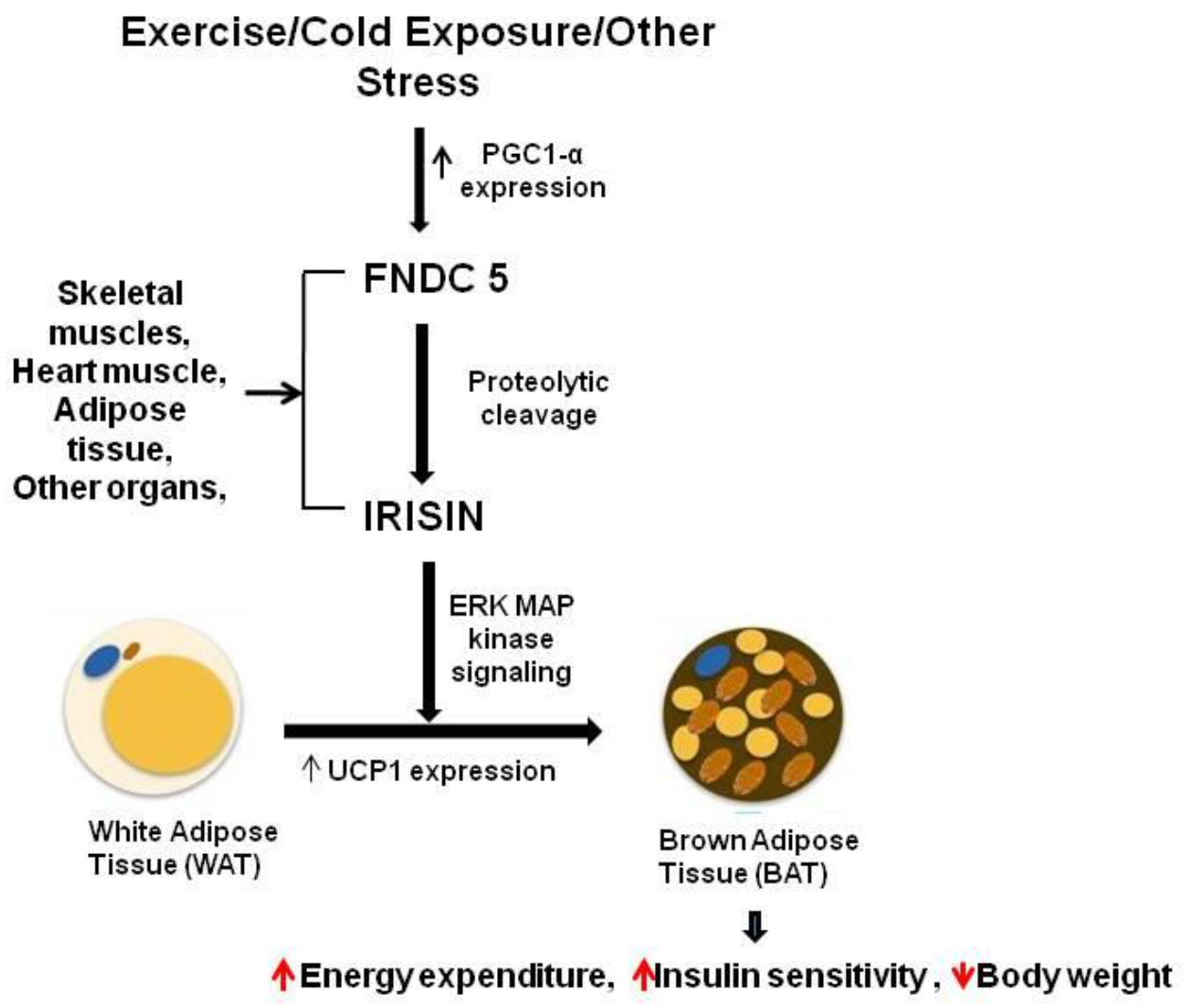
2.1. Biosynthesis and Secretion of Irisin
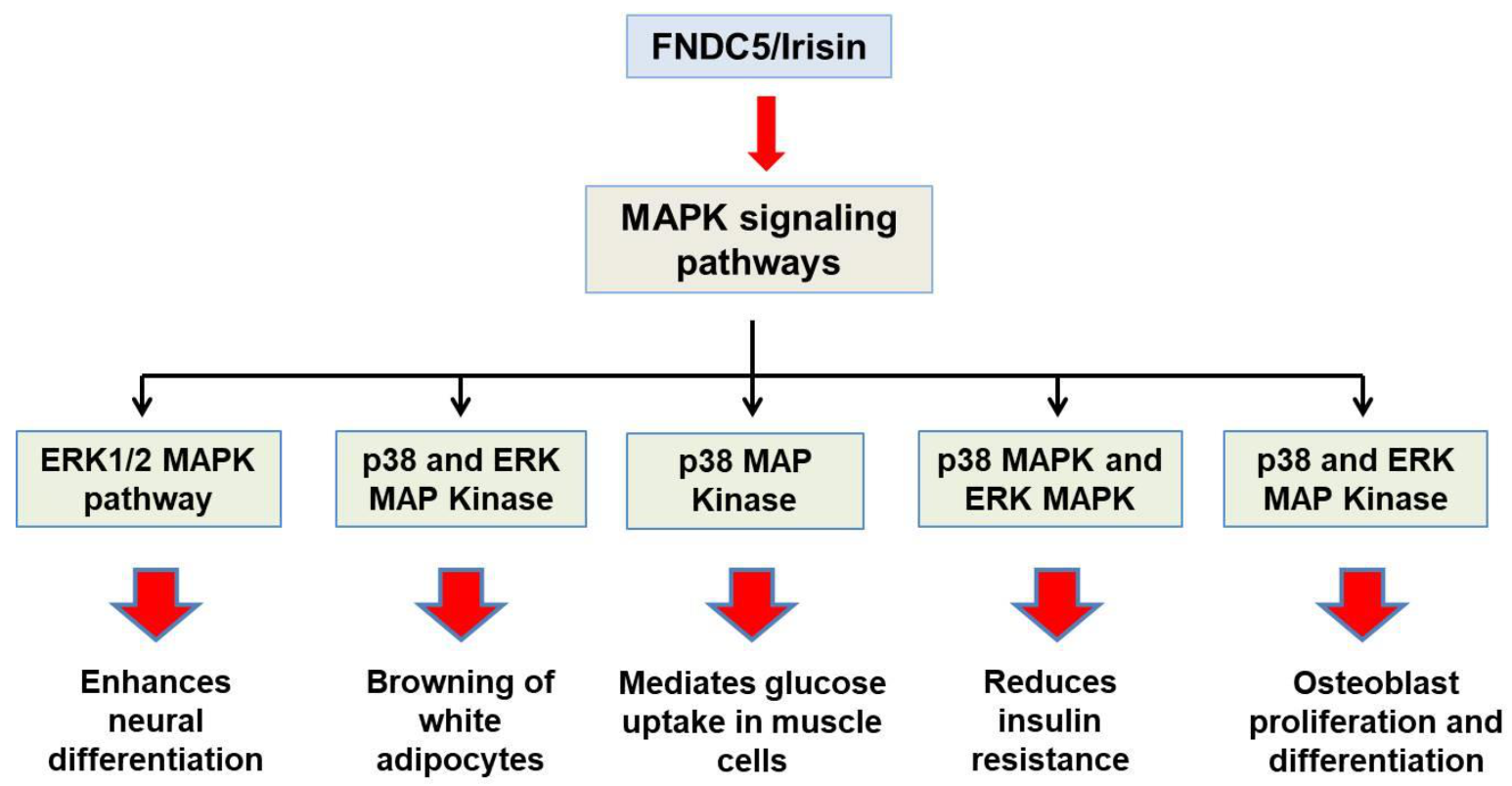
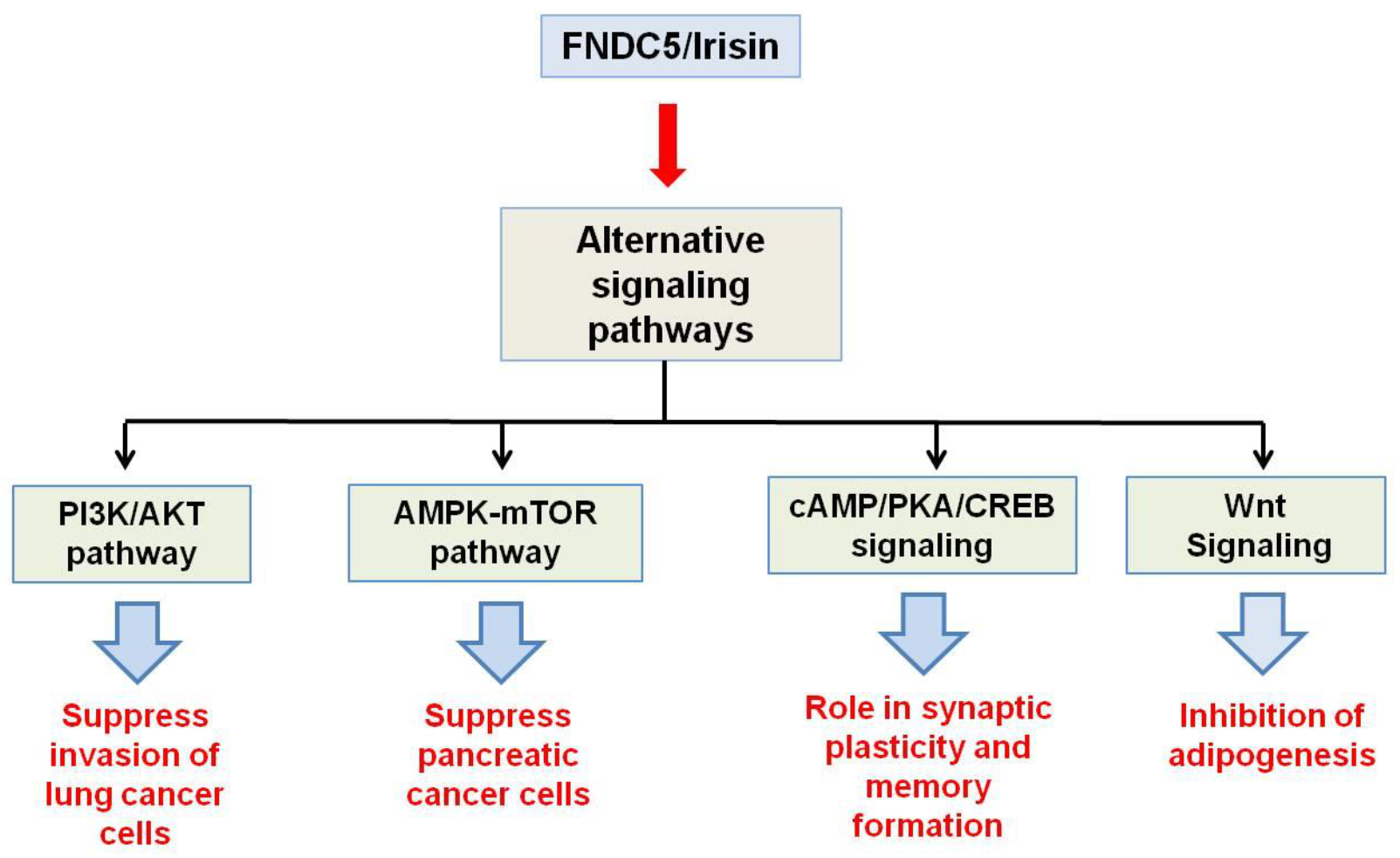
2.2. Structural Features and Signaling Pathways
2.3. Irisin Receptor
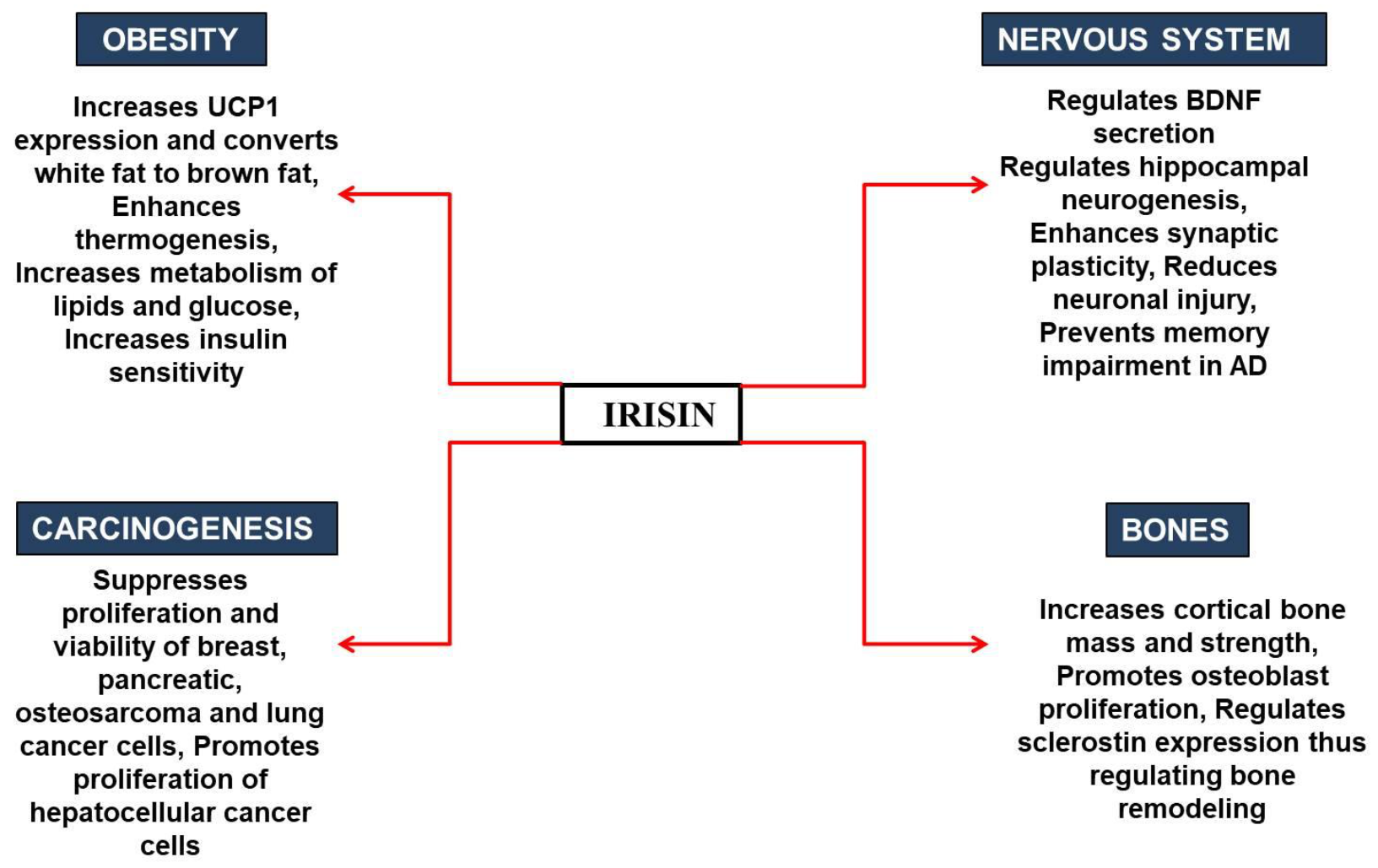
3. The Role of Irisin in Human Pathophysiology
3.1. Irisin in Obesity and Diabetes
3.2. Irisin in the Nervous System
3.3. Irisin in Bone Metabolism
3.4. Irisin in Carcinogenesis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FNDC5 | Fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 |
| FGF21 | Fibroblast growth factor 21 |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| WAT | White adipose tissue |
| BAT | Brown adipose tissue |
| UCP1 | Uncoupling protein 1 |
| PGC1 α | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPAR-γ) coactivator 1-α |
| FNDC9 | Fibronectin type III domain containing 9 |
| PRDM16 | PR domain zinc finger protein 16 |
| AMPK | Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| ERK1/2 | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 |
| EMT | Epithelial-mesenchyme transition |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine 3, 5- monophosphate |
| CREB | cAMP response element binding |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| APP | Amyloid precursor protein |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| MARK4 | Microtubule Affinity Regulating Kinase 4 |
References
- Carson, B.P. The potential role of contraction-induced myokines in the regulation of metabolic function for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delezie, J.; Handschin, C. Endocrine crosstalk between skeletal muscle and the brain. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boström, P.; Wu, J.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Korde, A.; Ye, L.; Lo, J.C.; Rasbach, K.A.; Boström, E.A.; Choi, J.H.; Long, J.Z. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature 2012, 481, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korta, P.; Pocheć, E.; Mazur-Biały, A. Irisin as a multifunctional protein: Implications for health and certain diseases. Medicina 2019, 55, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Duan, H.; Liu, Q.; Umar, M.; Luo, W.; Yang, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, M. Construction of a Pichia pastoris strain efficiently secreting irisin and assessment of its bioactivity in HepG2 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Pan, J. Irisin ameliorates depressive-like behaviors in rats by regulating energy metabolism. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 474, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Yin, C.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Liang, S.; Li, D.; Lin, X.; et al. Recombinant irisin prevents the reduction of osteoblast differentiation induced by stimulated microgravity through increasing β-catenin expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colaianni, G.; Cuscito, C.; Mongelli, T.; Pignataro, P.; Buccoliero, C.; Liu, P.; Lu, P.; Sartini, L.; di Comite, M.; Mori, G. The myokine irisin increases cortical bone mass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12157–12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jodeiri Farshbaf, M.; Alviña, K. Multiple roles in neuroprotection for the exercise derived myokine Irisin. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piya, M.K.; Harte, A.L.; Sivakumar, K.; Tripathi, G.; Voyias, P.D.; James, S.; Sabico, S.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Saravanan, P.; Barber, T.M. The identification of irisin in human cerebrospinal fluid: Influence of adiposity, metabolic markers, and gestational diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E512–E518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, K.I.; Weinstein, A.M.; Lopez, O.L. Physical activity, brain plasticity, and Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Med. Res. 2012, 43, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panati, K.; Suneetha, Y.; Narala, V. Irisin/FNDC5–An updated review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 689–697. [Google Scholar]
- Waseem, R.; Shamsi, A.; Mohammad, T.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Kazim, S.N.; Hassan, M.I.; Ahmad, F.; Islam, A. Multispectroscopic and Molecular Docking Insight into Elucidating the Interaction of Irisin with Rivastigmine Tartrate: A Combinational Therapy Approach to Fight Alzheimer’s Disease. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 7910–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norheim, F.; Langleite, T.M.; Hjorth, M.; Holen, T.; Kielland, A.; Stadheim, H.K.; Gulseth, H.L.; Birkeland, K.I.; Jensen, J.; Drevon, C.A. The effects of acute and chronic exercise on PGC-1α, irisin and browning of subcutaneous adipose tissue in humans. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clin, A. The Relationship between High-Fat Diet and Fibronectin Type-III Domain-Containing Protein 5 mRNA Expression. Anatol. Clin. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 23, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Ortega, F.; Serrano, M.; Guerra, E.; Pardo, G.; Tinahones, F.; Ricart, W.; Fernández-Real, J.M. Irisin is expressed and produced by human muscle and adipose tissue in association with obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E769–E778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedrychowski, M.P.; Wrann, C.D.; Paulo, J.A.; Gerber, K.K.; Szpyt, J.; Robinson, M.M.; Nair, K.S.; Gygi, S.P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Detection and quantitation of circulating human irisin by tandem mass spectrometry. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raschke, S.; Elsen, M.; Gassenhuber, H.; Sommerfeld, M.; Schwahn, U.; Brockmann, B.; Jung, R.; Wisløff, U.; Tjønna, A.E.; Raastad, T. Evidence against a beneficial effect of irisin in humans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanin, E.F. Processed pseudogenes: Characteristics and evolution. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1985, 19, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, E.; Norheim, F.; Thiede, B.; Holen, T.; Ohashi, T.; Schering, L.; Lee, S.; Brenmoehl, J.; Thomas, S.; Drevon, C.A. Irisin–a myth rather than an exercise-inducible myokine. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, P.; Linderman, J.D.; Smith, S.; Brychta, R.J.; Wang, J.; Idelson, C.; Perron, R.M.; Werner, C.D.; Phan, G.Q.; Kammula, U.S. Irisin and FGF21 are cold-induced endocrine activators of brown fat function in humans. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Ruan, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Ma, C.; Yu, Z. Detection and quantitation of irisin in human cerebrospinal fluid by tandem mass spectrometry. Peptides 2018, 103, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Yang, L.; Ruan, J.; Gu, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yu, Z. The effects of both age and sex on irisin levels in paired plasma and cerebrospinal fluid in healthy humans. Peptides 2019, 113, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colaianni, G.; Errede, M.; Sanesi, L.; Notarnicola, A.; Celi, M.; Zerlotin, R.; Storlino, G.; Pignataro, P.; Oranger, A.; Pesce, V. Irisin correlates positively with BMD in a cohort of older adult patients and downregulates the senescent marker p21 in osteoblasts. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2021, 36, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaianni, G.; Storlino, G.; Sanesi, L.; Colucci, S.; Grano, M. Myokines and osteokines in the pathogenesis of muscle and bone diseases. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2020, 18, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.F.; Valaris, S.; Wrann, C.D. A role for FNDC5/Irisin in the beneficial effects of exercise on the brain and in neurodegenerative diseases. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 62, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, M.A.; Chinnam, N.; Ohashi, T.; Shah, R.S.; Erickson, H.P. The structure of irisin reveals a novel intersubunit β-sheet fibronectin type III (FNIII) dimer: Implications for receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 33738–33744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korta, P.; Pocheć, E. Glycosylation of thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor. Endokrynol. Pol. 2019, 70, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Meng, Y.; Li, S.; Donelan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Cui, T. Irisin stimulates browning of white adipocytes through mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 MAP kinase and ERK MAP kinase signaling. Diabetes 2014, 63, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabiee, F.; Lachinani, L.; Ghaedi, S.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H.; Megraw, T.L.; Ghaedi, K. New insights into the cellular activities of Fndc5/Irisin and its signaling pathways. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, N.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y. Irisin inhibits pancreatic cancer cell growth via the AMPK-mTOR pathway. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, L.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Song, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, F.; Li, H. Irisin suppresses the migration, proliferation, and invasion of lung cancer cells via inhibition of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 485, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenco, M.V.; Frozza, R.L.; de Freitas, G.B.; Zhang, H.; Kincheski, G.C.; Ribeiro, F.C.; Gonçalves, R.A.; Clarke, J.R.; Beckman, D.; Staniszewski, A. Exercise-linked FNDC5/irisin rescues synaptic plasticity and memory defects in Alzheimer’s models. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E.B.; Sahar, N.E.; Jeong, M.; Huh, J.Y. Irisin exerts inhibitory effect on adipogenesis through regulation of Wnt signaling. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Wrann, C.D.; Jedrychowski, M.; Vidoni, S.; Kitase, Y.; Nagano, K.; Zhou, C.; Chou, J.; Parkman, V.-J.A.; Novick, S.J. Irisin mediates effects on bone and fat via αV integrin receptors. Cell 2018, 175, 1756–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pignataro, P.; Dicarlo, M.; Zerlotin, R.; Zecca, C.; Dell’Abate, M.T.; Buccoliero, C.; Logroscino, G.; Colucci, S.; Grano, M. FNDC5/Irisin System in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegenerative Diseases: Update and Novel Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Guo, J.; Chen, Y.; Meng, C. The neuroprotective effect of irisin in ischemic stroke. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Nie, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, R.; Yin, W.; Hu, Y.; Xu, W.; Xu, L. Irisin promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation via activating the MAP kinase signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, E.D.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipocytes as regulators of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Nature 2006, 444, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Seale, P. Control of brown and beige fat development. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Qiao, X.; Ma, Y.; Deng, H.; Xu, C.C.; Xu, L. Disordered metabolism in mice lacking irisin. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.H.; Zaichenko, L.; Brinkoetter, M.; Thakkar, B.; Sahin-Efe, A.; Joung, K.E.; Tsoukas, M.A.; Geladari, E.V.; Huh, J.Y.; Dincer, F. Circulating irisin in relation to insulin resistance and the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4899–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Du, F.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Duan, R.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Effects and underlying mechanisms of irisin on the proliferation and apoptosis of pancreatic β cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Jia, S. Irisin, an exercise-induced myokine as a metabolic regulator: An updated narrative review. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-K.; Kim, M.-K.; Bae, K.H.; Seo, H.-A.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Lee, W.-K.; Kim, J.-G.; Lee, I.-K.; Park, K.-G. Serum irisin levels in new-onset type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 100, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-J.; Wong, M.D.; Toy, W.C.; Tan, C.S.; Liu, S.; Ng, X.W.; Tavintharan, S.; Sum, C.F.; Lim, S.C. Lower circulating irisin is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2013, 27, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xin, C.; Zhang, F.; Lee, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lian, K.; Yan, W. Irisin improves endothelial function in type 2 diabetes through reducing oxidative/nitrative stresses. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2015, 87, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, J.H.; Huang, C.; Ge, M.; Cai, G.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Y.; Mu, Y. Intense exercise promotes adult hippocampal neurogenesis but not spatial discrimination. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novelle, M.G.; Contreras, C.; Romero-Picó, A.; López, M.; Diéguez, C. Irisin, two years later. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wrann, C.D.; White, J.P.; Salogiannnis, J.; Laznik-Bogoslavski, D.; Wu, J.; Ma, D.; Lin, J.D.; Greenberg, M.E.; Spiegelman, B.M. Exercise induces hippocampal BDNF through a PGC-1α/FNDC5 pathway. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, H.-S.; Dincer, F.; Mantzoros, C.S. Pharmacological concentrations of irisin increase cell proliferation without influencing markers of neurite outgrowth and synaptogenesis in mouse H19-7 hippocampal cell lines. Metabolism 2013, 62, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pesce, M.; Ballerini, P.; Paolucci, T.; Puca, I.; Farzaei, M.H.; Patruno, A. Irisin and autophagy: First update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, T.; Lu, C. Irisin activates Opa1-induced mitophagy to protect cardiomyocytes against apoptosis following myocardial infarction. Aging 2020, 12, 4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, Y.; Gorjipour, F.; Behrouzifar, S.; Vakili, A. Irisin peptide protects brain against ischemic injury through reducing apoptosis and enhancing BDNF in a rodent model of stroke. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Jin, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, X.; Ke, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Q. Effects of irisin on the dysfunction of blood–brain barrier in rats after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Brain Behav. 2019, 9, e01425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Deng, X.; Huang, W.; Yu, J.-H.; Wang, J.-X.; Wang, J.-P.; Yang, S.-B.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Irisin protects against neuronal injury induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation in part depends on the inhibition of ROS-NLRP3 inflammatory signaling pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 91, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Li, G.; Ding, Q.; Tao, L.; Li, J.; Sun, L.; Sun, X.; Yang, Y. Irisin protects brain against ischemia/reperfusion injury through suppressing TLR4/MyD88 pathway. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 49, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Guo, P.; Li, X.; Ke, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H. Neuroprotective effects of irisin against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via Notch signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 120, 109452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-J.; Li, Y.-H.; Yuan, H.-B.; Qu, L.-F.; Wang, P. The novel exercise-induced hormone irisin protects against neuronal injury via activation of the Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways and contributes to the neuroprotection of physical exercise in cerebral ischemia. Metabolism 2017, 68, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, O.Y.; Song, J. The role of irisin in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waseem, R.; Anwar, S.; Khan, S.; Shamsi, A.; Hassan, M.; Anjum, F.; Shafie, A.; Islam, A.; Yadav, D.K. MAP/Microtubule Affinity Regulating Kinase 4 Inhibitory Potential of Irisin: A New Therapeutic Strategy to Combat Cancer and Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, Y.; Kuzuya, A.; Tanigawa, K.; Araki, M.; Kawai, R.; Ma, B.; Sasakura, Y.; Maesako, M.; Tashiro, Y.; Miyamoto, M. Fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 interacts with APP and decreases amyloid β production in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Brain 2018, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, G.; Thabane, L.; Papaioannou, A.; Ioannidis, G.; Levine, M.A.; Adachi, J.D. An overview of osteoporosis and frailty in the elderly. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colaianni, G.; Cuscito, C.; Mongelli, T.; Oranger, A.; Mori, G.; Brunetti, G.; Colucci, S.; Cinti, S.; Grano, M. Irisin enhances osteoblast differentiation in vitro. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Estell, E.G.; Le, P.T.; Vegting, Y.; Kim, H.; Wrann, C.; Bouxsein, M.L.; Nagano, K.; Baron, R.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Rosen, C.J. Irisin directly stimulates osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption in vitro and in vivo. eLife 2020, 9, e58172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serbest, S.; Tiftikçi, U.; Tosun, H.B.; Kısa, Ü. The irisin hormone profile and expression in human bone tissue in the bone healing process in patients. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2017, 23, 4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singhal, V.; Lawson, E.A.; Ackerman, K.E.; Fazeli, P.K.; Clarke, H.; Lee, H.; Eddy, K.; Marengi, D.A.; Derrico, N.P.; Bouxsein, M.L. Irisin levels are lower in young amenorrheic athletes compared with eumenorrheic athletes and non-athletes and are associated with bone density and strength estimates. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Tao, F.; Liu, C.; Tu, Q.; Shen, G.; Chen, J.J. Irisin deficiency disturbs bone metabolism. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalouf, G.-E.; El Khoury, D. Exercise-induced irisin, the fat browning myokine, as a potential anticancer agent. J. Obes. 2019, 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, N.P.; Vaughan, R.A.; Garcia-Smith, R.; Bisoffi, M.; Trujillo, K.A. Effects of the exercise-inducible myokine irisin on malignant and non-malignant breast epithelial cell behavior in vitro. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E197–E202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Provatopoulou, X.; Georgiou, G.P.; Kalogera, E.; Kalles, V.; Matiatou, M.A.; Papapanagiotou, I.; Sagkriotis, A.; Zografos, G.C.; Gounaris, A. Serum irisin levels are lower in patients with breast cancer: Association with disease diagnosis and tumor characteristics. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinkowska, A.; Podhorska-Okołów, M.; Dzięgiel, P.; Nowińska, K. The Role of Irisin in Cancer Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, G.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Q.; Cheng, G. Irisin reverses the IL-6 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion through the STAT3/Snail signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2647–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altay, D.U.; Keha, E.E.; Karagüzel, E.; Menteşe, A.; Yaman, S.O.; Alver, A. The diagnostic value of FNDC5/Irisin in renal Cell Cancer. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2018, 44, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, R.; Shamsi, A.; Shahbaz, M.; Khan, T.; Kazim, S.N.; Ahmad, F.; Hassan, M.I.; Islam, A. Effect of pH on the structure and stability of irisin, a multifunctional protein: Multispectroscopic and molecular dynamics simulation approach. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1252, 132141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanni, C.; Masi, M.; Racchi, M.; Govoni, S. Cancer and Alzheimer’s disease inverse relationship: An age-associated diverging derailment of shared pathways. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 280–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Waseem, R.; Shamsi, A.; Mohammad, T.; Hassan, M.I.; Kazim, S.N.; Chaudhary, A.A.; Rudayni, H.A.; Al-Zharani, M.; Ahmad, F.; Islam, A. FNDC5/Irisin: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Molecules 2022, 27, 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031118
Waseem R, Shamsi A, Mohammad T, Hassan MI, Kazim SN, Chaudhary AA, Rudayni HA, Al-Zharani M, Ahmad F, Islam A. FNDC5/Irisin: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Molecules. 2022; 27(3):1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031118
Chicago/Turabian StyleWaseem, Rashid, Anas Shamsi, Taj Mohammad, Md. Imtaiyaz Hassan, Syed Naqui Kazim, Anis Ahmad Chaudhary, Hassan Ahmed Rudayni, Mohammed Al-Zharani, Faizan Ahmad, and Asimul Islam. 2022. "FNDC5/Irisin: Physiology and Pathophysiology" Molecules 27, no. 3: 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031118
APA StyleWaseem, R., Shamsi, A., Mohammad, T., Hassan, M. I., Kazim, S. N., Chaudhary, A. A., Rudayni, H. A., Al-Zharani, M., Ahmad, F., & Islam, A. (2022). FNDC5/Irisin: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Molecules, 27(3), 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031118










