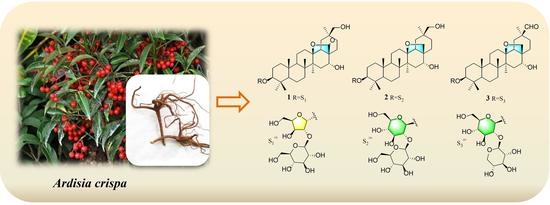
Cytotoxic 13,28 Epoxy Bridged Oleanane-Type Triterpenoid Saponins from the Roots of Ardisia crispa
Abstract
1. Introduction
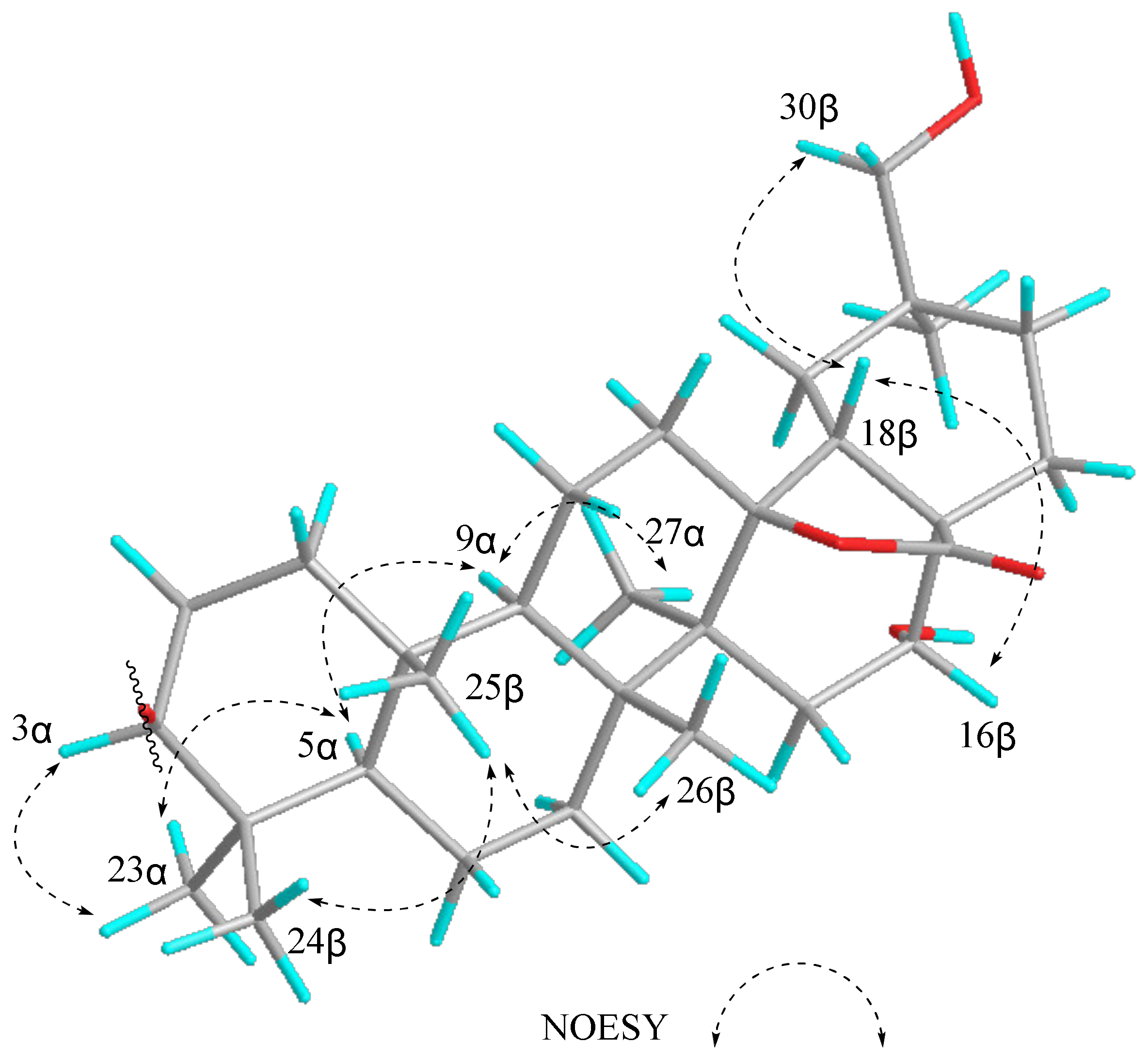
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Characterization of Compounds 1–3
3.5. Acid Hydrolysis of Ardisiacrispin D-F (1–3)
3.6. Cytotoxic Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Kobayashi, H.; Mejía, E. The genus Ardisia: A novel source of health-promoting compounds and phytopharmaceuticals. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 96, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Li, W.; Jia, Z.; Satou, T.; Fushiya, S.; Koike, K. Biologically active triterpenoid saponins from Ardisia japonica. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Tang, H.F.; Qiu, F.; Wang, X.J.; Chen, X.L.; Wen, A.D. Triterpenoid saponins from Ardisia pusilla and their cytotoxic activity. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, L.H.; Gong, Q.Q.; Zhao, H.X.; Liu, P. Triterpenoid saponins from Ardisia gigantifolia. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1248–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, L.H.; Wei, N.Y.; Liu, P. Cytotoxic triterpenoid saponins from Ardisia gigantifolia. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.F.; Xu, J.F.; Feng, Z.M.; Zhang, P.C. Cytotoxic triterpenoid saponins from the roots of Ardisia crenata. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2008, 10, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.Q.; Mu, L.H.; Liu, P.; Yang, S.L.; Wang, B.; Feng, Y.L. New triterpenoid sapoin from Ardisia gigantifolia Stapf. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2010, 21, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.F.; Yun, J.; Lin, H.W.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, X.J.; Cheng, G. Two new triterpenoid saponins cytotoxic to human glioblastoma U251MG cells from Ardisia pusilla. Chem. Biodivers. 2009, 6, 1443–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editorial Committee of Nan Jing University of Chinese Medicine, Chinese Materia Medica. Zhong Yao Da Ci Dian; Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 2014; Volume 1, p. 1181. [Google Scholar]
- Nordin, M.L.; Kadir, A.A.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Abdullah, R.; Abdullah, M. In vitro investigation of cytotoxic and antioxidative activities of Ardisia crispa against breast cancer cell lines, MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeong, L.T.; Hamid, R.A.; Yazan, L.S.; Khaza’ai, H.; Mohtarrudin, N. Low dose triterpene-quinone fraction from Ardisia crispa root precludes chemical-induced mouse skin tumor promotion. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jun, L.W.; Foong, C.P.; Hamid, R.A. Ardisia crispa root hexane fraction suppressed angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and in vivo zebrafish embryo model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeong, L.T.; Hamid, R.A.; Yazan, L.S.; Khaza’ai, H.; Hamsin, D. Synergistic action of compounds isolated from the hexane extract of Ardisia crispa root against tumour-promoting effect, in vitro. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 2026–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, R.A.; Othman, F.; Anthony, J.J.; Ting, Y.L. Chemopreventive effect of Ardisia crispa hexane fraction on the peri-initiation phase of mouse skin tumorigenesis. Med. Princ. Pract. 2013, 22, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordin, M.L.; Kadir, A.A.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Othman, F.; Abdullah, R.; Abdullah, M. Cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction of Ardisia crispa and its solvent partitions against Mus musculus mammary carcinoma cell line (4T1). Evid-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 9368079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamsin, D.; Hamid, R.A.; Yazan, L.S.; Taib, C.N.; Yeong, L.T. Ardisia crispa roots inhibit cyclooxygenase and suppress angiogenesis. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Hamsin, D.; Hamid, R.A.; Yazan, L.S.; Taib, C.N.; Yeong, L.T. The hexane fraction of Ardisia crispa Thunb. A. DC. roots inhibits inflammation-induced angiogenesis. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, H.; Hamid, R.A.; Yeong, L.T.; Othman, F. Anti-tumor effect of Ardisia crispa hexane fraction on 7, 12-dimethylbenz[α]anthracene-induced mouse skin papillomagenesis. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2012, 8, 404–410. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Koike, K.; Ohmoto, T.; Ni, M. Triterpenoid saponins from Ardisia crenata. Phytochemistry 1994, 37, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.N.; Sun, J.F.; Wang, J.M.; Jin, L.; Zong, T.Q.; Zhou, W.; Li, G. Two new phenolic glycosides from the fruits of Illicium verum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 24, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, K.; Tanaka, O. Saponins from Vietnamese ginseng, Panax vietnamensis HA et Grushv. Collected in central Vietnam. II. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 42, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Lavaud, C.; Massiot, G.; Moretti, C.; Men-Olivier, L.L. Triterpene saponins from Myrsine pellucida. Phytochemistry 1994, 37, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P. Biotransformation and antitumor activity of triterpenoid derivatives from Ardisia gigantifolia. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2018, 49, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, H.; Shimizu, N.; Takeda, T. Ardisimamillosides G and H, two new triterpenoid saponins from Ardisia mamillata. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 875–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yin, X.; Liu, Y.; Pan, J.; Ye, H.L.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, D.Y.; Kuang, H.X.; Yang, B.Y. Melongenaterpenes A-L, Vetispirane-Type Sesquiterpenoids from the Roots of Solanum melongena. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 3242–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.Y.; Yin, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D.Y.; Kuang, H.X. New steroidal saponins from the roots of Solanum melongena L. Fitoterapia 2018, 128, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.Y.; Yin, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Guan, W.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Kuang, H.X. Terpenes and lignans from the roots of Solanum melongena L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) |
| 1 | 40.0 | 1.78 (m) 0.98 (m) | 40.2 | 1.73 (m) 1.00 (m) | 40.2 | 1.73 (m) 0.97 (m) |
| 2 | 26.7 | 1.96 (m) 1.67 (m) | 27.3 | 1.95 (m) 1.70 (m) | 27.3 | 1.85 (m) 1.70 (m) |
| 3 | 89.4 | 3.15 (overlap) | 91.3 | 3.16 (overlap) | 91.3 | 3.14 (dd, 11.3, 4.2) |
| 4 | 40.0 | - | 40.5 | - | 40.6 | - |
| 5 | 56.5 | 0.79 (brd, 7.1) | 56.8 | 0.72 (brd, 11.1) | 56.8 | 0.72 (brd, 9.7) |
| 6 | 18.8 | 1.51 (m) 1.46 (m) | 18.7 | 1.51 (m) 1.42 (m) | 18.7 | 1.49 (m) 1.42 (m) |
| 7 | 34.8 | 1.59 (m) 1.24 (m) | 35.1 | 1.56 (m) 1.20 (m) | 35.1 | 1.54 (m) 1.20 (m) |
| 8 | 43.1 | - | 43.3 | - | 43.4 | - |
| 9 | 50.8 | 1.35 (overlap) | 51.6 | 1.46 (overlap) | 51.3 | 1.24 (overlap) |
| 10 | 37.8 | - | 37.7 | - | 37.8 | - |
| 11 | 19.4 | 1.65 (m) 1.50 (m) | 19.8 | 1.64 (m) 1.48 (m) | 19.8 | 1.63 (m) 1.48 (m) |
| 12 | 32.1 | 2.16 (m) 1.56 (m) | 32.8 | 2.05 (m) 1.33 (m) | 33.2 | 2.10 (m) 1.26 (m) |
| 13 | 95.0 | - | 88.5 | - | 88.2 | - |
| 14 | 43.0 | - | 45.3 | - | 45.3 | - |
| 15 | 37.4 | 1.78 (overlap) 1.44 (overlap) | 36.9 | 2.08 (overlap) 1.20 (overlap) | 37.0 | 2.07 (m) 1.20 (m) |
| 16 | 73.3 | 3.96 (brd, 5.2) | 78.0 | 3.89 (overlap) | 77.8 | 3.91 (brd, 4.9) |
| 17 | 49.5 | - | 45.2 | - | 44.8 | - |
| 18 | 51.9 | 1.85 (m) | 51.3 | 1.24 (m) | 54.0 | 1.12 (dd, 12.9, 2.1) |
| 19 | 33.1 | 2.35 (t, like, 12.4) 1.68 (m) | 33.8 | 2.25 (t, like, 12.6) 1.58 (m) | 34.0 | 2.50 (dd, 14.2, 12.9) 1.96 (dd, 14.2, 2.1) |
| 20 | 36.7 | - | 36.9 | - | 49.2 | - |
| 21 | 32.3 | 2.03 (m) 1.35 (m) | 33.2 | 2.04 (m) 1.28 (m) | 30.8 | 2.12 (m) 1.89 (m) |
| 22 | 28.6 | 1.84 (m) 1.60 (m) | 31.8 | 1.72 (m) 1.45 (m) | 32.8 | 1.84 (m) 1.32 (m) |
| 23 | 28.7 | 0.99 (s) | 28.3 | 1.06 (s) | 28.3 | 1.05 (s) |
| 24 | 16.8 | 0.78 (s) | 16.7 | 0.83 (s) | 16.7 | 0.83 (s) |
| 25 | 16.7 | 0.91 (s) | 16.7 | 0.89 (s) | 16.7 | 0.89 (s) |
| 26 | 18.2 | 1.08 (s) | 18.8 | 1.14 (s) | 18.8 | 1.13 (s) |
| 27 | 19.8 | 1.40 (s) | 20.0 | 1.25 (s) | 20.1 | 1.27 (s) |
| 28 | 181.0 | - | 78.6 | 3.50 (d, 7.6) 3.10 (d, 7.6) | 78.4 | 3.48 (d, 7.6) 2.98 (d, 7.6) |
| 29 | 28.3 | 0.92 (s) | 28.5 | 0.92 (s) | 24.3 | 0.97 (s) |
| 30 | 66.5 | 3.55 (d, 11.1) 3.25 (d, 11.1) | 66.5 | 3.55 (d, 10.9) 3.30 (d, 10.9) | 209.2 | 9.40 (s) |
| 1′ | 110.2 | 5.23 (brs) | 105.9 | 4.39(d, 7.8) | 106.0 | 4.40 (d, 7.0) |
| 2′ | 89.6 | 4.21 (d, 5.2) | 79.1 | 3.87 (m) | 80.9 | 3.56 (m) |
| 3′ | 75.8 | 4.26 (dd, 5.2, 2.0) | 76.3 | 3.20 (m) | 78.0 | 3.53 (m) |
| 4′ | 83.9 | 4.19 (m) | 70.3 | 3.83 (m) | 71.1 | 3.49 (m) |
| 5′ | 62.5 | 3.83 (dd, 11.6, 4.9) 3.75 (dd, 11.6, 6.4) | 76.2 | 3.47 (m) | 78.4 | 3.47 (m) |
| 6′ | - | - | 62.3 | 3.72 (overlap) 3.70 (overlap) | 63.0 | 3.81 (dd, 11.9, 2.0) 3.60 (dd, 11.9, 5.8) |
| 1″ | 104.2 | 4.44 (d, 7.8) | 104.6 | 4.65 (d, 7.7) | 104.6 | 4.65 (d, 7.7) |
| 2″ | 75.0 | 3.18 (m) | 75.4 | 3.66 (m) | 76.2 | 3.20 (m) |
| 3″ | 78.0 | 3.25 (m) | 78.2 | 3.22 (m) | 77.9 | 3.33 (m) |
| 4″ | 71.3 | 3.36 (m) | 71.9 | 3.21 (m) | 71.9 | 3.21 (m) |
| 5″ | 77.9 | 3.34 (m) | 77.9 | 3.34 (m) | 66.5 | 3.84 (overlap) 3.17 (overlap) |
| 6″ | 62.4 | 3.85 (dd, 12.0, 2.5) 3.72 (dd, 12.0, 5.0) | 63.1 | 3.81 (dd, 11.9, 2.2) 3.61 (dd, 11.9, 5.9) | - | - |
| Compounds | IC50 (Mean ± SD μM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HeLa | HepG2 | U87 MG | |
| 1 | 3.2 ± 0.7 | 8.8 ± 2.2 | 5.7 ± 1.8 |
| 2 | 4.4 ± 1.1 | 21.9 ± 6.1 | 6.8 ± 2.2 |
| 3 | 2.2 ± 0.6 | 33.6 ± 6.8 | 7.7 ± 0.9 |
| 4 | 6.8 ± 1.2 | 7.9 ± 2.2 | 6.6 ± 1.6 |
| 5 | 9.5 ± 1.8 | 14.4 ± 2.1 | 2.3 ± 0.4 |
| 6 | 5.4 ± 0.9 | 8.7 ± 1.2 | 6.8 ± 1.1 |
| 7 | 5.2 ± 1.3 | 38.2 ± 6.6 | 5.4 ± 0.9 |
| Cisplatin a | 9.8 ± 0.4 | 12.1 ± 0.3 | 16.7± 0.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, X.; Hu, R.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, Y. Cytotoxic 13,28 Epoxy Bridged Oleanane-Type Triterpenoid Saponins from the Roots of Ardisia crispa. Molecules 2022, 27, 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031061
Yin X, Hu R, Zhou Y, Zhu W, Zhou Y. Cytotoxic 13,28 Epoxy Bridged Oleanane-Type Triterpenoid Saponins from the Roots of Ardisia crispa. Molecules. 2022; 27(3):1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031061
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Xin, Ruihang Hu, Yongqiang Zhou, Weiqian Zhu, and Ying Zhou. 2022. "Cytotoxic 13,28 Epoxy Bridged Oleanane-Type Triterpenoid Saponins from the Roots of Ardisia crispa" Molecules 27, no. 3: 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031061
APA StyleYin, X., Hu, R., Zhou, Y., Zhu, W., & Zhou, Y. (2022). Cytotoxic 13,28 Epoxy Bridged Oleanane-Type Triterpenoid Saponins from the Roots of Ardisia crispa. Molecules, 27(3), 1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27031061