Application of Maillard Reaction Products Derived Only from Enzymatically Hydrolyzed Sesame Meal to Enhance the Flavor and Oxidative Stability of Sesame Oil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of Glucoamylase on Sugar Content in Hydrolysate
2.2. Changes in Sugars and Free Amino Acids after the Maillard Reaction
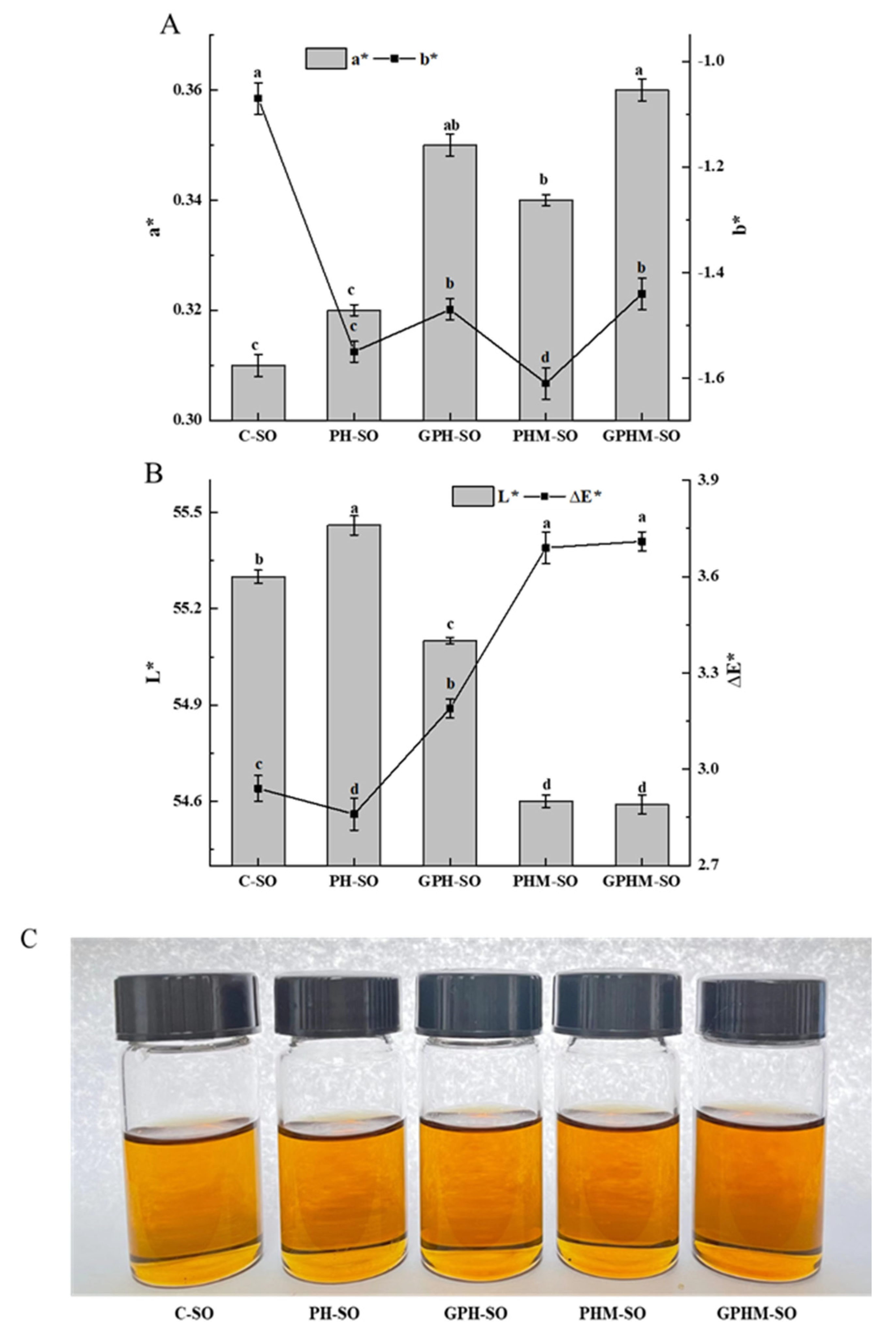
2.3. Color Changes in the Sesame Oils
2.4. Sensory Evaluation
2.5. Electronic Nose Analysis of the Oils
2.6. Volatile Compound Analysis
2.6.1. Volatile Compound Changes in Treated Oils
2.6.2. Aroma Activity Value Analysis
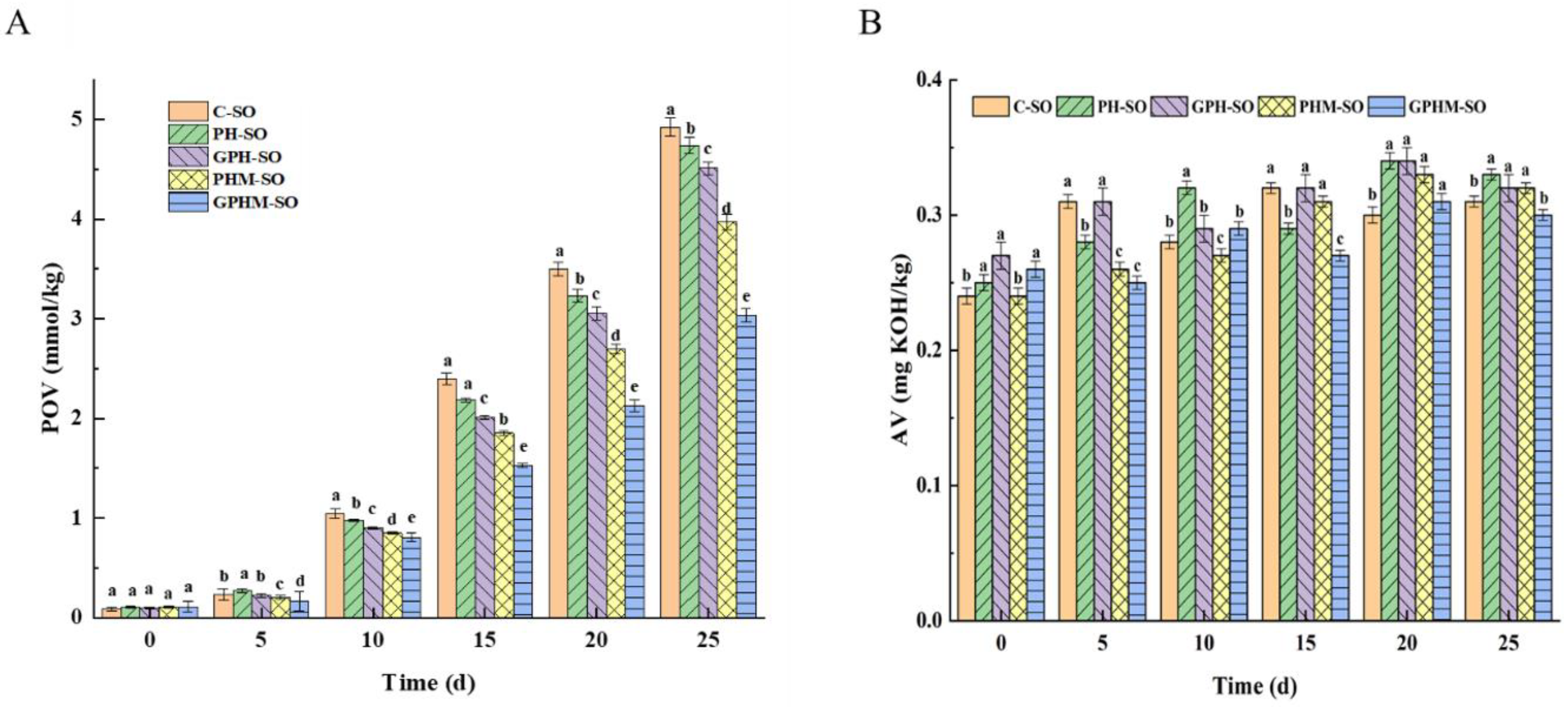
2.7. Oxidative Stability of Sesame Oil
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Sample Preparation
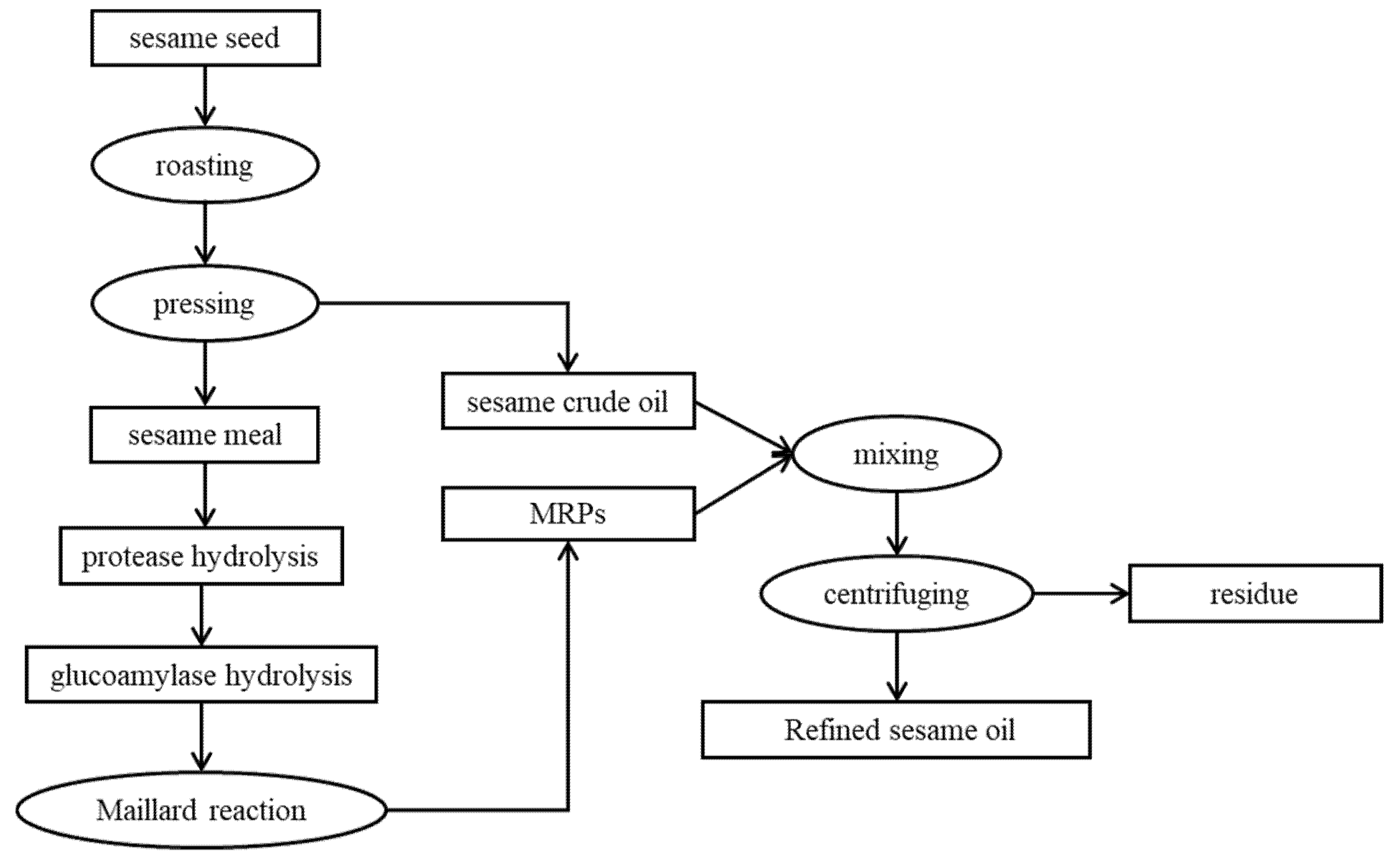
3.2.1. Preparation of Sesame Oil and Sesame Meal
3.2.2. Preparation of Sesame Meal Hydrolysate
3.2.3. Preparation of Maillard Reaction Products
3.2.4. Preparation of Oils Using MRPs
3.3. Analysis Methods
3.3.1. Determination of Reducing Sugar and Total Sugar Content
3.3.2. Determination of Free Amino Acids (FAAs)
3.3.3. Determination of Color
3.3.4. Descriptive Sensory Analysis of Sesame Oil
3.3.5. Electronic Nose Analysis of Sesame Oil
3.3.6. Volatile Compound Analysis by SPME-GC-MS
3.3.7. Calculation of Odor Activity Value
3.3.8. Oxidative Stability Analysis of Sesame Oil
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shin, B.R.; Song, H.W.; Lee, J.G.; Yoon, H.J.; Chung, M.S.; Kim, Y.S. Comparison of the contents of benzo(a)pyrene, sesamol and sesamolin, and volatiles in sesame oils according to origins of sesame seeds. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2016, 59, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langyan, S.; Yadava, P.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, N.C.; Bansal, R.; Yadav, R.; Kumar, A. Food and nutraceutical functions of Sesame oil: An underutilized crop for nutritional and health benefits. Food Chem. 2022, 389, 132990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Liu, Y.; Shi, L.; Wang, N.; Wang, X. Effect of roasting treatment on the chemical composition of sesame oil. LWT 2019, 101, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.A.M.; Uslu, N.; Özcan, M.M.; Juhaimi, F.A.; Ghafoor, K.; Babiker, E.E.; Osman, M.A.; Alqah, H.A. Effect of conventional oven roasting treatment on the physicochemical quality attributes of sesame seeds obtained from different locations. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arab, R.; Casal, S.; Pinho, T.; Cruz, R.; Freidja, M.L.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Hano, C.; Madani, K.; Boulekbache-Makhlouf, L. Effects of Seed Roasting Temperature on Sesame Oil Fatty Acid Composition, Lignan, Sterol and Tocopherol Contents, Oxidative Stability and Antioxidant Potential for Food Applications. Molecules 2022, 27, 4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Huang, F.; Huang, Y. Identification of key aroma-active compounds in sesame oil from microwaved seeds using E-nose and HS-SPME-GC× GC-TOF/MS. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, P.; Xi, H.; Zhao, W.; Wang, D.; Mao, J.; Zhang, S.; Sun, S.; Xie, J. Characterization of Traditional Chinese Sesame Oil by Using Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction/Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry, Electronic Nose, Sensory Evaluation, and RapidOxy. Foods 2022, 11, 3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, R.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Yue, X.; Ma, F.; Mao, J.; Wang, X.; Li, P. Adulteration detection of essence in sesame oil based on headspace gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 131373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chen, H.; Bai, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Long, W.; Lan, W.; She, Y.; Fu, H. Visual classification for sesame oil adulteration detection and quantification of compounds used as adulterants using flavor compounds targeted array sensor in combination with DD-SIMCA and PLS. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 357, 131335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Geng, F.; Deng, Q.; Huang, F.; Wang, J. Dynamic analysis of polar metabolites and volatile compounds in sesame seeds during roasting. Cereal Chem. 2019, 96, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Cui, Y.; Su, D.; Bin, T.; Yuan, Y.; He, S. Process optimization and anti-oxidative activity of peanut meal Maillard reaction products. LWT 2018, 97, 573–580. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, X.; Liu, P.; Xia, S.; Jia, C.; Mukunzi, D.; Zhang, X.; Xia, W.; Tian, H.; Xiao, Z. Temperature effect on the non-volatile compounds of Maillard reaction products derived from xylose–soybean peptide system: Further insights into thermal degradation and cross-linking. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Han, Y.F.; Wang, N.N.; Liu, H.M.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Wang, X.D. Improvement of the oxidative stability of cold-pressed sesame oil using products from the Maillard reaction of sesame enzymatically hydrolyzed protein and reducing sugars. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1524–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.-T.; Elam, E.; Ni, Z.-J.; Shen, Y.; Xia, B.; Thakur, K.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, J.-G.; Wei, Z.-J. The structure and flavor of low sodium seasoning salts in combination with different sesame seed meal protein hydrolysate derived Maillard reaction products. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Hu, L.-T.; Xia, B.; Ni, Z.-J.; Elam, E.; Thakur, K.; Zhang, J.-G.; Wei, Z.-J. Effects of different sulfur-containing substances on the structural and flavor properties of defatted sesame seed meal derived Maillard reaction products. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.F.; Cao, H.; Wei, C.K.; Thakur, K.; Liao, A.M.; Huang, J.H.; Wei, Z.J. Effect of sugar types on structural and flavor properties of peony seed derived Maillard reaction products. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Elfalleh, W.; He, S.; Tang, M.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, J.; Sun, H. Heating and cysteine effect on physicochemical and flavor properties of soybean peptide Maillard reaction products. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 2137–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.Z.; Zhao, J.L.; Tian, W.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, M.Y.; Zhao, G.M. Contribution of histidine and lysine to the generation of volatile compounds in Jinhua ham exposed to ripening conditions via Maillard reaction. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.T.; Ma, X.T.; Li, S.J.; Liu, H.M.; Shi, R. Comparison of key aroma-active compounds between roasted and cold-pressed sesame oils. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, E.; Hamzalıoğlu, A.; Gökmen, V. Investigations on the Maillard reaction in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) seeds induced by roasting. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4923–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yu, X.; Xu, L.; Gao, J.-M. Novel method for the producing area identification of Zhongning Goji berries by electronic nose. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.H.; Jeong, M.K.; Yeo, J.; Son, H.J.; Lim, C.L.; Hong, E.J.; Noh, B.S.; Lee, J. Application of solid phase-microextraction (SPME) and electronic nose techniques to differentiate volatiles of sesame oils prepared with diverse roasting conditions. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C80–C88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, S.M.; James, D.; Ali, Z. Data analysis for electronic nose systems. Mikrochim Acta 2006, 156, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.Q.; Liu, W.Y.; Xi, W.P.; Cao, D.; Zhang, H.J.; Ding, M.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y.Y.; Huang, K.X. Comparison of volatile compounds of hot-pressed, cold-pressed and solvent-extracted flaxseed oils analyzed by SPME-GC/MS combined with electronic nose: Major volatiles can be used as markers to distinguish differently processed oils. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, F. Effect of oilseed roasting on the quality, flavor and safety of oil: A comprehensive review. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150, 110791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cui, H.; Zhang, M.; Hayat, K.; Yu, J.; Xia, S.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, X. Improving the flavor and oxidation resistance of processed sunflower seeds with Maillard peptides. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2019, 12, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.S.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Ma, R.; Thakur, K.; Wei, Z.J. Effects of roasting level on physicochemical, sensory, and volatile profiles of soybeans using electronic nose and HS-SPME-GC-MS. Food Chem. 2020, 340, 127880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Physicochemical and sensory variables of Maillard reaction products obtained from Takifugu obscurus muscle hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2019, 290, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asikin, Y.; Kamiya, A.; Mizu, M.; Takara, K.; Tamaki, H.; Wada, K. Changes in the physicochemical characteristics, including flavour components and Maillard reaction products, of non-centrifugal cane brown sugar during storage. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Ni, Z.-J.; Hu, L.-T.; Elam, E.; Thakur, K.; Zhang, J.-G.; Wei, Z.-J. Development of meat flavors in peony seed-derived Maillard reaction products with the addition of chicken fat prepared under different conditions. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsoula, Z.; Liakopoulou-Kyriakides, M. Effect of endogenous antioxidants of sesame seeds and sesame oil to the thermal stability of edible vegetable oils. LWT 2010, 43, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Jeung, M.K.; Park, M.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.H. Effects of roasting conditions of sesame seeds on the oxidative stability of pressed oil during thermal oxidation. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-T.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.-M.; Xiao, W.-J.; Liu, S.-H.; Xia, W.-C.; Liu, Z.-L.; Yi, L.; Jiang, Z.-B. Synergistic effect of cellulase and xylanase during hydrolysis of natural lignocellulosic substrates. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Han, J.; Wei, C. Changes in the volatile profile, fatty acid composition and oxidative stability of flaxseed oil during heating at different temperatures. LWT 2021, 151, 112137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chong, Y.; Ding, Y.; Gu, S.; Liu, L. Determination of the effects of different washing processes on aroma characteristics in silver carp mince by MMSE–GC–MS, e-nose and sensory evaluation. Food Chem. 2016, 207, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.C.; Sivakanthan, S.; Vasantharuba, S. Effect of Star Fruit (Averrhoa carambola L.) By-product on Oxidative Stability of Sesame (Sesamum indicum) Oil under Accelerated Oven Storage and during Frying. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No Glucoamylase Treatment | Glucoamylase Treatment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of Sugar | Sugar Content (mg/g) | Consumption Rate (%) | Sugar Content (mg/g) | Consumption Rate (%) | ||
| PH | PHM | GPH | GPHM | |||
| Total sugar | 10.23 ± 0.36 | 8.18 ± 0.34 | 20.04 | 10.58 ± 0.28 | 8.04 ± 0.25 | 24.01 |
| Reducing sugar | 6.51 ± 0.21 | 4.74 ± 0.18 | 27.19 | 9.07 ± 0.24 | 5.97 ± 0.22 | 34.18 |
| No. | Amino Acids | Free Amino Acids (µg/g) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | GPH | PHM | GPHM | ||
| 1 | Asp | 19.48 ± 0.3 b | 22.17 ± 0.59 a | 14.41 ± 0.67 d | 17.19 ± 0.35 c |
| 2 | Thr | 9.11 ± 0.66 c | 9.37 ± 0.75 c | 12.72 ± 1.06 a | 10.52 ± 1.01 b |
| 3 | Ser | 2.85 ± 0.72 ab | 3.62 ± 0.45 a | 2.82 ± 0.27 b | 3.38 ± 0.29 ab |
| 4 | Glu | 4.37 ± 0.13 b | 6.33 ± 0.30 a | 4.68 ± 0.23 b | 6.82 ± 0.34 a |
| 5 | Gly | 10.31 ± 0.31 b | 10.49 ± 1.10 a | 9.89 ± 0.44 b | 10.70 ± 0.75 a |
| 6 | Ala | 51.32 ± 0.96 b | 52.80 ± 2.33 a | 47.85 ± 0.72 d | 49.49 ± 0.92 c |
| 7 | Cys | 0.41 ± 0.03 b | 0.35 ± 0.09 b | - | - |
| 8 | Val | 26.32 ± 1.24 a | 28.43 ± 1.30 ab | 23.17 ± 1.74 c | 25.14 ± 1.69 bc |
| 9 | Met | 69.56 ± 1.73 a | 69.07 ± 1.44 a | 64.15 ± 1.78 b | 64.33 ± 1.89 b |
| 10 | Ile | 123.27 ± 4.45 a | 123.30 ± 3.64 a | 116.25 ± 3.32 ab | 114.82 ± 3.23 b |
| 11 | Leu | 7.07 ± 0.78 b | 10.33 ± 0.77 a | 6.39 ± 0.71 b | 9.62 ± 0.72 a |
| 12 | Tyr | 91.77 ± 3.04 a | 89.39 ± 3.40 a | 83.49 ± 2.42 b | 80.42 ± 1.83 b |
| 13 | Phe | 10.30 ± 0.87 a | 8.58 ± 0.48 bc | 9.34 ± 0.69 ab | 7.47 ± 0.67 c |
| 14 | His | 86.57 ± 2.85 a | 77.37 ± 1.96 b | 52.57 ± 2.10 c | 45.39 ± 1.26 d |
| 15 | Lys | 11.84 ± 1.57 a | 6.16 ± 0.45 b | 7.12 ± 0.77 b | 5.24 ± 0.74 b |
| 16 | Arg | 5.07 ± 0.70 a | 4.94 ± 0.71 a | 3.68 ± 0.34 b | 5.36 ± 0.42 a |
| 17 | Pro | - | - | 5.03 ± 0.23 a | 4.89 ± 0.19 b |
| Samples | Toasted Sesame Aroma | Caramel Aroma | Aroma Persistence | Off-Flavor | Overall Satisfaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-SO | 5.54 ± 0.78 c | 2.76 ± 0.12 d | 4.65 ± 0.65 e | 3.66 ± 0.24 a | 5.65 ± 0.84 d |
| PH-SO | 5.78 ± 0.65 c | 2.83 ± 0.35 d | 4.88 ± 0.54 d | 3.74 ± 0.36 a | 5.82 ± 0.57 cd |
| GPH-SO | 5.65 ± 0.53 c | 3.45 ± 0.48 c | 5.21 ± 0.38 c | 2.32 ± 0.25 c | 5.93 ± 0.68 c |
| PHM-SO | 6.42 ± 0.69 b | 4.51 ± 0.46 b | 6.23 ± 0.86 b | 2.65 ± 0.46 b | 6.21 ± 0.75 b |
| GPHM-SO | 7.12 ± 1.02 a | 5.73 ± 0.63 a | 6.56 ± 0.75 a | 1.82 ± 0.22 d | 7.08 ± 0.85 a |
| No. | Chemical Compound | 1 Kis | Content (μm/mL) | 2 Odors | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-SO | PH-SO | GPH-SO | PHM-SO | GPHM-SO | S-SO | ||||
| Pyrazines | |||||||||
| 1 | Methylpyrazine | 781 | 13.48 ± 0.12 c | 24.41 ± 0.13 c | 26.02 ± 0.21 c | 29.98 ± 0.47 b | 32.38 ± 0.29 a | 28.28 ± 0.24 b | chocolate, meaty |
| 2 | 2,5-Dimethylpyrazine | 894 | 3.44 ± 0.08 d | 13.63 ± 0.23 c | 13.52 ± 0.29 c | 16.26 ± 0.65 b | 18.23 ± 0.37 a | 16.56 ± 0.32 b | potato-like |
| 3 | 2,6-Dimethylpyrazine | 894 | 10.79 ± 0.67 e | 11.19 ± 0.89 d | 11.88 ± 0.83 c | 13.41 ± 0.73 b | 15.11 ± 0.85 a | 11.18 ± 0.56 d | roasted, nutty |
| 4 | Ethylpyrazine | 881 | 7.27 ± 0.08 a | 3.77 ± 0.31 d | 4.30 ± 0.16 cd | 4.80 ± 0.46 bc | 5.29 ± 0.08 b | 3.23 ± 0.25 d | peanut buttery |
| 5 | 2,3-Dimethylpyrazine | 894 | 1.50 ± 0.11 c | 2.89 ± 0.26 b | 2.88 ± 0.19 b | 3.64 ± 0.15 ab | 3.86 ± 0.28 a | - | cocoa-like |
| 6 | 2-Ethyl-5-methylpyrazine | 994 | 9.03 ± 0.24 d | 8.80 ± 0.23 d | 8.75 ± 0.53 d | 10.56 ± 0.28 b | 11.74 ± 0.66 a | 9.80 ± 0.33 c | grassy |
| 7 | Trimethyl-pyrazine | 1008 | 8.06 ± 0.32 e | 10.39 ± 0.37 d | 10.49 ± 0.18 d | 12.48 ± 0.58 b | 13.03 ± 0.18 a | 11.29 ± 0.47 c | roasted |
| 8 | 3-Ethyl-2,5-dimethylpyrazine | 1107 | 4.85 ± 0.17 d | 6.33 ± 0.53 c | 6.15 ± 0.09 c | 7.55 ± 0.56 b | 8.41 ± 0.32 a | 7.38 ± 0.64 b | roasted |
| 9 | 2,3-Dimethyl-5-ethylpyrazine | 1102 | - | - | - | - | - | 5.23 ± 0.52 a | roasted, nutty |
| 10 | 2-Ethenyl-6-methylpyrazine | 984 | 0.52 ± 0.02 d | 0.73 ± 0.02 c | 0.72 ± 0.03 c | 1.03 ± 0.04 b | 1.15 ± 0.06 a | - | - |
| 11 | 2-Acetyl-3-methylpyrazine | 1130 | 5.78 ± 0.14 a | 3.49 ± 0.27 d | 3.34 ± 0.47 d | 4.04 ± 0.28 c | 4.56 ± 0.25 b | 4.23 ± 0.41 bc | grain-roasted |
| Furans | |||||||||
| 12 | 2-Pentyl-furan | 1040 | 0.15 ± 0.02 c | 0.11 ± 0.01 d | 0.30 ± 0.02 a | 0.31 ± 0.03 a | 0.27 ± 0.01 b | 0.25 ± 0.01 b | fruity |
| 13 | 1-(2-Furanyl)-ethanone | 878 | 1.75 ± 0.08 b | 1.49 ± 0.29 cd | 1.55 ± 0.08 c | 1.78 ± 0.09 b | 1.92 ± 0.09 a | 1.45 ± 0.16 d | coffee aroma |
| 14 | 2-Furanmethanol, acetate | 1009 | 0.46 ± 0.01 d | 0.56 ± 0.04 c | 0.58 ± 0.04 c | 0.63 ± 0.06 b | 0.72 ± 0.05 a | - | - |
| 15 | 2-Furanmethanol | 885 | 1.32 ± 0.06 d | 2.54 ± 0.08 c | 2.51 ± 0.05 c | 2.99 ± 0.12 b | 3.42 ± 0.14 a | 2.58 ± 0.21 c | cooked sugar |
| 16 | 2-Acetylfuran | 925 | - | - | - | - | - | 1.65 ± 0.12 a | sweet, popcorn |
| 17 | 5-Methyl-2-furancarboxaldehyde | 920 | 5.28 ± 0.14 c | 5.44 ± 0.28 c | 5.43 ± 0.29 c | 6.42 ± 0.42 b | 7.09 ± 0.18 a | 5.68 ± 0.24 c | caramel-like |
| 18 | 2-Acetyl-5-methylfuran | 967 | 0.33 ± 0.02 c | 0.34 ± 0.02 c | 0.34 ± 0.01 c | 0.42 ± 0.02 b | 0.49 ± 0.01 a | - | nutty aroma |
| Sulfur compounds | |||||||||
| 19 | 4-Methylthiazole | 832 | - | - | - | 0.84 ± 0.02 b | 0.94 ± 0.03 a | - | nutty, green |
| 20 | 2,4-Dimethylthiazole | 922 | - | 0.49 ± 0.02 d | 0.48 ± 0.02 d | 0.60 ± 0.03 c | 0.72 ± 0.01 b | 0.82 ± 0.06 a | like garlic |
| 21 | Dimethyl trisulfide | 972 | 0.67 ± 0.02 d | 0.87 ± 0.02 c | 0.96 ± 0.02 b | 1.10 ± 0.06 a | 1.14 ± 0.05 a | 0.78 ± 0.05 c | fresh onion |
| 22 | 2-Methyl-2-thiazoline | - | - | - | - | - | 1.16 ± 0.08 a | sulfurous | |
| 23 | 1-(2-Thienyl)-ethanone | 1030 | 0.57 ± 0.02 a | 0.37 ± 0.02 e | 0.40 ± 0.01 d | 0.48 ± 0.02 c | 0.53 ± 0.01 b | - | Sulfurous, nutty |
| Pyrroles | |||||||||
| 24 | 1-Methyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxaldehyde | 1054 | 1.73 ± 0.15 d | 1.74 ± 0.13 d | 1.67 ± 0.12 e | 1.89 ± 0.10 c | 2.25 ± 0.14 a | 2.12 ± 0.16 b | - |
| 25 | 1-Ethyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxaldehyde | 955 | 0.73 ± 0.07 b | 0.61 ± 0.06 c | 0.59 ± 0.04 c | 0.73 ± 0.04 ab | 0.86 ± 0.06 a | 0.79 ± 0.05 a | - |
| 26 | 1-(1H-Pyrrol-2-yl)-ethanone | 1035 | 2.81 ± 0.17 a | 1.88 ± 0.13 d | 1.66 ± 0.13 e | 2.17 ± 0.19 c | 2.52 ± 0.21 b | 2.26 ± 0.14 c | walnut |
| 27 | 1H-Pyrrole-2-carboxaldehyde | 988 | 5.08 ± 0.08 c | 5.00 ± 0.04 c | 4.95 ± 0.15 c | 6.05 ± 0.19 b | 6.62 ± 0.21 a | 5.25 ± 0.15 c | - |
| 28 | Methyl pyrrole-2-carboxylate | 1066 | 0.33 ± 0.04 b | 0.14 ± 0.01 b | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 0.15 ± 0.02 b | 0.16 ± 0.02 a | - | - |
| Pyridines | |||||||||
| 29 | 2-Methyl-pyridine | 787 | - | 0.35 ± 0.03 c | 0.54 ± 0.02 b | 0.27 ± 0.01 c | 0.71 ± 0.08 a | 0.57 ± 0.01 b | unpleasant |
| 30 | 1-(2-Pyridinyl)-ethanone | 1023 | 0.50 ± 0.05 a | 0.38 ± 0.03 c | 0.36 ± 0.02 c | 0.49 ± 0.04 ab | 0.46 ± 0.03 b | 0.59 ± 0.04 a | tobacco-like |
| 31 | Methyl nicotinate | 1054 | 0.82 ± 0.06 a | 0.47 ± 0.03 d | 0.46 ± 0.04 d | 0.58 ± 0.05 c | 0.69 ± 0.06 b | 0.27 ± 0.05 e | caramellic nutty |
| Aldehydes | |||||||||
| 32 | Hexanal | 806 | - | - | - | - | 0.88 ± 0.05 a | - | fruity, woody |
| 33 | Furfural | 831 | 6.81 ± 0.25 a | 5.22 ± 0.21 c | 5.44 ± 0.24 c | 6.10 ± 0.12 b | 6.79 ± 0.13 a | 5.14 ± 0.31 c | almond-like |
| 34 | Benzaldehyde | 982 | 1.71 ± 0.11 d | 1.79 ± 0.10 d | 1.81 ± 0.08 d | 2.18 ± 0.16 b | 2.40 ± 0.27 a | 1.92 ± 0.12 c | almond-like |
| 35 | (E)-2-Octenal | 1013 | 1.14 ± 0.04 d | 1.24 ± 0.02 bc | 1.19 ± 0.05 cd | 1.33 ± 0.07 ab | 1.37 ± 0.05 a | 1.09 ± 0.08 d | cooked rice |
| 36 | Heptanal | 917 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.78 ± 0.06 a | fatty, rancid |
| Ketones | |||||||||
| 37 | 3-Octen-2-one | 960 | - | 0.03 ± 0.01 b | - | 0.03 ± 0.01 b | 0.12 ± 0.02 a | - | fruity, lemon |
| 38 | Isophorone | 1097 | - | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 0.12 ± 0.02 b | 0.14 ± 0.01 a | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | 0.15 ± 0.01 a | like camphor |
| 39 | 1,4-Cyclohex-2-enedione | 1044 | 0.26 ± 0.02 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 b | 0.19 ± 0.02 b | 0.24 ± 0.02 b | 0.29 ± 0.02 a | - | - |
| 40 | Acetophenone | 1029 | 1.13 ± 0.03 d | 1.60 ± 0.08 c | 1.57 ± 0.05 c | 1.84 ± 0.06 b | 2.12 ± 0.11 a | 1.75 ± 0.11 b | oranges |
| 41 | 2-Octanone | 1007 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.56 ± 0.04 a | soapy, buttery |
| Phenols | |||||||||
| 42 | 2- Methoxy-phenol | 1090 | 8.79 ± 0.14 d | 9.62 ± 0.19 c | 8.93 ± 0.11 d | 11.18 ± 0.15 b | 12.81 ± 0.28 a | 7.56 ± 0.25 e | smoky |
| 43 | Phenol | 901 | 0.61 ± 0.03 a | 0.45 ± 0.03 c | 0.42 ± 0.02 c | 0.54 ± 0.04 b | 0.63 ± 0.05 a | 0.53 ± 0.04 b | fried meat |
| 44 | 4-Ethyl-2-methoxyphenol | 1303 | 0.51 ± 0.04 a | 0.30 ± 0.02 c | 0.27 ± 0.03 c | 0.36 ± 0.02 b | 0.29 ± 0.03 c | - | slightly sweet |
| 45 | 2-Methoxy-4-vinylphenol | 1293 | 0.96 ± 0.07 b | 0.81 ± 0.04 c | 0.68 ± 0.05 d | 0.91 ± 0.06 b | 1.17 ± 0.08 a | 0.88 ± 0.06 c | roasted peanut |
| 46 | 2,3-Methylenedioxyphenol | 1245 | 0.98 ± 0.09 c | 1.42 ± 0.08 b | 1.04 ± 0.06 c | 1.44 ± 0.07 b | 1.89 ± 0.06 a | 1.53 ± 0.05 b | - |
| Alcohols | |||||||||
| 47 | 1-Octen-3-ol | 969 | 1.12 ± 0.06 c | 1.00 ± 0.08 c | 1.06 ± 0.07 c | 1.22 ± 0.05 b | 1.37 ± 0.05 a | 1.23 ± 0.05 b | strong earthy |
| 48 | 1-Octanol | 1059 | - | 0.28 ± 0.02 b | 0.33 ± 0.07 ab | 0.34 ± 0.03 ab | 0.38 ± 0.03 a | 0.24 ± 0.03 b | orange–rose |
| 49 | Benzyl alcohol | 1036 | 0.18 ± 0.02 b | 0.17 ± 0.02 b | 0.15 ± 0.01 b | 0.18 ± 0.02 b | 0.23 ± 0.01 a | 0.14 ± 0.02 b | slightly sweet |
| No. | Chemical | Odor Threshold (mg/m3) | OAVs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | C-SO | PH-SO | GPH-SO | PHM-SO | GPHM-SO | S-SO | ||
| 1 | Methyl-pyrazine | 27 | 0.50 | 0.90 | 0.96 | 1.11 | 1.20 | 1.05 |
| 2 | 2,5-Dimethyl-pyrazine | 2.6 | 1.32 | 5.24 | 5.20 | 6.25 | 7.01 | 6.37 |
| 3 | 2,6-Dimethyl-Pyrazine | 1.021 | 10.57 | 10.96 | 11.64 | 13.13 | 14.80 | 10.95 |
| 4 | 2,3-Dimethyl-pyrazine | 0.123 | 12.20 | 23.50 | 23.41 | 29.59 | 31.38 | - |
| 5 | 2-Ethyl-5-methyl-pyrazine | 0.32 | 28.24 | 27.53 | 27.36 | 33.03 | 36.71 | 30.63 |
| 6 | Trimethyl-pyrazine | 0.29 | 27.82 | 35.84 | 36.18 | 43.05 | 44.94 | 38.93 |
| 7 | 3-Ethyl-2,5-dimethyl-pyrazine | 0.024 | 202.10 | 263.80 | 256.30 | 314.60 | 350.40 | 307.50 |
| 8 | 2-Pentyl-furan | 0.1 | 1.50 | 1.20 | 3.10 | 3.20 | 2.80 | 2.50 |
| 9 | 4-Methylthiazole | 0.055 | - | - | - | 15.27 | 17.09 | - |
| 10 | Dimethyl-trisulfide | 0.0025 | 268.00 | 348.00 | 384.00 | 440.00 | 460.00 | 328.00 |
| 11 | Hexanal | 0.08 | - | - | - | - | 11.00 | - |
| 12 | Benzaldehyde | 0.06 | 28.57 | 29.67 | 30.17 | 36.17 | 39.83 | 32.06 |
| 13 | 2- Methoxy-phenol | 3 | 2.93 | 3.21 | 2.98 | 3.72 | 4.27 | 2.52 |
| 14 | 1-Octen-3-ol | 0.001 | 1120.23 | 1000.28 | 1061.13 | 1217.51 | 1367.56 | 1230.80 |
| Oil Samples | Logistic Fitting Curve | R2 | Forecast Storage Time (d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C-SO | 0.996 | 31 | |
| PH-SO | 0.997 | 33 | |
| GPH-SO | 0.998 | 33 | |
| PHM-SO | 0.995 | 53 | |
| GPHM-SO | 0.988 | 60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, G.; He, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Sun, H. Application of Maillard Reaction Products Derived Only from Enzymatically Hydrolyzed Sesame Meal to Enhance the Flavor and Oxidative Stability of Sesame Oil. Molecules 2022, 27, 8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248857
Ma G, He S, Liu S, Zhang Z, Zhang T, Wang L, Ma Y, Sun H. Application of Maillard Reaction Products Derived Only from Enzymatically Hydrolyzed Sesame Meal to Enhance the Flavor and Oxidative Stability of Sesame Oil. Molecules. 2022; 27(24):8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248857
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Gang, Shudong He, Shuyun Liu, Zuoyong Zhang, Tao Zhang, Lei Wang, Youshui Ma, and Hanju Sun. 2022. "Application of Maillard Reaction Products Derived Only from Enzymatically Hydrolyzed Sesame Meal to Enhance the Flavor and Oxidative Stability of Sesame Oil" Molecules 27, no. 24: 8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248857
APA StyleMa, G., He, S., Liu, S., Zhang, Z., Zhang, T., Wang, L., Ma, Y., & Sun, H. (2022). Application of Maillard Reaction Products Derived Only from Enzymatically Hydrolyzed Sesame Meal to Enhance the Flavor and Oxidative Stability of Sesame Oil. Molecules, 27(24), 8857. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248857







