A Model Iron Gall Ink: An In-Depth Study of Ageing Processes Involving Gallic Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Method Optimisation
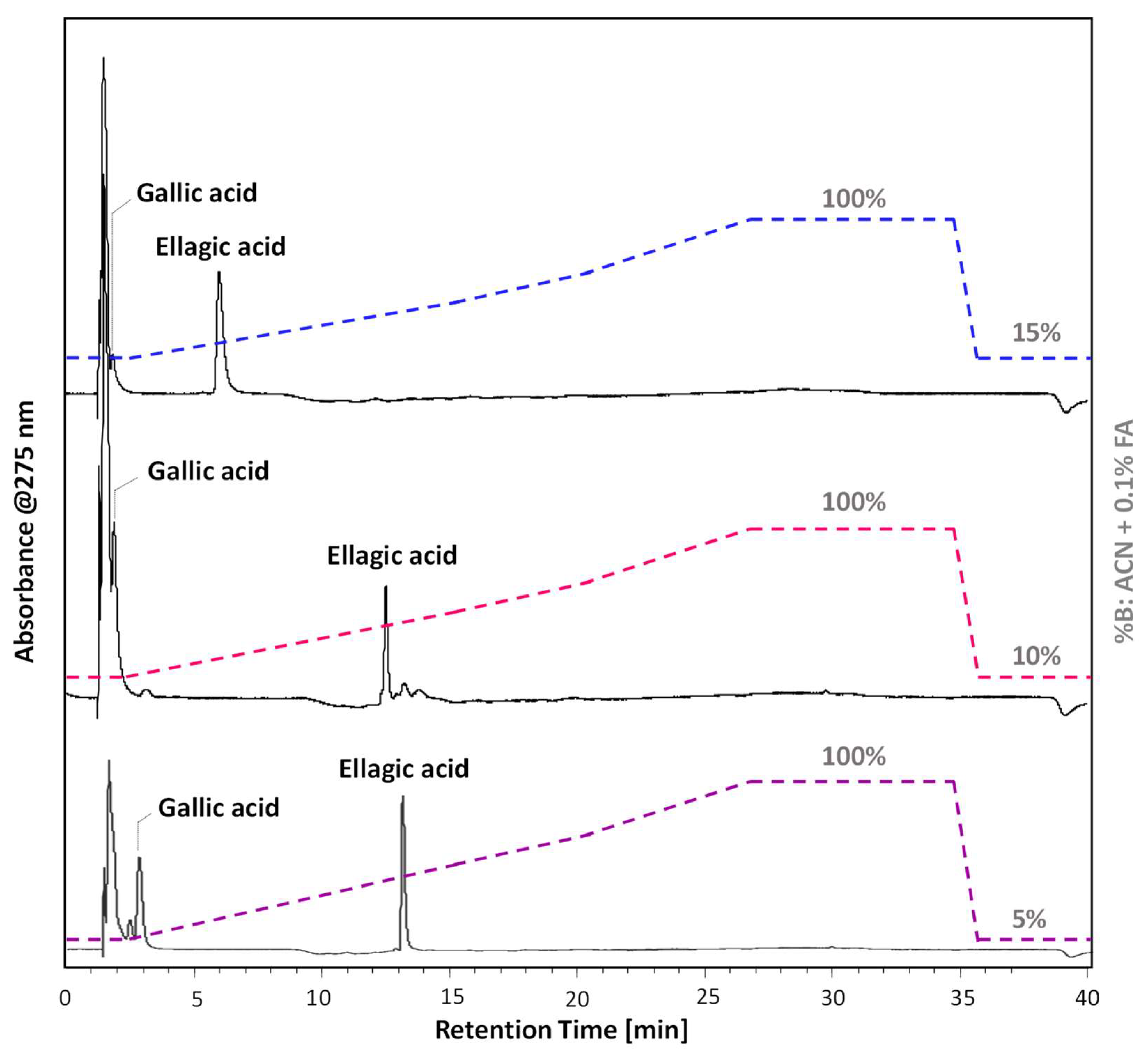
2.1.1. Chromatographic Method Optimisation
2.1.2. Extraction Method Optimisation
2.2. Model Gallic Acid Ink
- the dimerisation promotes the formation of digallic acids intermediates, and subsequently the C-C bond is formed and a dehydration reaction takes place.
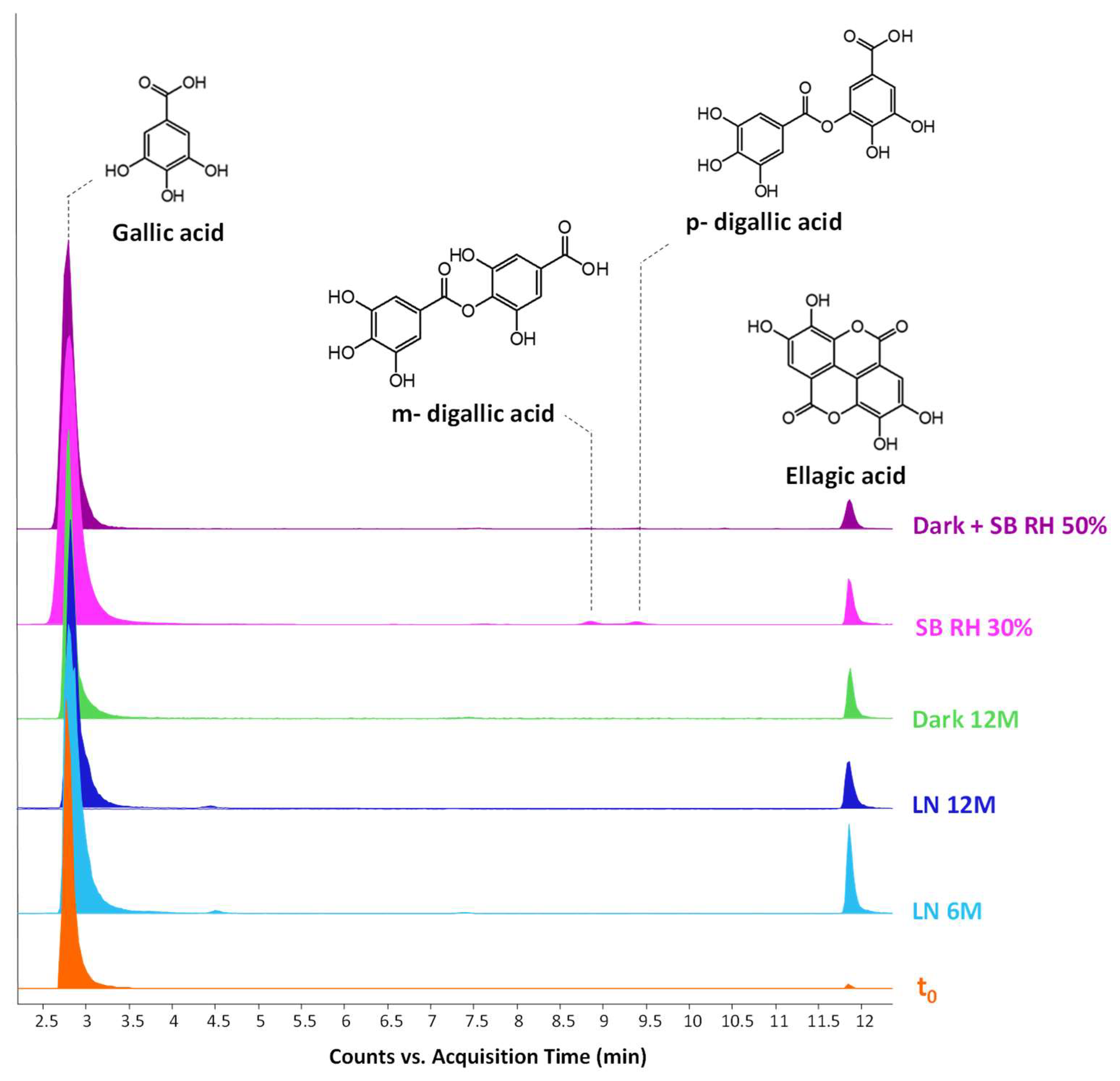
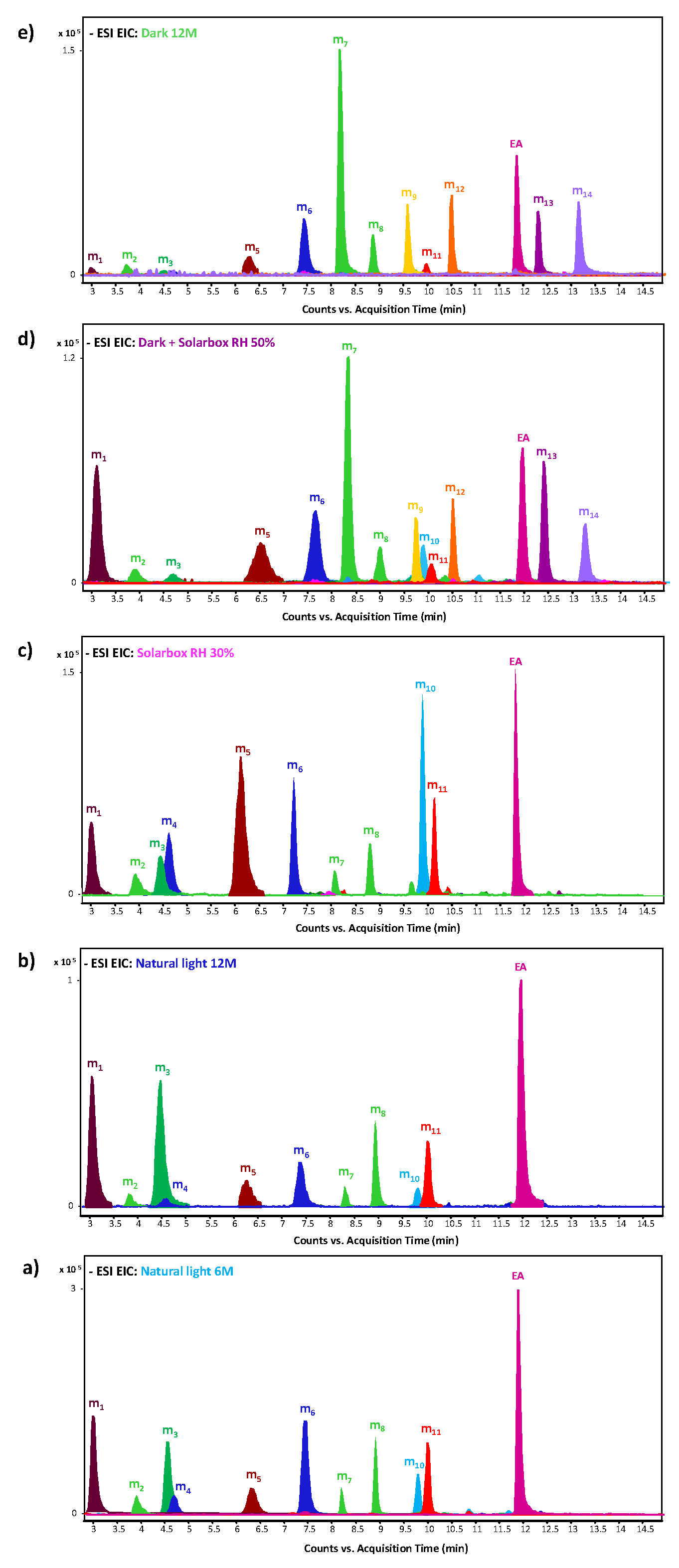
2.3. Ageing Degradation Markers
2.4. Colorimetric Measurements
2.5. Cases Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Solvents
3.2. Reference Model Ink
3.3. Reference Mock-Ups and Ageing Tests
3.4. Historical Samples of Ink Handwriting
3.5. Sample Treatments
3.6. Colorimetric Measurements
3.7. HPLC-DAD-MS2 Analysis
3.8. Quantitative Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Sharma, N.; Agarwal, A.; Negi, Y.; Bhardwaj, H.; Jaiswal, J. History and Chemistry of Ink—A Review. World J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 3, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar]
- Laporte, G.M.; Stephens, J.C. Analysis Techniques Used for the Forensic Examination of Writing and Printing Inks. In Forensic Chemistry Handbook; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 225–250. [Google Scholar]
- Drury, N.; Ramotowski, R.; Moini, M. A Comparison between DART-MS and DSA-MS in the Forensic Analysis of Writing Inks. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 289, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pines, C.C. The Story of Ink. Am. J. Police Sci 1931, 2, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, N.; Nabais, P.; de Freitas, V.; Lopes, J.A.; Melo, M.J. In-Depth Phenolic Characterization of Iron Gall Inks by Deconstructing Representative Iberian Recipes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz Hidalgo, R.J.; Córdoba, R.; Nabais, P.; Silva, V.; Melo, M.J.; Pina, F.; Teixeira, N.; Freitas, V. New Insights into Iron-Gall Inks through the Use of Historically Accurate Reconstructions. Herit. Sci. 2018, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, J.; Strlic, M. Iron Gall Inks: On Manufacture Characterisation, Degradation and Stabilisation; National and University Library of Slovenia: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2006; ISBN 9616551191. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, D.N. Forty Centuries of Ink or a Chronological Narrative Concerning Ink and Its Backgrounds; C.Griffin & Company Ltd.: London, UK, 1904. [Google Scholar]
- Degano, I.; Mattonai, M.; Sabatini, F.; Colombini, M.P. A Mass Spectrometric Study on Tannin Degradation within Dyed Woolen Yarns. Molecules 2019, 24, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, A.F.; Özkasikci, D.; Fürtauer, S.; Reinelt, M. The Effect of Deprotonation on the Reaction Kinetics of an Oxygen Scavenger Based on Gallic Acid. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, A.F.; Sangerlaub, S.; Muller, K. Gallic Acid as an Oxygen Scavenger in Bio-Based Multilayer Packaging Films. Materials 2017, 10, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkhili, E.; Loonis, M.; Mihai, S.; El Hajji, H.; Dangles, O. Reactivity of Food Phenols with Iron and Copper Ions: Binding, Dioxygen Activation and Oxidation Mechanisms. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1186–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhani, B.; Sharma, N.; Kakkar, R. Gallic Acid: A Versatile Antioxidant with Promising Therapeutic and Industrial Applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 27540–27557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahkeshani, N.; Farzaei, F.; Fotouhi, M.; Alavi, S.S.; Bahramsoltani, R.; Naseri, R.; Momtaz, S.; Abbasabadi, Z.; Rahimi, R.; Farzaei, M.H.; et al. Pharmacological Effects of Gallic Acid in Health and Disease: A Mechanistic Review. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2019, 22, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, M.J.; Otero, V.; Nabais, P.; Teixeira, N.; Pina, F.; Casanova, C.; Fragoso, S.; Sequeira, S.O. Iron—Gall Inks: A Review of Their Degradation Mechanisms and Conservation Treatments. Herit. Sci. 2022, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouchon, V.; Belhadj, O.; Duranton, M.; Gimat, A.; Massiani, P. Application of Arrhenius Law to DP and Zero-Span Tensile Strength Measurements Taken on Iron Gall Ink Impregnated Papers: Relevance of Artificial Ageing Protocols. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, J.; Strlič, M.; Budnar, M.; Malešič, J.; Šelih, V.S.; Simčič, J. Stabilisation of Corrosive Iron Gall Inks. Acta Chim. Slov. 2003, 50, 763–770. [Google Scholar]
- Strlič, M.; Menart, E.; Cigić, I.K.; Kolar, J.; de Bruin, G.; Cassar, M. Emission of Reactive Oxygen Species during Degradation of Iron Gall Ink. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kolar, J.; Štolfa, A.; Strlič, M.; Pompe, M.; Pihlar, B.; Budnar, M.; Simčič, J.; Reissland, B. Historical Iron Gall Ink Containing Documents—Properties Affecting Their Condition. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 555, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, O.; Malzer, W.; Kanngiesser, B.; Beckhoff, B. Characterization of Iron-Gall Inks in Historical Manuscripts and Music Compositions Using x-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry. X-ray Spectrom. 2004, 33, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duh, J.; Krstić, D.; Desnica, V.; Fazinić, S. Non-Destructive Study of Iron Gall Inks in Manuscripts. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2018, 417, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerf, A.; Wagner, F.E.; Dreher, M.; Espejo, T.; Pérez-Rodríguez, J.L. Mössbauer Study of Iron Gall Inks on Historical Documents. Herit. Sci. 2021, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, B.; Bulska, E.; Stahl, B.; Heck, M.; Ortner, H.M. Analysis of Fe Valence States in Iron-Gall Inks from XVIth Century Manuscripts by 57Fe Mössbauer Spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 527, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcon, I.; Kolar, J.; Kodre, A.; Hanzel, D.; Strlič, M. XANES Analysis of Fe Valence in Iron Gall Inks. X-ray Spectrom. 2007, 36, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, M.; Hahn, O.; Woodland, A.B.; Rickers, K. The Oxidation State of Iron Determined by Fe K-Edge XANES -Application to Iron Gall Ink in Historical Manuscripts. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2009, 24, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proost, K.; Janssens, K.; Wagner, B.; Bulska, E.; Schreiner, M. Determination of Localized Fe2+/Fe3+ Ratios in Inks of Historic Documents by Means of μ-XANES. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2004, 213, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouchon-Quillet, V.; Remazeilles, C.; Bernard, J.; Wattiaux, A.; Fournes, L. The Impact of Gallic Acid on Iron Gall Ink Corrosion. Appl. Phys. A 2004, 79, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursescu, M.; Mǎluţan, T.; Ciovicǎ, S. Iron Gall Inks Influence on Papers’ Thermal Degradation FTIR Spectroscopy Applications. Eur. J. Sci. Theol. 2009, 5, 71–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer, N.; Carme Sistach, M. Analysis of Sediments on Iron Gall Inks in Manuscripts. Restaurator 2013, 34, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, S.; Guild, S.; Orlandini, V.; Trojan-Bedynski, M. Microfade Testing of 19th Century Iron Gall Inks. Res. Tech. Stud. Spec. Group Postprints 2010, 2, 56–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kosek, J.; Barry, C. Investigating the Condition of Iron Gall Ink Drawings: Developing an Assessment Survey. J. Inst. Conserv. 2019, 42, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fearn, T.; Strlič, M. Photodegradation of Iron Gall Ink Affected by Oxygen, Humidity and Visible Radiation. Dye Pigment 2022, 198, 109947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.S.; Mahon, P.J.; Creagh, D.C. Raman Analysis of Iron Gall Inks on Parchment. Vib. Spectrosc. 2006, 41, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degano, I.; La Nasa, J. Trends in High Performance Liquid Chromatography for Cultural Heritage. Top. Curr. Chem. 2016, 374, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degano, I.; Ribechini, E.; Modugno, F.; Colombini, M.P. Analytical Methods for the Characterization of Organic Dyes in Artworks and in Historical Textiles. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2009, 44, 363–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daley, S.K.; Downer-Riley, N. The Biomimetic Synthesis of Balsaminone A and Ellagic Acid via Oxidative Dimerization. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2026–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolić, G.; Veselinović, A.; Mitić, Ž.; Živanović, S. HPLC-DAD Study of Gallic Acid Autoxidation in Alkaline Aqueous Solutions and the Influence of MG(II) Ion. Acta Fac. Med. Naissensis 2011, 28, 219–224. [Google Scholar]
- Caregnato, P.; Gara, P.M.D.; Bosio, G.N.; Gonzalez, C.; Michelini, C.; Ma, D.O. Theoretical and Experimental Investigation on the Oxidation of Gallic Acid by Sulfate Radical Anions. J. Phys. Chem. A 2008, 112, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, D.; Andreux, P.A.; Valdés, P.; Singh, A.; Rinsch, C.; Auwerx, J. Impact of the Natural Compound Urolithin A on Health, Disease, and Aging. Trends Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toney, A.M.; Fox, D.; Chaidez, V.; Ramer-Tait, A.E.; Chung, S. Immunomodulatory Role of Urolithin a on Metabolic Diseases. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Barrio, R.; Edwards, C.A.; Crozier, A. Colonic Catabolism of Ellagitannins, Ellagic Acid, and Raspberry Anthocyanins: In Vivo and in Vitro Studies. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2011, 39, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reissland, B.; Cowan, M.W. The Light Sensitivity of Iron Gall Inks. Stud. Conserv. 2002, 47, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csefalvayová, L.; Havlínová, B.; Čeppan, M.; Jakubíková, Z. The Influence of Iron Gall Ink on Paper Ageing. Restaurator 2007, 28, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Extraction Method | mg/g (Average) of Gallic Acid | S (mg/g) | CV % |
|---|---|---|---|
| EDTA-DMF (0.1% of EDTA in H2O/DMF 1:1) | 10.4 | 0.4 | 4 |
| Methanolysis (HCl/MeOH 1:30) redissolved in H2O/MeOH | 2.7 | 0.6 | 23 |
| Ageing Marker | tR (min) | [M-H]− | MS2 | Raw Formula (ppm) | Hypothesised Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m1 | 2.9 | 213.0041 | 151.002, 123.007, 107.014 | C8H6O7 −0.3 | 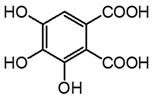 |
| m2 | 3.9 | 221.0094 | 177.016, 149.023, 132.018, 121.026, 109.029, 105.031 | C10H6O6 1.2 | 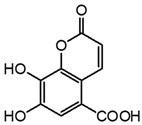 |
| m3 | 4.4 | 197.0097 | 152.010, 125.024, 107.013 | C8H6O6 3.1 | 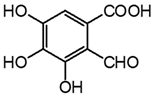 |
| m4 | 4.6 | 211.0254 | 167.032, 150.915, 139.040, 124.016, 109.028 | C9H8O6 3.2 | n.a. |
| m5 | 6.2 | 181.0139 | 137.022, 109.029 | C8H6O5 −1.4 |  |
| m6 | 7.3 | 211.0245 | 167.032, 150.920, 132.904, 124.015, 107.013 | C9H8O6 −1.7 | n.a. |
| m7 | 8.2 | 221.0093 | 177.015, 166.859, 148.012, 133.025, 123.008, 115.016, 103.016 | C10H6O6 0.1 | 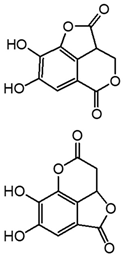 |
| m8 | 8.9 | 221.0088 | 177.015, 160.014, 149.021, 133.025, 121.029, 105.031 | C10H6O6 −1.8 | |
| m9 | 9.5 | 347.0040 | 259.026, 213.021, 187.041, 109.030 | C15H8O10 −1.8 |  |
| m10 | 9.7 | 195.0303 | 150.031, 136.017, 123.044, 108.021 | C9H8O5 1.9 | 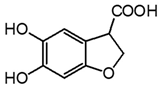 |
| m11 | 9.9 | 239.0169 | 193.009, 167.035, 152.011, 125.024, 107.013 | C10H8O7 −3.5 |  |
| m12 | 10.5 | 389.0145 | 301.037, 258.018, 165.020, 123.010 | C17H10O11 −1.2 | n.a. |
| m13 | 12.3 | 287.0198 | 243.025, 225.015, 197.020, 171.042, 159.041, 143.047 | C14H8O7 0.3 | 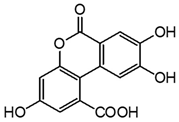 |
| m14 | 13.2 | 315.0145 | 287.021, 271.024, 243.031, 215.036, 197.025, 187.040, 171.046, 159.047, 143.050 | C15H8O8 0.5 | 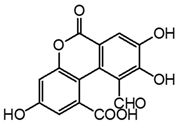 |
| Analyte | Chemical Structure | tR (min) HPLC-DAD | λmax (nm) | tR (Min) HPLC-MS | MS ([M-H]−) | MS2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gallic acid | 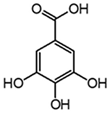 | 2.8 | 271 | 2.8 | 169.014 | 125.024, 107.014 |
| Ellagic acid | 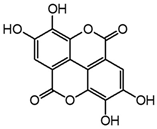 | 13.1 | 255, 367 | 11.8 | 300.997 | 300.994, 283.993, 257.006, 229.014, 185.026, 145.029 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferretti, A.; Sabatini, F.; Degano, I. A Model Iron Gall Ink: An In-Depth Study of Ageing Processes Involving Gallic Acid. Molecules 2022, 27, 8603. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238603
Ferretti A, Sabatini F, Degano I. A Model Iron Gall Ink: An In-Depth Study of Ageing Processes Involving Gallic Acid. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8603. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238603
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerretti, Adele, Francesca Sabatini, and Ilaria Degano. 2022. "A Model Iron Gall Ink: An In-Depth Study of Ageing Processes Involving Gallic Acid" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8603. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238603
APA StyleFerretti, A., Sabatini, F., & Degano, I. (2022). A Model Iron Gall Ink: An In-Depth Study of Ageing Processes Involving Gallic Acid. Molecules, 27(23), 8603. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238603








