Aptamer Molecular Beacon Sensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Ochratoxin A
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
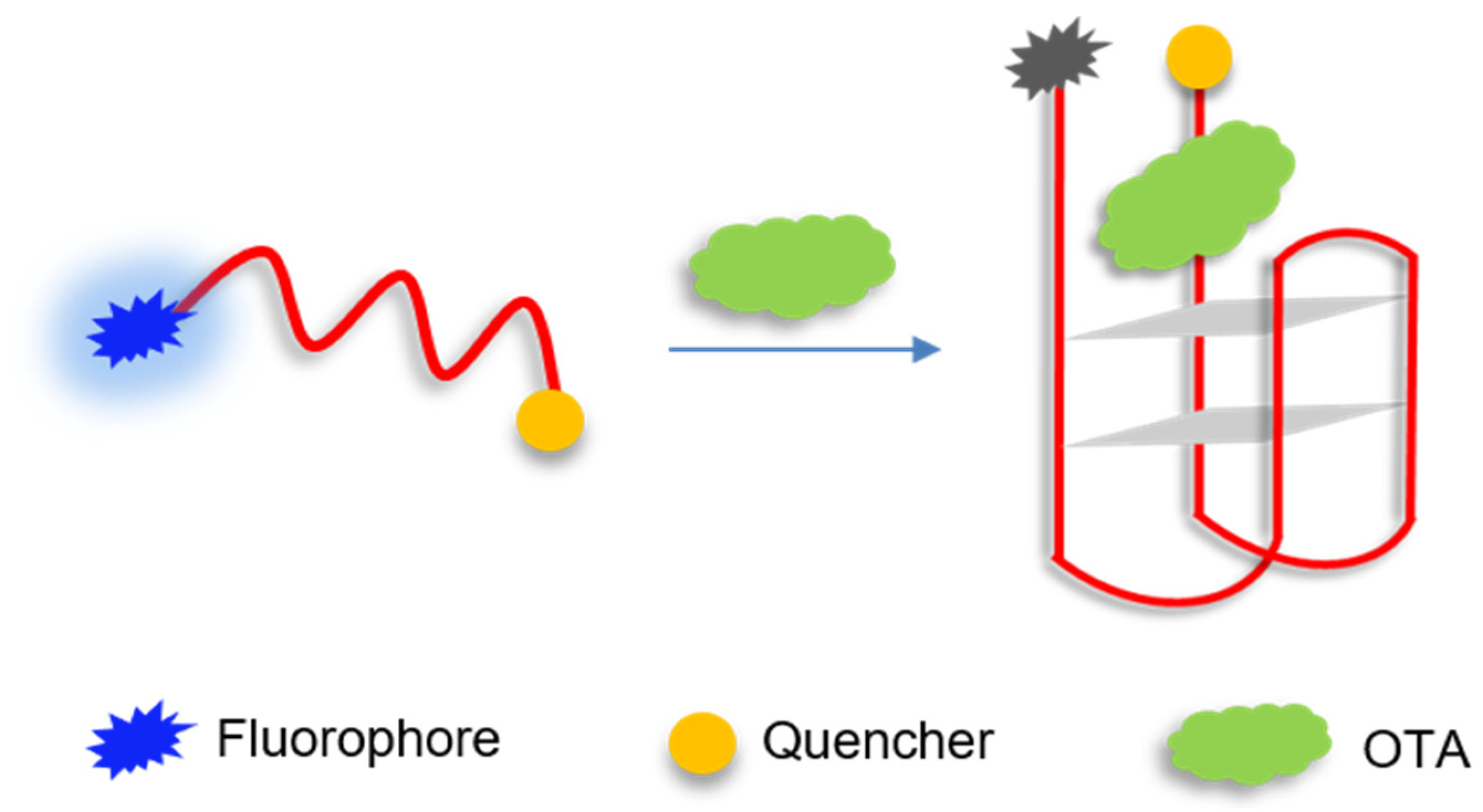
2.1. Principle of Molecular Aptamer Beacon Sensor for OTA
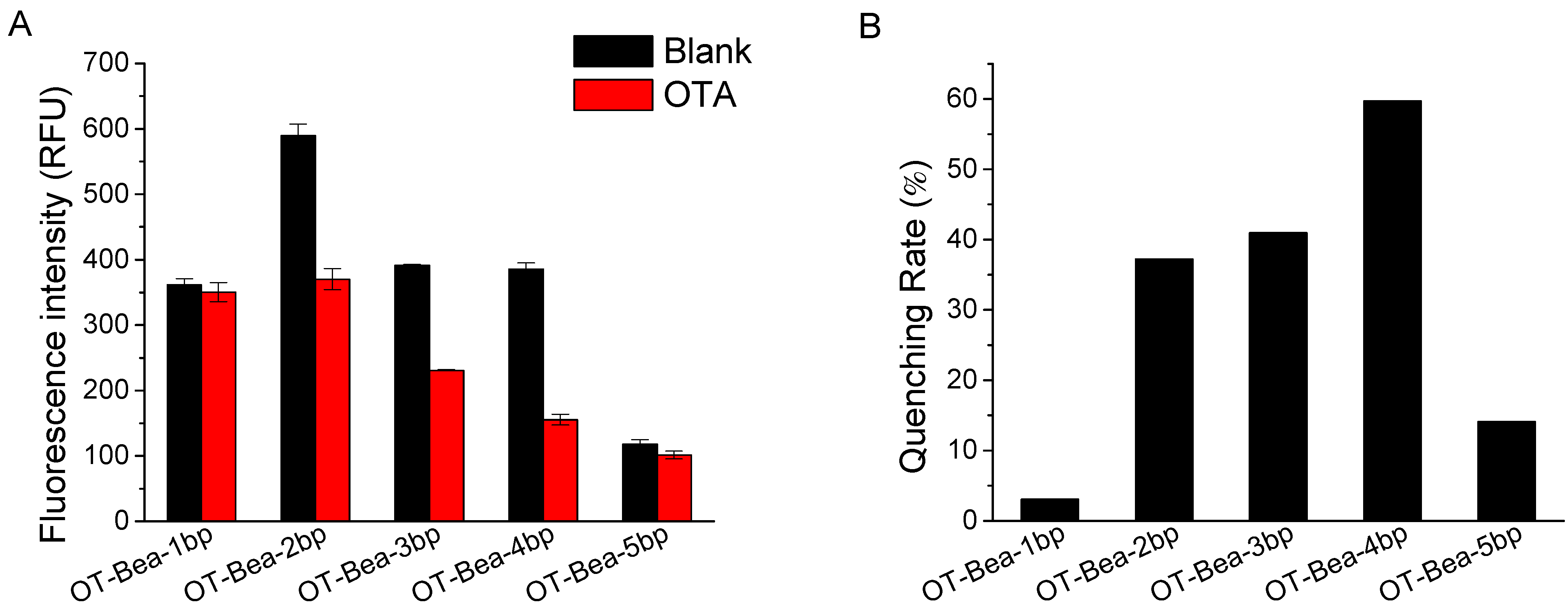
2.2. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
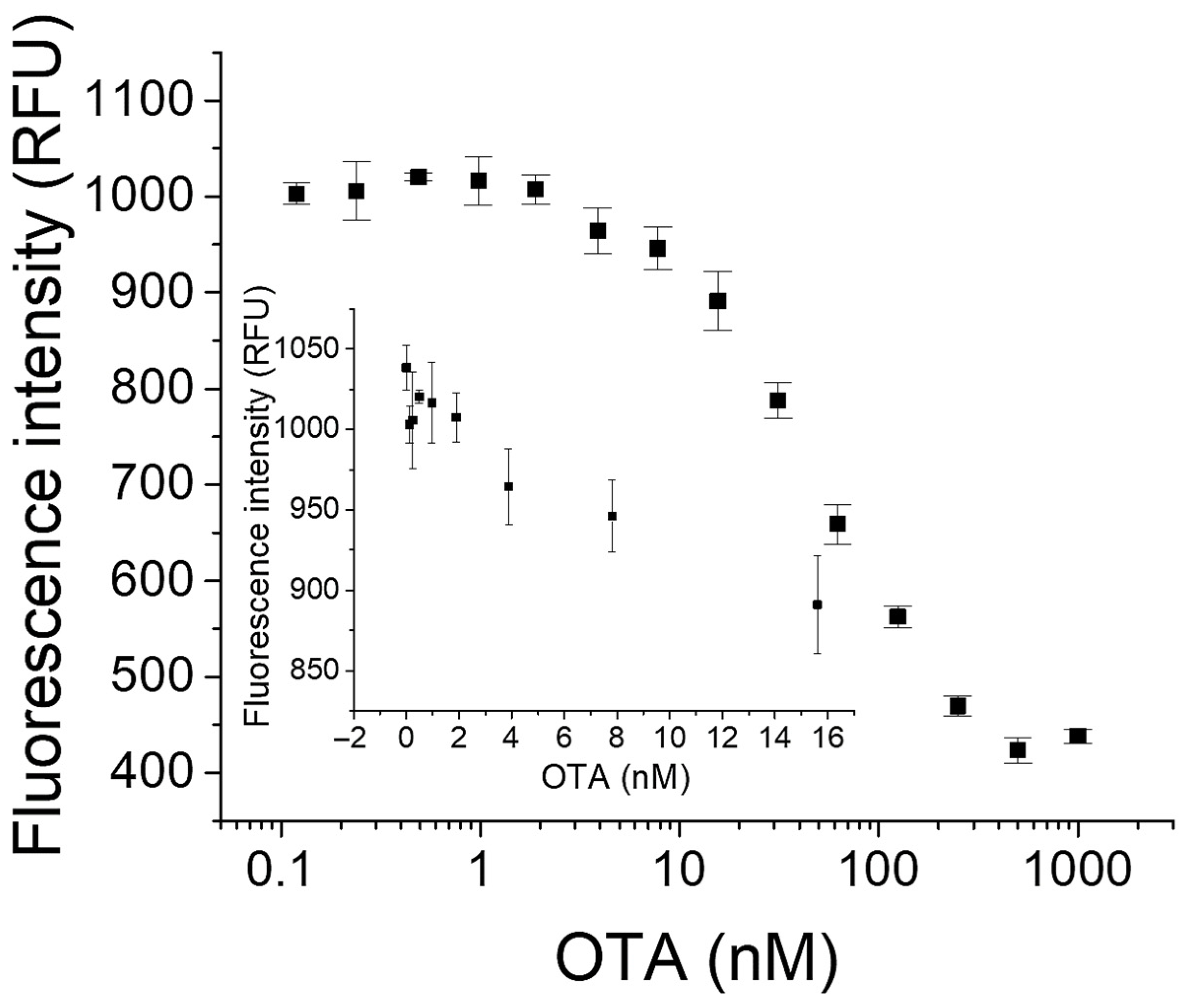
2.3. Determination of OTA
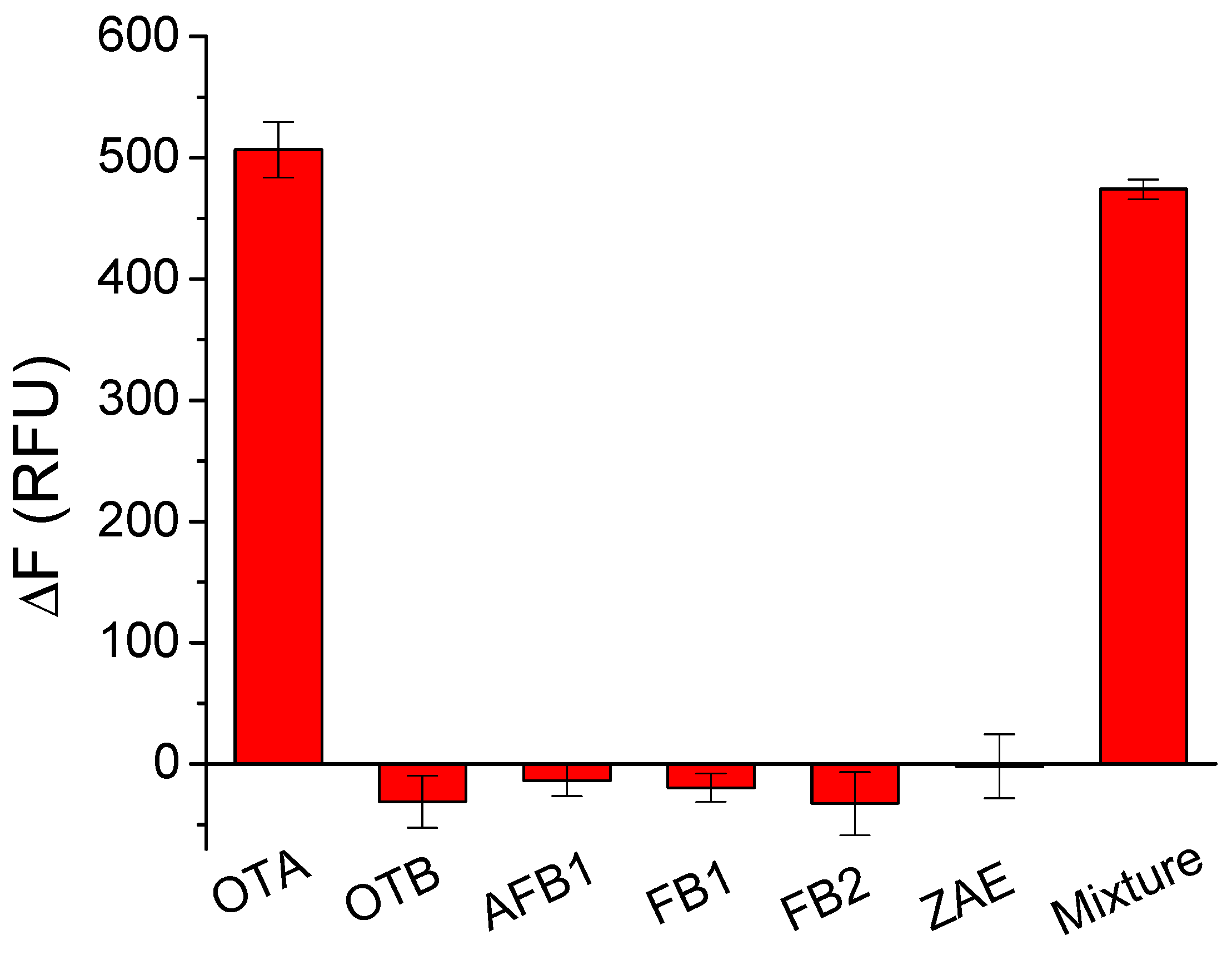
2.4. Selectivity Test
2.5. OTA Detection in Complex Samples
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. OTA Detection
3.3. OTA Detection in Complex Sample Matrixes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bayman, P.; Baker, J.L.; Doster, M.A.; Michailides, T.J.; Mahoney, N.E. Ochratoxin production by the Aspergillus ochraceus group and Aspergillus alliaceus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2326–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heussner, A.H.; Bingle, L.E.H. Comparative Ochratoxin Toxicity: A Review of the Available Data. Toxins 2015, 7, 4253–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.C.; Pushparaj, K.; Meyyazhagan, A.; Arumugam, V.A.; Pappuswamy, M.; Bhotla, H.K.; Baskaran, R.; Issara, U.; Balasubramanian, B.; Khaneghah, A.M. Ochratoxin A as an alarming health threat for livestock and human: A review on molecular interactions, mechanism of toxicity, detection, detoxification, and dietary prophylaxis. Toxicon 2022, 213, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Manderville, R.A. Ochratoxin A: An overview on toxicity and carcinogenicity in animals and humans. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 61–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, B. Accurate determination of ochratoxin A in Korean fermented soybean paste by isotope dilution-liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavon, M.A.; Gonzalez, I.; de la Cruz, S.; Martin, R.; Lacarra, T.G. The use of high-performance liquid chromatography to detect ochratoxin A in dried figs from the Spanish market. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittet, A.; Royer, D. Rapid, low cost thin-layer chromatographic screening method for the detection of ochratoxin A in green coffee at a control level of 10 μg/kg. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment-RNA ligands to bacteriophage-T4 DNA-polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.Z.; Ye, M.; Donovan, M.J.; Song, E.Q.; Zhao, Z.L.; Tan, W.H. Nucleic acid aptamers: An emerging frontier in cancer therapy. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10472–10480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xu, S.J.; Yan, H.; Li, X.W.; Yazd, H.S.; Li, X.; Huang, T.; Cui, C.; Jiang, J.H.; Tan, W.H. Nucleic Acid Aptamers for Molecular Diagnostics and Therapeutics: Advances and Perspectives. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2021, 60, 2221–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhang, H.Q.; Wang, Z.X.; Newbigging, A.M.; Reid, M.S.; Li, X.F.; Le, X.C. Aptamers Facilitating Amplified Detection of Biomolecules. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 274–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Aguado, J.A.; Penner, G. Determination of Ochratoxin A with a DNA Aptamer. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10456–10461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Lv, Q.; Wang, H. Identification of Allosteric Nucleotide Sites of Tetramethylrhodamine-Labeled Aptamer for Noncompetitive Aptamer-Based Fluorescence Anisotropy Detection of a Small Molecule, Ochratoxin A. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.P.; Zhang, N.; Wang, H.L.; Zhao, Q. Fluorescence Anisotropy-Based Signal-Off and Signal-On Aptamer Assays Using Lissamine Rhodamine B as a Label for Ochratoxin A. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4277–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Marty, J.L.; Yang, X.R. Aptamer-based colorimetric biosensing of Ochratoxin A using unmodified gold nanoparticles indicator. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2724–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Tian, F.Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Fu, R.J.; Jiao, B.N. Colorimetric aptasensor for ochratoxin A detection based on enzyme-induced gold nanoparticle aggregation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhamoud, Y.; Yang, D.T.; Kenston, S.S.F.; Liu, G.Z.; Liu, L.Y.; Zhou, H.B.; Ahmed, F.; Zhao, J.S. Advances in biosensors for the detection of ochratoxin A: Bio-receptors, nanomaterials, and their applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidar, N.; Amini, M.; Oroojalian, F.; Baradaran, B.; Hosseini, S.S.; Shahbazi, M.A.; Hashemzaei, M.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Hamblin, M.R.; de la Guardia, M. Molecular beacon strategies for sensing purpose. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 134, 116143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.H.; Wang, K.M.; Drake, T.J. Molecular beacons. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2004, 8, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Yang, R.H.; Shi, M.L.; Wu, C.C.; Fang, X.H.; Li, Y.H.; Li, J.H.; Tan, W.H. Rationally designed molecular beacons for bioanalytical and biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3036–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.W.J.; Fang, X.H.; Tan, W.H. Molecular aptamer beacons for real-time protein recognition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 292, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.M.; Tang, Z.W.; Yang, C.Y.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Fang, X.H.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.R.; Medley, C.D.; Cao, Z.H.; Li, J.; et al. Molecular Engineering of DNA: Molecular Beacons. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2009, 48, 856–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moutsiopoulou, A.; Broyles, D.; Dikici, E.; Daunert, S.; Deo, S.K. Molecular Aptamer Beacons and Their Applications in Sensing, Imaging, and Diagnostics. Small 2019, 15, 1902248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulko, A.A.; Li, F.; Le, X.C. Bioanalytical applications of aptamer and molecular-beacon probes in fluorescence-affinity assays. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 878–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.H.; Zhao, J.J.; Yu, H.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, X.; Li, C.G.; Liu, M.L. Structural insights into the mechanism of high-affinity binding of ochratoxin A by a DNA aptamer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 7731–7740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torimura, M.; Kurata, S.; Yamada, K.; Yokomaku, T.; Kamagata, Y.; Kanagawa, T.; Kurane, R. Fluorescence-quenching phenomenon by photoinduced electron transfer between a fluorescent dye and a nucleotide base. Anal. Sci. 2001, 17, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, M.; Bowser, M.T. Methods for measuring aptamer-protein equilibria: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 686, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Li, D.H.; Liu, R.J.; Cui, C.B.; Guo, Z.J. Label-free aptasensor for ochratoxin A detection using SYBR Gold as a probe. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2017, 246, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, V.; Boisjoli, S.; DeRosa, M.C. Adsorption-desorption nano-aptasensors: Fluorescent screening assays for ochratoxin A. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 13727–13739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.K.; Tan, R.; Chen, D. Fluorescence method for quickly detecting ochratoxin A in flour and beer using nitrogen doped carbon dots and silver nanoparticles. Talanta 2018, 182, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.Y.; Li, B.X.; Du, J.X.; Yang, Z.Q. A fluorometric aptamer-based assay for ochratoxin A by using exonuclease III-assisted recycling amplification. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Xiang, X.Y.; Chen, M.J.; Ma, C.B. Aptamer-Based Fluorometric Ochratoxin A Assay Based on Photoinduced Electron Transfer. Toxins 2019, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| OT-Bea-1bp | FAM-TCG GGT GTG GGT GGC GTA AAG GGA GCA-BHQ1 |
| OT-Bea-2bp | FAM-ATC GGG TGT GGG TGG CGT AAA GGG AGC AT-BHQ1 |
| OT-Bea-3bp | FAM-GAT CGG GTG TGG GTG GCG TAA AGG GAG CAT C-BHQ1 |
| OT-Bea-4bp | FAM-CGA TCG GGT GTG GGT GGC GTA AAG GGA GCA TCG-BHQ1 |
| OT-Bea-5bp | FAM-GCG ATC GGG TGT GGG TGG CGT AAA GGG AGC ATC GC-BHQ1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, H.; Zhao, Q. Aptamer Molecular Beacon Sensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Ochratoxin A. Molecules 2022, 27, 8267. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238267
Yu H, Zhao Q. Aptamer Molecular Beacon Sensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Ochratoxin A. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8267. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238267
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Hao, and Qiang Zhao. 2022. "Aptamer Molecular Beacon Sensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Ochratoxin A" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8267. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238267
APA StyleYu, H., & Zhao, Q. (2022). Aptamer Molecular Beacon Sensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Ochratoxin A. Molecules, 27(23), 8267. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238267





