Edible Pueraria lobata-Derived Exosomes Promote M2 Macrophage Polarization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Isolation of Exosomes
2.3. Dynamic Light Scattering Instrument (DLS)
2.4. Standard Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.5. Exosome Uptake
2.6. Isolation of Peritoneal Macrophages
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
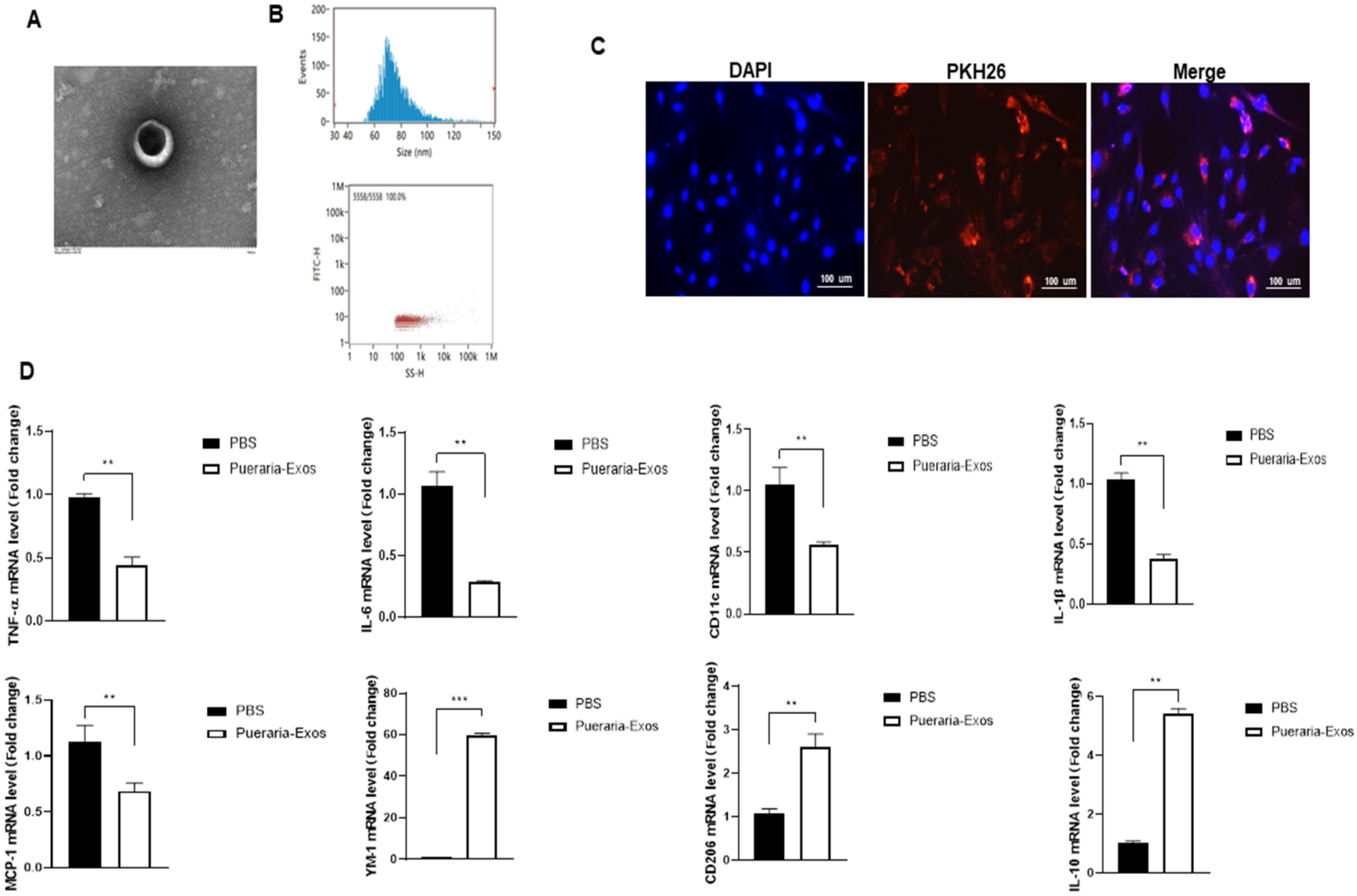
3. Results and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Lu, H.; Lai, J.; He, Y.; Liu, S.; Guo, X. Pueraria lobata for diabetes mellitus: Past, present and future. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 47, 1419–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdy, H.M.; Mohamed, M.R.; Emam, M.A.; Karim, A.M.; Abdel-Naim, A.; Khalifa, A.E. The anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory properties of puerarin attenuate 3-nitropropionic-acid induced neurotoxicity in rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 92, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, D.; Yuan, H.; Yin, X.; Wu, Y.; He, R.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y. Puerarin inhibits hyperglycemia-induced inter-endothelial junction through suppressing endothelial Nlrp3 inflammasome activation via ROS-dependent oxidative pathway. Phytomedicine 2019, 55, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Lin, L.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, D. Effects of puerarin on lipid accumulation and metabolism in high-fat diet-fed mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, W.; Lin, S.; Yang, L. Puerarin suppresses LPS-induced breast cancer cell migration, invasion and adhesion by blockage NF-κB and Erk pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-G.; Yin, X.-C.; Liu, X.-F.; Meng, K.-W.; Tang, K.; Huang, F.-L.; Xu, G.; Gao, J. Puerarin induces hepatocellular carcinoma cell apoptosis modulated by MAPK signaling pathways in a dose-dependent manner. Anticancer. Res. 2017, 37, 4425–4431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xue, R.; Wang, J.; Ren, H. Puerarin inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis through miR-21-mediated PTEN/AKT signaling to suppress the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, e8882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.Y.; Kang, S.J.; Rhee, W.J. Isolation of cabbage exosome-like nanovesicles and investigation of their biological activities in human cells. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4321–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, J.; Zhuang, X.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Deng, Z.B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.; Kakar, S.; Jun, Y.; Miller, D. Interspecies communication between plant and mouse gut host cells through edible plant derived exosome-like nanoparticles. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1561–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Viennois, E.; Xu, C.; Merlin, D. Plant derived edible nanoparticles as a new therapeutic approach against diseases. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4, e1134415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, S.; Mu, J.; Dokland, T.; Zhuang, X.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, H.; Xiang, X.; Deng, Z.-B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L. Grape exosome-like nanoparticles induce intestinal stem cells and protect mice from DSS-induced colitis. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1345–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Viennois, E.; Prasad, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Han, M.K.; Xiao, B.; Xu, C.; Srinivasan, S. Edible ginger-derived nanoparticles: A novel therapeutic approach for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated cancer. Biomaterials 2016, 101, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Robertis, M.; Sarra, A.; D’oria, V.; Mura, F.; Bordi, F.; Postorino, P.; Fratantonio, D. Blueberry-derived exosome-like nanoparticles counter the response to TNF-α-Induced change on gene expression in EA. hy926 cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.H.; Hong, Y.D.; Kim, D.; Park, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, H.-M.; Yoon, E.J.; Cho, J.-S. Confirmation of plant-derived exosomes as bioactive substances for skin application through comparative analysis of keratinocyte transcriptome. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2022, 65, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Ma, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Du, Z.; Xu, J.; You, J.; Chen, N.; Deng, X.; Wu, J. Edible Pueraria lobata-Derived Exosomes Promote M2 Macrophage Polarization. Molecules 2022, 27, 8184. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238184
Wu J, Ma X, Lu Y, Zhang T, Du Z, Xu J, You J, Chen N, Deng X, Wu J. Edible Pueraria lobata-Derived Exosomes Promote M2 Macrophage Polarization. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8184. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238184
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jiaqi, Xiaoyu Ma, Yu Lu, Tao Zhang, Zuoqin Du, Jin Xu, Jingcan You, Ni Chen, Xin Deng, and Jianbo Wu. 2022. "Edible Pueraria lobata-Derived Exosomes Promote M2 Macrophage Polarization" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8184. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238184
APA StyleWu, J., Ma, X., Lu, Y., Zhang, T., Du, Z., Xu, J., You, J., Chen, N., Deng, X., & Wu, J. (2022). Edible Pueraria lobata-Derived Exosomes Promote M2 Macrophage Polarization. Molecules, 27(23), 8184. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238184





