Effects of Sorafenib and Quercetin Alone or in Combination in Treating Hepatocellular Carcinoma: In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Declaration
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Animals
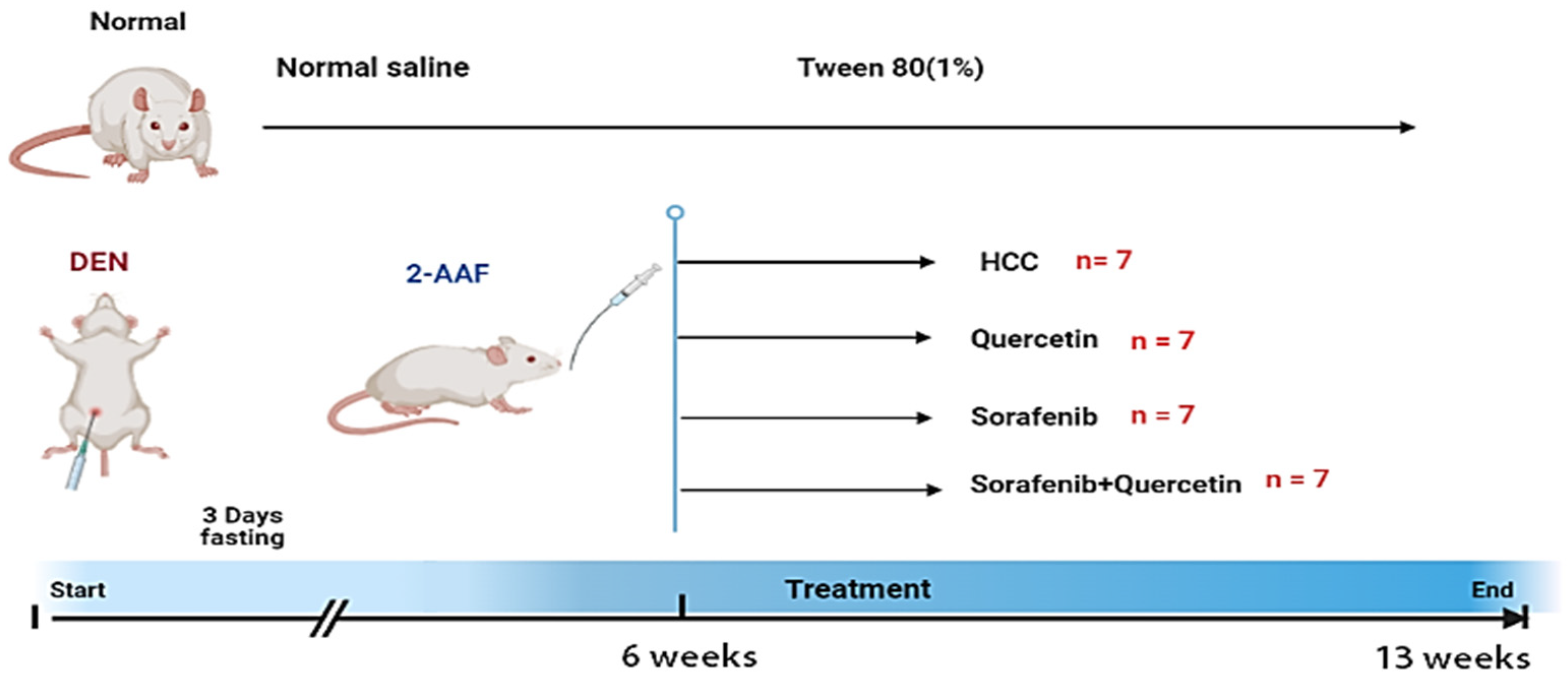
2.4. Experimental Protocol
2.5. Serum Biochemical Markers of Liver Damage Measurement
2.6. Determination of Inflammation Biomarkers
2.7. Assessment of Liver Oxidative Stress
2.8. Determination of Tumor Marker Levels
2.9. Histological and Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.10. Gene Expression Analysis
2.11. Cell Growth
2.12. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.13. Cell Cycle Examination
2.14. Apoptosis Assays
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
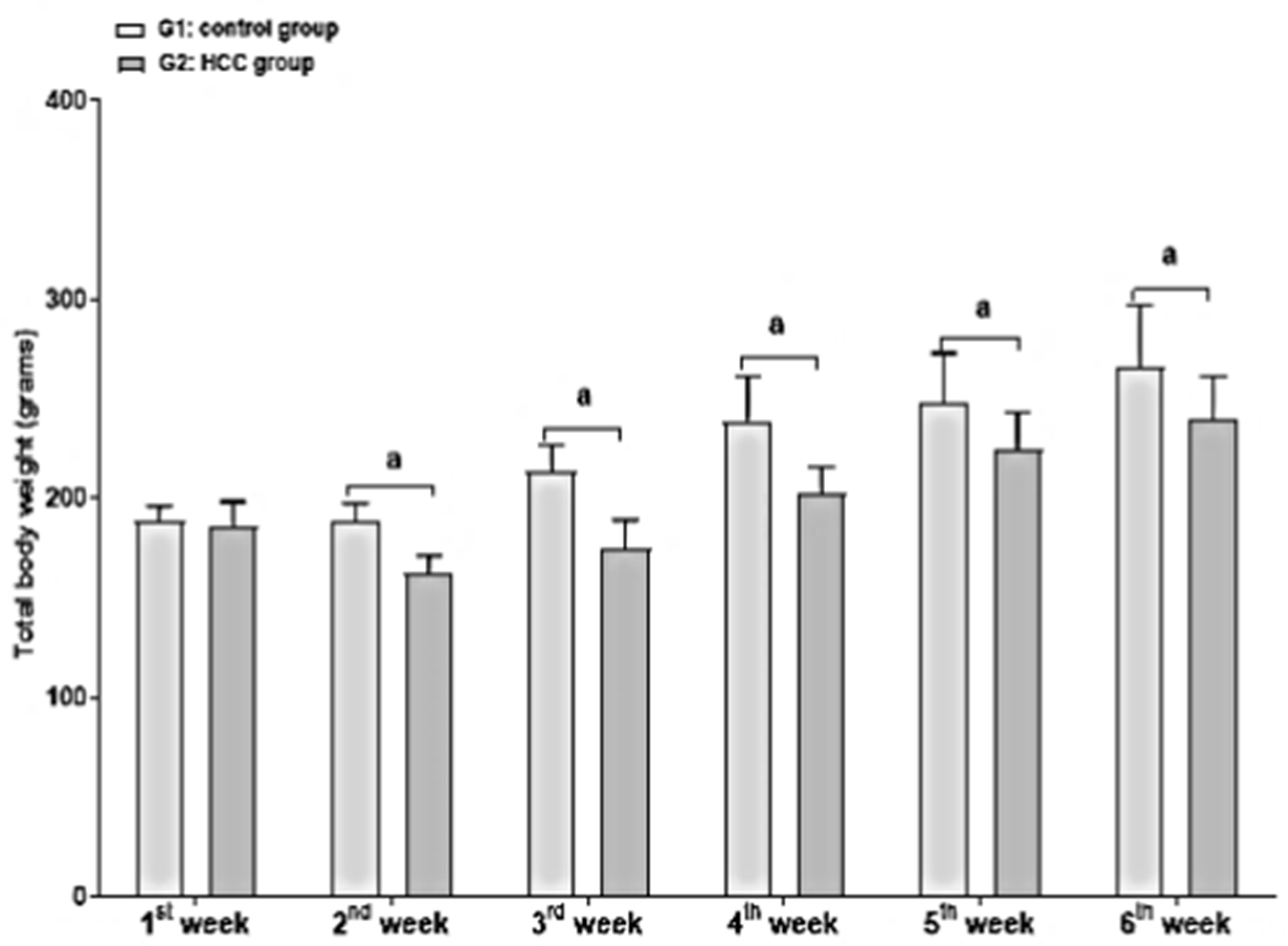
3.1. Effect of Treatment on Body and Liver Weights
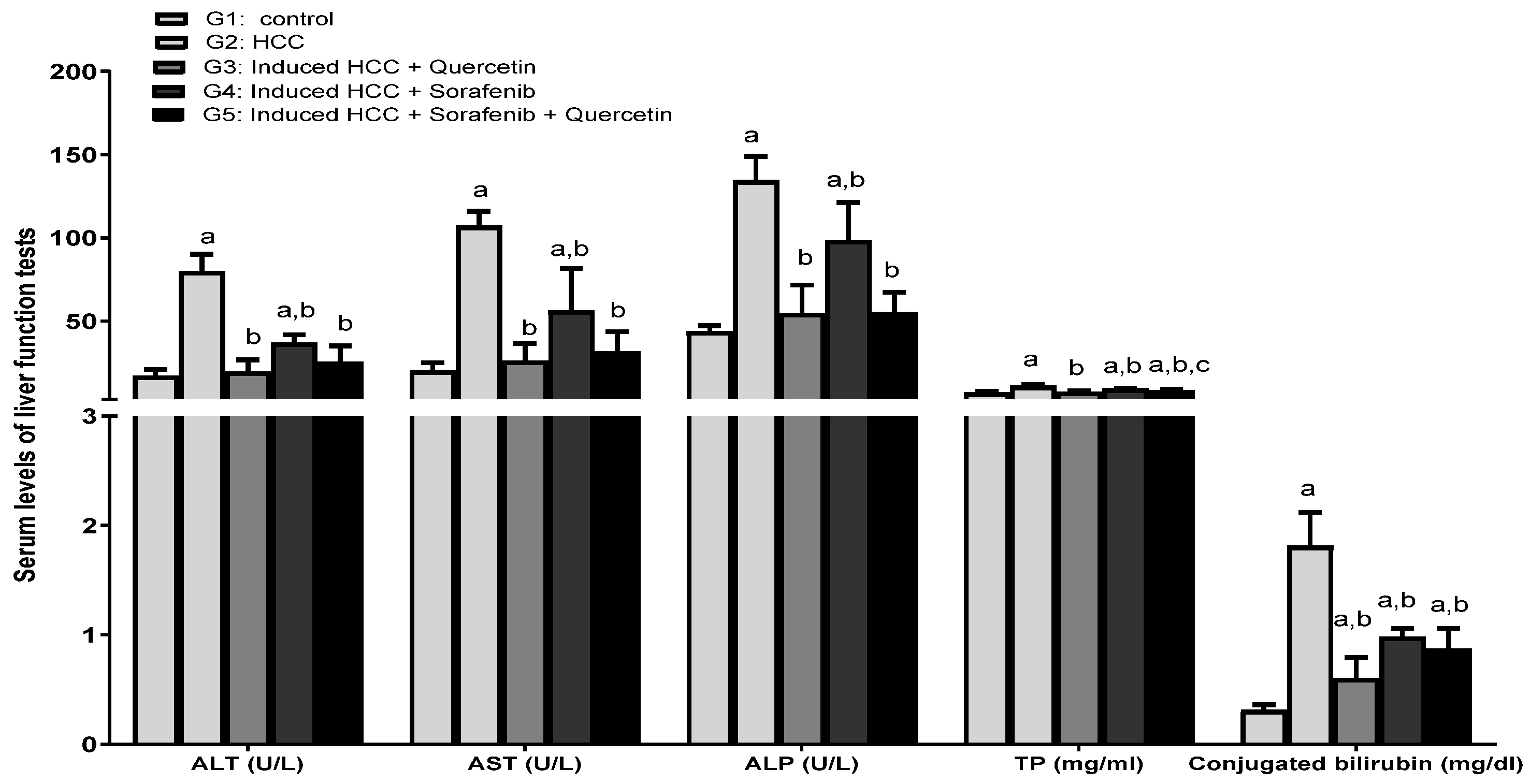
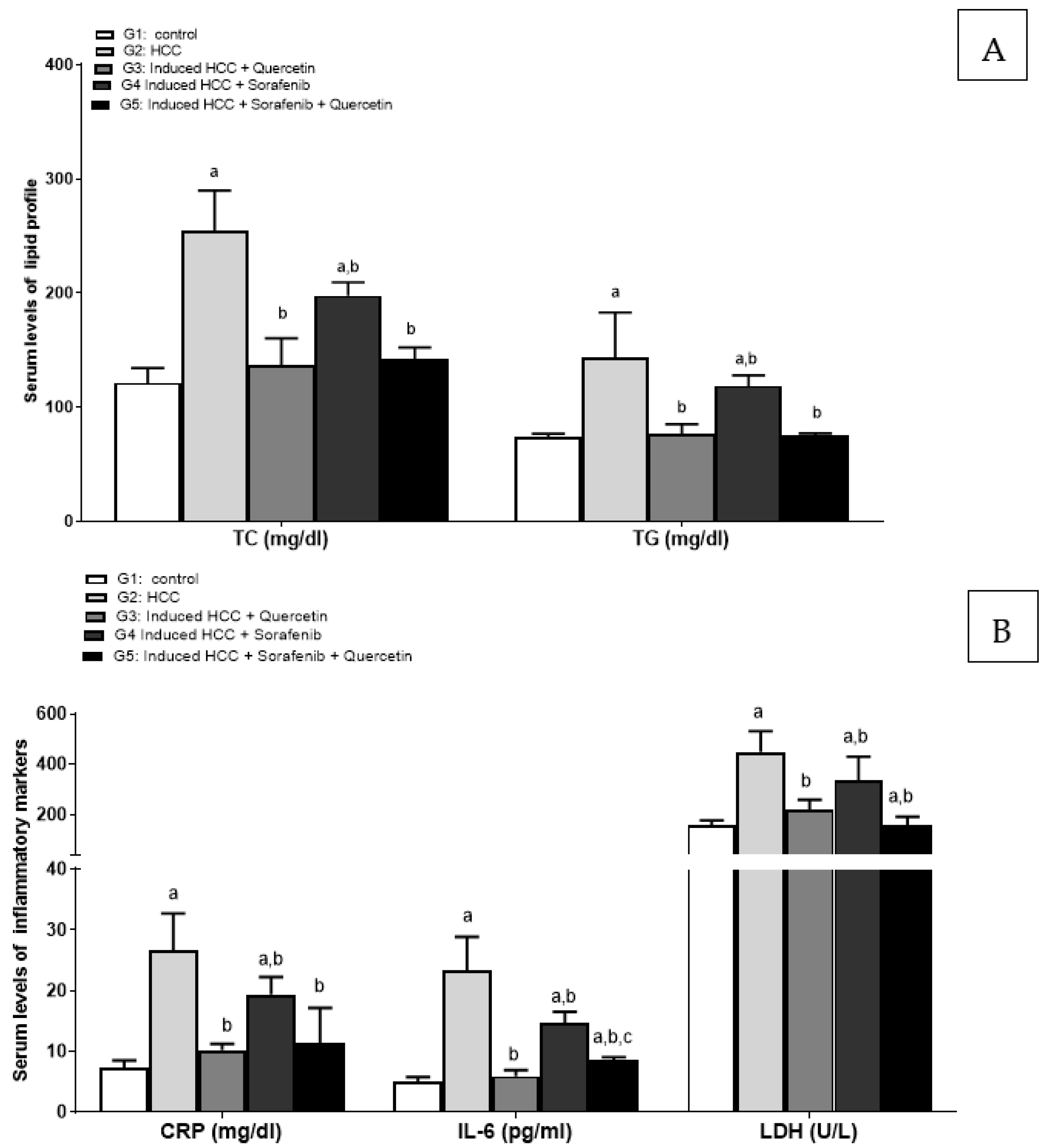
3.2. Effect of the Treatments on Liver Function Enzymes and Lipid Profile
3.3. Effect on Inflammatory Markers
3.4. Effect on the Levels of Oxidative Stress
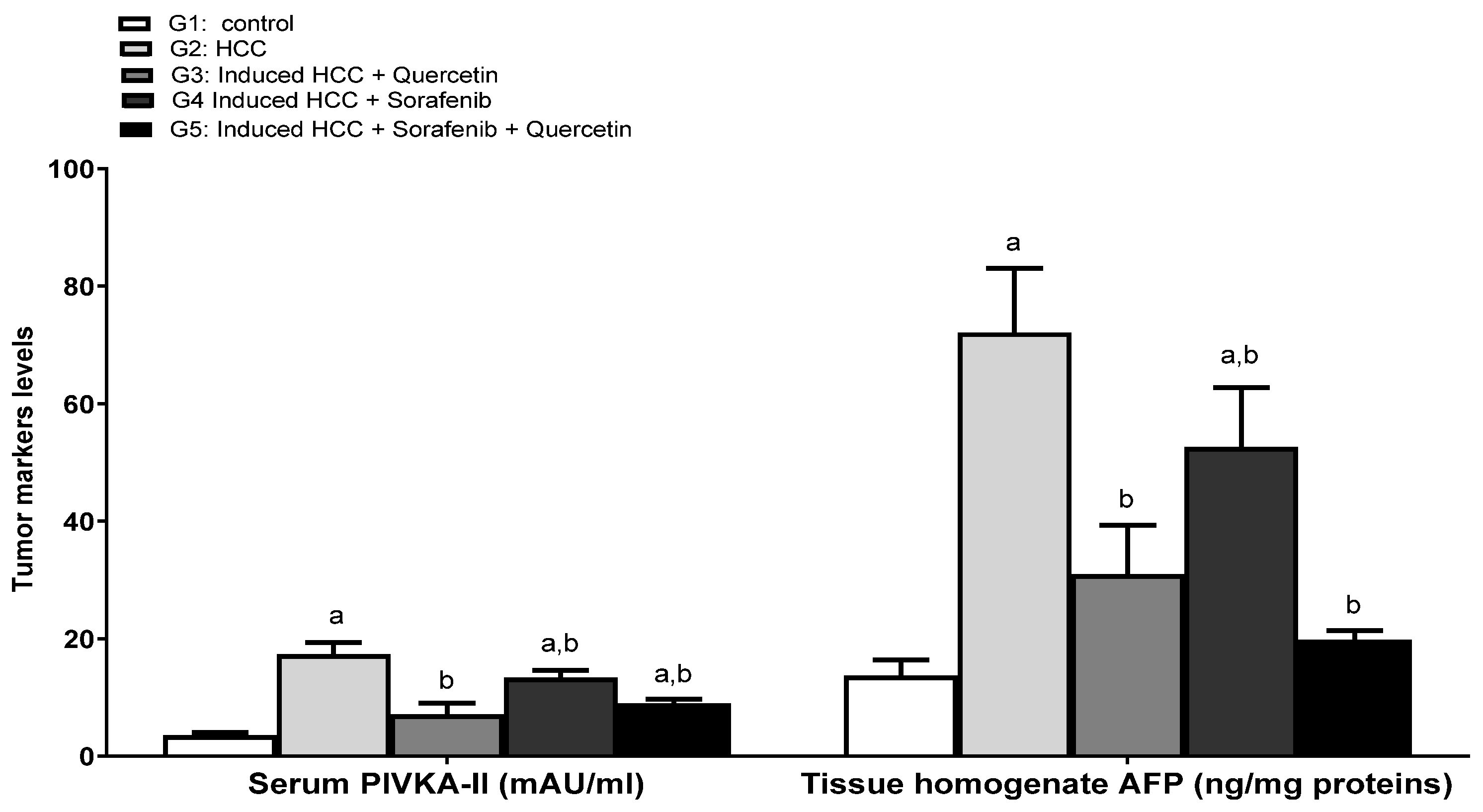
3.5. Effect on the Levels of Tumor Prognostic Markers
3.6. Effect of the Treatments on Hepatic Tumor Area and Liver Architecture
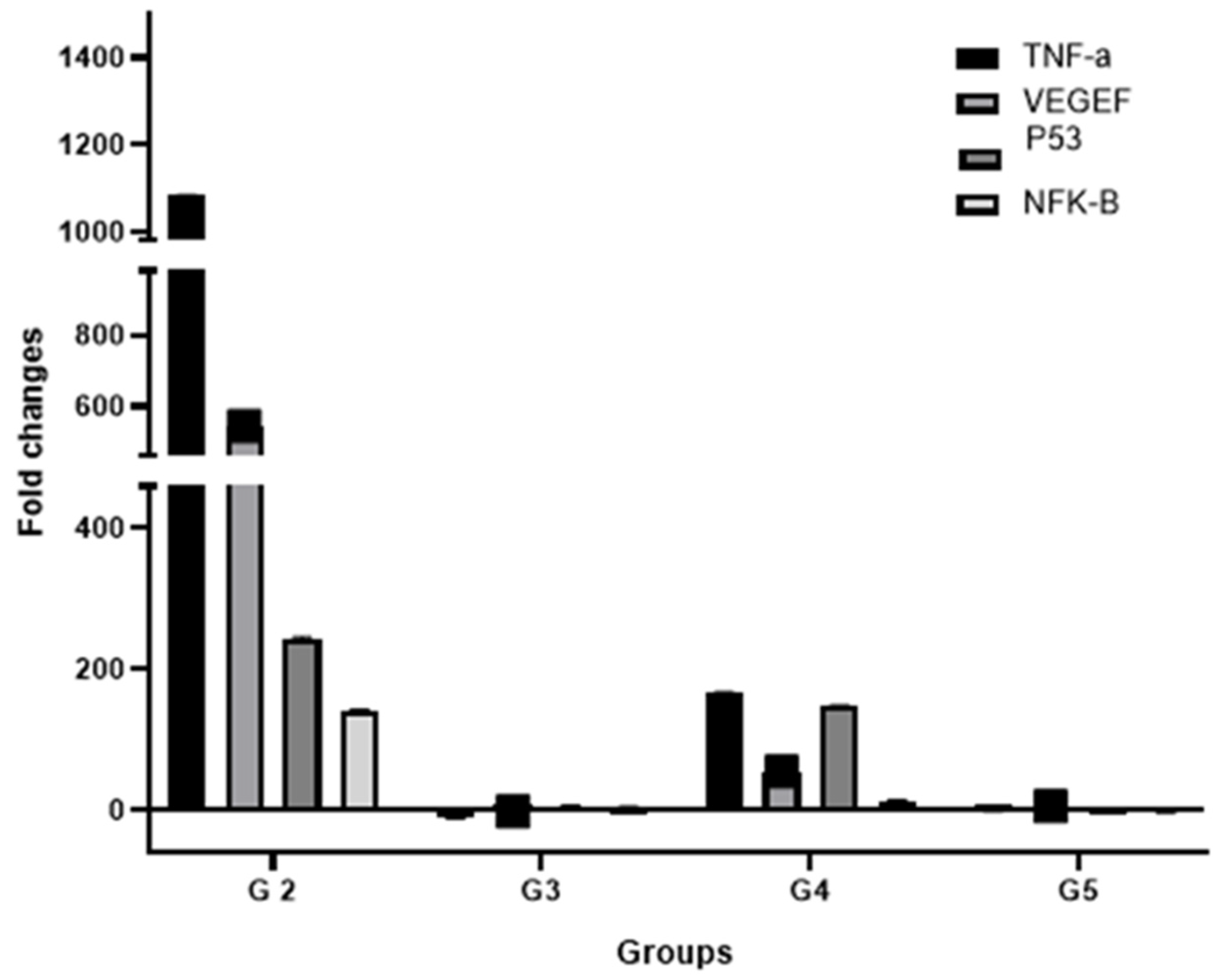
3.7. Effect of Treatments on the Expression of Key HCC Genes
3.8. Measurement of the Cytotoxicity of Quercetin and Sorafenib Using the MTT Assay
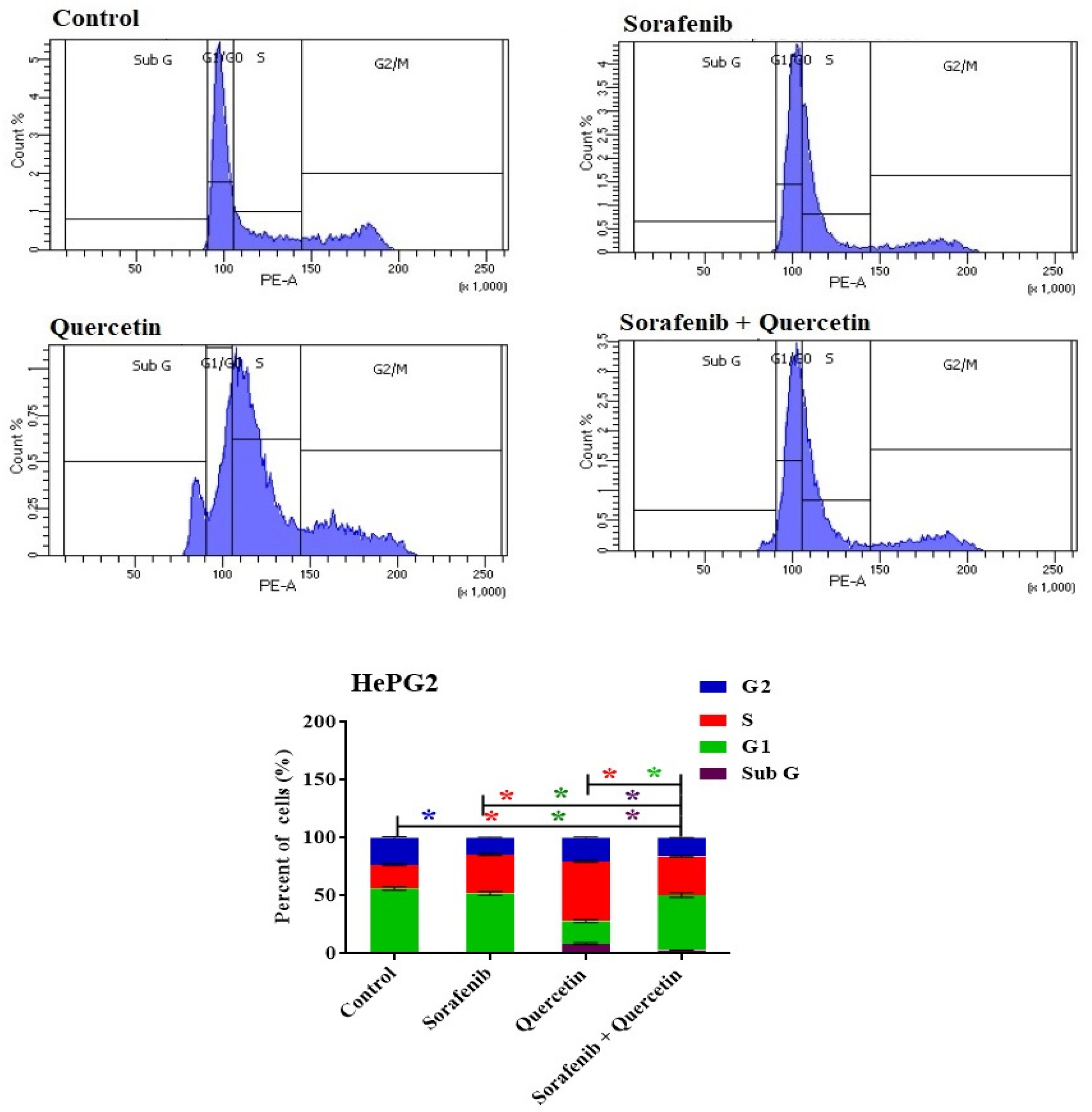
3.9. Cell Cycle
3.10. Annexin–V-FITC Analysis (Apoptosis Assay)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 73, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordan, J.D.; Kennedy, E.B.; Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Beg, M.S.; Brower, S.T.; Gade, T.P.; Goff, L.; Gupta, S.; Guy, J.; Harris, W.P. Systemic therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: ASCO guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 4317–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; De Baere, T.; Kulik, L.; Haber, P.K.; Greten, T.F.; Meyer, T.; Lencioni, R. Locoregional therapies in the era of molecular and immune treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 293–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K. Selection of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma for sorafenib. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2009, 7, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, E.M.; Sanoff, H.K. Optimal therapy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and resistance or intolerance to sorafenib: Challenges and solutions. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2017, 4, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, R.; Fetterly, G.; Lugade, A.; Thanavala, Y. Sorafenib: A clinical and pharmacologic review. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2010, 11, 1943–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takezawa, K.; Okamoto, I.; Yonesaka, K.; Hatashita, E.; Yamada, Y.; Fukuoka, M.; Nakagawa, K. Sorafenib inhibits non–small cell lung cancer cell growth by targeting B-RAF in KRAS wild-type cells and C-RAF in KRAS mutant cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6515–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.-F.; De Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.-L.; Forner, A. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussaarts, K.G.; van Doorn, L.; Eechoute, K.; Damman, J.; Fu, Q.; van Doorn, N.; Eisenmann, E.D.; Gibson, A.A.; Oomen-de Hoop, E.; de Bruijn, P. Influence of Probenecid on the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Sorafenib. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathia, C.; Lettieri, J.; Cihon, F.; Gallentine, M.; Radtke, M.; Sundaresan, P. Lack of effect of ketoconazole-mediated CYP3A inhibition on sorafenib clinical pharmacokinetics. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2006, 57, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Sheu, A.Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Kim, D.-H.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Omary, R.A.; Shea, L.D.; Larson, A.C. Poly (lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres for MRI-monitored transcatheter delivery of sorafenib to liver tumors. J. Control. Release 2014, 184, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdu, S.B.; Al-Bogami, F.M. Influence of resveratrol on liver fibrosis induced by dimethylnitrosamine in male rats. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdu, S.B.; Abdu, F.; Khalil, W.K.B. Ginger nanoparticles modulate the apoptotic activity in male rats exposed to dioxin-induced cancer initiation. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 13, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez-Garzón, V.R.; Macias-Pérez, J.R.; Jiménez-García, M.N.; Villegas, V.; Fattel-Fazenta, S.; Villa-Treviño, S. The Chemopreventive Capacity of Quercetin to Induce Programmed Cell Death in Hepatocarcinogenesis. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 41, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Avendaño, I.; Reyes-Jiménez, E.; González-García, K.; Pérez-Figueroa, D.C.; Baltiérrez-Hoyos, R.; Tapia-Pastrana, G.; Sánchez-Chino, X.M.; Villa-Treviño, S.; Arellanes-Robledo, J.; Vásquez-Garzón, V.R. Quercetin Regulates Key Components of the Cellular Microenvironment during Early Hepatocarcinogenesis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juaid, N.; Amin, A.; Abdalla, A.; Reese, K.; Alamri, Z.; Moulay, M.; Abdu, S.; Miled, N. Anti-hepatocellular carcinoma biomolecules: Molecular targets insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Palanca, P.; Fondevila, F.; Méndez-Blanco, C.; Tuñón, M.J.; González-Gallego, J.; Mauriz, J.L. Antitumor effects of quercetin in hepatocarcinoma in vitro and in vivo models: A systematic review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, Y.A.; El-Karef, A.; El Gayyar, A.M.; Abdel-Rahman, N. Beyond its antioxidant properties: Quercetin targets multiple signalling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma in rats. Life Sci. 2019, 236, 116933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.N.; Jang, H.D. Protective Mechanism of Quercetin and Rutin Using Glutathione Metabolism on H2O2-induced Oxidative Stress in HepG2 Cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1171, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granado-Serrano, A.B.; Martín, M.Á.; Bravo, L.; Goya, L.; Ramos, S. Quercetin attenuates TNF-induced inflammation in hepatic cells by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Gao, Q.; Qiu, J.; Yuan, J.; Wu, G.; Shen, G. Quercetin induces apoptosis and enhances 5-FU therapeutic efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor. Biol. 2016, 37, 6307–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casella, M.L.; Parody, J.P.; Ceballos, M.P.; Quiroga, A.D.; Ronco, M.T.; Francés, D.E.; Monti, J.A.; Pisani, G.B.; Carnovale, C.E.; Carrillo, M.C. Quercetin prevents liver carcinogenesis by inducing cell cycle arrest, decreasing cell proliferation and enhancing apoptosis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, A.F.; Ribeiro, M.; Abrantes, A.M.; Mamede, A.C.; Laranjo, M.; Casalta-Lopes, J.E.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Sarmento-Ribeiro, A.B.; Tralhão, J.G.; Botelho, M.F. New approach for treatment of primary liver tumors: The role of quercetin. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granado-Serrano, A.B.; Martín, M.A.; Bravo, L.; Goya, L.; Ramos, S. Quercetin induces apoptosis via caspase activation, regulation of Bcl-2, and inhibition of PI-3-kinase/Akt and ERK pathways in a human hepatoma cell line (HepG2). J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2715–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdu, S.; Juaid, N.; Amin, A.; Moulay, M.; Miled, N. Therapeutic Effects of Crocin Alone or in Combination with Sorafenib against Hepatocellular Carcinoma: In Vivo & In Vitro Insights. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1645. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, A.; A Hamza, A.; Daoud, S.; Khazanehdari, K.; Al Hrout, A.; Baig, B.; Chaiboonchoe, A.; E Adrian, T.; Zaki, N.; Salehi-Ashtiani, K. Saffron-based crocin prevents early lesions of liver cancer: In vivo, in vitro and network analyses. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2016, 11, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, Q.; Yao, Q.; Xu, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Tu, C. The flavonoid quercetin ameliorates liver inflammation and fibrosis by regulating hepatic macrophages activation and polarization in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashmail, H.A.; Alamoudi, A.A.; Noorwali, A.; Hegazy, G.A.; AJabnoor, G.; Choudhry, H.; Al-Abd, A.M. Thymoquinone synergizes gemcitabine anti-breast cancer activity via modulating its apoptotic and autophagic activities. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, D. Protein measurements with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, N.M.; Minhaj, A.A.; Maldonado, K.L.; Kingsley, C.V.; Cortes, A.C.; Taghavi, H.; Polak, U.; Mitchell, J.M.; Ensor, J.E.; Bankson, J.A. Comparison of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and contrast-enhanced ultrasound for evaluation of the effects of sorafenib in a rat model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 57, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ALmohaimeed, H.M.; Mohammedsaleh, Z.M.; Batawi, A.H.; Balgoon, M.J.; Ramadan, O.I.; Baz, H.A.; Al Jaouni, S.; Ayuob, N.N. Synergistic Anti-inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects of Cinnamomum cassia and Zingiber officinale Alleviate Diabetes-Induced Hippocampal Changes in Male Albino Rats: Structural and Molecular Evidence. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 727049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpanty, G.; Chen, S.; Shohet, R.; Ding, J.-h.; Yang, B.-z.; Frenkel, P.; Grayburn, P. Targeting of VEGF-mediated angiogenesis to rat myocardium using ultrasonic destruction of microbubbles. Gene Ther. 2005, 12, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bima, A.I.; Mahdi, A.S.; Al Fayez, F.F.; Khawaja, T.M.; Abo El-Khair, S.M.; Elsamanoudy, A.Z. Cellular Senescence and Vitamin D Deficiency Play a Role in the Pathogenesis of Obesity-Associated Subclinical Atherosclerosis: Study of the Potential Protective Role of Vitamin D Supplementation. Cells 2021, 10, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermanian, F.; Soleimani, M.; Pourheydar, B.; Samzadeh-Kermani, A.; Mohammadzadeh, F.; Mehdizadeh, M. Effects of adenosine A2a receptor agonist and antagonist on cerebellar nuclear factor-kB expression preceded by MDMA toxicity. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran 2014, 28, 120. [Google Scholar]
- Kobashi, K.; Nishimura, K.; Kawate, Y.; Horiuchi, T. Synthesis of diamonds by use of microwave plasma chemical-vapor deposition: Morphology and growth of diamond films. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 38, 4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munetomo, A.; Ishii, H.; Miyamoto, T.; Sakuma, Y.; Kondo, Y. Puerperal and parental experiences alter rat preferences for pup odors via changes in the oxytocin system. J. Reprod. Dev. 2016, 62, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Fang, Y.-Z.; Yang, S.; Lupton, J.R.; Turner, N.D. Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, I.; Buonomo, A.R.; Scotto, R.; Zappulo, E.; Carriero, C.; Piccirillo, M.; Izzo, F.; Rizzo, M.; Cerasuolo, D.; Borgia, G. Diagnostic accuracy of PIVKA-II, alpha-fetoprotein and a combination of both in diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients affected by chronic HCV infection. In Vivo 2017, 31, 695–700. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, D.; Blaser, H.; Mak, T.W. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor signalling: Live or let die. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-L.; Li, F.-Q.; Liu, L.-X.; Li, B.; Zhou, Z.-P. TNF-α, HGF and macrophage in peritumoural liver tissue relate to major risk factors of HCC Recurrence. Hepato. Gastroenterol. 2013, 60, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Rodríguez, R.; Romero-Gutiérrez, M.; Artaza-Varasa, T.; González-Frutos, C.; Ciampi-Dopazo, J.J.; de-la-Cruz-Pérez, G.; Sánchez-Ruano, J.J. The value of the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer and alpha-fetoprotein in the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2012, 104, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Luedde, T.; Schwabe, R.F. NF-κB in the liver—Linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perabo, F.G.; Landwehrs, G.; Frössler, C.; Schmidt, D.H.; Mueller, S. Antiproliferative and apoptosis inducing effects of indirubin-3′-monoxime in renal cell cancer cells. In Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 815–820. [Google Scholar]
- Demarcq, C.; Bunch, R.T.; Creswell, D.; Eastman, A. The role of cell cycle progression in cisplatin-induced apoptosis in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell Growth Differ. Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 1994, 5, 983–994. [Google Scholar]
- Dera, A.; Rajagopalan, P. Thymoquinone attenuates phosphorylation of AKT to inhibit kidney cancer cell proliferation. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLachlan, T.K.; Sang, N.; Giordano, A. Cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases and cdk inhibitors: Implications in cell cycle control and cancer. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 1995, 5, 127–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Somasagara, R.R.; Hegde, M.; Nishana, M.; Tadi, S.K.; Srivastava, M.; Choudhary, B.; Raghavan, S.C. Quercetin, a natural flavonoid interacts with DNA, arrests cell cycle and causes tumor regression by activating mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mediavilla, V.; Crespo, I.; Collado, P.S.; Esteller, A.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; Tuñón, M.J.; González-Gallego, J. The anti-inflammatory flavones quercetin and kaempferol cause inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2 and reactive C-protein, and down-regulation of the nuclear factor kappaB pathway in Chang Liver cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 557, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Shi, D.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Kang, T.; Deng, W. Quercetin suppresses cyclooxygenase-2 expression and angiogenesis through inactivation of P300 signaling. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.-S.; Ku, J.M.; Choi, H.-S.; Choi, Y.K.; Woo, J.-K.; Kim, M.; Kim, I.; Na, C.H.; Hur, H.; Jang, B.H. Quercetin induces caspase-dependent extrinsic apoptosis through inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling in HER2-overexpressing BT-474 breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, H.; Jeong, J.-C.; Jeong, Y.S.; Kim, E.-J.; Um, S.-J. Quercetin potentiates apoptosis by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappaB signaling in H460 lung cancer cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratheeshkumar, P.; Budhraja, A.; Son, Y.-O.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, S.; Wang, L.; Hitron, A.; Lee, J.-C.; Xu, M. Quercetin inhibits angiogenesis mediated human prostate tumor growth by targeting VEGFR-2 regulated AKT/mTOR/P70S6K signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vafadar, A.; Shabaninejad, Z.; Movahedpour, A.; Fallahi, F.; Taghavipour, M.; Ghasemi, Y.; Akbari, M.; Shafiee, A.; Hajighadimi, S.; Moradizarmehri, S. Quercetin and cancer: New insights into its therapeutic effects on ovarian cancer cells. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palchaudhuri, R.; Hergenrother, P.J. DNA as a target for anticancer compounds: Methods to determine the mode of binding and the mechanism of action. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, G.M.; Duarte, T.L.; Farmer, P.B.; Steward, W.P.; Jones, G.D. Multiple end-point analysis reveals cisplatin damage tolerance to be a chemoresistance mechanism in a NSCLC model: Implications for predictive testing. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1810–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Zhong, Q.; Kwak, J.-Y.; Lee, W.-H. Hypersensitivity of Brca1-deficient MEF to the DNA interstrand crosslinking agent mitomycin C is associated with defect in homologous recombination repair and aberrant S-phase arrest. Oncogene 2005, 24, 4009–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrov, Z.; Shishodia, S.; Faderl, S.; Harris, D.; Van, Q.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Talpaz, M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Resveratrol blocks interleukin-1β–induced activation of the nuclear transcription factor NF-κB, inhibits proliferation, causes S-phase arrest, and induces apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 2003, 102, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Chen, H.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, K.; Liu, R. Co-delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs with vitamin E TPGS by porous PLGA nanoparticles for enhanced chemotherapy against multi-drug resistance. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2391–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, A.J.; Burd, R. Hormesis and synergy: Pathways and mechanisms of quercetin in cancer prevention and management. Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louisa, M.; Wardhani, B.W. Quercetin improves the efficacy of sorafenib in triple negative breast cancer cells through the modulation of drug efflux transporters expressions. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2019, 11, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Gene | Forward Primer (5′ to 3′) | Reverse Primer (5′ to 3′) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-a | 5′CCCTGGTACTAACTCCCAGAAA-3′ | 5′TGTATGAGAGGGACGGAACC-3′ | [31] |
| VEGF | 5′ACAGAAGGGGAGCAGAAAGCCCAT-3′ | 5′CGCTCTGACCAAGGCTCACAGT-3′ | [32] |
| p53 | 5′CCTATCCGGTCAGTTGTTGGA-3′ | 5′TTGCAGAGTGGAGGAAATGG-3′ | [33] |
| NFκB | 5′GCAAACCTGGGAATACTTCATGTGACTAAG-3′ | 5′ATAGGCAAGGTCAGAATGCACCAGAAGTCC-3′ | [34] |
| GAPDH | 5′CAACTCCCTCAAGATTGTCAGCAA-3′ | 5′GGCATGGACTGTGGTCATGA-3′ | [35] |
| Data | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | Group 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial body weight (grams) | 278.16 ± 29.56 | 247.19 ± 17.40 a | 277.77 ± 29.24 b | 263.74 ± 19.60 | 251.63 ± 15.73 a |
| Final body weights (grams) | 319.58 ± 4.04 | 269.90 ± 33.36 a | 304.84 ± 40.84 b | 316.55 ± 26.53 b | 290.09 ± 28.73 |
| Ratio body weight increase (%) | 14.89% | 9.19% | 9.75% | 20.02% | 15.28% |
| Liver weights (grams) | 8.78 ± 1.31 | 7.98 ± 1.37 | 8.81 ± 1.39 | 8.50 ± 1.11 | 8.22 ± 0.62 |
| Liver index (%) | 2.75 ± 0.13 | 2.95 ± 0.29 | 2.89 ± 0.16 | 2.68 ± 0.22 b | 2.84 ± 0.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdu, S.; Juaid, N.; Amin, A.; Moulay, M.; Miled, N. Effects of Sorafenib and Quercetin Alone or in Combination in Treating Hepatocellular Carcinoma: In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches. Molecules 2022, 27, 8082. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27228082
Abdu S, Juaid N, Amin A, Moulay M, Miled N. Effects of Sorafenib and Quercetin Alone or in Combination in Treating Hepatocellular Carcinoma: In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches. Molecules. 2022; 27(22):8082. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27228082
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdu, Suzan, Nouf Juaid, Amr Amin, Mohamed Moulay, and Nabil Miled. 2022. "Effects of Sorafenib and Quercetin Alone or in Combination in Treating Hepatocellular Carcinoma: In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches" Molecules 27, no. 22: 8082. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27228082
APA StyleAbdu, S., Juaid, N., Amin, A., Moulay, M., & Miled, N. (2022). Effects of Sorafenib and Quercetin Alone or in Combination in Treating Hepatocellular Carcinoma: In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches. Molecules, 27(22), 8082. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27228082






