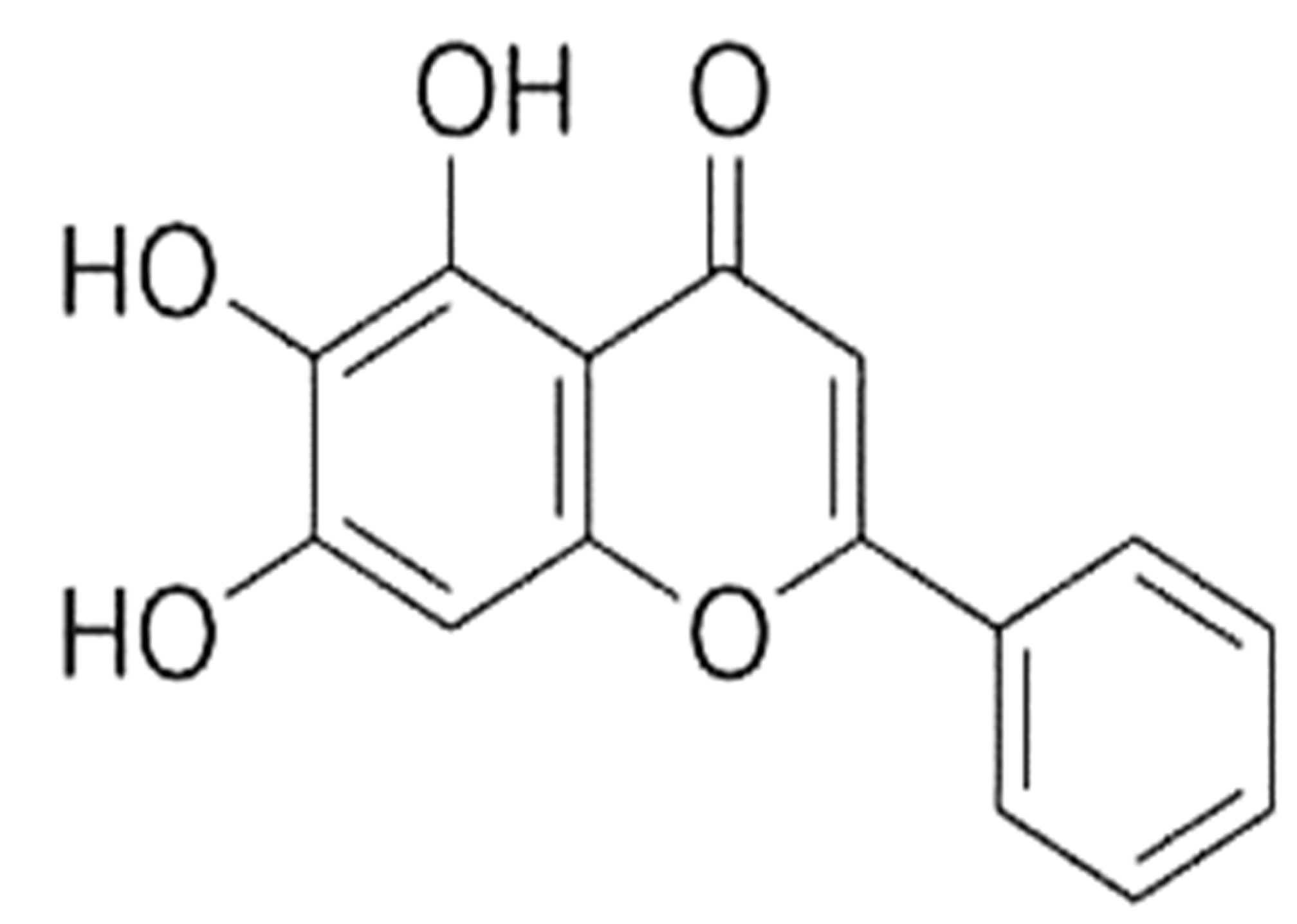
The Multifaceted Role of Baicalein in Cancer Management through Modulation of Cell Signalling Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
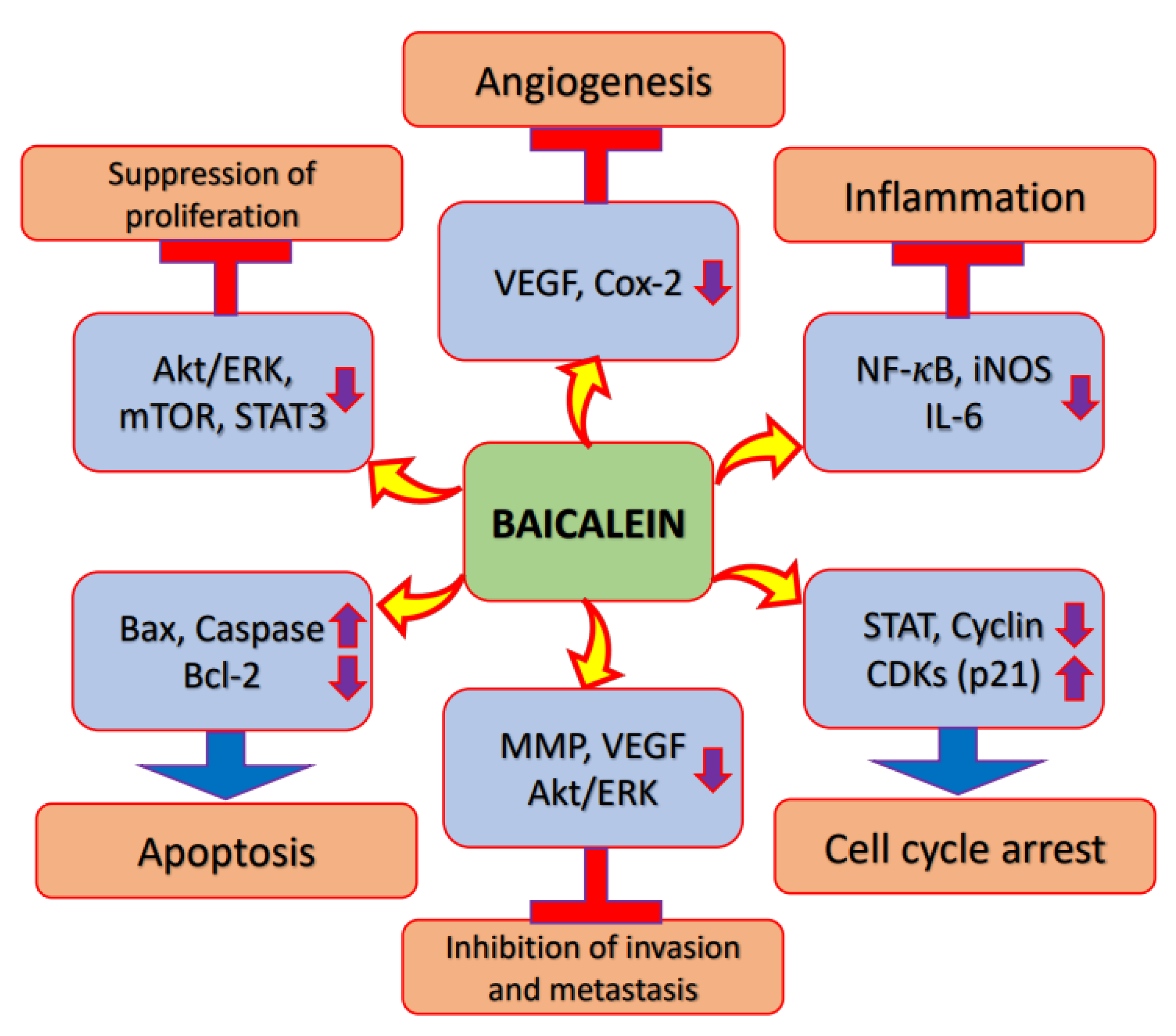
2. Mechanism of Action of Baicalein in Cancer Prevention and Treatment
2.1. Inflammation
2.2. Akt/PI3K/mTOR Signalling Pathway
2.3. Apoptosis
2.4. Cell Cycle
2.5. Angiogenesis
2.6. Autophagy
2.7. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3)
2.8. Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
2.9. Tumor Suppressor Genes
2.10. ERK/p38/MAPK Pathway
| Genes/Pathway | Mechanism | Refs. |
|---|---|---|
| NF-Κb | Baicalein decreased the activation of NF-κB and the anti-inflammatory effects of baicalein might be initiated via PPARγ activation. | [26] |
| Matrix metalloproteinase | Baicalein treatment efficiently denies B(a)P-induced upregulated expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and 9. | [27] |
| PI3K/Akt | Baicalein treatment notably decreased the phosphorylation of PI3K and Akt proteins. The study concluded that baicalein might inhibit the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. | [30] |
| Baicalein regulates the autophagy and apoptosis of cancer cells through the PI3K/Akt pathway. | [17] | |
| Apoptosis | In baicalein-treated groups, the expression of cleaved caspase-3 and caspase-3 activity was even more significant with chloroquine addition. Over all, baicalein treatment improved the caspase-3 pathway of apoptosis through autophagy inhibition. | [33] |
| Baicalein decreased migration, invasion, cell viability and proliferation, and increased G1 phase numbers, apoptosis and the expression levels of p27, p21, cleaved caspase 3/9, Bax, ZO-1 and E-cad, in a dose-dependent way. | [35] | |
| Apoptosis and reactive oxygen species caused BNIP3 expression in cancer cells with baicalein treatment. The findings advocate that baicalein has powerful potential as an anti-osteosarcoma drug. | [36] | |
| Baicalein induced AIF as well as Endo G release from mitochondria demonstrating that baicalein stimulates apoptosis via the caspase-independent pathway, whereas undergoing apoptosis, there was a noteworthy accumulation of G2/M cells. | [18] | |
| Cyclin-dependent kinase | Baicalein induces G1 cell cycle arrest through decreasing cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and cyclin D1. | [42] |
| Cell cycle-regulatory molecule studies established that baicalein decreased the levels of cdk 4, cyclin D1 and B1. | [36] | |
| VEGF | VEGF protein levels were inhibited by treatment. | [49] |
| Tumor xenografts revealed decreased expressions of both VEGF and 12-lipoxygenase proteins in baicalein-treated tumors. | [50] | |
| Gene expression profiling demonstrated a decrease in both FGFR2 and VEGF following baicalein treatment. | [51] | |
| Autophagy | Baicalein induced autophagy and apoptosis in the FRO cells, via regulating the PI3K/Akt and ERK pathways. | [58] |
| STAT3 | Baicalein played a role in the inhibition of cell viability and epithelial–mesenchymal transition, and the induction of cell apoptosis, via the enhancement of miR-183 following the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway’s inactivation. | [63] |
| Wnt/β-catenin | Baicalein and miR-25 decreased the expressions of Axin2 and β-catenin, whereas expression of GSK-3β increased. | [64] |
| Baicalein improved the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway through disrupting its translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus. | [65] | |
| PTEN | Baicalein inhibited hypoxia-induced Akt phosphorylation through enhancing PTEN accumulation. | [69] |
| Baicalein upregulated PTEN expression, downregulated miR-424-3p, and downregulated PI3K and p-Akt. | [70] | |
| ERK/MAPK | The combination of baicalin and baicalein treatment caused the activation of ERK and p38 MAPK, and the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and ERK. | [77] |
| Baicalein decreased the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and MEK1 in a concentration-dependent fashion. | [78] |
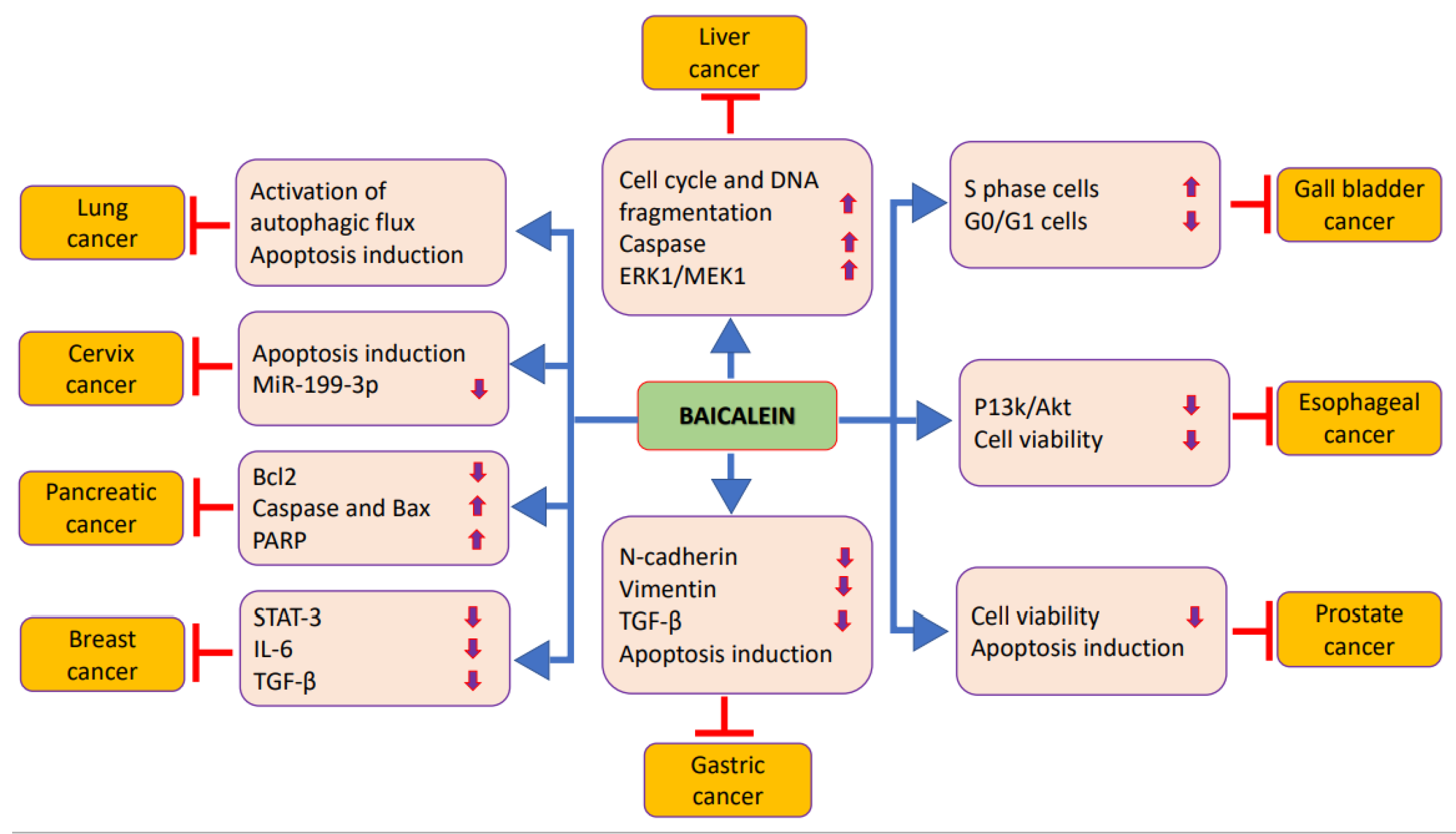
3. Role of Baicalein in Prevention and Treatment of Different Cancers
3.1. Prostate Cancer
3.2. Liver Cancer
3.3. Pancreatic Cancer
3.4. Gastric Cancer
3.5. Gallbladder Cancer
3.6. Bladder Cancer
| Cancers | Cell Lines | Outcome | Refs. |
| Prostate | PC-3 and DU145 | Baicalein inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells in a time- and dose-dependent way. | [81] |
| Baicalin and baicalein showed dose-dependent growth inhibitory effects on umbilical vein endothelial cells and human prostate cancer cells. | [82] | ||
| Liver | Bel-7402 | Baicalein inhibits the proliferation of liver cancer cells through cell cycle arrest induction at the S and G2/M phase. Besides this, baicalein alters the miRNA expression profiles in liver cancer cells. | [83] |
| Hep J2 and Hep G2 | Baicalein inhibited the cell cycle in the S phase and baicalein treatment damaged the integrity of the cell membrane and decreased mitochondrial transmembrane potential. | [84] | |
| HepG2, BEL-7402, SMMC-7721 | Baicalein especially inhibits liver tumor growth via MEK-ERK inhibition signaling and by encouraging intrinsic apoptosis. | [85] | |
| Pancreas | CAPAN-2 | Baicalein induce dose-dependent as well as specific anticancer effects. The antiproliferative effects were seen due to the induction of apoptosis and increased apoptotic cells with increasing the concentration of the used molecule. | [88] |
| PANC-1, MIA PaCa-2 and HPAF-II | Baicalein showed synergistic potential with gemcitabine or docetaxel on the treatment of cancer cells. | [89] | |
| BxPC-3, HPAF-II, Capan-2, AsPc-1, MIA PaCa-2, and Panc-1 | Baicalein encourages apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells via anti-apoptotic Mcl-1 protein downregulation. | [90] | |
| Gastric | AGS | Baicalein inhibited the invasion and migration of cancer cells. | [91] |
| SGC-7901 | Baicalein strongly caused arrest at the S phase. It induced cancer cell apoptosis as well as disturbing the mitochondrial membrane potential in a dose-dependent way. | [92] | |
| Gall bladder | GBC-SD and SGC996 | Baicalein induced an important inhibitory effect on proliferation and caused apoptosis promotion. Moreover, treatment via baicalein inhibited the metastasis of cancer cells. | [93] |
| Urinary bladder | T24 | Baicalein suppressed the inhibition of growth and induction of apoptosis via loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential and activation of caspase-3 and 9. | [94] |
| 5637 | Baicalein played a role in the regulation of apoptic protein expression via increased Bcl-2 expression and decreased Bax expression. | [96] | |
| Bile ducts | HUH28 and TFK1, HUCCT1, QBC939 and MZ-ChA-1 | Baicalein showed potential anti-cancer activities through suppressing multiple malignant phenotypes as well as most possibly via inhibiting the activation of the STAT3 and Akt/NF-κB signaling pathways. | [97] |
| Colorectal | HT-29 | Baicalein encouraged apoptosis through the activation of Akt in a p53-dependent way in colon cancer cells. | [98] |
| HT-29, HCT-116, SW480, and SW620 | Inhibition of autophagy increased the induction of apoptotic cell death via baicalein treatment in colon cancer cell lines. | [33] | |
| Breast | MDA-MB-231 | Baicalein played a role in the inhibition of proliferation, suggesting that baicalein can meaningfully inhibit the proliferation, invasiveness and migration of cancer cells via downregulation of SATB1expression. | [99] |
| MCF-7 | Baicalein suppress 17beta-estradiol-induced transactivation in cells expressing estrogen receptor alpha. | [100] | |
| MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 | Co-culturing with M2 macrophages meaningfully enhanced the EMT of both MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 and cancer cells. Baicalein regulates the polarization of M2 and reduces the secretion of TGF-β1. | [101] | |
| Cervix | SiHa and HeLa | Baicalein suspended the cell cycle at the G0/G1 phase through cyclin D1 downregulation via the signaling pathway of Akt-GSK3β. | [102] |
| HeLa, SiHa, ME-180, and Caski | Baicalein downregulated long noncoding RNA (BDLNR) initiating the anti-cancer effects of baicalein. | [103] | |
| HeLa and SiHa | Baicalin showed anti-cancer effects on cervical cancer cells via STAT3 targeting regulated signaling pathways. | [104] | |
| Ovarian | OVCAR-3 and CP-70 | Baicalein is more potent in inhibiting cancer cell viability as well as the expression of HIF-1α, vascular endothelial growth factor, cMyc, and NF-κB. | [49] |
| SKOV3, and CAOV3 | Baicalein inhibits the expression of MMP-2 and the invasion ability of cancer cells, probably via the p38 MAPK-dependent NF-κB signaling pathway. | [105] | |
| Oesophagus | EC-109 | Baicalein meaningfully inhibits growth and causes the induction of apoptosis in cancer cells. | [106] |
| Lung | A549 and H1299 | Baicalein activated AMP-activated protein kinase pathway. The knockdown of AMP-activated protein kinase with lentivirus encoded AMPKα reduced Baicalein-induced mitochondrial fission, autophagy and apoptosis. | [107] |
| Bone | MG-63 and Saos-2 | Baicalein inhibits migration, proliferation, as well as invasion, and encourages apoptosis in cancer cells. | [108] |
| MG-63 and 143B | Baicalein meaningfully decreases the proliferation of cancer cells in a concentration- and time-dependent fashion. In addition, baicalein induces apoptosis as well as cell cycle arrest and decreases cell motility. | [109] | |
| Oral | Cal27 | Baicalein enhances autophagy via the promotion of reactive oxygen species signaling pathways in oral cancer. | [110] |
| SCC25, CAL27 and HSC3 | Baicalein suppresses the growth of oral cancer cells via an Sp1/NF-κB-dependent mechanism. | [111] | |
| HSC-3 | In HSC-3 the decrease in pRb is mediated via baicalein through both the facilitation of cyclin D1 degradation and the activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor. | [112] | |
| Thyroid | 8505c ATC | The combination of baicalein and docetaxel meaningfully inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis. The combination treatment meaningfully inhibited the expressions of VEGF, Bax, TGF-β1, caspase-3, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and mTOR. | [113] |
| MDA-T68 | Baicalein induced dose-dependent suppression in the proliferation of thyroid cancer cells. Baicalein induced cell apoptosis in a concentration-dependent fashion. | [57] | |
| Brain | U251 | Baicalein inhibits glioblastoma cells’ viability and induces apoptosis through inhibiting the activity of NF-kB-p65, suggesting that Baicalein is a potential therapeutic agent for glioblastoma. | [114] |
| Skin | A375 and SK-MEL-2 | The suppression of baicalein on melanoma cells through the inhibition of tumor cell glucose uptake and metabolism via affecting the mTOR-HIF-1α signaling pathway. | [115] |
| B16F10 | Baicalein inhibits melanoma cell migration as well as invasion through decreasing the expression of matrix metalloproteinase and tightening TJ via claudin expression suppression. | [116] | |
| Blood | CMK, CMY, Y10, 6133, and 6133 MPL/W515L | Baicalein strongly inhibited proliferation of multiple Akt megakaryoblastic leukemia | [117] |
| HL-60 | Baicalein-induced apoptosis was noticeably blocked by the broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor. | [118] | |
| U266, NOP2, AMO1, and ILKM2 | Baicalein is a strong inhibitor of protein phosphorylation induced through Interlukin-6, and therefore may be a valuable agent for the treatment of myeloma. | [119] | |
| Lymphatic | EL4 | Baicalein treatment led to important reductions in the activity of thioredoxin reductase as well as nuclear levels of thioredoxin-1, thus enhancing caspase-3 activity and ASK1 levels. | [120] |
3.7. Bile Duct Cancer
3.8. Colorectal Cancer
3.9. Breast Cancer
3.10. Cervix Cancer
3.11. Ovarian Cancer
3.12. Esophageal Cancer
3.13. Lung Cancer
3.14. Bone Cancer
3.15. Oral Cancer
3.16. Thyroid Cancer
3.17. Brain Cancer
3.18. Skin Cancer
3.19. Leukemia
3.20. Myeloma
3.21. Lymphoma
4. Bioavailability and Strategies to Improve the Baicalein Delivery
| Nanoformulation | Outcome | Refs. |
|---|---|---|
| Baicalein–theophylline (BE-TH) co-crystals | Baicalein–theophylline (BE-TH) co-crystals significantly improved the solubility of baicalein. Co-crystals confirmed higher rates of dissolution than baicalein in hydrochloric acid as well as phosphate buffer. | [132] |
| Baicalein nanocrystal | The pulmonary baicalein nanocrystal showed fast as well as extensive absorption, and had nearly the same pharmacokinetic parameters as intravenous baicalein injection. | [133] |
| Baicalein-loaded aelf-microemulsifying drug delivery | The absorption of baicalein from the self-microemulsifying drug delivery system resulted in an increase in the relative bioavailability (about 200.7%) as compared with that of the baicalein suspension. | [134] |
| Baiclein-2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (HP-beta-CD) | After intravenous administration, the Ba/HP-beta-CD co-lyophilized product displays similar pharmacokinetics to free baicalein. | [135] |
| Baicalein-loaded long-circulating nanoliposomes (LCNs) | Long circulating nanoliposome-encapsulated baicalein yields better oral bioavailability. | [136] |
| Co-crystallization between baicalein and nicotinamide (NCT) | BE-NCT co-crystals enabled meaningfully better solubility and dissolution of baicalein | [137] |
| Liposomal baicalein | Liposomal baicalein inhibited leukemia cell growth, demonstrating that the liposome may be a potential vehicle to deliver baicalein for the treatment of leukemia. | [138] |
| Baicalein-loaded nanoliposomes (BAI-LP) | BAI-LP showed good antitumor effects, with a higher inhibition rate percentage than free baicalein. | [139] |
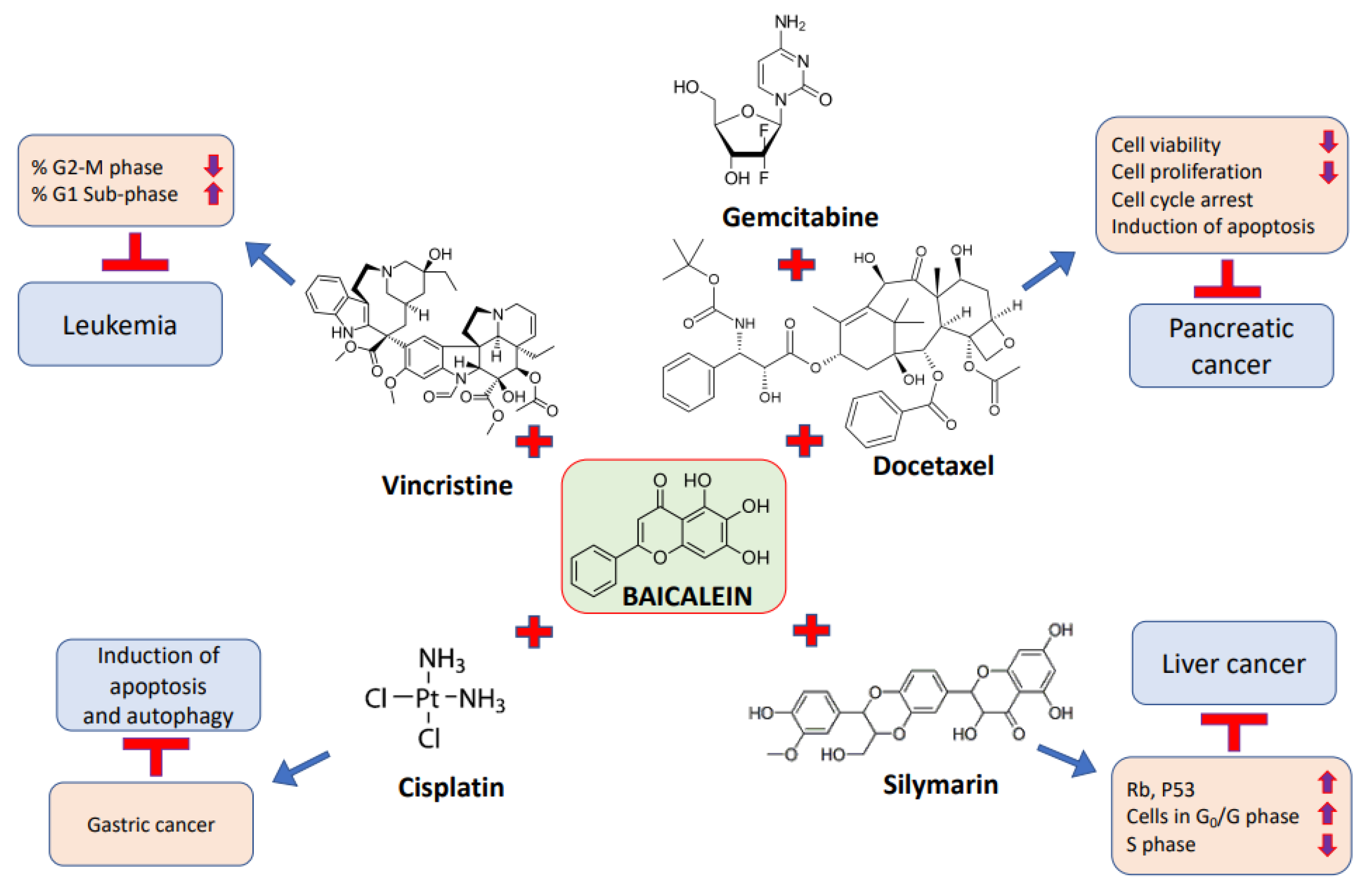
5. Synergistic Effect of Baicalein in Combination with Anti-Cancerous Drugs against Cancer Cells
| Cancer | Anti-Cancer Drug/Compound | Effects | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pancreatic cancer | Gemcitabine/docetaxel | Baicalein (low concentration) in combination with either gemcitabine or docetaxel achieved the powerful suppression of the migration of cancer cells. | [89] |
| Liver cancer | Silymarin | Baicalein in combination with silymarin caused an additive effect and a synergistic effect. | [140] |
| Leukemia | Lincristine | Synergistic therapeutic efficacy was noted in the combination of baicalein with vincristine. | [127] |
| Gastric cancer | Cisplatin | The combination of baicalein and cisplatin suppressed invasive capability and induced apoptosis and autophagy. | [56] |
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Devi, K.P.; Rajavel, T.; Nabavi, S.F.; Setzer, W.N.; Ahmadi, A.; Mansouri, K. Hesperidin: A promising anticancer agent from nature. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 76, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vineis, P.; Wild, C.P. Global cancer patterns: Causes and prevention. Lancet 2013, 383, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhu, W.; Thompson, P.; Hannun, Y.A. Evaluating intrinsic and non-intrinsic cancer risk factors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames, B.N. Mutagenesis and carcinogenesis: Endogenous and exogenous factors. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1989, 14, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.P.; Harris, C.C. Molecular epidemiology and carcinogenesis: Endogenous and exogenous carcinogens. Mutat. Res. 2000, 462, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatroodi, S.; Alnuqaydan, A.; Alsahli, M.; Khan, A.; Rahmani, A. Thymoquinone, the Most Prominent Constituent of Nigella Sativa, Attenuates Liver Damage in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats via Regulation of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Cyclooxygenase-2 Protein Expression. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzohairy, M.A.; Khan, A.A.; Ansari, M.A.; Babiker, A.Y.; Alsahli, M.A.; Almatroodi, S.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Protective Effect of Quercetin, a Flavonol against Benzo(a)pyrene-Induced Lung Injury via Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Angiogenesis and Cyclooxygenase-2 Signalling Molecule. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatroodi, S.A.; Alsahli, M.A.; Alharbi, H.M.; Khan, A.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG), An Active Constituent of Green Tea: Implications in the Prevention of Liver Injury Induced by Diethylnitrosamine (DEN) in Rats. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatroodi, S.A.; Alsahli, M.A.; Almatroudi, A.; Rahmani, A.H. Garlic and its Active Compounds: A Potential Candidate in The Prevention of Cancer by Modulating Various Cell Signalling Pathways. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Potential Therapeutic Targets of Curcumin, Most Abundant Active Compound of Turmeric Spice: Role in the Management of Various Types of Cancer. Recent Patents Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatroudi, A.; Alsahli, M.A.; Alrumaihi, F.; Allemailem, K.S.; Rahmani, A.H. Ginger: A Novel Strategy to Battle Cancer through Modulating Cell Signalling Pathways: A Review. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomasset, S.C.; Berry, D.P.; Garcea, G.; Marczylo, T.; Steward, W.P.; Gescher, A.J. Dietary polyphenolic phytochemicals—Promising cancer chemopreventive agents in humans? A review of their clinical properties. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 120, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, B.; Sun, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, W.; Yang, J.; Huang, C.; Li, Z. Baicalein: A review of its anti-cancer effects and mechanisms in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, J.; Wang, Z.; Ma, L.; Peng, B.; Mao, K.; Li, C.; Su, M.; Zhou, C.; Peng, G. Baicalein and baicalin inhibit colon cancer using two distinct fashions of apoptosis and senescence. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 20089–20102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Hou, R.; Gao, S.; Song, D.; Feng, Y. Baicalein inhibits proliferation activity of human colorectal cancer cells HCT116 through downregulation of Ezrin. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, X.; Yan, X.I.; Zhang, K. Baicalein inhibits the migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via suppression of the AKT signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 2016, 11, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Ma, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, S. Baicalein induces apoptosis and autophagy of breast cancer cells via inhibiting PI3K/AKT pathway in vivo and vitro. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 3961–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.-M.; Tsai, H.-C.; Lin, Y.-L.; Yang, J.-S.; Huang, A.-C.; Yang, M.-D.; Hsu, S.-C.; Chung, M.-C.; Wood, W.G.; Chung, J.-G. Mitochondrial-Dependent Caspase Activation Pathway Is Involved in Baicalein-Induced Apoptosis in Human Hepatoma J5 Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 35, 717–724. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.-H.; Yin, L.-H.; Grahn, T.H.M.; Ye, A.-F.; Zhao, Y.-R.; Zhang, Q.-Y. Anticancer Effects of Baicalein on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siveen, K.S.; Sikka, S.; Surana, R.; Dai, X.; Zhang, J.; Kumar, A.P.; Tan, B.K.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Targeting the STAT3 signaling pathway in cancer: Role of synthetic and natural inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2014, 1845, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A. Molecular pathways linking inflammation and cancer. Curr. Mol. Med. 2010, 10, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.W.; Karin, M. A cytokine-mediated link between innate immunity, inflammation, and cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujii, M.; Kawano, S.; Tsuji, S.; Sawaoka, H.; Hori, M.; DuBois, R.N. Cyclooxygenase Regulates Angiogenesis Induced by Colon Cancer Cells. Cell 1998, 93, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujii, M.; DuBois, R.N. Alterations in cellular adhesions and apoptosis in epithelial cells overexpressing prostaglandin en-doperoxidase synthase. Cell 1995, 83, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.-Z.; Liu, C.-H.; Wei, B.; Qiao, J.; Lu, T.; Wei, H.-C.; Chen, H.-D.; He, C.-D. Baicalein Inhibits DMBA/TPA-Induced Skin Tumorigenesis in Mice by Modulating Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Inflammation. Inflammation 2012, 36, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Hossain, M.A.; Kang, Y.J.; Jang, J.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Im, E.; Yoon, J.-H.; Kim, H.S.; Chung, H.Y.; Kim, N.D. Baicalein, an active component of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cells and prevents AOM/DSS-induced colon cancer in mice. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, N.; Selvamani, A.; Subramanian, R.; Pandi, A.; Thiruvengadam, D. Baicalein inhibits pulmonary carcinogene-sis-associated inflammation and interferes with COX-2, MMP-2 and MMP-9 expressions in-vivo. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 261, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katso, R.; Okkenhaug, K.; Ahmadi, K.; White, S.; Timms, J.; Waterfield, M.D. Cellular function of phosphoinositide 3-kinases: Impli-cations for development, homeostasis, and cancer. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2001, 17, 615–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, M.; De Santis, M.C.; Braccini, L.; Gulluni, F.; Hirsch, E. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: An updated review. Ann. Med. 2014, 46, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, D.; Li, Y.; Xing, J.; Sun, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Ren, X.; Lin, Z.; Jin, J.; et al. Baicalein inhibits PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and induces autophagy of MGC-803 cells. Chin. J. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 35, 613–618. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.; Watari, H.; AbuAlmaaty, A.; Ohba, Y.; Sakuragi, N. Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 150845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, R.M.; Muqbil, I.; Lowe, L.; Yedjou, C.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Lin, L.-T.; Siegelin, M.D.; Fimognari, C.; Kumar, N.B.; Dou, Q.P.; et al. Broad targeting of resistance to apoptosis in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, S78–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, T.; Nguyen, V.H.; Salazar, M.A.; Wong, P.; Diamond, D.J.; Yim, J.H.; Melstrom, L.G. Inhibition of Autophagy Amplifies Baicalein-Induced Apoptosis in Human Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2020, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, X.; Han, X.; Chen, P.; Wu, Q.; Feng, J.; Duan, T.; Chen, X.; Pan, T.; Yan, L.; Jin, T.; et al. Baicalin Induces Apoptosis and Suppresses the Cell Cycle Progression of Lung Cancer Cells Through Downregulating Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 7, 602282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Hao, Y.; Wan, X.; He, J.; Tong, Y. Baicalein inhibits cell development, metastasis and EMT and induces apoptosis by regu-lating ERK signaling pathway in osteosarcoma. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2020, 40, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zou, Y.; Han, H.; Huang, J. Baicalein induces human osteosarcoma cell line MG-63 apoptosis via ROS-induced BNIP3 expression. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 4731–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elledge, S.J. Cell Cycle Checkpoints: Preventing an Identity Crisis. Science 1996, 274, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartek, J.; Lukas, J. Mammalian G1- and S-phase checkpoints in response to DNA damage. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2001, 13, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, P.; Liu, J.; Broaddus, R.R.; Xue, F.; Zhang, W. Centrosome-associated regulators of the G2/M checkpoint as targets for cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer. 2009, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbrich, M.; Jeggo, P.A. The impact of a negligent G2/M checkpoint on genomic instability and cancer induction. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastan, M.B.; Bartek, J. Cell-cycle checkpoints and cancer. Nature 2004, 432, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, L.; Cai, L.; Wei, R.; Hu, H.; Jin, W. Effects of baicalein on apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Z.; Leung, H.W.C.; Lai, M.Y.; Wu, C.H. Baicalein induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human lung squamous carcinoma CH27 cells. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Shen, K.; Dai, Y. Baicalein Represses Cervical Cancer Cell Growth, Cell Cycle Progression and Promotes Apoptosis via Blocking AKT/mTOR Pathway by the Regulation of circHIAT1/miR-19a-3p Axis. Oncol. Targets Ther. 2021, 9, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, L.; O’Reilly, M.S.; Folkman, J. Dormancy of micrometastases: Balanced proliferation and apoptosis in the presence of angiogenesis suppression. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor. Eur. J. Cancer 1996, 32A, 2413–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.H.; Ababiker, A.Y.; Alsahli, M.A.; Almatroodi, S.A.; Husain, N.E.O.S. Prognostic Significance of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Her-2 Protein in the Genesis of Cervical Carcinoma. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiker, A.Y.; Almatroodi, S.A.; Almatroudi, A.; Alrumaihi, F.; Abdalaziz, M.S.; Alsahli, M.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Clinicopathological significance of VEGF and pAkt expressions in oral squamous cell car-cinoma. All Life 2020, 13, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, A.Y.; Ye, X.; Luo, H.; Rankin, G.O.; Chen, Y.C. Inhibitory Effect of Baicalin and Baicalein on Ovarian Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6012–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-G.; Choi, J.; Jung, H.-K.; Kim, B.; Kim, C.; Park, S.-Y.; Seol, J.-W. Baicalein inhibits tumor progression by inhibiting tumor cell growth and tumor angiogenesis. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 3011–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathcart, M.-C.; Useckaite, Z.; Drakeford, C.; Semik, V.; Lysaght, J.; Gately, K.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Pidgeon, G.P. Anti-cancer effects of baicalein in non-small cell lung cancer in-vitro and in-vivo. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.H.; Staudt, L.M. Toll-like receptor signaling. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a011247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, A.; Kaarniranta, K.; Kauppinen, A. Beclin 1 interactome controls the crosstalk between apoptosis, autophagy and inflammasome activation: Impact on the aging process. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 520–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, P.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Das, D.N.; Sinha, N.; Naik, P.P.; Bhutia, S.K. Mechanism of autophagic regulation in carcinogenesis and cancer therapeutics. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 39, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, P.; Kim, K.; Park, P.-H.; Ham, S.; Cho, J.; Song, K. Baicalein induces autophagic cell death through AMPK/ULK1 activation and downregulation of mTORC1 complex components in human cancer cells. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 4644–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Hu, J.; Shi, B.; Tie, J. Baicalein enhanced cisplatin sensitivity of gastric cancer cells by inducing cell apoptosis and autophagy via Akt/mTOR and Nrf2/Keap 1 pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 531, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Liu, G.; Wu, Y.; Liang, Q.; Li, L. Baicalein suppresses the growth of the human thyroid cancer cells by inducing mitotic ca-tastrophe, apoptosis and autophagy via NF-kB signalling pathway. J. BUON 2020, 25, 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Qiu, S.; Qin, J. Baicalein induced apoptosis and autophagy of undifferentiated thyroid cancer cells by the ERK/PI3K/Akt pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 3341–3352. [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg, J.F.; Wrzeszczynska, M.H.; Devgan, G.; Zhao, Y.; Pestell, R.G.; Albanese, C.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell 1999, 98, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortylewski, M.; Kujawski, M.; Wang, T.; Wei, S.; Zhang, S.; Pilon-Thomas, S.; Niu, G.; Kay, H.; Mulé, J.; Kerr, W.G.; et al. Inhibiting Stat3 signaling in the hematopoietic system elicits multicomponent an-titumor immunity. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Chen, S.J.; Tweardy, D.J. Cross-talk between retinoic acid and STAT3 signaling pathways in acute promyelocytic leu-kemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2003, 44, 2023–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susmitha, G.D.; Miyazato, K.; Ogura, K.; Yokoyama, S.; Hayakawa, Y. Anti-metastatic Effects of Baicalein by Targeting STAT3 Activity in Breast Cancer Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 1899–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.; Shi, J.; Teng, Y.; Song, C.; Zou, L.; Ye, F.; Zhang, H. Baicalein modulates the radiosensitivity of cervical cancer cells in vitro via miR-183 and the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 30, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaylagül, E.; Ülger, C. The effect of baicalein on Wnt/β-catenin pathway and miR-25 expression in Saos-2 osteosarcoma cell line. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 50, 1168–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.W.; Peng, L.Y.; Shi, C.J.; Li, J.C.; Pang, F.X.; Fu, W.M.; Fu, W.; Pan, X.; Zhang, J. Baicalein mediates the anti-tumor activity in Osteosarcoma through lncRNA-NEF driven Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulatory axis. J. Orthop. Transl. 2022, 33, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, A.; Alzohairy, M.; Babiker, A.Y.; Rizvi, M.A.; Elkarimahmad, H.G. Clinicopathological significance of PTEN and bcl2 ex-pressions in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2012, 5, 965–971. [Google Scholar]
- Babiker, A.Y.; Almatroudi, A.; Allemailem, K.S.; Husain, N.E.O.S.; Alsammani, M.A.; Alsahli, M.A.; Rahmani, A.H. Clinicopathologic Aspects of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix: Role of PTEN, BCL2 and P53. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, R.; Baker, S.J.; Barata, J.T.; Carracedo, A.; Cid, V.J.; Chin-Sang, I.D.; Davé, V.; Hertog, J.D.; Devreotes, P.; Eickholt, B.J.; et al. A Unified Nomenclature and Amino Acid Numbering for Human PTEN. Sci. Signal 2014, 7, pe15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhuang, M.; Zhong, C.; Peng, J.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y. Baicalein reverses hypoxia-induced 5-FU re-sistance in gastric cancer AGS cells through suppression of glycolysis and the PTEN/Akt/HIF-1α signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Yang, R.; Li, H.; Zhang, G. Baicalein inhibits cell growth and increases cisplatin sensitivity of A549 and H460 cells via miR-424-3p and targeting PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 2478–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikov, A.; Flores, K.; Maik-Rachline, G.; Zehorai, E.; Kapri-Pardes, E.; Berti, D.A.; Hanoch, T.; Besser, M.J.; Seger, R. The nuclear translocation of ERK1/2 as an anticancer target. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koul, H.K.; Pal, M.; Koul, S. Role of p38 MAP Kinase Signal Transduction in Solid Tumors. Genes Cancer 2013, 4, 342–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burotto, M.; Chiou, V.L.; Lee, J.-M.; Kohn, E.C. The MAPK pathway across different malignancies: A new perspective. Cancer 2014, 120, 3446–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakis, J.M.; Avruch, J. Mammalian MAPK Signal Transduction Pathways Activated by Stress and Inflammation: A 10-Year Update. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 689–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Davis, R.J.; Flavell, R.A. MAP Kinases in the Immune Response. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.-M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.-Y.; Wang, X.-F.; Motoo, Y.; Su, S.-B. The combination of baicalin and baicalein enhances apoptosis via the ERK/p38 MAPK pathway in human breast cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 1648–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, S.; Ji, Y.; Li, J.; An, P.; Ren, H.; Liang, R.; Yang, J.; Li, Z. Baicalein Inhibits the Invasion and Metastatic Capabilities of Hepato-cellular Carcinoma Cells via Down-Regulation of the ERK Pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72927. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzmaurice, C.; Allen, C.; Barber, R.M.; Barregard, L.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brenner, H.; Dicker, D.J.; Chimed-Orchir, O.; Dandona, R.; Dandona, L.; et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 524. [Google Scholar]
- Leslie, S.W.; Soon-Sutton, T.L.; Sajjad, H.; Siref, L.E. Prostate Cancer. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Hu, X.; Xing, Z.; Xing, R.; Lv, R.; Cheng, X.; Su, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, Z.; Nilsson, S.; et al. Baicalein inhibits prostate cancer cell growth and metastasis via the caveolin-1/AKT/mTOR pathway. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2015, 406, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miocinovic, R.; McCabe, N.; Keck, R.; Jankun, J.; Hampton, J.; Selman, S. In vivo and in vitro effect of baicalein on human prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 26, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bie, B.; Sun, J.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, W.; Huang, C.; Yang, J.; Li, Z. Baicalein, a Natural Anti-Cancer Compound, Alters MicroRNA Expression Profiles in Bel-7402 Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-H.; Huang, L.L.H.; Huang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Lee, Y.; Lu, F.-J. Baicalein, a Novel Apoptotic Agent for Hepatoma Cell Lines:A Potential Medicine for Hepatoma. Nutr. Cancer 2000, 38, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, R.R.; Zhang, S.; Qi, J.A.; Wang, Z.D.; Li, J.; Liu, P.J.; Huang, C.; Le, X.F.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.F. Preferential inhibition of hepatocellular car-cinoma by the flavonoid Baicalein through blocking MEK-ERK signaling. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Tang, W.; Yang, Y.; Tang, L.; Dai, R.; Pu, B.; Feng, C.; Xia, J. Long noncoding RNA NKILA enhances the anti-cancer effects of baicalein in hepatocellular carcinoma via the regulation of NF-κB signaling. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 285, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Duan, B.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, R.; Sun, J.; Bie, B.; Yang, S.; Huang, C.; Yang, J.; Li, Z. Baicalein sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to 5-FU and Epirubicin by activating apoptosis and ameliorating P-glycoprotein activity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 98, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; He, J.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L. Baicalein flavone targets cisplatin resistant human pancreatic cancer cells via inducing S-phase cell cycle arrest, inhibition of cell migration and invasion, caspase activation and mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. J. BUON 2020, 25, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Feng, J.; Sun, M.; Yuan, W.; Xiao, R.; Xiong, J.; Huang, X.; Xiong, M.; Chen, W.; Yu, X.; et al. Synergistic effects of baicalein with gemcitabine or docetaxel on the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 1878–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Chen, M.C.; Pham, H.; Angst, E.; King, J.C.; Park, J.; Brovman, E.Y.; Ishiguro, H.; Harris, D.M.; Reber, H.A.; et al. Baicalein, a component of Scutellaria baicalensis, induces apoptosis by Mcl-1 down-regulation in human pancreatic cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhuang, M.; Peng, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, T.; Li, S.; Lin, M.; Lin, H.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Baicalein inhibits migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells through suppression of the TGF-β signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 1999–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Liu, T.; Jiang, L.; Wu, X.; Cao, Y.; Li, M.; Dong, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H. The Traditional Chinese Medicine Baicalein Potently Inhibits Gastric Cancer Cells. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-Y.; Gong, W.; Tan, Z.-J.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.-S.; Weng, H.; Ding, Q.; Shu, Y.-J.; Bao, R.-F.; Cao, Y.; et al. Baicalein Inhibits Progression of Gallbladder Cancer Cells by Downregulating ZFX. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0114851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liang, R.-R.; Li, J.; An, P.; Wang, Z.-M.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.-F. Baicalein induces apoptosis via a mitochondrial-dependent caspase activation pathway in T24 bladder cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Y.; Tsai, K.W.; Li, Y.Z.; Chang, Y.S.; Lai, Y.C.; Laio, Y.H.; Wu, J.D.; Liu, Y.W. Anti-Bladder-Tumor Effect of Baicalein from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi and Its Application In Vivo. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 579751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.-O.; Park, C.; Hwang, H.-J.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, G.-Y.; Cho, E.-J.; Kim, W.-J.; Choi, Y.H. Baicalein induces apoptosis via ROS-dependent activation of caspases in human bladder cancer 5637 cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, P.; Shang, J.; Chen, D.L.; Li, S.Y.; Fan, R.; Li, R.H.; Li, H.Q.; Zhang, S.Y.; Shen, D.Y. Baicalein mediates anticancer effect on cholan-giocarcinoma through co-targeting the AKT/NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathway. Process Biochem. 2021, 102, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, H.-R.; Lee, S.-H.; Cho, S.-D.; Choi, C.-S.; Nam, J.-S.; Jung, J.-Y. Antitumor actions of baicalein and wogonin in HT-29 human colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.-Y.; Xue, X.-H.; Ma, Y.-N.; Zhang, S.-Q. Effect of baicalein on the expression of SATB1 in human breast cancer cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 1665–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Po, L.S.; Chen, Z.Y.; Tsang, D.S.; Leung, L.K. Baicalein and genistein display differential actions on estrogen receptor (ER) transac-tivation and apoptosis in MCF-7 cells. Cancer Lett. 2002, 187, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Qu, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, X.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Q.; Yan, W.; Zhao, Z.; Hui, Y.; et al. Baicalein suppress EMT of breast cancer by mediating tumor-associated macrophages polarization. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 1528–1540. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Yang, Z.; Dang, H.; Peng, H.; Dai, Z. Baicalein Inhibits the Proliferation of Cervical Cancer Cells Through the GSK3β-Dependent Pathway. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2018, 26, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Tang, L.; Chen, F.; Xia, J. Baicalein inhibits cervical cancer progression via downregulating long noncoding RNA BDLNR and its downstream PI3 K/Akt pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 94, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Zhao, X. Baicalin Inhibits Human Cervical Cancer Cells by Suppressing Protein Kinase C/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (PKC/STAT3) Signaling Pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 1955–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Xin, S.; Wang, H.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Wei, H. Baicalein inhibits MMP-2 expression in human ovarian cancer cells by sup-pressing the p38 MAPK-dependent NF-κB signaling pathway. Anticancer Drugs 2015, 26, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-B.; Lu, P.; Guo, Q.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Meng, X.-Y. Baicalein induces apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells through modulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 5, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Sun, X.; Huang, J.; Dong, J. Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission contributes to baicalein-induced apoptosis and autophagy in lung cancer via activation of AMPK signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1403–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, W.; Wang, W. Baicalein inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion through the miR 183/Ezrin pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Zheng, D.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; Liu, G.; Song, Q.; Sun, X.; Tao, C.; Hu, Q.; Gao, T.; et al. Baicalein inhibits progression of osteosarcoma cells through inactivation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 86098–86116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lu, M.; Jiang, X.X.; Pan, M.X.; Mao, J.W.; Chen, M. Inhibiting reactive oxygen species-dependent autophagy enhanced bai-calein-induced apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 71, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Lv, J. Baicalein inhibits the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by downregulating the expression of transcription factor SpInt. J. Oncol. 2019, 56, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-H.; Li, L.-A.; Lin, P.; Cheng, L.-C.; Hung, C.-H.; Chang, N.W.; Lin, C. Baicalein induces G1 arrest in oral cancer cells by enhancing the degradation of cyclin D1 and activating AhR to decrease Rb phosphorylation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 263, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Han, S.E.; Nam-Goong, I.S.; Kim, Y.I.; Kim, E.S. Combined Effects of Baicalein and Docetaxel on Apoptosis in 8505c An-aplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells via Downregulation of the ERK and Akt/mTOR Pathways. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 33, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H. Baicalein Induces the Apoptosis of U251 Glioblastoma Cell Lines via the NF-kB-P65-Mediated Mechanism. Anim. Cell Syst. 2016, 20, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Peng, B.; Nayak, Y.; Wang, C.; Si, F.; Liu, X.; Dou, J.; Xu, H.; Peng, G. Baicalein and Baicalin Promote Melanoma Apoptosis and Senescence via Metabolic Inhibition. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.-O.; Cho, E.-J.; Jeong, J.-W.; Park, C.; Hong, S.-H.; Hwang, H.-J.; Moon, S.-K.; Son, C.G.; Kim, W.-J.; Choi, Y.H. Baicalein Inhibits the Migration and Invasion of B16F10 Mouse Melanoma Cells through Inactivation of the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Biomol. Ther. 2017, 25, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zeng, J.; Yan, Z.; Ma, Z.; Liu, S.; Huang, Z. Baicalein antagonizes acute megakaryoblastic leukemia in vitro and in vivo by inducing cell cycle arrest. Cell Biosci. 2016, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tyan, Y.; Kuo, H.; Chang, W.; Hsia, T.; Chung, J. Baicalein induced in vitro apoptosis undergo caspases activity in human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 42, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ma, Z.; Cai, H.; Li, Q.; Rong, W.; Kawano, M. Inhibitory effect of baicalein on IL-6-mediated signaling cascades in human myeloma cells. Eur. J. Haematol. 2010, 84, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwardhan, R.S.; Pal, D.; Checker, R.; Sharma, D.; Sandur, S.K. Baicalein induces cell death in murine T cell lymphoma via inhibition of thioredoxin system. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 91, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.-Q.; Zhou, Y.-R.; Rao, X.; Yang, H.; Zhuang, X.H.; Ke, X.-J.; Peng, G.-Y.; Zhou, C.-L.; Shen, B.-Y.; Dou, J. Baicalein induces the apoptosis of HCT116 human colon cancer cells via the upregulation of DEPP/Gadd45a and activation of MAPKs. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 750–760. [Google Scholar]
- Yersal, O.; Barutca, S. Biological subtypes of breast cancer: Prognostic and therapeutic implications. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliu-Piqué, M.; Pandiella, A.; Ocana, A. Breast Cancer Heterogeneity and Response to Novel Therapeutics. Cancers 2020, 12, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Xia, J.; Cao, Y.; Tang, L.; Tang, X.; Li, Z. SNHG1 represses the anti-cancer roles of baicalein in cervical cancer through regu-lating miR-3127-5p/FZD4/Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-F.; Xu, Y.-L.; Tang, Z.-H.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.-L.; Chen, X.; Lu, J.; Leung, C.-H.; Ma, D.-L.; Qiang, W.-A.; et al. Baicalein Induces Beclin 1- and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase-Dependent Autophagy in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2017, 45, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.-R.; Jiang, Y.-S. Effect of treatment with baicalein on the intracerebral tumor growth and survival of orthotopic glioma models. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2015, 124, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Wu, C.S.; Shieh, J.J.; Wu, J.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Chung, T.W.; Chen, Y.K.; Lin, C.C. Baicalein Triggers Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis and Enhances the Antileukemic Effect of Vincristine in Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia CCRF-CEM Cells. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 124747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-P.; He, L.; Zhang, Q.-P.; Zeng, X.-T.; Liu, S.-Q. Baicalein Inhibits Proliferation of Myeloma U266 Cells by Downregulating IKZF1 and IKZF. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 2809–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.-Y.; Liu, L.-P.; Qin, J.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Tang, J.-Z.; Mo, S.-L. Baicalein decreases side population proportion via inhibition of ABCG2 in multiple myeloma cell line RPMI 8226 in vitro. Fitoterapia 2014, 94, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; He, G.; Song, J.; Wang, S.; Xin, W.; Zhang, D.; Du, G. Pharmacokinetic study of baicalein after oral administration in monkeys. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shi, A.; Pang, H.; Xue, W.; Li, Y.; Cao, G.; Yan, B.; Dong, F.; Li, K.; Xiao, W.; et al. Safety, tolerability, and pharma-cokinetics of a single ascending dose of baicalein chewable tablets in healthy subjects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 28, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, S.; Qi, D.; Li, N.; Guo, P.; Liu, Z. A strategy to improve the oral availability of baicalein: The baicalein-theophylline cocrystal. Fitoterapia 2018, 129, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lv, H.; Jiang, K.; Gao, Y. Enhanced bioavailability after oral and pulmonary administration of baicalein nanocrystal. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Tian, R.; Hu, W.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. Preparation and evaluation of self-microemulsifying drug delivery system of baicalein. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1532–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Qiu, L.; Gao, J.; Jin, Y. Preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation of formulation of baicalein with hydroxypro-pyl-beta-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 7, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wu, W.; Liu, Q.; Chen, S. Long-circulating nanoliposomes (LCNs) sustained delivery of baicalein (BAI) with desired oral bioavailability in vivo. Drug Deliv. 2013, 20, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, L. Baicalein-nicotinamide cocrystal with enhanced solubility, dissolution, and oral bioavailability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 2330–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.X.; Wen, X.; Bell, C.; Appiah, S. Liposome-delivered baicalein induction of myeloid leukemia K562 cell death via reactive oxygen species generation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 4524–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, H.; Gao, L.; Zhai, Y.; Shi, M.; Li, J.; Xiu, C.; Cao, J.; Cheng, S.; Jiang, L.; et al. Preparation and Characterization of Baicalein-Loaded Nanoliposomes for Antitumor Therapy. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 2861915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-H.; Huang, T.-S.; Wong, C.-H.; Hong, C.-L.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Liang, C.-C.; Lu, F.-J.; Chang, W.-H. Synergistic anti-cancer effect of baicalein and silymarin on human hepatoma HepG2 Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahmani, A.H.; Almatroudi, A.; Khan, A.A.; Babiker, A.Y.; Alanezi, M.; Allemailem, K.S. The Multifaceted Role of Baicalein in Cancer Management through Modulation of Cell Signalling Pathways. Molecules 2022, 27, 8023. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27228023
Rahmani AH, Almatroudi A, Khan AA, Babiker AY, Alanezi M, Allemailem KS. The Multifaceted Role of Baicalein in Cancer Management through Modulation of Cell Signalling Pathways. Molecules. 2022; 27(22):8023. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27228023
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahmani, Arshad Husain, Ahmad Almatroudi, Amjad Ali Khan, Ali Yousif Babiker, Malak Alanezi, and Khaled S. Allemailem. 2022. "The Multifaceted Role of Baicalein in Cancer Management through Modulation of Cell Signalling Pathways" Molecules 27, no. 22: 8023. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27228023
APA StyleRahmani, A. H., Almatroudi, A., Khan, A. A., Babiker, A. Y., Alanezi, M., & Allemailem, K. S. (2022). The Multifaceted Role of Baicalein in Cancer Management through Modulation of Cell Signalling Pathways. Molecules, 27(22), 8023. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27228023








