1. Introduction
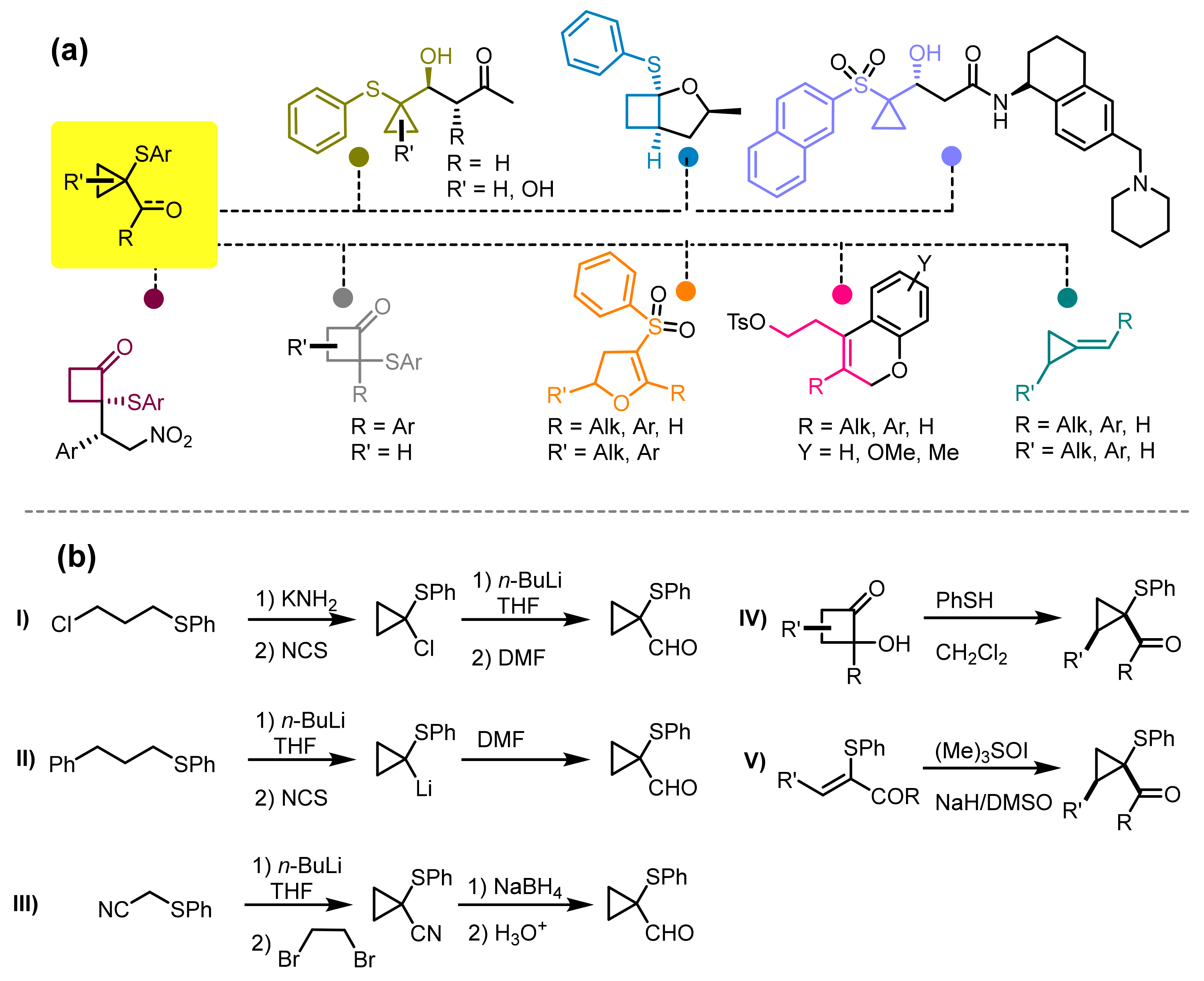
Cyclopropyl carbaldehydes and cyclopropyl ketones represent a very useful synthetic tool for the construction of complex molecular structures that have been used in the preparation of bioactive molecules [
1,
2], building blocks [
3,
4,
5,
6] and enantiomerically enriched, strained carbocyclic systems [
7,
8,
9] (
Figure 1a). Since the 1970s, several authors have highlighted the synthetic potential of this class of compounds, proposing for their preparation various strategies that mainly involve the use of organolithium reactants in deprotonation procedures involving bis-arylthiopropanes or (3-chloropropyl)(phenyl)sulfane [
10,
11,
12], the deprotonation of the commercially available phenylthiocyclopropane [
13,
14] and the capture of suitable electrophiles [
15] or, alternatively, the cyclopropanation of sulfanylnitriles [
16,
17] (
Figure 1b). Moreover, their preparation represents a crucial step in the synthesis of complex molecules, cyclobutanone derivatives and other strained carbocyclic compounds [
18], polycyclic molecular architectures [
19] or heterocyclic compounds such as dihydrofuran and dihydropyran adducts [
20,
21], thus extending their potential uses as fundamental reagents in organic synthesis.
Recently, our research group has developed a new protocol for the construction of these derivatives that exploits the nucleophilic-acid-catalyzed attack of alkyl- and arylthiols to 2-hydroxycyclobutanones (HCBs) [
22]. This process allows us to obtain cyclopropyl aldehydes and ketones in high chemical yields, with good tolerance of functional groups and with a high potential for scale-up. An extension of this protocol also allowed access to the synthesis of cyclobutanone systems through the generation of transient cyclopropyl carbaldehyde species and their C3-C4 ring expansion to access 2-sulfanylcyclobutanones [
23]. This last result was obtained using sulfonic resins such as nafion-50 (NR-50), which could be recovered after the synthetic process and reused several times, without particular loss of the catalytic performance. Despite these achievements, the developed strategies for the preparation of acid-catalyzed cyclopropyl carbaldehydes or ketones and their derivatives suffer from a series of limitations, the first of which is the use of toxic or unpleasant reagents such as thiols, which must be suitably handled [
24,
25,
26]. Secondly, the acquisition of large quantities of product shows the classic disadvantages linked to batch reactions, such as the control and tuning of optimal reaction conditions for scale-up purposes and the formation of non-negligible amounts of disulfides as unwanted by-products. On the other hand, the continuous-flow synthesis of sulfur-containing adducts from thiols has been successfully performed, highlighting the advantages of these methods [
27,
28]. Nevertheless, a certain number of continuous-flow cyclopropane derivative synthesis methods have been reported by several authors in the last decade, including light-mediated borocyclopropanation [
29] and ethyldiazoacetate addition to styrene [
30,
31] and the transition-metal-catalyzed synthesis of cyclopropyl phosphonates [
32], and esters have been also achieved [
33].
However, up-to-date continuous-flow processes for the synthesis of arylthio cyclopropyl derivatives from HCB C4-C3 ring contraction are unreported.
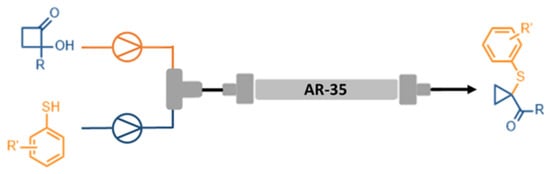
To implement our previous synthetic protocols, herein, we propose the continuous-flow synthesis of a series of cyclopropyl carbaldehydes and ketones by using an Amberlyst (Amberlyst 15 (AR-15) or Amberlyst 35 (AR-35)) packed bed, which allowed us to afford the desired compounds in good to excellent chemical yields, perform the evaluation of the catalytic performance of this stationary phase over time and assess its reuse during a substrate-scope investigation.
2. Results and Discussion
To develop an efficient and scalable process to access cyclopropylcarbonyl compounds, starting from our previous achievements [
22,
23], we first evaluated the catalytic performance of two commercially available sulfonic resins, AR-15 and AR-35, in batch experiments, using 1 mmol of 2-hydroxycyclobutanone
1a and benzenethiol
2a (1.0 equiv.) as a model reaction. The choice of using acid resins to promote this process stems from the fact that these polymeric matrices are widely available on the market, are inexpensive, can be regenerated and have already been used in various industrial processes, generally with excellent results.
Batch control reactions were carried out in different solvents at room temperature and monitored by GC-MS analysis, as shown in
Table 1. In line with the results obtained in our previous work [
22], dichloromethane (DCM) proved to be an excellent solvent, allowing us to obtain the compound
3a in 88% conversion in reactions carried out with AR-15 and 93% with AR-35 (entries 1 and 2). Excellent results were also obtained with tetrahydrofuran (THF), which allowed us to obtain comparable conversion values after 6 h reaction (entries 3 and 4). Moreover, aiming to reduce the environmental impact associated with the use of problematic or hazardous solvents, we also considered 2-methyl tetrahydrofuran (2Me-THF) as a potential greener alternative (entries 7 and 8) [
34,
35]. These reactions led to the conversion of
1a into the corresponding carbaldehyde
3a in 87% and 94%, respectively. On the other hand, experiments carried out in 1,4 dioxane performed less well (entry 5 and 6).
Although AR-15 and AR-35 show similar structural features, such as pore size (approx. 24 nm) and a surface area that varies between 37.3 m
2/g
−1 for AR-15 and 40.7 m
2/g
−1 for AR-35 [
36,
37,
38], in this investigation, AR-35 exhibited better catalytic properties in the abovementioned experiments. For this reason, we decide to use this cationic resin for the realization of our continuous-flow system, obtaining comparable results with the batch protocol. In more detail, the dry resin used in this work [H
+] ≅ 5.3 mmol/g was ground by a zirconia ball mill (one ZrO
2 ball) for 15 min at 20 Hz [
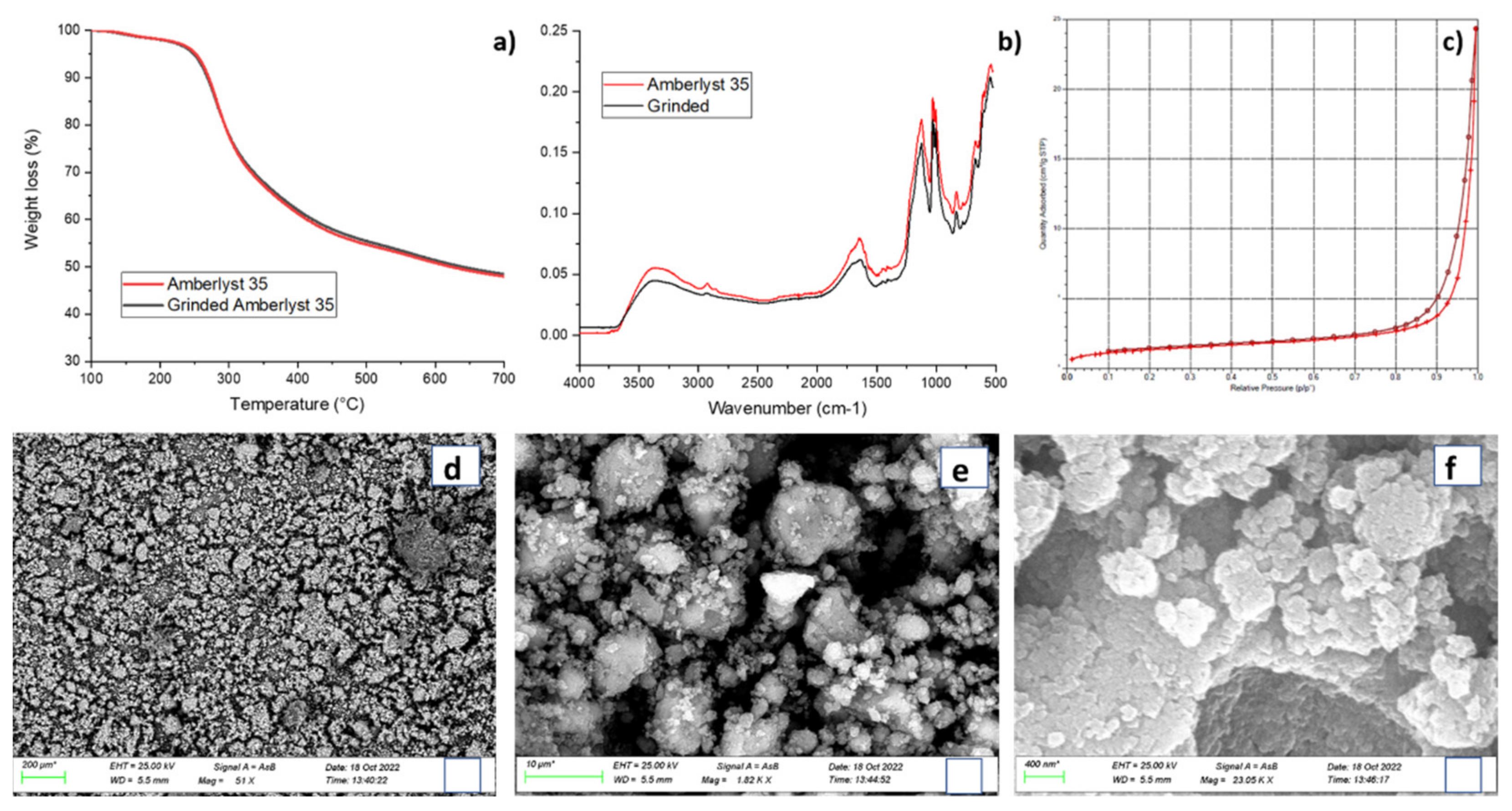
39]. Once recovered from the jars, the powders were submitted to thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) to highlight potential modifications of the material. However, the analysis of pre- and post-grinding AR-35 samples showed identical behavior, maintaining the same characteristics and thermal stability, reflecting their structure (
Figure 2a). This result was also in accordance with the ATR-FTIR analysis, which showed superimposable spectra for the commercial resin and the ball-milled AR-35 (
Figure 2b). The only difference found between the two forms was a greater tendency of the ground AR-35 to adsorb moisture. Therefore, in the first TGA analyses, we observed a loss of approximately 10–15% of water compared to the commercial product. On the other hand, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area analysis of neat AR-35 showed a BET surface area of 286,015 m
2/g and BJH adsorption average pore width (4V/A) of around 34.6760 nm. Meanwhile, the ground sample showed a considerable surface area reduction to 48,426 m
2/g and a pore width (4V/A) of approximately 37.0067 nm (a complete BET analysis of the powders is reported in the ESI). Finally, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) studies were carried out to determine the particle morphology, distribution and dimensions (
Figure 2d 51×,
Figure 2e 1800× and
Figure 2f 23,000×). These captures showed that after the grinding process, AR-35 appeared as a globular and amorphous material, poorly sorted and well defined. The images also indicated evidently variable grains (50 nm–2
µ), emphasizing a distinct and marked tendency to amalgamate. In addition, energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX) was performed to determine the abundancy of the sulfur element, having a parameter attributable to the quantity of sulfonic groups in the investigated material (see ESI for further details).
After these characterizations, AR-35 was loaded (ca. 4 grams) onto a 5 cm stainless steel column with an inner diameter of 0.8 cm and suitably packed by compressing the powders by means of a piston (internal volume 2.51 cm
3) [
40,
41]. The columns were sealed with their corresponding frits (inner/outer) and secured with nuts. The obtained packed bed was connected from one part (inlet) to a T-mixer, which allowed the connection with two independent syringe pump systems to dispense the THF solutions of
1a and
2a. The output was connected to a collection bottle, as shown in
Scheme 1. Columns with the same internal diameter and different lengths (2, 10, 15 cm) were also filled with AR-35, following the same procedure described above, and studied in subsequent tests [
42,
43] (
Figure 3).
Initially, 1.0 M solutions of HCB
1a (20 mL) and 1.0 M thiol
2a (20 mL) were fluxed with high flow rates, resulting in low conversions of the corresponding adduct
3a (entry 1),
Table 2. Reducing the flow rates led to an improvement in the conversion (entry 2). Keeping the flow rate constant and using 0.1 M solutions of
1a and
2a, we were able to obtain better results, reaching conversions equal to 75% (entry 3). Further reductions of the flow rate to 0.3 mL/min allowed us to increase the conversion to a maximum of 90% (entry 4). The use of longer columns containing greater quantities of resin, and tuning the residence times of the reagents, allowed us to obtain excellent results when a flow rate of 0.5 mL/min was set (entry 5 and 6), recovering ca. 1.8 g (93% yield) of carbaldehyde
3a. Further attempts to increase the conversion of the product
3a by using more concentrated solutions of
1a and
2a did not allow us to obtain equally satisfactory results (entry 7), and the formation of a certain amount of disulfides (15%) was observed. For this reason, we decided to use, for our further investigations, the following set-up as optimal operational conditions: 0.5 M reagent solutions, 15-cm-long AR-35 packed-bed columns and 0.5 mL/min flow rate (τ
res = 5.6 min, V
0 = 2.8 cm
3) (entry 8, see also ESI). The preparation of
3a was also performed in 2Me-THF, obtaining superimposable results with those obtained in THF (entry 9).
With these conditions in hand, we proceeded to explore the scope of this transformation.
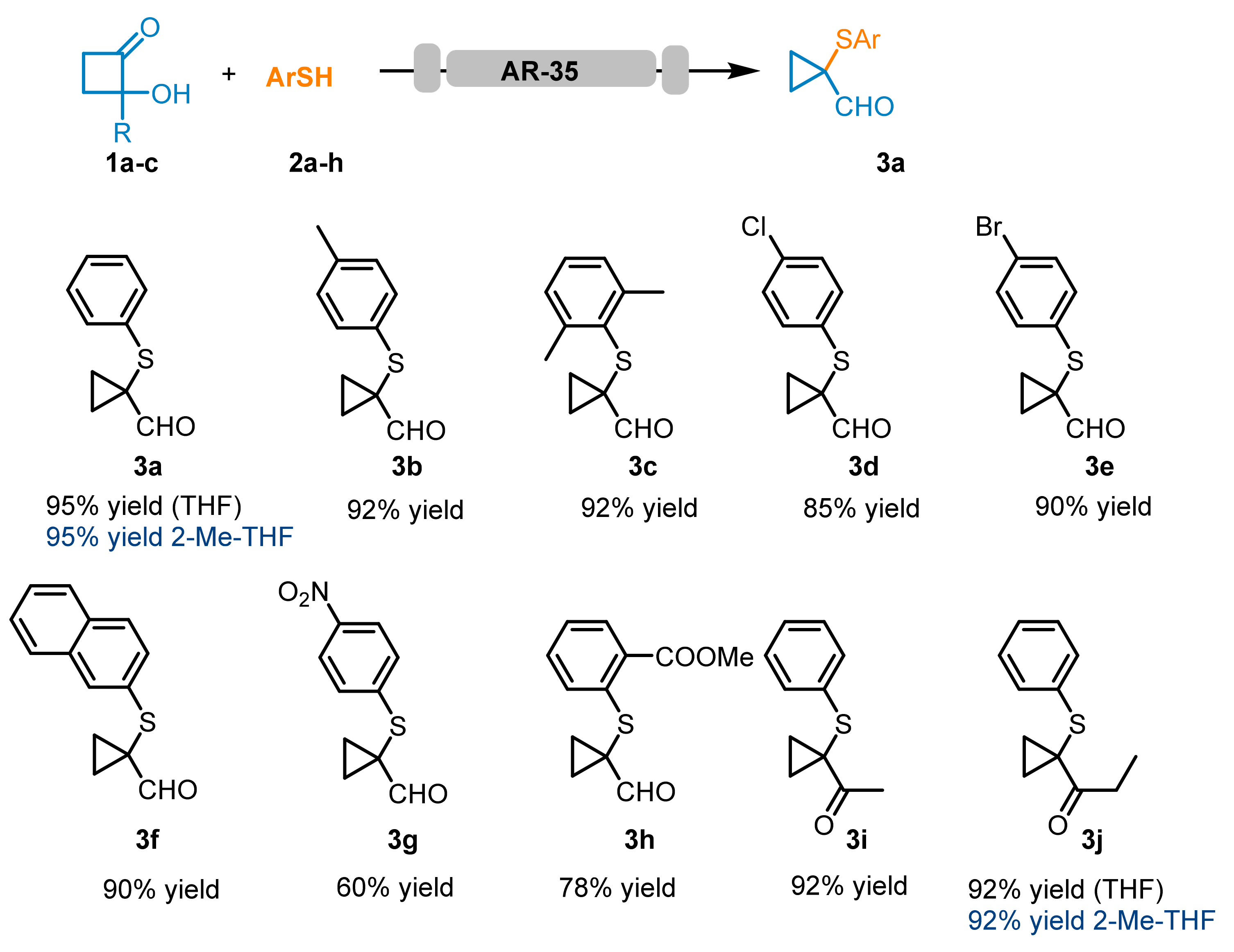
As reported in
Scheme 1, all the screened thiols reacted smoothly, forming the corresponding cyclopropyl carbaldehydes
3a–f and cyclopropyl ketones
3i and
3j with good to excellent isolated yields. Moreover, GC-MS analysis of the collected reaction solutions revealed low amounts of the corresponding disulfides (< 5%). Compound (
3j) was also prepared using 2Me-THF as a solvent, obtaining high yields (92%). However, thiols containing electron-withdrawing groups, such as 4-nitrobenzene thiol
2g and methyl 2-mercaptobenzoate
3h, showed reduced reactivity, leading to the isolation of the corresponding adducts
3g and
3h, respectively, in 60 and 78% yield.
The continuous-flow synthesis of the cyclopropyl derivatives
3a–
j was carried out using a dedicated column for each thiol included in the panel. Meanwhile, in a second set of experiments, to investigate the general use of these columns, a further 15 cm column was used to evaluate the possibility of carrying out the preparation of selected compounds
3c,
3f and
3h, alternating washing cycles with THF (THF HPLC grade, 0.5 M reagent conc., total vol. 40 mL, 0.5 mL/min flow rate). These experiments are summarized in
Table 3. The experiments thus conducted allowed the isolation of the corresponding carbaldehyde derivatives in good chemical yields, without observing large fluctuations in yield, compared to the reactions previously conducted and reported within the scope of this study (
Scheme 1). This result led us to posit that it is therefore possible to use the AR-35 packed columns as a reusable and general system for this type of reaction, at least on a laboratory scale.
Delighted by these results, we proceeded to evaluate the scale-up of this process [
23] and its suitability for multigram-scale synthesis via the implementation of HPLC pumps (instead of syringe pumps), which were connected by a T-mixer to a 15 cm AR-35 packed-bed column (inner pressure 1250 psi). This new set-up allowed us to obtain 31.4 g (ca. 86%) of the corresponding cyclopropyl ketone
3i in 24 h, using THF as a solvent.
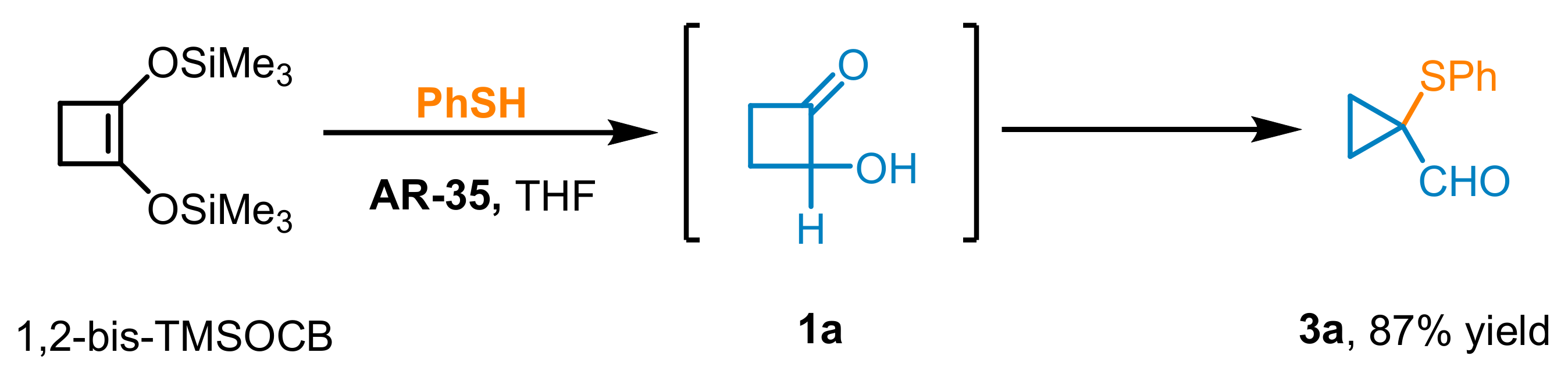
Finally, in a separate experiment, commercially available 1,2-bis((trimethylsilyl)oxy)cyclobut-1-ene (1,2-bis-TMSOCB), the synthetic precursor of HCB
1a via acid-promoted trimethylsilyl cleavage (0.1 mol), was reacted with
2a under the standardized operational conditions to afford the corresponding adduct
3a in 84% (15.5 g) yield after a 7-h run (
Scheme 2).
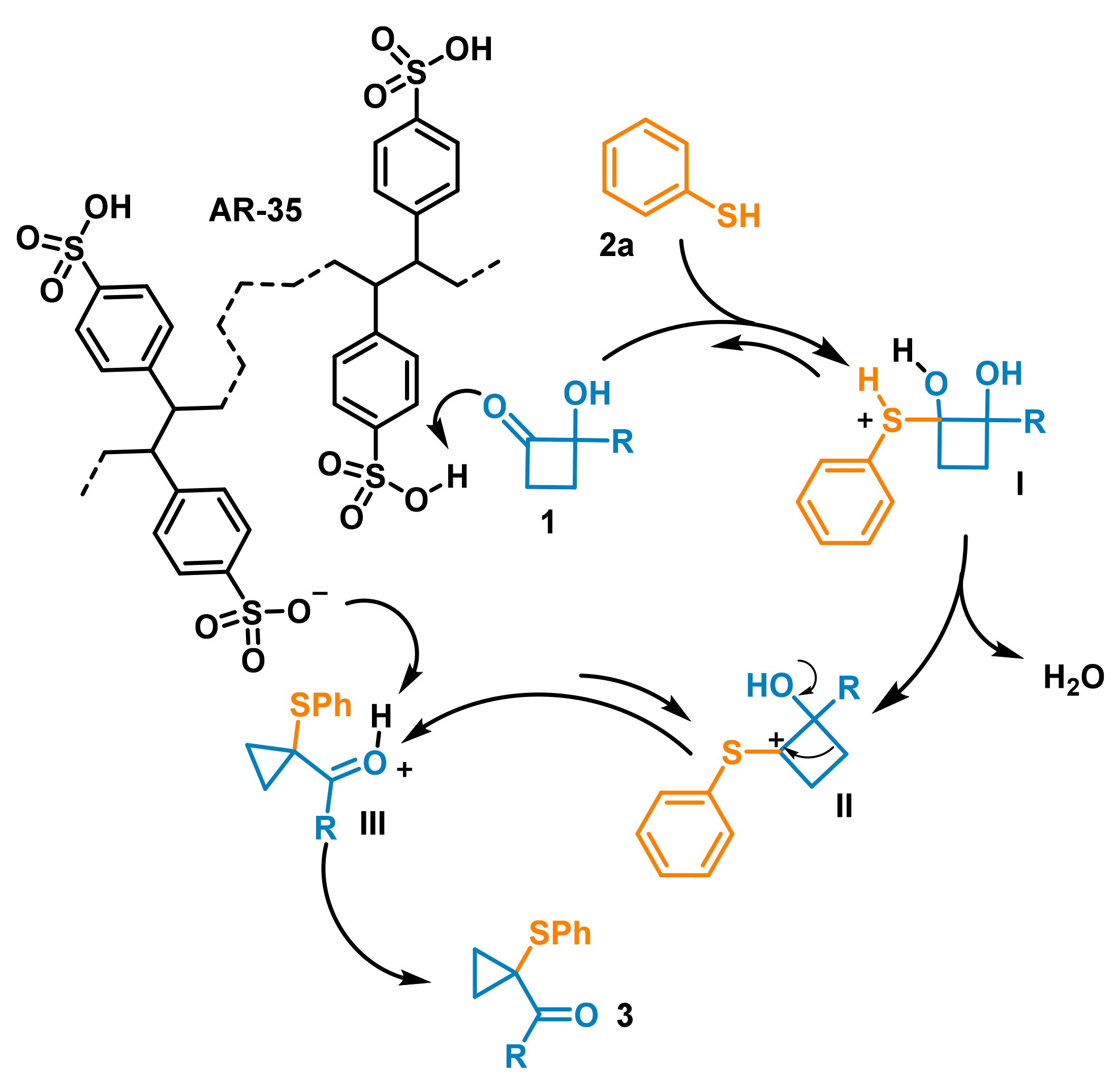
In agreement with our recent achievements [
22,
23], a plausible mechanism that supports these results is reported in
Scheme 3. The sulfonic resin AR-35 promotes the protonation of HCB
1. Benzenethiol nucleophilic addition leads to the formation of the diol-intermediate
I, which undergoes dehydration, furnishing the carbocation
II. At room temperature, this species is subjected to spontaneous C4-C3 ring contraction, leading to the formation of the corresponding protonated carbaldehyde intermediate
III (the same mechanistic explanation is also valid for the homologous ketone). Deprotonation of
III from the AR-35-conjugated base or by the intervention of water should finally furnish the arylthio-cyclopropane carbonyl compounds
3.
This mechanism also suggests that, for each produced molecule of carbaldehyde, a water molecule is generated at the same time by the loss of one of the hydroxyl groups of the diol intermediate I. This leads to an increase in water content in the resin, which would slowly modify the catalytic properties of AR-35, especially if used for a long period. With the aim of evaluating this aspect, a series of additional tests were carried out to evaluate the lifetime of the AR-35 packed columns. In particular, a 15-cm-long column was used repeatedly for six cycles of 40 min to catalyze the reaction between
1b and
2a, washing the column with pure THF for 20–50 min between cycles. As shown in
Figure 4a, the resin exhibited high catalytic activity under the reaction conditions, mediating the process and displaying good performance (
3i yields 90–93% over six cycles). This result is also in agreement with the previous data reported in
Table 3. The process was monitored constantly using a Raman probe placed on the outlet of the column to identify the species every 2 min, as reported in
Figure 4c. This result, together with the other experiments mentioned above, leads us to suppose the relative stability of the cationic resin over time and for a number of cycles that is certainly higher than that evaluated in this study.
A further experiment (
Figure 4b) was then carried out on a single ten-hour run in order to highlight the decrease in the catalytic activity of the system compared to short-duration cycles. During this investigation, we observed a progressive decrease in the catalytic properties of the system to convert
1b into
3j after 5–6 h, causing a significant reduction in conversion, from > 93% in the first few hours to ca. 75% after eight hours of the experiment. As hypothesized in
Scheme 3, this phenomenon can be justified by taking into account two main facts. First of all, the increase in water content, which remains between the interstices of the polymer, might modify in a certain way the reaction kinetics, slowing down the process. Secondly, the amount of water produced during the tandem acid-catalyzed addition ring contraction process between the thiols
2 and the cyclobutanones
1 would remove some of the resin acid protons, gradually depleting it. Nevertheless, this would correspond to a global reduction in the active sites of the resin, thus reducing its performance. However, it should be mentioned that it is possible to restore the original catalytic properties of the resin, reaching optimal conversion values (approx. 90–92%), by reconditioning the column by fluxing (1.0 mL/min) a 10% THF solution of methane sulfonic acid (MSA) (see
Supplementary Materials).
Taking into consideration the properties of AR-35 and referring to the number of acidic sites of the resin, we calculated the indicative turnover number (TON) of the process [
44,
45]. To do this, we took into consideration the number of moles of product 3i obtained in the timeframe in which the catalyst showed its acceptable efficiency (93–70% yield over 24 h). In this way we calculated a TON of 2.43 and a turnover frequency (TOF) of 0.0017 mol/min (see
Supplementary Materials).
Finally, to demonstrate the synthetic versatility of the carbaldehydes obtained through this procedure, the compound
3a was subjected to a series of selective oxidations on the sulfur atom and transformations of the carbonyl group, as reported in
Scheme 4.
Oxidation of cyclopropyl carbaldehyde
3a to sulfoxide
4 was achieved using
t-butyl hydroperoxide in the presence of
N-(1
H-tetrazol-5-yl)benzamide (5-TBA) in dichloromethane (95%) [
46]. Meanwhile, sulfone
5 was prepared from
3a in 98% yield by reacting with two equivalents of
meta-chloroperbenzoic acid (
m-CPBA) in CHCl
3 at 0 °C [
22].
Again, AgNO
3 was efficiently used for the direct oxidation of
3a to the corresponding carboxylic acid
6 [
47]. After
1H NMR analysis of the crude product, the carboxylic acid was directly converted into the corresponding methyl ester
7, adding SOCl
2 to a methanol solution of crude
6 (overall yield 84%). On the other hand, two-step selective transformation of
3a to carboxymethyl ester
7 was accomplished (88%) by using a tandem oxidation–esterification reaction mediated by I
2/KOH in MeOH [
48,
49,
50]. Finally, 2-(1-(phenylthio)cyclopropyl)oxirane
8 (92%) was synthetized from
3a through a Corey–Chaykovsky epoxidation reaction with trimethylsulfoxonium iodide in the presence of stoichiometric amounts of NaH in DMSO at 50 °C [
20,
21].
3. Experimental Section
Unless stated otherwise, the synthesis of compounds
3a–
j was performed at room temperature using a continuous-flow system constituted by an AR-35 packed column, two syringe pumps from KD Scientific Legato Syringe or two HPLC pumps, Hitachi Elite la Chrom D2130) and a collecting flask. Synthesis of compounds
4–
8 was performed at the indicated temperatures in a round-bottom flask equipped with a stirring bar. Commercially available reagents were used as received, unless otherwise noted. The resins used in this work were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (Amberlyst 15 and Amberlyst 35) and used after ball mill grinding. All the organic solvents used in these reactions were considered HPLC-grade. Compounds
1b–
1c were synthetized following our previously reported procedure [
22,
44].
1H NMR spectra were recorded on 400 and 500 MHz Varian spectrometers at 300.15 K, using CDCl
3 (ref. 7.27 ppm) as a solvent.
13C NMR were recorded at 101 MHz and 126 MHz (ref. CDCl
3 77.00 ppm) at 300.15 K, using CDCl
3 as a solvent. Chemical shifts (δ) are given in ppm. Coupling constant values (
J) are reported in Hz. Infrared spectra were recorded on an FT-IR Bruker Equinox-55 spectrophotometer and are reported in wavenumbers (cm
−1). Low mass spectra analysis was performed on an Agilent-HP GC-MS (E.I. 70 eV). High-resolution mass spectra (HRMS) were obtained using a Bruker High-Resolution Mass Spectrometer in fast atom bombardment (FAB
+) ionization mode. Melting points were determined with a Büchi M-560. Analytical thin-layer chromatography was performed using 0.25 mm Aldrich silica gel 60-F plates. Flash chromatography was performed using Merk 70–200 mesh silica gel. Yields refer to chromatography and spectroscopically pure materials or were obtained using a Biotage Selekt Flash Chromatography instrument.
3.1. Catalyst Milling Procedure
Amberlyst 15 and Amberlyst 35 (1.0 g) were loaded into a zirconia SmartSnap™ grinding jar (15 mL) equipped with 1 ball (Ø = 8 mm). The jar was sealed and shaken for 15 min at a frequency of 20 Hz using a FormTech FTS-1000 Shaker Mill® apparatus.
3.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Cyclopropane Arylthiols 3 using a Syringe Pump System
Hydroxy cyclobutanone 1 (2.0 mmol, in 20 mL of THF, conc. 0.1 M) and arylthiol 2 (2.0 mmol, in 20 mL of THF, conc. 0.1 M) were dispensed by a syringe pump (0.5 mL min). This system was connected to a steel T-mixer, which in turn was connected in series to the inlet of a steel column (length 15.0 cm, inner diameter 0.8 cm) packed with AR-35. The output of the column was connected to a glass bottle used for collecting the solution containing the reaction product. The THF solution was filtered on a pad of K2CO3, concentrated under a high vacuum and analyzed by 1H-NMR. When the arylthiol concentration was higher than 3%, the obtained crude oils were subjected to purification by silica gel flash chromatography using light petroleum/Et2O (95:5–90:10) as eluents to afford the corresponding pure products.
1-(Phenylthio)cyclopropanecarbaldehyde 3a. Yield: 338 mg (95%); yellow oil,
1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 9.60 (s, 1H), 7.29–7.19 (m, 5H), 1.75 (dd,
J = 4.5, 7.9 Hz, 2H), 1.54 (s, 1H), 1.46 (dd,
J = 5.0, 7.6 Hz, 2H);
13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 200.6, 129.0, 128.1, 126.3, 107.3, 20.8; HRMS (ESI): Calcd for C
10H
11OS: 179,0531 [M+H]+, found: 179,0544. All analytical data were in good accordance with reported data [
22].
1-(p-Tolylthio)cyclopropanecarbaldehyde 3b. Yield: 350 mg (92%); yellow oil,
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 9.59 (s, 1H), 7.22 (d,
J = 8.2 Hz, 3H), 7.10 (d,
J = 8.2 Hz, 3H), 2.32 (s, 3H), 1.71 (q,
J = 4.3 Hz, 2H), 1.45 (q,
J = 4.3 Hz, 2H);
13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 200.7, 136.7, 132.9, 129.8, 129.0, 54.6, 20.9, 20.7. All analytical data were in good accordance with reported data [
22].
1-((2,6-Dimethylphenyl)thio)cyclopropanecarbaldehyde 3c. Yield: 380 mg (92%); yellow oil;
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 9.71 (s, 1H), 7.17–6.97 (m, 3H), 2.46 (s, 6H), 1.53 (q,
J = 4.4 Hz, 2H), 1.22 (q,
J = 4.4 Hz, 2H);
13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 200.9, 143.0, 131.8, 128.7, 128.3, 127.8, 36.8, 22.8, 21.6. All analytical data were in good accordance with reported data [
22].
1-((4-Chlorophenyl)thio)cyclopropanecarbaldehyde 3d. Yield: 375 mg (89%); yellow oil;
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 9.48 (s, 1H), 7.27–7.24 (m, 2H), 7.24–7.20 (m, 2H), 1.75 (q,
J = 4.5 Hz, 2H), 1.47 (q,
J = 4.5 Hz, 2H);
13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 199.7, 134.2, 132.5, 129.5, 129.1, 34.7, 20.4. All analytical data were in good accordance with reported data [
22].
1-((4-Bromophenyl)thio)cyclopropanecarbaldehyde 3e. Yield: 465 mg (91%); yellow oil;
1H (400 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 9.43 (d,
J = 1.0 Hz, 1H), 7.35 (dd,
J = 6.9, 1.6 Hz, 2H), 7.15–7.04 (m, 2H), 1.76–1.62 (m, 2H), 1.49–1.32 (m, 2H);
13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 199.7, 134.9, 132.0, 129.6, 120.3, 34.5, 20.4. All analytical data were in good accordance with reported data [
24,
25,
26].
1-(Naphthalen-2-ylthio)cyclopropanecarbaldehyde 3f. Yield: 410 mg (90%); yellow solid.
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 9.62 (s, 1H), 7.74 (dd,
J = 11.6, 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.68 (d,
J = 6.7 Hz, 1H), 7.47–7.38 (m, 2H), 7.34 (dd,
J = 8.6, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 1.78 (q,
J = 4.4 Hz, 2H), 1.49 (q,
J = 4.4 Hz, 2H);
13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 200.6, 133.6, 133.2, 131.9, 128.7, 127.7, 127.1, 126.7, 126.2, 126.1, 125.9, 34.5, 20.9. All analytical data were in good accordance with reported data [
22].
1-((4-Nitrophenyl)thio)cyclopropanecarbaldehyde3g. Yield: 267 mg (60%); yellow oil;
1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 9.34 (s, 1H), 8.06 (t,
J = 2.0 Hz), 7.25 (t,
J = 2.0 Hz, 2H), 1.83 (dd,
J = 7.5, 4.5 Hz, 2H), 1.46 (dd,
J = 7.5, 3.5 Hz, 2H);
13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 198.3, 146.1, 145.6, 126.0, 124.1, 33.2, 20.1. All analytical data were in good accordance with reported data [
22].
Methyl 2-((1-formylcyclopropyl)thio)benzoate3h. Yield: 368 mg (78%); colorless oil.
1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 9.52 (s, 1H), 7.96 (d,
J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.39–7.31 (m, 1H), 7.25 (d,
J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.12 (t,
J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 1.90–1.71 (m, 2H), 1.50–1.28 (m, 2H);
13C NMR (101 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 201.2, 166.8, 141.7, 132.9, 131.9, 126.6, 125.7, 124.7, 52.3, 32.8, 21.0. All analytical data were in good accordance with reported data [
22].
1-(1-(Phenylthio)cyclopropyl)ethenone 3i. Yield: 357 mg (93%); colorless oil.
1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 7.28 (t,
J = 7.5 Hz, 2H), 7.20 (d,
J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.14 (td,
J = 7.4, 1.0 Hz, 1H), 2.91 (tt,
J = 7.1, 3.6 Hz, 2H), 1.89–1.72 (m, 2H), 1.37–1.20 (m, 2H), 1.00 (td,
J = 7.2, 0.9 Hz, 3H);
13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 210.3, 137.2, 129.0, 125.8, 125.3, 33.4, 32.2, 22.0, 8.3. All analytical data were in good accordance with reported data [
23].
1-(1-(Phenylthio)cyclopropyl)propan-1-one 3j. Yield: 379 mg (92%); colorless oil.
1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 3.39 (br. s, 1H), 3.52 (br. s, 1H), 2.99–2.83 (m, 1H), 2.83–2.71 (m, 1H), 2.18–2.07 (m, 1H), 2.07–1.98 (m, 1H), 1.44 (s, 3H);
13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 211.9, 88.3, 39.3, 28.1, 22.2. All analytical data were in good accordance with reported data [
22].
3.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Cyclopropane Arylthiols 3 using a HPLC Pump System
Hydroxy cyclobutanone 1b (0.18 mol in 360 mL of THF, conc. 0.1M) and arylthiol 2a (0.18 mol in 360 mL of THF, conc. 0.1 M) were dispensed by a syringe pump (0.5 mL min). This system was connected to a steel T-mixer, which in turn was connected in series to the inlet of a steel column (length 15.0 cm, inner diameter 0.8 cm) packed with AR-35. The output of the column was connected to a glass bottle used for collecting the solution containing the reaction product. The THF solution was filtered on a pad of K2CO3, concentrated under a high vacuum and analyzed by 1H-NMR. When the arylthiol concentration was higher than 3%, the obtained crude oils were subjected to purification by silica gel flash chromatography using light petroleum/Et2O (95:5–90:10) as eluents to afford the corresponding pure products.
1-(Phenylsulfinyl)cyclopropanecarbaldehyde 4. To a solution of 3a (200 mg, 1.1 mmol) and N-(1H-tetrazol-5-yl)benzamide (5-TBA, 0.2 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (5 mL), tert-butyl hydroperoxide was added ((5.5 M in decane, 1.5 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 16 h and then filtered on a 3 cm celite pad. CH2Cl2 was evaporated under reduced pressure and the crude oil was submitted to flash chromatography light petroleum/Et2O (95:5–90:10) to afford 4 as a colorless oil, yield 95% (240 mg). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 9.15 (s, 1H), 7.68 (dt, J = 5.6, 3.6 Hz, 2H), 7.55 – 7.38 (m, 3H), 1.78 (ddd, J = 9.6, 7.9, 4.7 Hz, 1H), 1.67 – 1.61 (m, 1H), 1.61 – 1.53 (m, 1H), 1.39 (ddd, J = 9.3, 8.1, 4.9 Hz, 1H); 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 195.4, 142.4, 131.3, 129.0, 124.5, 50.4, 13.3, 11.4; HRMS (ESI): Calcd for C10H10NaO2S: 217,0299 (M+Na), found: 217,0302.
1-(phenylsulfonyl)cyclopropanecarbaldehyde5. To a solution of
3f (300 mg, 1.3 mmol) in CHCl
3 (10 mL),
m-CPBA was added in one portion (~60%, 2.6 mmol, 754 mg) at 0 °C. The reaction mixture was stirred for 10 h and then filtered on a 5 cm K
2CO
3 pad and washed twice with CHCl
3. The resulting solution was evaporated under reduced pressure and the crude oil was submitted to flash chromatography light petroleum/Et
2O (95:5–90:10) to afford
5 as a white solid, yield 98% (331 mg). Mp = 120–124 °C.
1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 9.92 (s, 1H), 8.54 (d,
J = 1.1 Hz, 1H), 8.03 (d,
J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 8.02 (m, 1H), 7.95 (d,
J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.87 (dd,
J = 8.7, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.68 (dtd,
J = 16.2, 7.0, 1.2 Hz, 2H), 2.05 (q,
J = 4.4 Hz, 2H), 1.69 (q,
J = 4.5 Hz, 2H);
13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 192.9, 136.4, 135.4, 132.2, 130.0, 129.9, 129.6, 129.5, 128.0, 127.9, 122.5, 29.6, 18.4; HRMS (ESI): Calcd for C
10H
10NaO
3S: 233,0248 (M+Na), found: 233,0254. Spectral data are in agreement with the literature [
22].
1-(Phenylthio)cyclopropanecarboxylic acid 6 and esterification to ester
7. To a room-temperature stirred suspension of AgNO
3 (407 mg, 2.4 mmol) and NaOH (100 mg, 2.5 mmol) in 10 mL of distilled water,
3a (200 mg, 1.1 mmol) was added dropwise. After 4 h, HCl (1 M, 30 mL) was added and the reaction mixture was filtered and extracted with EtOAc. The organic phase was dried with Na
2SO
4 and concentrated under reduced pressure.
1H NMR (CDCl
3) δ: 7.52–7.51 (m, 1H), 7.36–7.34 (m, 1H), 7.30–7.27 (m, 2H), 7.20–7.17 (m, 1H), 1.85 (dd,
J = 5.0, 7.4 Hz, 2H), 1.40 (dd,
J = 4.8, 7.4 Hz, 2H); M.p: 78–82 °C [
30]. The thus-obtained crude oil was diluted in 10 mL of MeOH and SOCl
2 (2 drops) was added, and the reaction mixture was refluxed for 8 h. After cooling to rt, the methanolic solution was evaporated and the remaining crude oil was purified by flash chromatography light petroleum/Et
2O (90:10) to afford the compound
7 as a yellow oil, yield 84% (201 mg).
1H NMR (CDCl
3) δ: 7.23–7.18 (m, 4H), 7.10–7.07 (m, 1H), 3.62 (s, 3H), 1.72 (dd,
J = 4.8, 7.4 Hz, 2H), 1.26 (dd,
J = 4.8, 7.2 Hz, 2H);
13C NMR (CDCl
3) δ: 200.9, 130.0, 129.2, 128.8, 126.6, 54.8, 20.9; HRMS (ESI): Calcd for C
11H
12NaO
4S: 263,0354 (M+Na), found: 263,0357. Spectral data are in agreement with the literature [
48].
Methyl 1-(phenylthio)cyclopropanecarboxylate7. To a solution of
3a (200 mg, 1.1 mmol) in MeOH (15 mL), KOH (168 mg, 3.0 mmol) and I
2 (381 mg, 1.5 mmol) in MeOH (5 mL each) were successively added at 0 °C. After 1 h, the reaction mixture was diluted with Et
2O and treated with a water solution of Na
2S
2O
3. The organic phase was dried on Na
2SO
4 and evaporated under reduced pressure. The crude oil was purified by flash chromatography light petroleum/EtOAc (90:10) to afford the compound
7 as a yellow oil, yield 92% (176 mg).
1H NMR (CDCl
3) δ: 0.88–1.26 (m, 4H), 2.49 (dd, 1H,
J = 2.4, 5.1 Hz), 2.70 (dd, 1H,
J = 3.9, 5.1 Hz), 3.22 (dd, 1H,
J = 2.4, 3.9 Hz), 7.17–7.45 (m, 5H).
13C NMR (CDCl
3) δ: 11.2, 13.9, 25.1, 46.8, 54.1, 126.2, 128.7, 129.1, 135.7. Spectral data are in agreement with the literature [
48].
2-(1-(Phenylthio)cyclopropyl)oxirane 8. (Me)
3SOI (286 mg, 1.3 mmol) was added portionwise to a stirred suspension of pentane-washed NaH (~60%, 1.5 mmol, 60 mg) in DMSO (5 mL) at room temperature under argon. After 2 h,
3a (200 mg, 1.1 mmol) was added in DMSO (3 mL). The resulting reaction mixture was warmed to 50 °C and stirred for 12 h. Once cooled to room temperature, the reaction mixture was diluted with Et
2O and washed twice with brine. The resulting organic solution was dried on Na
2SO
4 and evaporated under reduced pressure. The crude oil was purified by flash chromatography light petroleum/EtOAc (97:3) to afford the compound
6 as a yellow oil, yield 92% (176 mg).
1H NMR (CDCl
3) δ: 0.88–1.26 (m, 4H), 2.49 (dd, 1H,
J = 2.4, 5.1 Hz), 2.70 (dd, 1H,
J = 3.9, 5.1 Hz), 3.22 (dd, 1H,
J = 2.4, 3.9 Hz), 7.17–7.45 (m, 5H).
13C NMR (CDCl
3) δ: 11.2, 13.9, 25.1, 46.8, 54.1, 126.2, 128.7, 129.1, 135.7; HRMS (ESI): Calcd for C
11H
12NaO
3S: 247,0405 (M+Na), found: 247,0411. Spectral data are in agreement with the literature [
19].