Aminoquinolones and Their Benzoquinone Dimer Hybrids as Modulators of Prion Protein Conversion
Abstract
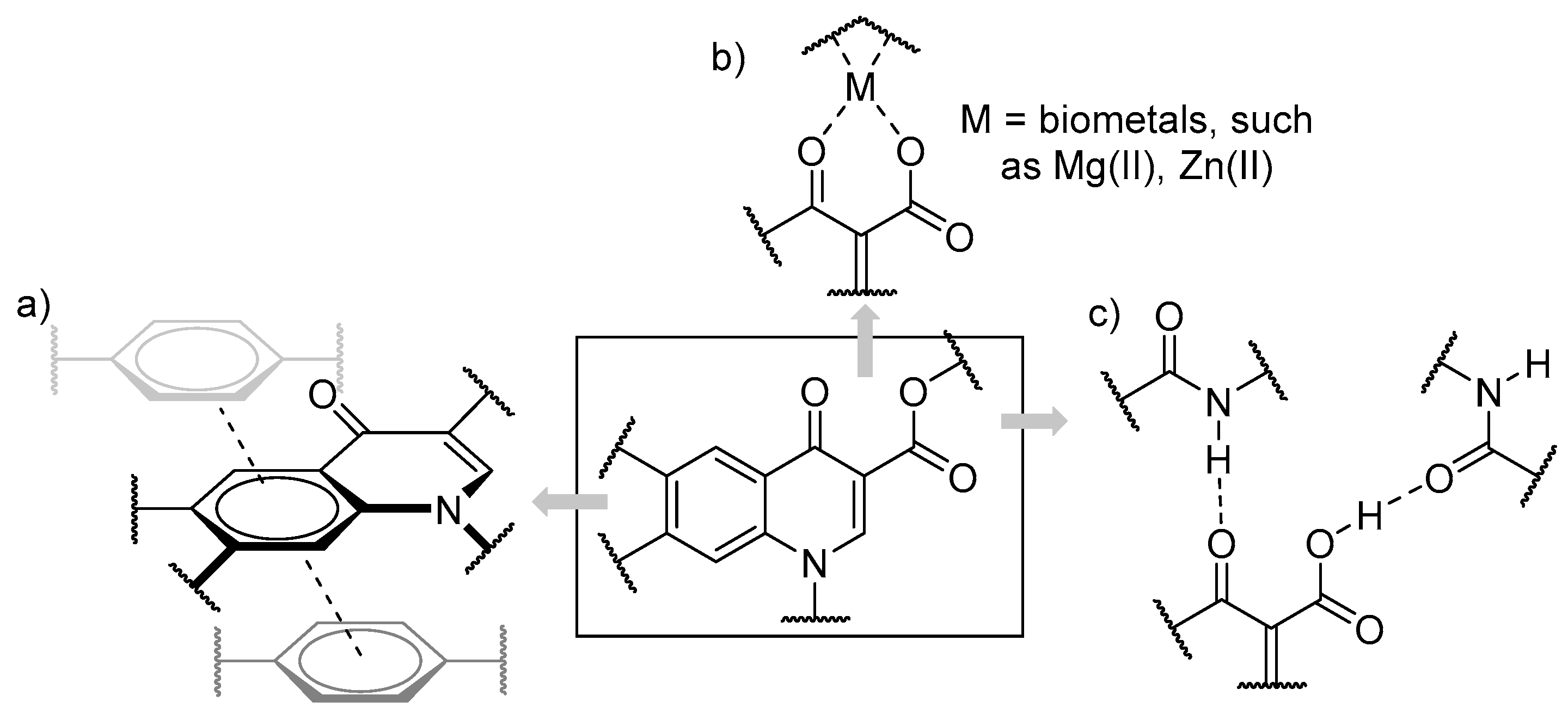
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
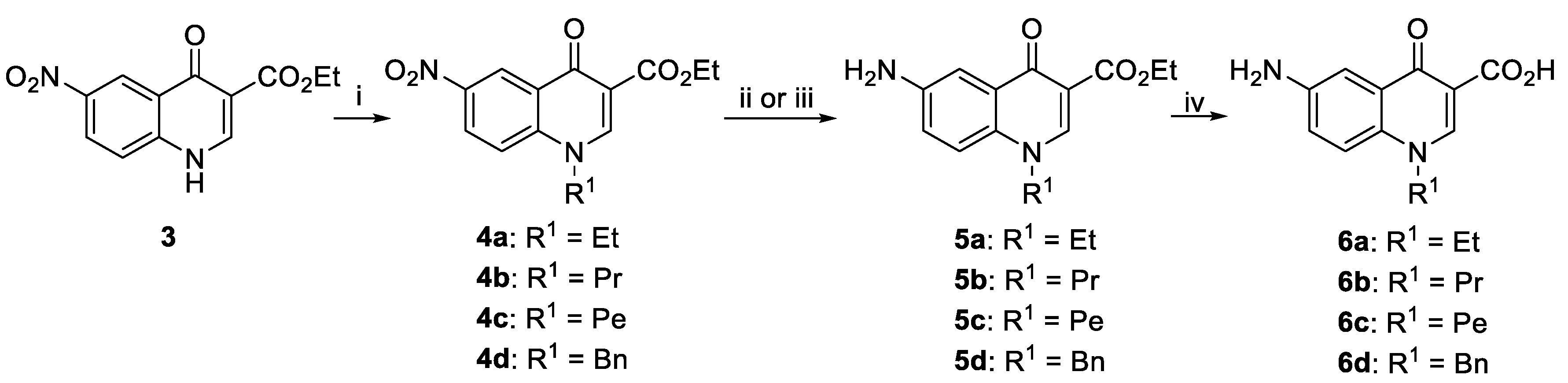
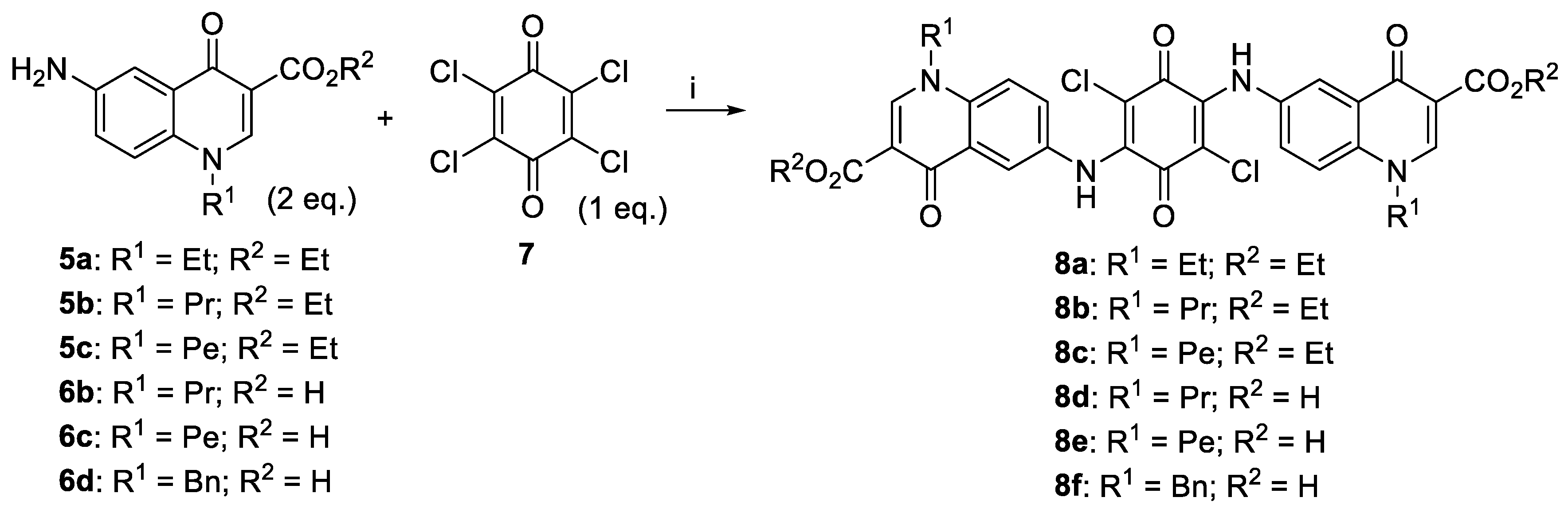
2.1. Synthesis
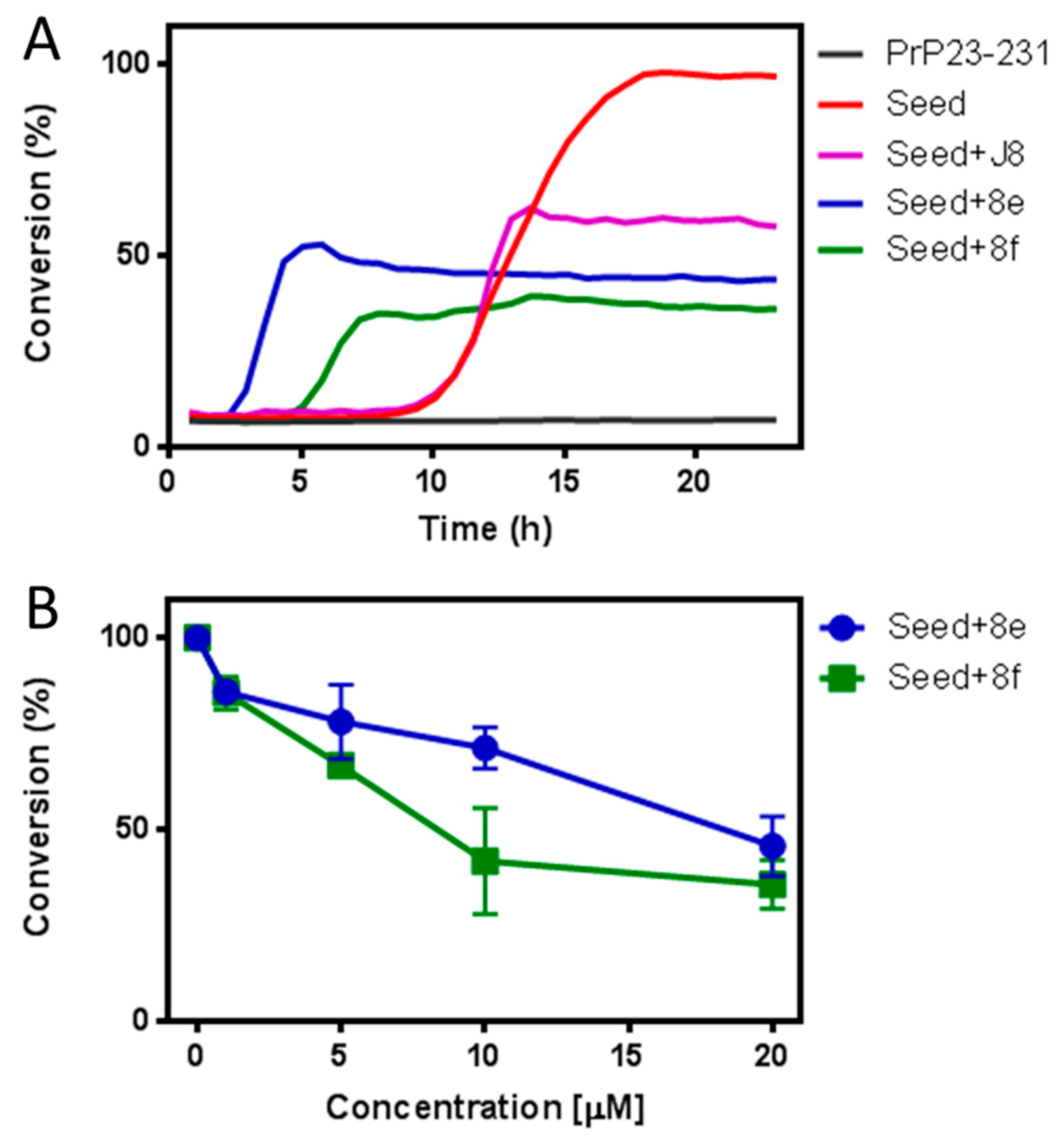
2.2. Biological Assays
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis
4.1.1. General
4.1.2. Ester Hydrolysis: General Procedure
4.1.3. Dimerization through Benzoquinone Amination: General Procedure
4.2. Biological Assays
4.2.1. Prion Protein Expression and Purification
4.2.2. In Vitro-Produced Fibril Preparation and Amplification
4.2.3. Spectroscopic Measurements
4.2.4. MTT Assays
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Riesner, D. Biochemistry and structure of PrPC and PrPSc. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 66, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissmann, C.; Enari, M.; Klöhn, P.-C.; Rossi, D.; Flechsig, E. Molecular biology of prions. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2002, 62, 153–166. [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner, S.B. Prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, B.M.; Gever, J.R.; Li, Z.; Gallardo-Godoy, A.; Renslo, A.R.; Widjaja, K.; Irwin, J.J.; Rao, S.; Jacobson, M.P.; Ghaemmaghami, S.; et al. Antiprion compounds that reduce PrPSc levels in dividing and stationary-phase cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, P.J.; Kim, H.O.; Bryant, D.; Kinzel, N.J.; Reilly, C.; Priola, S.A.; Ward, A.E.; Goodman, P.A.; Olson, K.; Seelig, D.M. Treatment of Prion Disease with Heterologous Prion Proteins. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zattoni, M.; Legname, G. Tackling prion diseases: A review of the patent landscape. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2021, 31, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spagnolli, G.; Massignan, T.; Astolfi, A.; Biggi, S.; Rigoli, M.; Brunelli, P.; Libergoli, M.; Ianeselli, A.; Orioli, S.; Boldrini, A.; et al. Pharmacological inactivation of the prion protein by targeting a folding intermediate. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguzzi, A.; Lakkaraju, A.K.K.; Frontzek, K. Toward Therapy of Human Prion Diseases. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 58, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreca, M.; Iraci, N.; Biggi, S.; Cecchetti, V.; Biasini, E. Pharmacological Agents Targeting the Cellular Prion Protein. Pathogens 2018, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes, M.C.; Santos, J.B.; dos Anjos, D.M.; Rangel, L.P.; Vieira, T.C.R.G.; Moaddel, R.; da Silva, J.L. Prion protein-coated magnetic beads: Synthesis, characterization and development of a new ligands screening method. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1379, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, T.C.R.G.; Silva, J.L. In Vitro Prion Amplification Methodology for Inhibitor Screening. In Protein Misfolding Diseases; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongarzone, S.; Tran, H.N.A.; Cavalli, A.; Roberti, M.; Carloni, P.; Legname, G.; Bolognesi, M.L. Parallel Synthesis, Evaluation, and Preliminary Structure−Activity Relationship of 2,5-Diamino-1,4-benzoquinones as a Novel Class of Bivalent Anti-Prion Compound. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.N.A.; Bongarzone, S.; Carloni, P.; Legname, G.; Bolognesi, M.L. Synthesis and evaluation of a library of 2,5-bisdiamino-benzoquinone derivatives as probes to modulate protein–protein interactions in prions. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangir, N.; Poonam, D.S.; Jangid, D.K. Recent advances in the synthesis of five- and six-membered heterocycles as bioactive skeleton: A concise overview. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202103139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampilek, J. Heterocycles in Medicinal Chemistry. Molecules 2019, 24, 3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilkin, V.G.; Filimonov, V.O.; Seliverstova, E.A.; Novikov, M.S.; Beryozkina, T.V.; Gagarin, A.A.; Belskaya, N.P.; Muthipeedika, N.J.; Bakulev, V.A.; Dehaen, W. Thioisomünchnones versus Acrylamides via Copper-Catalyzed Reaction of Thioamides with Diazocarbonyl Compounds. J. Org Chem. 2022, 87, 12196–12213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.; Joy, M.N.; Sunil, K.; Sajith, A.M.; Santra, S.; Zyryanov, G.V.; Konovalova, O.A.; Butorin, I.I.; Muniraju, K. Towards novel tacrine analogues: Pd(dppf)Cl2·CH2Cl2 catalyzed improved synthesis, in silico docking and hepatotoxicity studies. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 22476–22491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemallapudi, B.R.; Zyryanov, G.V.; Avula, B.; Guda, M.R.; Cirandur, S.R.; Venkataramaiah, C.; Rajendra, W.; Gundala, S. Meglumine as a green, efficient and reusable catalyst for synthesis and molecular docking studies of bis(indolyl)methanes as antioxidant agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krinochkin, A.P.; Starnovskaya, E.S.; Valieva, M.I.; Kopchuk, D.S.; Santra, S.; Slepukhin, P.A.; Zyryanov, G.V.; Majee, A.; Chupakhin, O.N. One-pot synthesis of cyclopentane-fused 5’-aryl-4-cycloalkylamino-2,2’-bipyridines via the aza-Diels–Alder/SNipso reactions. Mendeleev Commun. 2022, 32, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veligeti, R.; Madhu, R.B.; Anireddy, J.; Pasupuleti, V.R.; Avula, V.K.R.; Ethiraj, K.S.; Uppalanchi, S.; Kasturi, S.; Perumal, Y.; Anantaraju, H.S.; et al. Synthesis of novel cytotoxic tetracyclic acridone derivatives and study of their molecular docking, ADMET, QSAR, bioactivity and protein binding properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millanao, A.R.; Mora, A.Y.; Villagra, N.A.; Bucarey, S.A.; Hidalgo, A.A. Biological Effects of Quinolones: A Family of Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Agents. Molecules 2021, 26, 7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Advani, R.H.; Hurwitz, H.I.; Gordon, M.S.; Ebbinghaus, S.W.; Mendelson, D.S.; Wakelee, H.A.; Hoch, U.; Silverman, J.A.; Havrilla, N.A.; Berman, C.J.; et al. Voreloxin, a First-in-Class Anticancer Quinolone Derivative, in Relapsed/Refractory Solid Tumors: A Report on Two Dosing Schedules. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalha, P.; Vieira de Souza, M.C.; Peña-Cabrera, E.; Cruz, D.; Santos Boechat, F.D. Quinolones in the Search for New Anticancer Agents. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshtalab, M.; Ahmed, A. Nonclassical Biological Activities of Quinolone Derivatives. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalha, P.N.; da Forezi, S.M.L.; Tolentino, N.M.d.C.; Sagrillo, F.S.; de Oliveira, V.G.; de Souza, M.C.B.V.; da Boechat, C.S.F. 4-Oxoquinoline Derivatives as Antivirals: A Ten Years Overview. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, D.A.; Gouvea, L.R.; Muniz, G.S.V.; Louro, S.R.W.; Batista, D.d.G.J.; Soeiro, M.d.N.C.; Teixeira, L.R. Norfloxacin and N-Donor Mixed-Ligand Copper(II) Complexes: Synthesis, Albumin Interaction, and Anti- Trypanosoma cruzi Activity. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2016, 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.G.; dos Santos Faiões, V.; Gonçalves, G.B.R.; Lima, M.F.O.; Boechat, F.C.S.; Cunha, A.C.; de Andrade-Neto, V.V.; de C.d.Silva, F.; Torres-Santos, E.C.; de Souza, M.C.B.V. Design, Synthesis and Antileishmanial Activity of Naphthotriazolyl-4- Oxoquinolines. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Quinolone derivatives and their antifungal activities: An overview. Arch. Pharm. 2019, 352, 1800382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Das, R.; Kumar Mehta, D.; Gupta, S.; Venugopala, K.N.; Mailavaram, R.; Nair, A.B.; Shakya, A.K.; Kishore Deb, P. Recent insight into the biological activities and SAR of quinolone derivatives as multifunctional scaffold. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2022, 59, 116674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.R.P.; de Andrade, K.N.; Moreira, M.L.S.; Oliveira, V.G.; Carneiro, J.W.M.; da CS Boechat, S.; de Souza, M.C.B.V.; Fiorot, R.G.; Teixeira, R.I.; de Lucas, N.C.; et al. Unveiling the photophysical properties of 3-acyl-6-amino-4-quinolones and their use as proton probes. Dyes Pigment. 2022, 207, 110692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willbold, D.; Strodel, B.; Schröder, G.F.; Hoyer, W.; Heise, H. Amyloid-type Protein Aggregation and Prion-like Properties of Amyloids. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 8285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.C.F.; de Oliveira, G.A.P.; Cino, E.A.; Soares, I.N.; Rangel, L.P.; Silva, J.L. Aggregation and Prion-Like Properties of Misfolded Tumor Suppressors: Is Cancer a Prion Disease? Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a023614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, N.C.; Ascari, L.M.; Hughson, A.G.; Cavalheiro, G.R.; Góes, C.F.; Fernandes, P.N.; Hollister, J.R.; da Conceição, R.A.; Silva, D.S.; Souza, A.M.T.; et al. A Promising Antiprion Trimethoxychalcone Binds to the Globular Domain of the Cellular Prion Protein and Changes Its Cellular Location. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01441-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, T.C.R.G.; Cordeiro, Y.; Caughey, B.; Silva, J.L. Heparin binding confers prion stability and impairs its aggregation. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tycko, R. Physical and structural basis for polymorphism in amyloid fibrils. Protein Sci. 2014, 23, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziaunys, M.; Sakalauskas, A.; Mikalauskaite, K.; Snieckute, R.; Smirnovas, V. Temperature-Dependent Structural Variability of Prion Protein Amyloid Fibrils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yagi, H.; Lee, Y.-H.; Kitayama, H.; Sakurai, K.; So, M.; Ogi, H.; Naiki, H.; Goto, Y. Distinguishing crystal-like amyloid fibrils and glass-like amorphous aggregates from their kinetics of formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamachi, N.G.; Chakrabarty, S. Temperature-Induced Misfolding in Prion Protein: Evidence of Multiple Partially Disordered States Stabilized by Non-Native Hydrogen Bonds. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, Y.; Kraineva, J.; Ravindra, R.; Lima, L.M.T.R.; Gomes, M.P.B.; Foguel, D.; Winter, R.; Silva, J.L. Hydration and Packing Effects on Prion Folding and β-Sheet Conversion. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 32354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


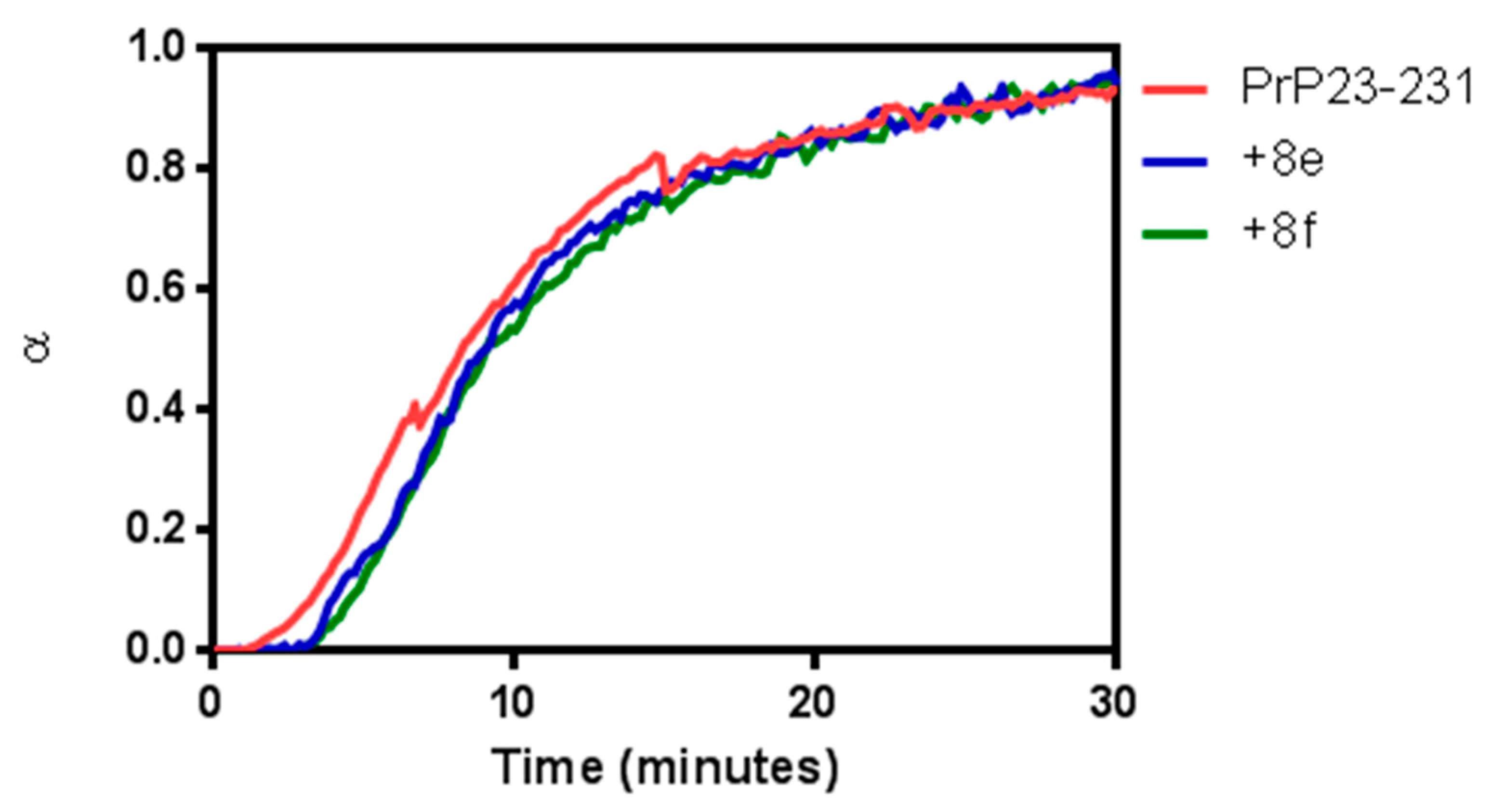
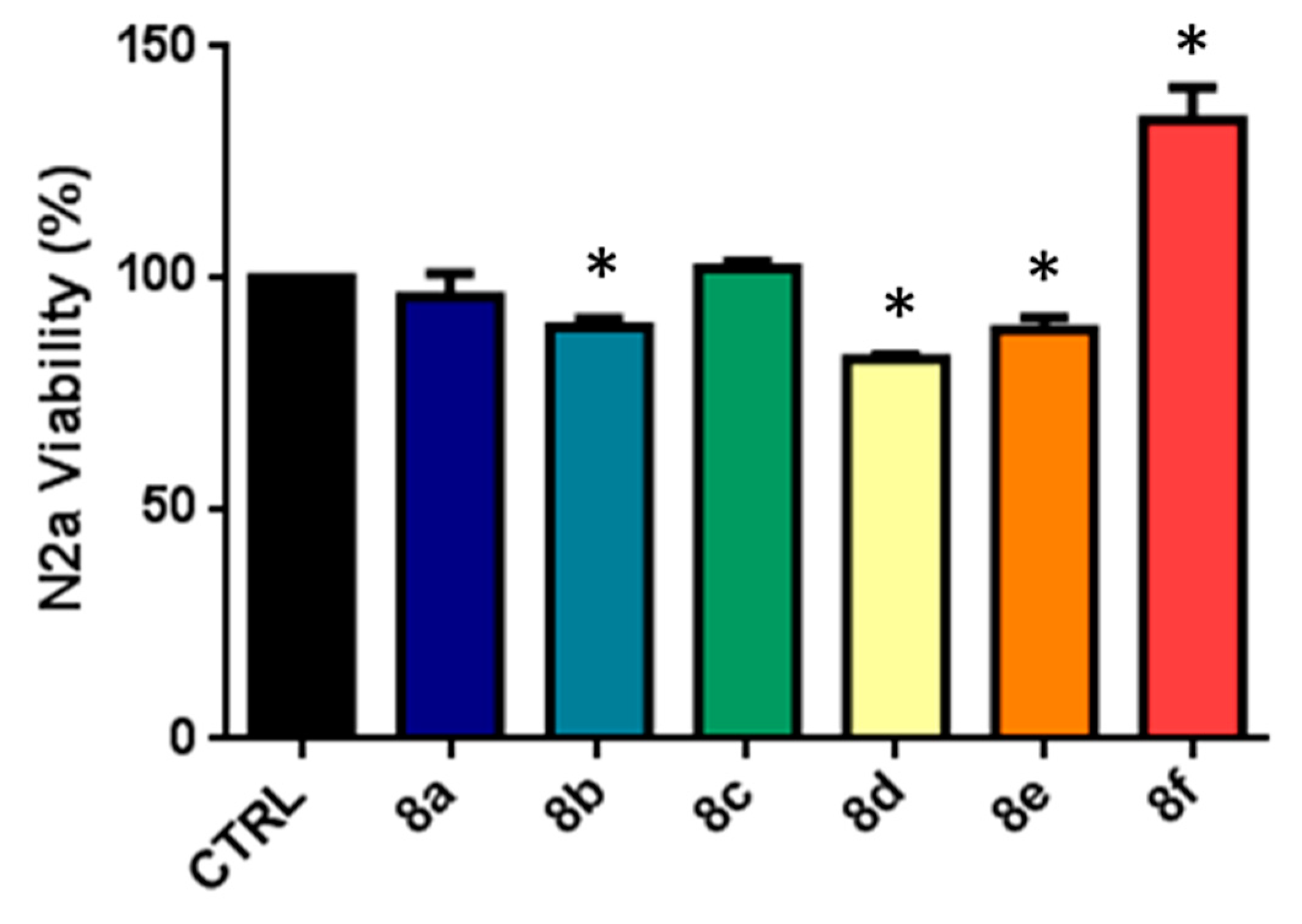
| Compound | % Conversion |
|---|---|
| 5a | 109 ± 22 |
| 5b | 118 ± 13 |
| 5c | 90 ± 14 |
| 5d | 100 ± 15 |
| 6a | 102 ± 3 |
| 6b | 73 ± 24 |
| 6c | 94 ± 5 |
| 6d | 83 ± 9 |
| 8a | 97 ± 12 |
| 8b | 78 ± 7 |
| 8c | 113 ± 10 |
| 8d | 62 ± 4 |
| 8e | 44 ± 10 |
| 8f | 27 ± 3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, A.R.P.; Muxfeldt, M.; Boechat, F.d.C.S.; de Souza, M.C.B.V.; Silva, J.L.; de Moraes, M.C.; Rangel, L.P.; Vieira, T.C.R.G.; Batalha, P.N. Aminoquinolones and Their Benzoquinone Dimer Hybrids as Modulators of Prion Protein Conversion. Molecules 2022, 27, 7935. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227935
Costa ARP, Muxfeldt M, Boechat FdCS, de Souza MCBV, Silva JL, de Moraes MC, Rangel LP, Vieira TCRG, Batalha PN. Aminoquinolones and Their Benzoquinone Dimer Hybrids as Modulators of Prion Protein Conversion. Molecules. 2022; 27(22):7935. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227935
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Amanda Rodrigues Pinto, Marcelly Muxfeldt, Fernanda da Costa Santos Boechat, Maria Cecília Bastos Vieira de Souza, Jerson Lima Silva, Marcela Cristina de Moraes, Luciana Pereira Rangel, Tuane Cristine Ramos Gonçalves Vieira, and Pedro Netto Batalha. 2022. "Aminoquinolones and Their Benzoquinone Dimer Hybrids as Modulators of Prion Protein Conversion" Molecules 27, no. 22: 7935. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227935
APA StyleCosta, A. R. P., Muxfeldt, M., Boechat, F. d. C. S., de Souza, M. C. B. V., Silva, J. L., de Moraes, M. C., Rangel, L. P., Vieira, T. C. R. G., & Batalha, P. N. (2022). Aminoquinolones and Their Benzoquinone Dimer Hybrids as Modulators of Prion Protein Conversion. Molecules, 27(22), 7935. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227935










