Structural Basis for (2R,3R)-Taxifolin Binding and Reaction Products to the Bacterial Chalcone Isomerase of Eubacterium ramulus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Crystal Structures
2.2. Common Structural Features of the Proteins
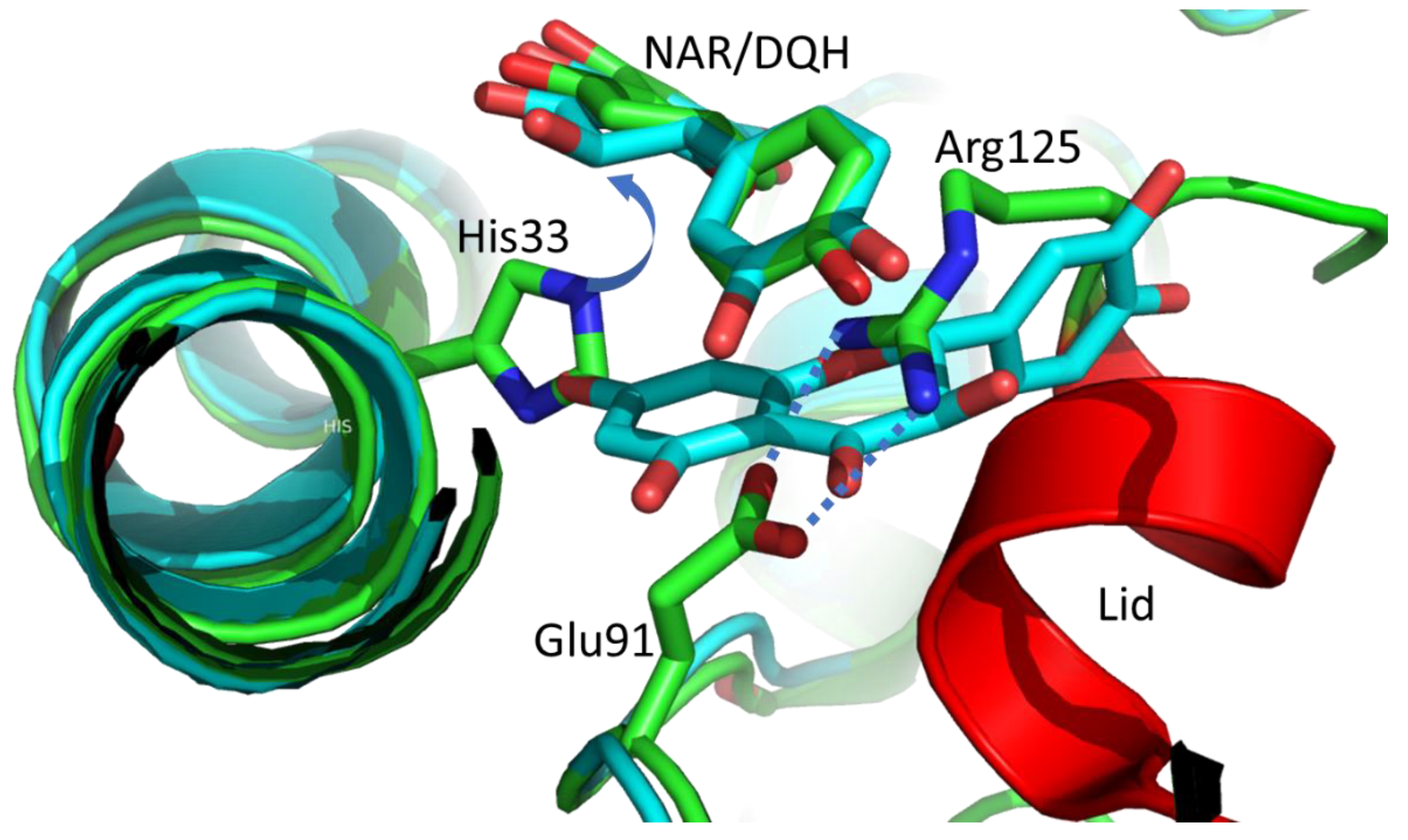
2.3. The Taxifolin Binding to CHI_H33A
2.4. The Taxifolin Binding to Native CHI
2.5. Minor Comments on CHI Folding
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Protein Preparation and Crystallisation
4.2. X-ray Data Collection Processing
4.3. Structure Determination and Refinement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Protein–Ligand | CHI_H33A– Taxifolin-Overload | CHI_H33A– Taxifolin | CHI–Taxifolin |
|---|---|---|---|
| PDB entry | 8B7Z | 8B7U | 8B7R |
| Radiation source | Rigaku MSC | BESSY II | BESSY II |
| beam line | MicroMax 007 | BL 14.1 | BL 14.1 |
| Detector | Saturn 92 CCD | DECTRIS PILATUS 6M | DECTRIS PILATUS 6M |
| Wavelength (Å) | 1.5418 | 0.9184 | 0.9184 |
| Temperature (K) | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| unit cell parameters | |||
| a (Å) | 186.36 | 187.58 | 173.82 |
| b (Å) | 204.68 | 203.74 | 193.15 |
| c (Å) | 561.90 | 560.39 | 205.29 |
| orthorhombic space group | I212121 | I212121 | I212121 |
| Resolution range (highest shell) (Å) * | 33.93–2.95 | 49.42–2.78 | 48.82–2.13 |
| (3.05–2.95) | (2.95–2.78) | (2.25–2.13) | |
| Measured reflections | 871370 (65227) | 3660626 (562212) | 1447977 (229327) |
| Unique reflections | 222025 (21202) | 266311 (42262) | 191642 (30350) |
| Averaged Redundancy | 3.92 (3.06) | 13.7 (13.3) | 7.56 (7.56) |
| Completeness (%) | 98.8 (95.1) | 99.3 (98.2) | 99.5 (98.3) |
| Rmeas (%) | 28.9 (76) | 36.8 (158) | 18.8 (110) |
| Mean I/σ(I) | 4.1 (1.0) | 9.3 (1.76) | 10.74 (1.93) |
| CC ½ | 0.99 (0.24) | 1.0 (0.33) | |
| Wilson B-factor (Å2) | 47.3 | 42.4 | 36.5 |
| Protein–Ligand | CHI_H33A– Taxifolin-Overload | CHI_H33A– Taxifolin | CHI–Taxifolin |
|---|---|---|---|
| PDB entry | 8B7Z | 8B7U | 8B7R |
| Resolution range | 33.95–3.00 | 49.42–2.80 | 48.82–2.15 |
| Rcryst (%)/number of reflections | 24.9/206779 | 21.3/257795 | 16.3/183628 |
| Rfree (%)/number of reflections | 26.8/4272 | 22.4/2736 | 19.0/2035 |
| Number of non-hydrogen atoms: protein/solvent/ligands | 39253 all 38066/45/1142 | 39179 all 38164/233/782 | 14852 all 12890/1830/132 |
| RMSD * bond lengths (Å) | 0.009 | 0.007 | 0.011 |
| RMSD bond angles (°) | 1.50 | 1.33 | 1.54 |
| RMSD torsion angles (°) | 7.77 | 8.01 | 7.73 |
| Ramachandran parameters (%) favoured/allowed/outlier | |||
| 88.1/11.8/– | 87.5/12.5/– | 90.4/9.6/– | |
| Average B-factors (Å2) | 58.1 | 66.9 | 35.3 |
| Matthews coefficient VM (A3 Da−1) | 4.88 | 4.88 | 4.14 |
| Corresponding solvent content (%) | 75 | 75 | 70 |
References
- Ferreyra, M.L.F.; Rius, S.P.; Casati, P. Flavonoids: Biosynthesis, biological functions, and biotechnological applications. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmin, J.L.; Wilson, K.E.; Rossen, L.; Johnston, A.W.B. Flavonoid activation of nodulation genes in Rhizobium reversed by other compounds present in plants. Nature 1986, 324, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, B.; Pagano, E.; Montanaro, V.; Fortunato, A.L.; Milic, N.; Borrelli, F. Novel Insights into the Pharmacology of Flavonoids. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 1588–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gensheimer, M. Chalcone isomerase family and fold: No longer unique to plants. Protein Sci. 2004, 13, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, H.; Blaut, M. Anaerobic degradation of flavonoids by Eubacterium ramulus. Arch. Microbiol. 2000, 173, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinert, H.; Yi, D.; Zirpel, B.; Schuiten, E.; Geißler, T.; Gross, E.; Brückner, S.I.; Hartmann, B.; Röttger, C.; Ley, J.P.; et al. Discovery of Novel Bacterial Chalcone Isomerases by a Sequence-Structure-Function-Evolution Strategy for Enzymatic Synthesis of (S)-Flavanones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 16874–16879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nising, C.F.; Bräse, S. Recent developments in the field of oxa-Michael reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 41, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngaki, M.N.; Louie, G.V.; Philippe, R.N.; Manning, G.; Pojer, F.; Bowman, M.E.; Li, L.; Larsen, E.; Wurtele, E.S.; Noel, J.P. Evolution of the chalcone-isomerase fold from fatty-acid binding to stereospecific catalysis. Nature 2012, 485, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jez, J.M.; Bowman, M.E.; Dixon, R.A.; Noel, J.P. Structure and mechanism of the evolutionarily unique plant enzyme chalcone isomerase. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jez, J.M.; Bowman, M.E.; Noel, J.P. Role of Hydrogen Bonds in the Reaction Mechanism of Chalcone Isomerase. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 5168–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jez, J.M.; Noel, J.P. Reaction Mechanism of Chalcone Isomerase-pH dependence, diffusion control, and product binding differences. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, H.; Schwiertz, A.; Collins, M.D.; Blaut, M. Anaerobic transformation of quercetin-3-glucoside by bacteria from the human intestinal tract. Arch. Microbiol. 1999, 171, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braune, A.; Gütschow, M.; Engst, W.; Blaut, M. Degradation of Quercetin and Luteolin by Eubacterium ramulus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 5558–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herles, C.; Braune, A.; Blaut, M. First bacterial chalcone isomerase isolated from Eubacterium ramulus. Arch. Microbiol. 2004, 181, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, D.M.; Thomsen, D.M.; Peters, D.C.; Pavlidis, I.V.; Jonczyk, M.S.P.; Grünert, M.S.P.P.; Beutel, S.; Scheper, T.; Gross, E.; Backes, M.; et al. Enzymatic Conversion of Flavonoids using Bacterial Chalcone Isomerase and Enoate Reductase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 53, 1439–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoefer, L.; Braune, A.; Blaut, M. Cloning and Expression of a Phloretin Hydrolase Gene from Eubacterium ramulus and Characterization of the Recombinant Enzyme. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6131–6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, M.; Tuukkanen, A.; Dickerhoff, J.; Palm, G.J.; Kratzat, H.; Svergun, D.I.; Weisz, K.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Hinrichs, W. Structure and catalytic mechanism of the evolutionarily unique bacterial chalcone isomerase. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2015, 71, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsinghorst, P.W.; Cavlar, T.; Müller, A.; Braune, A.; Blaut, M.; Gütschow, M. The Thermal and Enzymatic Taxifolin–Alphitonin Rearrangement. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2243–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braune, A.; Engst, W.; Elsinghorst, P.W.; Furtmann, N.; Bajorath, J.; Gütschow, M.; Blaut, M. Chalcone Isomerase from Eubacterium ramulus Catalyzes the Ring Contraction of Flavanonols. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 2965–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkholz, D.S.; Driggers, C.M.; Shapovalov, M.V.; Dunbrack, R.L.; Karplus, P.A. Nonplanar peptide bonds in proteins are common and conserved but not biased toward active sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.J.; Headd, J.J.; Moriarty, N.W.; Prisant, M.G.; Videau, L.L.; Deis, L.N.; Verma, V.; Keedy, D.A.; Hintze, B.J.; Chen, V.B.; et al. MolProbity: More and better reference data for improved all-atom structure validation. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkers, G.; Damas, J.M.; Palm, G.J.; Panjikar, S.; Soares, C.; Hinrichs, W. Putative dioxygen-binding sites and recognition of tigecycline and minocycline in the tetracycline-degrading monooxygenase TetX. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2013, 69, 1758–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflugrath, J.W. The finer things in X-ray diffraction data collection. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1999, 55, 1718–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winn, M.D.; Ballard, C.C.; Cowtan, K.D.; Dodson, E.J.; Emsley, P.; Evans, P.R.; Keegan, R.M.; Krissinel, E.B.; Leslie, A.G.W.; McCoy, A.; et al. Overview of theCCP4 suite and current developments. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D-Struct. Biol. 2011, 67, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, U.; Darowski, N.; Fuchs, M.; Förster, R.; Hellmig, M.; Paithankar, K.; Pühringer, S.; Steffien, M.; Zocher, G.; Weiss, M.S. Facilities for macromolecular crystallography at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2012, 19, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabsch, W. XDS. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, M.; Weiss, M.S.; Heinemann, U.; Mueller, U. XDSAPP: A graphical user interface for the convenient processing of diffraction data usingXDS. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2012, 45, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phasercrystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshudov, G.N.; Skubák, P.; Lebedev, A.A.; Pannu, N.S.; Steiner, R.A.; Nicholls, R.A.; Winn, M.D.; Long, F.; Vagin, A.A. REFMAC5 for the refinement of macromolecular crystal structures. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalevskiy, O.; Nicholls, R.A.; Long, F.; Carlon, A.; Murshudov, G.N. Overview of refinement procedures withinREFMAC5: Utilizing data from different sources. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D-Biol. Crystallogr. 2018, 74, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D-Struct. Biol. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, V.B.; Arendall, W.B., III.; Headd, J.J.; Keedy, D.A.; Immormino, R.M.; Kapral, G.J.; Murray, L.W.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. MolProbity: All-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. Sec. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLano, W.L. Pymol molecular viewer: Updates and refinements. In Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, E.C.; Yorke, B.A.; Pearson, A.R.; Mehrabi, P. Best practices for time-resolved serial synchrotron crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Struct. Biol. 2022, 78, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palm, G.J.; Thomsen, M.; Berndt, L.; Hinrichs, W. Structural Basis for (2R,3R)-Taxifolin Binding and Reaction Products to the Bacterial Chalcone Isomerase of Eubacterium ramulus. Molecules 2022, 27, 7909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227909
Palm GJ, Thomsen M, Berndt L, Hinrichs W. Structural Basis for (2R,3R)-Taxifolin Binding and Reaction Products to the Bacterial Chalcone Isomerase of Eubacterium ramulus. Molecules. 2022; 27(22):7909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227909
Chicago/Turabian StylePalm, Gottfried J., Maren Thomsen, Leona Berndt, and Winfried Hinrichs. 2022. "Structural Basis for (2R,3R)-Taxifolin Binding and Reaction Products to the Bacterial Chalcone Isomerase of Eubacterium ramulus" Molecules 27, no. 22: 7909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227909
APA StylePalm, G. J., Thomsen, M., Berndt, L., & Hinrichs, W. (2022). Structural Basis for (2R,3R)-Taxifolin Binding and Reaction Products to the Bacterial Chalcone Isomerase of Eubacterium ramulus. Molecules, 27(22), 7909. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227909






