Immunomodulatory Activity of Punicalagin, Punicalin, and Ellagic Acid Differs from the Effect of Pomegranate Peel Extract
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
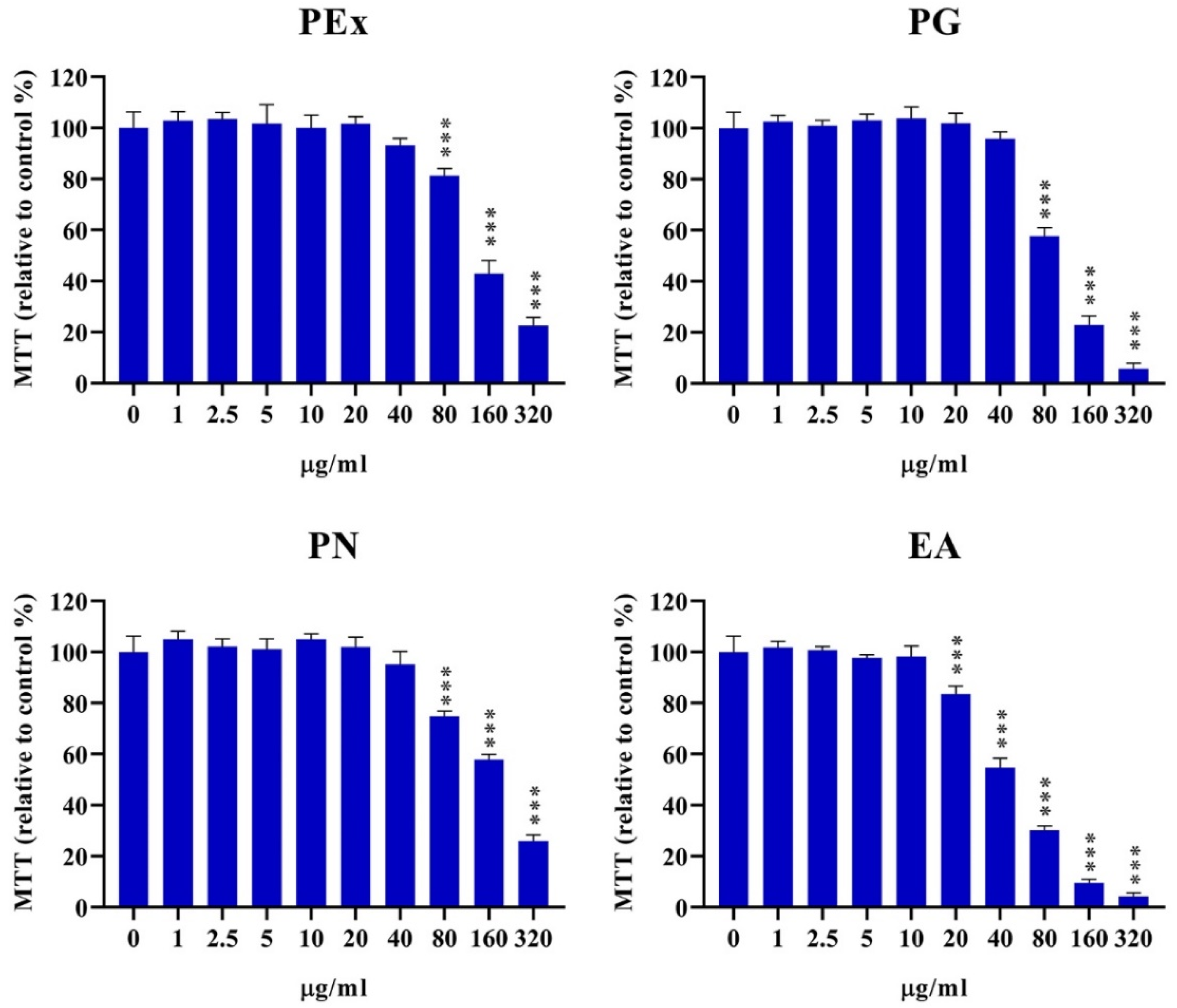
2.1. Cytotoxicity of Ellagitannin Components from PEx
2.2. Proliferative Activity of PBMC by the Influence of Ellagitannin Components from PEx
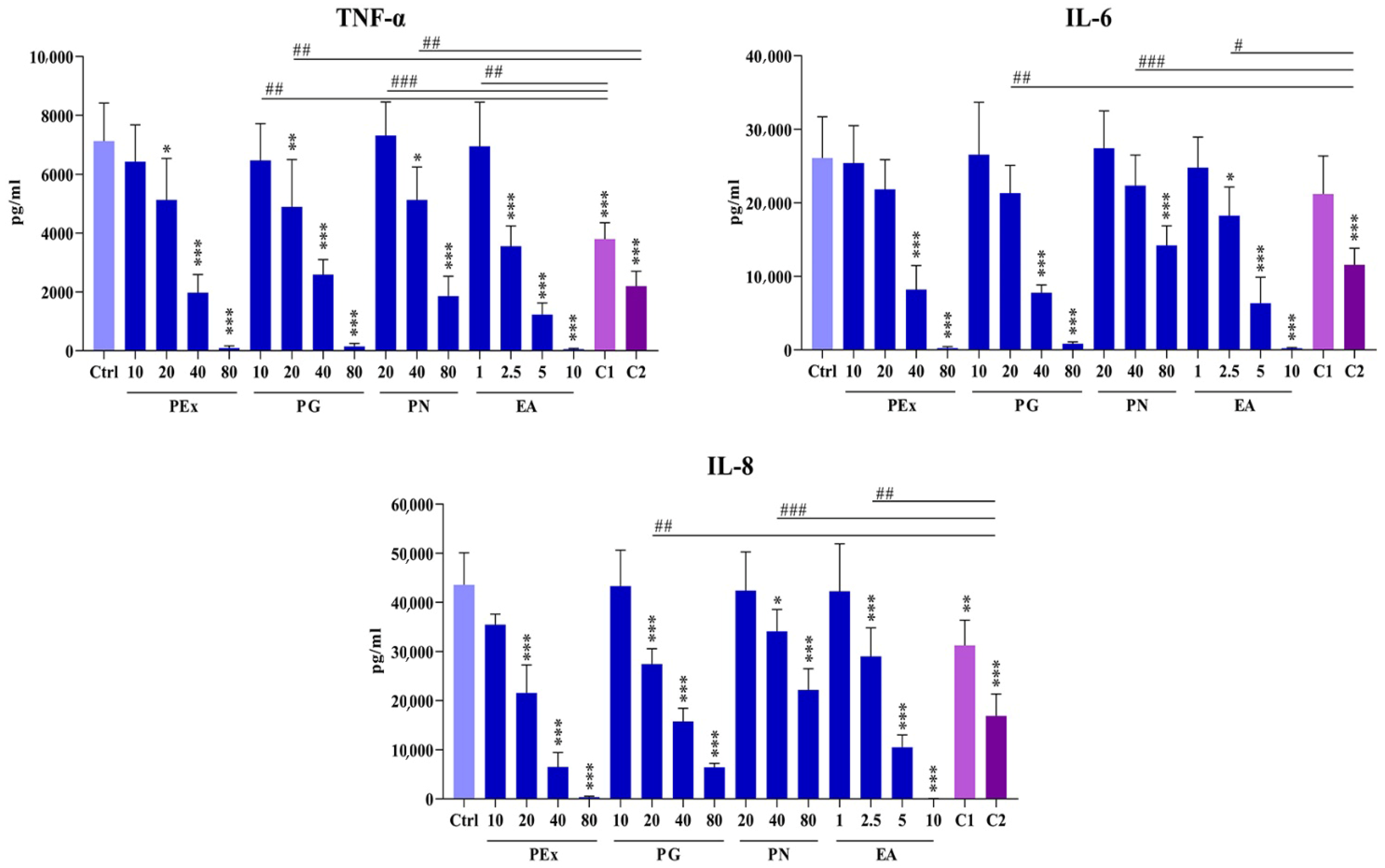
2.3. Effect of Ellagitannin Components and Their Combinations on the Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines in PBMC Cultures
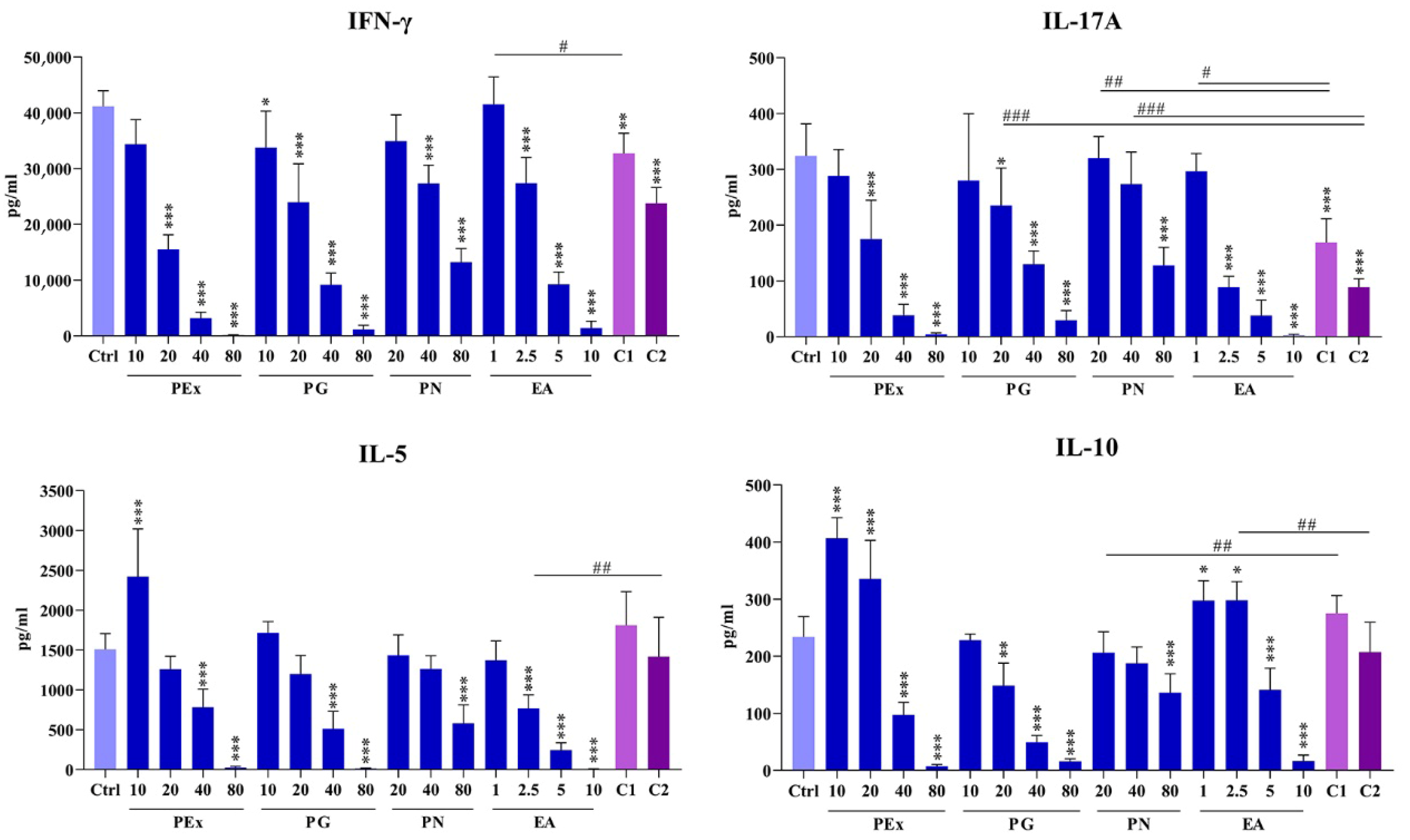
2.4. Effect of Ellagitannin Components and Their Combinations on the Production of T-Cell Subset Cytokines in PBMC Cultures
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Protocol
4.2. Pomegranate Peel Extract and Ellagitannin Components
4.3. HPLC Analysis
4.4. PBMC Cultures
4.5. MTT Assay
4.6. Proliferation Assay
4.7. Cytokine Measurement
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baradaran Rahimi, V.; Ghadiri, M.; Ramezani, M.; Askari, V.R. Antiinflammatory and anti-cancer activities of pomegranate and its constituent, ellagic acid: Evidence from cellular, animal, and clinical studies. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 685–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, T.; Sestili, P.; Akhtar, S. Pomegranate peel and fruit extracts: A review of potential anti-inflammatory and anti-infective effects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 143, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omer, H.A.A.; Abdel-Magid, S.S.; Awadalla, I.M. Nutritional and chemical evaluation of dried pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) peels and studying the impact of level of inclusion in ration formulation on productive performance of growing Ossimi lambs. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venusova, E.; Kolesarova, A.; Horky, P.; Slama, P. Physiological and Immune Functions of Punicalagin. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, T.; Akhtar, S.; Sestili, P.; Riaz, M.; Ismail, A.; Labbe, R.G. Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Urease Inhibitory Activities of Phenolics-Rich Pomegranate Peel Hydro-Alcoholic Extracts. J. Food Biochem. 2016, 40, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjha, M.; Kanwal, R.; Shafique, B.; Arshad, R.N.; Irfan, S.; Kieliszek, M.; Kowalczewski, P.L.; Irfan, M.; Khalid, M.Z.; Roobab, U.; et al. A Critical Review on Pulsed Electric Field: A Novel Technology for the Extraction of Phytoconstituents. Molecules 2021, 26, 4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Elswijk, D.A.; Schobel, U.P.; Lansky, E.P.; Irth, H.; van der Greef, J. Rapid dereplication of estrogenic compounds in pomegranate (Punica granatum) using on-line biochemical detection coupled to mass spectrometry. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirzadeh, M.; Caporaso, N.; Rauf, A.; Shariati, M.A.; Yessimbekov, Z.; Khan, M.U.; Imran, M.; Mubarak, M.S. Pomegranate as a source of bioactive constituents: A review on their characterization, properties and applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 982–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, C.V.S.; Prakash, I. Bioactive Chemical Constituents from Pomegranate (Punica granatum) Juice, Seed and Peel. Int. J. Res. Chem. Environ. 2011, 1, 182. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, K.B.; Rizvi, S.I. Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2009, 2, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, E.; Sangiovanni, E.; Dell’agli, M. A review on the anti-inflammatory activity of pomegranate in the gastrointestinal tract. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 247145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, J.F.; Garreto, D.V.; da Silva, M.C.; Fortes, T.S.; de Oliveira, R.B.; Nascimento, F.R.; Da Costa, F.B.; Grisotto, M.A.; Nicolete, R. Therapeutic potential of biodegradable microparticles containing Punica granatum L. (pomegranate) in murine model of asthma. Inflamm. Res. 2013, 62, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fikry, E.M.; Gad, A.M.; Eid, A.H.; Arab, H.H. Caffeic acid and ellagic acid ameliorate adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats via targeting inflammatory signals, chitinase-3-like protein-1 and angiogenesis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, D.M.; Bugert, J.; Denyer, S.P.; Heard, C.M. Anti-inflammatory activity of Punica granatum L. (Pomegranate) rind extracts applied topically to ex vivo skin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 112, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morzelle, M.C.; Salgado, J.M.; Telles, M.; Mourelle, D.; Bachiega, P.; Buck, H.S.; Viel, T.A. Neuroprotective Effects of Pomegranate Peel Extract after Chronic Infusion with Amyloid-beta Peptide in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balbir-Gurman, A.; Fuhrman, B.; Braun-Moscovici, Y.; Markovits, D.; Aviram, M. Consumption of pomegranate decreases serum oxidative stress and reduces disease activity in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: A pilot study. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2011, 13, 474–479. [Google Scholar]
- Ertam, I.; Mutlu, B.; Unal, I.; Alper, S.; Kivcak, B.; Ozer, O. Efficiency of ellagic acid and arbutin in melasma: A randomized, prospective, open-label study. J. Dermatol. 2008, 35, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavipour, M.; Sotoudeh, G.; Tavakoli, E.; Mowla, K.; Hasanzadeh, J.; Mazloom, Z. Pomegranate extract alleviates disease activity and some blood biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis patients. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, B.; Saedisomeolia, A.; Wood, L.G.; Yaseri, M.; Tavasoli, S. Effects of pomegranate extract supplementation on inflammation in overweight and obese individuals: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2016, 22, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razani, Z.; Dastani, M.; Kazerani, H.R. Cardioprotective Effects of Pomegranate (Punica granatum) Juice in Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha, L.R.; Muniz-Junqueira, M.I.; Borges, T.K.D.S. Impact of polyphenols in phagocyte functions. J. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 12, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakoor, H.; Feehan, J.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Platat, C.; Al Dhaheri, A.S.; Ali, H.I.; Ismail, L.C.; Bosevski, M.; Stojanovska, L. Immunomodulatory Effects of Dietary Polyphenols. Nutrients 2021, 13, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Jiang, H.; Fang, J. Regulation of Immune Function by Polyphenols. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1264074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colic, M.; Bekic, M.; Tomic, S.; Dokic, J.; Radojevic, D.; Savikin, K.; Miljus, N.; Markovic, M.; Skrbic, R. Immunomodulatory Properties of Pomegranate Peel Extract in a Model of Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell Culture. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.G.; Huang, M.H.; Li, J.H.; Lai, F.I.; Lee, H.M.; Hsu, Y.N. Punicalagin induces apoptotic and autophagic cell death in human U87MG glioma cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mady, F.M.; Shaker, M.A. Enhanced anticancer activity and oral bioavailability of ellagic acid through encapsulation in biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7405–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkoz, M.; Yalin, S.; Yildirim, M.; Yalin, A.E.; Comelekoglu, U. Punicalagin and Punicalin Suppress the Adipocyte Differentiation through the Transcription Factors. Acta Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almowallad, S.; Huwait, E.; Al-Massabi, R.; Saddeek, S.; Gauthaman, K.; Prola, A. Punicalagin Regulates Key Processes Associated with Atherosclerosis in THP-1 Cellular Model. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.M.M.; Brito, L.M.; Souza, A.C.; Queiroz, B.; de Carvalho, T.P.; Batista, J.F.; Oliveira, J.; de Mendonca, I.L.; Lira, S.R.S.; Chaves, M.H.; et al. Gallic and ellagic acids: Two natural immunomodulator compounds solve infection of macrophages by Leishmania major. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2017, 390, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiki-Ito, A.; Chewonarin, T.; Tang, M.; Pitchakarn, P.; Kuno, T.; Ogawa, K.; Asamoto, M.; Shirai, T.; Takahashi, S. Ellagic acid, a component of pomegranate fruit juice, suppresses androgen-dependent prostate carcinogenesis via induction of apoptosis. Prostate 2015, 75, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silacci, P.; Tretola, M. Pomegranate’s Ellagitannins: Metabolism and Mechanisms of Health Promoting Properties. Nutr. Food Sci. Int. J. 2019, 9, 555766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeram, N.P.; Adams, L.S.; Henning, S.M.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Nair, M.G.; Heber, D. In vitro antiproliferative, apoptotic and antioxidant activities of punicalagin, ellagic acid and a total pomegranate tannin extract are enhanced in combination with other polyphenols as found in pomegranate juice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2005, 16, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.U.; Kim, L.K.; Choi, J.M. Revisiting the Concept of Targeting NFAT to Control T Cell Immunity and Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojanathammanee, L.; Puig, K.L.; Combs, C.K. Pomegranate polyphenols and extract inhibit nuclear factor of activated T-cell activity and microglial activation in vitro and in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.; Mun, C.H.; Park, S.H.; Jeon, D.; Kim, S.J.; Yoon, T.; Ko, E.; Jo, S.; Park, Y.B.; Namkung, W.; et al. Punicalagin Ameliorates Lupus Nephritis via Inhibition of PAR2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, K.; Mishra, S.; Saha, M.; Mahapatra, S.; Saha, C.; Yenge, G.; Gaikwad, N.; Pal, R.; Oulkar, D.; Banerjee, K.; et al. Amelioration of diabetic nephropathy using pomegranate peel extract-stabilized gold nanoparticles: Assessment of NF-kappaB and Nrf2 signaling system. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1753–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Yan, C.; Frost, B.; Wang, X.; Hou, C.; Zeng, M.; Gao, H.; Kang, Y.; Liu, J. Pomegranate extract decreases oxidative stress and alleviates mitochondrial impairment by activating AMPK-Nrf2 in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhami, V.M.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Syed, D.N.; Lall, R.K.; Mukhtar, H. Oral infusion of pomegranate fruit extract inhibits prostate carcinogenesis in the TRAMP model. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Sarrias, A.; Espin, J.C.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Garcia-Conesa, M.T. Gene expression, cell cycle arrest and MAPK signalling regulation in Caco-2 cells exposed to ellagic acid and its metabolites, urolithins. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, H.; Hou, X.; Li, D.; He, S.; Wan, C.; Yin, P.; Liu, M.; Liu, F.; Xu, J. Punicalagin Induces Nrf2/HO-1 Expression via Upregulation of PI3K/AKT Pathway and Inhibits LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 380218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjha, M.M.A.N.; Shafique, B.; Wang, L.; Irfan, S.; Safdar, M.N.; Murtaza, M.A.; Nadeem, M.; Mahmood, S.; Mueed-ud-Din, G.; Nadeem, H.R. A comprehensive review on phytochemistry, bioactivity and medicinal value of bioactive compounds of pomegranate (Punica granatum). Adv. Tradit. Med. 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, K.W.; Murugan, D.; Leong, X.F.; Abas, R.; Alias, A.; Mustafa, M.R. Flavonoids as Natural Anti-Inflammatory Agents Targeting Nuclear Factor-Kappa B (NFkappaB) Signaling in Cardiovascular Diseases: A Mini Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruterbusch, M.; Pruner, K.B.; Shehata, L.; Pepper, M. In Vivo CD4(+) T Cell Differentiation and Function: Revisiting the Th1/Th2 Paradigm. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 705–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golubovskaya, V.; Wu, L. Different Subsets of T Cells, Memory, Effector Functions, and CAR-T Immunotherapy. Cancers 2016, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanović, I.; Šavikin, K.; Đedović, N.; Živković, J.; Saksida, T.; Momčilović, M.; Koprivica, I.; Vujičić, M.; Stanisavljević, S.; Miljković, Đ.; et al. Pomegranate peel extract ameliorates autoimmunity in animal models of multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 35, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, V.; Vassallo, A.; Pisano, C.; Signorino, G.; Cardile, F.; Sorrentino, M.; Colelli, F.; Fucci, A.; D’Andrea, E.L.; De Tommasi, N.; et al. A Herbal Mixture from Propolis, Pomegranate, and Grape Pomace Endowed with Anti-Inflammatory Activity in an In Vivo Rheumatoid Arthritis Model. Molecules 2020, 25, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessler, H.; Djaldetti, M. On the link between ellagic acid and the immune balance between human mononuclear and colon carcinoma cells. Immunol. Curr. Res. 2017, 1, 1000101. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Kaur, M.; Katnoria, J.K.; Nagpal, A.K. Polyphenols in Food: Cancer Prevention and Apoptosis Induction. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 4740–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Yan, H.; Han, C.; Wang, W.; Tian, Y.; Chen, X. Polyphenols from blueberries modulate inflammation cytokines in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 69, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OyetakinWhite, P.; Tribout, H.; Baron, E. Protective mechanisms of green tea polyphenols in skin. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 560682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramstead, A.G.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Quinn, M.T.; Jutila, M.A. Oenothein B, a Cyclic Dimeric Ellagitannin Isolated from Epilobium angustifolium, Enhances IFNγ Production by Lymphocytes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramstead, A.G.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Todd, K.; Loeffelholz, J.; Berardinelli, J.G.; Quinn, M.T.; Jutila, M.A. Aging influences the response of T cells to stimulation by the ellagitannin, oenothein B. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 26, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas, A.; Saavedra, N.; Salazar, L.A.; Abdalla, D.S. Modulation of immune function by polyphenols: Possible contribution of epigenetic factors. Nutrients 2013, 5, 2314–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benvenuto, M.; Focaccetti, C.; Ciuffa, S.; Fazi, S.; Bei, A.; Miele, M.T.; Albonici, L.; Cifaldi, L.; Masuelli, L.; Bei, R. Polyphenols affect the humoral response in cancer, infectious and allergic diseases and autoimmunity by modulating the activity of TH1 and TH2 cells. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2021, 60, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, K.C.; Teuber, S.S. Ellagic acid and polyphenolics present in walnut kernels inhibit in vitro human peripheral blood mononuclear cell proliferation and alter cytokine production. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1190, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, T.; Nishida, N.; Ito, H. The Inhibitory Effect of a Polyphenol Concentrate from Pomegranate Juice on 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced Contact Hypersensitivity in Mice. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2018, 24, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Les, F.; Arbones-Mainar, J.M.; Valero, M.S.; Lopez, V. Pomegranate polyphenols and urolithin A inhibit alpha-glucosidase, dipeptidyl peptidase-4, lipase, triglyceride accumulation and adipogenesis related genes in 3T3-L1 adipocyte-like cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 220, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemann, C.; Wagner, L.; Stephan, M.; von Horsten, S. Cut to the chase: A review of CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase-4′s (DPP4) entanglement in the immune system. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2016, 185, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Das, S.; Saha, A.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.K. Ellagic acid facilitates indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer healing via COX-2 up-regulation. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2012, 44, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.; Li, M. Potential Application of Plant-Based Functional Foods in the Development of Immune Boosters. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 637782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Jantan, I.; Kumolosasi, E.; Bukhari, S.N. Immunostimulatory effects of the standardized extract of Tinospora crispa on innate immune responses in Wistar Kyoto rats. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 2961–2973. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gunther, S.; Fagone, P.; Jalce, G.; Atanasov, A.G.; Guignabert, C.; Nicoletti, F. Role of MIF and D-DT in immune-inflammatory, autoimmune, and chronic respiratory diseases: From pathogenic factors to therapeutic targets. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, T.H.; Britton, G.J.; Hill, E.V.; Verhagen, J.; Burton, B.R.; Wraith, D.C. Regulation of adaptive immunity, the role of interleukin-10. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.Y.; Han, B.; Deng, X.; Deng, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Shen, P.X.; Hui, T.; Chen, R.H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Pomegranate peel extract ameliorates the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via modulation of gut microbiota. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1857515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shitany, N.A.; El-Bastawissy, E.A.; El-desoky, K. Ellagic acid protects against carrageenan-induced acute inflammation through inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B, inducible cyclooxygenase and proinflammatory cytokines and enhancement of interleukin-10 via an antioxidant mechanism. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 19, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahfoufi, N.; Alsadi, N.; Jambi, M.; Matar, C. The Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Polyphenols. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comalada, M.; Ballester, I.; Bailon, E.; Sierra, S.; Xaus, J.; Galvez, J.; de Medina, F.S.; Zarzuelo, A. Inhibition of pro-inflammatory markers in primary bone marrow-derived mouse macrophages by naturally occurring flavonoids: Analysis of the structure-activity relationship. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouvezier, S.; Powell, B.; Keir, D.; Yaqoob, P. The effects of phenolic components of tea on the production of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines by human leukocytes in vitro. Cytokine 2001, 13, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi-Boroujeni, A.; Mahmoudian-Sani, M.R. Anti-inflammatory potential of Quercetin in COVID-19 treatment. J. Inflamm. 2021, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.M.; Jialal, I.; Devaraj, S. Effects of epigallocatechin gallate on regulatory T cell number and function in obese v. lean volunteers. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Waterman, P.G.; Mole, S. Analysis of Phenolic Plant Metabolites; Oxford Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1994; pp. 73–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhishen, J.; Mengcheng, T.; Jianming, W. The determination of flavonoid contents in mulberry and their scavenging effects on superoxide radicals. Food Chem. 1999, 64, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, M.; Turovskaya, O.; Kim, G.; Madan, R.; Karp, C.L.; Cheroutre, H.; Kronenberg, M. Interleukin 10 acts on regulatory T cells to maintain expression of the transcription factor Foxp3 and suppressive function in mice with colitis. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Čolić, M.; Mihajlović, D.; Bekić, M.; Marković, M.; Dragišić, B.; Tomić, S.; Miljuš, N.; Šavikin, K.; Škrbić, R. Immunomodulatory Activity of Punicalagin, Punicalin, and Ellagic Acid Differs from the Effect of Pomegranate Peel Extract. Molecules 2022, 27, 7871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227871
Čolić M, Mihajlović D, Bekić M, Marković M, Dragišić B, Tomić S, Miljuš N, Šavikin K, Škrbić R. Immunomodulatory Activity of Punicalagin, Punicalin, and Ellagic Acid Differs from the Effect of Pomegranate Peel Extract. Molecules. 2022; 27(22):7871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227871
Chicago/Turabian StyleČolić, Miodrag, Dušan Mihajlović, Marina Bekić, Milan Marković, Branka Dragišić, Sergej Tomić, Nataša Miljuš, Katarina Šavikin, and Ranko Škrbić. 2022. "Immunomodulatory Activity of Punicalagin, Punicalin, and Ellagic Acid Differs from the Effect of Pomegranate Peel Extract" Molecules 27, no. 22: 7871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227871
APA StyleČolić, M., Mihajlović, D., Bekić, M., Marković, M., Dragišić, B., Tomić, S., Miljuš, N., Šavikin, K., & Škrbić, R. (2022). Immunomodulatory Activity of Punicalagin, Punicalin, and Ellagic Acid Differs from the Effect of Pomegranate Peel Extract. Molecules, 27(22), 7871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227871





