Analyses of Fatty Acids, Proteins, Ascorbic Acid, Bioactive Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Canadian Barley Cultivars and Elite Germplasm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
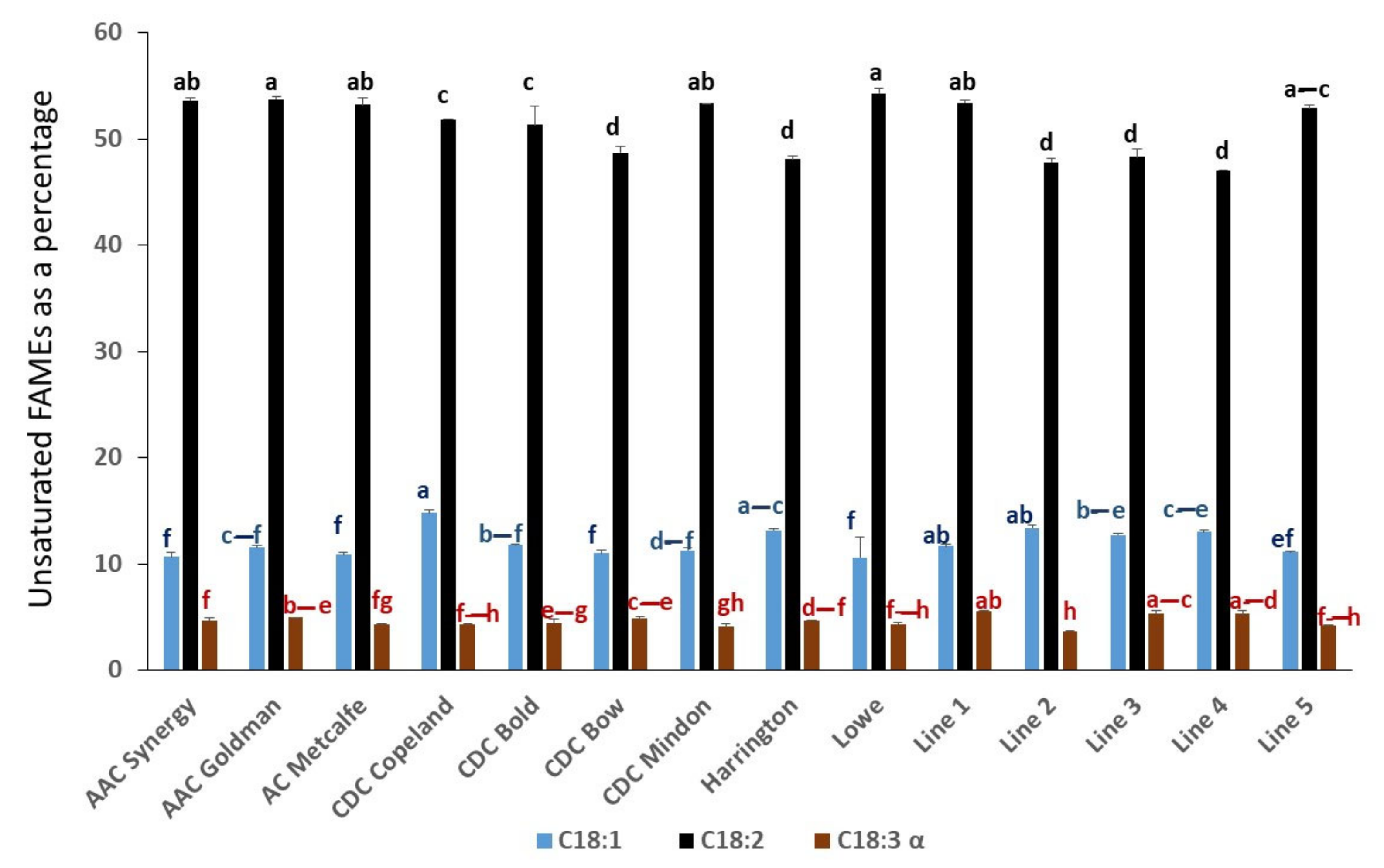
2.1. Comparison of Fatty Acid Composition in Selected Genotypes of Canadian Barley Grains
2.2. Comparative Analysis of Protein Content in Barley Genotypes
2.3. Assessment of Ascorbic Acid Content
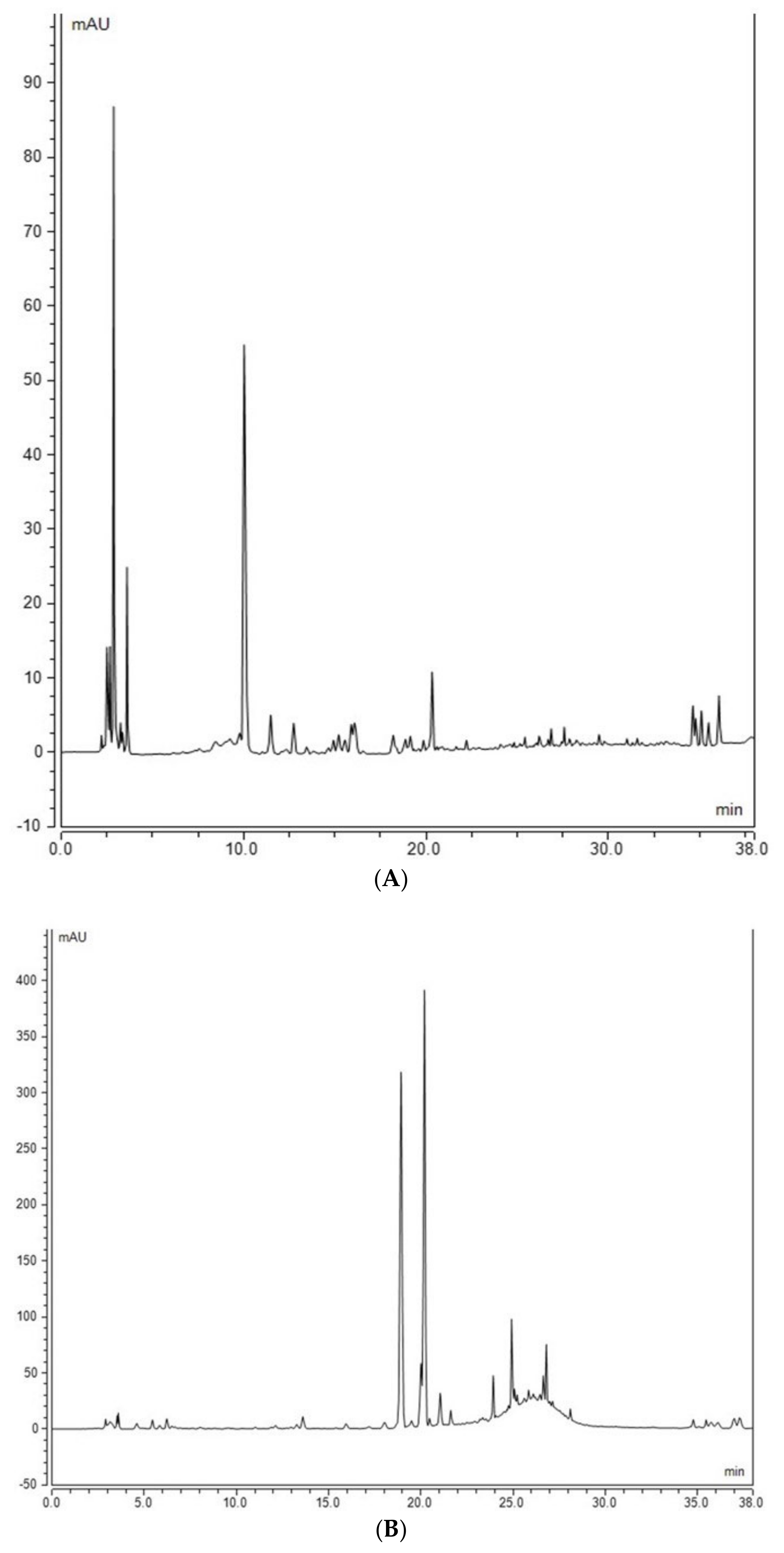
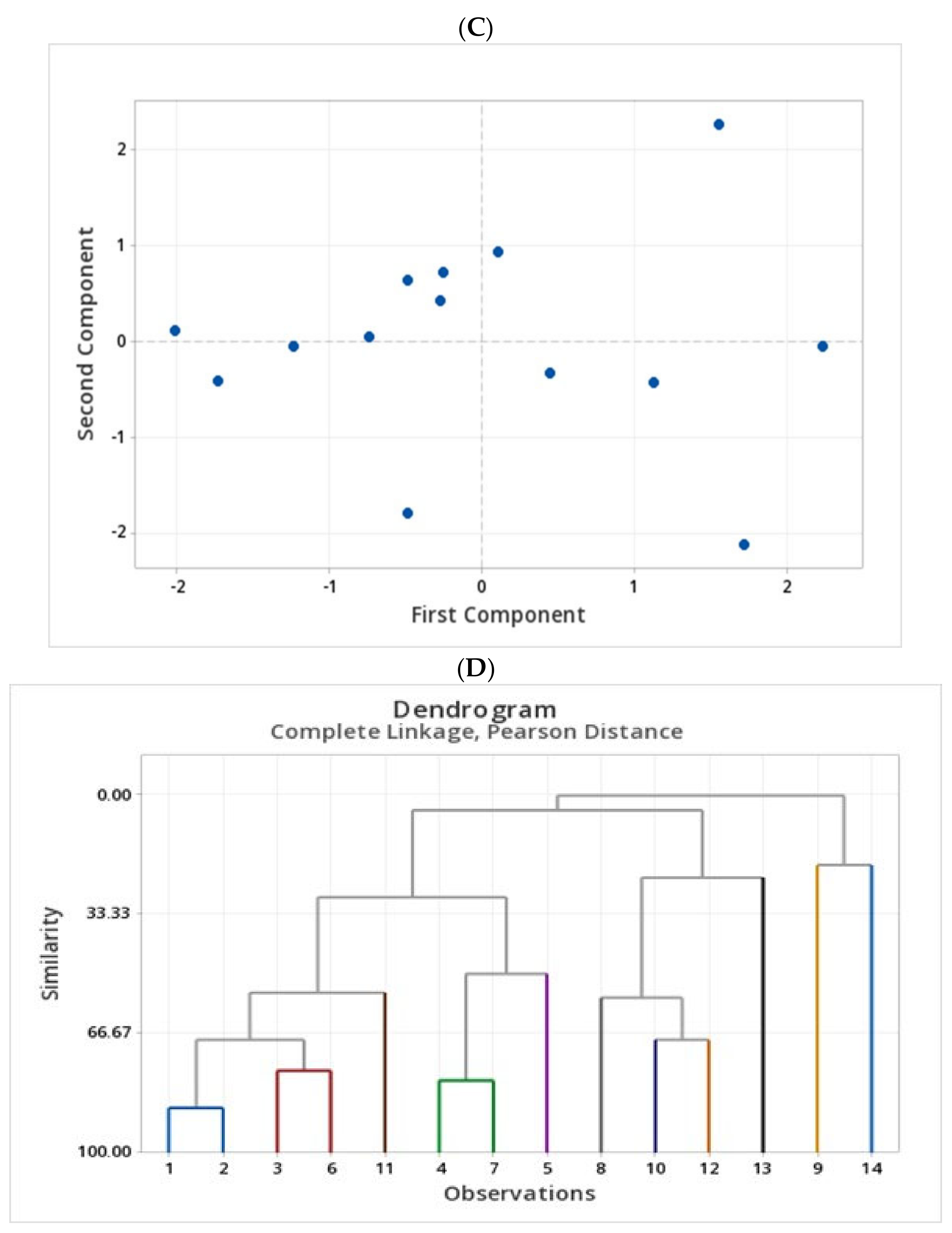
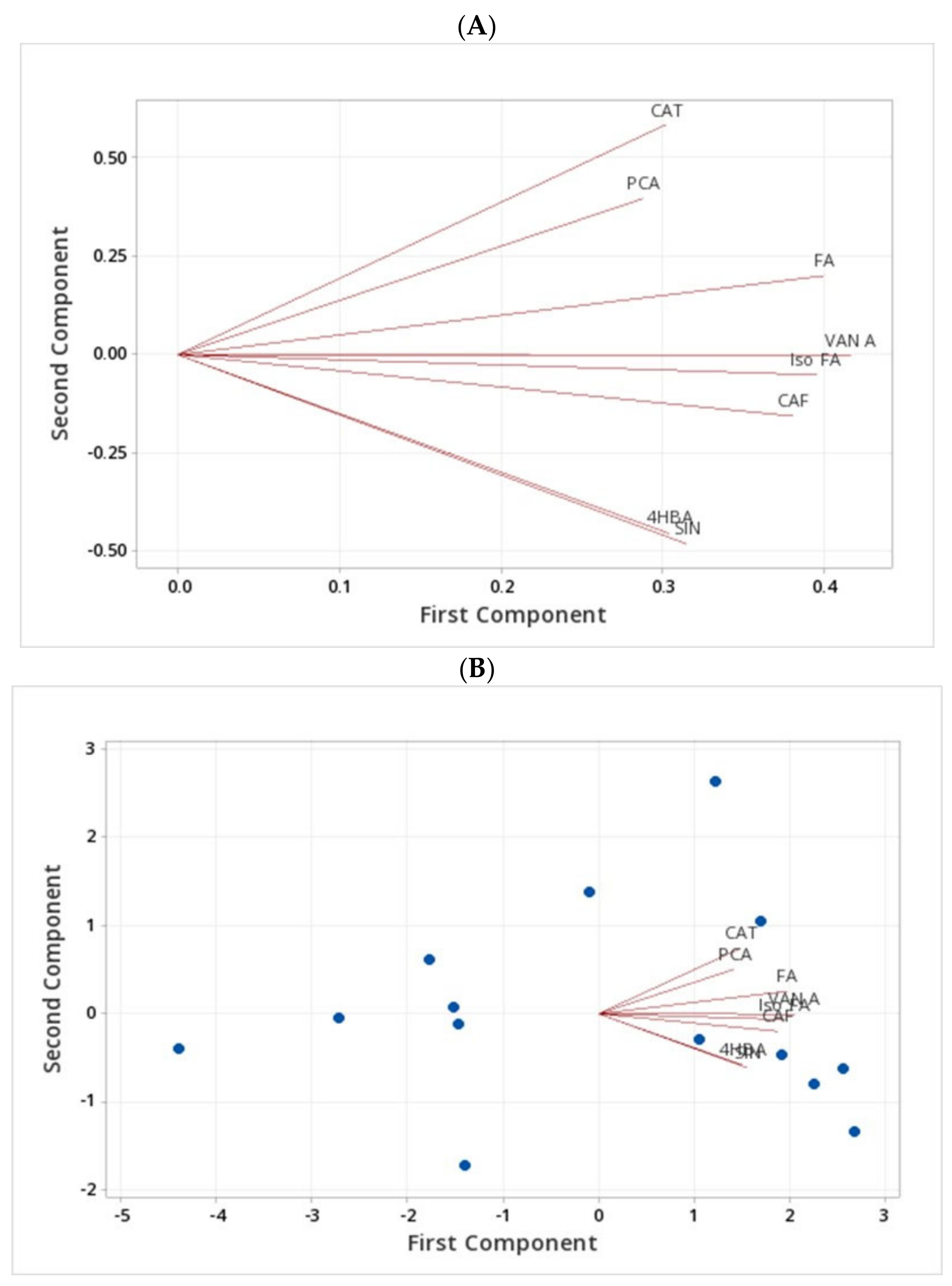
2.4. Assessment of Phenolic Compounds in Grains of Selected Canadian Barley Genotypes
2.5. Antioxidant Activity Assay Analysis
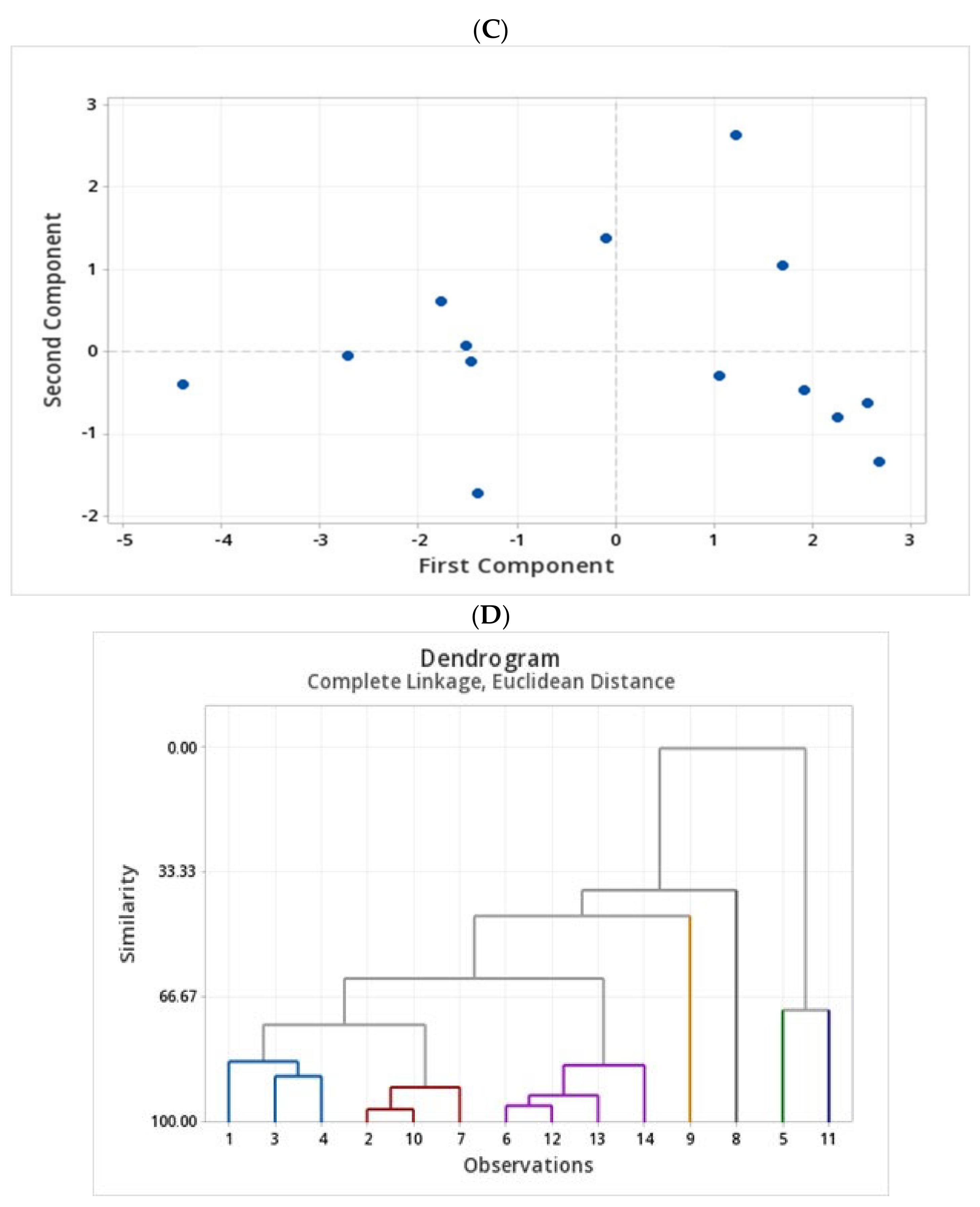
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Samples for the Extraction and Analysis
4.2. Chemical Standards
4.3. Extraction and Analysis of FAMEs by GC/MS
4.4. Protein Composition Analysis
4.5. Determination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C)
4.6. Analysis of Free Phenolic Compounds in Barley Using HPLC
4.7. Analysis of Bound Phenolic Compounds in Barley Using HPLC
4.8. Antioxidant Activity Assay in Barley
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iftikhar, M.; Khan, M. Amaranth. In Bioactive Factors and Processing Technology for Cereal Foods; Tsao, R., Baoguo, S., Wang, J., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbandeh, M. Barley Production Worldwide 2008/2009–2021/2022. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/271973/world-barley-production-since-2008/#:~:text=Jul%208%2C%202021%20The%20global%20production%20volume%20of,from%20around%20156.41%20million%20metric%20tons%20in%202019%2F2020 (accessed on 21 February 2022).
- Badea, A.; Wijekoon, C. Benefits of barley grain in animal and human diets. In Cereal Grains; Goyal, A.K., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; Volume 1, Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/75956 (accessed on 19 October 2022).
- Quifer-Rada, P.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Martínez-Huélamo, M.; Chiva-Blanch, G.; Jáuregui, O.; Estruch, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R. A comprehensive characterisation of beer polyphenols by high resolution mass spectrometry (LC–ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS). Food Chem. 2015, 169, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambra, R.; Pastore, G.; Lucchetti, S. The Role of Bioactive Phenolic Compounds on the Impact of Beer on Health. Molecules 2021, 26, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cereals Canada 2022. Available online: https://cerealscanada.ca/cereal-grains/barley/ (accessed on 3 March 2022).
- Canadian Malting Barley Technical Centre 2022. Available online: https://cmbtc.com/ (accessed on 3 March 2022).
- Izydorczyk, M.S.; McMillan, T. Annual Barley Harvest Report, Grain Research Laboratory. 2021. Available online: https://www.grainscanada.gc.ca/en/grain-research/export-quality/cereals/malting-barley/2021/ (accessed on 3 March 2022).
- Klepacka, J.; Gujska, E.; Michalak, J. Phenolic compounds as cultivar- and variety-distinguishing factors in some plant products. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2011, 66, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goupy, P.; Hugues, M.; Boivin, P.; Amiot, M.J. Antioxidant composition and activity of barley (Hordeum vulgare) and malt extracts and of isolated phenolic compounds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 1625–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Luan, H.; Lin, S.; Lv, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu, R. Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Two Barley Cultivars (Hordeum vulgare L.) with Contrasting Grain Protein Content. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Yu, G.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, G.; Jin, X. Grain protein content variation and its association analysis in barley. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedak, G.; De La Roche, I. Lipid and fatty acid composition of barley kernels. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1977, 57, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mosa, K.A.; Ji, L.; Kage, U.; Dhokane, D.; Karre, S.; Madalageri, D.; Pathania, N. Metabolomics-assisted biotechnological interventions for developing plant-based functional foods and nutraceuticals. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1791–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legge, W.G.; Tucker, J.R.; Fetch, T.G., Jr.; Haber, S.; Menzies, J.G.; Tekauz, A.; Turkington, T.K.; Savard, M.E. AAC Synergy barley. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2014, 94, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legge, W.G.; Badea, A.; Tucker, J.R.; Fetch, T.G., Jr.; Banik, M.; Haber, S.; Menzies, J.G.; Tekauz, A.; Turkington, T.K.; Martin, R.A.; et al. AAC Goldman barley. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2018, 98, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legge, W.G.; Metcalfe, D.R.; Haber, S.; Harder, D.E.; Noll, J.S.; Tekauz, A.; Thomas, P.L. AC Metcalfe barley. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2003, 83, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) CDC Copeland. Available online: https://inspection.canada.ca/english/plaveg/pbrpov/cropreport/bar/app00002297e.shtml (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) CDC Bold. Available online: https://inspection.canada.ca/active/netapp/regvar/regvare.aspx?id=2441 (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) CDC Bow. Available online: https://inspection.canada.ca/english/plaveg/pbrpov/cropreport/bar/app00010031e.shtml (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Rossnagel, B.G.; Zatorski, T.; Voth, W.D.; Scoles, G.J.; Legge, W.G.; Tucker, J.R.; Tekauz, A.; Savard, M. Registration of ‘CDC Mindon’ Barley. J. Plant Regist. 2008, 2, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, B.L.; Rossnagel, B.G. Harrington Barley. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1984, 64, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juskiw, P.E.; Oatway, L.; Oro, M.; Nyachiro, J.M.; Anbessa, Y.; Xi, K.; Turkington, T.K.; Lohr, S.; Bowness, J.; Capettini, F. Registration of ‘Lowe’, a Two-Rowed Malting Barley with Enhanced Resistance to Fusarium Head Blight. J. Plant Regist. 2019, 3, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Ali, S.; Hussain, A.; Hussain, Z.; Manzoor, M.F.; Hussain, A.; Ali, A.; Mahmood, T.; Abbasi, K.S.; Karrar, E.; et al. Compositional profile of barley landlines grown in different regions of Gilgit-Baltistan. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 2605–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hung, P. Phenolic Compounds of Cereals and Their Antioxidant Capacity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J.; Dang, B.; Fan, M.T. Free and bound phenolic compound content and antioxidant activity of different cultivated blue highland barley varieties from the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Molecules 2018, 23, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonoli, M.; Marconi, E.; Caboni, M.F. Free and bound phenolic compounds in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) flours: Evaluation of the extraction capability of different solvent mixtures and pressurized liquid methods by micellar electrokinetic chromatography and spectrophotometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1057, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoor, K. Optimized Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Seed and their radical scavenging properties. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2015, 9, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Xiang, Z.; Lin, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, K.; Liu, T.; Xia, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Identification and quantification of free, esterified, and insoluble-bound phenolics in grains of hulless barley varieties and their antioxidant activities. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, T.; Mansouri, S.; Vecino-Bello, X.; Cruz-Freire, J.M.; Rezgui, S.; Ferchichi, A. Identification and characterization of phenolic compounds extracted from barley husks by LC-MS and antioxidant activity in vitro. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 81, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, I.S.; Teixeira, M.C.; Brodelius, M. Fatty acids profile of selected Artemisia spp. plants: Health promotion. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijekoon, C.; Netticadan, T.; Siow, Y.L.; Sabra, A.; Yu, L.; Raj, P.; Prashar, S. Potential associations among bioactive molecules, antioxidant activity and resveratrol production in Vitis vinifera fruits of North America. Molecules 2022, 27, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, C.S.; Cleary, L.J. The potential use of cereal (1→ 3, 1→ 4)-β-D-glucans as functional food ingredients. J. Cereal Sci. 2005, 42, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroula, A.; Amgain, N.K.R.; Adhikari, S.; Acharya, J. Pigments, ascorbic acid, total polyphenols and antioxidant capacities in deetiolated barley (Hordeum vulgare) and wheat (Triticum aestivum) microgreens. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khakimov, B.; Jespersen, B.M.; Engelsen, S.B. Comprehensive and comparative metabolomic profiling of wheat, barley, oat and rye using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and advanced chemometrics. Foods 2014, 3, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z. Metabolism of Antioxidants and Nitrosothiols in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Seeds during Germination and Seedling Growth. Ph.D. Thesis, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John’s, NL, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]




| # | Name | Class | Registration | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AAC Synergy | Malting | 2012 | [15] |
| 2 | AAC Goldman | Malting | 2018 | [16] |
| 3 | AC Metcalfe | Malting | 1997 | [17] |
| 4 | CDC Copeland | Malting | 1999 | [18] |
| 5 | CDC Bold | General purpose | 1999 | [19] |
| 6 | CDC Bow | Malting | 2016 | [20] |
| 7 | CDC Mindon | General purpose | 2007 | [21] |
| 8 | Harrington | Malting | 1981 | [22] |
| 9 | Lowe | Malting | 2016 | [23] |
| 10 | Line 1 | intended for Malting | na | na |
| 11 | Line 2 | intended for Malting | na | na |
| 12 | Line 3 | intended for Malting | na | na |
| 13 | Line 4 | intended for Malting | na | na |
| 14 | Line 5 | intended for Malting | na | na |
| Genotypes | ASA CONTENT (μg/g dwt) |
|---|---|
| AAC Synergy | 361 ± 12 b |
| AAC Goldman | 259 ± 22 b |
| AC Metcalfe | 366 ± 40 b |
| CDC Copeland | 460 ± 21 a |
| CDC Bold | 522 ± 91 a |
| CDC Bow | 350 ± 96 b |
| CDC Mindon | 453 ± 48 a |
| Harrington | 425 ± 28 a |
| Lowe | 425 ± 38 a |
| Line 1 | 354 ± 62 b |
| Line 2 | 332 ± 3.5 b |
| Line 3 | 340 ± 15 b |
| Line 4 | 407 ± 30 a |
| Line 5 | 307 ± 11 b |
| Genotypes | Phenolic Compound Content (μg/g dwt) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCA | SIN | FA | CAT | VANILLIN | |
| AAC Synergy | ND | 0.23 ± 0.01 cd | 2.19 ± 0.1 c | 15.8 ± 1.1 bc | 0.88 ± 0.03 b |
| AAC Goldman | ND | 0.19 ± 0.1 cd | 2.00 ± 0.1 cd | 16.1 ± 1.4 bc | 0.87 ± 0.04 b |
| AC Metcalfe | ND | 0.17 ± 0.08 cd | 1.79 ± 0.1 d | 13.3 ± 1.0 c | 0.86 ± 0.06 b |
| CDC Copeland | 0.056 ± 0.02 b | 0.34 ± 0.2 cd | 2.48 ± 0.2 ab | 18.3 ± 0.6 b | 0.82 ± 0.11 b |
| CDC Bold | 0.109 ± 0.04 b | 0.36 ± 0.1 ce | 2.50 ± 0.2 ab | 26.9 ± 0.9 a | 0.86 ± 0.02 b |
| CDC Bow | ND | 0.11 ± 0.04 d | 1.79 ± 0.2 d | 20.1 ± 5.1 b | 0.85 ± 0.12 b |
| CDC Mindon | ND | 0.42 ± 0.2 c | 2.61 ± 0.1 ab | 15.5 ± 1.0 bc | 0.80 ± 0.05 b |
| Harrington | ND | 0.35 ± 0.04 cd | 2.78 ± 0.1 a | 13.8 ± 1.0 c | 1.11 ± 0.09 a |
| Lowe | 0.283 ± 0.03 a | 0.25 ± 0.1 cd | 2.44 ± 0.1 ab | 8.1 ± 0.5 d | 0.95 ± 0.10 ab |
| Line 1 | 0.102 ± 0.07 b | 0.31 ± 0.1 cd | 2.37 ± 0.2 bc | 16.3 ± 1.3 bc | 1.01 ± 0.08 ab |
| Line 2 | ND | 0.71 ± 0.04 b | 1.97 ± 0.1 cd | 13.5 ± 0.1 c | 0.91 ± 0.06 ab |
| Line 3 | ND | 0.23 ± 0.006 cd | 2.40 ± 0.1 ab | 12.3 ± 0.3 cd | 0.97 ± 0.02 ab |
| Line 4 | ND | 1.48 ± 0.1 a | 2.52 ± 0.1 ab | 13.2 ± 1.0 c | 0.94 ± 0.01 ab |
| Line 5 | ND | ND | 2.28 ± 0.1 b | ND | 0.87 ± 0.15 b |
| Genotypes | Phenolic Compound (μg/g dwt) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCA | CAF | SIN | FA | Iso FA | CAT | 4HBA | VAN A | VANILLIN | |
| AAC Synergy | 214 ± 22 ab | 12.8 ± 1.0 ab | 19.8 ± 0.9 a | 382 ± 14.3 a | 22.5 ± 1.0 ab | 20.3 ± 2.0 ab | 2.90 ± 0.32 a | 9.21 ± 1.21 a | 7.99 ± 1.13 ab |
| AAC Goldman | 245 ± 54 a | 14.5 ± 0.8 a | 20.0 ± 2.9 a | 377 ± 33.2 a | 21.8 ± 1.4 ab | 18.0 ± 2.9 ab | 3.18 ± 0.12 a | 9.33 ± 1.41 a | 7.39 ± 0.78 ab |
| AC Metcalfe | 202 ± 23 b | 11.1 ± 0.8 ab | 14.4 ± 0.1 b | 338 ± 15.4 a | 20.9 ± 1.3 ab | 19.2 ± 3.3 ab | 2.81 ± 0.09 a | 9.88 ± 1.71 a | 6.32 ± 1.02 ab |
| CDC Copeland | 236 ± 34 ab | 10.6 ± 2.1 ab | 15.2 ± 2.5 a | 342 ± 4.2 a | 16.9 ± 2.9 ab | 21.5 ± 7.1 a | 1.64 ± 0.24 ab | 8.19 ± 1.49 ab | 7.25 ± 0.76 ab |
| CDC Bold | 140 ± 17 b | 8.6 ± 2.6 b | 8.9 ± 1.9 b | 191 ± 46.5 b | 12.2 ± 4.1 b | 12.8 ± 0.8 b | 1.81 ± 0.27 b | 4.85 ± 0.25 b | 5.56 ± 0.71 b |
| CDC Bow | 228 ± 53 ab | 9.9 ± 0.7 b | 15.7 ± 1.7 a | 293 ± 41.5 b | 14.2 ± 1.8 ab | 15.9 ± 2.1 ab | 1.88 ± 0.07 b | 6.74 ± 1.23 b | 5.58 ± 0.74 b |
| CDC Mindon | 265 ± 35 a | 15.8 ± 3.3 a | 20.3 ± 3.7 a | 375 ± 51.5 a | 22.5 ± 5.5 ab | 17.5 ± 3.1 ab | 2.33 ± 0.11 ab | 9.37 ± 1.65 a | 8.80 ± 0.91 a |
| Harrington | 209 ± 27 ab | 13.5 ± 2.1 ab | 13.3 ± 2.9 b | 469 ± 101 a | 24.2 ± 7.0 a | 20.2 ± 1.8 ab | 1.88 ± 0.13 b | 8.41 ± 0.08 ab | 9.13 ± 1.48 a |
| Lowe | 331 ± 96 a | 10.4 ± 1.1 ab | 11.3 ± 0.8 b | 368 ± 25.5 a | 17.4 ± 1.5 ab | 24.6 ± 2.9 a | 2.21 ± 0.25 b | 9.41 ± 1.45 a | 8.33 ± 1.12 ab |
| Line 1 | 239 ± 30 a | 11.8 ± 0.4 ab | 21.0 ± 1.0 a | 370 ± 17.5 a | 21.7 ± 0.9 ab | 19.6 ± 2.8 ab | 2.52 ± 0.19 ab | 9.37 ± 0.99 a | 7.70 ± 0.70 ab |
| Line 2 | 116 ± 18 b | 10.1 ± 2.0 ab | 10.2 ± 2.1 b | 273 ± 64.0 b | 17.7 ± 6.1 ab | 15.2 ± 4.6 ab | 1.54 ± 0.19 b | 6.19 ± 1.07 b | 5.86 ± 1.36 b |
| Line 3 | 216 ± 23 ab | 9.7 ± 1.4 b | 15.6 ± 2.2 a | 297 ± 8.6 b | 13.7 ± 2.2 ab | 16.8 ± 4.2 ab | 2.21 ± 0.26 b | 6.45 ± 1.14 b | 6.41 ± 0.22 ab |
| Line 4 | 232 ± 31 ab | 10.0 ± 3.7 b | 11.2 ± 2.5 b | 310 ± 60.8 b | 14.6 ± 5.3 ab | 15.2 ± 2.1 ab | 1.83 ± 0.05 b | 6.76 ± 1.72 b | 7.14 ± 0.87 ab |
| Line 5 | 191 ± 16 b | 9.3 ± 1.7 b | 17.7 ± 1.2 a | 294 ± 53.2 b | 14.1 ± 1.7 ab | 10.5 ± 2.5 b | 2.39 ± 0.27 ab | 8.26 ± 0.28 ab | 6.69 ± 0.18 ab |
| Antioxidant | PCA | CAF | SIN A | FA | Iso FA | CAT | 4HBA | VAN A | VANILLIN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antioxidant | 0.44 | 0.22 | 0.095 | 0.04 | 0.209 | 0.034 | 0.204 | 0.166 | −0.23 | |
| PCA | 0.334 | 0.33 | 0.551 * | 0.244 | 0.691 ** | 0.078 | 0.607 * | 0.534 * | ||
| CAF | 0.587 * | 0.736 ** | 0.859 *** | 0.368 | 0.387 | 0.56 * | 0.691 ** | |||
| SIN A | 0.436 | 0.5 | 0.117 | 0.554 * | 0.572 * | 0.382 | ||||
| FA | 0.837 *** | 0.666 ** | 0.325 | 0.723 ** | 0.797 *** | |||||
| Iso FA | 0.519 | 0.591 * | 0.723 ** | 0.686 ** | ||||||
| CAT | 0.262 | 0.584 * | 0.486 | |||||||
| 4HBA | 0.626 * | 0.064 | ||||||||
| VAN | 0.541 * | |||||||||
| VANILLIN |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wijekoon, C.; Netticadan, T.; Sabra, A.; Yu, L.; Kodikara, C.; Badea, A. Analyses of Fatty Acids, Proteins, Ascorbic Acid, Bioactive Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Canadian Barley Cultivars and Elite Germplasm. Molecules 2022, 27, 7852. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227852
Wijekoon C, Netticadan T, Sabra A, Yu L, Kodikara C, Badea A. Analyses of Fatty Acids, Proteins, Ascorbic Acid, Bioactive Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Canadian Barley Cultivars and Elite Germplasm. Molecules. 2022; 27(22):7852. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227852
Chicago/Turabian StyleWijekoon, Champa, Thomas Netticadan, Ali Sabra, Liping Yu, Chamali Kodikara, and Ana Badea. 2022. "Analyses of Fatty Acids, Proteins, Ascorbic Acid, Bioactive Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Canadian Barley Cultivars and Elite Germplasm" Molecules 27, no. 22: 7852. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227852
APA StyleWijekoon, C., Netticadan, T., Sabra, A., Yu, L., Kodikara, C., & Badea, A. (2022). Analyses of Fatty Acids, Proteins, Ascorbic Acid, Bioactive Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Canadian Barley Cultivars and Elite Germplasm. Molecules, 27(22), 7852. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227852








