Synthesis of Nanosilica for the Removal of Multicomponent Cd2+ and Cu2+ from Synthetic Water: An Experimental and Theoretical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
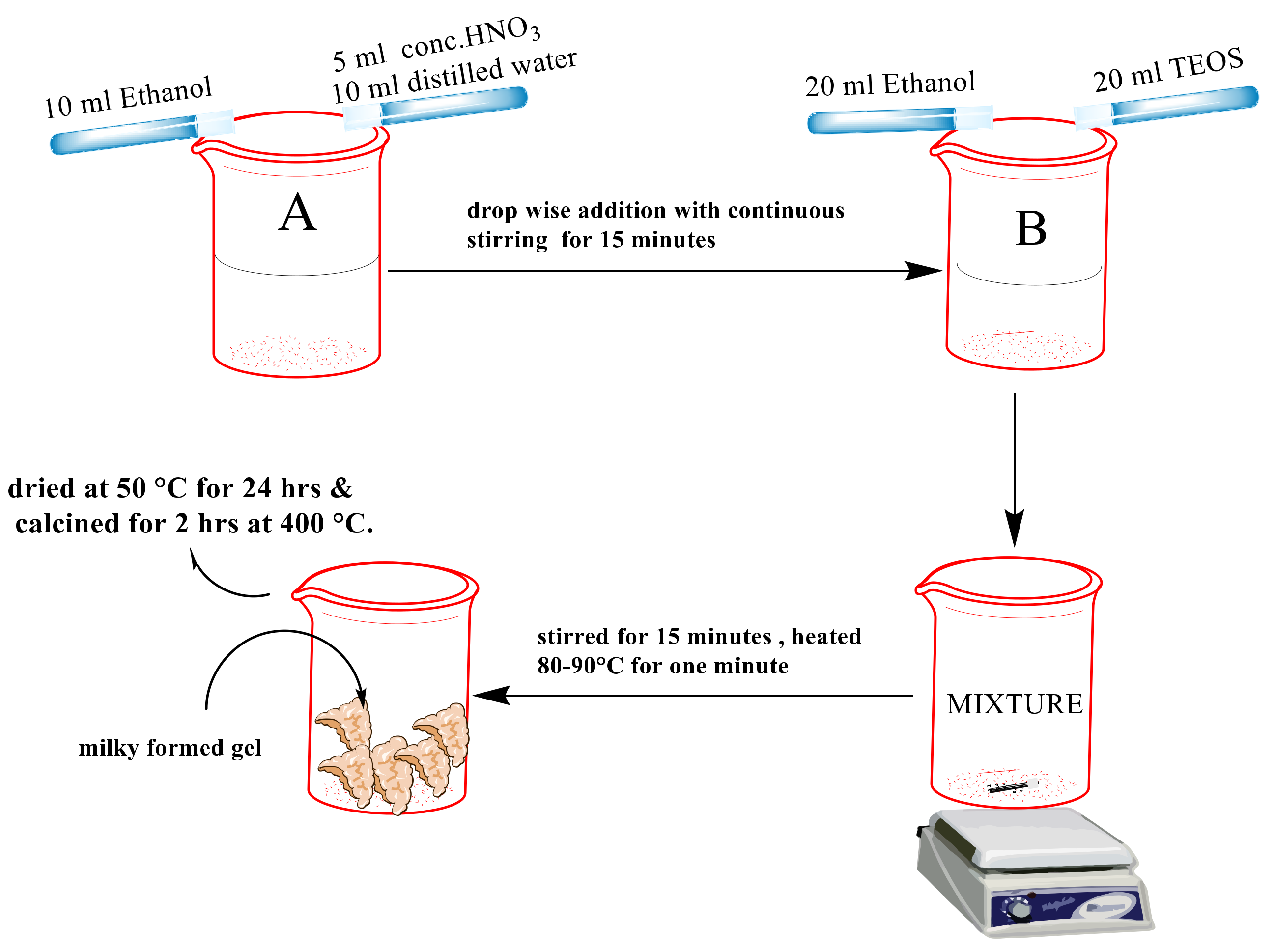
3.2. Synthesis of the Nanosilica Material
3.3. Characterization of Nanosilica Materials
3.4. Adsorption Isotherms
4. Results and Discussion
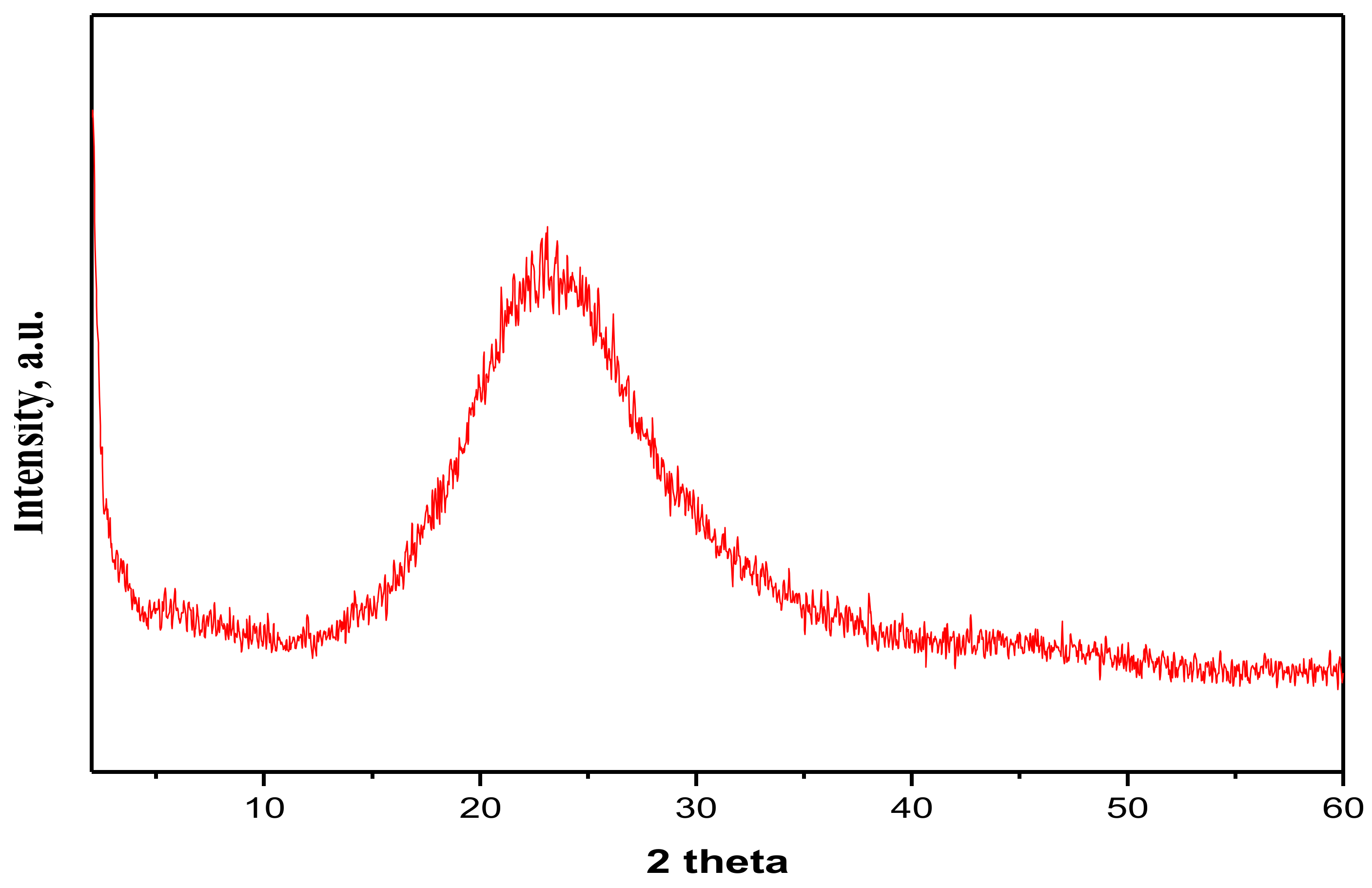
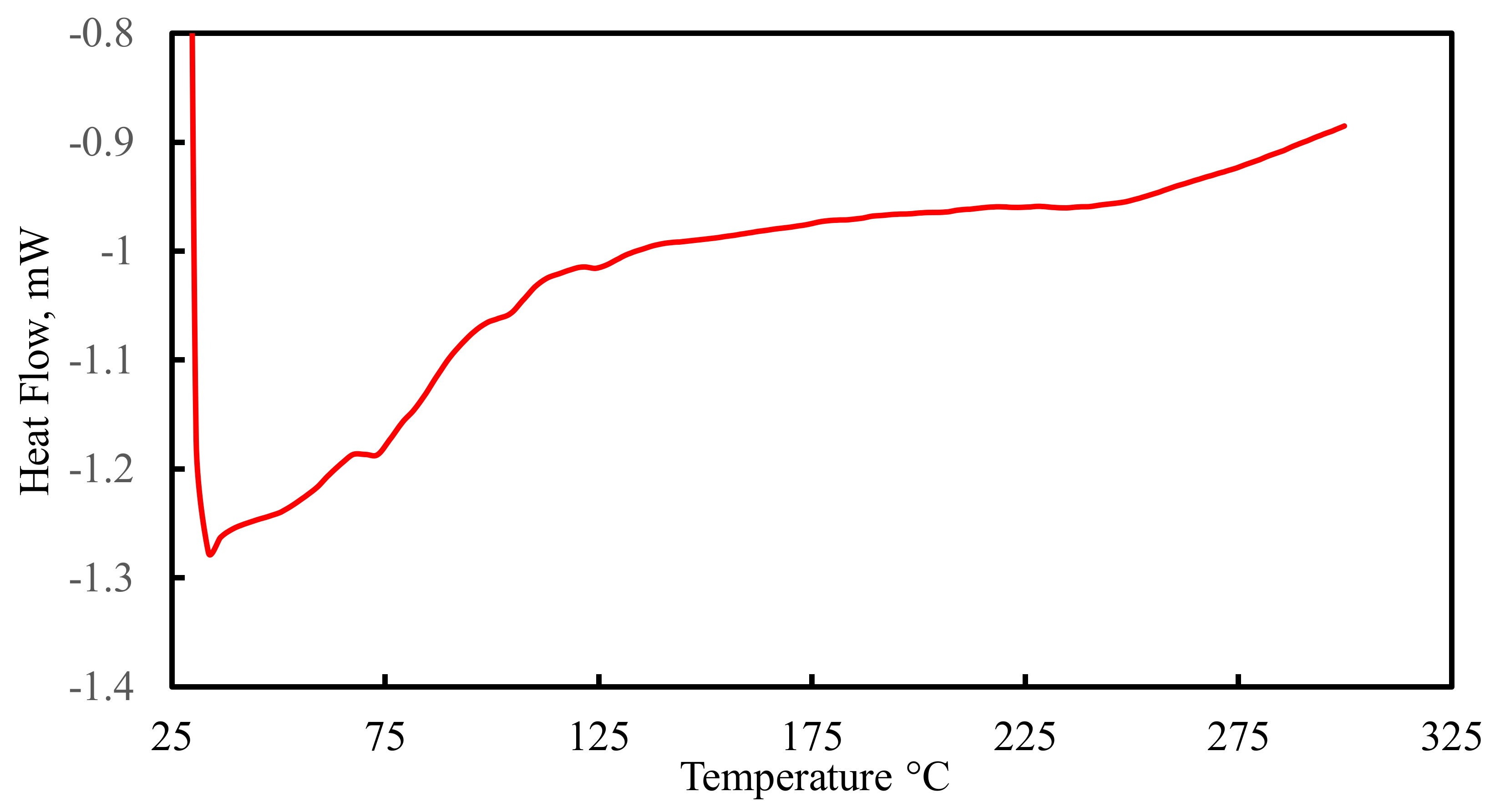
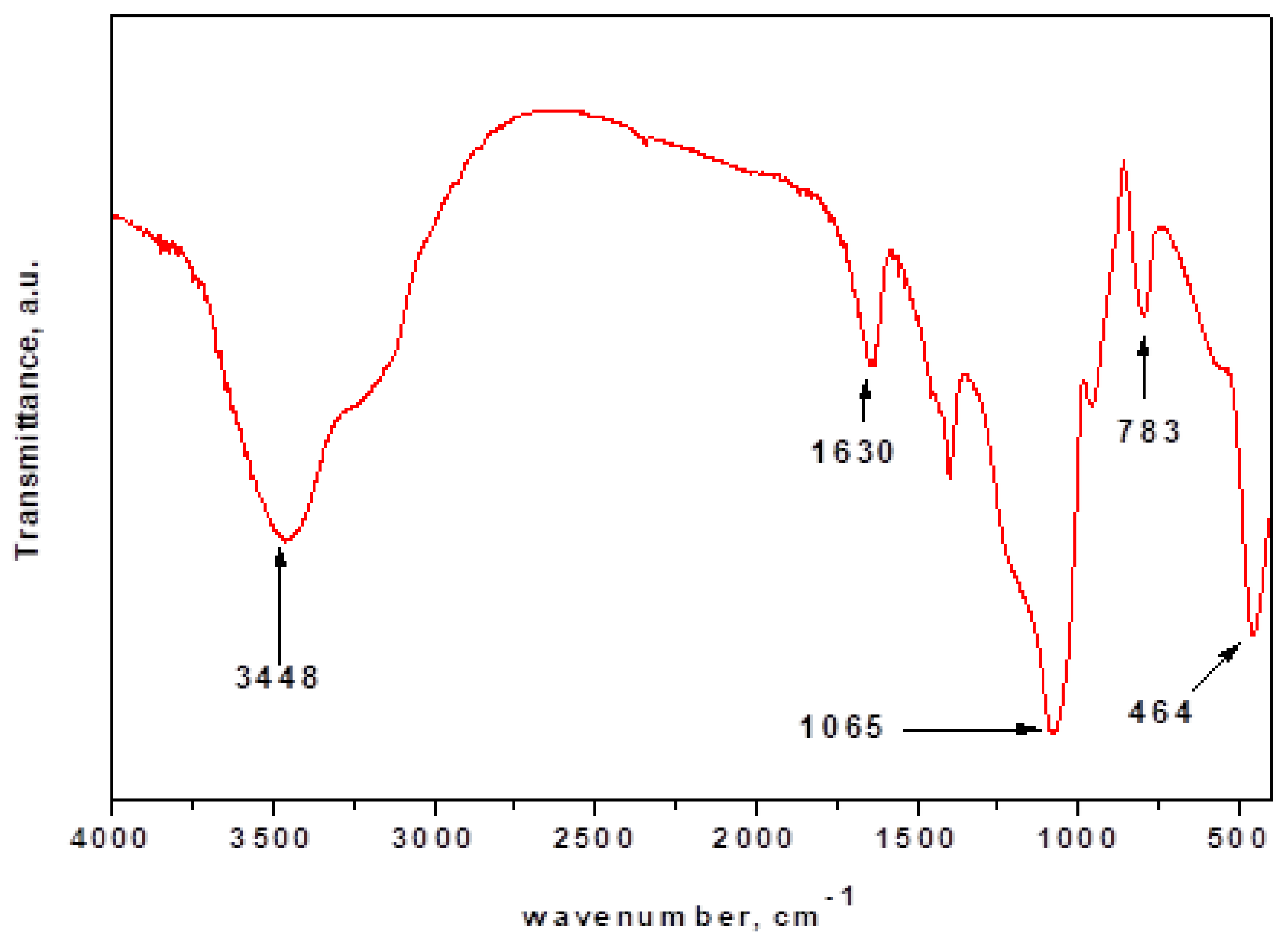
4.1. Structure Characterization of the Nanosilica
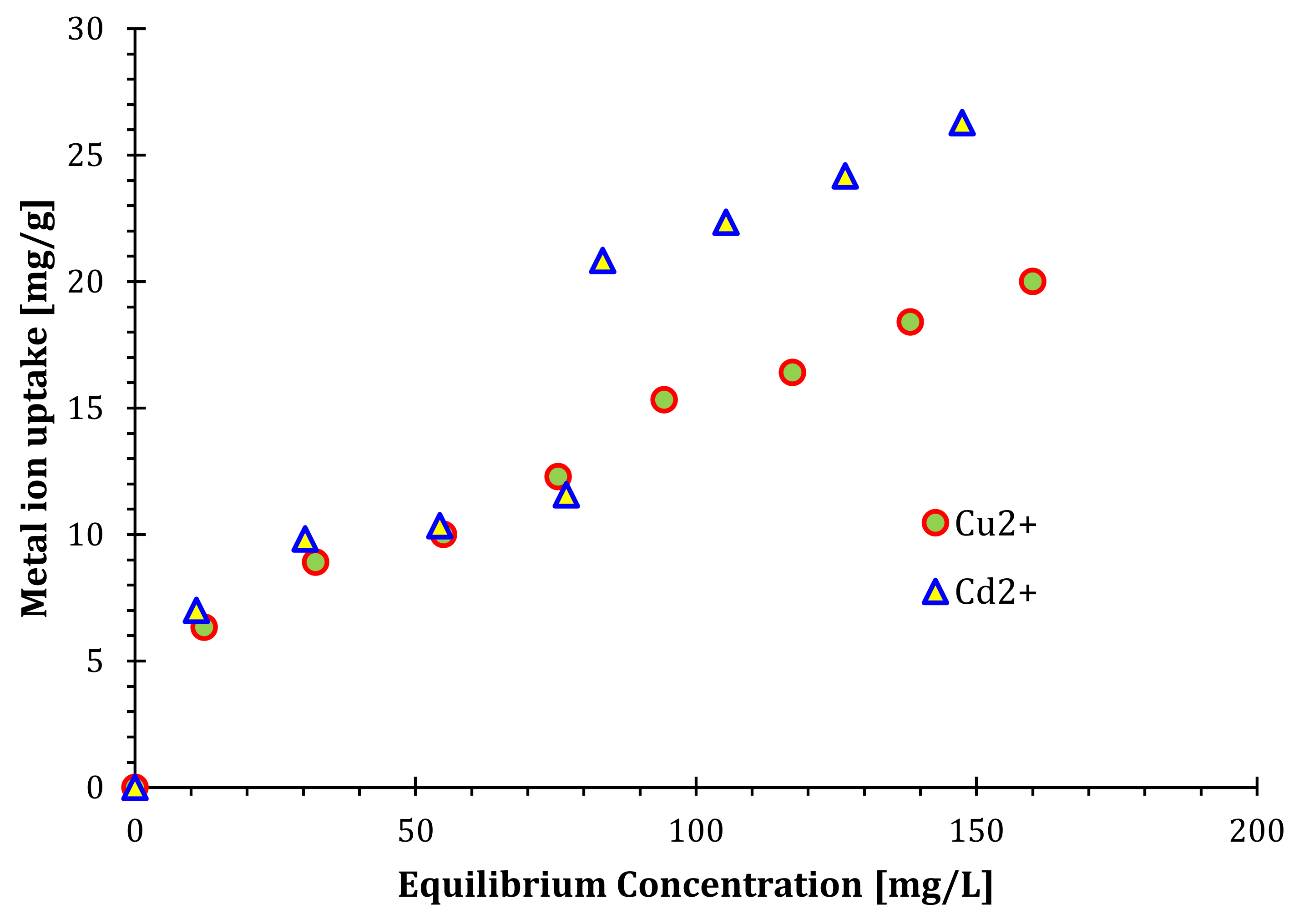
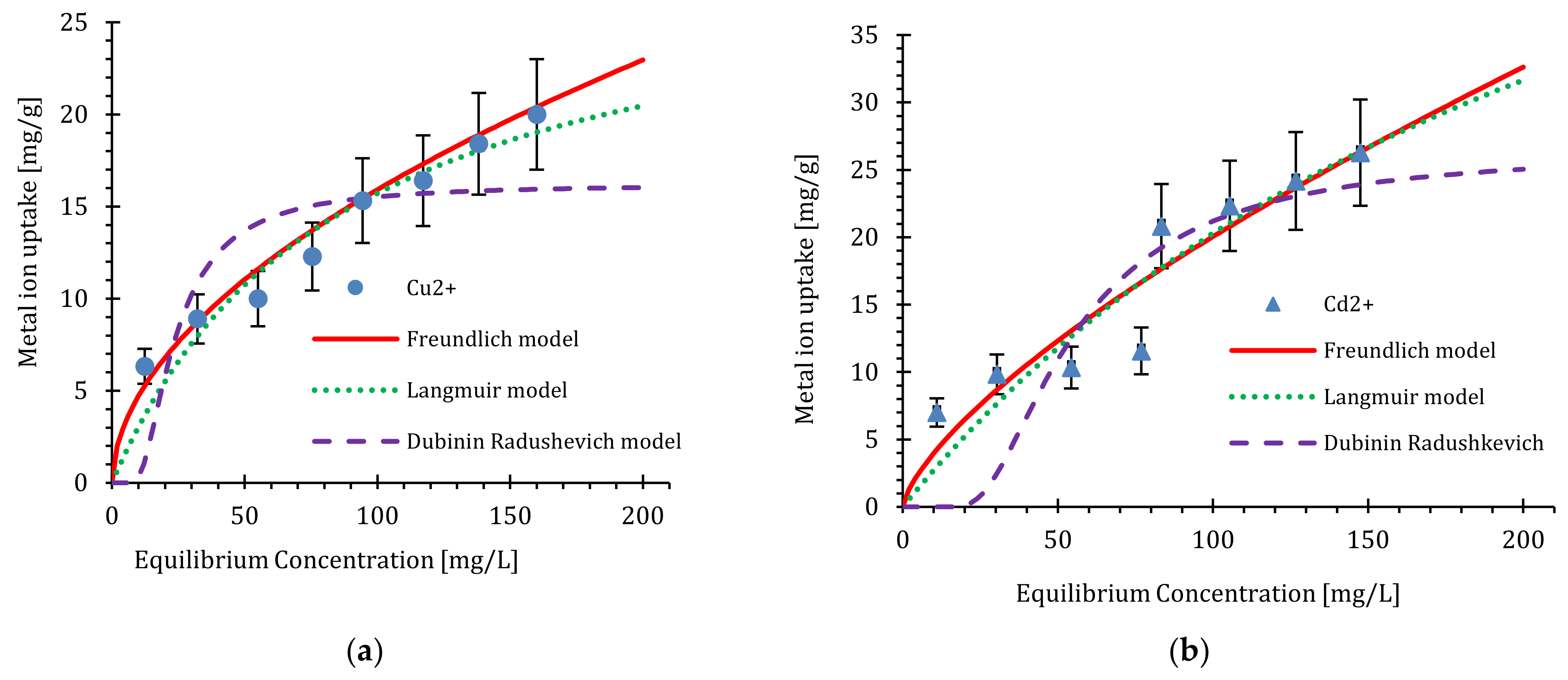
4.2. Adsorption Isotherms of Cu2+ and Cd2+ by the Nanosilica
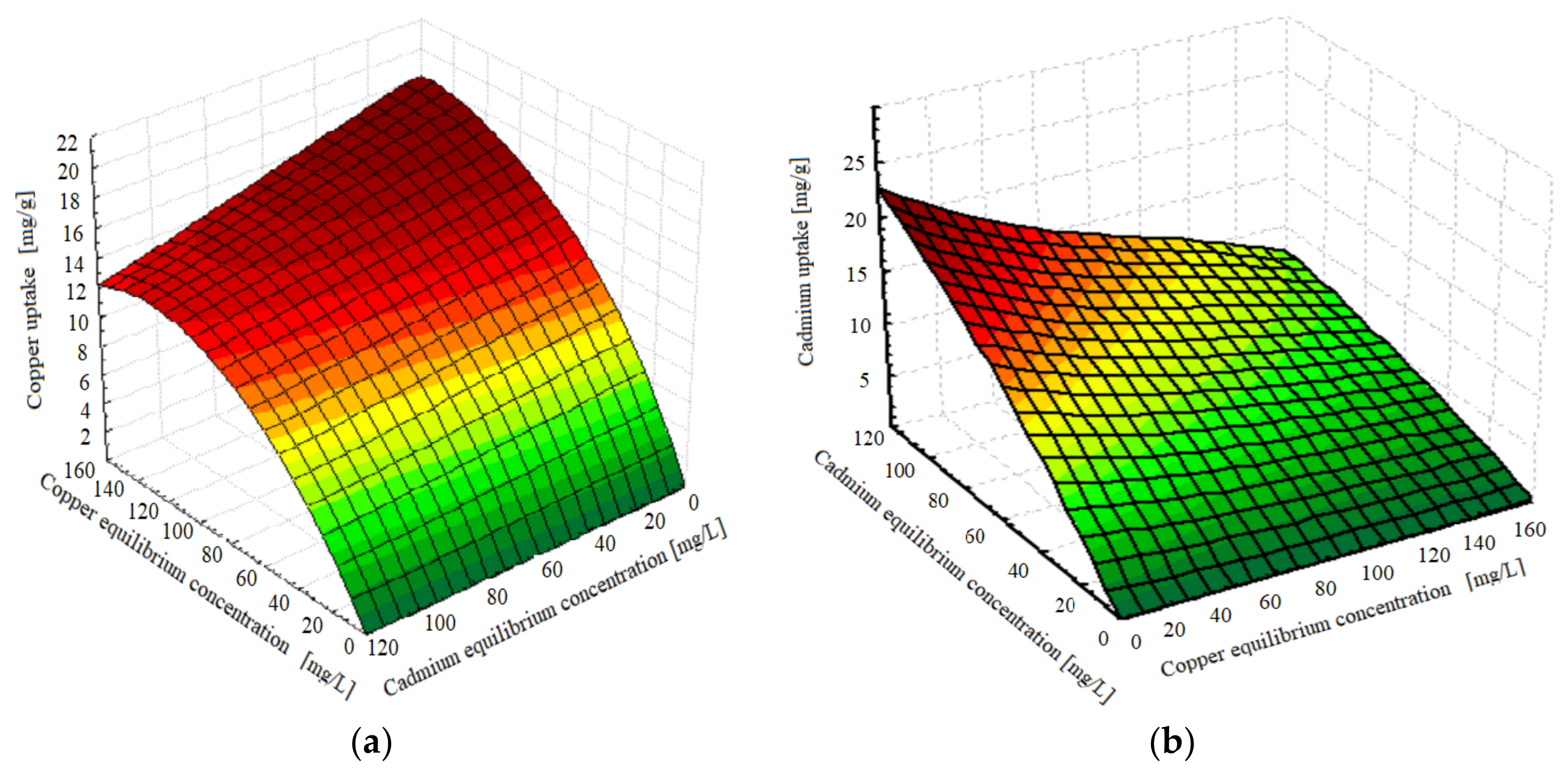
4.3. Binary Component Isotherm
4.4. Regeneration of the Adsorbent
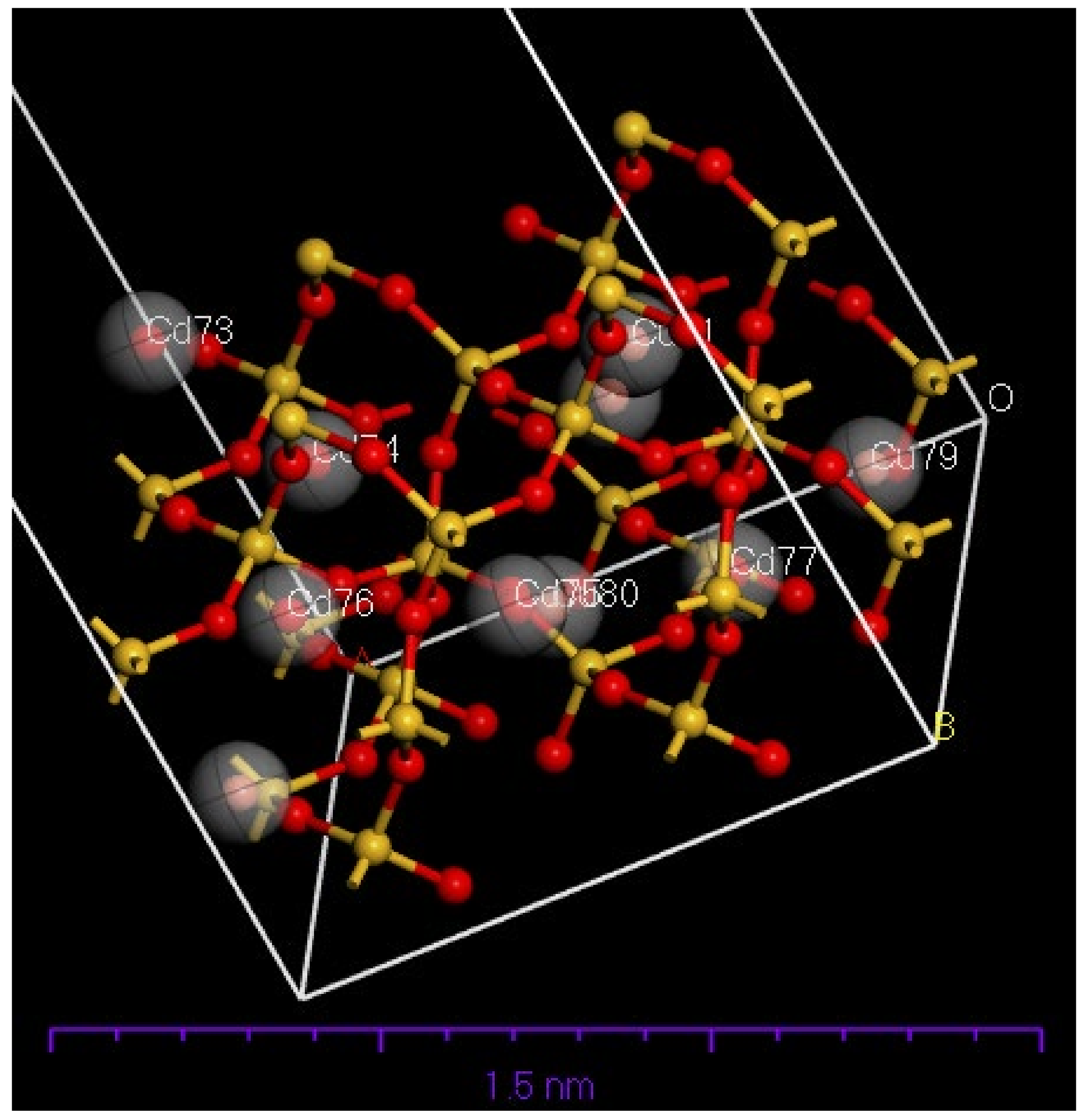
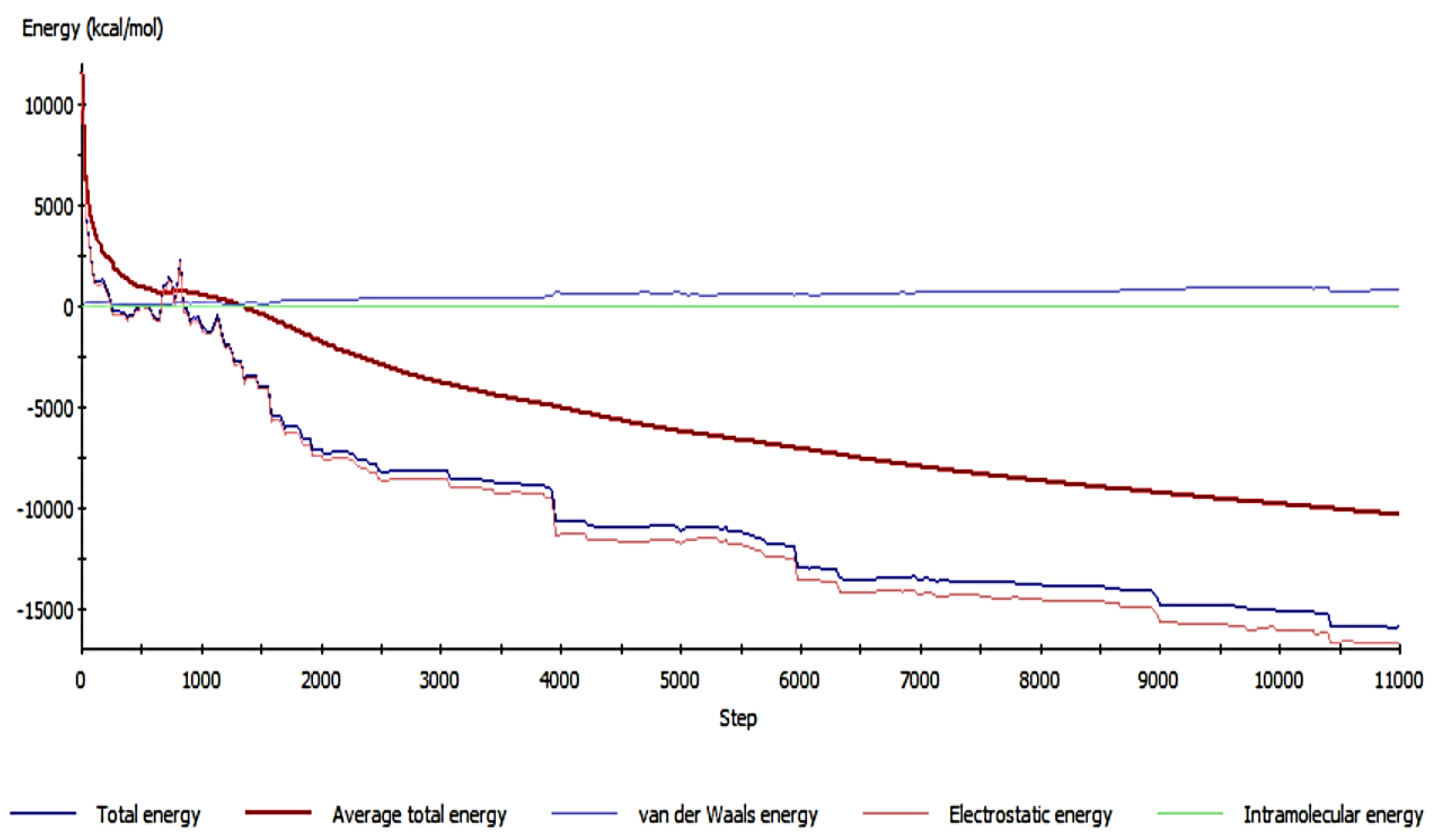
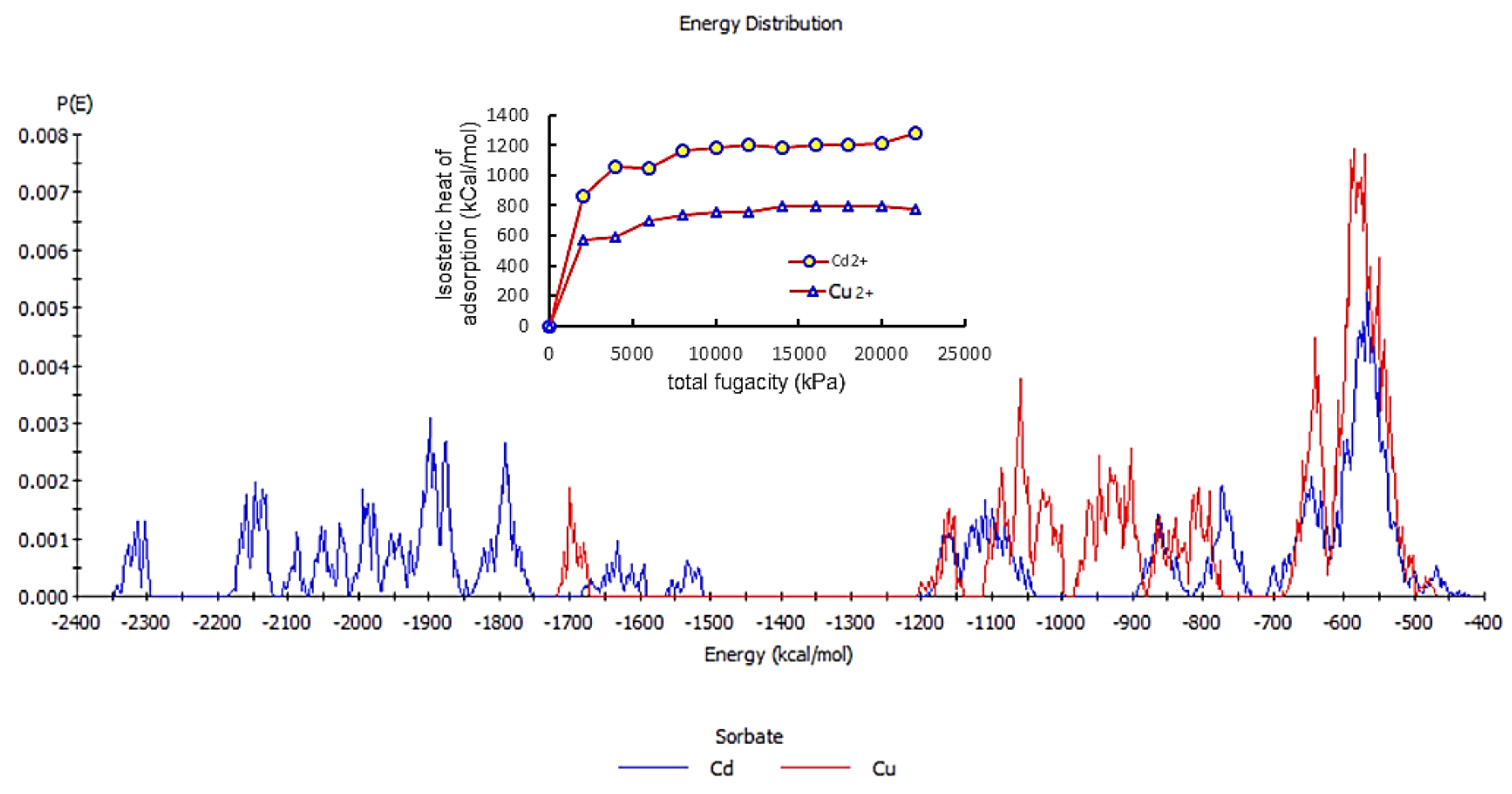
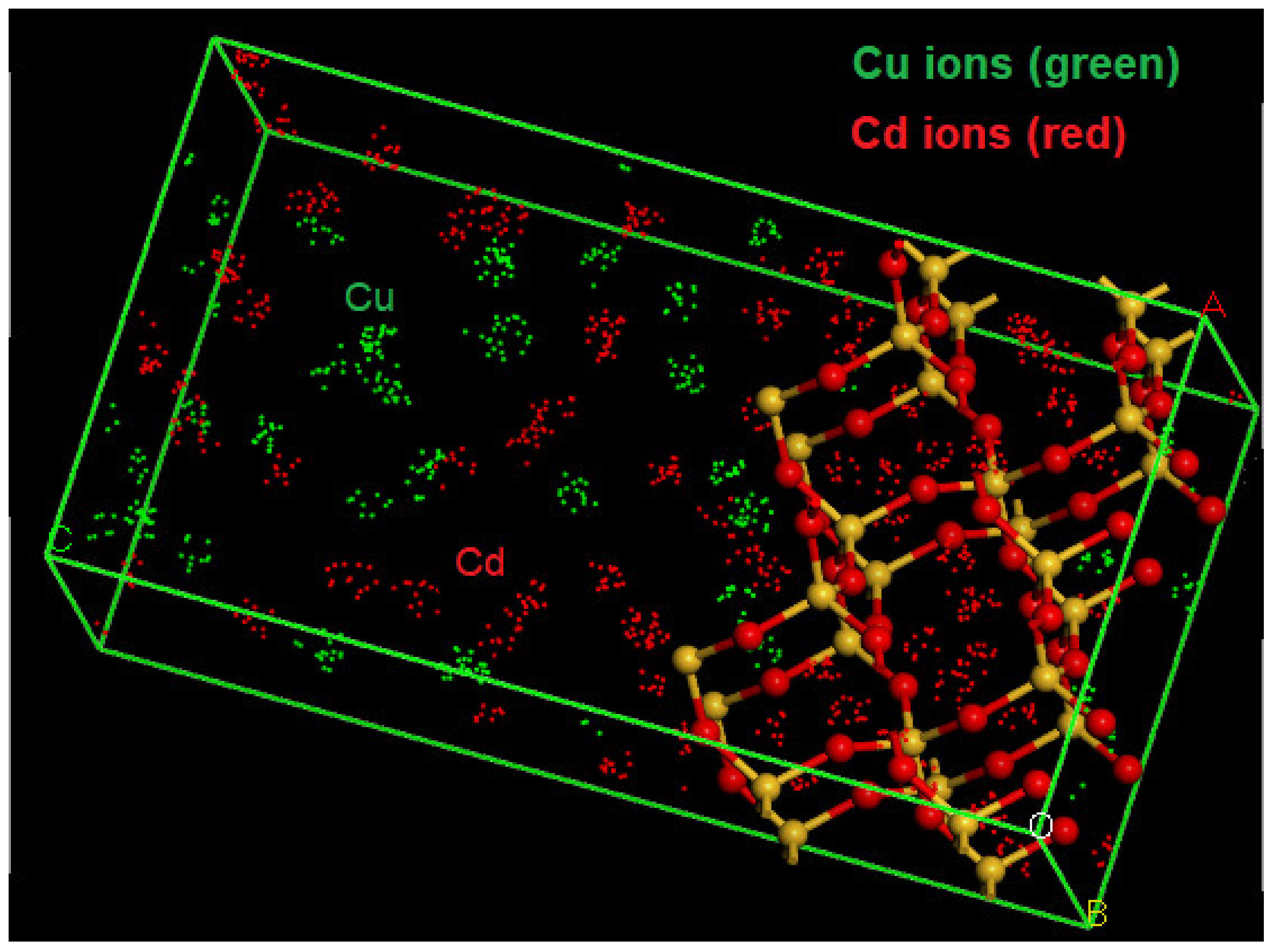
4.5. The Molecular Dynamics of Cu and Cd on SiO2 Crystalline Structure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Al-Saida, B.; Amer, W.; Kandyel, E.E.; Ayad, M.M. Enhanced dual catalytic activities of silver-polyaniline/titanium dioxide magnetic nanocomposite. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2020, 392, 112423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, W.A.; Al-Saida, B.; Ayad, M.M. Rational design of a polypyrrole-based competent bifunctional magnetic nanocatalyst. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 18245–18255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawabkeh, R.; Rockstraw, D.A.; Bhada, R.K. Copper and strontium adsorption by a novel carbon material manufactured from pecan shells. Carbon 2002, 40, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, A.; Aslam, Z.; Kamal, M.S.; Ahmad, W.; Abbas, A.; Shawabkeh, R.A. Development of novel cross-linked chitosan for the removal of anionic Congo red dye. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 244, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawabkeh, R.; Al-Harahsheh, A.; Al-Otoom, A. Copper and zinc sorption by treated oil shale ash. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 40, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Degs, Y.S.; Tutunju, M.F.; Shawabkeh, R.A. The feasibility of using diatomite and Mn–diatomite for remediation of Pb2+, Cu2+, and Cd2+ from water. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2000, 35, 2299–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiyu, Q.; Hongen, L.; Zhaojun, N.; Rengel, Z.; Wei, G.; Chang, L.; Peng, Z. Toxicity of cadmium and its competition with mineral nutrients for uptake by plants: A review. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 168–180. [Google Scholar]
- Kiran, M.G.; Pakshirajan, K.; Das, G. Heavy metal removal from multicomponent system by sulfate reducing bacteria: Mechanism and cell surface characterization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ding, P.; Zhou, L.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Jiao, F. Preparation of diamine modified mesoporous silica on multi-walled carbon nanotubes for the adsorption of heavy metals in aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 282, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATSDR. Substances Priority List; Division of Toxicology and Human Health Sciences: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2021; p. 30329. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, Y.; Gu, J.; Han, J.; Wu, Q.; Jiang, J. Effects of cellulose/salicylaldehyde thiosemicarbazone complexes on PVA based hydrogels: Portable, reusable, and high-precision luminescence sensing of Cu2+. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Khan, Z.U.H.; Iqbal, J.; Shah, N.S.; Muzammil, S.; Ali, S.; Muhammad, N.; Aziz, A.; Murtaza, B.; Naeem, M.A. Potential of siltstone and its composites with biochar and magnetite nanoparticles for the removal of cadmium from contaminated aqueous solutions: Batch and column scale studies. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saydeh, S.A.; El-Naas, M.H.; Zaidi, S.J. Copper removal from industrial wastewater: A comprehensive review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 56, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charerntanyarak, L. Heavy metals removal by chemical coagulation and precipitation. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.-B.; Song, Y.-L.; Huang, C.-P.; Li, Y.-X.; Chen, B.-H. Synthesis of novel lignin-based ion-exchange resin and its utilization in heavy metals removal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkwa, J.-B.; Oturan, N.; Acayanka, E.; Laminsi, S.; Oturan, M.A. Photo-Fenton oxidation of Orange G azo dye: Process optimization and mineralization mechanism. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Shao, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, L.; Luo, L. Optimization of flocculation conditions for soluble cadmium removal using the composite flocculant of green anion polyacrylamide and PAC by response surface methodology. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Tan, W.; Liu, C.; Dang, Z.; Qiu, G. Electrochemical adsorption of cadmium and arsenic by natural Fe-Mn nodules. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devatha, C.; Shivani, S. Novel application of maghemite nanoparticles coated bacteria for the removal of cadmium from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 258, 110038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawabkeh, R.A. Adsorption of chromium ions from aqueous solution by using activated carbo-aluminosilicate material from oil shale. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 299, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.C.; Rodrigues, D.F. Carbon-based nanomaterials for removal of chemical and biological contaminants from water: A review of mechanisms and applications. Carbon 2015, 91, 122–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Chan, G.Y.; Lo, W.-H.; Babel, S. Physico–chemical treatment techniques for wastewater laden with heavy metals. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 118, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, R.; Mohammadi, R.; Adeleye, A.S.; Farjadfard, S.; Esvandi, Z.; Arfaeinia, H.; Sorial, G.A.; Ramavandi, B.; Sahebi, S. Efficient arsenic (V) removal from contaminated water using natural clay and clay composite adsorbents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 29748–29762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Bhatti, H.N.; MacKinnon, G. Re-use of agricultural wastes for the removal and recovery of Zr (IV) from aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 59, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Hasan, I.; Mittal, A. Adsorption of Cr (VI) and Cd (II) on chitosan grafted polyaniline-OMMT nanocomposite: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics studies. Desalin Water Treat 2017, 58, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, D.S.; Krivoshein, P.K.; Mikheev, I.V.; Proskurnin, M.A. Pristine detonation nanodiamonds as regenerable adsorbents for metal cations. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020, 110, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, H.N.M.E.; Huq, A.O.; Yahya, R.B. The removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater/aqueous solution using polypyrrole-based adsorbents: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 14778–14791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, N.; Li, S.; Yan, F.; Su, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z. An all-in-one strategy for the adsorption of heavy metal ions and photodegradation of organic pollutants using steel slag-derived calcium silicate hydrate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 121120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourshadlou, S.; Mobasherpour, I.; Majidian, H.; Salahi, E.; Bidabadi, F.S.; Mei, C.-T.; Ebrahimi, M. Adsorption system for Mg2+ removal from aqueous solutions using bentonite/γ-alumina nanocomposite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 568, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, R.; Mohammadi, R.; Peighambardoust, S.J.; Jalali, S.; Ramavandi, B. Application of nano-silica particles generated from offshore white sandstone for cadmium ions elimination from aqueous media. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 101031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, S.; Wen, N.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Y. Highly effective removal of lead and cadmium ions from wastewater by bifunctional magnetic mesoporous silica. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 265, 118341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, H. Nano-Silica effect on the physicomechanical properties of geopolymer composites. Adv. Nano Res. 2016, 4, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milonjic, S.; Cerović, L.; Cokesa, D.; Zec, S. The influence of cationic impurities in silica on its crystallization and point of zero charge. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 309, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, A.; Polshettiwar, V. Dendritic fibrous nanosilica for catalysis, energy harvesting, carbon dioxide mitigation, drug delivery, and sensing. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Pan, B.; Wang, Q.; Niu, Y.; Tai, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, K. Crucial roles of graphene oxide in preparing alginate/nanofibrillated cellulose double network composites hydrogels. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, H.; Xiong, T.; Xu, A.; Pan, B.; Tang, K. Graphene Oxide Reinforced Alginate/PVA Double Network Hydrogels for Efficient Dye Removal. Polymers 2018, 10, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štefanko, A.U.; Leszczynska, D. Evaluation of Cd2+, Cu2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+ Removal by Cow Manure and Corn Stover Biochar with the Emphasis on the Solubility-Normalized Dubinin-Radushkevich Approach for the Computation of the Adsorption Potential (ϵ). J. Environ. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Tang, X.; Tang, L.; Zhang, B.; Mao, H. Synthesis and formation mechanism of amorphous silica particles via sol–gel process with tetraethylorthosilicate. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 7673–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozainee, M.; Ngo, S.P.; Salema, A.; Tan, K.G.; Ariffin, M.; Zainura, Z. Effect of fluidising velocity on the combustion of rice husk in a bench-scale fluidised bed combustor for the production of amorphous rice husk ash. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, A.; Elabasy, A.; Waqas, M.; Lin, L.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, Z.-H. Entomotoxic effect of silicon dioxide nanoparticles on Plutella xylostella (L.)(Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) under laboratory conditions. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2018, 100, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosa, A.; Saddam, B. Synthesis and characterization of nanosilica from rice husk with applications to polymer composites. Am. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 7, 223–231. [Google Scholar]
- Golbamaki, N.; Rasulev, B.; Cassano, A.; Robinson, R.L.M.; Benfenati, E.; Leszczynski, J.; Cronin, M.T. Genotoxicity of metal oxide nanomaterials: Review of recent data and discussion of possible mechanisms. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2154–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrisor, G.; Ficai, D.; Motelica, L.; Trusca, R.D.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Vasile, B.S.; Voicu, G.; Oprea, O.C.; Semenescu, A.; Ficai, A.; et al. Mesoporous Silica Materials Loaded with Gallic Acid with Antimicrobial Potential. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Gao, B.; Li, A.; Yang, H. Evaluation of the selective adsorption of silica-sand/anionized-starch composite for removal of dyes and Cupper (II) from their aqueous mixtures. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Yin, P.; Qu, R.; Wang, C.; Zheng, H.; Yu, Z. Removal of transition metal ions from aqueous solutions by adsorption using a novel hybrid material silica gel chemically modified by triethylenetetraminomethylenephosphonic acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhon, R. Adsorption of Cu(II) and Ni(II) Ions on Functionalized Colloidal Silica Particles Model Studies for Wastewater Treatment. Doctoral Dissertation, Université de Franche-Comté, Besançon, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Alan, B.O.; Barisik, M.; Ozcelik, H.G. Roughness Effects on the Surface Charge Properties of Silica Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 7274–7286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, H.; Müller, E.A. How does the shape and surface energy of pores affect the adsorption of nanoconfined fluids? AIChE J. 2021, 67, e17011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alosaimi, E.H.; Alsohaimi, I.H.; Dahan, T.E.; Chen, Q.; Melhi, S. Adsorptive performance of tetracarboxylic acid-modified magnetic silica nanocomposite for recoverable efficient removal of toxic Cd(II) from aqueous environment: Equilibrium, isotherm, and reusability studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachan, D.; Ramesh, A.; Das, G. Green synthesis of silica nanoparticles from leaf biomass and its application to remove heavy metals from synthetic wastewater: A comparative analysis. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Yakout, A.A.; Abdel-Aal, H.; Osman, M.M. Enhanced biosorptive removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions by silicon dioxide nano-powder, heat inactivated and immobilized Aspergillus ustus. Desalination 2011, 279, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinraide, T.B.; Yermiyahu, U. A scale of metal ion binding strengths correlating with ionic charge, Pauling electronegativity, toxicity, and other physiological effects. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2007, 101, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Park, B.C.; Ham, W.S.; Pan, L.; Kim, Y.K. Effect of the magnetic core size of amino-functionalized Fe3O4-mesoporous SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles on the removal of heavy metal ions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 531, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, S.; Shao, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, D. Amino-functionalized Fe3O4@ SiO2 core–shell magnetic nanomaterial as a novel adsorbent for aqueous heavy metals removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 349, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, R.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, X.; Baig, S.A.; Xu, X. Multifunctional nanocomposites Fe3O4@ SiO2-EDTA for Pb (II) and Cu (II) removal from aqueous solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 369, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, S.H.; Grier, D.G. The charge of glass and silica surfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 6716–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

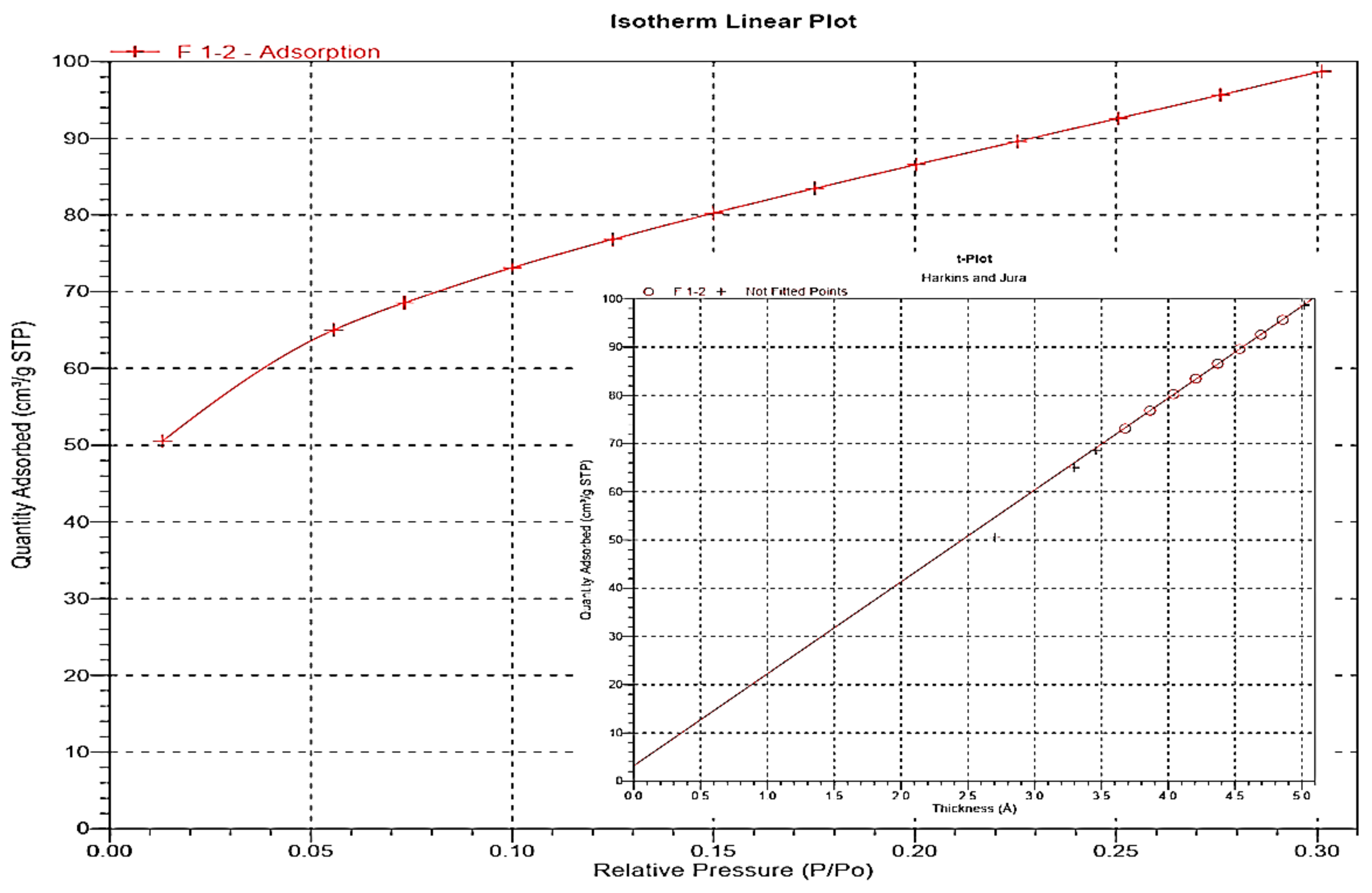



| Langmuir Equation | BET Method | t-Plot with H–J Thickness Equation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m2/g) | (m2/g) | (m2/g) | (m2/g) | (m2/g) | () |
| 461.06 | 307.64 | - | 294.75 | 12.89 | 4.95 |
| Model | Parameters and Values | |
|---|---|---|
| Cu2+ | Cd2+ | |
| Freundlich | ||
| Langmuir | ||
| Dubinin–Radushkevich | ||
| Catalyst | Initial Conc. (ppm) | Total Surface Area m2/g | Cu2+ Uptake (mg/g) | Cd2+ Uptake (mg/g) | Competitive Total Uptake (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4-mesoporousSiO2 core-shell | 5 | 483.78 | 84.4 | 80.5 | - | [53] |
| Amino-functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2 | 50 | 216.2 | 29.9 | 22.5 | - | [54] |
| Nanosilica from offshore white sandstone | 25 | 298.71 | - | 55.18 | - | [30] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2-EDTA | 25 | 70.99 | - | - | 34.65 | [55] |
| Silicon dioxide-nano-powder (N-Si) | 56 | - | - | 67.45 | 48 | [51] |
| This work | 200 | 307.64 | 29.28 | 72.13 | 18 for Cu2+ 23 for Cd2+ |
| Element | First Cycle Uptake (%) | Second Cycle Uptake (%) | Third Cycle Uptake (%) | Fourth Cycle Uptake (%) | Fifth Cycle Uptake (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd+2 | Cu+2 | Cd+2 | Cu+2 | Cd+2 | Cu+2 | Cd+2 | Cu+2 | Cd+2 | Cu+2 | |
| Single component Cd+2 | 100 | - | 96 | - | 94 | - | 94 | - | 92 | - |
| Single component Cu+2 | - | 56 | - | 50 | - | 48 | - | 47 | - | 44 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Saida, B.; Sandouqa, A.; Shawabkeh, R.A.; Hussein, I. Synthesis of Nanosilica for the Removal of Multicomponent Cd2+ and Cu2+ from Synthetic Water: An Experimental and Theoretical Study. Molecules 2022, 27, 7536. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217536
Al-Saida B, Sandouqa A, Shawabkeh RA, Hussein I. Synthesis of Nanosilica for the Removal of Multicomponent Cd2+ and Cu2+ from Synthetic Water: An Experimental and Theoretical Study. Molecules. 2022; 27(21):7536. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217536
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Saida, Basel, Arwa Sandouqa, Reyad A. Shawabkeh, and Ibnelwaleed Hussein. 2022. "Synthesis of Nanosilica for the Removal of Multicomponent Cd2+ and Cu2+ from Synthetic Water: An Experimental and Theoretical Study" Molecules 27, no. 21: 7536. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217536
APA StyleAl-Saida, B., Sandouqa, A., Shawabkeh, R. A., & Hussein, I. (2022). Synthesis of Nanosilica for the Removal of Multicomponent Cd2+ and Cu2+ from Synthetic Water: An Experimental and Theoretical Study. Molecules, 27(21), 7536. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217536







