Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green Effective Medium for Quaternization Reactions
Abstract
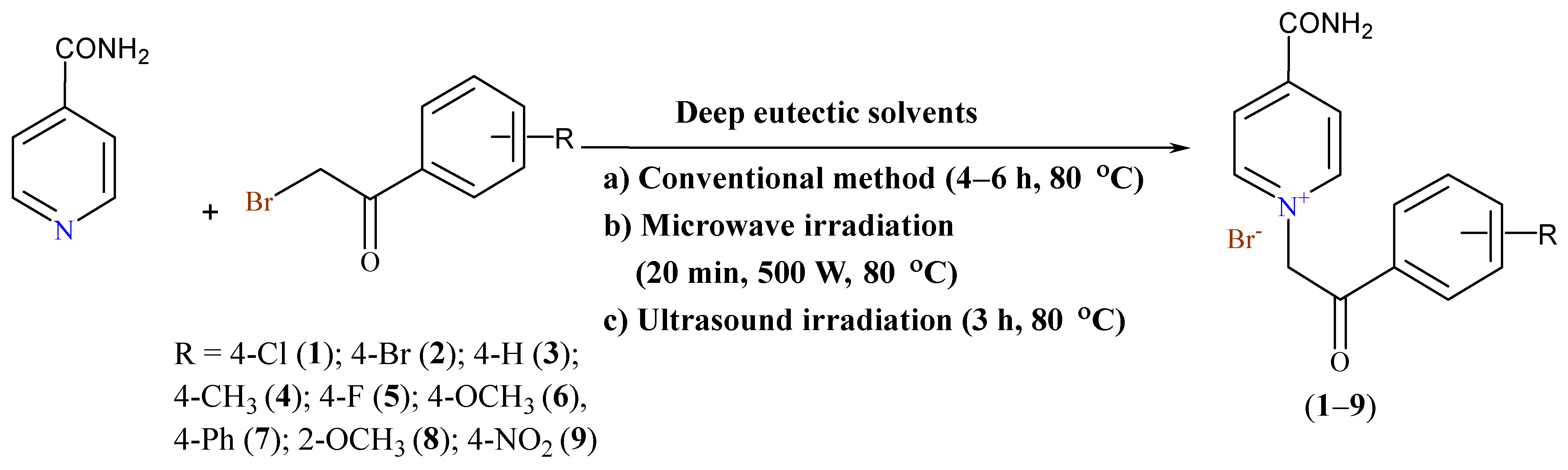
1. Introduction
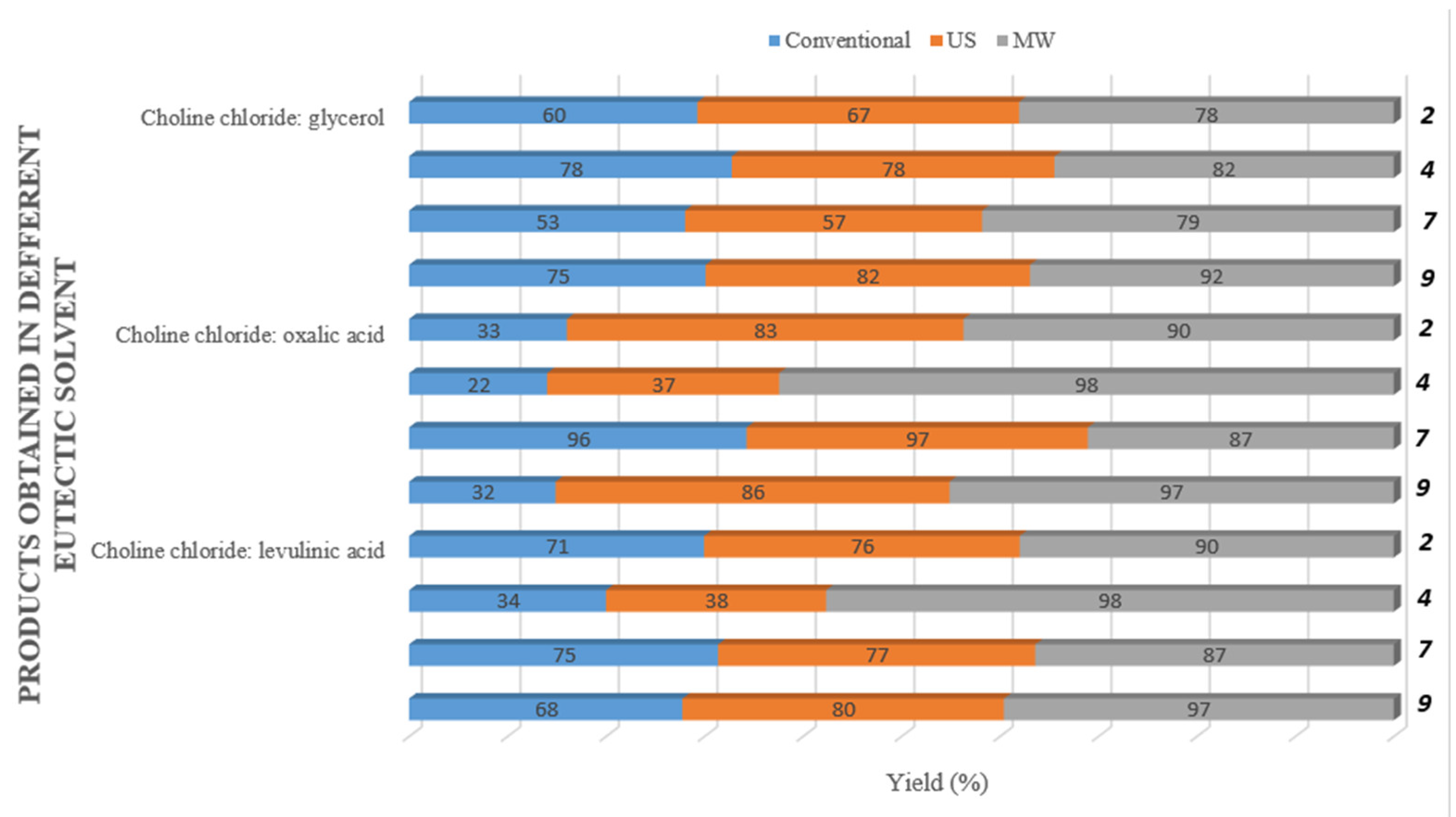
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials and Methods
3.2. Preparation of Deep Eutectic Solvents
3.3. Quaternization Reaction
3.3.1. Conventional Method
3.3.2. Microwave Method
3.3.3. Ultrasonic Method
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VOS | volatile organic species |
| DCM | dichloromethane |
| DMF | dimethylformamide |
| ACN | acetonitrile |
| DES | deep eutectic solvents |
| INA | isonicotinamide |
| ChCl | choline chloride |
| HBA | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| HBD | hydrogen bond donor |
| MW | microwave |
| US | ultrasound |
| EtOH | ethanol |
References
- Gašo-Sokač, D.; Katalinić, M.; Kovarik, Z.; Bušić, V.; Kovač, S. Synthesis and evaluation of novel analogues of vitamin B6 as reactivators of tabun and paraoxon inhibited acetylcholinesterase. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 187, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pidlypnyi, N.; Kaul, S.; Wolf, S.; Drafz, M.H.H.; Schmidt, A. Syntheses and Characterization of N-(Indolyl)pyridinium Salts and of Their Ylides. Z. Naturforsch. 2014, 69, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobraz, T.; Braiki, A.; Maraković, N.; Renou, J.; de la Mora, E.; Maček Hrvat, N.; Katalinić, M.; Silman, I.; Sussman, L.J.; Mercey, G.; et al. Potent 3-Hydroxy-2-Pyridine Aldoxime Reactivators of Organophosphate-Inhibited Cholinesterases with Predicted Blood-Brain Barrier Penetration. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 9675–9969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung Lee, H.; Andrys, R.; Jonczyk, J.; Kim, K.; Vishakantegowda, A.; Malinak, D.; Skarka, A.; Schmidt, M.; Vaskova, M.; Latka, K.; et al. Pyridinium-2-carbaldoximes with quinolinium carboxamide moiety are simultaneous reactivators of actylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibited by nerve agent surrogates. J. Enzyme Inhib Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, P.T.; Warner, J.C. Green Chem. Theory and Practice, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press Inc.: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, D.A.; Baeza, A.; Chinchilla, R.; Guillena, G.; Pastor, I.M.; Ramớn, D.J. Deep Eutectic Solvents: The Organic Reaction Medium of the Century. EurJOC 2016, 4, 612–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, N.; Dezfooli, S.; Khajeh, M.; Hashemi, M.M. Efficient deep eutectic solvents catalyzed synthesis of pyran and benzopyran derivatives. J. Mol. Liq. 2013, 186, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, H.R.; Singh, B.S.; Shankarling, G.S. Bio-compatible eutectic mixture for multi-component synthesis: A valuable acidic catalyst for synthesis of novel 2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one derivatives. Catal. Commun. 2012, 27, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, S.; Tailor, Y.K.; Kumar, M. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) as eco-friendly and sustainable solvent/catalyst systems in organic transformations. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 345–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaabani, A.; Hooshmand, S.E. Choline chloride/urea as a deep eutectic solvent/organocatalyst promoted three-component synthesis of 3-aminoimidazo-fused heterocycles via Groebke–Blackburn–Bienayme process. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, B.S.; Lobo, H.R.; Pinjari, D.V.; Jarag, K.J.; Pandit, A.B.; Shankarling, G.S. Ultrasound and deep eutectic solvent (DES): A novel blend of techniques for rapid and energy efficient synthesis of oxazoles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hao, J.; Mo, L.; Zhang, Z. Recent advances in the application of deep eutectic solvents as sustainable media as well as catalysts in organic reactions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 48675–48704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Hu, X.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H.; Chen, L.; Zhiwen, Q. Overview of acidic deep eutectic solvents on synthesis, properties and applications. GEE 2020, 5, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Han, Q.; Shi, L.; Bi, C. Application of Deep-Eutectic Solvents in Green Organic Synthesis. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 36, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jérôme, F. Deep eutectic solvents: Syntheses, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, S.; Kirchner, B.; Mollenhauer, D. Charge Spreading in Deep Eutectic Solvents. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2016, 17, 3354–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bušić, V.; Roca, S.; Vikić-Topić, D.; Vrandečić, K.; Ćosić, J.; Molnar, M.; Gašo-Sokač, D. Eco-friendly quaternization of nicotinamide and 2-bromoacetophenones in deep eutectic solvents. Antifungal activity of the products. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radošević, K.; Cvjetko Bubalo, M.; Gaurina Srček, V.; Grgas, D.; Landeka Dragičević, T.; Radojčić Redovniković, I. Evaluation of toxicity and biodegradability of choline chloride based deep eutectic solvents. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 112, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, R.; Hemmateenejad, B.; Safavi, A.; Shojaeifard, Z.; Mohabbati, M.; Firuzi, O. Assessment of cytotoxicity of choline chloride-based natural deep eutectic solvents against human HEK-293 cells: A QSAR analysis. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macário, I.P.E.; Oliveira, H.; Menezes, A.C.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Pereira, J.L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Gonçalves, F.J.M. Cytotoxicity profiling of deep eutectic solvents to human skin cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitar, A.; Panić, M.; Prlić Kardum, J.; Halambek, J.; Sander, A.; Kučan, K.Z.; Radojčić Redovniković, I.; Radošević, K. Physicochemical Properties, Cytotoxicity, and Antioxidative Activity of Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents Containing Organic Acid. CABEQ 2019, 33, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bušić, V.; Vrandečić, K.; Siber, T.; Roca, S.; Vikić-Topić, D.; Gašo-Sokač, D. A Rapid Microwave Induced Synthesis of Isonicotinamide Derivatives and their Antifungal Activity. CCA 2019, 92, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, G.; Aparicio, S.; Ullah, R.; Atilhan, M. Deep Eutectic Solvents: Physicochemical Properties and Gas Separation Applications. Energy Fuel. 2015, 29, 2616–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Li, C.; Yin, J.; Li, V.; Jia, Y.; Bao, M. Design, synthesis and properties of acidic deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 236, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Gray, S. Design of Improved Deep Eutectic Solvents Using Hole Theory. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2006, 7, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, M.; Periš, I.; Komar, M. Choline Chloride Based Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Tuneable Medium for Synthesis of Coumarinyl 1,2,4-Triazoles: Effect of Solvent Type and Temperature. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2688–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troter, D.Z.; Todorović, Z.B.; Đokić-Stojanović, D.R.; Đorđević, B.S.; Todorović, V.; Kostantinović, S.S.; Veljković, V.B. The physico-chemical and thermodynamic properties of the choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2017, 82, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, Z.; de María, P.D. Novel choline-chloride-based deep-eutectic-solvents with renewable hydrogen bond donors: Levulinic acid and sugar-based polyols. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florindo, C.; Oliveira, M.M.; Branco, L.C.; Marrucho, I.M. Carbohydrates-based deep eutectic solvents: Thermophysical properties and rice straw dissolution. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 247, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacki, K.; Hiléia, K.S.; Souza Cláudio, M.R.; Almeida Alexandre, L.; Magalhães, M.P.G. Physicochemical Properties of Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents with Polyols: An Experimental and Theoretical Investigation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 18712–18728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Harris, R.C.; Ryder, K.S.; D’Agostino, C.; Gladden, L.F.; Mantle, M.D. Glycerol eutectics as sustainable solvent systems. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Harris, R.C.; Ryder, K.S. Application of Hole Theory to Define Ionic Liquids by their Transport Properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4910–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.Y.; Xu, P.; Yang, F.X.; Wu, H.; Zong, M.H.; Lou, W.Y. Biocompatible Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Choline Chloride: Characterization and Application to the Extraction of Rutin from Sophora japonica. ASC Sus. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; van Spronsen, J.; Dai, Y.; Verberne, M.; Hollmann, F.; Arends, I.W.C.E.; Witkamp, G.J.; Verpoorte, R. Are natural deep eutectic solvents the missing link in understanding cellular metabolism and physiology? Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alañóna, M.E.; Ivanović, M.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; Arráez-Román, D.; Segura-Carretero, A. Choline chloride derivative-based deep eutectic liquids as novel green alternative solvents for extraction of phenolic compounds from olive leaf. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 13, 1685–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.M.; Prieto, P.; de la Hoz, A.; Díaz-Ortiz, Ý.; Martín, D.R.; García, J.I. Influence of Polarity and Activation Energy in Microwave– Assisted Organic Synthesis (MAOS). Chem. Open. 2015, 4, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Boothby, D.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K. Deep Eutectic Solvents Formed between Choline Chloride and Carboxylic Acids: Versatile Alternatives to Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9142–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, G.H.; Kadhom, M.A. Studying of two choline chloride’s deep eutectic solvents in their aqueous mixtures. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2016, 12, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hayyan, A.; Mjalli, F.S.; AlNashefc, I.M.; Al-Wahaibia, T.; Al-Wahaibia, Y.M.; Hashim, M.A. Fruit sugar-based deep eutectic solvents and their physical properties. Thermochim. Acta. 2012, 541, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| HBA | HBD | Molar Ratio ChCl/HBD | Water Content (%) | Viscosity (Pa s) | Conductivity (μS cm−1) | Density (ρ) (g cm−3) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChCl | Urea | 1:2 | 1.89 ± 0.01 | 0.214 (30 °C) | 1287 | 1.1879 | [26] |
| ChCl | N-methylurea | 1:3 | [27] | ||||
| ChCl | Thiourea | 1:2 | 2.972 (35 °C) | 1.36 | [28] | ||
| ChCl | Glucose | 1:1 | 34.400 (50 °C) | [29] | |||
| ChCl | Fructose | 1:1 | 1.272 | [30] | |||
| ChCl | Xylitol | 1:1 | 1.21 ± 0.01 | 3.867 (30 °C) | 172.6 | 1.2445 | [31] |
| ChCl | Sorbitol | 1:1 | 1.10 ± 0.02 | 13.736 (30 °C) | 63.3 | 1.2794 | [31] |
| ChCl | Glycerol | 1:2 | 1.68 ± 0.01 | 0.177 (30 °C) | 1647 | 1.18 | [32,33] |
| ChCl | Acetamide | 1:2 | 2.83 ± 0.02 | 0.127 (30 °C) | 2710 | 1.09 | [34] |
| ChCl | Malic acid | 1:1 | 1.72 ± 0.01 | 11.475 (30 °C) | 41.4 | 1.2796 | [35] |
| ChCl | Citric acid | 1:2 | [34] | ||||
| ChCl | Malonic acid | 1:1 | 3.36 ± 0.01 | 0.616 (30 °C) | 732 | 1.2112 | [34] |
| ChCl | Oxalic acid | 1:1 | 6.68 ± 0.02 | 0.089 (30 °C) | 2350 | 1.2371 | [34] |
| ChCl | Lactic acid | 1:2 | 1.138 | [36] | |||
| ChCl | Levulinic acid | 1:2 | 2.55 ± 0.01 | 0.119 (30 °C) | 1422 | 1.1320 | [34] |
| ChCl | Trans-cinnamic acid | 1:1 | 1.259 | [29] |
| Entry | DES (ChCl:HBD) | Reaction Time | Yield (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBD | Molar Ratio | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||
| 1 | Urea | 1:2 | 4 | 3 | 12 | 18 | 37 | 44 | 46 | 48 | 32 | 71 |
| 2 | N-methylurea | 1:3 | 4 | 8 | 10 | 44 | 30 | 24 | 39 | 29 | 22 | 44 |
| 3 | Thiourea | 1:2 | 4 | / a | 14 | 17 | 15 | 22 | 25 | 37 | 31 | 32 |
| 4 | Glucose | 1:1 | 6 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 5 | Fructose | 1:1 | 6 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 6 | Xylitol | 1:1 | 6 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 7 | Sorbitol | 1:1 | 6 | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 8 | Glycerol | 1:2 | 4 | 8 | 60 | 47 | 67 | 23 | 42 | 53 | 6 | 75 |
| 9 | Acetamide | 1:2 | 4 | 31 | 12 | 24 | 32 | 32 | 40 | 24 | 23 | 34 |
| 10 | Malic acid | 1:1 | 4 | 7 | 23 | 17 | 44 | 47 | 46 | 50 | 31 | 43 |
| 11 | Citric acid | 1:2 | 4 | 2 | 60 | 33 | 27 | 23 | 25 | 53 | 16 | 22 |
| 12 | Malonic acid | 1:1 | 4 | 24 | 8 | 30 | 10 | 16 | 44 | 47 | 10 | 64 |
| 13 | Oxalic acid | 1:1 | 4 | 26 | 33 | 13 | 22 | 30 | 41 | 96 | 35 | 32 |
| 14 | Lactic acid | 1:2 | 4 | / | 11 | 36 | 25 | 22 | 27 | 18 | 5 | 18 |
| 15 | Levulinic acid | 1:2 | 4 | 30 | 71 | 36 | 34 | 23 | 69 | 75 | 15 | 68 |
| 16 | Trans-cinnamic acid | 1:1 | 6 | 7 | 27 | 31 | 40 | 34 | 22 | 16 | 6 | 25 |
| Entry | DES (ChCl:HBD) | Yield (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBD | Molar Ratio | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
| 1 | Urea | 1:2 | 7 | 14 | 28 | 55 | 57 | 60 | 52 | 11 | 53 |
| 2 | N-methylurea | 1:3 | 24 | 12 | 50 | 35 | 34 | 56 | 34 | 15 | 46 |
| 3 | Thiourea | 1:2 | / a | 14 | 21 | 30 | 33 | 34 | 40 | 20 | 57 |
| 4 | Glucose | 1:1 | / | / | 4 | 5 | / | / | / | / | 10 |
| 5 | Fructose | 1:1 | / | / | 4 | 3 | / | / | / | / | 6 |
| 6 | Xylitol | 1:1 | / | 18 | 13 | 11 | 20 | 23 | 12 | 18 | 22 |
| 7 | Sorbitol | 1:1 | / | 20 | 15 | 21 | 14 | 33 | 10 | 23 | 15 |
| 8 | Glycerol | 1:2 | 28 | 67 | 84 | 78 | 25 | 53 | 57 | 26 | 82 |
| 9 | Acetamide | 1:2 | 10 | 38 | 44 | 56 | 42 | 43 | 50 | 31 | 88 |
| 10 | Malic acid | 1:1 | 25 | 23 | 10 | 33 | 46 | 47 | 57 | 34 | 76 |
| 11 | Citric acid | 1:2 | 15 | 24 | 27 | 35 | 34 | 45 | 47 | 24 | 52 |
| 12 | Malonic acid | 1:1 | 10 | 23 | 48 | 10 | 34 | 44 | 40 | 29 | 55 |
| 13 | Oxalic acid | 1:1 | 34 | 83 | 49 | 37 | 48 | 62 | 97 | 41 | 86 |
| 14 | Lactic acid | 1:2 | 10 | 14 | 31 | 30 | 22 | 50 | 25 | 22 | 40 |
| 15 | Levulinic acid | 1:2 | 38 | 76 | 94 | 38 | 54 | 72 | 77 | 45 | 80 |
| 16 | Trans-cinnamic acid | 1:1 | 10 | 36 | 43 | 42 | 27 | 57 | 45 | 30 | 71 |
| Entry | DES (ChCl:HBD) | Yield (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBD | Molar Ratio | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
| 1 | Urea | 1:2 | 78 | 89 | 87 | 85 | 84 | 89 | 70 | 62 | 93 |
| 2 | N-methylurea | 1:3 | 59 | 36 | 78 | 40 | 34 | 44 | 62 | 65 | 67 |
| 3 | Thiourea | 1:2 | 66 | 56 | 69 | 47 | 55 | 37 | 61 | 44 | 58 |
| 4 | Glucose | 1:1 | 36 | 18 | 34 | 25 | 26 | 20 | 12 | 33 | 20 |
| 5 | Fructose | 1:1 | 22 | 28 | 43 | 30 | 24 | 19 | 26 | 48 | 21 |
| 6 | Xylitol | 1:1 | 32 | 30 | 41 | 47 | 26 | 13 | 37 | 27 | 29 |
| 7 | Sorbitol | 1:1 | 37 | 41 | 57 | 55 | 48 | 56 | 48 | 47 | 18 |
| 8 | Glycerol | 1:2 | 68 | 78 | 70 | 82 | 50 | 67 | 70 | 76 | 92 |
| 9 | Acetamide | 1:2 | 45 | 66 | 87 | 89 | 60 | 54 | 83 | 54 | 90 |
| 10 | Malic acid | 1:1 | 77 | 88 | 89 | 93 | 66 | 97 | 86 | 61 | 48 |
| 11 | Citric acid | 1:2 | 80 | 62 | 74 | 77 | 59 | 77 | 89 | 46 | 62 |
| 12 | Malonic acid | 1:1 | 89 | 80 | 80 | 72 | 50 | 77 | 88 | 58 | 67 |
| 13 | Oxalic acid | 1:1 | 96 | 90 | 87 | 98 | 78 | 80 | 87 | 54 | 97 |
| 14 | Lactic acid | 1:2 | 35 | 44 | 32 | 72 | 39 | 86 | 56 | 41 | 43 |
| 15 | Levulinic acid | 1:2 | 78 | 65 | 95 | 92 | 90 | 81 | 90 | 78 | 87 |
| 16 | Trans-cinnamic acid | 1:1 | 43 | 38 | 45 | 39 | 41 | 40 | 56 | 37 | 45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bušić, V.; Molnar, M.; Tomičić, V.; Božanović, D.; Jerković, I.; Gašo-Sokač, D. Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green Effective Medium for Quaternization Reactions. Molecules 2022, 27, 7429. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217429
Bušić V, Molnar M, Tomičić V, Božanović D, Jerković I, Gašo-Sokač D. Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green Effective Medium for Quaternization Reactions. Molecules. 2022; 27(21):7429. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217429
Chicago/Turabian StyleBušić, Valentina, Maja Molnar, Vice Tomičić, Dalia Božanović, Igor Jerković, and Dajana Gašo-Sokač. 2022. "Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green Effective Medium for Quaternization Reactions" Molecules 27, no. 21: 7429. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217429
APA StyleBušić, V., Molnar, M., Tomičić, V., Božanović, D., Jerković, I., & Gašo-Sokač, D. (2022). Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green Effective Medium for Quaternization Reactions. Molecules, 27(21), 7429. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217429









