Antimicrobial Efficacy of Glass Ionomer Cement in Incorporation with Biogenic Zingiber officinale Capped Silver-Nanobiotic, Chlorhexidine Diacetate and Lyophilized Miswak
Abstract
1. Introduction
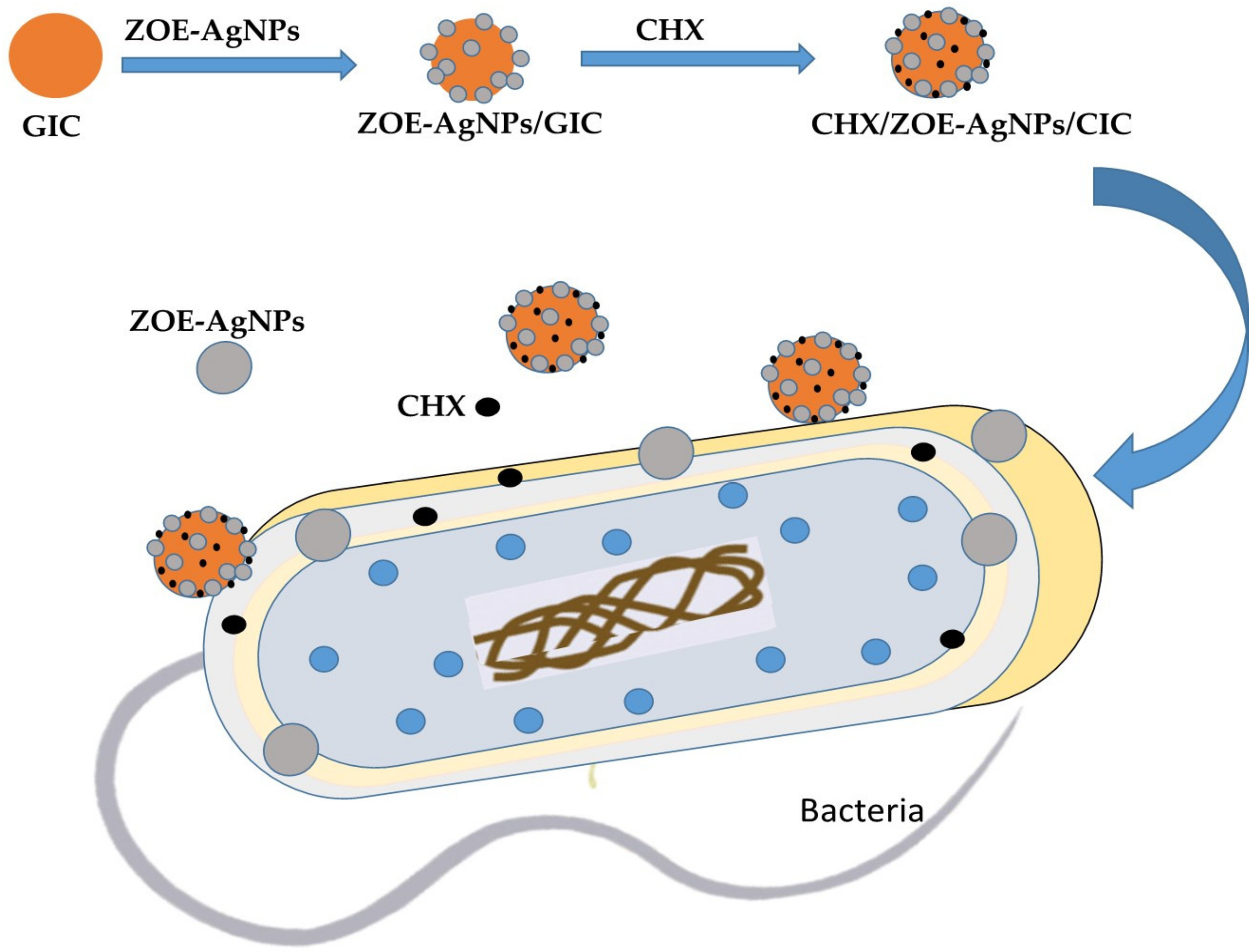
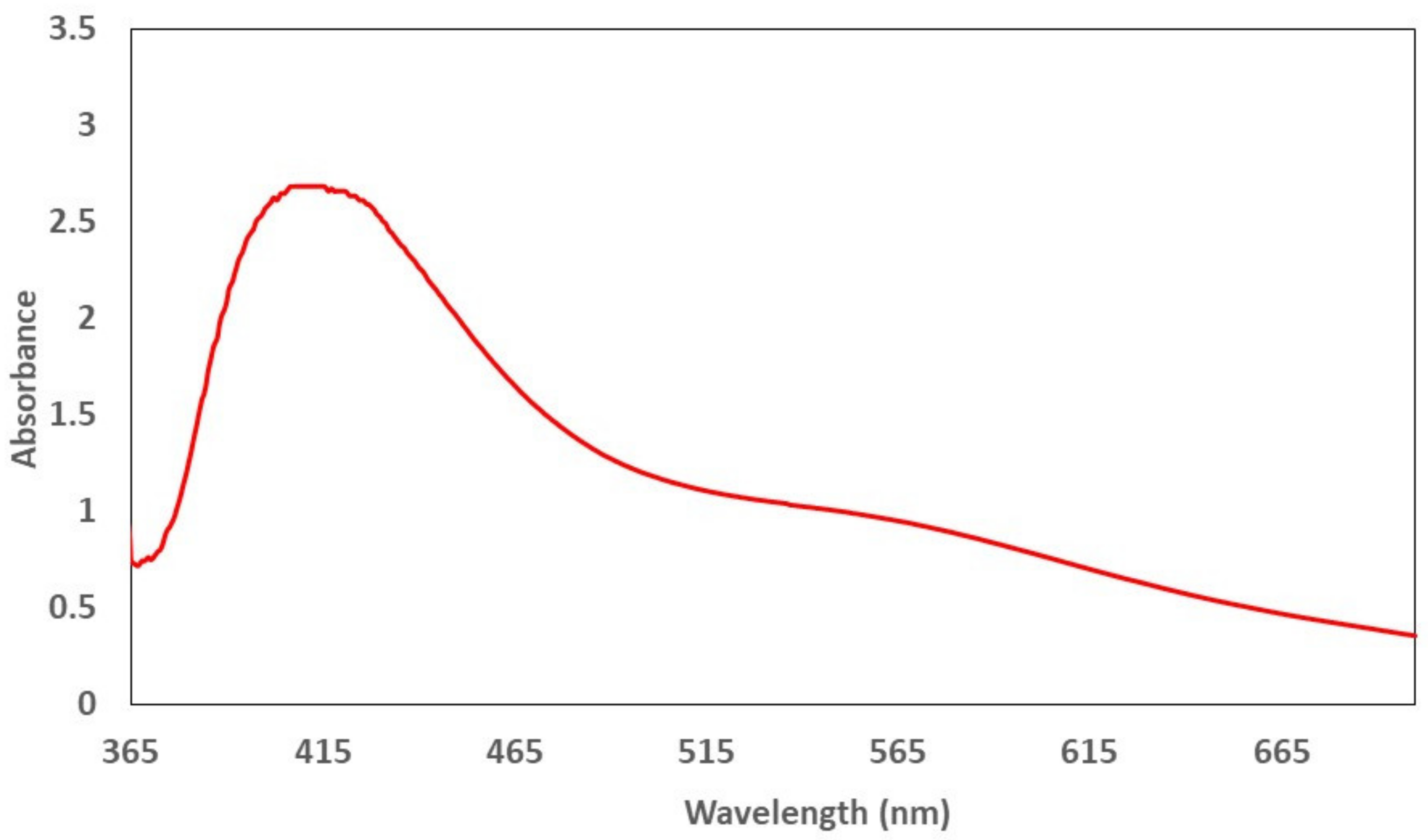
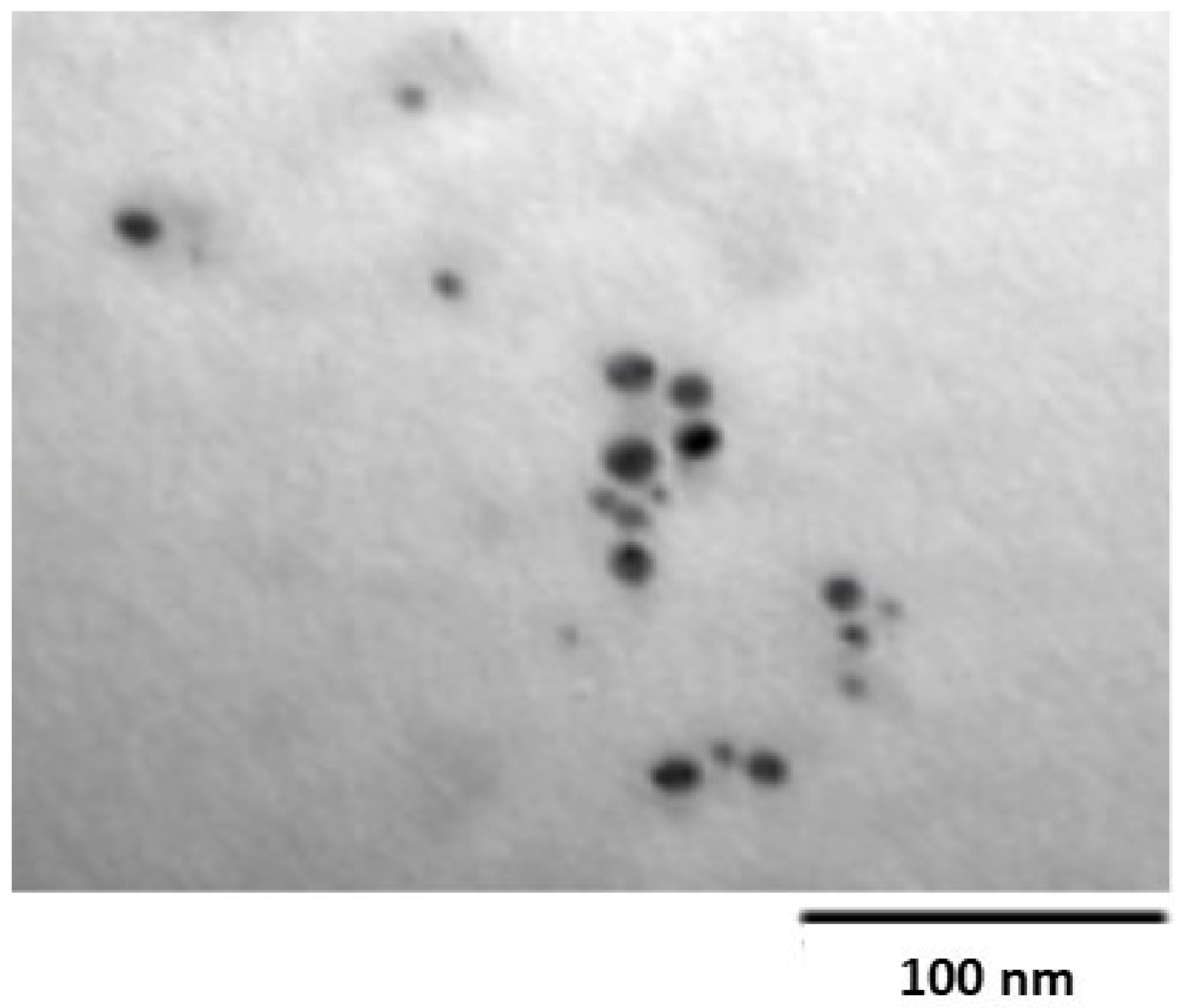
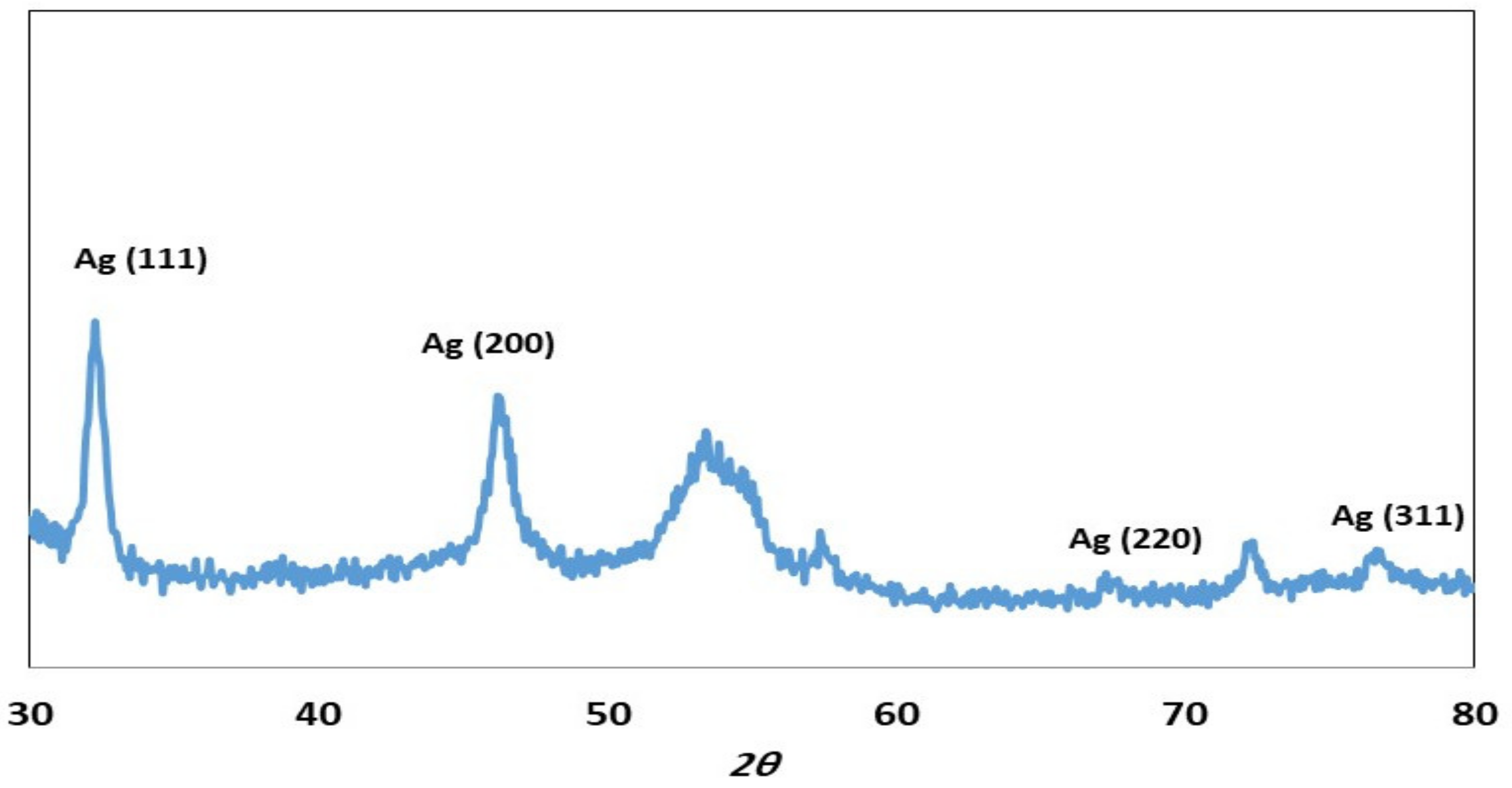
2. Results and Discussion
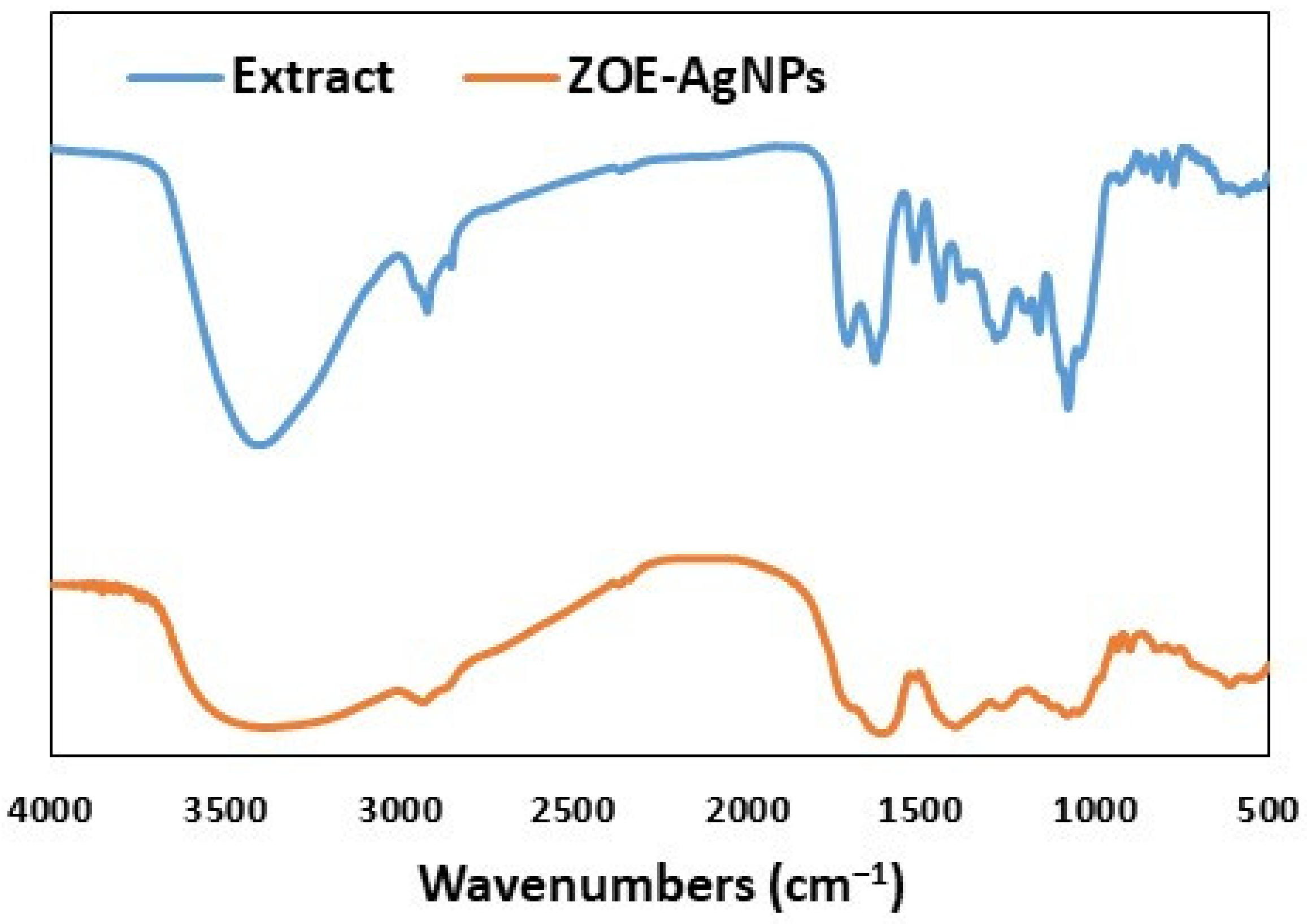
2.1. Characterization of ZOE-AgNPS
2.2. Charcterization of Miswak
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity
2.4. Compressive Strength Measurement
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Design, Microbial Strains Used, and Ethical Approval
- (a)
- The roots of miswak/Salvadora persica (SP) that were at least six months old, purchased from a local market, Taif City, KSA.
- (b)
- The Zingiber officinale plant, purchased from a local market, Taif City, KSA.
- (c)
- Conventional GIC (GC Fuji IX, Tokyo, Japan).
- (d)
- Chlorhexidine diacetate powder (RM1659-25G, HiMedia Laboratories, Mumbai, India).
3.2. Preparation of Test Specimens
3.3. Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles
3.4. Preparation of GIC Combination Specimens
3.5. Determination of Antimicrobial Activity
3.6. Compressive Strength Measurement
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Sidhu, S.K.; Nicholson, J.W. A Review of Glass-Ionomer Cements for Clinical Dentistry. J. Funct. Biomater. 2016, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mickenautsch, S.; Yengopal, V. Absence of carious lesions at margins of glass-ionomer cement and amalgam restorations: An update of systematic review evidence. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholtanus, J.D.; Huysmans, M.C. Clinical failure of class-II restorations of a highly viscous glass-ionomer material over a 6-year period: A retrospective study. J. Dent. 2007, 35, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Amaral, G. Restorative materials containing antimicrobial agents: Is there evidence for their antimicrobial and anticaries effects? A systematic review. Br. Dent. J. 2016, 220, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tüzüner, T.; Dimkov, A.; Nicholson, J.W. The effect of antimicrobial additives on the properties of dental glass-ionomer cements: A review. Acta Biomater. Odontol. Scand. 2019, 5, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Soni, H.; Sharma, D.K.; Mittal, K.; Pathania, V.; Sharma, S. Comparative evaluation of the antibacterial and physical properties of conventional glass ionomer cement containing chlorhexidine and antibiotics. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2015, 5, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, C.C.; Sokolonski, A.R.; Fonseca, M.S.; Stanisic, D.; Araújo, D.B.; Azevedo, V.; Portela, R.D.; Tasic, L. Applications of Silver Nanoparticles in Dentistry: Advances and Technological Innovation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monowar, T.; Rahman, M.S.; Bhore, S.J.; Raju, G.; Sathasivam, K.V. Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Using the Endophytic Bacterium Pantoea ananatis are Promising Antimicrobial Agents against Multidrug Resistant Bacteria. Molecules 2018, 23, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Cristóbal, L.F.; Holguín-Meráz, C.; Zaragoza-Contreras, E.A.; Martínez-Martínez, R.E.; Donohue-Cornejo, A.; Loyola-Rodríguez, J.P.; Cuevas-González, J.C.; Reyes-López, S.Y. Antimicrobial and Substantivity Properties of Silver Nanoparticles against Oral Microbiomes Clinically Isolated from Young and Young-Adult Patients. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 3205971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, S.; Mishra, P. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of curcumin-silver nanoparticles with improved stability and selective toxicity to bacteria over mammalian cells. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018, 207, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Nalini, S.P. Biotemplates in the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles. Biotechnol. J. 2010, 5, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Yngard, R.A.; Lin, Y. Silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, L.; Fidalgo, T.K.S.; da Costa, L.P.; Maia, L.C.; Balan, L.; Anselme, K.; Ploux, L.; Thiré, R.M.S.M. Antibacterial properties and compressive strength of new one-step preparation silver nanoparticles in glass ionomer cements (NanoAg-GIC). J. Dent. 2018, 69, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowkar, Z.; Jowkar, M.; Shafiei, F. Mechanical and dentin bond strength properties of the nanosilver enriched glass ionomer cement. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2019, 11, e275–e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porenczuk, A.; Grzeczkowicz, A.; Maciejewska, I.; Gołaś, M.; Piskorska, K.; Kolenda, A.; Gozdowski, D.; Kopeć-Swoboda, E.; Granicka, L.; Olczak-Kowalczyk, D. An initial evaluation of cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and antibacterial effectiveness of a disinfection liquid containing silver nanoparticles alone and combined with a glass-ionomer cement and dentin bonding systems. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 28, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, P.C.; Magalhães, A.P.; Pires, W.C.; Pereira, F.C.; Silveira-Lacerda, E.P.; Carrião, M.S.; Bakuzis, A.F.; Souza-Costa, C.A.; Lopes, L.G.; Estrela, C. Cytotoxicity of glass ionomer cements containing silver nanoparticles. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2015, 7, e622–e627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, L.; Bierbaum, G.; Kehl, K.; Bourauel, C. Evaluation of the antimicrobial activity and compressive strength of a dental cement modified using plant extract mixture. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2020, 31, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, S.; Hashmi, K.; Fasih, F.; Sharafat, S.; Khanani, R. In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial effect of miswak against common oral pathogens. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 30, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Tatari, A.; de Soet, J.J.; Abou Shelib, M.; van Amerongen, W.E. Influence of Salvadora persica (miswak) extract on physical and antimicrobial properties of glass ionomer cement. Eur. Arch. Paediatr. Dent. 2011, 12, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabil, N.S.; Badran, A.S.; Wassel, M.O. Effect of the addition of chlorhexidine and miswak extract on the clinical performance and antibacterial properties of conventional glass ionomer: An in vivo study. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2017, 27, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, C.; Aida, K.L.; Pereira, J.A.; Teixeira, G.S.; Caldo-Teixeira, A.S.; Perrone, L.R.; Caiaffa, K.S.; Negrini, T.C.; Castilho, A.R.F.; Costa, C.A.S. In vitro and in vivo evaluations of glass-ionomer cement containing chlorhexidine for Atraumatic Restorative Treatment. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2017, 25, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellis, C.A.; Addison, O.; Nobbs, A.H.; Duckworth, P.F.; Holder, J.A.; Barbour, M.E. Glass ionomer cements with milled, dry chlorhexidine hexametaphosphate filler particles to provide long-term antimicrobial properties with recharge capacity. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, J.S.; Roshan, N.M.; Sakeenabi, B.; Poornima, P.; Nagaveni, N.B.; Subbareddy, V.V. Inhibition of Residual Cariogenic Bacteria in Atraumatic Restorative Treatment by Chlorhexidine: Disinfection or Incorporation. Pediatr. Dent. 2017, 39, 308–312. [Google Scholar]
- Charannya, S.; Duraivel, D.; Padminee, K.; Poorni, S.; Nishanthine, C.; Srinivasan, M.R. Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles and 2% Chlorhexidine Gluconate When Used Alone and in Combination Assessed Using Agar Diffusion Method: An in-vitro Study. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2018, 9 (Suppl. S2), S204–S209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, D.; Rakhamimova, A.; Pollack, A.; Loewy, Z. Oral Biofilms: Development, Control, and Analysis. High Throughput 2018, 7, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Enan, E.T.; Ashour, A.A.; Basha, S.; Felemban, N.H.; Gad El-Rab, S.M.F. Antimicrobial activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles, amoxicillin, and glass-ionomer cement against Streptococcus mutans and Staphylococcus aureus. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 215101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad El-Rab, S.M.F.; Basha, S.; Ashour, A.A.; Enan, E.T.; Alyamani, A.A.; Felemban, N.H. Green Synthesis of Copper Nano-Drug and Its Dental Application upon Periodontal Disease-Causing Microorganisms. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halawani, E.M.; Hassan, A.M.; El-Rab, S.M.G. Nanoformulation of Biogenic Cefotaxime-Conjugated-Silver Nanoparticles for Enhanced Antibacterial Efficacy against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Anticancer Studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 1889–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehata, M.S. Green route synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plants/ginger extracts with enhanced surface plasmon resonance and degradation of textile dye. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 273, 115418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, S.; Ashour, A.A.; Felemban, N.H.; Enan, E.T.; Felemban, M.F.; Alyamani, A.A.; Gad El-Rab, S.M.F. Antimicrobial and synergistic compassion of miswak, nano-silver drug, and chlorhexidine alone and their combinations upon Streptococcus mutans, Staphylococcus aureus, and Candida albicans. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, H.; Bowen, W.H. Candida albicans and Streptococcus mutans: A potential synergistic alliance to cause virulent tooth decay in children. Future Microbiol. 2014, 9, 1295–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsetta, M.L.; Klein, M.I.; Colonne, P.M.; Scott-Anne, K.; Gregoire, S.; Pai, C.H.; Gonzalez-Begne, M.; Watson, G.; Krysan, D.J.; Bowen, W.H.; et al. Symbiotic relationship between Streptococcus mutans and Candida albicans synergizes virulence of plaque biofilms in vivo. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 1968–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Huang, X.; Alkhers, N.; Alzamil, H.; Alzoubi, S.; Wu, T.T.; Castillo, D.A.; Campbell, F.; Davis, J.; Herzog, K.; et al. Candida albicans and Early Childhood Caries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Caries Res. 2018, 52, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, C.J.; Leung, K.C.; Wong, C.H.; Lee, S.F.; Li, X.; Leung, P.C.; Lau, C.B.; Wat, E.; Jin, L. Nanoparticle-encapsulated chlorhexidine against oral bacterial biofilms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.C.; Seneviratne, C.J.; Li, X.; Leung, P.C.; Lau, C.B.; Wong, C.H.; Pang, K.Y.; Wong, C.W.; Wat, E.; Jin, L. Synergistic Antibacterial Effects of Nanoparticles Encapsulated with Scutellaria baicalensis and Pure Chlorhexidine on Oral Bacterial Biofilms. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriari, S.; Barekatain, M.; Shahtalebi, M.A.; Farhad, S.Z. Evaluation of antibacterial properties of a glass-ionomer cement containing purified powder of Salvia officinalis: An in vitro study. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2019, 10, 110. [Google Scholar]
- Mozayeni, M.A.; Hadian, A.; Bakhshaei, P.; Dianat, O. Comparison of antifungal activity of 2% chlorhexidine, calcium hydroxide, and nanosilver gels against Candida albicans. J. Dent. 2015, 12, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Koneman, E.W.; Allen, S.D.; Janda, W.M.; Schreckenberger, P.C.; Winn, W.C., Jr. Color Atlas and Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology, 5th ed.; Lippincott-Raven Publishers: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gad El-Rab, S.M.F.; Halawani, E.M.; Alzahrani, S.S.S. Biosynthesis of silver nano-drug using Juniperus excelsa and its synergistic antibacterial activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria for wound dressing applications. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad El-Rab, S.M.F.; Halawani, E.M.; Hassan, A.M. Formulation of Ceftriaxone Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles and Their Medical Applications against Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase Producing Bacteria and Breast Cancer. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad El-Rab, S.M.F.; Abo-Amer, A.E.; Asiri, A.M. Biogenic Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles and Its Potential Use as Antimicrobial Agent against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 1767–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad El-Rab, S.M.F.; Ashour, A.A.; Basha, S.; Alyamani, A.A.; Felemban, N.H.; Enan, E.T. Well-Orientation Strategy Biosynthesis of Cefuroxime-Silver Nanoantibiotic for Reinforced Biodentine™ and Its Dental Application against Streptococcus mutans. Molecules 2021, 26, 6832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudzicki, J. Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Test Protocol; American Society of Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
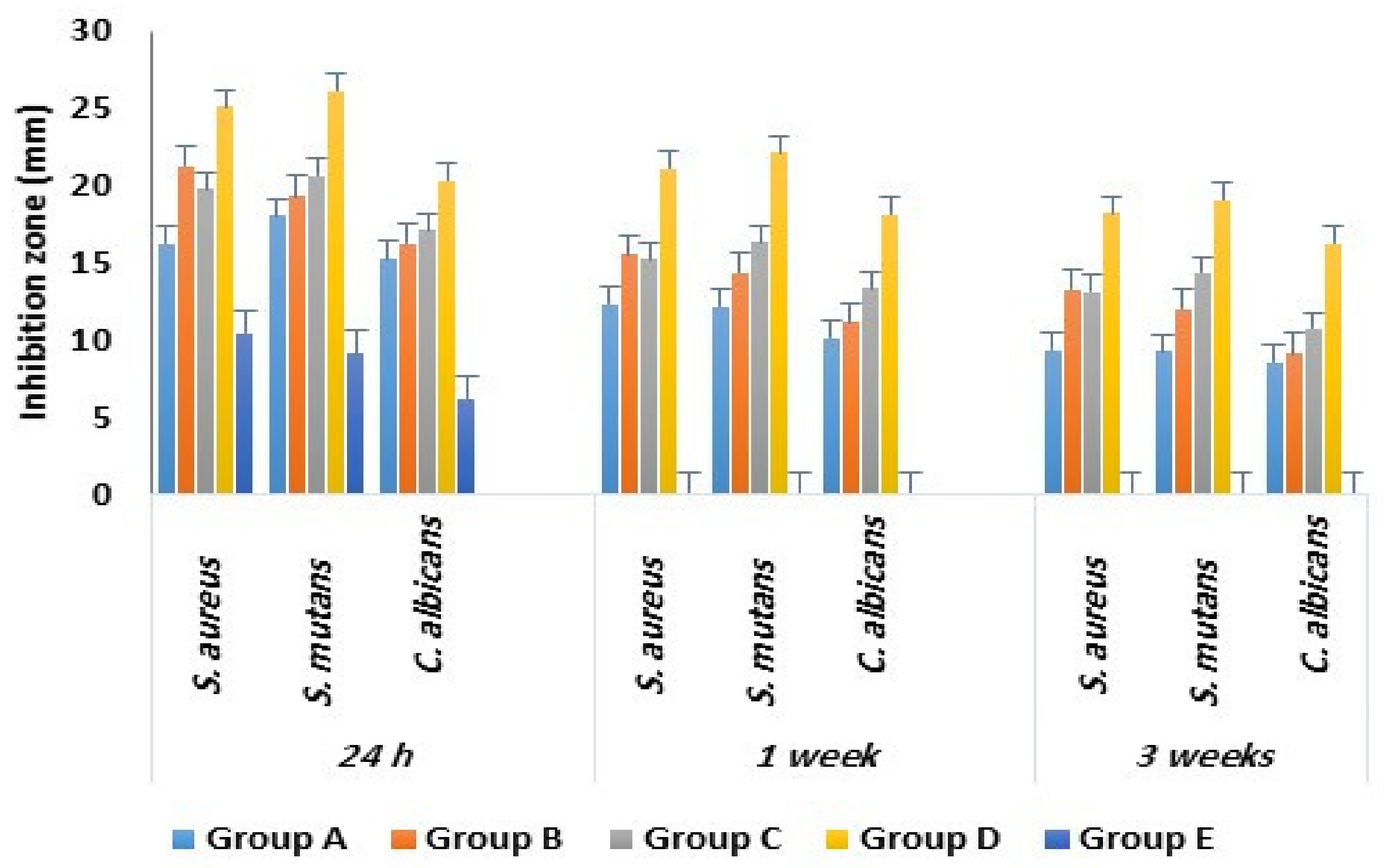
| Study Groups with Tested Microbes | Inhibition Zone in mm | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| InZ 24 h | InZ 1 Week | InZ 3 Week | |
| S. aureus | |||
| a- Group A (n = 30) | 16.3 ± 2.1 | 12.4 ± 1.1 | 9.4 ± 1.1 |
| b- Group B (n = 30) | 21.3 ± 1.4 | 15.6 ± 1.2 | 13.3 ± 1.1 |
| c- Group C (n = 30) | 19.8 ± 1.9 | 15.3 ± 1.2 | 13.2 ± 1.1 |
| d- Group D (n = 30) | 25.2 ± 2.2 | 21.2 ± 1.8 | 18.3 ± 1.3 |
| e- Group E (n = 30) | 10.5 ± 1.6 | 0 | 0 |
| ANOVA, F value | 16.712 | 7.172 | 6.341 |
| ANOVA, p value | 0.0001 | 0.003 | 0.03 |
| Tukey post Hoc | d > e, d > a, d > c, d > b, b > e, b > a, c > e, a > e | d > a, d > c, d > b | d > a, d > b, d >c |
| S. mutans | |||
| a- Group A (n = 30) | 18.1 ± 1.9 | 12.2 ± 1.2 | 9.3 ± 1.1 |
| b- Group B (n = 30) | 19.4 ± 2.1 | 14.4 ± 1.1 | 12.1 ± 0.9 |
| c- Group C (n = 30) | 20.7 ± 1.5 | 16.4 ± 1.6 | 14.4 ± 1.5 |
| d- Group D (n = 30) | 26.2 ± 2.6 | 22.2 ± 2.1 | 19.1 ± 1.7 |
| e- Group E (n = 30) | 9.2 ± 1.2 | 0 | 0 |
| ANOVA, F value | 17.821 | 5.328 | 6.723 |
| ANOVA, p value | 0.0001 | 0.04 | 0.03 |
| Tukey post Hoc | d > e, d > a, d > c, d > b, b > e, c > e, a > e | d > a, d > b, d > c, c > a | d > a, d > b, d >c, b > a, c > a |
| C. albicans | |||
| a- Group A (n = 30) | 15.3 ± 1.1 | 10.2 ± 1.2 | 8.6 ± 0.9 |
| b- Group B (n = 30) | 16.3 ± 1.1 | 11.2 ± 1.5 | 9.2 ± 1.3 |
| c- Group C (n = 30) | 17.2 ± 1.2 | 13.4 ± 1.3 | 10.8 ± 1.1 |
| d- Group D (n = 30) | 20.4 ± 2.1 | 18.2 ± 1.9 | 16.3 ± 1.3 |
| e- Group E (n = 30) | 2.3 ± 1.1 | 0 | 0 |
| ANOVA, F value | 14.231 | 6.421 | 6.723 |
| ANOVA, p value | 0.0001 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Tukey post Hoc | d > e, d > a, d > c, d > b, b > e, c > e, a > e | d > a, d > b, d > c, c > a | d > a, d > b, d >c, c > a |
| Materials | Concentration | Bacteria | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Study Groups | n | Mean ± SD | ANOVA F Value | ANOVA p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group A | 10 | 43.2 ± 3.1 | 2.326 | 0.07 |
| Group B | 10 | 44.7 ± 4.8 | ||
| Group C | 10 | 43.9 ± 3.6 | ||
| Group D | 10 | 45.8 ± 5.4 | ||
| Group E | 10 | 42.4 ± 2.7 |
| Group | Abbreviation | Components |
|---|---|---|
| Group A |
|
|
| Group B |
|
|
| Group C |
|
|
| Group D |
|
|
| Group E |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ashour, A.A.; Basha, S.; Felemban, N.H.; Enan, E.T.; Alyamani, A.A.; Gad El-Rab, S.M.F. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Glass Ionomer Cement in Incorporation with Biogenic Zingiber officinale Capped Silver-Nanobiotic, Chlorhexidine Diacetate and Lyophilized Miswak. Molecules 2022, 27, 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27020528
Ashour AA, Basha S, Felemban NH, Enan ET, Alyamani AA, Gad El-Rab SMF. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Glass Ionomer Cement in Incorporation with Biogenic Zingiber officinale Capped Silver-Nanobiotic, Chlorhexidine Diacetate and Lyophilized Miswak. Molecules. 2022; 27(2):528. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27020528
Chicago/Turabian StyleAshour, Amal Adnan, Sakeenabi Basha, Nayef H. Felemban, Enas T. Enan, Amal Ahmed Alyamani, and Sanaa M. F. Gad El-Rab. 2022. "Antimicrobial Efficacy of Glass Ionomer Cement in Incorporation with Biogenic Zingiber officinale Capped Silver-Nanobiotic, Chlorhexidine Diacetate and Lyophilized Miswak" Molecules 27, no. 2: 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27020528
APA StyleAshour, A. A., Basha, S., Felemban, N. H., Enan, E. T., Alyamani, A. A., & Gad El-Rab, S. M. F. (2022). Antimicrobial Efficacy of Glass Ionomer Cement in Incorporation with Biogenic Zingiber officinale Capped Silver-Nanobiotic, Chlorhexidine Diacetate and Lyophilized Miswak. Molecules, 27(2), 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27020528






