New Advances in Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFI) Technology for Food Safety Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET)
3. Aptamer
4. Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS)
5. Quantum Dots (QDs)
6. Electrochemical Sensor Strips
7. Biosensor Strips
8. Conclusions and Future Scope
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LFI | Lateral flow immunoassay |
| FRET | Fluorescence resonance energy transfer |
| SERS | Surface enhanced raman spectroscopy |
| QDs | Quantum dots |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| OTA | Ochratoxin A |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LF | Lateral flow |
| T Line | Detection line |
| IC | Inhibitory concentration |
| POCT | Point-of-care testing |
| MOF | Metal organic framework |
| RSD | Relative standard deviation |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| 4-MBA | 4-mercaptobenzaldehyde |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| SAA | Serum amyloid A |
| CRP | C reactive protein |
| LCPS | Liquid crystal polymers |
| GMO | Genetically modified organism |
| GMP | Good manufacturing practice |
| SMR | Silver mirror reaction |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| SNPs | Single nucleotide polymorphisms |
| CIP | Ciprofloxacin |
| MRLs | Maximum residue limits |
| QDM | Quantum dot microsphere |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| ICST | Immunochromatographic banding test |
| BQ | Benzoquinone |
| PEDs | Paper electrochemical devices |
| gPAD | Gas-sensitive paper-based device |
| ePAD | Electrochemical paper-based analytical device |
| PMPC-SH | Poly(2-methacryloyloxyethylphosphorylcholine) |
| SPE | Screen printed electrode |
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| SPR | Surface plasmon resonance |
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
| GNP | Gold nanoparticles |
| DON | Eoxynivalenol |
| ZEN | Zearalenone |
| E.coli | Escherichia coli |
| ITS | Immunochromatography test strip |
| CAP | Chloramphenicol |
References
- Liu, C.; Fang, S.; Tian, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, D.P.; Li, Y.; Hou, D.; Liu, Q. Rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in milk, bread, and jelly by lac dye coloration-based bidirectional lateral flow immunoassay strip. J. FoodSaf. 2021, 41, e12862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Cai, S.; Ye, Q.; Wu, Q.P.; Shao, Y.N.; Qu, X.Y.; Xiang, X.; Zhu, B.; Ding, Y.; Chen, M.; et al. Quantum dot nanobeads-labelled lateral flow immunoassay strip for rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella Typhimurium based on strand displacement loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Engineering, 2021; In press. [Google Scholar]
- Salvador, J.P.; Vasylieva, N.; Gonzalez-Garcia, I.; Jin, M.J.; Caster, R.; Sieel, J.B.; Hammock, D.B. Nanobody-Based Lateral Flow Immunoassay for the Rapid Detection of Aflatoxin B1 in Almond Milk. ACS Food Sci.Technol. 2022, 2, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, B.; Atzberger, P.J. Förster resonance energy transfer: Role of diffusion of fluorophore orientation and separation in observed shifts of FRET efficiency. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonsomboon, K.; Noppakuadrittidej, P.; Sutikulsombat, S.; Petdum, A.; Panchan, W.; Wanichacheva, N.; Sooksimuang, T.; Karoonuthaisiri, N. Turn-On fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based electrospun fibrous membranes: Rapid and ultrasensitive test strips for on-site detection of Mercury (II) ion. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-L.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Dai, X.; Miao, J.-Y.; Zhao, B.-X. An effective colorimetric and ratiometric fluorescent probe based FRET with a large Stokes shift for bisulfite. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.-K.; Joung, H.-A.; Jung, M.; Lee, H.; Kim, M.-G. Rapid and Simple Detection of Ochratoxin A using Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer on Lateral Flow Immunoassay (FRET-LFI). Toxins 2019, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jing, L.; Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Wang, B.; Xia, X.; Han, Q. Rapid Detection of Rongalite via a Sandwich Lateral Flow Strip Assay Using a Pair of Aptamers. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhu, C.; Huang, Y.; Yan, J.; Chen, A. A Lateral Flow Strip Based Aptasensor for Detection of Ochratoxin A in Corn Samples. Molecules 2018, 23, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, J.G. Application of DNA Aptamers and Quantum Dots to Lateral Flow Test Strips for Detection of Foodborne Pathogens with Improved Sensitivity versus Colloidal Gold. Pathogens 2014, 3, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Cheng, L.; Ding, S.; Wang, G.; Choo, J.; Chen, L. SERS-based test strips: Principles, designs and applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 189, 113360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Yu, Q. The development of lateral flow immunoassay strip tests based on surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy coupled with gold nanoparticles for the rapid detection of soybean allergen β-conglycinin. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 241, 118640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Trinh, B.T.; Kim, K.H.; Moon, J.; Kang, H.; Jo, K.; Akter, R.; Jeong, J.; Lim, E.-K.; Jung, J.; et al. Au@ZIF-8 SERS paper for food spoilage detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 179, 113063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Huang, J.; Sun, Y.; Huang, J.; Yin, M.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G. Utilization of a lateral flow colloidal gold immunoassay strip based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for ultrasensitive detection of antibiotics in milk. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 197, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Geng, W.; Hassan, M.; Zuo, M.; Wei, W.; Wu, X.; Ouyang, Q.; Chen, Q. Rapid detection of chloramphenicol in food using SERS flexible sensor coupled artificial intelligent tools. Food Control 2021, 128, 108186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Hassan, M.; Ali, S.; Li, H.; Sheng, R.; Chen, Q. Evolving trends in SERS-based techniques for food quality and safety: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Naqvi, T.K.; Tripathi, S.K.; Kulkarni, M.M.; Dwivedi, P.K. Paper based low-cost flexible SERS sensor for food adulterant detection. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Aptamer based SERS detection of Salmonella typhimurium using DNA-assembled gold nanodimers. Mikrochim. Acta 2018, 185, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Hua, T.; Guo, R.; Miao, D.; Jiang, S. Flexible, stable and sensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering of graphite/titanium-cotton substrate for conformal rapid food safety detection. Cellulose 2020, 27, 941–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, E.; Lu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Dai, Z. Simultaneous and ultrasensitive detection of three pesticides using a surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based lateral flow assay test strip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 181, 113149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Gu, C.; Wei, G.; Jiang, T. Improved lateral flow strip based on hydrophilic−hydrophobic SERS substrate for ultra−sensitive and quantitative immunoassay. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 529, 147121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; He, L. Recent advance in SERS techniques for food safety and quality analysis: A brief review. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 28, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Li, K.; Liu, H.; Xiao, R.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, S. Fe3O4@ Au SERS tags-based lateral flow assay for simultaneous detection of serum amyloid A and C-reactive protein in unprocessed blood sample. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 320, 128350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Xu, J.; Cheng, J.; Yao, B.; Zheng, L.; Liu, G.; Chen, W. Simultaneous and accurate screening of multiple genetically modified organism (GMO) components in food on the same test line of SERS-integrated lateral flow strip. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boles, M.A.; Ling, D.; Hyeon, T.; Talapin, D.V. The surface science of nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabzehmeidani, M.M.; Kazemzad, M. Quantum dots based sensitive nanosensors for detection of antibiotics in natural products: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 810, 151997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovaya, M.; Horiunova, I.; Plokhovska, S.; Pushkarova, N.; Blume, Y.; Yemets, A. Synthesis, Properties and Bioimaging Applications of Silver-Based Quantum Dots. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahle, R.; Kumbhakar, P.; Nayar, D.; Narayanan, T.N.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Tiwary, C.S.; Banerjee, R. Current advances in bio-fabricated quantum dots emphasising the study of mechanisms to diversify their catalytic and biomedical applications. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 14062–14080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, R.; Naderi-Manesh, H.; Farzin, L.; Vaezi, Z.; Ayarri, N.; Samandari, L.; Shamsipur, M. Fluorescence sensing and imaging with carbon-based quantum dots for early diagnosis of cancer: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 212, 114628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Lee, C. The Current Status and Future Outlook of Quantum Dot-Based Biosensors for Plant Virus Detection. Plant Pathol. J. 2018, 34, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zeng, L.; Xiong, Y.; Leng, Y.; Wang, H.; Xiong, Y. Fluorescence ELISA based on glucose oxidase-mediated fluorescence quenching of quantum dots for highly sensitive detection of Hepatitis B. Talanta 2018, 181, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, L.T.; Paira, P.; Paira, L.T.B.A.P. Current Application of Quantum Dots (QD) in Cancer Therapy: A Review. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taranova, N.; Berlina, A.; Zherdev, A.; Dzantiev, B. ‘Traffic light’ immunochromatographic test based on multicolor quantum dots for the simultaneous detection of several antibiotics in milk. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Du, D.; Wang, J.; Smith, J.N.; Timchalk, C.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y. Quantum Dot-Based Immunochromatographic Fluorescent Biosensor for Biomonitoring Trichloropyridinol, a Biomarker of Exposure to Chlorpyrifos. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5125–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Liu, L.; Ma, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, L.; Kuang, H.; Xu, C. Fluorescent strip sensor for rapid determination of toxins. Chem. Commun. 2010, 47, 1574–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlina, A.N.; Taranova, N.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Vengerov, Y.Y.; Dzantiev, B.B. Quantum dot-based lateral flow immunoassay for detection of chloramphenicol in milk. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 4997–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapountzi, E.A.; Tragoulias, S.; Kalogianni, D.P.; Ioannou, P.; Christopoulos, T.K. Lateral flow devices for nucleic acid analysis exploiting quantum dots as reporters. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 864, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon-Gamboa, S.M.; Poutou-Pinales, R.A.; Carrascal-Camacho, A.K. Antimicrobial Resistance of Non-Typhoid Salmonella in Meat and Meat Products. Foods 2021, 10, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramatla, T.; Ngoma, L.; Adetunji, M.; Mwanza, M. Evaluation of Antibiotic Residues in Raw Meat Using Different Analytical Methods. Antibiotics 2017, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Huang, H.; Jian, D.; Lu, Y.A.; Shan, Y.K.; Wang, S.Y.; Liu, F. Quantitative ciprofloxacin on-site rapid detections using quantum dot microsphere based immunochromatographic test strips. Food Chem. 2020, 335, 127596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, F.; Anfossi, L.; Giovannoli, C.; Passini, C.; Goftman, V.V.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; Baggiani, C. A fluorescent immunochromatographic strip test using Quantum Dots for fumonisins detection. Talanta 2016, 150, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowska, N.E.; Kundys, M.; Jelen, P.S.; Jonsson-Niedziolka, M. Electrochemical Glucose Sensing: Is There Still Room for Improvement? Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11271–11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, M.A.U.; Kim, K.H.; Salih, A.R.C.; Hyun, K.; Park, S.H.; Kang, B.; Soomro, A.M.; Ali, M.; Jun, Y.; Huh, D.; et al. High performance inkjet printed embedded electrochemical sensors for monitoring hypoxia in a gut bilayer microfluidic chip. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 1764–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, R.; Cheong, Y.H.; Ahamed, A.; Lisak, G. Heavy Metals Detection with Paper-Based Electrochemical Sensors. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 1880–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordbar, M.M.; Sheini, A.; Hashemi, P.; Hajian, A.; Bagheri, H. Disposable Paper-Based Biosensors for the Point-of-Care Detection of Hazardous Contaminations—A Review. Biosensors 2021, 11, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.-T.; Song, S.; Park, S.; Joo, C. Recent advances in high-sensitivity detection methods for paper-based lateral-flow assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 152, 112015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Liang, H. Electrochemical biotoxicity detection on a microfluidic paper-based analytical device via cellular respiratory inhibition. Talanta 2019, 202, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Alkhamis, O.; Liu, X.; Yu, H.; Canoura, J.; Xiao, Y. Aptamer-Integrated Multianalyte-Detecting Paper Electrochemical Device. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 17330–17339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pungjunun, K.; Chaiyo, S.; Praphairaksit, N.; Siangproh, W.; Ortner, A.; Kalcher, K.; Chailapakul, O.; Mehmeti, E. Electrochemical detection of NOx gas based on disposable paper-based analytical device using a copper nanoparticles-modified screen-printed graphene electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 143, 111606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, S.; Zhang, L.; Cui, K.; Zhao, P.; Yan, M.; Yu, J. Triggerable H2O2–Cleavable Switch of Paper-Based Biochips Endows Precision of Chemometer/Ratiometric Electrochemical Quantification of Analyte in High-Efficiency Point-of-Care Testing. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10273–10281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.X.G.; Dias, A.A.; Carvalho, L.L.; Cardoso, T.M.G.; Colmati, F.; Coltro, W.K.T. Determination of Ascorbic Acid in Commercial Tablets Using Pencil Drawn Electrochemical Paper-based Analytical Devices. Anal. Sci. 2018, 34, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinyorospathum, C.; Chaiyo, S.; Sae-Ung, P.; Hoven, V.P.; Damsongsang, P.; Siangproh, W.; Chailapakul, O. Disposable paper-based electrochemical sensor using thiol-terminated poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) for the label-free detection of C-reactive protein. Mikrochim. Acta. 2019, 186, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Han, G.C.; Xiao, H.; Chen, Z.; Fang, C. A novel 3D paper-based microfluidic electrochemical glucose biosensor based on rGO-TEPA/PB sensitive film. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2020, 1096, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panraksa, Y.; Siangproh, W.; Khampieng, T.; Chailapakul, O.; Apilux, A. Paper-based amperometric sensor for determination of acetylcholinesterase using screen-printed graphene electrode. Talanta 2018, 178, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotsiri, Z.; Vidic, J.; Vantarakis, A. Applications of biosensors for bacteria and virus detection in food and water–A systematic review. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 111, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anany, H.; Brovko, L.; Eldougdoug, N.; Sohar, J.; Fenn, H.; AlAsiri, N.; Jabrane, T.; Mangin, P.; Ali, M.M.; Kannan, B.; et al. Print to detect: A rapid and ultrasensitive phage-based dipstick assay for foodborne pathogens. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 1217–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, P.C.; Chan, Y.Y.; Mohamed, M.; Wong, W.K.; Najian, A.N.; Lim, B.H. Development of a thermostabilised triplex LAMP assay with dry-reagent four target lateral flow dipstick for detection of Entamoeba histolytica and non-pathogenic Entamoeba spp. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 966, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitratos, S.D.; Hommel, A.S.; Konrad, K.D.; Simpson, L.M.; Wu-Woods, J.J.; Woods, D.F. Biosensors to Monitor Water Quality Utilizing Insect Odorant-Binding Proteins as Detector Elements. Biosensors 2019, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, S.; Neumann, A.-C.; Karongo, R.; Dirndorfer, S.; Stübler, M.; Ibl, V.; Niessner, R.; Knopp, D.; Stoger, E. Cloning and plant-based production of antibody MC10E7 for a lateral flow immunoassay to detect [4-arginine]microcystin in freshwater. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, L.; Thakur, M. Dipstick based immunochemiluminescence biosensor for the analysis of vitamin B12 in energy drinks: A novel approach. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 722, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, N.; Kumar, S.; Yashini, M.; Rajeshwari, S.; Mamathi, C.A.; Thirunavookarasu, S.; Sunil, C.K.; Thirunavookarasu, S.N. Recent advances in Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) biosensors for food analysis: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ning, J.; Cheng, G.; Ahmad, I.; Li, J.; Mingyue, L.; Qu, W.; Iqbal, M.; Shabbir, M.; Yuan, Z. Receptor-based screening assays for the detection of antibiotics residues – A review. Talanta 2017, 166, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Kavanagh, O.; Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Deng, S.; Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Xie, C.; Situ, C.; Yuan, Z. Surface plasmon resonance biosensor for the determination of 3-methyl-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid, the marker residue of olaquindox, in swine tissues. Food Chem. 2019, 302, 124623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikas Yadav, M.K.; Kumar, P.; Verma, R.K. Detection of adulteration in pure honey utilizing Ag-graphene oxide coated fiber optic SPR probes. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houhoula, D.P.; Kouzilou, M.; Tzogias, C.; Kyrana, V.; Sflomos, C.; Tsaknis, J.; Lougovois, V.P. Effectual Gold Nanoprobe Sensor for Screening Horse Adulteration in Meat Products. J. Food Res. 2021, 6, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. A Surface Plasmon Resonance-Based Optical Fiber Probe Fabricated with Electropolymerized Molecular Imprinting Film for Melamine Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, M.; Fathi, F.; Jalili, R.; Shoeibie, S.; Dastmalchi, S.; Khataee, A.; Rashidi, M.-R. SPR enhanced DNA biosensor for sensitive detection of donkey meat adulteration. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainuddin, N.; Ariannejad, M.; Thirunavakkarasu, P.; Harun, S.; Zakaria, R. Investigation of cladding thicknesses on silver SPR based side-polished optical fiber refractive-index sensor. Results Phys. 2019, 13, 102255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
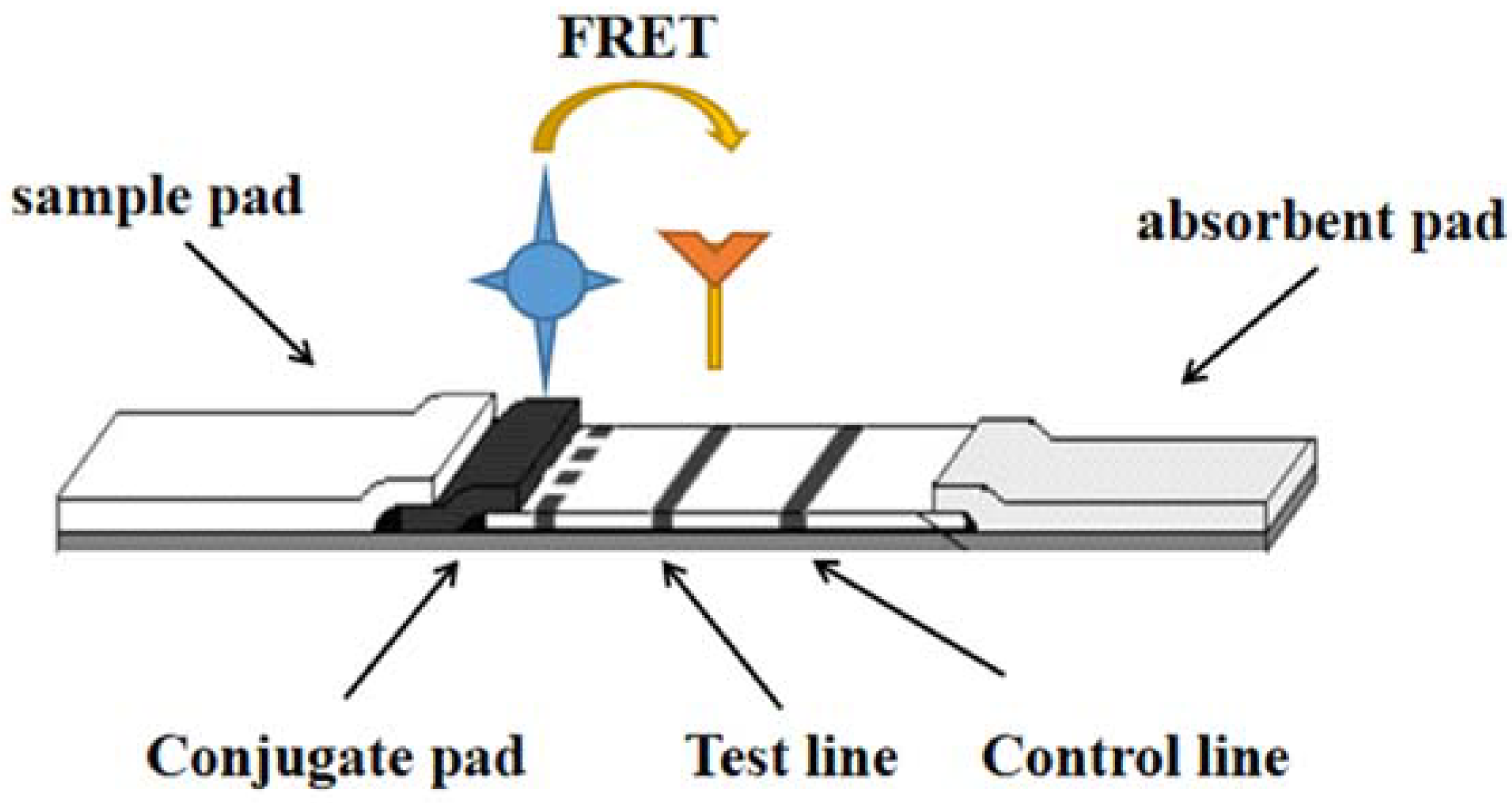
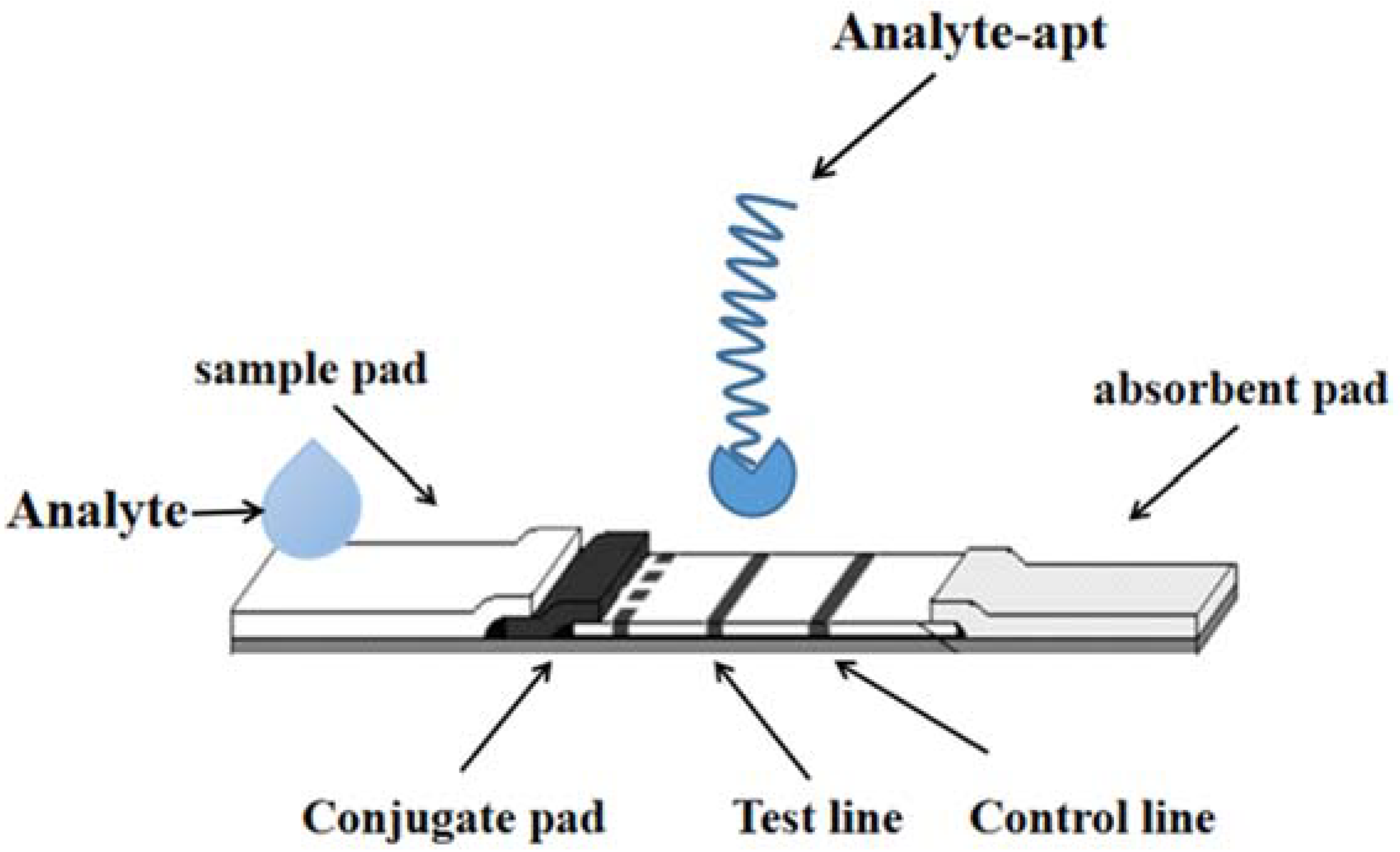
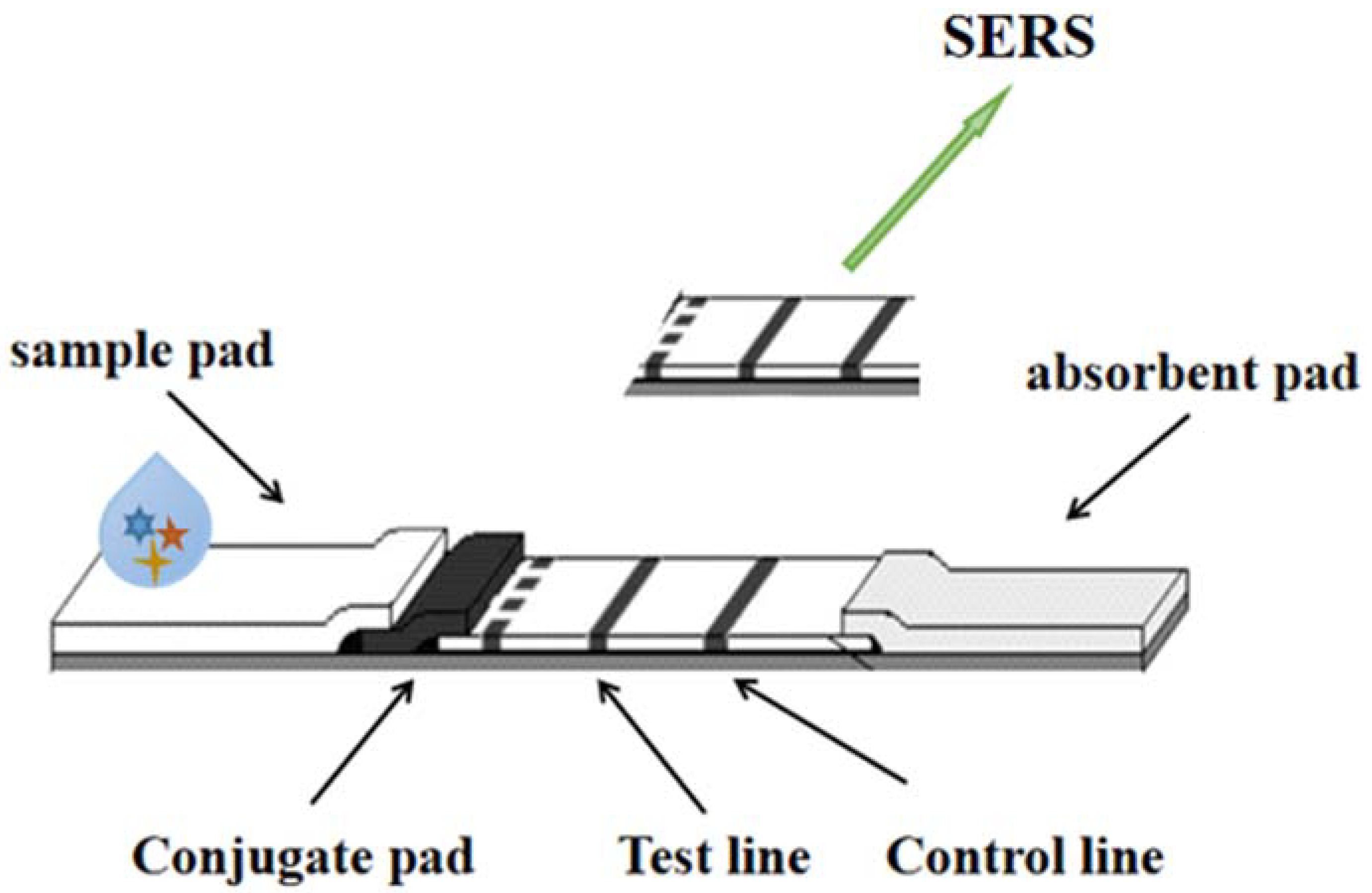
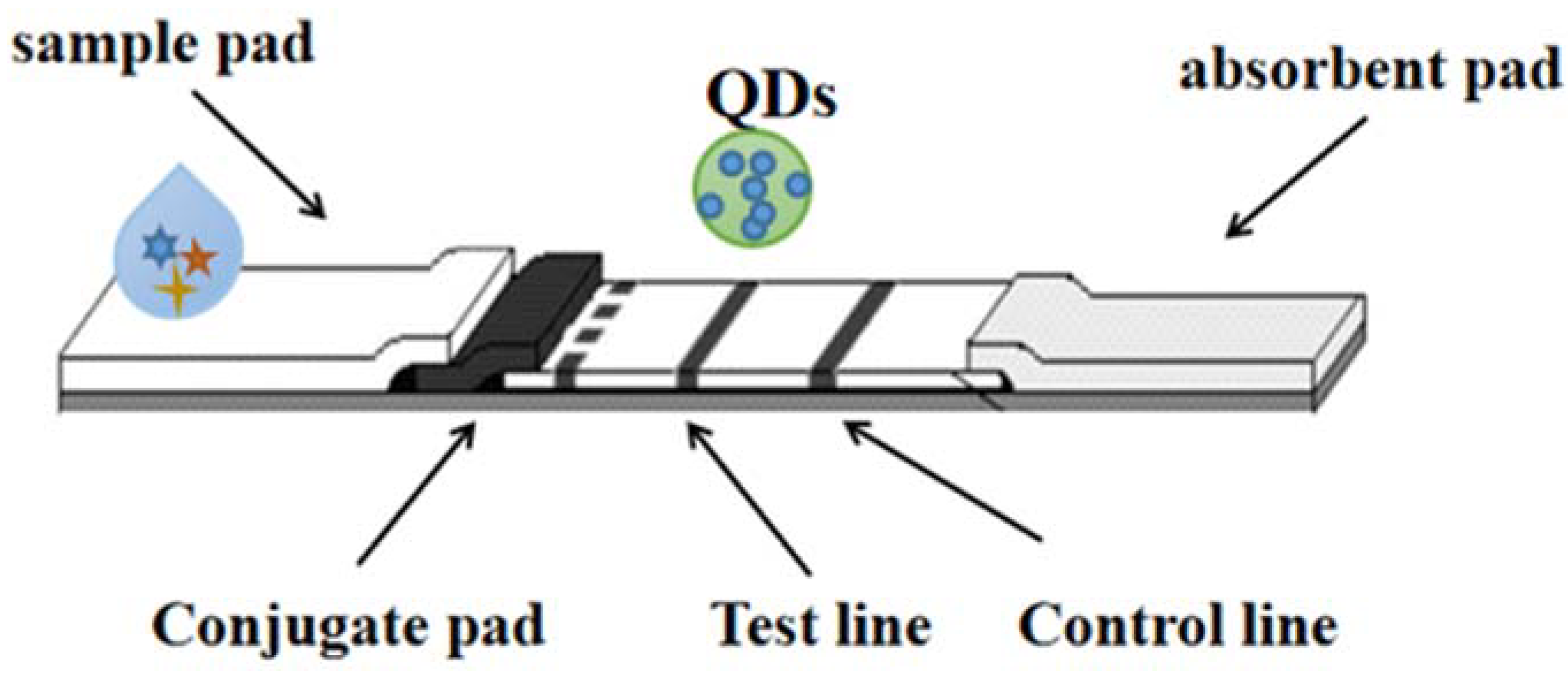
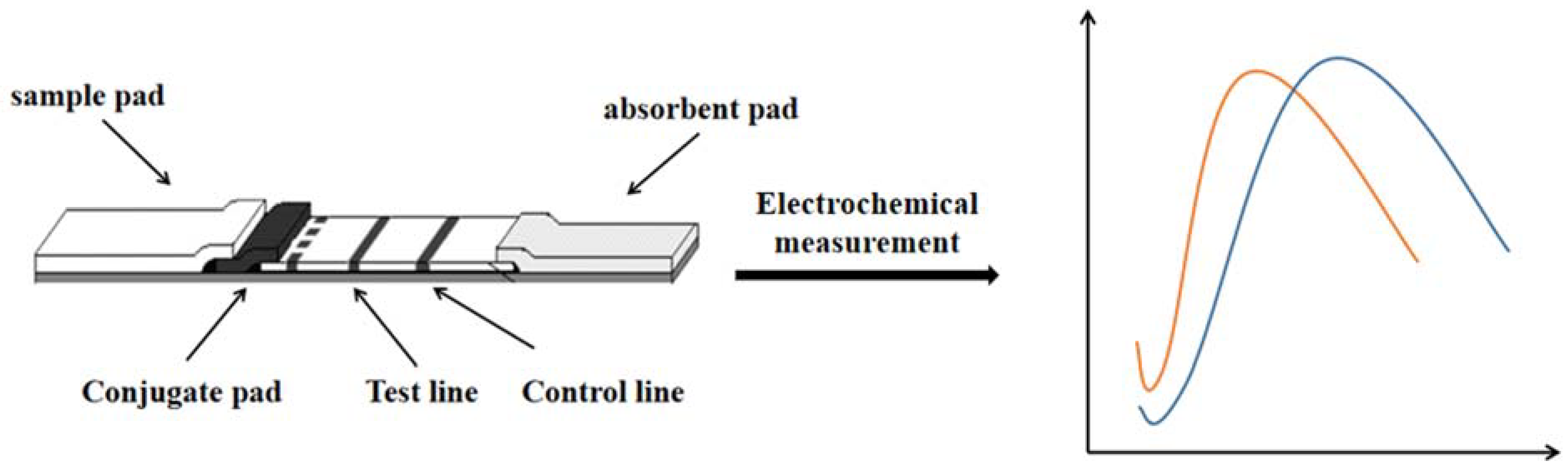
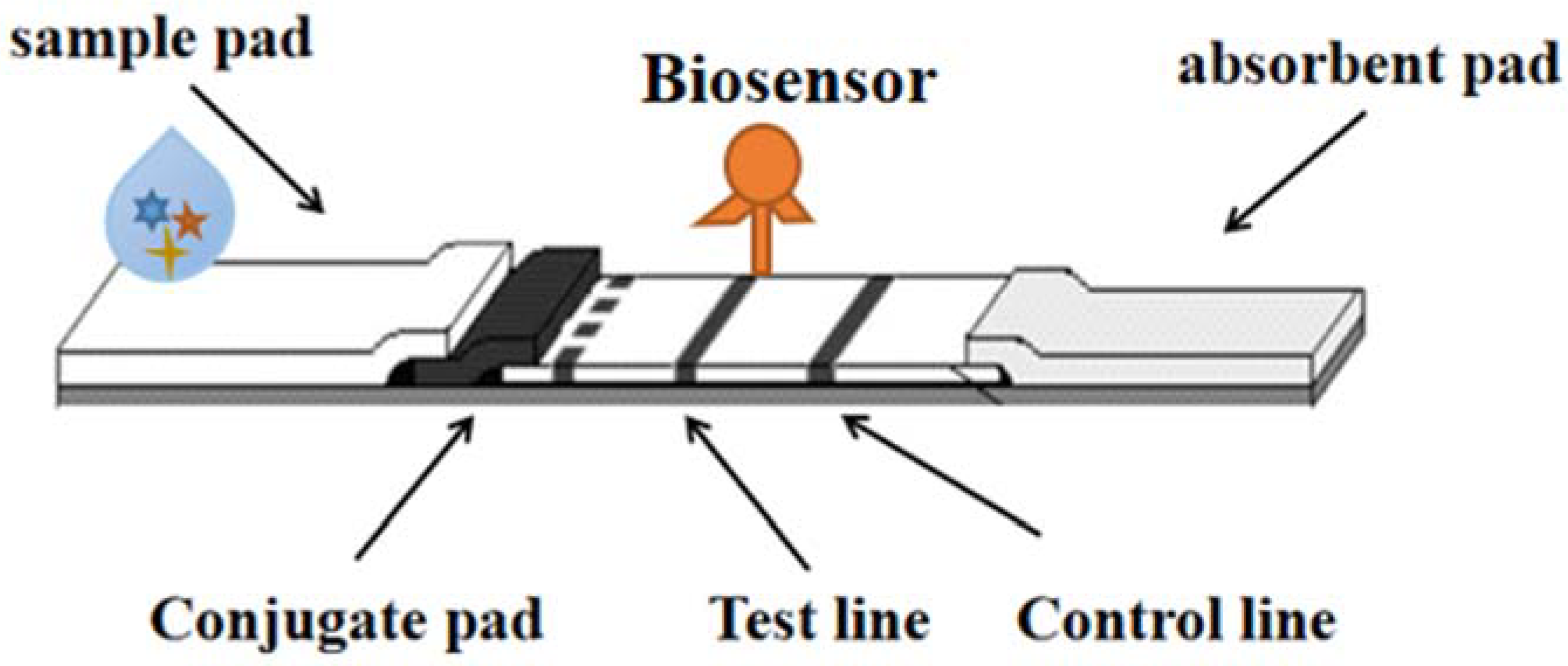
| Type of Detection | Analyte | LOD | Analyzed Samples | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FRET | Hg2+ | 0.309 μg/L | water, skin whitening serum | [5] |
| FRET | HSO3− | 45 nM | cell | [6] |
| FRET | Hematoxin A | 0.64 ng/mL | coffee | [7] |
| Aptamer | Rongalite | 1 μg/mL | food | [8] |
| Aptamer | aflatoxin B | 0.16ng/mL | almonds, peanuts, dried figs | [9] |
| Aptamer | Hematoxin A | 3.46 ng/mL | corn | [10] |
| SERS | β-Conglycinin | 1 μg/mL | Skimmed milk | [13] |
| SERS | antibiotics | 0.216 pg/mL | milk | [14] |
| SERS | Cadaverine, putrescine | 76.99 and 115.88 μg/mL | spoiled pork, beef, chicken | [15] |
| SERS | S.typhimurium | 35 cfu/mL | milk | [19] |
| SERS | C reactive protein erum amyloid A | 0.01 and 0.1 ng/mL | [23] | |
| QDs | antibiotics | 0.3, 0.12, 0.2 ng/mL | milk | [34] |
| QDs | ochratoxin A | 1.9 ng/mL | Red win | [35] |
| QDs | ciprofloxacin | 0.05 ng/mL | fish | [40] |
| QDs | fumonisins | 2.8 µg/L | corn | [41] |
| Electrochemical sensor | E. coli | 13.5 μg/mL | cucumber | [47] |
| Electrochemical sensor | C-reactive protein | 1.6 ng/mL | human serum | [52] |
| Electrochemical sensor | glucose | 25 μM | human sweat and blood shows | [53] |
| Electrochemical sensor | acetylcholinesterase | 0.1 U/mL | blood | [54] |
| Biosensor | foodborne pathogens | 10–50 CFU/mL | spinach, ground beef and chicken homogenates | [57] |
| Biosensor | odorant-binding protein | 100 mg/L | water | [59] |
| Biosensor | [Arg4]-microcystins | 12.5 ng/L | water | [60] |
| Biosensor | Vitamin B12 | 1 ng/mL | energy drinks | [61] |
| Biosensor | 3-methyl-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid | 1.4 µg/kg and 2.7 µg/kg | swine muscle and liver | [64] |
| Biosensor | glucose and fructose | 5.67 × 10−4 and 2.9 × 10−3 RIU | honey | [65] |
| Biosensor | 12.3 fg/μL | horse meat | [66] | |
| Biosensor | Melamine | 2.5 mg/L | [67] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, G.; Sun, X.; Li, N.; Li, X.; Wu, T.; Wang, F. New Advances in Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFI) Technology for Food Safety Detection. Molecules 2022, 27, 6596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196596
Xing G, Sun X, Li N, Li X, Wu T, Wang F. New Advances in Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFI) Technology for Food Safety Detection. Molecules. 2022; 27(19):6596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196596
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Guangxu, Xuefeng Sun, Ning Li, Xuewu Li, Tiantian Wu, and Fangyu Wang. 2022. "New Advances in Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFI) Technology for Food Safety Detection" Molecules 27, no. 19: 6596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196596
APA StyleXing, G., Sun, X., Li, N., Li, X., Wu, T., & Wang, F. (2022). New Advances in Lateral Flow Immunoassay (LFI) Technology for Food Safety Detection. Molecules, 27(19), 6596. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196596





