Chrysanthemum boreale Makino Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Neuronal Damage in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells by Suppressing MAPK-Regulated Apoptosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
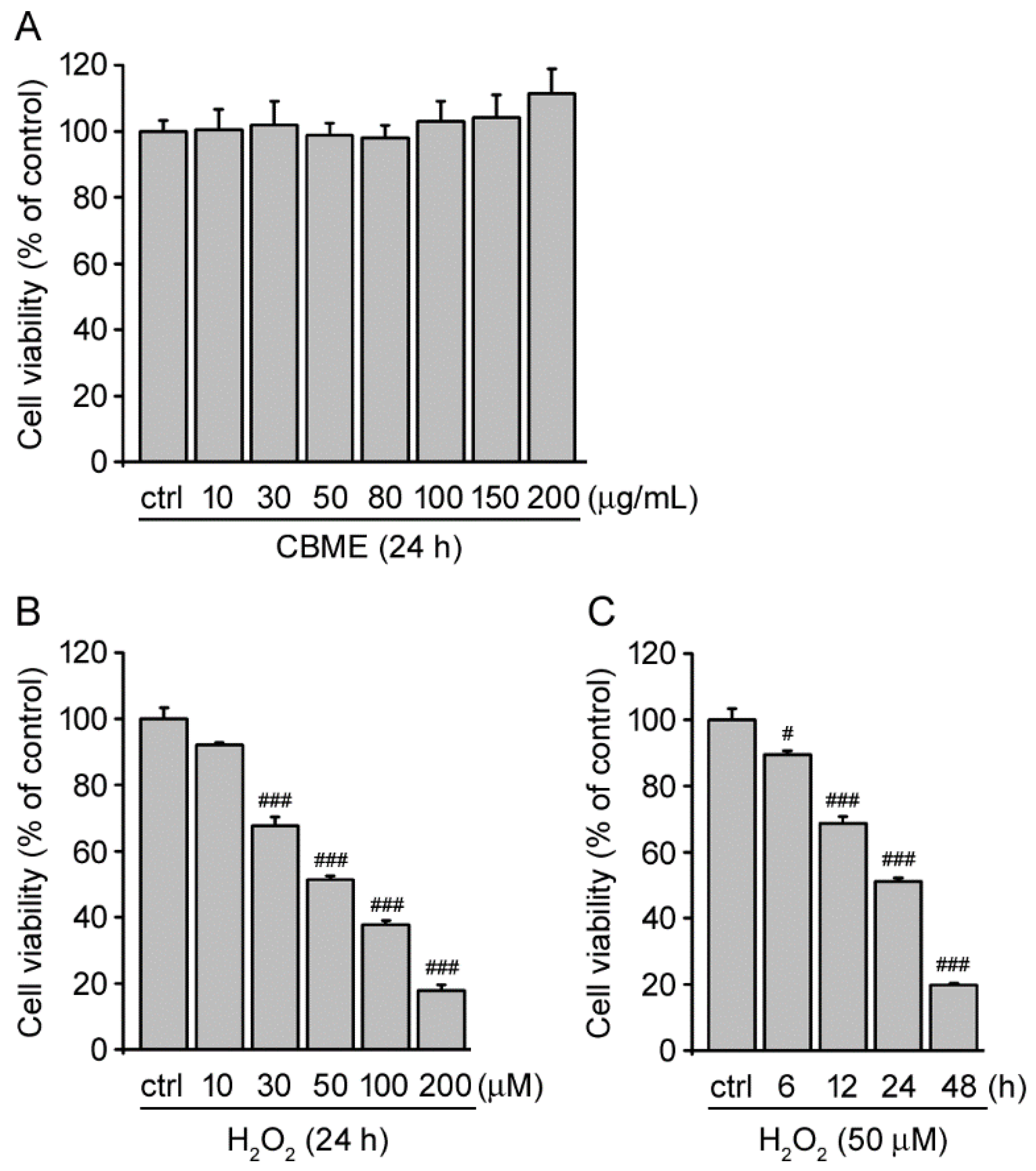
2.1. Chrysanthemum boreale Makino Extract Exhibited No Obvious Cytotoxic Effects in SH-SY5Y Cells
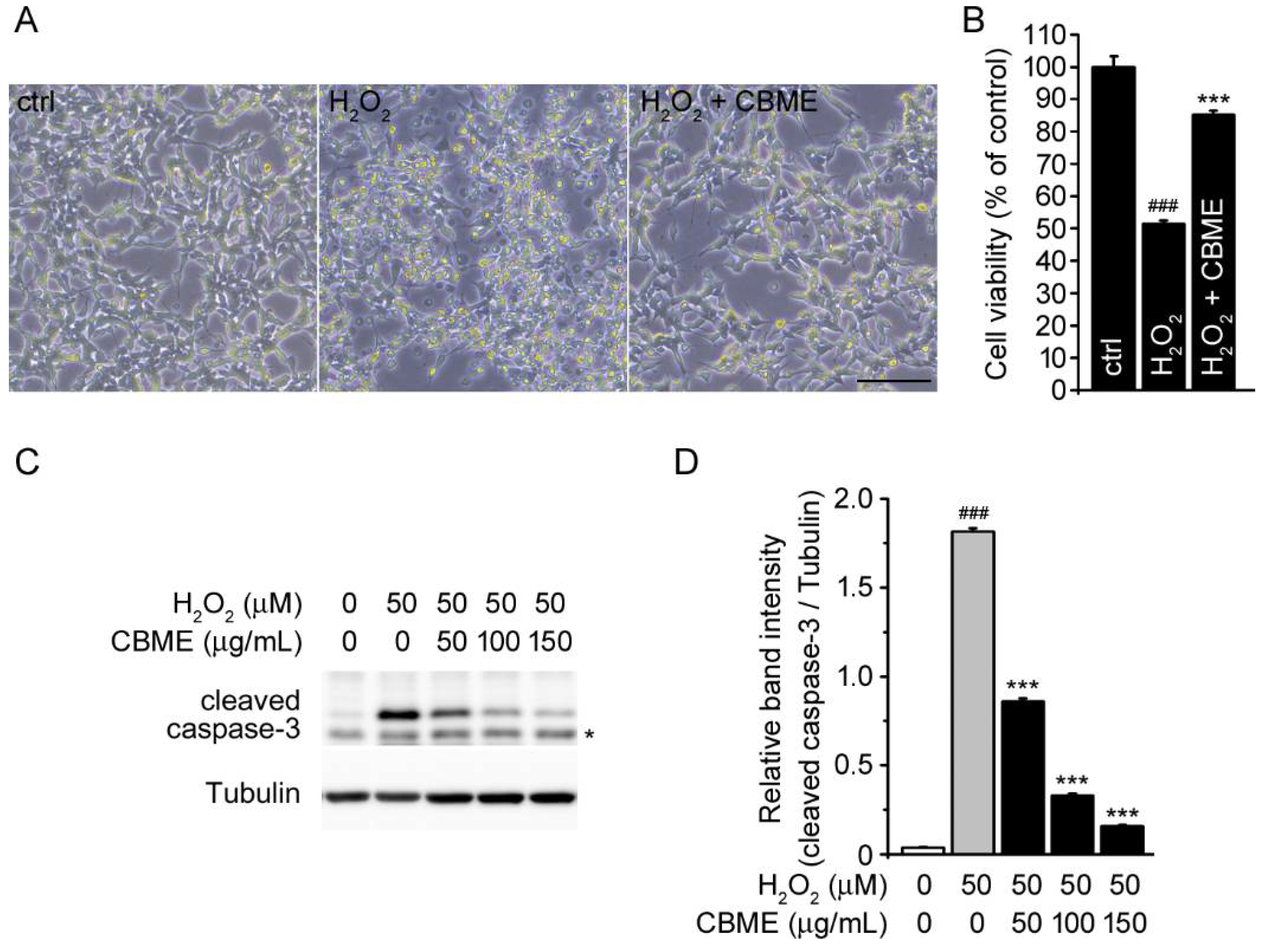
2.2. Chrysanthemum boreale Makino Extract Inhibited Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2)-Induced Neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells
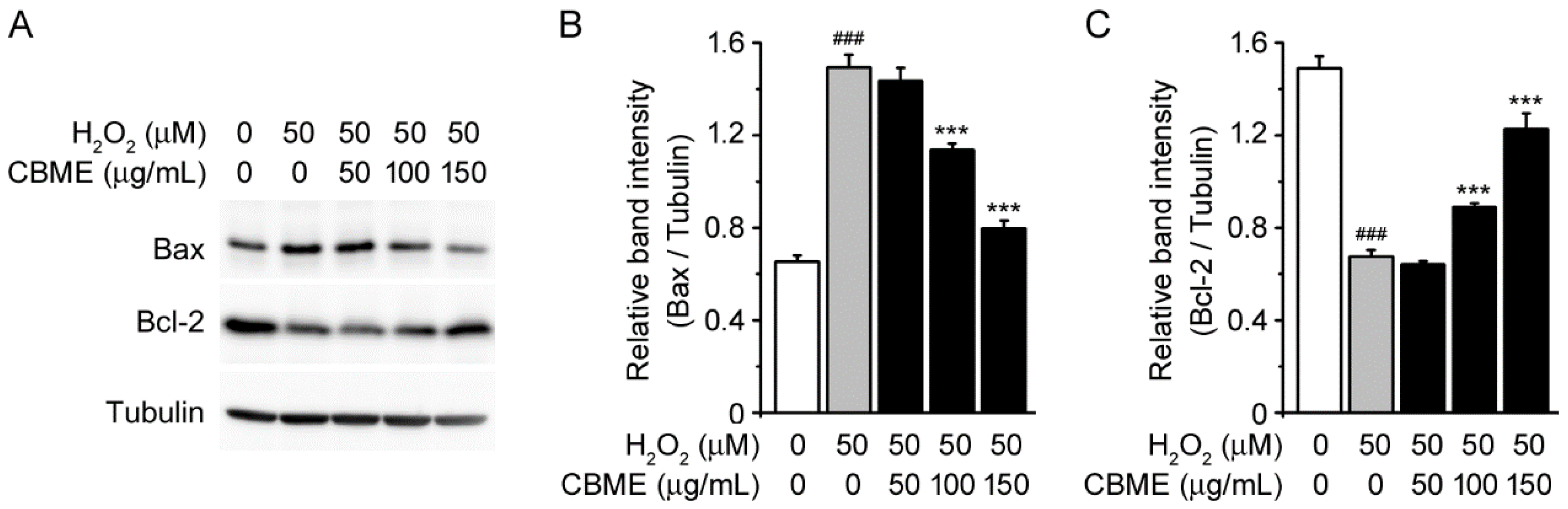
2.3. Chrysanthemum boreale Makino Extract Inhibited H2O2-Stimulated Bax/Bcl-2 Pathway in SH-SY5Y Cells
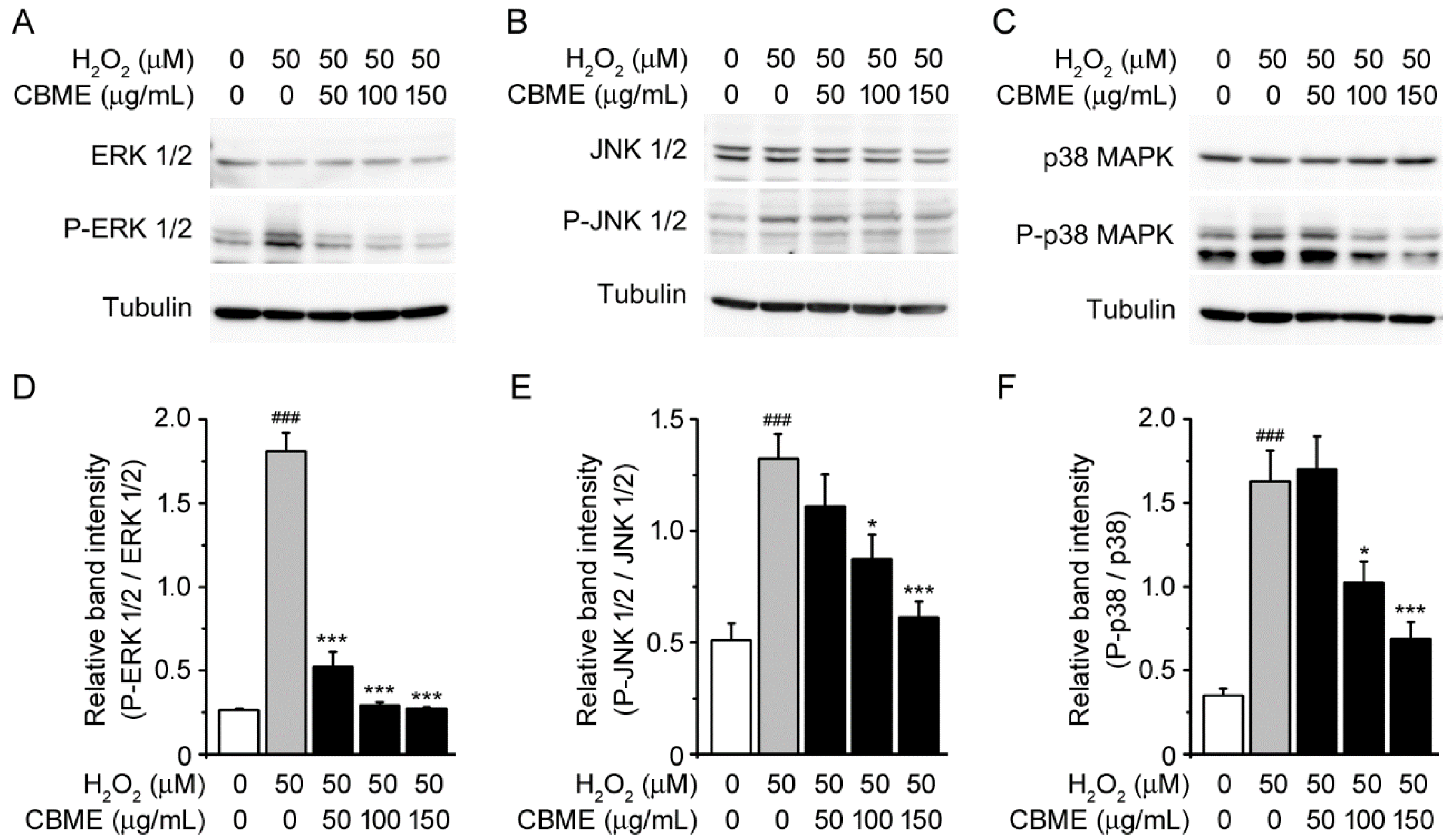
2.4. Chrysanthemum boreale Makino Extract Suppressed H2O2-Induced Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Pathway
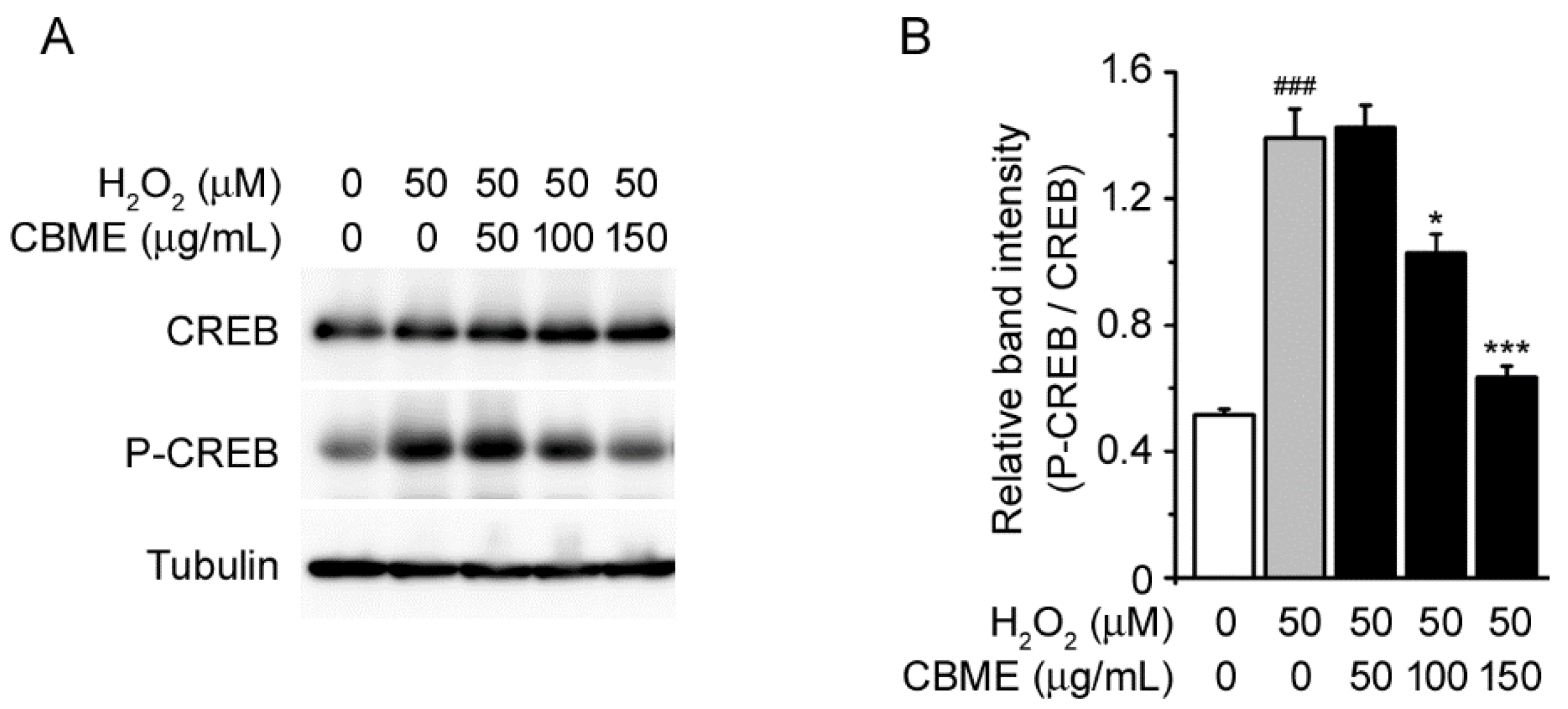
2.5. Chrysanthemum boreale Makino Extract Prevented H2O2-Induced Phosphorylation of CREB in SH-SY5Y Cells
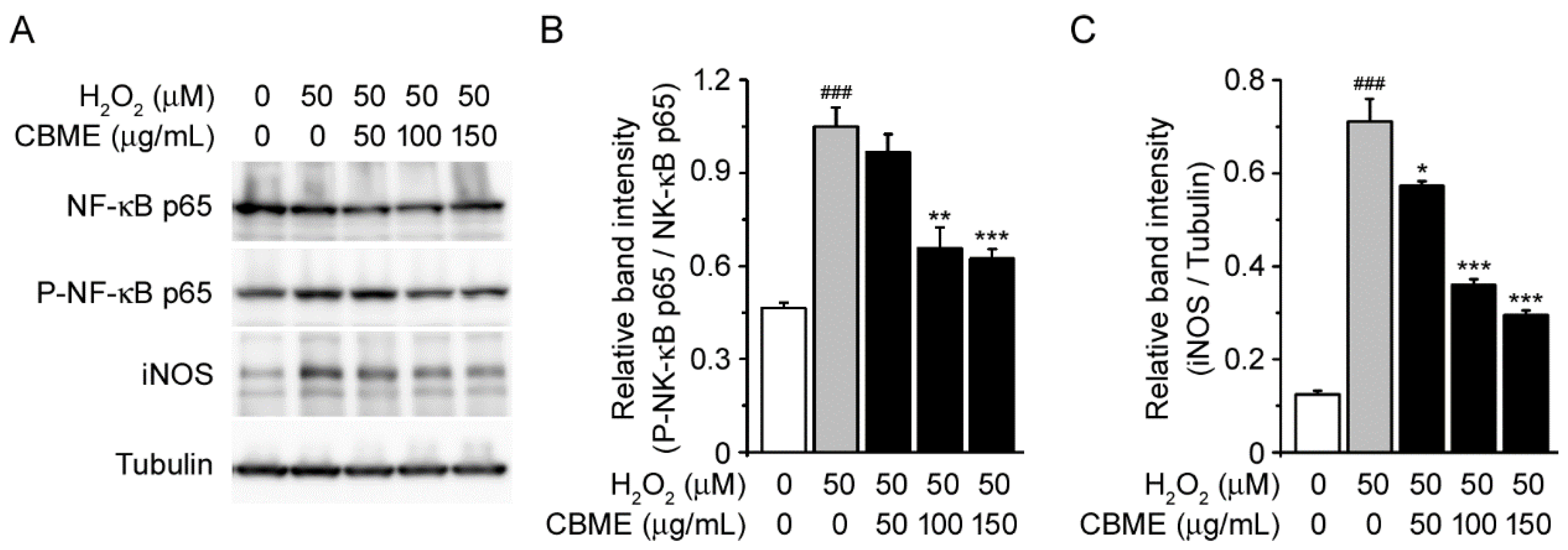
2.6. Chrysanthemum boreale Makino Extract Attenuated H2O2-Induced NF-kB Phosphorylation and iNOS Induction
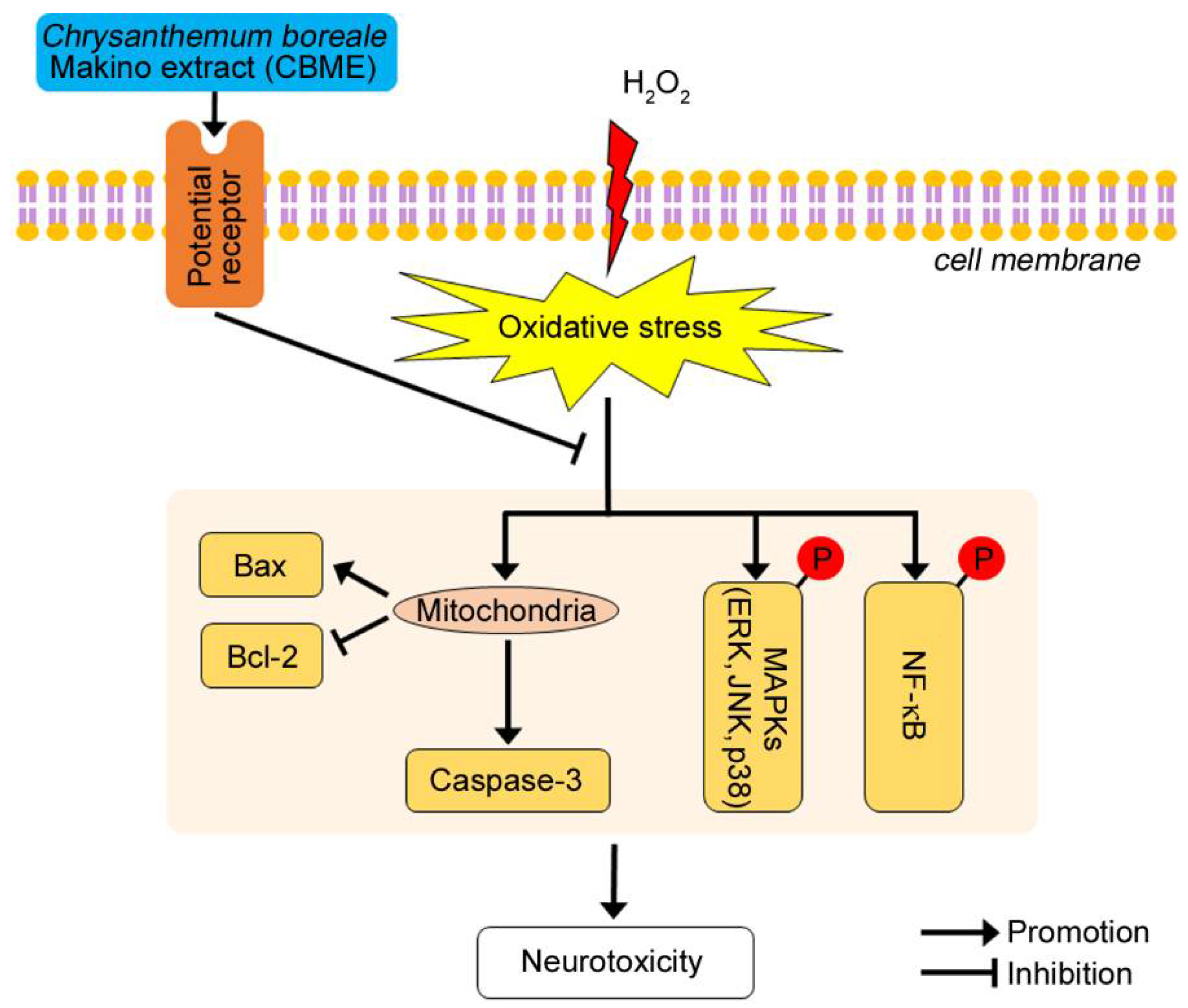
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Preparation of Chrysanthemum boreale Makino Extract
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Immunoblot Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cenini, G.; Lloret, A.; Cascella, R. Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases: From a Mitochondrial Point of View. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 2105607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, T.; Ziegler, A.C.; Dimitrion, P.; Zuo, L. Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 2525967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Satoh, T.; Enokido, Y.; Nishio, C.; Ikeuchi, T.; Hatanaka, H. Generation of reactive oxygen species, release of L-glutamate and activation of caspases are required for oxygen-induced apoptosis of embryonic hippocampal neurons in culture. Brain Res. 1999, 824, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherer, T.B.; Betarbet, R.; Stout, A.K.; Lund, S.; Baptista, M.; Panov, A.V.; Cookson, M.R.; Greenamyre, J.T. An in vitro model of Parkinson’s disease: Linking mitochondrial impairment to altered alpha-synuclein metabolism and oxidative damage. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 7006–7015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, D.K.; Peden, C.J.; Hall, A.S.; Sargentoni, J.; Whitwam, J.G. Magnetic resonance for the anaesthetist. Part I: Physical principles, applications, safety aspects. Anaesthesia 1992, 47, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.R. Antioxidants of Natural Products. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyee, Y.; Chung, H.J.; Choi, T.J.; Park, H.J.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, S.S.; Lee, S.K. Suppression of inflammatory responses by handelin, a guaianolide dimer from Chrysanthemum boreale, via downregulation of NF-kappaB signaling and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Park, S.J.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, K.H.; Choi, N.Y.; Lee, Y.R.; Lee, Y.E.; You, Y.O. Inhibitory Effects of Chrysanthemum boreale Essential Oil on Biofilm Formation and Virulence Factor Expression of Streptococcus mutans. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 616309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.; Lee, D.; Jung, S.H.; Lee, K.J.; Jin, H.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, H.M.; Kim, B.; Won, K.J. Sabinene Prevents Skeletal Muscle Atrophy by Inhibiting the MAPK-MuRF-1 Pathway in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.Y.; Jung, J.A.; Kim, J.S. The complete chloroplast genome of Chrysanthemum boreale (Asteraceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2018, 3, 549–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.Y.; Jung, J.A.; Kim, J.S. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Chrysanthemum boreale (Asteraceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2018, 3, 529–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.R.; Yang, M.S.; Lee, J.; Hwang, S.W.; Kho, Y.H.; Park, K.H. New guaianolides from leaves and stems of Chrysanthemum boreale. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 880–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugroho, A.; Lim, S.C.; Choi, J.; Park, H.J. Identification and quantification of the sedative and anticonvulsant flavone glycoside from Chrysanthemum boreale. Arch Pharm. Res. 2013, 36, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Won, K.J.; Yoon, M.S.; Yu, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Kim, B.; Lee, H.M. Chrysanthemum boreale flower floral water inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated migration and proliferation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Won, K.J.; Hwang, D.I.; Park, S.M.; Kim, B.; Lee, H.M. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Anti-melanogenic Activities of Essential Oils from Chrysanthemum boreale Makino at Different Harvesting Stages. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1700506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.Q.; Chen, K.; Shi, Q.; Kilkuskie, R.E.; Cheng, Y.C.; Lee, K.H. Anti-AIDS agents, 10. Acacetin-7-O-beta-D-galactopyranoside, an anti-HIV principle from Chrysanthemum morifolium and a structure-activity correlation with some related flavonoids. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Yu, H.H.; Jeong, S.I.; Cha, J.D.; Kil, B.S.; You, Y.O. Antibacterial activity and chemical composition of essential oil of Chrysanthemum boreale. Planta Med. 2003, 69, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, M.S.; Yoon, T.; Lee, D.Y.; Choi, G.; Moon, B.C.; Lee, A.Y.; Choo, B.K.; Kim, H.K. Chrysanthemum indicum Linne extract inhibits the inflammatory response by suppressing NF-kappaB and MAPKs activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 122, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Choi, G.; Yoon, T.; Cheon, M.S.; Choo, B.K.; Kim, H.K. Anti-inflammatory activity of Chrysanthemum indicum extract in acute and chronic cutaneous inflammation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 123, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Sung, J.; Sung, M.; Choi, Y.; Jeong, H.S.; Lee, J. Involvement of heme oxygenase-1 in the anti-inflammatory activity of Chrysanthemum boreale Makino extracts on the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in RAW264.7 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 131, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Won, K.J.; Yoon, M.S.; Hwang, D.I.; Yoon, S.W.; Park, J.H.; Kim, B.; Lee, H.M. Chrysanthemum boreale Makino essential oil induces keratinocyte proliferation and skin regeneration. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.S.; Hong, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Hong, J.; Lee, K.T. beta-Caryophyllene in the Essential Oil from Chrysanthemum Boreale Induces G1 Phase Cell Cycle Arrest in Human Lung Cancer Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, A.M.; Xu, F.H.; Fady, C.; Jacoby, F.J.; Duffey, D.C.; Tu, Y.; Lichtenstein, A. Apoptotic vs. nonapoptotic cytotoxicity induced by hydrogen peroxide. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 22, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Lee, A.S.; Choi, I. Melandrii Herba Extract Attenuates H(2)O(2)-Induced Neurotoxicity in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells and Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in Mice. Molecules 2017, 22, 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Jha, N.; Boonplueang, R.; Andersen, J.K. Caspase 3 inhibition attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced DNA fragmentation but not cell death in neuronal PC12 cells. J. Neurochem. 2001, 76, 1745–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, A.F.; Nobel, C.S.; Orrenius, S. The role of intracellular oxidants in apoptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1271, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.D. Reactive oxygen species and programmed cell death. Trends. Biochem. Sci. 1996, 21, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, A.J.; Fernandes, R.S.; Samali, A.; Cotter, T.G. Anti-oxidants and apoptosis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1996, 24, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, A.F.; Stefan, C.; Nobel, I.; van den Dobbelsteen, D.J.; Orrenius, S. Intracellular redox changes during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1996, 3, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Alnemri, E.S.; Livingston, D.J.; Nicholson, D.W.; Salvesen, G.; Thornberry, N.A.; Wong, W.W.; Yuan, J. Human ICE/CED-3 protease nomenclature. Cell 1996, 87, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, B.S.; Kholodilov, N.G.; Oo, T.F.; Kim, S.Y.; Tomaselli, K.J.; Srinivasan, A.; Stefanis, L.; Burke, R.E. Activation of caspase-3 in developmental models of programmed cell death in neurons of the substantia nigra. J. Neurochem. 1999, 73, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hartmann, A.; Hunot, S.; Michel, P.P.; Muriel, M.P.; Vyas, S.; Faucheux, B.A.; Mouatt-Prigent, A.; Turmel, H.; Srinivasan, A.; Ruberg, M.; et al. Caspase-3: A vulnerability factor and final effector in apoptotic death of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2875–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsura, T.; Kai, M.; Fujii, Y.; Ito, H.; Yamada, K. Hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in HL-60 cells requires caspase-3 activation. Free Radic. Res. 1999, 30, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollazadeh, S.; Fazly Bazzaz, B.S.; Kerachian, M.A. Role of apoptosis in pathogenesis and treatment of bone-related diseases. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2015, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyton, K.Z.; Liu, Y.; Gorospe, M.; Xu, Q.; Holbrook, N.J. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by H2O2. Role in cell survival following oxidant injury. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 4138–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, I.; Blanco, R.; Carmona, M.; Puig, B.; Barrachina, M.; Gomez, C.; Ambrosio, S. Active, phosphorylation-dependent mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK/ERK), stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAPK/JNK), and p38 kinase expression in Parkinson’s disease and Dementia with Lewy bodies. J. Neural. Transm. (Vienna) 2001, 108, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, H.; Nakajima, A.; Sakon-Komazawa, S.; Piao, J.H.; Xue, X.; Okumura, K. Reactive oxygen species mediate crosstalk between NF-kappaB and JNK. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, T.E.; Habener, J.F. Cyclic adenosine 3’,5’-monophosphate response element binding protein (CREB) and related transcription-activating deoxyribonucleic acid-binding proteins. Endocr. Rev. 1993, 14, 269–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montminy, M.R.; Gonzalez, G.A.; Yamamoto, K.K. Regulation of cAMP-inducible genes by CREB. Trends. Neurosci. 1990, 13, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, M.R.; Dragunow, I. Is CREB a key to neuronal survival? Trends. Neurosci. 2000, 23, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Tanabe, K.; Wada, K.; Shimoke, K.; Ishikawa, Y.; Ikeuchi, T.; Koizumi, S.; Hatanaka, H. Differences in survival-promoting effects and intracellular signaling properties of BDNF and IGF-1 in cultured cerebral cortical neurons. J. Neurochem. 2001, 78, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourtchuladze, R.; Frenguelli, B.; Blendy, J.; Cioffi, D.; Schutz, G.; Silva, A.J. Deficient long-term memory in mice with a targeted mutation of the cAMP-responsive element-binding protein. Cell 1994, 79, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzowski, J.F.; McGaugh, J.L. Antisense oligodeoxynucleotide-mediated disruption of hippocampal cAMP response element binding protein levels impairs consolidation of memory for water maze training. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2693–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.C.; Tully, T. CREB and the formation of long-term memory. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1996, 6, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaywitz, A.J.; Greenberg, M.E. CREB: A stimulus-induced transcription factor activated by a diverse array of extracellular signals. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999, 68, 821–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, B.; Montminy, M. Transcriptional regulation by the phosphorylation-dependent factor CREB. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amor, S.; Puentes, F.; Baker, D.; van der Valk, P. Inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology 2010, 129, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilstra, J.S.; Clauson, C.L.; Niedernhofer, L.J.; Robbins, P.D. NF-kappaB in Aging and Disease. Aging Dis. 2011, 2, 449–465. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Sullards, M.C.; Olzmann, J.A.; Rees, H.D.; Weintraub, S.T.; Bostwick, D.E.; Gearing, M.; Levey, A.I.; Chin, L.S.; Li, L. Oxidative damage of DJ-1 is linked to sporadic Parkinson and Alzheimer diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 10816–10824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoy, N.; Mackay, G.M.; Forrest, C.M.; Christofides, J.; Egerton, M.; Stone, T.W.; Darlington, L.G. Tryptophan metabolism and oxidative stress in patients with Huntington’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2005, 93, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellingham, M.C. A review of the neural mechanisms of action and clinical efficiency of riluzole in treating amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: What have we learned in the last decade? CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2011, 17, 4–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, B.S.; Lee, W.C.; Chung, K.H.; Ko, J.H.; Kim, C.H. A water extract of Curcuma longa L. (Zingiberaceae) rescues PC12 cell death caused by pyrogallol or hypoxia/reoxygenation and attenuates hydrogen peroxide induced injury in PC12 cells. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 2363–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, S.A.; Amit, T.; Weinreb, O.; Reznichenko, L.; Youdim, M.B. Simultaneous manipulation of multiple brain targets by green tea catechins: A potential neuroprotective strategy for Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2008, 14, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Liu, J.; Wu, F.; Yew, D.T. Ginkgo biloba extract in Alzheimer’s disease: From action mechanisms to medical practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandareesh, M.D.; Mythri, R.B.; Srinivas Bharath, M.M. Bioavailability of dietary polyphenols: Factors contributing to their clinical application in CNS diseases. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 89, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmaladevi, D.; Venkataramana, M.; Chandranayaka, S.; Ramesha, A.; Jameel, N.M.; Srinivas, C. Neuroprotective effects of bikaverin on H2O2-induced oxidative stress mediated neuronal damage in SH-SY5Y cell line. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 34, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.Y.; Lee, G.H.; Park, C.H.; Kim, H.J.; Park, S.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, K.S.; Won, B.Y.; Lee, H.G.; et al. A novel compound, maltolyl p-coumarate, attenuates cognitive deficits and shows neuroprotective effects in vitro and in vivo dementia models. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 85, 2500–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabner, B.J.; Turnbull, S.; El-Agnaf, O.; Allsop, D. Production of reactive oxygen species from aggregating proteins implicated in Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2001, 1, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N.J. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, W.; Su, J.; Liu, W.; Altura, B.T.; Altura, B.M. Hydrogen peroxide induces apoptosis in cerebral vascular smooth muscle cells: Possible relation to neurodegenerative diseases and strokes. Brain. Res. Bull. 2003, 62, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamakawa, H.; Ito, Y.; Naganawa, T.; Banno, Y.; Nakashima, S.; Yoshimura, S.; Sawada, M.; Nishimura, Y.; Nozawa, Y.; Sakai, N. Activation of caspase-9 and -3 during H2O2-induced apoptosis of PC12 cells independent of ceramide formation. Neurol. Res. 2000, 22, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kale, J.; Osterlund, E.J.; Andrews, D.W. BCL-2 family proteins: Changing partners in the dance towards death. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.H.; Surh, Y.J. Possible role of NF-kappaB in Bcl-X(L) protection against hydrogen peroxide-induced PC12 cell death. Redox. Rep. 2004, 9, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsmeyer, S.J. BCL-2 gene family and the regulation of programmed cell death. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 1693s–1700s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, J.C. Bcl-2 family proteins. Oncogene 1998, 17, 3225–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffels, J.; Griffin, M.; Dickenson, J.M. Activation of ERK1/2, JNK and PKB by hydrogen peroxide in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: Role of ERK1/2 in H2O2-induced cell death. Eur. J. Pharmacol 2004, 483, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicer, Z.; Millhorn, D.E. Oxygen sensing in neuroendocrine cells and other cell types: Pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells as an experimental model. Endocr. Pathol. 2003, 14, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzaki, Y.; Yoshizumi, M.; Kagami, S.; Koyama, A.H.; Taketani, Y.; Houchi, H.; Tsuchiya, K.; Takeda, E.; Tamaki, T. Hydrogen peroxide stimulates c-Src-mediated big mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (BMK1) and the MEF2C signaling pathway in PC12 cells: Potential role in cell survival following oxidative insults. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 9614–9621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.L.; Liu, X.H.; Jia, Y.L.; Wu, D.; Xiong, Q.H.; Gong, Q.H.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.Z. A novel compound derived from danshensu inhibits apoptosis via upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression in SH-SY5Y cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 2861–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonni, A.; Brunet, A.; West, A.E.; Datta, S.R.; Takasu, M.A.; Greenberg, M.E. Cell survival promoted by the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Science 1999, 286, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xing, J.; Ginty, D.D.; Greenberg, M.E. Coupling of the RAS-MAPK pathway to gene activation by RSK2, a growth factor-regulated CREB kinase. Science 1996, 273, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Kim, S.C.; Yu, T.; Yi, Y.S.; Rhee, M.H.; Sung, G.H.; Yoo, B.C.; Cho, J.Y. Functional roles of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in macrophage-mediated inflammatory responses. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 352371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lin, A. Role of JNK activation in apoptosis: A double-edged sword. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakis, J.M.; Avruch, J. Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 807–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pua, L.J.W.; Mai, C.W.; Chung, F.F.; Khoo, A.S.; Leong, C.O.; Lim, W.M.; Hii, L.W. Functional Roles of JNK and p38 MAPK Signaling in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korea Plant Extract Bank. Available online: https://portal.kribb.re.kr/kpeb (accessed on 19 October 2020).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, P.; Choi, S.Y.; Hwang, J.S.; Park, H.C.; Kim, K.K.; Son, H.-J.; Hong, C.-O.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, W.; Lee, K.M. Chrysanthemum boreale Makino Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Neuronal Damage in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells by Suppressing MAPK-Regulated Apoptosis. Molecules 2022, 27, 5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175498
Song P, Choi SY, Hwang JS, Park HC, Kim KK, Son H-J, Hong C-O, Kim Y-J, Kim W, Lee KM. Chrysanthemum boreale Makino Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Neuronal Damage in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells by Suppressing MAPK-Regulated Apoptosis. Molecules. 2022; 27(17):5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175498
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Parkyong, Seo Young Choi, Ji Sun Hwang, Hyeon Cheal Park, Keun Ki Kim, Hong-Joo Son, Chang-Oh Hong, Yu-Jin Kim, Wanil Kim, and Kwang Min Lee. 2022. "Chrysanthemum boreale Makino Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Neuronal Damage in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells by Suppressing MAPK-Regulated Apoptosis" Molecules 27, no. 17: 5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175498
APA StyleSong, P., Choi, S. Y., Hwang, J. S., Park, H. C., Kim, K. K., Son, H.-J., Hong, C.-O., Kim, Y.-J., Kim, W., & Lee, K. M. (2022). Chrysanthemum boreale Makino Inhibits Oxidative Stress-Induced Neuronal Damage in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells by Suppressing MAPK-Regulated Apoptosis. Molecules, 27(17), 5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27175498





